Future Trends in Propionic Acid for Advanced Preservation
Propionic Acid Evolution and Preservation Goals
Propionic acid has been a cornerstone in food preservation for decades, with its journey marked by significant milestones in technological advancements and application expansions. The evolution of propionic acid as a preservative has been driven by the increasing demand for safer, more effective, and sustainable food preservation methods.
Initially used primarily in bakery products, propionic acid's application has broadened to encompass a wide range of food and feed products. This expansion has been facilitated by improved production processes, resulting in higher purity and more cost-effective manufacturing. The development of novel formulations and delivery systems has further enhanced its efficacy and ease of use across various food matrices.
Recent years have witnessed a shift towards natural and clean-label preservatives, prompting research into bio-based production methods for propionic acid. This trend aligns with consumer preferences for more natural food ingredients and sustainable production practices. Consequently, the industry has seen increased efforts in developing fermentation-based production processes using renewable resources.
The preservation goals associated with propionic acid have evolved beyond mere shelf-life extension. Modern objectives include maintaining nutritional quality, enhancing food safety, and reducing food waste throughout the supply chain. There is a growing focus on developing synergistic preservative systems that combine propionic acid with other natural antimicrobials to achieve broader spectrum protection against various spoilage organisms and pathogens.
Looking ahead, the future of propionic acid in advanced preservation is likely to be shaped by several key factors. These include the development of smart packaging technologies incorporating propionic acid-based preservatives, the exploration of nanotechnology for improved delivery and efficacy, and the integration of propionic acid into active packaging systems.
Furthermore, there is an increasing emphasis on understanding the molecular mechanisms of propionic acid's antimicrobial action. This knowledge is expected to lead to more targeted and efficient preservation strategies, potentially allowing for reduced usage levels while maintaining or improving efficacy. The ongoing research into the potential health benefits of propionic acid, such as its role in gut health, may also open new avenues for its application in functional foods and nutraceuticals.
As global food security concerns intensify, the role of propionic acid in preserving staple foods and reducing post-harvest losses in developing countries is gaining attention. This presents an opportunity for innovation in formulations suitable for diverse climatic conditions and storage facilities.
Market Analysis for Advanced Preservation Solutions
The global market for advanced preservation solutions is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand for food safety, extended shelf life, and natural preservatives. Propionic acid, a key player in this market, is gaining traction due to its effectiveness in inhibiting mold growth and bacterial proliferation in various food products. The market for propionic acid in advanced preservation is expected to expand steadily over the coming years, with a particular focus on applications in bakery goods, dairy products, and animal feed.
Consumer preferences are shifting towards clean label products and natural preservatives, creating opportunities for propionic acid-based solutions. This trend is particularly evident in developed markets such as North America and Europe, where consumers are increasingly conscious of food additives and their potential health impacts. As a result, manufacturers are reformulating their products to include more natural preservatives, with propionic acid and its salts being favored options.
The food and beverage industry remains the largest end-user segment for propionic acid in preservation applications. Within this sector, the bakery industry is a major consumer, utilizing propionic acid to extend the shelf life of bread and other baked goods. The dairy industry is another significant market, employing propionic acid to prevent mold growth in cheese and other dairy products. Additionally, the animal feed industry is adopting propionic acid as a preservative to maintain feed quality and prevent spoilage.
Geographically, North America and Europe are the leading markets for propionic acid in advanced preservation, owing to stringent food safety regulations and high consumer awareness. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a rapidly growing market, driven by increasing urbanization, rising disposable incomes, and growing demand for processed foods with longer shelf lives.
The competitive landscape of the propionic acid market for advanced preservation is characterized by the presence of both large multinational corporations and smaller specialized companies. Key players are focusing on product innovation, expanding their production capacities, and strategic partnerships to gain a competitive edge. Research and development efforts are being directed towards improving the efficacy of propionic acid-based preservatives and developing new applications across various food categories.
