How AMOLED impacts biostimulatory device effectiveness?
JUL 17, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
AMOLED in Biostimulation: Background and Objectives
Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode (AMOLED) technology has emerged as a revolutionary advancement in display technology, offering superior image quality, energy efficiency, and flexibility. In recent years, its potential applications have expanded beyond consumer electronics into the realm of biomedical devices, particularly in the field of biostimulation. This convergence of AMOLED technology with biostimulatory devices represents a significant leap forward in the development of more effective and efficient medical treatments.
The evolution of AMOLED technology can be traced back to the late 1980s, with the discovery of electroluminescent organic materials. Over the decades, continuous improvements in materials science and manufacturing processes have led to the development of highly efficient, bright, and flexible AMOLED displays. The unique properties of AMOLED, such as its ability to emit light directly without the need for backlighting, have made it an attractive option for various applications, including smartphones, televisions, and wearable devices.
In the context of biostimulation, AMOLED technology offers several potential advantages. Biostimulatory devices typically rely on the precise delivery of light or electrical stimuli to target tissues or cells, aiming to promote healing, reduce pain, or modulate biological processes. The integration of AMOLED displays into these devices could potentially enhance their effectiveness through improved control over light intensity, wavelength, and spatial distribution.
The primary objective of exploring AMOLED technology in biostimulation is to overcome the limitations of current light-based therapies. Traditional light sources used in biostimulatory devices, such as LEDs or lasers, often lack the flexibility and precision required for optimal treatment outcomes. AMOLED displays, with their ability to produce a wide range of colors and intensities at the pixel level, could potentially offer more targeted and personalized treatment options.
Furthermore, the thin and flexible nature of AMOLED panels opens up new possibilities for the design of wearable biostimulatory devices. This could lead to more comfortable and less intrusive treatment options for patients, potentially improving compliance and overall treatment efficacy. The energy efficiency of AMOLED technology also aligns well with the need for portable, long-lasting medical devices.
As we delve deeper into the potential impact of AMOLED on biostimulatory device effectiveness, it is crucial to consider the technical challenges and biological implications of this integration. Questions regarding the optimal light spectra for various therapeutic applications, the long-term stability of organic materials in medical contexts, and the development of suitable control systems for precise light delivery will need to be addressed.
The evolution of AMOLED technology can be traced back to the late 1980s, with the discovery of electroluminescent organic materials. Over the decades, continuous improvements in materials science and manufacturing processes have led to the development of highly efficient, bright, and flexible AMOLED displays. The unique properties of AMOLED, such as its ability to emit light directly without the need for backlighting, have made it an attractive option for various applications, including smartphones, televisions, and wearable devices.
In the context of biostimulation, AMOLED technology offers several potential advantages. Biostimulatory devices typically rely on the precise delivery of light or electrical stimuli to target tissues or cells, aiming to promote healing, reduce pain, or modulate biological processes. The integration of AMOLED displays into these devices could potentially enhance their effectiveness through improved control over light intensity, wavelength, and spatial distribution.
The primary objective of exploring AMOLED technology in biostimulation is to overcome the limitations of current light-based therapies. Traditional light sources used in biostimulatory devices, such as LEDs or lasers, often lack the flexibility and precision required for optimal treatment outcomes. AMOLED displays, with their ability to produce a wide range of colors and intensities at the pixel level, could potentially offer more targeted and personalized treatment options.
Furthermore, the thin and flexible nature of AMOLED panels opens up new possibilities for the design of wearable biostimulatory devices. This could lead to more comfortable and less intrusive treatment options for patients, potentially improving compliance and overall treatment efficacy. The energy efficiency of AMOLED technology also aligns well with the need for portable, long-lasting medical devices.
As we delve deeper into the potential impact of AMOLED on biostimulatory device effectiveness, it is crucial to consider the technical challenges and biological implications of this integration. Questions regarding the optimal light spectra for various therapeutic applications, the long-term stability of organic materials in medical contexts, and the development of suitable control systems for precise light delivery will need to be addressed.
Market Analysis for AMOLED-Based Biostimulatory Devices
The AMOLED-based biostimulatory device market is experiencing rapid growth, driven by the convergence of advanced display technology and medical applications. This sector represents a niche but promising segment within the broader medical devices industry, with significant potential for expansion in the coming years.
