How Sulfamic Acid Aids in Analytical Chromatography Techniques
JUL 30, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sulfamic Acid in Chromatography: Background and Objectives
Sulfamic acid has emerged as a crucial component in analytical chromatography techniques, revolutionizing the field of chemical separation and analysis. The journey of sulfamic acid in chromatography began in the mid-20th century when researchers discovered its unique properties that could enhance separation processes. Since then, its application has expanded significantly, becoming an integral part of various chromatographic methods.
The evolution of sulfamic acid in chromatography has been closely tied to the advancements in analytical chemistry and the growing demand for more precise and efficient separation techniques. Initially used as a simple acidic modifier, sulfamic acid's role has grown to include improving peak resolution, enhancing detection sensitivity, and stabilizing mobile phases in various chromatographic systems.
One of the primary objectives in utilizing sulfamic acid in chromatography is to improve the overall performance and reliability of analytical methods. Researchers aim to exploit its unique chemical properties to overcome common challenges in chromatographic separations, such as peak tailing, poor resolution, and inconsistent retention times. By incorporating sulfamic acid into chromatographic systems, scientists seek to develop more robust and reproducible analytical methods.
Another key goal is to expand the application range of chromatographic techniques. Sulfamic acid's versatility allows it to be used across different types of chromatography, including high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), ion chromatography, and gas chromatography. This versatility opens up new possibilities for analyzing complex mixtures and detecting trace amounts of analytes in various sample matrices.
The ongoing research in this field is driven by the need for more sensitive, selective, and efficient analytical methods. As industries such as pharmaceuticals, environmental monitoring, and food safety continue to demand higher standards of analysis, the role of sulfamic acid in chromatography is expected to grow. Researchers are exploring novel ways to incorporate sulfamic acid into chromatographic systems, aiming to push the boundaries of what is possible in terms of separation efficiency and detection limits.
Furthermore, the use of sulfamic acid aligns with the broader trend towards green chemistry in analytical methods. Its relatively low toxicity and environmental impact make it an attractive alternative to more hazardous acids traditionally used in chromatography. This aspect is particularly important as laboratories worldwide strive to adopt more sustainable practices without compromising analytical performance.
The evolution of sulfamic acid in chromatography has been closely tied to the advancements in analytical chemistry and the growing demand for more precise and efficient separation techniques. Initially used as a simple acidic modifier, sulfamic acid's role has grown to include improving peak resolution, enhancing detection sensitivity, and stabilizing mobile phases in various chromatographic systems.
One of the primary objectives in utilizing sulfamic acid in chromatography is to improve the overall performance and reliability of analytical methods. Researchers aim to exploit its unique chemical properties to overcome common challenges in chromatographic separations, such as peak tailing, poor resolution, and inconsistent retention times. By incorporating sulfamic acid into chromatographic systems, scientists seek to develop more robust and reproducible analytical methods.
Another key goal is to expand the application range of chromatographic techniques. Sulfamic acid's versatility allows it to be used across different types of chromatography, including high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), ion chromatography, and gas chromatography. This versatility opens up new possibilities for analyzing complex mixtures and detecting trace amounts of analytes in various sample matrices.
The ongoing research in this field is driven by the need for more sensitive, selective, and efficient analytical methods. As industries such as pharmaceuticals, environmental monitoring, and food safety continue to demand higher standards of analysis, the role of sulfamic acid in chromatography is expected to grow. Researchers are exploring novel ways to incorporate sulfamic acid into chromatographic systems, aiming to push the boundaries of what is possible in terms of separation efficiency and detection limits.
Furthermore, the use of sulfamic acid aligns with the broader trend towards green chemistry in analytical methods. Its relatively low toxicity and environmental impact make it an attractive alternative to more hazardous acids traditionally used in chromatography. This aspect is particularly important as laboratories worldwide strive to adopt more sustainable practices without compromising analytical performance.
Market Demand for Enhanced Chromatographic Techniques
The demand for enhanced chromatographic techniques has been steadily increasing across various industries, driven by the need for more precise and efficient analytical methods. Sulfamic acid has emerged as a valuable aid in this field, offering significant improvements in chromatographic performance. The market for chromatography equipment and consumables is projected to grow substantially, with a particular focus on high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and gas chromatography (GC) systems.
