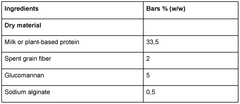
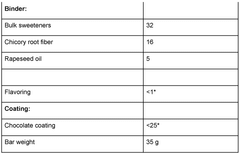
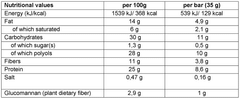
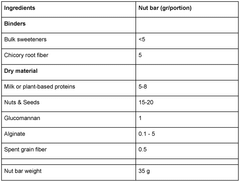
How Sodium Alginate Elevates Nutraceutical Product Quality?
JUL 14, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sodium Alginate in Nutraceuticals: Background and Objectives
Sodium alginate, a versatile polysaccharide derived from brown seaweed, has emerged as a pivotal ingredient in the nutraceutical industry. Its journey from marine flora to a key component in health supplements and functional foods represents a fascinating intersection of natural resource utilization and technological innovation. The evolution of sodium alginate's applications in nutraceuticals has been driven by increasing consumer demand for natural, plant-based ingredients that offer both functional benefits and improved product quality.
The primary objective of incorporating sodium alginate into nutraceutical formulations is to enhance product quality across multiple dimensions. This includes improving texture, stability, and bioavailability of active ingredients, as well as extending shelf life. As the nutraceutical market continues to expand globally, manufacturers are seeking innovative ways to differentiate their products and meet consumer expectations for efficacy and safety.
Historically, the use of sodium alginate in food and pharmaceutical industries dates back to the early 20th century. However, its potential in nutraceuticals has only been fully recognized and exploited in recent decades. This shift has been propelled by advancements in extraction and purification techniques, allowing for the production of high-quality sodium alginate suitable for nutraceutical applications.
The technological trajectory of sodium alginate in nutraceuticals has been marked by continuous improvements in its functionality. Research has focused on understanding and manipulating its unique properties, such as its ability to form gels, act as a thickening agent, and encapsulate bioactive compounds. These properties have opened up new possibilities for innovative product formulations and delivery systems.
Current trends in the nutraceutical industry, including the rise of personalized nutrition and clean label products, have further amplified the importance of sodium alginate. Its natural origin aligns well with consumer preferences for minimally processed ingredients, while its versatility allows for customization of product characteristics to meet specific health and wellness goals.
Looking ahead, the objectives for sodium alginate in nutraceuticals are multifaceted. There is a growing emphasis on developing sustainable sourcing methods to ensure a stable supply chain while minimizing environmental impact. Additionally, researchers are exploring ways to enhance the bioactivity of sodium alginate itself, potentially expanding its role from a functional ingredient to an active nutraceutical component.
As we delve deeper into the technological landscape of sodium alginate in nutraceuticals, it becomes clear that this marine-derived compound holds significant promise for elevating product quality and driving innovation in the industry. The ongoing research and development efforts aim to unlock its full potential, paving the way for next-generation nutraceutical products that offer superior quality, efficacy, and consumer appeal.
The primary objective of incorporating sodium alginate into nutraceutical formulations is to enhance product quality across multiple dimensions. This includes improving texture, stability, and bioavailability of active ingredients, as well as extending shelf life. As the nutraceutical market continues to expand globally, manufacturers are seeking innovative ways to differentiate their products and meet consumer expectations for efficacy and safety.
Historically, the use of sodium alginate in food and pharmaceutical industries dates back to the early 20th century. However, its potential in nutraceuticals has only been fully recognized and exploited in recent decades. This shift has been propelled by advancements in extraction and purification techniques, allowing for the production of high-quality sodium alginate suitable for nutraceutical applications.
The technological trajectory of sodium alginate in nutraceuticals has been marked by continuous improvements in its functionality. Research has focused on understanding and manipulating its unique properties, such as its ability to form gels, act as a thickening agent, and encapsulate bioactive compounds. These properties have opened up new possibilities for innovative product formulations and delivery systems.
Current trends in the nutraceutical industry, including the rise of personalized nutrition and clean label products, have further amplified the importance of sodium alginate. Its natural origin aligns well with consumer preferences for minimally processed ingredients, while its versatility allows for customization of product characteristics to meet specific health and wellness goals.
Looking ahead, the objectives for sodium alginate in nutraceuticals are multifaceted. There is a growing emphasis on developing sustainable sourcing methods to ensure a stable supply chain while minimizing environmental impact. Additionally, researchers are exploring ways to enhance the bioactivity of sodium alginate itself, potentially expanding its role from a functional ingredient to an active nutraceutical component.
