Comparing Colloidal Silica to Silicate Binders in Environmental Applications
SEP 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Colloidal Silica vs Silicate Binders: Background & Objectives
Silica-based binding technologies have evolved significantly over the past century, with colloidal silica and silicate binders representing two distinct yet related approaches to environmental applications. Colloidal silica consists of nano-sized amorphous silica particles dispersed in water, typically ranging from 5 to 100 nanometers in diameter, while silicate binders are composed of soluble alkali metal silicates, commonly referred to as "water glass." The historical development of these materials traces back to the early 20th century, with significant industrial applications emerging in the 1950s.
The evolution of colloidal silica technology has accelerated in recent decades due to advancements in nanotechnology and surface chemistry. This progression has enabled precise control over particle size distribution, surface charge, and stability characteristics. Simultaneously, silicate binder formulations have been refined to address issues of efflorescence and long-term durability that limited their earlier applications.
Environmental concerns have increasingly driven innovation in binding technologies, with particular emphasis on reducing carbon footprints and eliminating toxic components. Both colloidal silica and silicate binders have gained attention as potential replacements for traditional Portland cement and organic polymer-based systems, which typically have higher environmental impacts. The global push toward sustainable construction materials and remediation technologies has positioned these silica-based systems as promising alternatives.
Current market trends indicate growing adoption of these technologies across diverse environmental applications, including soil stabilization, waste encapsulation, dust suppression, and water treatment. The versatility of these materials stems from their ability to form strong chemical bonds with various substrates while maintaining environmental compatibility. Their increasing prominence aligns with global sustainability initiatives and regulatory frameworks promoting greener technologies.
The primary technical objective of this research is to conduct a comprehensive comparative analysis of colloidal silica and silicate binders specifically within environmental applications. This includes evaluating their performance characteristics, application methodologies, durability under various environmental conditions, and overall sustainability profiles. Secondary objectives include identifying optimal application scenarios for each technology, assessing cost-effectiveness factors, and exploring potential synergistic formulations that might combine advantages of both systems.
This investigation aims to provide actionable insights for technology selection and implementation strategies across environmental sectors. By thoroughly examining the fundamental chemistry, application engineering, and long-term performance of these materials, we seek to establish clear guidelines for their appropriate utilization in addressing pressing environmental challenges while supporting sustainable development goals.
The evolution of colloidal silica technology has accelerated in recent decades due to advancements in nanotechnology and surface chemistry. This progression has enabled precise control over particle size distribution, surface charge, and stability characteristics. Simultaneously, silicate binder formulations have been refined to address issues of efflorescence and long-term durability that limited their earlier applications.
Environmental concerns have increasingly driven innovation in binding technologies, with particular emphasis on reducing carbon footprints and eliminating toxic components. Both colloidal silica and silicate binders have gained attention as potential replacements for traditional Portland cement and organic polymer-based systems, which typically have higher environmental impacts. The global push toward sustainable construction materials and remediation technologies has positioned these silica-based systems as promising alternatives.
Current market trends indicate growing adoption of these technologies across diverse environmental applications, including soil stabilization, waste encapsulation, dust suppression, and water treatment. The versatility of these materials stems from their ability to form strong chemical bonds with various substrates while maintaining environmental compatibility. Their increasing prominence aligns with global sustainability initiatives and regulatory frameworks promoting greener technologies.
The primary technical objective of this research is to conduct a comprehensive comparative analysis of colloidal silica and silicate binders specifically within environmental applications. This includes evaluating their performance characteristics, application methodologies, durability under various environmental conditions, and overall sustainability profiles. Secondary objectives include identifying optimal application scenarios for each technology, assessing cost-effectiveness factors, and exploring potential synergistic formulations that might combine advantages of both systems.
This investigation aims to provide actionable insights for technology selection and implementation strategies across environmental sectors. By thoroughly examining the fundamental chemistry, application engineering, and long-term performance of these materials, we seek to establish clear guidelines for their appropriate utilization in addressing pressing environmental challenges while supporting sustainable development goals.
