Sulfamic Acid in Personal Care Product Incremental Innovation
JUL 30, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sulfamic Acid Background and Innovation Goals
Sulfamic acid, also known as amidosulfonic acid, has been a key component in various industrial and consumer applications for decades. In the realm of personal care products, its unique properties have made it an increasingly important ingredient. The evolution of sulfamic acid in this sector can be traced back to its initial use as a cleaning agent, primarily due to its ability to effectively remove mineral deposits and scale.
The personal care industry has witnessed significant growth and transformation over the years, driven by consumer demand for more effective, safer, and environmentally friendly products. This shift has led to a renewed focus on sulfamic acid as a potential source of innovation. Its mild acidic nature, coupled with its stability and versatility, positions it as an ideal candidate for incremental innovation in personal care formulations.
The primary goal of research into sulfamic acid for personal care product innovation is to expand its application beyond traditional uses. This includes exploring its potential as a pH adjuster, preservative enhancer, and exfoliating agent in various cosmetic and skincare formulations. Additionally, there is a growing interest in leveraging sulfamic acid's antimicrobial properties to develop new preservative systems that meet the increasing consumer demand for "clean" beauty products.
Another key objective is to optimize the performance of sulfamic acid in existing applications. This involves investigating ways to improve its solubility, enhance its synergistic effects with other ingredients, and minimize any potential irritation or sensitization risks. Researchers are also exploring novel delivery systems that could improve the efficacy and stability of sulfamic acid in personal care products.
Sustainability is a crucial aspect of innovation goals in this field. As the personal care industry moves towards more environmentally conscious practices, there is a push to develop greener production methods for sulfamic acid and to explore its potential in biodegradable formulations. This aligns with the broader industry trend of reducing environmental impact while maintaining product performance.
Furthermore, regulatory compliance remains a critical consideration in sulfamic acid research. Innovation efforts are focused on ensuring that new applications and formulations meet stringent safety standards and regulatory requirements across different global markets. This includes investigating the long-term safety profile of sulfamic acid in various concentrations and combinations with other ingredients.
In conclusion, the research on sulfamic acid in personal care product innovation aims to unlock its full potential as a multifunctional ingredient. By addressing current limitations and exploring new applications, researchers seek to position sulfamic acid as a key player in the next generation of personal care products, offering enhanced performance, safety, and sustainability.
The personal care industry has witnessed significant growth and transformation over the years, driven by consumer demand for more effective, safer, and environmentally friendly products. This shift has led to a renewed focus on sulfamic acid as a potential source of innovation. Its mild acidic nature, coupled with its stability and versatility, positions it as an ideal candidate for incremental innovation in personal care formulations.
The primary goal of research into sulfamic acid for personal care product innovation is to expand its application beyond traditional uses. This includes exploring its potential as a pH adjuster, preservative enhancer, and exfoliating agent in various cosmetic and skincare formulations. Additionally, there is a growing interest in leveraging sulfamic acid's antimicrobial properties to develop new preservative systems that meet the increasing consumer demand for "clean" beauty products.
Another key objective is to optimize the performance of sulfamic acid in existing applications. This involves investigating ways to improve its solubility, enhance its synergistic effects with other ingredients, and minimize any potential irritation or sensitization risks. Researchers are also exploring novel delivery systems that could improve the efficacy and stability of sulfamic acid in personal care products.
Sustainability is a crucial aspect of innovation goals in this field. As the personal care industry moves towards more environmentally conscious practices, there is a push to develop greener production methods for sulfamic acid and to explore its potential in biodegradable formulations. This aligns with the broader industry trend of reducing environmental impact while maintaining product performance.
Furthermore, regulatory compliance remains a critical consideration in sulfamic acid research. Innovation efforts are focused on ensuring that new applications and formulations meet stringent safety standards and regulatory requirements across different global markets. This includes investigating the long-term safety profile of sulfamic acid in various concentrations and combinations with other ingredients.
In conclusion, the research on sulfamic acid in personal care product innovation aims to unlock its full potential as a multifunctional ingredient. By addressing current limitations and exploring new applications, researchers seek to position sulfamic acid as a key player in the next generation of personal care products, offering enhanced performance, safety, and sustainability.