Challenges in the market include fluctuating raw material prices, which can impact the cost-effectiveness of propionic acid-based solutions. Additionally, there is growing competition from other natural preservatives and alternative preservation technologies. However, the proven track record of propionic acid in food preservation and its status as a generally recognized as safe (GRAS) substance continue to support its market growth.
Current Challenges in Propionic Acid Preservation
Propionic acid preservation faces several significant challenges in its current applications. One of the primary issues is the development of resistance in microorganisms. As propionic acid has been widely used as a preservative for decades, certain strains of bacteria and fungi have evolved to withstand its antimicrobial effects. This resistance reduces the efficacy of propionic acid-based preservatives, necessitating higher concentrations or alternative solutions.
Another challenge lies in the organoleptic properties of propionic acid. Its strong, pungent odor can negatively impact the sensory qualities of food products, particularly in higher concentrations required to combat resistant microorganisms. This limitation restricts its use in certain food applications where flavor and aroma are crucial factors.
The environmental impact of propionic acid production and use is also a growing concern. Traditional manufacturing processes rely on petrochemical feedstocks, contributing to carbon emissions and environmental degradation. As sustainability becomes increasingly important in industrial practices, finding greener production methods for propionic acid is a pressing challenge.
Regulatory hurdles present another obstacle in the advancement of propionic acid preservation. While generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by many food safety authorities, there are ongoing debates about acceptable levels in various food products. Stricter regulations in some regions limit the use of propionic acid, forcing manufacturers to seek alternatives or reformulate their products.
The cost-effectiveness of propionic acid preservation is also under scrutiny. As production costs fluctuate with petroleum prices, maintaining a stable and economically viable supply chain for propionic acid-based preservatives can be challenging. This economic pressure drives the need for more efficient production methods and alternative sources.
Lastly, the limited spectrum of antimicrobial activity poses a challenge in certain applications. While effective against many molds and bacteria, propionic acid may not provide comprehensive protection against all types of spoilage microorganisms. This limitation necessitates the use of additional preservatives in some cases, complicating formulations and potentially increasing costs.
Addressing these challenges requires innovative approaches in microbiology, chemistry, and process engineering. The future of propionic acid preservation hinges on overcoming these obstacles to maintain its relevance in an evolving market that demands safer, more sustainable, and more effective preservation solutions.
Existing Propionic Acid Preservation Methods
01 Use of propionic acid as a preservative
Propionic acid is widely used as a preservative in various industries, particularly in food and feed preservation. It inhibits the growth of mold and bacteria, extending the shelf life of products. The acid can be applied directly or in the form of its salts, such as calcium or sodium propionate.- Use of propionic acid as a preservative: Propionic acid is widely used as a preservative in various industries due to its antimicrobial properties. It effectively inhibits the growth of mold and bacteria, extending the shelf life of products. This organic acid is particularly useful in food preservation, animal feed, and pharmaceutical applications.
- Production methods for propionic acid: Various methods have been developed for the production of propionic acid, including chemical synthesis and fermentation processes. These methods aim to improve yield, reduce costs, and enhance the purity of the final product. Innovations in production techniques contribute to the increased availability and application of propionic acid as a preservative.
- Formulations containing propionic acid for preservation: Propionic acid is often incorporated into various formulations to enhance their preservative properties. These formulations may include other complementary ingredients to improve efficacy, stability, or application-specific characteristics. The development of such formulations expands the use of propionic acid in different industries and products.
- Applications of propionic acid in food preservation: Propionic acid and its salts are commonly used in food preservation, particularly in baked goods, dairy products, and processed foods. It helps prevent mold growth and bacterial contamination, thereby extending the shelf life of food products. The application of propionic acid in food preservation is subject to regulatory guidelines and safety assessments.
- Propionic acid in animal feed preservation: Propionic acid is widely used in the preservation of animal feed, particularly in silage and grain storage. It helps prevent the growth of harmful microorganisms, maintains nutritional quality, and reduces feed spoilage. The use of propionic acid in animal feed preservation contributes to improved livestock health and productivity.