The global market for biostimulatory devices is projected to grow substantially, with AMOLED-based devices expected to capture an increasing share. This growth is fueled by rising demand for non-invasive medical treatments, increasing prevalence of chronic conditions, and growing awareness of the benefits of biostimulation therapies.
Key market segments for AMOLED-based biostimulatory devices include pain management, wound healing, and neurological disorders. The pain management segment is particularly robust, as these devices offer a drug-free alternative for chronic pain sufferers. The wound healing segment is also showing strong growth potential, especially in the context of an aging population and the rising incidence of diabetes-related complications.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market, owing to advanced healthcare infrastructure and higher adoption rates of innovative medical technologies. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth, driven by improving healthcare access, rising disposable incomes, and increasing awareness of advanced medical treatments.
The integration of AMOLED technology in biostimulatory devices is creating new opportunities for market expansion. AMOLED displays offer superior visual quality, energy efficiency, and flexibility, which can significantly enhance the user experience and effectiveness of these devices. This technological advancement is attracting both medical professionals and patients, potentially broadening the market base.
Consumer trends indicate a growing preference for home-based medical devices, which bodes well for portable AMOLED-based biostimulatory devices. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated this trend, as patients seek alternatives to in-person medical treatments.
Regulatory landscape plays a crucial role in shaping the market. While stringent regulations can pose challenges for market entry, they also ensure product safety and efficacy, which is crucial for building consumer trust in this emerging technology.
Competition in this market is intensifying, with both established medical device manufacturers and new entrants vying for market share. Companies that can effectively combine AMOLED technology with proven biostimulatory techniques are likely to gain a competitive edge.
In conclusion, the market for AMOLED-based biostimulatory devices shows strong growth potential, driven by technological advancements, changing healthcare needs, and evolving consumer preferences. As the technology matures and gains wider acceptance, it is poised to play an increasingly important role in the future of medical treatments.
The global market for biostimulatory devices is projected to grow substantially, with AMOLED-based devices expected to capture an increasing share. This growth is fueled by rising demand for non-invasive medical treatments, increasing prevalence of chronic conditions, and growing awareness of the benefits of biostimulation therapies.
Key market segments for AMOLED-based biostimulatory devices include pain management, wound healing, and neurological disorders. The pain management segment is particularly robust, as these devices offer a drug-free alternative for chronic pain sufferers. The wound healing segment is also showing strong growth potential, especially in the context of an aging population and the rising incidence of diabetes-related complications.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the market, owing to advanced healthcare infrastructure and higher adoption rates of innovative medical technologies. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth, driven by improving healthcare access, rising disposable incomes, and increasing awareness of advanced medical treatments.
The integration of AMOLED technology in biostimulatory devices is creating new opportunities for market expansion. AMOLED displays offer superior visual quality, energy efficiency, and flexibility, which can significantly enhance the user experience and effectiveness of these devices. This technological advancement is attracting both medical professionals and patients, potentially broadening the market base.
Consumer trends indicate a growing preference for home-based medical devices, which bodes well for portable AMOLED-based biostimulatory devices. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated this trend, as patients seek alternatives to in-person medical treatments.
Regulatory landscape plays a crucial role in shaping the market. While stringent regulations can pose challenges for market entry, they also ensure product safety and efficacy, which is crucial for building consumer trust in this emerging technology.
Competition in this market is intensifying, with both established medical device manufacturers and new entrants vying for market share. Companies that can effectively combine AMOLED technology with proven biostimulatory techniques are likely to gain a competitive edge.
In conclusion, the market for AMOLED-based biostimulatory devices shows strong growth potential, driven by technological advancements, changing healthcare needs, and evolving consumer preferences. As the technology matures and gains wider acceptance, it is poised to play an increasingly important role in the future of medical treatments.
Current AMOLED Technology in Biostimulation: Status and Challenges
The integration of AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology into biostimulatory devices represents a significant advancement in the field of biomedical engineering. However, this integration also presents unique challenges that need to be addressed for optimal device effectiveness.
AMOLED displays offer several advantages for biostimulatory applications, including high contrast ratios, wide color gamut, and excellent energy efficiency. These characteristics enable the creation of more precise and customizable light stimuli, potentially enhancing the efficacy of biostimulation treatments. The thin and flexible nature of AMOLED panels also allows for the development of more compact and ergonomic devices, improving patient comfort and treatment adherence.