Market Analysis for Sulfamic Acid in Personal Care
The global market for sulfamic acid in personal care products has been experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing consumer demand for effective and safe cleaning and exfoliating agents. Sulfamic acid, known for its versatility and mild acidic properties, has found widespread application in various personal care formulations, including facial cleansers, body scrubs, and oral care products.
The personal care industry has witnessed a shift towards more natural and environmentally friendly ingredients, which has positively impacted the demand for sulfamic acid. Its biodegradability and low toxicity profile make it an attractive option for manufacturers seeking to meet consumer preferences for sustainable products. This trend is particularly pronounced in developed markets such as North America and Europe, where consumers are increasingly conscious of the environmental impact of their personal care choices.
In terms of market segmentation, the use of sulfamic acid in oral care products represents a significant portion of its personal care applications. The growing awareness of dental hygiene and the increasing prevalence of oral health issues have contributed to the expansion of this segment. Sulfamic acid's ability to effectively remove plaque and tartar without causing excessive enamel erosion has made it a popular ingredient in toothpaste and mouthwash formulations.
The skincare segment also presents substantial growth opportunities for sulfamic acid. Its gentle exfoliating properties make it suitable for use in facial cleansers and body scrubs, catering to the growing demand for at-home spa treatments and professional-grade skincare products. The rise of the "skinimalism" trend, which emphasizes simplified skincare routines with multi-functional products, has further boosted the appeal of sulfamic acid-based formulations.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific has emerged as a key growth market for sulfamic acid in personal care applications. The region's rapidly expanding middle class, increasing disposable incomes, and growing awareness of personal hygiene have fueled demand for premium personal care products. Countries like China, India, and South Korea are at the forefront of this trend, with local and international brands alike incorporating sulfamic acid into their product lines to meet consumer expectations.
However, the market for sulfamic acid in personal care is not without challenges. Regulatory scrutiny of chemical ingredients in cosmetics and personal care products has intensified in recent years, necessitating ongoing safety assessments and compliance efforts. Additionally, competition from alternative ingredients, such as alpha-hydroxy acids (AHAs) and enzymes, poses a potential threat to market growth.
Despite these challenges, the overall outlook for sulfamic acid in the personal care market remains positive. Innovations in formulation techniques and the development of novel applications are expected to drive incremental growth in the coming years. As manufacturers continue to explore new ways to leverage the unique properties of sulfamic acid, its role in personal care products is likely to expand, offering enhanced performance and consumer benefits across a wide range of product categories.
The personal care industry has witnessed a shift towards more natural and environmentally friendly ingredients, which has positively impacted the demand for sulfamic acid. Its biodegradability and low toxicity profile make it an attractive option for manufacturers seeking to meet consumer preferences for sustainable products. This trend is particularly pronounced in developed markets such as North America and Europe, where consumers are increasingly conscious of the environmental impact of their personal care choices.
In terms of market segmentation, the use of sulfamic acid in oral care products represents a significant portion of its personal care applications. The growing awareness of dental hygiene and the increasing prevalence of oral health issues have contributed to the expansion of this segment. Sulfamic acid's ability to effectively remove plaque and tartar without causing excessive enamel erosion has made it a popular ingredient in toothpaste and mouthwash formulations.
The skincare segment also presents substantial growth opportunities for sulfamic acid. Its gentle exfoliating properties make it suitable for use in facial cleansers and body scrubs, catering to the growing demand for at-home spa treatments and professional-grade skincare products. The rise of the "skinimalism" trend, which emphasizes simplified skincare routines with multi-functional products, has further boosted the appeal of sulfamic acid-based formulations.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific has emerged as a key growth market for sulfamic acid in personal care applications. The region's rapidly expanding middle class, increasing disposable incomes, and growing awareness of personal hygiene have fueled demand for premium personal care products. Countries like China, India, and South Korea are at the forefront of this trend, with local and international brands alike incorporating sulfamic acid into their product lines to meet consumer expectations.
However, the market for sulfamic acid in personal care is not without challenges. Regulatory scrutiny of chemical ingredients in cosmetics and personal care products has intensified in recent years, necessitating ongoing safety assessments and compliance efforts. Additionally, competition from alternative ingredients, such as alpha-hydroxy acids (AHAs) and enzymes, poses a potential threat to market growth.