In the pharmaceutical industry, there is a growing demand for advanced chromatographic techniques to support drug discovery, development, and quality control processes. Sulfamic acid's ability to enhance peak resolution and reduce tailing in HPLC analyses has made it particularly attractive for pharmaceutical applications. This has led to increased adoption of sulfamic acid-based methodologies in drug purity assessments and impurity profiling.
The food and beverage sector is another key driver of market demand for improved chromatographic techniques. With increasing consumer awareness and regulatory scrutiny regarding food safety and quality, there is a pressing need for more sensitive and accurate analytical methods. Sulfamic acid's role in improving the separation of complex food matrices and detecting trace contaminants has positioned it as a valuable tool in this industry.
Environmental monitoring and analysis represent another significant market segment for enhanced chromatographic techniques. The ability of sulfamic acid to aid in the detection and quantification of environmental pollutants, such as pesticides and heavy metals, has led to its increased use in environmental laboratories. This trend is expected to continue as global environmental regulations become more stringent.
The biotechnology and life sciences sectors are also contributing to the growing demand for advanced chromatographic methods. Sulfamic acid's applications in protein and peptide analysis, as well as in the purification of biopharmaceuticals, have made it an essential component in many bioanalytical workflows. As the biopharmaceutical industry continues to expand, the demand for sulfamic acid-enhanced chromatographic techniques is likely to increase correspondingly.
In the academic and research sector, there is a constant push for more sophisticated analytical tools to support cutting-edge scientific investigations. Sulfamic acid's versatility in improving various chromatographic techniques has made it a valuable resource for researchers across multiple disciplines, from chemistry and biochemistry to materials science and forensics.
The market demand is further bolstered by the ongoing technological advancements in chromatography instrumentation. As manufacturers develop more sensitive and high-throughput systems, the need for complementary chemical aids like sulfamic acid to optimize these instruments' performance becomes more pronounced. This synergy between instrument development and chemical innovation is expected to drive continued growth in the market for enhanced chromatographic techniques.
In the pharmaceutical industry, there is a growing demand for advanced chromatographic techniques to support drug discovery, development, and quality control processes. Sulfamic acid's ability to enhance peak resolution and reduce tailing in HPLC analyses has made it particularly attractive for pharmaceutical applications. This has led to increased adoption of sulfamic acid-based methodologies in drug purity assessments and impurity profiling.
The food and beverage sector is another key driver of market demand for improved chromatographic techniques. With increasing consumer awareness and regulatory scrutiny regarding food safety and quality, there is a pressing need for more sensitive and accurate analytical methods. Sulfamic acid's role in improving the separation of complex food matrices and detecting trace contaminants has positioned it as a valuable tool in this industry.
Environmental monitoring and analysis represent another significant market segment for enhanced chromatographic techniques. The ability of sulfamic acid to aid in the detection and quantification of environmental pollutants, such as pesticides and heavy metals, has led to its increased use in environmental laboratories. This trend is expected to continue as global environmental regulations become more stringent.
The biotechnology and life sciences sectors are also contributing to the growing demand for advanced chromatographic methods. Sulfamic acid's applications in protein and peptide analysis, as well as in the purification of biopharmaceuticals, have made it an essential component in many bioanalytical workflows. As the biopharmaceutical industry continues to expand, the demand for sulfamic acid-enhanced chromatographic techniques is likely to increase correspondingly.
In the academic and research sector, there is a constant push for more sophisticated analytical tools to support cutting-edge scientific investigations. Sulfamic acid's versatility in improving various chromatographic techniques has made it a valuable resource for researchers across multiple disciplines, from chemistry and biochemistry to materials science and forensics.
The market demand is further bolstered by the ongoing technological advancements in chromatography instrumentation. As manufacturers develop more sensitive and high-throughput systems, the need for complementary chemical aids like sulfamic acid to optimize these instruments' performance becomes more pronounced. This synergy between instrument development and chemical innovation is expected to drive continued growth in the market for enhanced chromatographic techniques.
Current State and Challenges in Analytical Chromatography
Analytical chromatography has witnessed significant advancements in recent years, with sulfamic acid emerging as a crucial component in enhancing separation techniques. The current state of analytical chromatography is characterized by a continuous pursuit of improved resolution, sensitivity, and efficiency in separating complex mixtures.
One of the primary challenges in analytical chromatography is the need for more robust and versatile mobile phases. Sulfamic acid has proven to be an effective additive in this regard, particularly in reversed-phase liquid chromatography. Its ability to act as both an ion-pairing agent and a pH modifier has led to improved peak shapes and increased retention of basic compounds.
