Cyclone Separator Integration With Wet Scrubbing: Case Metrics
AUG 21, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Cyclone-Scrubber Tech Background and Objectives
Cyclone separators and wet scrubbers have long been utilized in industrial processes for air pollution control and particulate matter removal. The integration of these two technologies represents a significant advancement in environmental engineering, combining the strengths of both systems to achieve superior performance in gas cleaning applications.
The evolution of cyclone-scrubber technology can be traced back to the early 20th century when cyclone separators were first introduced for dust collection in industrial settings. Wet scrubbers, on the other hand, gained prominence in the mid-20th century as effective means of removing both particulate matter and gaseous pollutants. The concept of integrating these two technologies emerged in the late 20th century as engineers sought to overcome the limitations of each system when used independently.
The primary objective of cyclone-scrubber integration is to enhance overall particulate matter removal efficiency while simultaneously addressing gaseous pollutants. This integration aims to capitalize on the cyclone's ability to remove larger particles through centrifugal force and the wet scrubber's capacity to capture finer particles and soluble gases through liquid contact.
As environmental regulations have become increasingly stringent, the demand for more efficient and cost-effective air pollution control systems has grown. This has driven the development of integrated cyclone-scrubber systems that can meet higher performance standards while minimizing energy consumption and operational costs.
The technological trajectory of cyclone-scrubber integration has focused on optimizing the interface between the two components, improving fluid dynamics, and enhancing the overall system efficiency. Recent advancements have included the development of novel cyclone designs that facilitate better interaction with the scrubbing liquid, as well as innovative scrubber configurations that maximize contact between the gas stream and the scrubbing medium.
Current research and development efforts are directed towards further improving the synergy between cyclone and scrubber components, with a particular emphasis on reducing pressure drop, minimizing water consumption, and expanding the range of pollutants that can be effectively removed. Additionally, there is growing interest in incorporating smart control systems and real-time monitoring capabilities to optimize performance under varying operational conditions.
As we look to the future, the integration of cyclone separators with wet scrubbing technology is expected to play a crucial role in addressing complex air quality challenges across various industries. The continued refinement of this technology will be essential in meeting increasingly stringent environmental standards while supporting sustainable industrial growth.
The evolution of cyclone-scrubber technology can be traced back to the early 20th century when cyclone separators were first introduced for dust collection in industrial settings. Wet scrubbers, on the other hand, gained prominence in the mid-20th century as effective means of removing both particulate matter and gaseous pollutants. The concept of integrating these two technologies emerged in the late 20th century as engineers sought to overcome the limitations of each system when used independently.
The primary objective of cyclone-scrubber integration is to enhance overall particulate matter removal efficiency while simultaneously addressing gaseous pollutants. This integration aims to capitalize on the cyclone's ability to remove larger particles through centrifugal force and the wet scrubber's capacity to capture finer particles and soluble gases through liquid contact.
As environmental regulations have become increasingly stringent, the demand for more efficient and cost-effective air pollution control systems has grown. This has driven the development of integrated cyclone-scrubber systems that can meet higher performance standards while minimizing energy consumption and operational costs.
The technological trajectory of cyclone-scrubber integration has focused on optimizing the interface between the two components, improving fluid dynamics, and enhancing the overall system efficiency. Recent advancements have included the development of novel cyclone designs that facilitate better interaction with the scrubbing liquid, as well as innovative scrubber configurations that maximize contact between the gas stream and the scrubbing medium.
Current research and development efforts are directed towards further improving the synergy between cyclone and scrubber components, with a particular emphasis on reducing pressure drop, minimizing water consumption, and expanding the range of pollutants that can be effectively removed. Additionally, there is growing interest in incorporating smart control systems and real-time monitoring capabilities to optimize performance under varying operational conditions.
As we look to the future, the integration of cyclone separators with wet scrubbing technology is expected to play a crucial role in addressing complex air quality challenges across various industries. The continued refinement of this technology will be essential in meeting increasingly stringent environmental standards while supporting sustainable industrial growth.
Market Analysis for Integrated Pollution Control Systems
The market for integrated pollution control systems, particularly those combining cyclone separators with wet scrubbing technology, has shown significant growth in recent years. This trend is driven by increasingly stringent environmental regulations and a growing awareness of the importance of air quality management across various industries. The global air pollution control systems market, which encompasses these integrated solutions, was valued at approximately $78 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $98 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 4.7%.