Despite these challenges, the overall outlook for sulfamic acid in the personal care market remains positive. Innovations in formulation techniques and the development of novel applications are expected to drive incremental growth in the coming years. As manufacturers continue to explore new ways to leverage the unique properties of sulfamic acid, its role in personal care products is likely to expand, offering enhanced performance and consumer benefits across a wide range of product categories.
Technical Challenges in Sulfamic Acid Application
The application of sulfamic acid in personal care products faces several technical challenges that hinder its widespread adoption and incremental innovation. One of the primary issues is the stability of sulfamic acid in various formulations. When exposed to high temperatures or certain pH levels, sulfamic acid can undergo hydrolysis, leading to the formation of ammonium bisulfate. This degradation not only reduces the efficacy of the product but also potentially alters its pH, affecting the overall stability and performance of the formulation.
Another significant challenge is the compatibility of sulfamic acid with other ingredients commonly used in personal care products. Its acidic nature can interact unfavorably with certain active ingredients, preservatives, or fragrances, potentially causing unwanted chemical reactions or reducing the effectiveness of these components. This limitation restricts the range of formulations in which sulfamic acid can be effectively incorporated, posing a barrier to innovation in product development.
The concentration of sulfamic acid in personal care products is also a critical factor that presents technical difficulties. While higher concentrations may provide enhanced benefits, they can also increase the risk of skin irritation and sensitization in some individuals. Determining the optimal concentration that balances efficacy and safety requires extensive research and testing, which can be time-consuming and costly for manufacturers.
Furthermore, the solubility of sulfamic acid in various cosmetic bases poses challenges in formulation. Its limited solubility in certain mediums can lead to precipitation or crystallization, affecting the texture, appearance, and stability of the final product. This issue is particularly problematic in anhydrous or low-water formulations, where achieving uniform dispersion of sulfamic acid can be difficult.
The potential for metal ion complexation is another technical hurdle in sulfamic acid application. Its ability to form complexes with metal ions present in water or other ingredients can lead to reduced efficacy and potential discoloration of the product. This characteristic necessitates careful consideration of water quality and the selection of compatible packaging materials to prevent unwanted interactions.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape surrounding sulfamic acid usage in personal care products presents challenges for innovation. Varying regulations across different regions regarding permissible concentrations and applications can complicate product development and global marketing strategies. Manufacturers must navigate these regulatory requirements while striving to innovate and improve product formulations.
Addressing these technical challenges requires a multifaceted approach, combining advanced formulation techniques, innovative delivery systems, and comprehensive stability testing. Overcoming these hurdles is crucial for unlocking the full potential of sulfamic acid in personal care products and driving incremental innovation in this sector.
Another significant challenge is the compatibility of sulfamic acid with other ingredients commonly used in personal care products. Its acidic nature can interact unfavorably with certain active ingredients, preservatives, or fragrances, potentially causing unwanted chemical reactions or reducing the effectiveness of these components. This limitation restricts the range of formulations in which sulfamic acid can be effectively incorporated, posing a barrier to innovation in product development.
The concentration of sulfamic acid in personal care products is also a critical factor that presents technical difficulties. While higher concentrations may provide enhanced benefits, they can also increase the risk of skin irritation and sensitization in some individuals. Determining the optimal concentration that balances efficacy and safety requires extensive research and testing, which can be time-consuming and costly for manufacturers.
Furthermore, the solubility of sulfamic acid in various cosmetic bases poses challenges in formulation. Its limited solubility in certain mediums can lead to precipitation or crystallization, affecting the texture, appearance, and stability of the final product. This issue is particularly problematic in anhydrous or low-water formulations, where achieving uniform dispersion of sulfamic acid can be difficult.
The potential for metal ion complexation is another technical hurdle in sulfamic acid application. Its ability to form complexes with metal ions present in water or other ingredients can lead to reduced efficacy and potential discoloration of the product. This characteristic necessitates careful consideration of water quality and the selection of compatible packaging materials to prevent unwanted interactions.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape surrounding sulfamic acid usage in personal care products presents challenges for innovation. Varying regulations across different regions regarding permissible concentrations and applications can complicate product development and global marketing strategies. Manufacturers must navigate these regulatory requirements while striving to innovate and improve product formulations.
Addressing these technical challenges requires a multifaceted approach, combining advanced formulation techniques, innovative delivery systems, and comprehensive stability testing. Overcoming these hurdles is crucial for unlocking the full potential of sulfamic acid in personal care products and driving incremental innovation in this sector.