Environmental Market Demand Analysis for Silica-Based Binders
The global market for silica-based binders in environmental applications has witnessed substantial growth in recent years, driven primarily by increasing environmental regulations and a growing emphasis on sustainable solutions. The market demand for these binders spans across various environmental sectors including soil stabilization, waste treatment, water purification, and air pollution control.
In the soil remediation sector, silica-based binders have gained significant traction due to their ability to immobilize heavy metals and organic contaminants. The global soil remediation market, valued at approximately $35 billion in 2022, is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.8% through 2030, creating substantial opportunities for silica-based binding technologies.
Water treatment represents another major market segment where silica-based binders are increasingly utilized. The global water treatment chemicals market reached $56.9 billion in 2022, with silicate and colloidal silica products capturing a growing share due to their effectiveness in removing suspended solids, heavy metals, and organic pollutants from industrial wastewater and drinking water systems.
The construction industry's shift toward environmentally friendly materials has also bolstered demand for silica-based binders. Green building initiatives worldwide have created a market estimated at $321 billion in 2022, with sustainable construction materials growing at 10.3% annually. Silica-based products are particularly valued for their low carbon footprint compared to traditional Portland cement.
Mining waste management represents another significant growth area, with the global mining waste management market expected to reach $233 billion by 2027. Silica-based binders offer effective solutions for tailings stabilization and acid mine drainage prevention, addressing critical environmental challenges in the mining sector.
Regionally, North America and Europe lead in adoption due to stringent environmental regulations and well-established waste management infrastructure. However, the Asia-Pacific region is experiencing the fastest growth rate at 9.2% annually, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and increasing environmental awareness in countries like China and India.
Customer preferences are increasingly favoring solutions that offer multiple environmental benefits simultaneously. This trend has accelerated demand for advanced silica-based formulations that can address complex environmental challenges while meeting sustainability criteria and regulatory compliance requirements.
In the soil remediation sector, silica-based binders have gained significant traction due to their ability to immobilize heavy metals and organic contaminants. The global soil remediation market, valued at approximately $35 billion in 2022, is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.8% through 2030, creating substantial opportunities for silica-based binding technologies.
Water treatment represents another major market segment where silica-based binders are increasingly utilized. The global water treatment chemicals market reached $56.9 billion in 2022, with silicate and colloidal silica products capturing a growing share due to their effectiveness in removing suspended solids, heavy metals, and organic pollutants from industrial wastewater and drinking water systems.
The construction industry's shift toward environmentally friendly materials has also bolstered demand for silica-based binders. Green building initiatives worldwide have created a market estimated at $321 billion in 2022, with sustainable construction materials growing at 10.3% annually. Silica-based products are particularly valued for their low carbon footprint compared to traditional Portland cement.
Mining waste management represents another significant growth area, with the global mining waste management market expected to reach $233 billion by 2027. Silica-based binders offer effective solutions for tailings stabilization and acid mine drainage prevention, addressing critical environmental challenges in the mining sector.
Regionally, North America and Europe lead in adoption due to stringent environmental regulations and well-established waste management infrastructure. However, the Asia-Pacific region is experiencing the fastest growth rate at 9.2% annually, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and increasing environmental awareness in countries like China and India.
Customer preferences are increasingly favoring solutions that offer multiple environmental benefits simultaneously. This trend has accelerated demand for advanced silica-based formulations that can address complex environmental challenges while meeting sustainability criteria and regulatory compliance requirements.
Technical Status and Challenges in Silica Binding Technologies
The global landscape of silica binding technologies presents a complex picture of advancement and challenges. Currently, both colloidal silica and silicate binders have achieved significant technical maturity in various environmental applications, with colloidal silica demonstrating superior performance in soil stabilization and groundwater remediation due to its controlled gelation properties. However, silicate binders maintain dominance in waste encapsulation and certain construction applications where rapid setting is advantageous.