The integration of sulfamic acid into chromatographic methods has also addressed the issue of peak tailing, a common problem in the analysis of basic analytes. By suppressing the ionization of residual silanol groups on silica-based stationary phases, sulfamic acid helps to minimize unwanted secondary interactions, resulting in sharper, more symmetrical peaks.
Another significant challenge in the field is the demand for faster analysis times without compromising separation quality. Sulfamic acid has shown promise in this area by enabling the use of higher flow rates and shorter columns while maintaining good peak resolution. This has been particularly beneficial in high-throughput screening applications and rapid method development.
The increasing complexity of sample matrices in various industries, such as pharmaceuticals and environmental analysis, poses a continuous challenge to chromatographic techniques. Sulfamic acid has demonstrated its utility in improving the separation of closely eluting compounds and reducing matrix effects, thereby enhancing the overall analytical performance.
However, the use of sulfamic acid is not without its challenges. One of the primary concerns is its potential for corrosion of metal components in chromatographic systems, particularly when used at higher concentrations or for extended periods. This necessitates careful consideration of instrument compatibility and maintenance protocols.
Furthermore, the optimal concentration of sulfamic acid can vary significantly depending on the specific application and analytes of interest. Determining the ideal conditions often requires extensive method development and validation, which can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
As analytical chromatography continues to evolve, there is a growing emphasis on developing more environmentally friendly and sustainable methods. While sulfamic acid offers many advantages, its environmental impact and disposal considerations present ongoing challenges that researchers are actively addressing through the exploration of alternative additives and green chemistry approaches.
One of the primary challenges in analytical chromatography is the need for more robust and versatile mobile phases. Sulfamic acid has proven to be an effective additive in this regard, particularly in reversed-phase liquid chromatography. Its ability to act as both an ion-pairing agent and a pH modifier has led to improved peak shapes and increased retention of basic compounds.
The integration of sulfamic acid into chromatographic methods has also addressed the issue of peak tailing, a common problem in the analysis of basic analytes. By suppressing the ionization of residual silanol groups on silica-based stationary phases, sulfamic acid helps to minimize unwanted secondary interactions, resulting in sharper, more symmetrical peaks.
Another significant challenge in the field is the demand for faster analysis times without compromising separation quality. Sulfamic acid has shown promise in this area by enabling the use of higher flow rates and shorter columns while maintaining good peak resolution. This has been particularly beneficial in high-throughput screening applications and rapid method development.
The increasing complexity of sample matrices in various industries, such as pharmaceuticals and environmental analysis, poses a continuous challenge to chromatographic techniques. Sulfamic acid has demonstrated its utility in improving the separation of closely eluting compounds and reducing matrix effects, thereby enhancing the overall analytical performance.
However, the use of sulfamic acid is not without its challenges. One of the primary concerns is its potential for corrosion of metal components in chromatographic systems, particularly when used at higher concentrations or for extended periods. This necessitates careful consideration of instrument compatibility and maintenance protocols.
Furthermore, the optimal concentration of sulfamic acid can vary significantly depending on the specific application and analytes of interest. Determining the ideal conditions often requires extensive method development and validation, which can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
As analytical chromatography continues to evolve, there is a growing emphasis on developing more environmentally friendly and sustainable methods. While sulfamic acid offers many advantages, its environmental impact and disposal considerations present ongoing challenges that researchers are actively addressing through the exploration of alternative additives and green chemistry approaches.
Existing Applications of Sulfamic Acid in Chromatography
01 Synthesis and production of sulfamic acid
Various methods and processes for synthesizing and producing sulfamic acid are described. These include reactions involving sulfur trioxide and ammonia, as well as other chemical precursors. The processes aim to improve yield, purity, and efficiency in the production of sulfamic acid.- Synthesis and production of sulfamic acid: Various methods for synthesizing and producing sulfamic acid are described. These processes often involve the reaction of sulfur trioxide with ammonia or urea, followed by purification steps. The production methods aim to improve yield, purity, and efficiency of sulfamic acid manufacturing.
- Applications in cleaning and descaling: Sulfamic acid is widely used in cleaning and descaling formulations. It is effective in removing mineral deposits, rust, and scale from various surfaces and equipment. These applications include household cleaners, industrial descaling agents, and specialized cleaning products for specific industries.