Despite these benefits, the current state of AMOLED technology in biostimulation faces several challenges. One primary concern is the long-term stability of organic materials used in AMOLED displays. Exposure to biological environments and repeated sterilization processes can degrade these materials, potentially affecting the consistency and reliability of light output over time. This degradation may lead to variations in treatment efficacy and require more frequent device replacements.
Another significant challenge lies in the power management of AMOLED-based biostimulatory devices. While AMOLEDs are generally energy-efficient, the specific light intensities and patterns required for effective biostimulation may demand higher power consumption. Balancing the need for precise light control with battery life and device portability remains a key area of development.
The integration of AMOLED technology with biofeedback systems presents both opportunities and challenges. On one hand, the high refresh rates and color accuracy of AMOLED displays enable real-time visualization of physiological responses, potentially improving treatment customization. On the other hand, ensuring seamless communication between the display and biofeedback sensors while maintaining low latency is a complex technical hurdle.
Heat management is another critical factor affecting the effectiveness of AMOLED-based biostimulatory devices. The localized heat generated by AMOLED displays during operation can interfere with the intended biological effects of light stimulation. Developing efficient heat dissipation mechanisms without compromising device form factor or user comfort is an ongoing challenge for engineers and designers.
Lastly, the cost of implementing AMOLED technology in biostimulatory devices remains a significant barrier to widespread adoption. While AMOLED production costs have decreased in recent years, they still represent a premium component in medical devices. Balancing the enhanced capabilities offered by AMOLED displays with overall device affordability is crucial for market penetration and accessibility of advanced biostimulation treatments.
AMOLED displays offer several advantages for biostimulatory applications, including high contrast ratios, wide color gamut, and excellent energy efficiency. These characteristics enable the creation of more precise and customizable light stimuli, potentially enhancing the efficacy of biostimulation treatments. The thin and flexible nature of AMOLED panels also allows for the development of more compact and ergonomic devices, improving patient comfort and treatment adherence.
Despite these benefits, the current state of AMOLED technology in biostimulation faces several challenges. One primary concern is the long-term stability of organic materials used in AMOLED displays. Exposure to biological environments and repeated sterilization processes can degrade these materials, potentially affecting the consistency and reliability of light output over time. This degradation may lead to variations in treatment efficacy and require more frequent device replacements.
Another significant challenge lies in the power management of AMOLED-based biostimulatory devices. While AMOLEDs are generally energy-efficient, the specific light intensities and patterns required for effective biostimulation may demand higher power consumption. Balancing the need for precise light control with battery life and device portability remains a key area of development.
The integration of AMOLED technology with biofeedback systems presents both opportunities and challenges. On one hand, the high refresh rates and color accuracy of AMOLED displays enable real-time visualization of physiological responses, potentially improving treatment customization. On the other hand, ensuring seamless communication between the display and biofeedback sensors while maintaining low latency is a complex technical hurdle.
Heat management is another critical factor affecting the effectiveness of AMOLED-based biostimulatory devices. The localized heat generated by AMOLED displays during operation can interfere with the intended biological effects of light stimulation. Developing efficient heat dissipation mechanisms without compromising device form factor or user comfort is an ongoing challenge for engineers and designers.
Lastly, the cost of implementing AMOLED technology in biostimulatory devices remains a significant barrier to widespread adoption. While AMOLED production costs have decreased in recent years, they still represent a premium component in medical devices. Balancing the enhanced capabilities offered by AMOLED displays with overall device affordability is crucial for market penetration and accessibility of advanced biostimulation treatments.
Existing AMOLED Solutions for Biostimulation
01 AMOLED display efficiency and power consumption
AMOLED displays offer improved efficiency and reduced power consumption compared to traditional LCD displays. This is achieved through pixel-level control of light emission, allowing for selective activation of pixels and better energy management. The technology also enables deeper blacks and higher contrast ratios, contributing to overall display effectiveness.- AMOLED display efficiency and power consumption: AMOLED displays offer improved efficiency and reduced power consumption compared to traditional LCD displays. This is achieved through pixel-level control of light emission, allowing for selective activation of pixels and better energy management. The technology also enables deeper blacks and higher contrast ratios, contributing to overall display effectiveness.