A primary technical challenge facing colloidal silica implementation is the precise control of gelation time in diverse environmental conditions. Temperature, pH, and the presence of various ions significantly affect gelation kinetics, making standardization difficult across different field applications. Research indicates that even minor variations in groundwater chemistry can alter setting times by 30-400%, creating substantial operational uncertainties.
For silicate binders, leachability remains a persistent concern, particularly in waste management applications. Studies have documented leaching rates of 5-15% for certain heavy metals from silicate-bound matrices over accelerated aging tests, compared to 1-3% for colloidal silica alternatives. This performance gap represents a significant technical hurdle for silicate technologies in sensitive environmental contexts.
Geographic distribution of technical expertise shows concentration in North America, Western Europe, and East Asia, with Japan and the United States leading patent filings in colloidal silica applications. European research institutions have pioneered silicate binder formulations for specialized environmental remediation, while China has rapidly expanded manufacturing capacity for both technologies in the past decade.
Scale-up challenges persist for both binding systems. Colloidal silica applications face difficulties in achieving uniform distribution in heterogeneous subsurface environments, with field studies showing effectiveness variations of up to 40% across treatment zones. Silicate binders struggle with batch-to-batch consistency at industrial scales, particularly when incorporating waste materials with variable compositions.
Recent technical innovations have focused on hybrid systems that combine properties of both binding technologies. These include modified colloidal silica with enhanced mechanical properties and environmentally-optimized silicate formulations with reduced leaching potential. However, these hybrid approaches often come with increased production complexity and cost premiums of 30-60% over conventional formulations.
Regulatory frameworks present another significant challenge, with environmental standards for binding technologies varying substantially across jurisdictions. This regulatory heterogeneity complicates technology transfer and standardization, particularly for multinational implementation projects requiring consistent performance across diverse geological and regulatory landscapes.
A primary technical challenge facing colloidal silica implementation is the precise control of gelation time in diverse environmental conditions. Temperature, pH, and the presence of various ions significantly affect gelation kinetics, making standardization difficult across different field applications. Research indicates that even minor variations in groundwater chemistry can alter setting times by 30-400%, creating substantial operational uncertainties.
For silicate binders, leachability remains a persistent concern, particularly in waste management applications. Studies have documented leaching rates of 5-15% for certain heavy metals from silicate-bound matrices over accelerated aging tests, compared to 1-3% for colloidal silica alternatives. This performance gap represents a significant technical hurdle for silicate technologies in sensitive environmental contexts.
Geographic distribution of technical expertise shows concentration in North America, Western Europe, and East Asia, with Japan and the United States leading patent filings in colloidal silica applications. European research institutions have pioneered silicate binder formulations for specialized environmental remediation, while China has rapidly expanded manufacturing capacity for both technologies in the past decade.
Scale-up challenges persist for both binding systems. Colloidal silica applications face difficulties in achieving uniform distribution in heterogeneous subsurface environments, with field studies showing effectiveness variations of up to 40% across treatment zones. Silicate binders struggle with batch-to-batch consistency at industrial scales, particularly when incorporating waste materials with variable compositions.
Recent technical innovations have focused on hybrid systems that combine properties of both binding technologies. These include modified colloidal silica with enhanced mechanical properties and environmentally-optimized silicate formulations with reduced leaching potential. However, these hybrid approaches often come with increased production complexity and cost premiums of 30-60% over conventional formulations.
Regulatory frameworks present another significant challenge, with environmental standards for binding technologies varying substantially across jurisdictions. This regulatory heterogeneity complicates technology transfer and standardization, particularly for multinational implementation projects requiring consistent performance across diverse geological and regulatory landscapes.
Current Technical Solutions for Environmental Applications
01 Colloidal silica as binder for refractory materials
Colloidal silica serves as an effective binder for refractory materials, providing high temperature resistance and strength. When combined with refractory aggregates, it forms strong bonds upon drying and firing, making it suitable for applications in foundries, steel plants, and high-temperature industrial settings. The colloidal silica particles create a network that binds the refractory particles together, resulting in improved mechanical properties and thermal stability.- Colloidal silica as binder for refractory materials: Colloidal silica serves as an effective binder for refractory materials, providing high temperature resistance and strength. When combined with refractory aggregates, it forms a strong bond upon drying and firing, making it suitable for applications in foundries, steel plants, and other high-temperature environments. The colloidal silica particles create a network structure that enhances the mechanical properties of the refractory material while maintaining thermal stability.