- Use in water treatment and purification: Sulfamic acid plays a role in water treatment and purification processes. It is used for pH adjustment, scale prevention, and as a component in water treatment chemicals. The compound's properties make it suitable for various water-related applications in industrial and municipal settings.
- Agricultural and horticultural applications: Sulfamic acid finds use in agricultural and horticultural contexts. It is employed in fertilizer formulations, soil pH adjustment, and as a component in certain pesticides or herbicides. The compound's properties contribute to various plant growth and crop protection applications.
- Industrial and chemical processing uses: Sulfamic acid has diverse applications in industrial and chemical processing. It is used as a sulfonating agent, in the production of artificial sweeteners, as a catalyst in certain reactions, and in the manufacture of various chemical compounds. Its versatility makes it valuable in multiple industrial sectors.
02 Applications in cleaning and descaling
Sulfamic acid is widely used in cleaning and descaling formulations. It is effective in removing mineral deposits, rust, and other stubborn stains. Applications include household cleaners, industrial descaling agents, and specialized cleaning products for various surfaces.Expand Specific Solutions03 Use in water treatment and purification
Sulfamic acid plays a role in water treatment and purification processes. It is used for pH adjustment, scale prevention, and as a component in water treatment chemicals. The compound helps in maintaining water quality in various industrial and municipal applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Agricultural and horticultural applications
Sulfamic acid finds use in agricultural and horticultural settings. It is employed in fertilizer formulations, soil treatments, and as a component in plant growth regulators. The compound contributes to soil pH adjustment and nutrient availability for plants.Expand Specific Solutions05 Industrial and chemical processing
Sulfamic acid is utilized in various industrial and chemical processes. It serves as a reagent in organic synthesis, a catalyst in certain reactions, and a component in electroplating baths. The compound's properties make it valuable in diverse manufacturing and processing applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Analytical Chemistry and Chromatography
The competitive landscape for sulfamic acid in analytical chromatography techniques is characterized by a mature market with steady growth. The global market size for chromatography reagents, including sulfamic acid, is estimated to be in the billions of dollars, driven by increasing demand in pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and environmental testing sectors. Technologically, the field is well-established, with ongoing incremental improvements rather than disruptive innovations. Key players like BASF, Shin-Etsu Chemical, and Wanhua Chemical Group are leading suppliers of sulfamic acid and related chemicals, while companies such as Agilent Technologies and Shimadzu Corporation provide advanced chromatography systems and solutions. Academic institutions like Sichuan University and Korea University contribute to research and development in this area, fostering collaborations between industry and academia to enhance chromatographic techniques.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF Corporation has leveraged its expertise in chemical manufacturing to develop high-purity sulfamic acid products specifically designed for analytical chromatography applications. Their Selectipure® line of sulfamic acid offers exceptional purity levels (>99.9%) and low metal content, making it ideal for use in HPLC mobile phases and as a cleaning agent for chromatography systems[7]. BASF has also formulated specialized sulfamic acid-based solutions for ion-pair chromatography, enabling improved separation of polar and ionic compounds[8]. Additionally, the company provides technical support and application notes to assist chromatographers in optimizing sulfamic acid usage in various analytical methods[9].
Strengths: High-quality sulfamic acid products, extensive chemical expertise, global distribution network. Weaknesses: Focus primarily on chemical supply rather than instrument development.
Sichuan University
Technical Solution: Researchers at Sichuan University have made significant contributions to the application of sulfamic acid in analytical chromatography techniques. They have developed novel stationary phases incorporating sulfamic acid moieties for improved separation of basic compounds in HPLC[10]. The university's analytical chemistry department has also explored the use of sulfamic acid as a mobile phase additive in hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC) for the analysis of polar pharmaceuticals and metabolites[11]. Furthermore, Sichuan University scientists have investigated the synergistic effects of combining sulfamic acid with other additives to enhance chromatographic performance in complex biological sample analyses[12].
Strengths: Cutting-edge research in chromatography, innovative stationary phase development. Weaknesses: Limited commercial product offerings, primarily focused on academic research.