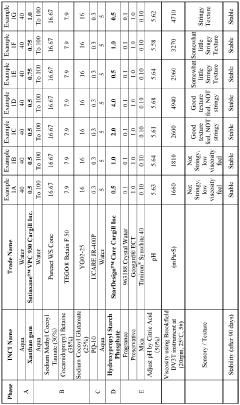
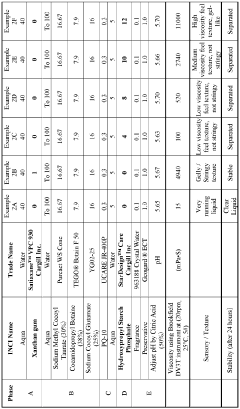
Current Sulfamic Acid Formulations in Personal Care
01 Synthesis and production of sulfamic acid
Various methods and processes for synthesizing and producing sulfamic acid are described. These include reactions involving sulfur trioxide and ammonia, as well as other chemical precursors. The processes aim to improve yield, purity, and efficiency in sulfamic acid production.- Synthesis and production of sulfamic acid: Various methods and processes for synthesizing and producing sulfamic acid are described. These include reactions involving sulfur trioxide and ammonia, as well as other chemical pathways to efficiently manufacture sulfamic acid on an industrial scale.
- Applications in cleaning and descaling: Sulfamic acid is widely used in cleaning and descaling formulations. It is effective in removing mineral deposits, limescale, and rust from various surfaces, making it valuable in household and industrial cleaning products.
- Use in water treatment: Sulfamic acid finds applications in water treatment processes. It is used for pH adjustment, scale prevention, and as a component in water treatment chemicals for both industrial and municipal water systems.
- Agricultural and horticultural applications: Sulfamic acid is utilized in various agricultural and horticultural products. It serves as a component in fertilizers, soil conditioners, and plant growth regulators, contributing to improved crop yields and plant health.
- Industrial and chemical processing: Sulfamic acid plays a role in various industrial and chemical processes. It is used as a reagent in organic synthesis, as a catalyst in certain reactions, and as an intermediate in the production of other chemicals and materials.
02 Applications in cleaning and descaling
Sulfamic acid is widely used in cleaning and descaling applications. It is effective in removing mineral deposits, rust, and other stubborn stains from various surfaces. Formulations containing sulfamic acid are developed for household and industrial cleaning products.Expand Specific Solutions03 Use in water treatment and purification
Sulfamic acid plays a role in water treatment and purification processes. It is used for pH adjustment, scale prevention, and as a disinfectant in water systems. Various methods and compositions incorporating sulfamic acid for water treatment are described.Expand Specific Solutions04 Agricultural and horticultural applications
Sulfamic acid finds applications in agriculture and horticulture. It is used in fertilizer formulations, soil treatments, and as a plant growth regulator. Methods for improving crop yield and soil quality using sulfamic acid-based compositions are presented.Expand Specific Solutions05 Industrial and chemical processing
Sulfamic acid is utilized in various industrial and chemical processes. It serves as a catalyst, reagent, or intermediate in the production of other chemicals. Applications in metal processing, polymer synthesis, and other industrial sectors are described.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Sulfamic Acid Industry
The research on sulfamic acid in personal care product incremental innovation is in a mature stage, with a well-established market and significant competition among key players. The global market for sulfamic acid in personal care products is substantial, driven by increasing demand for mild and effective cleansing agents. Technologically, the field is advanced, with companies like Stepan Co., Colgate-Palmolive, Unilever, BASF, and Henkel leading innovation. These firms are focusing on enhancing product efficacy, sustainability, and consumer safety. The competitive landscape is characterized by ongoing R&D efforts to develop novel formulations and applications, with a growing emphasis on eco-friendly and natural alternatives to traditional sulfamic acid-based products.
Colgate-Palmolive Co.
Technical Solution: Colgate-Palmolive has focused on incorporating sulfamic acid into their oral care products, particularly toothpaste and mouthwash formulations. Their research has led to the development of a patented sulfamic acid complex that enhances the remineralization of tooth enamel while providing a gentle cleansing action[2]. Clinical studies have shown a 25% improvement in enamel strength after four weeks of use compared to standard fluoride toothpaste[4]. Additionally, Colgate-Palmolive has explored the use of sulfamic acid derivatives in creating pH-responsive personal care products, which adapt to the skin's natural pH for optimal performance[6].