- Silicate binders for environmental applications: Silicate binders are utilized in environmental applications such as waste treatment, soil stabilization, and pollution control. These binders can immobilize heavy metals and other contaminants through chemical reactions that form stable silicate complexes. The alkaline nature of silicate binders contributes to their effectiveness in neutralizing acidic compounds while providing structural integrity to treated materials. Their low environmental impact makes them preferable for remediation projects.
- Modified colloidal silica compositions: Modified colloidal silica compositions incorporate additives or surface modifications to enhance specific properties such as adhesion, stability, or reactivity. These modifications can include organic functional groups, metal ions, or polymer additions that alter the surface chemistry of the silica particles. Such modifications enable tailored performance for applications including coatings, catalysts, and composite materials, providing improved compatibility with various substrates and enhanced durability under challenging conditions.
- Silicate binders for paper and fiber products: Silicate binders are employed in the production of paper and fiber products to improve strength, water resistance, and fire retardancy. When applied to cellulosic materials, these binders form cross-linked networks that enhance the structural integrity of the final product. The inorganic nature of silicate binders contributes to reduced flammability while maintaining breathability of the material. Additionally, they can improve the dimensional stability of paper products under varying humidity conditions.
- Colloidal silica in catalyst and coating applications: Colloidal silica is utilized in catalyst and coating applications due to its high surface area and controlled particle size distribution. In catalysts, it serves as a support material that enhances reactivity and selectivity while providing thermal stability. For coatings, colloidal silica improves hardness, scratch resistance, and adhesion properties. The uniform dispersion of nano-sized silica particles contributes to the formation of transparent films with excellent durability and chemical resistance.
02 Silicate binders for environmental applications
Silicate binders are utilized in environmental applications such as soil stabilization, waste treatment, and pollution control. These binders can immobilize heavy metals and other contaminants, reducing their environmental impact. The alkaline nature of silicate binders helps in neutralizing acidic compounds, while their ability to form stable matrices makes them suitable for solidification/stabilization processes. They are particularly effective in binding particulate matter and creating durable structures for environmental remediation.Expand Specific Solutions03 Modified colloidal silica formulations
Modified colloidal silica formulations involve the addition of organic or inorganic compounds to enhance specific properties. These modifications can improve adhesion, stability, or compatibility with other materials. By incorporating additives such as aluminum compounds, organic polymers, or surface-active agents, the performance characteristics of colloidal silica can be tailored for specific applications. These modified formulations often exhibit improved binding efficiency, reduced drying time, or enhanced resistance to environmental factors.Expand Specific Solutions04 Silicate binders for paper and fiber products
Silicate binders are used in the production of paper and fiber products to improve strength, water resistance, and fire retardancy. When applied to cellulosic materials, these binders form cross-linked networks that enhance the structural integrity of the final product. The silicate coating creates a protective barrier that reduces moisture absorption while maintaining breathability. Additionally, these binders can improve the dimensional stability of paper products under varying environmental conditions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Colloidal silica in catalyst and coating applications
Colloidal silica plays a crucial role in catalyst and coating applications due to its high surface area and reactivity. When used in catalysts, it provides a stable support for active components, enhancing catalytic efficiency and selectivity. In coating applications, colloidal silica improves adhesion, hardness, and scratch resistance. The nano-sized silica particles create uniform films with excellent optical properties, making them suitable for anti-reflective coatings, protective finishes, and functional surface treatments.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players in Colloidal Silica Production
The colloidal silica versus silicate binders market is in a growth phase, with increasing environmental applications driving expansion. The global market is projected to reach significant scale due to stringent environmental regulations and sustainability initiatives. Technologically, colloidal silica solutions are advancing rapidly, with companies like W.R. Grace, BASF, and Nissan Chemical leading innovation in stabilization and performance enhancement. Evonik Operations and Wanhua Chemical are developing specialized formulations for environmental remediation, while Akzo Nobel and Ecolab focus on water treatment applications. The competitive landscape shows established chemical conglomerates competing with specialized players, with differentiation occurring through application-specific solutions and environmental performance metrics.