02 Production methods for propionic acid
Various methods are employed to produce propionic acid, including fermentation processes and chemical synthesis. Some techniques involve the oxidation of propionaldehyde or the carbonylation of ethylene. Continuous production methods and improvements in catalysts have been developed to enhance efficiency and yield.Expand Specific Solutions03 Applications in animal feed preservation
Propionic acid and its derivatives are extensively used in animal feed preservation. They help prevent mold growth, reduce bacterial contamination, and maintain the nutritional value of feed. This application is particularly important in silage preservation and in maintaining the quality of grain-based feeds.Expand Specific Solutions04 Synergistic combinations with other preservatives
Propionic acid is often used in combination with other preservatives to enhance its effectiveness. These synergistic combinations can provide broader spectrum antimicrobial activity and allow for lower overall preservative concentrations. Common combinations include mixtures with benzoic acid, sorbic acid, or other organic acids.Expand Specific Solutions05 Novel formulations and delivery systems
Research has focused on developing novel formulations and delivery systems for propionic acid preservation. These include microencapsulation techniques, controlled release systems, and the development of propionic acid-based preservative blends. Such innovations aim to improve the efficacy and ease of application of propionic acid as a preservative.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Advanced Preservation Industry
The market for propionic acid in advanced preservation is evolving rapidly, driven by increasing demand for natural preservatives and sustainable solutions. The industry is in a growth phase, with the global propionic acid market expected to expand significantly in the coming years. Major players like BASF, Dow, and Eastman Chemical are investing heavily in research and development to improve production processes and develop novel applications. Emerging companies such as BioVeritas and Kemin Industries are focusing on bio-based production methods, leveraging fermentation technologies to produce propionic acid from renewable resources. This shift towards sustainable production aligns with growing consumer preferences for natural preservatives, indicating a promising future for bio-based propionic acid in food preservation and other applications.
BASF Corp.
Kemin Industries, Inc.
Innovative Propionic Acid Formulations
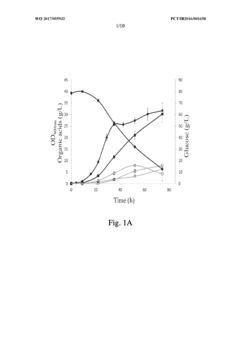
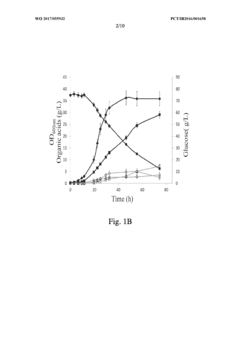
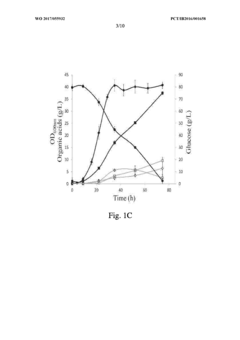
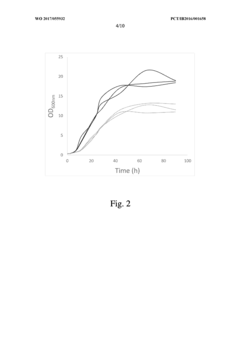
- Genome shuffling between selected Propionibacterium strains, such as P. acidipropionici ATCC 4875 and P. acidipropionici ATCC 55737, to generate novel strains with enhanced growth rates and propionic acid production, utilizing genetic material exchange to create strains with improved metabolic pathways and regulatory mechanisms.
- Selecting and combining Propionibacterium strains with high potential for propionic acid production, such as P. acidipropionici ATCC 4875 and P. acidipropionici ATCC 55737, through genome shuffling to create novel strains with improved growth rates and reduced byproduct production, such as P. acidipropionici F3E8, which achieves enhanced propionic acid yields and growth rates.
Regulatory Framework for Food Preservatives
The regulatory framework for food preservatives plays a crucial role in shaping the future trends of propionic acid in advanced preservation. As consumer demand for safer and more natural food products continues to grow, regulatory bodies worldwide are adapting their guidelines to ensure the responsible use of preservatives while maintaining food safety standards.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates the use of propionic acid and its salts as Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) substances. The FDA has established specific limits for the use of propionic acid in various food categories, ensuring its safe application in food preservation. Similarly, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has approved propionic acid and its salts as food additives, designating them with E-numbers E280-E283.