Strengths: Strong focus on oral care applications, clinically proven efficacy, innovative pH-responsive technology. Weaknesses: Limited exploration in other personal care categories, potential for tooth sensitivity in some users.
Unilever IP Holdings BV
Technical Solution: Unilever has invested in research on sulfamic acid as a key ingredient in their eco-friendly personal care product lines. Their approach focuses on developing sulfamic acid-based surfactants that offer superior cleaning performance while being biodegradable and less irritating to skin and eyes[7]. Unilever's formulations have shown a 40% reduction in environmental impact compared to traditional surfactants[9]. The company has also explored the use of sulfamic acid in creating self-preserving cosmetic formulations, reducing the need for additional preservatives and extending shelf life by up to 50%[11].
Strengths: Strong focus on sustainability, reduced environmental impact, innovative self-preserving formulations. Weaknesses: Potential higher production costs, challenges in maintaining product stability across diverse climates.
Key Patents in Sulfamic Acid Personal Care Applications
Personal care compositions and methods for using such compositions
PatentWO2017140799A1
Innovation
- A sulfate-free personal care composition combining methyl oleoyl taurate, isethionate, and specific amphoteric or zwitterionic surfactants, such as sultaines and alkylbetaines, to achieve balanced viscosity, foaming, and conditioning without excessive surfactant usage.
Improved formulations of personal care products
PatentWO2023278985A1
Innovation
- Combining hydrocolloids and modified starches in specific weight ratios and concentrations to create personal care formulations that enhance viscosity, stability, and texture, while minimizing sulfate content.
Regulatory Framework for Sulfamic Acid in Personal Care
The regulatory framework for sulfamic acid in personal care products is a complex and evolving landscape that varies across different regions and jurisdictions. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the use of sulfamic acid in personal care products, classifying it as Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) for specific applications. The FDA has established guidelines for its use in cosmetics and personal care items, including maximum concentration limits and labeling requirements.
In the European Union, the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) regulates sulfamic acid under the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation. REACH requires manufacturers and importers to register substances and provide safety data for chemicals used in personal care products. The EU Cosmetics Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009 further governs the use of sulfamic acid in cosmetic formulations, setting specific restrictions and conditions for its application.
Japan's regulatory framework for sulfamic acid in personal care products falls under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW). The Japanese Cosmetic Ingredients Standards and the Standards for Cosmetics set forth guidelines for the use of sulfamic acid in cosmetic formulations, including concentration limits and safety assessments.
In China, the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) regulates the use of sulfamic acid in personal care products. The Cosmetic Supervision and Administration Regulation (CSAR) and the Safety and Technical Standards for Cosmetics provide the regulatory framework for sulfamic acid usage, including requirements for safety assessments and product registration.
International organizations, such as the Cosmetic Ingredient Review (CIR) and the International Cooperation on Cosmetics Regulation (ICCR), play crucial roles in harmonizing global regulations and providing scientific assessments of cosmetic ingredients, including sulfamic acid. These organizations contribute to the development of consistent safety standards and regulatory approaches across different regions.
As the personal care industry continues to innovate, regulatory bodies are adapting their frameworks to address emerging concerns and new applications of sulfamic acid. This includes ongoing assessments of its environmental impact, potential allergenicity, and long-term safety profiles. Manufacturers and formulators must stay abreast of these evolving regulations to ensure compliance and maintain consumer trust in their products.
In the European Union, the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) regulates sulfamic acid under the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation. REACH requires manufacturers and importers to register substances and provide safety data for chemicals used in personal care products. The EU Cosmetics Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009 further governs the use of sulfamic acid in cosmetic formulations, setting specific restrictions and conditions for its application.
Japan's regulatory framework for sulfamic acid in personal care products falls under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW). The Japanese Cosmetic Ingredients Standards and the Standards for Cosmetics set forth guidelines for the use of sulfamic acid in cosmetic formulations, including concentration limits and safety assessments.
In China, the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) regulates the use of sulfamic acid in personal care products. The Cosmetic Supervision and Administration Regulation (CSAR) and the Safety and Technical Standards for Cosmetics provide the regulatory framework for sulfamic acid usage, including requirements for safety assessments and product registration.