As we delve deeper into the technological landscape of sodium alginate in nutraceuticals, it becomes clear that this marine-derived compound holds significant promise for elevating product quality and driving innovation in the industry. The ongoing research and development efforts aim to unlock its full potential, paving the way for next-generation nutraceutical products that offer superior quality, efficacy, and consumer appeal.
Market Demand for Enhanced Nutraceutical Products
The nutraceutical industry has witnessed a significant surge in demand for enhanced products, driven by increasing consumer awareness of health and wellness. This trend has created a robust market for innovative ingredients that can improve the quality and efficacy of nutraceutical formulations. Sodium alginate, a versatile compound derived from brown seaweed, has emerged as a key player in this evolving landscape.
Market research indicates that the global nutraceutical market is expected to grow substantially in the coming years, with a particular emphasis on products that offer improved bioavailability, stability, and targeted delivery of active ingredients. Consumers are increasingly seeking products that not only provide health benefits but also offer superior quality and performance. This shift in consumer preferences has created a fertile ground for ingredients like sodium alginate that can address these demands.
The demand for sodium alginate in nutraceutical applications is primarily driven by its unique properties that can enhance product quality. Its ability to form gels and act as a stabilizer makes it an attractive option for manufacturers looking to improve the texture, consistency, and shelf life of their products. Additionally, sodium alginate's potential to encapsulate and protect sensitive ingredients has garnered significant interest from companies developing advanced delivery systems for nutraceuticals.
Another factor contributing to the market demand is the growing preference for natural and plant-based ingredients. Sodium alginate, being derived from seaweed, aligns well with this consumer trend towards clean label products. This has led to increased adoption of sodium alginate in various nutraceutical formulations, including dietary supplements, functional foods, and beverages.
The market demand for sodium alginate in nutraceuticals is also influenced by regulatory factors. As health authorities worldwide tighten regulations on food additives and nutraceutical ingredients, sodium alginate's generally recognized as safe (GRAS) status in many countries positions it favorably in the market. This regulatory advantage has further fueled its adoption among manufacturers seeking compliant and safe ingredients for their products.
Geographically, the demand for enhanced nutraceutical products incorporating sodium alginate is particularly strong in North America and Europe, where health-conscious consumers are willing to pay premium prices for high-quality supplements. However, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are also showing rapid growth, driven by rising disposable incomes and increasing awareness of preventive healthcare.
In conclusion, the market demand for sodium alginate in enhancing nutraceutical product quality is robust and multifaceted. It is driven by consumer preferences for improved product performance, the need for natural and safe ingredients, and the regulatory landscape. As the nutraceutical industry continues to evolve, sodium alginate is well-positioned to play a crucial role in meeting the growing demand for high-quality, effective, and innovative health products.
Market research indicates that the global nutraceutical market is expected to grow substantially in the coming years, with a particular emphasis on products that offer improved bioavailability, stability, and targeted delivery of active ingredients. Consumers are increasingly seeking products that not only provide health benefits but also offer superior quality and performance. This shift in consumer preferences has created a fertile ground for ingredients like sodium alginate that can address these demands.
The demand for sodium alginate in nutraceutical applications is primarily driven by its unique properties that can enhance product quality. Its ability to form gels and act as a stabilizer makes it an attractive option for manufacturers looking to improve the texture, consistency, and shelf life of their products. Additionally, sodium alginate's potential to encapsulate and protect sensitive ingredients has garnered significant interest from companies developing advanced delivery systems for nutraceuticals.
Another factor contributing to the market demand is the growing preference for natural and plant-based ingredients. Sodium alginate, being derived from seaweed, aligns well with this consumer trend towards clean label products. This has led to increased adoption of sodium alginate in various nutraceutical formulations, including dietary supplements, functional foods, and beverages.
The market demand for sodium alginate in nutraceuticals is also influenced by regulatory factors. As health authorities worldwide tighten regulations on food additives and nutraceutical ingredients, sodium alginate's generally recognized as safe (GRAS) status in many countries positions it favorably in the market. This regulatory advantage has further fueled its adoption among manufacturers seeking compliant and safe ingredients for their products.