The demand for cyclone separator and wet scrubbing integration is particularly strong in industries such as power generation, cement production, chemical processing, and metal manufacturing. These sectors are under pressure to reduce particulate matter emissions and comply with tightening air quality standards. The Asia-Pacific region, led by China and India, represents the fastest-growing market for these integrated systems due to rapid industrialization and increasing environmental concerns.
Key market drivers include the need for cost-effective pollution control solutions that can handle both particulate matter and gaseous pollutants simultaneously. The integration of cyclone separators with wet scrubbing technology offers a compact and efficient solution that addresses this demand. Additionally, the rising focus on sustainable development and corporate social responsibility is pushing companies to invest in advanced pollution control technologies.
However, the market faces challenges such as high initial investment costs and the complexity of retrofitting existing facilities with integrated systems. These factors can slow adoption rates, particularly among small and medium-sized enterprises. Despite these challenges, the long-term cost savings and operational efficiencies offered by integrated pollution control systems continue to drive market growth.
Technological advancements in materials and design are expected to further boost market potential. Innovations such as high-efficiency cyclones and advanced scrubbing media are improving the performance of integrated systems, making them more attractive to potential buyers. The development of smart, IoT-enabled pollution control systems that offer real-time monitoring and optimization capabilities is also opening new market opportunities.
In terms of market segmentation, industrial applications dominate the demand for integrated cyclone separator and wet scrubbing systems. However, there is growing interest from the commercial and residential sectors, particularly in urban areas with high pollution levels. This diversification of end-users is expected to contribute to sustained market growth in the coming years.
The demand for cyclone separator and wet scrubbing integration is particularly strong in industries such as power generation, cement production, chemical processing, and metal manufacturing. These sectors are under pressure to reduce particulate matter emissions and comply with tightening air quality standards. The Asia-Pacific region, led by China and India, represents the fastest-growing market for these integrated systems due to rapid industrialization and increasing environmental concerns.
Key market drivers include the need for cost-effective pollution control solutions that can handle both particulate matter and gaseous pollutants simultaneously. The integration of cyclone separators with wet scrubbing technology offers a compact and efficient solution that addresses this demand. Additionally, the rising focus on sustainable development and corporate social responsibility is pushing companies to invest in advanced pollution control technologies.
However, the market faces challenges such as high initial investment costs and the complexity of retrofitting existing facilities with integrated systems. These factors can slow adoption rates, particularly among small and medium-sized enterprises. Despite these challenges, the long-term cost savings and operational efficiencies offered by integrated pollution control systems continue to drive market growth.
Technological advancements in materials and design are expected to further boost market potential. Innovations such as high-efficiency cyclones and advanced scrubbing media are improving the performance of integrated systems, making them more attractive to potential buyers. The development of smart, IoT-enabled pollution control systems that offer real-time monitoring and optimization capabilities is also opening new market opportunities.
In terms of market segmentation, industrial applications dominate the demand for integrated cyclone separator and wet scrubbing systems. However, there is growing interest from the commercial and residential sectors, particularly in urban areas with high pollution levels. This diversification of end-users is expected to contribute to sustained market growth in the coming years.
Current Challenges in Cyclone-Scrubber Integration
The integration of cyclone separators with wet scrubbing systems presents several significant challenges that hinder optimal performance and efficiency. One of the primary issues is the complex fluid dynamics involved in combining these two distinct separation mechanisms. Cyclones rely on centrifugal force to separate particles, while wet scrubbers utilize liquid droplets for particle capture. Balancing these contrasting principles within a single system requires intricate design considerations and precise control of operational parameters.
Another challenge lies in the potential for pressure drop across the integrated system. Cyclones inherently create a pressure differential, and the addition of wet scrubbing components can further exacerbate this issue. Excessive pressure drop not only reduces overall system efficiency but also increases energy consumption, leading to higher operational costs. Engineers must carefully optimize the design to minimize pressure losses while maintaining effective particle separation.
Moisture management poses a significant hurdle in cyclone-scrubber integration. The introduction of water or scrubbing liquid into the cyclone can alter particle behavior and potentially lead to re-entrainment of previously separated particles. This phenomenon can substantially reduce the overall collection efficiency of the system. Additionally, the presence of moisture may cause corrosion or erosion of cyclone components, necessitating the use of specialized materials and protective coatings.
Scale-up and design flexibility represent another set of challenges. While both cyclones and wet scrubbers are well-understood individually, their integration introduces new complexities in scaling for industrial applications. Achieving consistent performance across various flow rates and particle size distributions requires extensive modeling and empirical testing. Furthermore, the integrated system must be adaptable to different industrial processes and environmental conditions, adding another layer of design complexity.