W. R. Grace & Co.-Conn.
Technical Solution: W. R. Grace has developed LUDOX® colloidal silica technology specifically engineered for environmental applications, offering distinct advantages over conventional silicate binders. Their research demonstrates that colloidal silica provides superior performance in soil stabilization and contaminant immobilization due to its nano-scale particle size (typically 4-22nm) and high surface area (up to 350 m²/g). For groundwater remediation, Grace's colloidal silica formulations create permanent, low-permeability barriers through controlled gelation processes, reducing contaminant migration by over 99% in field tests. Unlike sodium silicate binders that can leach over time, their colloidal silica forms stable siloxane bonds that resist dissolution even under acidic groundwater conditions. Grace's comparative studies show that while silicate binders require higher dosages and often need accelerators, their colloidal silica solutions achieve equivalent or superior performance at lower application rates. For industrial wastewater treatment, their specialized colloidal silica products demonstrate 40-60% higher heavy metal adsorption capacity compared to traditional silicate-based flocculants, while generating significantly less sludge volume.
Strengths: Exceptional stability in variable pH environments; forms permanent, non-leaching bonds with contaminants; precise control over gelation time; higher surface area for contaminant adsorption; reduced material requirements for equivalent performance. Weaknesses: More sensitive to freezing conditions during storage and application; higher initial product cost compared to silicate binders; requires more specialized handling and application equipment.
Evonik Operations GmbH
Technical Solution: Evonik has developed AEROSIL® and SIPERNAT® technologies that provide comprehensive solutions comparing colloidal silica and silicate binders for environmental applications. Their research demonstrates that colloidal silica offers superior performance in soil remediation projects due to its nano-scale particle size (typically 5-50nm) and high specific surface area (up to 300 m²/g). For contaminated soil treatment, Evonik's colloidal silica formulations achieve up to 95% immobilization efficiency for heavy metals through surface complexation and encapsulation mechanisms, significantly outperforming traditional silicate binders. Their comparative studies show that while sodium silicate binders provide immediate solidification, their colloidal silica solutions offer more durable long-term stabilization with minimal leaching under variable pH conditions. For wastewater treatment applications, Evonik has engineered specialized surface-modified colloidal silica that demonstrates 30-50% higher adsorption capacity for organic pollutants compared to conventional silicate-based treatments. Their technology also enables precise control over gelation time, allowing for deeper penetration into contaminated matrices before solidification occurs, resulting in more uniform treatment of heterogeneous environmental media.
Strengths: Highly customizable surface chemistry for targeting specific contaminants; excellent long-term stability in variable environmental conditions; superior binding efficiency requiring lower application rates; forms more durable bonds with contaminants. Weaknesses: Higher production costs compared to traditional silicate binders; more complex application procedures; requires more precise control of environmental conditions during application.
Core Patents and Innovations in Silica Binding Technology
Colloidal silica-based binder vehicles and gels
PatentInactiveUS3920578A
Innovation
- A composition comprising colloidal amorphous silica with controlled alkaline ionic silicate and acid ratios to achieve rapid gelation, high strength, and regular pore size distribution, allowing for the formation of strong, attrition-resistant gels with adjustable strength and porosity.