Geographically, the demand for enhanced nutraceutical products incorporating sodium alginate is particularly strong in North America and Europe, where health-conscious consumers are willing to pay premium prices for high-quality supplements. However, emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are also showing rapid growth, driven by rising disposable incomes and increasing awareness of preventive healthcare.
In conclusion, the market demand for sodium alginate in enhancing nutraceutical product quality is robust and multifaceted. It is driven by consumer preferences for improved product performance, the need for natural and safe ingredients, and the regulatory landscape. As the nutraceutical industry continues to evolve, sodium alginate is well-positioned to play a crucial role in meeting the growing demand for high-quality, effective, and innovative health products.
Current Applications and Challenges of Sodium Alginate
Sodium alginate, a versatile polysaccharide derived from brown algae, has gained significant traction in the nutraceutical industry due to its unique properties and wide-ranging applications. Currently, it is extensively used as a thickening agent, stabilizer, and emulsifier in various nutraceutical products, contributing to improved texture, consistency, and shelf life.
In the realm of dietary supplements, sodium alginate serves as an effective encapsulation material for sensitive ingredients such as probiotics, vitamins, and minerals. This application helps protect these components from degradation during storage and facilitates controlled release in the digestive system, enhancing bioavailability and efficacy.
The food and beverage sector extensively utilizes sodium alginate in functional foods and drinks. It acts as a gelling agent in restructured foods, enables the creation of innovative textures in molecular gastronomy, and serves as a fat replacer in low-calorie products. Its ability to form heat-stable gels makes it particularly valuable in heat-processed nutraceutical formulations.
In the pharmaceutical domain, sodium alginate is employed in drug delivery systems, wound dressings, and dental impressions. Its biocompatibility and ability to form hydrogels have made it a popular choice for developing advanced drug delivery platforms, including sustained-release formulations and targeted delivery systems.
Despite its widespread use, sodium alginate faces several challenges in nutraceutical applications. One primary concern is the variability in quality and composition of alginate derived from different seaweed sources, which can affect its performance and consistency in final products. This necessitates rigorous quality control measures and standardization processes.
Another challenge lies in the limited solubility of sodium alginate in acidic conditions, which can restrict its use in certain formulations. Researchers are actively exploring chemical modifications and blending with other polymers to overcome this limitation and expand its applicability.
The potential for allergenicity, although rare, poses another challenge. As a marine-derived ingredient, sodium alginate may cause allergic reactions in some individuals, necessitating clear labeling and alternative options for sensitive consumers.
Lastly, the increasing demand for clean label and natural ingredients has prompted the need for more sustainable and eco-friendly production methods for sodium alginate. The industry is investigating alternative sources and extraction techniques to address environmental concerns and meet consumer preferences for natural, plant-based ingredients.
In the realm of dietary supplements, sodium alginate serves as an effective encapsulation material for sensitive ingredients such as probiotics, vitamins, and minerals. This application helps protect these components from degradation during storage and facilitates controlled release in the digestive system, enhancing bioavailability and efficacy.
The food and beverage sector extensively utilizes sodium alginate in functional foods and drinks. It acts as a gelling agent in restructured foods, enables the creation of innovative textures in molecular gastronomy, and serves as a fat replacer in low-calorie products. Its ability to form heat-stable gels makes it particularly valuable in heat-processed nutraceutical formulations.
In the pharmaceutical domain, sodium alginate is employed in drug delivery systems, wound dressings, and dental impressions. Its biocompatibility and ability to form hydrogels have made it a popular choice for developing advanced drug delivery platforms, including sustained-release formulations and targeted delivery systems.
Despite its widespread use, sodium alginate faces several challenges in nutraceutical applications. One primary concern is the variability in quality and composition of alginate derived from different seaweed sources, which can affect its performance and consistency in final products. This necessitates rigorous quality control measures and standardization processes.
Another challenge lies in the limited solubility of sodium alginate in acidic conditions, which can restrict its use in certain formulations. Researchers are actively exploring chemical modifications and blending with other polymers to overcome this limitation and expand its applicability.
The potential for allergenicity, although rare, poses another challenge. As a marine-derived ingredient, sodium alginate may cause allergic reactions in some individuals, necessitating clear labeling and alternative options for sensitive consumers.
Lastly, the increasing demand for clean label and natural ingredients has prompted the need for more sustainable and eco-friendly production methods for sodium alginate. The industry is investigating alternative sources and extraction techniques to address environmental concerns and meet consumer preferences for natural, plant-based ingredients.