Operational stability and control are critical aspects that demand attention in cyclone-scrubber integration. Fluctuations in inlet conditions, such as gas flow rate or particle concentration, can significantly impact the performance of both the cyclone and scrubber components. Developing robust control systems that can rapidly adjust operational parameters to maintain optimal performance under varying conditions remains a considerable challenge.
Lastly, the environmental impact and regulatory compliance of integrated cyclone-scrubber systems present ongoing challenges. While these systems aim to improve air quality, they must also address issues such as wastewater treatment from the scrubbing process and the disposal of collected particulates. Meeting increasingly stringent environmental regulations while maintaining cost-effectiveness requires continuous innovation in system design and operation.
Another challenge lies in the potential for pressure drop across the integrated system. Cyclones inherently create a pressure differential, and the addition of wet scrubbing components can further exacerbate this issue. Excessive pressure drop not only reduces overall system efficiency but also increases energy consumption, leading to higher operational costs. Engineers must carefully optimize the design to minimize pressure losses while maintaining effective particle separation.
Moisture management poses a significant hurdle in cyclone-scrubber integration. The introduction of water or scrubbing liquid into the cyclone can alter particle behavior and potentially lead to re-entrainment of previously separated particles. This phenomenon can substantially reduce the overall collection efficiency of the system. Additionally, the presence of moisture may cause corrosion or erosion of cyclone components, necessitating the use of specialized materials and protective coatings.
Scale-up and design flexibility represent another set of challenges. While both cyclones and wet scrubbers are well-understood individually, their integration introduces new complexities in scaling for industrial applications. Achieving consistent performance across various flow rates and particle size distributions requires extensive modeling and empirical testing. Furthermore, the integrated system must be adaptable to different industrial processes and environmental conditions, adding another layer of design complexity.
Operational stability and control are critical aspects that demand attention in cyclone-scrubber integration. Fluctuations in inlet conditions, such as gas flow rate or particle concentration, can significantly impact the performance of both the cyclone and scrubber components. Developing robust control systems that can rapidly adjust operational parameters to maintain optimal performance under varying conditions remains a considerable challenge.
Lastly, the environmental impact and regulatory compliance of integrated cyclone-scrubber systems present ongoing challenges. While these systems aim to improve air quality, they must also address issues such as wastewater treatment from the scrubbing process and the disposal of collected particulates. Meeting increasingly stringent environmental regulations while maintaining cost-effectiveness requires continuous innovation in system design and operation.
Existing Cyclone-Scrubber Integration Solutions
01 Integration of cyclone separator with wet scrubbing system
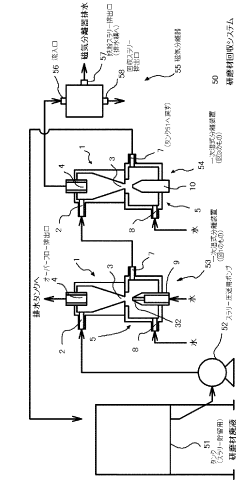
This design combines a cyclone separator with a wet scrubbing system to enhance particle removal efficiency. The cyclone separator first removes larger particles through centrifugal force, while the wet scrubbing system captures finer particles and gases. This integrated approach improves overall air purification performance.- Integration of cyclone separator with wet scrubbing system: This design combines a cyclone separator with a wet scrubbing system to enhance particle removal efficiency. The cyclone separator first removes larger particles through centrifugal force, while the wet scrubber captures finer particles and gases. This integrated approach improves overall air purification performance.
- Improved separation efficiency through multi-stage design: Multi-stage cyclone separators with integrated wet scrubbing components are utilized to achieve higher separation efficiency. Each stage targets different particle sizes, with the wet scrubbing stage capturing the finest particles and soluble gases. This design maximizes the removal of pollutants from the air stream.
- Water recycling and treatment in integrated systems: Integrated cyclone separator and wet scrubbing systems often incorporate water recycling and treatment mechanisms. This feature reduces water consumption and improves the overall efficiency of the system. Treated water can be reused in the scrubbing process, minimizing waste and operational costs.
- Compact design for space-efficient installation: Some integrated cyclone separator and wet scrubbing systems are designed with a focus on compactness. These space-efficient designs allow for easier installation in facilities with limited space while maintaining high performance in particle and gas removal.