Core Innovations in Sulfamic Acid-Based Chromatography
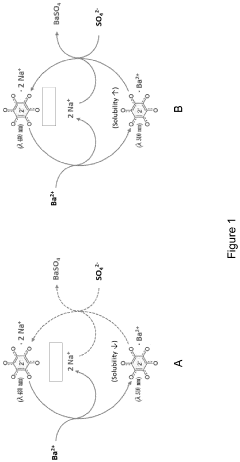
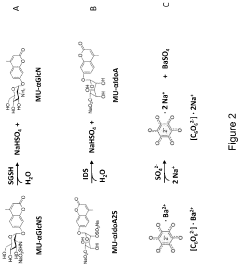
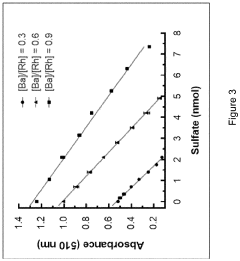
Sulfatase activity assay
PatentInactiveEP3741867A1
Innovation
- A colorimetric analysis method using a solution comprising methanol and specific solvents like 3-methoxy-1-propanol, which prevents precipitation and allows for stable readings beyond 2 hours, enabling direct measurement of enzymatic activity by solvating the barium-rhodizonate complex and eliminating the need for a curing step.
Method of producing antithrombin composition
PatentWO2008120801A1
Innovation
- A method involving Cellufine sulfate chromatography, combined with anion exchange and hydrophobic chromatography, is used to separate and purify antithrombin, adjusting conductivity and pH to achieve high yields of antithrombin compositions with specific α-form or β-form content and controlled sialic acid bonding.
Environmental Impact of Sulfamic Acid in Analytical Processes
The use of sulfamic acid in analytical chromatography techniques has raised concerns about its potential environmental impact. As a strong acid with corrosive properties, sulfamic acid can pose risks to aquatic ecosystems if not properly managed. When released into water bodies, it can lower the pH, potentially harming aquatic life and disrupting ecosystem balance. However, the environmental impact of sulfamic acid in analytical processes is generally considered to be minimal when proper handling and disposal procedures are followed.
In laboratory settings, the quantities of sulfamic acid used in chromatography are typically small, reducing the risk of significant environmental contamination. Nevertheless, it is crucial to implement proper waste management protocols to prevent any discharge into the environment. Many laboratories have established systems for collecting and treating acidic waste, including neutralization processes before disposal.
The production of sulfamic acid itself can have environmental implications. The manufacturing process may involve the use of sulfur trioxide and ammonia, which can contribute to air pollution if not properly controlled. However, modern production facilities often employ advanced emission control technologies to minimize environmental impact.
When considering the lifecycle of sulfamic acid in analytical processes, it is important to note that it is biodegradable under certain conditions. In the presence of water, sulfamic acid hydrolyzes to form ammonium bisulfate, which can be further broken down by environmental processes. This biodegradability helps mitigate long-term environmental persistence concerns.
Efforts to reduce the environmental footprint of analytical processes involving sulfamic acid include the development of greener alternatives and the optimization of chromatography techniques to minimize reagent use. Some researchers are exploring the use of less hazardous acids or alternative separation methods that do not require strong acids. Additionally, advancements in instrumentation have led to more efficient chromatography systems that require smaller sample sizes and, consequently, less reagent use.
The environmental impact of sulfamic acid in analytical processes should also be considered in the context of its benefits. By enabling precise and efficient chromatographic separations, sulfamic acid contributes to the accuracy and reliability of analytical results. This, in turn, supports various fields, including environmental monitoring and quality control, which are essential for protecting public health and the environment.
In laboratory settings, the quantities of sulfamic acid used in chromatography are typically small, reducing the risk of significant environmental contamination. Nevertheless, it is crucial to implement proper waste management protocols to prevent any discharge into the environment. Many laboratories have established systems for collecting and treating acidic waste, including neutralization processes before disposal.
The production of sulfamic acid itself can have environmental implications. The manufacturing process may involve the use of sulfur trioxide and ammonia, which can contribute to air pollution if not properly controlled. However, modern production facilities often employ advanced emission control technologies to minimize environmental impact.
When considering the lifecycle of sulfamic acid in analytical processes, it is important to note that it is biodegradable under certain conditions. In the presence of water, sulfamic acid hydrolyzes to form ammonium bisulfate, which can be further broken down by environmental processes. This biodegradability helps mitigate long-term environmental persistence concerns.
Efforts to reduce the environmental footprint of analytical processes involving sulfamic acid include the development of greener alternatives and the optimization of chromatography techniques to minimize reagent use. Some researchers are exploring the use of less hazardous acids or alternative separation methods that do not require strong acids. Additionally, advancements in instrumentation have led to more efficient chromatography systems that require smaller sample sizes and, consequently, less reagent use.