- Color accuracy and gamut in AMOLED displays: AMOLED technology provides enhanced color accuracy and a wider color gamut compared to conventional displays. This is due to the ability to control individual pixel colors more precisely, resulting in more vibrant and lifelike images. Advanced color management techniques are employed to optimize color reproduction and maintain consistency across different viewing conditions.
- AMOLED pixel structure and manufacturing improvements: Advancements in AMOLED pixel structure and manufacturing processes have led to increased display effectiveness. These improvements include optimized subpixel arrangements, enhanced thin-film transistor (TFT) designs, and refined deposition techniques. Such developments result in higher resolution, improved uniformity, and increased overall display quality.
- AMOLED display longevity and burn-in prevention: Efforts to improve AMOLED display longevity and prevent burn-in issues have enhanced the technology's effectiveness. This includes the development of compensation algorithms, pixel shifting techniques, and advanced materials that mitigate the effects of uneven pixel aging. These innovations contribute to longer-lasting and more reliable AMOLED displays.
- Integration of AMOLED with other technologies: The effectiveness of AMOLED displays is further enhanced through integration with complementary technologies. This includes the incorporation of in-display fingerprint sensors, under-display cameras, and flexible or foldable display capabilities. Such integrations expand the functionality and versatility of AMOLED-equipped devices, improving overall user experience and device effectiveness.
02 Color accuracy and gamut in AMOLED displays
AMOLED technology provides enhanced color accuracy and wider color gamut compared to conventional displays. This is achieved through precise control of individual organic light-emitting diodes, allowing for more vibrant and true-to-life color reproduction. Advanced color management systems and calibration techniques further improve the overall color performance of AMOLED displays.Expand Specific Solutions03 AMOLED pixel structure and driving methods
Innovations in AMOLED pixel structure and driving methods contribute to improved display performance. These advancements include optimized sub-pixel arrangements, enhanced thin-film transistor (TFT) designs, and novel driving schemes that reduce power consumption and increase display lifetime. Such improvements result in better overall effectiveness of AMOLED displays.Expand Specific Solutions04 AMOLED display longevity and burn-in prevention
Techniques to enhance AMOLED display longevity and prevent burn-in issues have been developed. These include pixel shifting algorithms, adaptive brightness control, and compensation circuits that adjust for pixel aging. Such methods significantly improve the long-term effectiveness and reliability of AMOLED displays, addressing one of the technology's historical limitations.Expand Specific Solutions05 Integration of additional functionalities in AMOLED displays
AMOLED technology allows for the integration of additional functionalities within the display itself. This includes embedding touch sensors, fingerprint scanners, and even cameras underneath the display surface. Such integrations enhance the overall effectiveness of devices using AMOLED displays by improving user interaction and reducing the need for separate components.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in AMOLED Biostimulation Industry
The AMOLED technology's impact on biostimulatory device effectiveness is at an early stage of development, with a growing market potential. The industry is transitioning from research to initial commercialization, driven by advancements in display technology. Key players like Samsung Electronics, BOE Technology, and TCL China Star Optoelectronics are leading the field, leveraging their expertise in AMOLED displays. The technology's maturity is progressing, with companies like Tianma Microelectronics and Everdisplay Optronics contributing to innovations. However, the application in biostimulatory devices is still emerging, requiring further research and development to fully realize its potential in enhancing device effectiveness and user experience.
BOE Technology Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: BOE has developed flexible AMOLED displays with integrated biosensors, enhancing the potential for biostimulatory device effectiveness. Their technology allows for real-time monitoring of physiological parameters while delivering targeted light therapy[2]. BOE's AMOLED panels feature high color accuracy and wide color gamut, enabling precise control of light spectra for various biostimulatory applications. Additionally, they have implemented advanced power management systems that optimize energy consumption, potentially extending the battery life of portable biostimulatory devices[4][6].
Strengths: Integration of biosensors, high color accuracy, and energy efficiency. Weaknesses: Less established in the biostimulatory market compared to some competitors.
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung has developed advanced AMOLED displays with enhanced biostimulatory capabilities. Their latest technology incorporates micro-LED elements within the AMOLED structure, allowing for precise control of light wavelengths and intensities[1]. This innovation enables targeted photobiomodulation, potentially improving the effectiveness of biostimulatory devices. Samsung's AMOLED displays also feature higher refresh rates and lower blue light emissions, which may contribute to reduced eye strain and improved circadian rhythm regulation in therapeutic applications[3][5].