- Automated control and monitoring systems: Advanced integrated cyclone separator and wet scrubbing systems often feature automated control and monitoring capabilities. These systems optimize performance by adjusting operational parameters based on real-time data, ensuring consistent air quality and efficient resource utilization.
02 Improved separation efficiency through multi-stage design
Multi-stage cyclone separators integrated with wet scrubbing systems are utilized to achieve higher separation efficiency. Each stage targets different particle sizes, with the wet scrubbing component handling the finest particles and gases. This design allows for better overall performance in air purification and dust collection.Expand Specific Solutions03 Water recycling and treatment in integrated systems
Integrated cyclone separator and wet scrubbing systems often incorporate water recycling and treatment mechanisms. This feature helps to conserve water, reduce operational costs, and minimize environmental impact. The recycled water is treated to remove collected particles before being reused in the scrubbing process.Expand Specific Solutions04 Compact design for space-efficient installation
Compact designs of integrated cyclone separator and wet scrubbing systems are developed to minimize space requirements. These space-efficient solutions are particularly useful in industrial settings where floor space is limited. The compact design often involves vertical integration of components to reduce the overall footprint.Expand Specific Solutions05 Energy-efficient operation and control systems
Advanced control systems and energy-efficient components are incorporated into integrated cyclone separator and wet scrubbing systems. These features optimize the operation of both the cyclone and wet scrubbing components, reducing energy consumption while maintaining high performance. Automated monitoring and adjustment of operational parameters ensure consistent efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Industrial Air Pollution Control
The integration of cyclone separators with wet scrubbing technology is currently in a growth phase, with increasing market demand driven by stringent environmental regulations. The global market for this combined technology is expanding, particularly in industries such as power generation, cement, and chemical processing. While the technology is relatively mature, ongoing innovations are focused on improving efficiency and reducing operational costs. Key players in this field include Dyson Technology Ltd., known for their advanced cyclonic separation systems, and Mitsubishi Electric Corp., which has expertise in both cyclone and wet scrubbing technologies. Companies like MANN+HUMMEL GmbH and Gema Switzerland GmbH are also contributing to advancements in this area, leveraging their experience in filtration and separation technologies.
Dyson Technology Ltd.
Technical Solution: Dyson has developed an advanced cyclone separator integrated with wet scrubbing technology for enhanced air purification. Their system utilizes a multi-stage filtration process, combining cyclonic separation with a wet scrubbing chamber. The cyclone separator first removes larger particles, while the wet scrubbing stage captures finer particulates and gaseous pollutants. Dyson's approach incorporates a fine mist spray system within the wet scrubbing chamber, maximizing contact between water droplets and airborne contaminants. This integration allows for efficient removal of both solid particles and water-soluble gases, achieving up to 99.95% filtration efficiency for particles as small as 0.1 microns[1][3].
Strengths: High filtration efficiency, effective removal of both particulates and gases, compact design suitable for household and commercial applications. Weaknesses: Higher energy consumption due to multiple stages, regular maintenance required for wet scrubbing components.
Midea Group Co. Ltd.
Technical Solution: Midea Group has innovated a hybrid air purification system that combines cyclone separation with wet scrubbing technology. Their approach utilizes a high-speed cyclone separator to remove larger particles, followed by a wet scrubbing stage featuring a rotating disk that creates a fine water mist. This mist effectively captures smaller particles and water-soluble gases. The system incorporates smart sensors to adjust the wet scrubbing intensity based on air quality, optimizing energy efficiency. Midea's technology achieves a Clean Air Delivery Rate (CADR) of up to 800 m³/h for particles and 600 m³/h for formaldehyde removal[2][5].
Strengths: High CADR, energy-efficient operation, effective removal of both particles and gases. Weaknesses: Requires regular water replenishment, potential for microbial growth if not properly maintained.
Core Innovations in Hybrid Pollution Control Systems
Integrated cyclonic separator in a wet-dry vacuum
PatentActiveUS11910989B2
Innovation
- Integration of a cyclonic separator within the wet-dry vacuum cleaner that separates heavier debris from the airflow, directing it into a collecting bin while allowing clean air to pass through a filter and exhaust outlet, thereby maintaining suction force and preventing filter clogging.