International organizations, such as the Cosmetic Ingredient Review (CIR) and the International Cooperation on Cosmetics Regulation (ICCR), play crucial roles in harmonizing global regulations and providing scientific assessments of cosmetic ingredients, including sulfamic acid. These organizations contribute to the development of consistent safety standards and regulatory approaches across different regions.
As the personal care industry continues to innovate, regulatory bodies are adapting their frameworks to address emerging concerns and new applications of sulfamic acid. This includes ongoing assessments of its environmental impact, potential allergenicity, and long-term safety profiles. Manufacturers and formulators must stay abreast of these evolving regulations to ensure compliance and maintain consumer trust in their products.
Environmental Impact of Sulfamic Acid Usage
The use of sulfamic acid in personal care products has raised concerns about its potential environmental impact. As a strong acid, sulfamic acid can alter the pH of aquatic ecosystems when released into water bodies. This pH change can have detrimental effects on aquatic life, particularly in sensitive ecosystems. The acidification of water can lead to the dissolution of metals from sediments, potentially increasing the bioavailability of toxic substances to aquatic organisms.
Furthermore, sulfamic acid can contribute to the formation of acid rain when released into the atmosphere. While its contribution is relatively small compared to other industrial emissions, the cumulative effect of widespread use in personal care products should not be overlooked. Acid rain can have far-reaching consequences, affecting soil chemistry, plant growth, and aquatic ecosystems far from the point of origin.
The production process of sulfamic acid also has environmental implications. The synthesis typically involves the reaction of urea with sulfuric acid or oleum, which can generate hazardous waste and emissions if not properly managed. The energy-intensive nature of the production process contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, further exacerbating climate change concerns.
In terms of biodegradability, sulfamic acid itself is not readily biodegradable. However, it can undergo hydrolysis in aqueous environments, breaking down into ammonium bisulfate. While this process reduces the direct impact of sulfamic acid, the resulting compounds can still affect water quality and aquatic life. The rate of hydrolysis depends on various environmental factors, including temperature and pH, making its environmental fate complex and variable.
The use of sulfamic acid in personal care products also raises concerns about its potential accumulation in the environment. While individual product usage may have minimal impact, the collective discharge from millions of consumers can lead to significant concentrations in wastewater treatment systems and natural water bodies. This accumulation may have long-term effects on ecosystem health that are not yet fully understood.
To address these environmental concerns, research into alternative formulations and more environmentally friendly substitutes for sulfamic acid in personal care products is crucial. Additionally, improved wastewater treatment technologies and stricter regulations on the use and disposal of sulfamic acid-containing products could help mitigate its environmental impact. As consumer awareness grows, there is also an increasing demand for eco-friendly personal care products, driving innovation in this sector towards more sustainable solutions.
Furthermore, sulfamic acid can contribute to the formation of acid rain when released into the atmosphere. While its contribution is relatively small compared to other industrial emissions, the cumulative effect of widespread use in personal care products should not be overlooked. Acid rain can have far-reaching consequences, affecting soil chemistry, plant growth, and aquatic ecosystems far from the point of origin.
The production process of sulfamic acid also has environmental implications. The synthesis typically involves the reaction of urea with sulfuric acid or oleum, which can generate hazardous waste and emissions if not properly managed. The energy-intensive nature of the production process contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, further exacerbating climate change concerns.
In terms of biodegradability, sulfamic acid itself is not readily biodegradable. However, it can undergo hydrolysis in aqueous environments, breaking down into ammonium bisulfate. While this process reduces the direct impact of sulfamic acid, the resulting compounds can still affect water quality and aquatic life. The rate of hydrolysis depends on various environmental factors, including temperature and pH, making its environmental fate complex and variable.
The use of sulfamic acid in personal care products also raises concerns about its potential accumulation in the environment. While individual product usage may have minimal impact, the collective discharge from millions of consumers can lead to significant concentrations in wastewater treatment systems and natural water bodies. This accumulation may have long-term effects on ecosystem health that are not yet fully understood.
To address these environmental concerns, research into alternative formulations and more environmentally friendly substitutes for sulfamic acid in personal care products is crucial. Additionally, improved wastewater treatment technologies and stricter regulations on the use and disposal of sulfamic acid-containing products could help mitigate its environmental impact. As consumer awareness grows, there is also an increasing demand for eco-friendly personal care products, driving innovation in this sector towards more sustainable solutions.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!