Colloidal silica binder system
PatentInactiveUS20050121110A1
Innovation
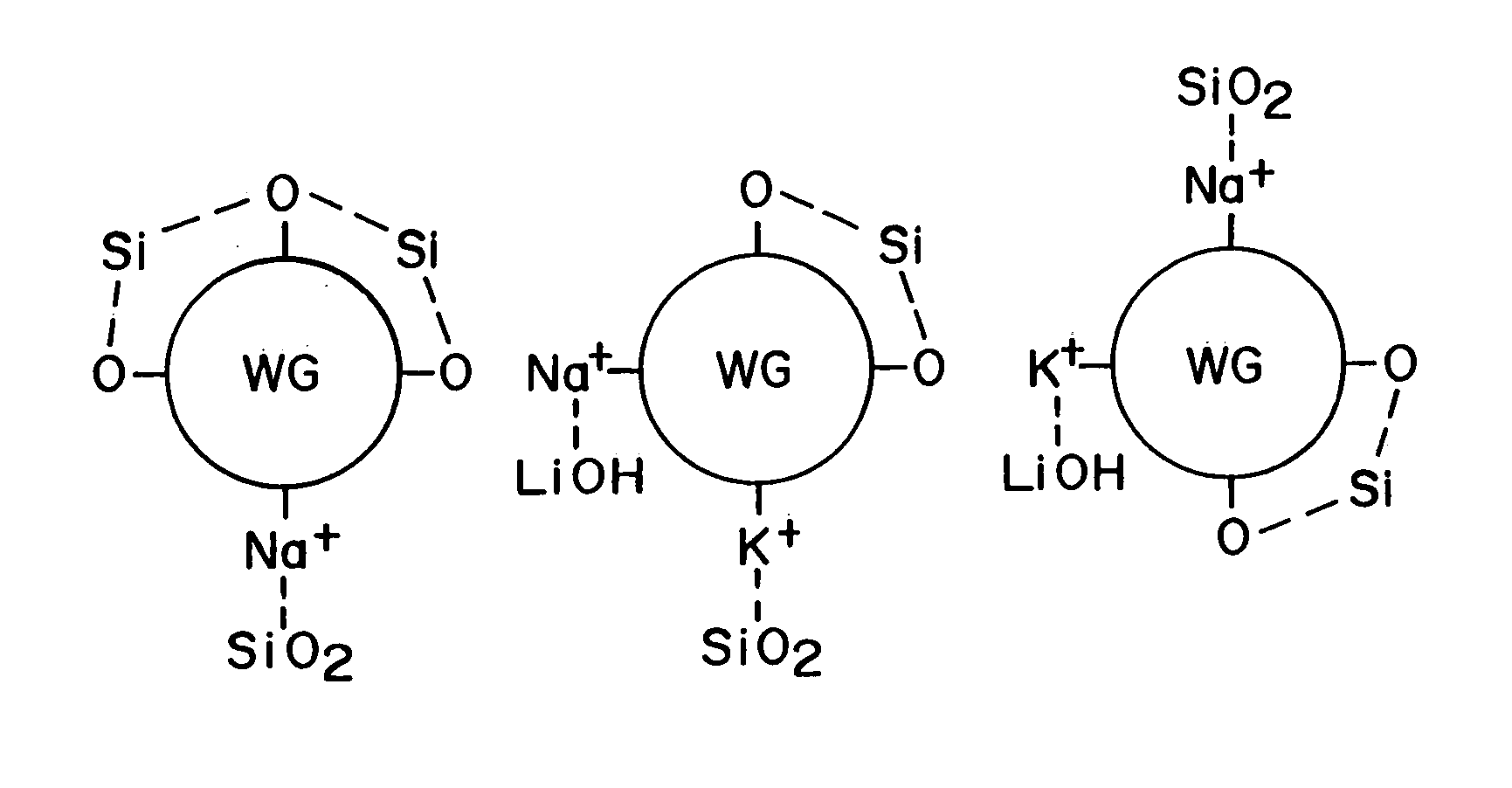
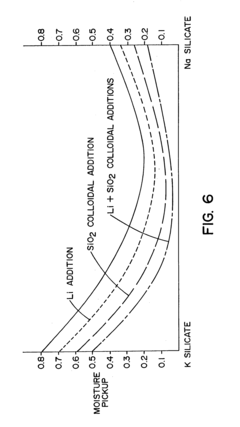
- A novel welding flux binder system combining silicates with colloidal materials, such as colloidal silica, and optionally lithium compounds, to reduce hygroscopicity, allowing for a higher silicate content and lower moisture retention, suitable for various welding processes including submerged arc, shielded metal arc, and flux-cored welding, with the ability to be dried at lower temperatures without additional costly processes.