Existing Formulations Using Sodium Alginate
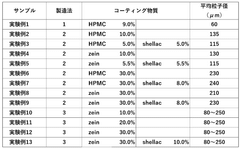
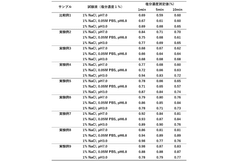
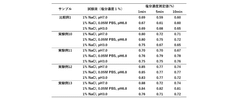
01 Purification and quality control methods
Various techniques are employed to purify sodium alginate and control its quality. These methods include filtration, precipitation, and advanced separation processes. Quality control measures involve testing for viscosity, molecular weight distribution, and impurity levels to ensure consistent product quality.- Purification and quality control methods: Various techniques are employed to purify sodium alginate and control its quality. These methods may include filtration, precipitation, and chromatography to remove impurities and ensure consistent product characteristics. Quality control measures often involve spectroscopic analysis, viscosity testing, and molecular weight determination to meet industry standards.
- Modification of sodium alginate properties: Researchers have developed methods to modify sodium alginate's properties, such as its viscosity, gelation behavior, and biocompatibility. These modifications can be achieved through chemical reactions, physical treatments, or blending with other polymers. The resulting modified sodium alginates often exhibit enhanced performance in specific applications.
- Extraction and production processes: Innovative extraction and production processes have been developed to improve the yield and quality of sodium alginate from various algal sources. These processes may involve optimized extraction conditions, enzymatic treatments, or novel separation techniques to obtain high-quality sodium alginate with desired characteristics.
- Characterization and analysis techniques: Advanced characterization and analysis techniques are employed to assess the quality and properties of sodium alginate products. These may include nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, gel permeation chromatography, and rheological analysis. Such techniques provide detailed information on the structure, composition, and behavior of sodium alginate, enabling better quality control and product development.
- Application-specific quality improvements: Researchers have focused on enhancing sodium alginate quality for specific applications, such as drug delivery, tissue engineering, and food additives. These improvements may involve tailoring the molecular weight distribution, modifying the guluronic to mannuronic acid ratio, or incorporating functional groups to optimize performance in the target application.
02 Modification of sodium alginate properties
Sodium alginate properties can be modified to enhance its performance in specific applications. This includes chemical modifications to improve solubility, stability, or gel-forming abilities. Techniques such as crosslinking or grafting with other polymers are used to tailor the alginate's characteristics.Expand Specific Solutions03 Extraction and production processes
Innovative extraction and production processes are developed to improve the yield and quality of sodium alginate. These processes focus on optimizing extraction conditions from seaweed sources, reducing processing time, and minimizing the use of harsh chemicals to produce high-quality sodium alginate.Expand Specific Solutions04 Application-specific quality requirements
Different applications of sodium alginate require specific quality attributes. For instance, food-grade sodium alginate has different purity requirements compared to that used in pharmaceutical or industrial applications. Tailoring the product quality to meet these specific needs is crucial for various end-use industries.Expand Specific Solutions05 Analytical techniques for quality assessment
Advanced analytical techniques are employed to assess the quality of sodium alginate products. These include spectroscopic methods, chromatography, and rheological analyses to determine chemical composition, molecular structure, and physical properties. Such techniques ensure accurate quality assessment and consistency in product performance.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Sodium Alginate Production and Application
The sodium alginate market in nutraceuticals is in a growth phase, driven by increasing consumer demand for natural and functional ingredients. The global market size is expanding, with projections indicating significant growth in the coming years. Technologically, sodium alginate applications are advancing, with companies like Colgate-Palmolive, Unilever, and Danisco (now part of IFF) leading innovation. Academic institutions such as Qingdao Agriculture University and Nanjing Agricultural University are contributing to research and development. The technology's maturity is moderate, with ongoing efforts to enhance its functionality and explore new applications in nutraceutical product formulations.
Zhejiang University of Technology
Technical Solution: The research team at Zhejiang University of Technology has focused on developing sodium alginate-based microencapsulation techniques for probiotics and other sensitive nutraceuticals. Their approach utilizes a combination of sodium alginate and chitosan to create a protective shell that significantly improves the survival rate of probiotics during processing and storage[8]. The team has also explored the use of alginate-based hydrogels as oral delivery systems for peptides and proteins, demonstrating enhanced bioavailability and controlled release profiles[10]. Additionally, they have developed a novel spray-drying technique that allows for the production of sodium alginate-encapsulated nutraceuticals with improved stability and dispersibility in various food matrices.