Strengths: Industry-leading AMOLED technology, high refresh rates, and precise light control. Weaknesses: Potentially higher cost and complexity in manufacturing for biostimulatory applications.
Core AMOLED Innovations for Biostimulation
Amoled double-side display
PatentActiveUS20200219957A1
Innovation
- An AMOLED double-sided display design featuring a substrate with alternating top-emitting and bottom-emitting OLED units, where the anode of top-emitting units is thicker and reflective, and the cathode of bottom-emitting units is thicker and light-transmissive, allowing for single IC control and eliminating mirrored images.
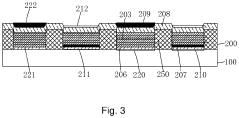
Organic light emitting display
PatentInactiveEP3098804A3
Innovation
- The proposed solution involves a pixel structure with a driving transistor, multiple transistors, and a capacitor to control the flow of current and compensate for threshold voltage changes, using an initial voltage lower than the low-level driving voltage to minimize unnecessary light emission and leakage current, and ensuring a sufficient sampling period for accurate compensation.
Regulatory Framework for AMOLED Biostimulatory Devices
The regulatory framework for AMOLED biostimulatory devices is a complex and evolving landscape that significantly impacts the development, approval, and market entry of these innovative medical technologies. As AMOLED (Active-Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode) technology continues to advance and find applications in biostimulatory devices, regulatory bodies worldwide are adapting their guidelines to ensure patient safety and device efficacy.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in regulating AMOLED biostimulatory devices. These devices typically fall under Class II or Class III medical devices, depending on their intended use and risk profile. The FDA's regulatory approach focuses on the device's safety and effectiveness, requiring manufacturers to submit comprehensive data through premarket notification (510(k)) or premarket approval (PMA) pathways.
The European Union's regulatory framework for AMOLED biostimulatory devices is governed by the Medical Device Regulation (MDR). This regulation, which came into full effect in May 2021, places greater emphasis on clinical evidence, post-market surveillance, and traceability. Manufacturers must comply with stricter requirements for technical documentation and clinical evaluation reports, ensuring that AMOLED-based devices meet the necessary safety and performance standards.
In Asia, countries like Japan and China have their own regulatory frameworks. Japan's Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) oversees the approval process for AMOLED biostimulatory devices, while China's National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) has implemented a classification-based system similar to the FDA's approach.
Regulatory bodies are particularly focused on several key aspects of AMOLED biostimulatory devices. These include the long-term stability and durability of AMOLED displays in medical applications, potential electromagnetic interference with other medical equipment, and the accuracy of light emission for therapeutic purposes. Additionally, regulators are concerned with the software and algorithms controlling these devices, especially when artificial intelligence or machine learning components are involved.
As the technology advances, regulatory frameworks are likely to evolve. There is a growing trend towards harmonization of international standards, such as the International Medical Device Regulators Forum (IMDRF) guidelines, which aim to streamline the regulatory process across different regions. This harmonization could potentially accelerate the global adoption of AMOLED-based biostimulatory devices while maintaining high safety and efficacy standards.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in regulating AMOLED biostimulatory devices. These devices typically fall under Class II or Class III medical devices, depending on their intended use and risk profile. The FDA's regulatory approach focuses on the device's safety and effectiveness, requiring manufacturers to submit comprehensive data through premarket notification (510(k)) or premarket approval (PMA) pathways.
The European Union's regulatory framework for AMOLED biostimulatory devices is governed by the Medical Device Regulation (MDR). This regulation, which came into full effect in May 2021, places greater emphasis on clinical evidence, post-market surveillance, and traceability. Manufacturers must comply with stricter requirements for technical documentation and clinical evaluation reports, ensuring that AMOLED-based devices meet the necessary safety and performance standards.
In Asia, countries like Japan and China have their own regulatory frameworks. Japan's Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) oversees the approval process for AMOLED biostimulatory devices, while China's National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) has implemented a classification-based system similar to the FDA's approach.