The environmental impact of sulfamic acid in analytical processes should also be considered in the context of its benefits. By enabling precise and efficient chromatographic separations, sulfamic acid contributes to the accuracy and reliability of analytical results. This, in turn, supports various fields, including environmental monitoring and quality control, which are essential for protecting public health and the environment.
Regulatory Considerations for Chromatographic Reagents
The use of sulfamic acid in analytical chromatography techniques is subject to various regulatory considerations. Chromatographic reagents, including sulfamic acid, must comply with stringent quality and safety standards set by regulatory bodies such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA).
One of the primary regulatory concerns is the purity of sulfamic acid used in chromatography. Regulatory agencies require that chromatographic reagents meet specific purity criteria to ensure accurate and reliable analytical results. Manufacturers must provide certificates of analysis detailing the purity levels and any potential impurities present in the sulfamic acid.
Safety is another crucial aspect of regulatory compliance. Sulfamic acid, being a strong acid, is classified as a hazardous substance. Consequently, its use in chromatographic techniques must adhere to safety regulations outlined in occupational health and safety guidelines. This includes proper labeling, storage, handling, and disposal procedures.
Environmental regulations also play a significant role in the use of sulfamic acid in chromatography. Disposal of chromatographic waste containing sulfamic acid must comply with local and national environmental protection laws. Many jurisdictions require special treatment or neutralization of acidic waste before disposal.
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and Good Laboratory Practices (GLP) are essential regulatory frameworks that govern the use of chromatographic reagents, including sulfamic acid. These practices ensure consistency, traceability, and reliability in analytical procedures. Laboratories using sulfamic acid in chromatography must maintain detailed records of reagent usage, instrument calibration, and analytical methods.
Regulatory bodies also mandate regular quality control checks and method validation when using sulfamic acid in chromatographic techniques. This includes periodic testing of the reagent's efficacy and stability, as well as validation of analytical methods to ensure reproducibility and accuracy of results.
In the pharmaceutical industry, the use of sulfamic acid in chromatography for drug analysis or quality control must comply with pharmacopeia standards. These standards provide specific guidelines on the use of reagents, including sulfamic acid, in pharmaceutical analysis.
Lastly, regulatory considerations extend to the documentation and reporting of chromatographic analyses using sulfamic acid. Laboratories must maintain comprehensive records of all analyses, including reagent information, method parameters, and results. These records are subject to regulatory audits and inspections to ensure compliance with established standards and practices.
One of the primary regulatory concerns is the purity of sulfamic acid used in chromatography. Regulatory agencies require that chromatographic reagents meet specific purity criteria to ensure accurate and reliable analytical results. Manufacturers must provide certificates of analysis detailing the purity levels and any potential impurities present in the sulfamic acid.
Safety is another crucial aspect of regulatory compliance. Sulfamic acid, being a strong acid, is classified as a hazardous substance. Consequently, its use in chromatographic techniques must adhere to safety regulations outlined in occupational health and safety guidelines. This includes proper labeling, storage, handling, and disposal procedures.
Environmental regulations also play a significant role in the use of sulfamic acid in chromatography. Disposal of chromatographic waste containing sulfamic acid must comply with local and national environmental protection laws. Many jurisdictions require special treatment or neutralization of acidic waste before disposal.
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and Good Laboratory Practices (GLP) are essential regulatory frameworks that govern the use of chromatographic reagents, including sulfamic acid. These practices ensure consistency, traceability, and reliability in analytical procedures. Laboratories using sulfamic acid in chromatography must maintain detailed records of reagent usage, instrument calibration, and analytical methods.
Regulatory bodies also mandate regular quality control checks and method validation when using sulfamic acid in chromatographic techniques. This includes periodic testing of the reagent's efficacy and stability, as well as validation of analytical methods to ensure reproducibility and accuracy of results.
In the pharmaceutical industry, the use of sulfamic acid in chromatography for drug analysis or quality control must comply with pharmacopeia standards. These standards provide specific guidelines on the use of reagents, including sulfamic acid, in pharmaceutical analysis.
Lastly, regulatory considerations extend to the documentation and reporting of chromatographic analyses using sulfamic acid. Laboratories must maintain comprehensive records of all analyses, including reagent information, method parameters, and results. These records are subject to regulatory audits and inspections to ensure compliance with established standards and practices.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!