Strengths: Enhanced protection for sensitive ingredients, improved bioavailability of peptides and proteins, and versatile application in various food systems. Weaknesses: Potential challenges in large-scale production and cost-effectiveness compared to traditional encapsulation methods.
Nanjing Agricultural University
Technical Solution: Researchers at Nanjing Agricultural University have developed a novel sodium alginate-based edible coating for fresh fruits and vegetables. This coating not only extends shelf life by reducing moisture loss and gas exchange but also serves as a carrier for nutraceutical compounds[7]. The team has successfully incorporated various antioxidants and antimicrobial agents into the alginate matrix, creating functional foods with enhanced nutritional profiles. Furthermore, they have explored the use of sodium alginate in creating 3D-printed personalized nutraceutical products, allowing for precise control over nutrient content and release profiles[9].
Strengths: Innovative application in fresh produce preservation, potential for personalized nutrition, and integration of multiple functional ingredients. Weaknesses: Scalability challenges for 3D-printed products and potential regulatory hurdles for novel food applications.
Innovative Sodium Alginate Technologies in Nutraceuticals
A nutritional food and drink product, and a method for manufacturing said product
PatentWO2024217689A1
Innovation
- A nutritional food or drink product comprising 0.4-6 grams of konjac mannan and 0-10 grams of sodium alginate, combined with high protein sources and dietary fibers, to create a high-fiber, high-protein, low-carbohydrate snack that delays gastric emptying and promotes satiety, thereby aiding in weight management.
Sodium excretion particles
PatentWO2020241650A1
Innovation
- Development of alginate-containing microcapsules with ammonium alginate as the active ingredient, encapsulated to a size of 10 to 3,000 μm, coated with water-soluble polymers or other materials, allowing them to be added to or attached to food without affecting taste, and disintegrating in the gastrointestinal tract to promote sodium excretion.
Regulatory Framework for Sodium Alginate in Nutraceuticals
The regulatory framework for sodium alginate in nutraceuticals is a complex and evolving landscape that plays a crucial role in ensuring product safety and quality. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the use of sodium alginate in dietary supplements and functional foods. The FDA has granted sodium alginate Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) status, allowing its use in various food applications, including nutraceuticals.
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has also evaluated sodium alginate and approved its use in food supplements. In the European Union, sodium alginate is listed as E401 in the list of food additives and is subject to specific purity criteria and usage limits. These regulations ensure that sodium alginate used in nutraceuticals meets stringent quality and safety standards.
In Japan, sodium alginate is recognized as a food additive under the Food Sanitation Act and is subject to specific regulations regarding its use in functional foods and dietary supplements. The Japanese regulatory framework emphasizes the importance of quality control and safety assessments for nutraceutical ingredients.
Many other countries have adopted similar regulatory approaches, often aligning with international standards set by organizations such as the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA). These global standards help harmonize regulations across different regions and facilitate international trade in nutraceutical products containing sodium alginate.
Manufacturers of nutraceuticals incorporating sodium alginate must adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and implement quality control measures to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. This includes maintaining detailed documentation of sourcing, processing, and testing procedures for sodium alginate used in their products.
Labeling regulations for nutraceuticals containing sodium alginate vary by region but generally require clear identification of the ingredient on product packaging. In some jurisdictions, specific health claims related to sodium alginate may be subject to pre-approval or strict scientific substantiation requirements.
As the nutraceutical industry continues to grow and innovate, regulatory bodies are likely to refine and update their frameworks for sodium alginate and other functional ingredients. This ongoing process aims to balance consumer safety with the potential health benefits offered by nutraceutical products, while also fostering innovation and market growth in this dynamic sector.
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has also evaluated sodium alginate and approved its use in food supplements. In the European Union, sodium alginate is listed as E401 in the list of food additives and is subject to specific purity criteria and usage limits. These regulations ensure that sodium alginate used in nutraceuticals meets stringent quality and safety standards.
In Japan, sodium alginate is recognized as a food additive under the Food Sanitation Act and is subject to specific regulations regarding its use in functional foods and dietary supplements. The Japanese regulatory framework emphasizes the importance of quality control and safety assessments for nutraceutical ingredients.
Many other countries have adopted similar regulatory approaches, often aligning with international standards set by organizations such as the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA). These global standards help harmonize regulations across different regions and facilitate international trade in nutraceutical products containing sodium alginate.