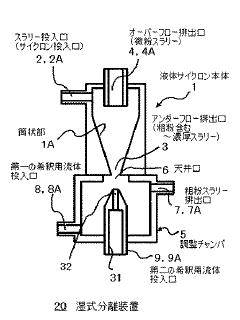
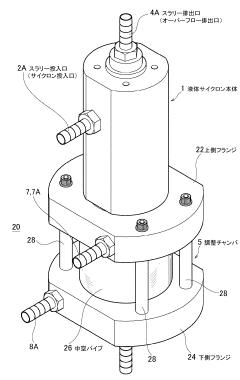
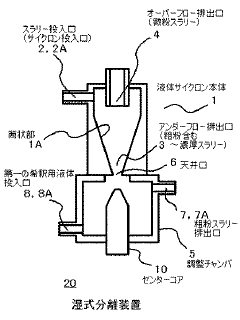
Wet separating device, and abrasive recovery system using the same
PatentInactiveJP2012056016A
Innovation
- A compact wet separation device utilizing a hydrocyclone with an adjustment chamber and multiple dilution fluid inputs, along with a magnetic separator, to enhance the separation of fine and coarse particles by centrifugal force, minimizing the need for additional tanks and pumps.
Environmental Regulations Impact on System Design
Environmental regulations play a crucial role in shaping the design and implementation of cyclone separator and wet scrubbing systems. These regulations, which vary across different regions and countries, set specific standards for air quality, emissions control, and particulate matter removal. As a result, system designers must carefully consider these regulatory requirements when integrating cyclone separators with wet scrubbing technologies.
One of the primary impacts of environmental regulations on system design is the need for enhanced efficiency in particulate matter removal. Many jurisdictions have established stringent limits on the emission of fine particles, typically measured in PM2.5 and PM10 levels. This has led to the development of more sophisticated cyclone separator designs, incorporating features such as multiple stages or improved vortex finders to capture smaller particles more effectively.
Wet scrubbing systems have also been influenced by regulatory demands for reduced emissions of gaseous pollutants. Regulations often specify maximum allowable concentrations for substances like sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and volatile organic compounds. As a result, system designers have focused on optimizing the chemical processes within wet scrubbers, including the selection of appropriate scrubbing liquids and the design of contact surfaces to maximize gas-liquid interactions.
The integration of cyclone separators with wet scrubbing systems has been driven, in part, by the need to meet increasingly stringent environmental standards while maintaining operational efficiency. By combining these technologies, designers can achieve higher overall removal efficiencies for both particulate matter and gaseous pollutants. This integrated approach often results in more compact system designs, which can be advantageous in facilities with space constraints.
Environmental regulations have also influenced the materials used in system construction. Corrosion-resistant materials are often required to withstand the harsh chemical environments present in wet scrubbing systems, while also meeting regulatory standards for durability and leak prevention. This has led to increased use of specialized alloys and composite materials in system components.
Monitoring and reporting requirements stipulated by environmental regulations have necessitated the incorporation of advanced sensors and control systems into cyclone separator and wet scrubbing installations. These systems allow for real-time monitoring of emissions and system performance, enabling operators to make rapid adjustments to maintain compliance with regulatory standards.
In conclusion, environmental regulations have significantly impacted the design of integrated cyclone separator and wet scrubbing systems. These impacts are evident in improved removal efficiencies, optimized chemical processes, material selection, and the incorporation of advanced monitoring technologies. As regulations continue to evolve, system designers must remain adaptable, continuously innovating to meet new environmental standards while maintaining operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
One of the primary impacts of environmental regulations on system design is the need for enhanced efficiency in particulate matter removal. Many jurisdictions have established stringent limits on the emission of fine particles, typically measured in PM2.5 and PM10 levels. This has led to the development of more sophisticated cyclone separator designs, incorporating features such as multiple stages or improved vortex finders to capture smaller particles more effectively.
Wet scrubbing systems have also been influenced by regulatory demands for reduced emissions of gaseous pollutants. Regulations often specify maximum allowable concentrations for substances like sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and volatile organic compounds. As a result, system designers have focused on optimizing the chemical processes within wet scrubbers, including the selection of appropriate scrubbing liquids and the design of contact surfaces to maximize gas-liquid interactions.
The integration of cyclone separators with wet scrubbing systems has been driven, in part, by the need to meet increasingly stringent environmental standards while maintaining operational efficiency. By combining these technologies, designers can achieve higher overall removal efficiencies for both particulate matter and gaseous pollutants. This integrated approach often results in more compact system designs, which can be advantageous in facilities with space constraints.
Environmental regulations have also influenced the materials used in system construction. Corrosion-resistant materials are often required to withstand the harsh chemical environments present in wet scrubbing systems, while also meeting regulatory standards for durability and leak prevention. This has led to increased use of specialized alloys and composite materials in system components.