Regulatory bodies are particularly focused on several key aspects of AMOLED biostimulatory devices. These include the long-term stability and durability of AMOLED displays in medical applications, potential electromagnetic interference with other medical equipment, and the accuracy of light emission for therapeutic purposes. Additionally, regulators are concerned with the software and algorithms controlling these devices, especially when artificial intelligence or machine learning components are involved.
As the technology advances, regulatory frameworks are likely to evolve. There is a growing trend towards harmonization of international standards, such as the International Medical Device Regulators Forum (IMDRF) guidelines, which aim to streamline the regulatory process across different regions. This harmonization could potentially accelerate the global adoption of AMOLED-based biostimulatory devices while maintaining high safety and efficacy standards.
Biocompatibility and Safety Considerations
The integration of AMOLED technology in biostimulatory devices raises important considerations regarding biocompatibility and safety. AMOLED displays, while offering superior visual performance, introduce new materials and components that must be carefully evaluated for their potential impact on biological systems.
One primary concern is the potential for chemical leaching from AMOLED components. The organic materials used in these displays, while encapsulated, may degrade over time and potentially release compounds that could interact with biological tissues. Rigorous testing protocols must be established to assess the long-term stability of these materials under various environmental conditions and their potential for eluting harmful substances.
Electromagnetic emissions from AMOLED displays present another safety consideration. While generally low, the electromagnetic fields generated by these devices must be thoroughly characterized to ensure they do not interfere with the intended biostimulatory effects or cause unintended biological responses. This is particularly crucial for implantable devices or those in close proximity to sensitive tissues.
The heat generation from AMOLED displays, although minimal compared to traditional LED technologies, must also be carefully managed in biostimulatory applications. Localized temperature increases, even if slight, could potentially alter the efficacy of biostimulation or cause unintended tissue responses. Thermal management strategies and heat dissipation mechanisms should be integral to the device design.
Photobiological safety is another critical aspect to consider. The high-contrast and vibrant colors produced by AMOLED displays may have unforeseen effects on light-sensitive biological processes. Extensive research is needed to understand how the specific light spectra emitted by these displays interact with various tissues and cellular mechanisms involved in biostimulation.
The potential for physical degradation of AMOLED components in biological environments must also be addressed. The breakdown of organic materials or protective layers could not only compromise device function but also introduce particulate matter into the surrounding tissues. Robust encapsulation techniques and biocompatible coating materials must be developed to ensure long-term stability and safety.
Lastly, the integration of AMOLED technology may introduce new failure modes that could pose safety risks. Comprehensive failure analysis and risk assessment protocols should be established to identify and mitigate potential hazards associated with display malfunction or degradation in biostimulatory applications.
One primary concern is the potential for chemical leaching from AMOLED components. The organic materials used in these displays, while encapsulated, may degrade over time and potentially release compounds that could interact with biological tissues. Rigorous testing protocols must be established to assess the long-term stability of these materials under various environmental conditions and their potential for eluting harmful substances.
Electromagnetic emissions from AMOLED displays present another safety consideration. While generally low, the electromagnetic fields generated by these devices must be thoroughly characterized to ensure they do not interfere with the intended biostimulatory effects or cause unintended biological responses. This is particularly crucial for implantable devices or those in close proximity to sensitive tissues.
The heat generation from AMOLED displays, although minimal compared to traditional LED technologies, must also be carefully managed in biostimulatory applications. Localized temperature increases, even if slight, could potentially alter the efficacy of biostimulation or cause unintended tissue responses. Thermal management strategies and heat dissipation mechanisms should be integral to the device design.
Photobiological safety is another critical aspect to consider. The high-contrast and vibrant colors produced by AMOLED displays may have unforeseen effects on light-sensitive biological processes. Extensive research is needed to understand how the specific light spectra emitted by these displays interact with various tissues and cellular mechanisms involved in biostimulation.
The potential for physical degradation of AMOLED components in biological environments must also be addressed. The breakdown of organic materials or protective layers could not only compromise device function but also introduce particulate matter into the surrounding tissues. Robust encapsulation techniques and biocompatible coating materials must be developed to ensure long-term stability and safety.
Lastly, the integration of AMOLED technology may introduce new failure modes that could pose safety risks. Comprehensive failure analysis and risk assessment protocols should be established to identify and mitigate potential hazards associated with display malfunction or degradation in biostimulatory applications.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!