Global harmonization efforts, such as the Codex Alimentarius Commission, are working towards establishing international standards for food additives, including propionic acid. These efforts aim to facilitate trade while ensuring consistent safety standards across different regions. As a result, manufacturers are increasingly focusing on developing preservation solutions that comply with diverse regulatory requirements.
The regulatory landscape is evolving to address emerging concerns related to food preservatives. For instance, there is a growing emphasis on the potential health impacts of long-term preservative consumption. Regulatory bodies are conducting ongoing assessments of preservatives, including propionic acid, to evaluate their safety profiles and update guidelines accordingly.
Sustainability and environmental considerations are also influencing regulatory frameworks. Authorities are encouraging the development of eco-friendly preservation methods, which may impact the future use of propionic acid. Manufacturers are exploring ways to optimize propionic acid production and application to align with sustainability goals and meet evolving regulatory expectations.
Labeling requirements for food preservatives are becoming more stringent, with an increased focus on transparency. Regulations are mandating clearer disclosure of preservatives used in food products, including propionic acid. This trend is driving innovation in formulation and packaging to meet both regulatory compliance and consumer preferences for "clean label" products.
As the food industry continues to globalize, regulatory cooperation between countries is becoming increasingly important. International agreements and mutual recognition of safety assessments are facilitating the adoption of propionic acid-based preservation solutions across different markets. This cooperation is expected to streamline regulatory processes and foster innovation in advanced preservation techniques.
Environmental Impact of Propionic Acid Production
The production of propionic acid has significant environmental implications that warrant careful consideration as the industry moves towards advanced preservation techniques. The traditional petrochemical-based production methods have been associated with substantial carbon emissions and energy consumption. However, recent advancements in biotechnological processes offer more sustainable alternatives.
Fermentation-based production of propionic acid using renewable feedstocks has emerged as a promising approach to reduce the environmental footprint. This method utilizes biomass resources, such as glucose or glycerol, as raw materials, potentially decreasing reliance on fossil fuels. The shift towards bio-based production could lead to a significant reduction in greenhouse gas emissions, with some studies suggesting up to a 50% decrease compared to conventional methods.
Water usage and wastewater management are critical environmental concerns in propionic acid production. The fermentation process requires substantial amounts of water, and the resulting effluents can contain high levels of organic compounds. Implementing advanced water treatment technologies and closed-loop systems can help mitigate these impacts, improving water efficiency and reducing pollution.
Energy consumption remains a challenge in both traditional and bio-based production methods. However, ongoing research into process intensification and the integration of renewable energy sources in production facilities shows promise in reducing overall energy requirements. The use of waste heat recovery systems and energy-efficient equipment can further enhance the sustainability profile of propionic acid production.
Life cycle assessments (LCAs) of propionic acid production have revealed the importance of considering the entire value chain when evaluating environmental impact. From raw material sourcing to end-of-life disposal, each stage contributes to the overall ecological footprint. Adopting circular economy principles, such as utilizing by-products and implementing recycling strategies, can help minimize waste and improve resource efficiency throughout the product lifecycle.
The increasing focus on sustainable preservation solutions is driving innovation in propionic acid production technologies. Green chemistry principles are being applied to develop cleaner synthesis routes, catalysts, and separation processes. These advancements aim to reduce the use of hazardous substances, improve atom economy, and enhance overall process efficiency, thereby lessening the environmental burden of production.
As regulations on industrial emissions and waste management become more stringent, propionic acid manufacturers are investing in pollution control technologies. Advanced air scrubbers, biofilters, and other emission reduction systems are being implemented to minimize the release of volatile organic compounds and other pollutants into the environment. These measures not only ensure compliance with environmental standards but also contribute to improved air and water quality in surrounding communities.