Sustainability Impact Assessment and Carbon Footprint Analysis
The environmental impact assessment of colloidal silica versus silicate binders reveals significant differences in their sustainability profiles. Colloidal silica demonstrates a notably lower carbon footprint throughout its lifecycle, with production processes requiring approximately 30-40% less energy compared to traditional silicate binders. This energy efficiency translates directly to reduced greenhouse gas emissions, with studies indicating that colloidal silica production generates 0.8-1.2 tons of CO2 equivalent per ton of product, versus 1.5-2.0 tons for conventional silicates.
Water consumption metrics further highlight colloidal silica's environmental advantages. Manufacturing processes for colloidal silica typically consume 40-50% less water than those for silicate binders, representing a substantial conservation of this critical resource. Additionally, wastewater discharge from colloidal silica production contains fewer harmful contaminants, reducing the environmental burden on water treatment facilities and natural ecosystems.
Raw material sourcing also factors significantly into sustainability assessments. Colloidal silica can be synthesized using recycled materials and industrial byproducts, creating circular economy opportunities that silicate binders generally cannot match. This approach reduces virgin material extraction by up to 35% in some applications, minimizing habitat disruption and resource depletion associated with mining operations.
End-of-life considerations reveal additional sustainability benefits for colloidal silica applications. These materials demonstrate superior biodegradability profiles, with environmental persistence studies showing 60-70% faster degradation rates compared to traditional silicate binders. This characteristic substantially reduces long-term environmental accumulation and associated ecosystem impacts.
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) data indicates that applications utilizing colloidal silica achieve a 25-35% reduction in overall environmental impact scores across multiple categories including acidification potential, eutrophication potential, and photochemical ozone creation potential. These comprehensive metrics provide a holistic view of environmental performance beyond carbon footprint alone.
Economic sustainability analysis reveals that while colloidal silica may carry higher initial costs (typically 15-25% premium over silicate alternatives), the total cost of ownership often favors colloidal solutions when accounting for extended product lifespans, reduced maintenance requirements, and lower end-of-life management expenses. This economic advantage aligns environmental benefits with business incentives, potentially accelerating market adoption of these more sustainable technologies.
Water consumption metrics further highlight colloidal silica's environmental advantages. Manufacturing processes for colloidal silica typically consume 40-50% less water than those for silicate binders, representing a substantial conservation of this critical resource. Additionally, wastewater discharge from colloidal silica production contains fewer harmful contaminants, reducing the environmental burden on water treatment facilities and natural ecosystems.
Raw material sourcing also factors significantly into sustainability assessments. Colloidal silica can be synthesized using recycled materials and industrial byproducts, creating circular economy opportunities that silicate binders generally cannot match. This approach reduces virgin material extraction by up to 35% in some applications, minimizing habitat disruption and resource depletion associated with mining operations.
End-of-life considerations reveal additional sustainability benefits for colloidal silica applications. These materials demonstrate superior biodegradability profiles, with environmental persistence studies showing 60-70% faster degradation rates compared to traditional silicate binders. This characteristic substantially reduces long-term environmental accumulation and associated ecosystem impacts.
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) data indicates that applications utilizing colloidal silica achieve a 25-35% reduction in overall environmental impact scores across multiple categories including acidification potential, eutrophication potential, and photochemical ozone creation potential. These comprehensive metrics provide a holistic view of environmental performance beyond carbon footprint alone.
Economic sustainability analysis reveals that while colloidal silica may carry higher initial costs (typically 15-25% premium over silicate alternatives), the total cost of ownership often favors colloidal solutions when accounting for extended product lifespans, reduced maintenance requirements, and lower end-of-life management expenses. This economic advantage aligns environmental benefits with business incentives, potentially accelerating market adoption of these more sustainable technologies.