Monitoring and reporting requirements stipulated by environmental regulations have necessitated the incorporation of advanced sensors and control systems into cyclone separator and wet scrubbing installations. These systems allow for real-time monitoring of emissions and system performance, enabling operators to make rapid adjustments to maintain compliance with regulatory standards.
In conclusion, environmental regulations have significantly impacted the design of integrated cyclone separator and wet scrubbing systems. These impacts are evident in improved removal efficiencies, optimized chemical processes, material selection, and the incorporation of advanced monitoring technologies. As regulations continue to evolve, system designers must remain adaptable, continuously innovating to meet new environmental standards while maintaining operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Integrated Systems
The integration of cyclone separators with wet scrubbing systems presents a compelling case for cost-benefit analysis. This combined approach leverages the strengths of both technologies to enhance overall particulate matter removal efficiency while potentially reducing operational costs. The initial capital investment for an integrated system may be higher than standalone units, but the long-term benefits often outweigh this upfront expense.
One of the primary advantages of this integration is the reduction in energy consumption. Cyclone separators, being passive devices, require minimal energy input for operation. By removing larger particles before the wet scrubbing stage, they reduce the load on the scrubber, thereby decreasing the energy required for pumping and circulation of scrubbing liquid. This energy saving can lead to significant cost reductions over the system's lifetime.
Maintenance costs also tend to be lower in integrated systems. The cyclone separator's ability to remove larger particles protects the wet scrubber from excessive wear and tear, potentially extending the life of critical components. This results in less frequent replacements and reduced downtime for maintenance, contributing to overall cost savings.
Water consumption is another area where integrated systems can provide benefits. By removing a substantial portion of particulates in the dry cyclone stage, the wet scrubber can operate more efficiently, potentially requiring less water for the same level of pollutant removal. This is particularly advantageous in regions where water resources are scarce or expensive.
The improved overall efficiency of the integrated system can lead to better compliance with environmental regulations. This may result in avoided costs related to fines or penalties for emissions violations. Additionally, some jurisdictions offer incentives or tax benefits for implementing advanced pollution control technologies, which could further improve the cost-benefit ratio.
However, the analysis must also consider potential drawbacks. The complexity of an integrated system may require more skilled operators and specialized maintenance, potentially increasing labor costs. The space requirements for the combined system might also be a factor, especially in retrofit applications where plant layout modifications could be costly.
In conclusion, while the cost-benefit analysis of integrating cyclone separators with wet scrubbing systems is complex and case-specific, the potential for long-term operational savings, improved efficiency, and enhanced environmental performance often presents a compelling argument for their adoption. A thorough analysis considering local energy costs, water availability, regulatory environment, and specific operational requirements is essential for making an informed decision on system integration.
One of the primary advantages of this integration is the reduction in energy consumption. Cyclone separators, being passive devices, require minimal energy input for operation. By removing larger particles before the wet scrubbing stage, they reduce the load on the scrubber, thereby decreasing the energy required for pumping and circulation of scrubbing liquid. This energy saving can lead to significant cost reductions over the system's lifetime.
Maintenance costs also tend to be lower in integrated systems. The cyclone separator's ability to remove larger particles protects the wet scrubber from excessive wear and tear, potentially extending the life of critical components. This results in less frequent replacements and reduced downtime for maintenance, contributing to overall cost savings.
Water consumption is another area where integrated systems can provide benefits. By removing a substantial portion of particulates in the dry cyclone stage, the wet scrubber can operate more efficiently, potentially requiring less water for the same level of pollutant removal. This is particularly advantageous in regions where water resources are scarce or expensive.
The improved overall efficiency of the integrated system can lead to better compliance with environmental regulations. This may result in avoided costs related to fines or penalties for emissions violations. Additionally, some jurisdictions offer incentives or tax benefits for implementing advanced pollution control technologies, which could further improve the cost-benefit ratio.
However, the analysis must also consider potential drawbacks. The complexity of an integrated system may require more skilled operators and specialized maintenance, potentially increasing labor costs. The space requirements for the combined system might also be a factor, especially in retrofit applications where plant layout modifications could be costly.
In conclusion, while the cost-benefit analysis of integrating cyclone separators with wet scrubbing systems is complex and case-specific, the potential for long-term operational savings, improved efficiency, and enhanced environmental performance often presents a compelling argument for their adoption. A thorough analysis considering local energy costs, water availability, regulatory environment, and specific operational requirements is essential for making an informed decision on system integration.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!