Manufacturers of nutraceuticals incorporating sodium alginate must adhere to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and implement quality control measures to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. This includes maintaining detailed documentation of sourcing, processing, and testing procedures for sodium alginate used in their products.
Labeling regulations for nutraceuticals containing sodium alginate vary by region but generally require clear identification of the ingredient on product packaging. In some jurisdictions, specific health claims related to sodium alginate may be subject to pre-approval or strict scientific substantiation requirements.
As the nutraceutical industry continues to grow and innovate, regulatory bodies are likely to refine and update their frameworks for sodium alginate and other functional ingredients. This ongoing process aims to balance consumer safety with the potential health benefits offered by nutraceutical products, while also fostering innovation and market growth in this dynamic sector.
Environmental Impact of Sodium Alginate Production
The production of sodium alginate, while beneficial for nutraceutical product quality, has significant environmental implications that warrant careful consideration. The primary source of sodium alginate is brown seaweed, and its harvesting and processing can impact marine ecosystems and coastal environments.
Seaweed harvesting for sodium alginate production can lead to the depletion of natural seaweed beds if not managed sustainably. This can disrupt marine habitats and affect biodiversity in coastal areas. However, many producers are now implementing sustainable harvesting practices, such as rotational harvesting and cultivation of seaweed farms, to mitigate these impacts.
The extraction process of sodium alginate from seaweed involves the use of chemicals, primarily sodium carbonate and calcium chloride. The disposal of these chemical waste products, if not properly managed, can lead to water pollution and affect aquatic life. Advanced wastewater treatment systems are increasingly being employed to minimize this environmental risk.
Energy consumption is another significant factor in the environmental impact of sodium alginate production. The drying and processing of seaweed, as well as the extraction and purification of sodium alginate, require substantial energy inputs. This contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and carbon footprint of the production process.
On the positive side, seaweed cultivation for sodium alginate production can have beneficial environmental effects. Seaweed acts as a carbon sink, absorbing CO2 from the atmosphere and helping to mitigate climate change. It also helps in reducing ocean acidification and can improve water quality by absorbing excess nutrients from the surrounding water.
The packaging and transportation of sodium alginate also contribute to its environmental impact. As a global commodity, sodium alginate is often shipped long distances, resulting in additional carbon emissions. Efforts to optimize packaging and explore more localized production could help reduce this impact.
In recent years, there has been a growing focus on developing more environmentally friendly extraction methods for sodium alginate. Research is being conducted on enzymatic extraction processes that could reduce chemical usage and energy consumption. Additionally, some companies are exploring the use of waste streams from other industries as alternative sources of alginate, which could lead to a more circular and sustainable production model.
Seaweed harvesting for sodium alginate production can lead to the depletion of natural seaweed beds if not managed sustainably. This can disrupt marine habitats and affect biodiversity in coastal areas. However, many producers are now implementing sustainable harvesting practices, such as rotational harvesting and cultivation of seaweed farms, to mitigate these impacts.
The extraction process of sodium alginate from seaweed involves the use of chemicals, primarily sodium carbonate and calcium chloride. The disposal of these chemical waste products, if not properly managed, can lead to water pollution and affect aquatic life. Advanced wastewater treatment systems are increasingly being employed to minimize this environmental risk.
Energy consumption is another significant factor in the environmental impact of sodium alginate production. The drying and processing of seaweed, as well as the extraction and purification of sodium alginate, require substantial energy inputs. This contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and carbon footprint of the production process.
On the positive side, seaweed cultivation for sodium alginate production can have beneficial environmental effects. Seaweed acts as a carbon sink, absorbing CO2 from the atmosphere and helping to mitigate climate change. It also helps in reducing ocean acidification and can improve water quality by absorbing excess nutrients from the surrounding water.
The packaging and transportation of sodium alginate also contribute to its environmental impact. As a global commodity, sodium alginate is often shipped long distances, resulting in additional carbon emissions. Efforts to optimize packaging and explore more localized production could help reduce this impact.
In recent years, there has been a growing focus on developing more environmentally friendly extraction methods for sodium alginate. Research is being conducted on enzymatic extraction processes that could reduce chemical usage and energy consumption. Additionally, some companies are exploring the use of waste streams from other industries as alternative sources of alginate, which could lead to a more circular and sustainable production model.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!