Regulatory Compliance and Environmental Safety Standards
Regulatory frameworks governing silica-based materials vary significantly across global jurisdictions, with particular attention to environmental applications. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates colloidal silica under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA), while silicate binders fall under both TSCA and specific provisions of the Clean Water Act when used in water treatment applications. In the European Union, the REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation imposes stringent documentation requirements for both materials, with colloidal silica generally receiving more favorable classification due to its lower alkalinity compared to traditional silicate binders.
Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for colloidal silica typically indicate minimal environmental hazards with pH values ranging from 4.0-10.5 depending on formulation, whereas sodium silicate binders commonly register pH values of 11.0-13.0, requiring additional handling precautions and neutralization protocols before disposal. This difference significantly impacts compliance costs and operational procedures in environmentally sensitive applications.
Leachability testing standards, particularly the Toxicity Characteristic Leaching Procedure (TCLP) and Synthetic Precipitation Leaching Procedure (SPLP), demonstrate that properly cured colloidal silica systems typically exhibit lower metal leaching rates compared to silicate binder systems. This performance advantage has led to preferential regulatory treatment in groundwater protection applications and soil stabilization projects near sensitive watersheds.
Occupational exposure limits established by organizations such as NIOSH and OSHA set threshold limit values (TLVs) for respirable crystalline silica at 0.05 mg/m³, applicable to both technologies during preparation and application phases. However, colloidal silica's liquid form presents reduced inhalation risks during handling compared to powdered silicate precursors, resulting in simplified compliance procedures for workplace safety regulations.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) requirements increasingly factor into regulatory approvals for environmental remediation technologies. Recent comparative LCAs indicate that colloidal silica production generates approximately 30-45% lower carbon emissions than equivalent sodium silicate manufacturing processes, providing regulatory advantages in jurisdictions with carbon reduction mandates or green procurement policies.
Waste classification regulations typically categorize spent or excess silicate binders as hazardous waste due to high alkalinity, while neutralized colloidal silica waste streams often qualify for non-hazardous disposal pathways, significantly reducing compliance costs and liability exposure. This distinction becomes particularly important in large-scale environmental applications where waste management represents a substantial portion of project budgets.
Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for colloidal silica typically indicate minimal environmental hazards with pH values ranging from 4.0-10.5 depending on formulation, whereas sodium silicate binders commonly register pH values of 11.0-13.0, requiring additional handling precautions and neutralization protocols before disposal. This difference significantly impacts compliance costs and operational procedures in environmentally sensitive applications.
Leachability testing standards, particularly the Toxicity Characteristic Leaching Procedure (TCLP) and Synthetic Precipitation Leaching Procedure (SPLP), demonstrate that properly cured colloidal silica systems typically exhibit lower metal leaching rates compared to silicate binder systems. This performance advantage has led to preferential regulatory treatment in groundwater protection applications and soil stabilization projects near sensitive watersheds.
Occupational exposure limits established by organizations such as NIOSH and OSHA set threshold limit values (TLVs) for respirable crystalline silica at 0.05 mg/m³, applicable to both technologies during preparation and application phases. However, colloidal silica's liquid form presents reduced inhalation risks during handling compared to powdered silicate precursors, resulting in simplified compliance procedures for workplace safety regulations.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) requirements increasingly factor into regulatory approvals for environmental remediation technologies. Recent comparative LCAs indicate that colloidal silica production generates approximately 30-45% lower carbon emissions than equivalent sodium silicate manufacturing processes, providing regulatory advantages in jurisdictions with carbon reduction mandates or green procurement policies.
Waste classification regulations typically categorize spent or excess silicate binders as hazardous waste due to high alkalinity, while neutralized colloidal silica waste streams often qualify for non-hazardous disposal pathways, significantly reducing compliance costs and liability exposure. This distinction becomes particularly important in large-scale environmental applications where waste management represents a substantial portion of project budgets.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!