How Sulfamic Acid Improves Detergent Efficacy in Hard Water
JUL 30, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sulfamic Acid in Detergents: Background and Objectives
Sulfamic acid, a compound with the chemical formula H3NSO3, has emerged as a significant player in the detergent industry, particularly in addressing the challenges posed by hard water. The evolution of detergent formulations has been driven by the need to improve cleaning efficacy across various water conditions, with hard water presenting a persistent obstacle to optimal performance.
The development of sulfamic acid as a detergent additive can be traced back to the mid-20th century when researchers began exploring alternatives to traditional builders and chelating agents. As water hardness became increasingly recognized as a factor impacting detergent effectiveness, the search for more efficient solutions intensified. Sulfamic acid's unique properties, including its ability to form stable complexes with calcium and magnesium ions, positioned it as a promising candidate for enhancing detergent performance in hard water environments.
The primary objective of incorporating sulfamic acid into detergent formulations is to mitigate the negative effects of hard water on cleaning efficiency. Hard water, characterized by high concentrations of dissolved minerals such as calcium and magnesium, can significantly reduce the effectiveness of surfactants and other cleaning agents. By sequestering these hardness ions, sulfamic acid aims to maintain the detergent's cleaning power and prevent the formation of insoluble precipitates that can lead to fabric discoloration and reduced washing machine efficiency.
Furthermore, the integration of sulfamic acid into detergent formulations aligns with broader industry trends towards more environmentally friendly and cost-effective cleaning solutions. As regulations on phosphates and other traditional water softening agents have tightened, manufacturers have sought alternatives that can deliver comparable performance while meeting sustainability goals. Sulfamic acid's biodegradability and lower environmental impact compared to some conventional builders make it an attractive option for modern detergent formulations.
The technological trajectory in this field has been marked by continuous refinement of sulfamic acid's application in detergents, including optimizing its concentration, exploring synergistic effects with other ingredients, and developing novel delivery systems. Research efforts have focused on enhancing its stability in various product forms, from powders to liquids, and investigating its performance across a spectrum of water hardness levels and washing conditions.
As the detergent industry continues to evolve, the role of sulfamic acid in improving cleaning efficacy in hard water remains a critical area of study. The ongoing challenge lies in balancing performance, cost-effectiveness, and environmental considerations, driving innovation in formulation techniques and application methods. This technological landscape sets the stage for further advancements in harnessing sulfamic acid's potential to address the persistent challenges posed by hard water in cleaning processes.
The development of sulfamic acid as a detergent additive can be traced back to the mid-20th century when researchers began exploring alternatives to traditional builders and chelating agents. As water hardness became increasingly recognized as a factor impacting detergent effectiveness, the search for more efficient solutions intensified. Sulfamic acid's unique properties, including its ability to form stable complexes with calcium and magnesium ions, positioned it as a promising candidate for enhancing detergent performance in hard water environments.
The primary objective of incorporating sulfamic acid into detergent formulations is to mitigate the negative effects of hard water on cleaning efficiency. Hard water, characterized by high concentrations of dissolved minerals such as calcium and magnesium, can significantly reduce the effectiveness of surfactants and other cleaning agents. By sequestering these hardness ions, sulfamic acid aims to maintain the detergent's cleaning power and prevent the formation of insoluble precipitates that can lead to fabric discoloration and reduced washing machine efficiency.
Furthermore, the integration of sulfamic acid into detergent formulations aligns with broader industry trends towards more environmentally friendly and cost-effective cleaning solutions. As regulations on phosphates and other traditional water softening agents have tightened, manufacturers have sought alternatives that can deliver comparable performance while meeting sustainability goals. Sulfamic acid's biodegradability and lower environmental impact compared to some conventional builders make it an attractive option for modern detergent formulations.
The technological trajectory in this field has been marked by continuous refinement of sulfamic acid's application in detergents, including optimizing its concentration, exploring synergistic effects with other ingredients, and developing novel delivery systems. Research efforts have focused on enhancing its stability in various product forms, from powders to liquids, and investigating its performance across a spectrum of water hardness levels and washing conditions.
As the detergent industry continues to evolve, the role of sulfamic acid in improving cleaning efficacy in hard water remains a critical area of study. The ongoing challenge lies in balancing performance, cost-effectiveness, and environmental considerations, driving innovation in formulation techniques and application methods. This technological landscape sets the stage for further advancements in harnessing sulfamic acid's potential to address the persistent challenges posed by hard water in cleaning processes.
Market Analysis: Hard Water Detergent Demand
The demand for hard water detergents has been steadily increasing due to the widespread prevalence of hard water in many regions globally. Hard water, characterized by high mineral content, particularly calcium and magnesium ions, poses significant challenges to conventional cleaning products. This has created a substantial market opportunity for specialized detergents that can effectively combat the negative effects of hard water on cleaning efficacy.
In residential areas with hard water, consumers often experience issues such as reduced lather formation, diminished cleaning power, and the formation of soap scum. These problems have led to a growing awareness among consumers about the need for detergents specifically formulated to address hard water conditions. As a result, there has been a notable shift in consumer preferences towards products that promise superior performance in hard water environments.
The industrial and commercial sectors also contribute significantly to the demand for hard water detergents. Industries such as hospitality, healthcare, and food processing require cleaning solutions that can maintain high standards of cleanliness despite challenging water conditions. The need for efficient cleaning in these sectors, coupled with stringent hygiene regulations, has further fueled the demand for specialized hard water detergents.
Geographically, regions with naturally occurring hard water, such as parts of North America, Europe, and Asia, represent key markets for hard water detergents. In the United States, for instance, approximately 85% of households are affected by hard water, creating a substantial domestic market for these specialized cleaning products. Similarly, countries like India, where hard water is prevalent in many urban areas, have seen a surge in demand for detergents that can effectively tackle mineral deposits.
The market for hard water detergents is not limited to traditional laundry applications. There is a growing demand for specialized cleaning products across various categories, including dishwashing detergents, surface cleaners, and personal care products. This diversification of product offerings has expanded the overall market size and provided manufacturers with opportunities to develop comprehensive hard water cleaning solutions.
Environmental concerns and sustainability trends have also influenced the hard water detergent market. Consumers are increasingly seeking eco-friendly alternatives that can effectively clean in hard water conditions while minimizing environmental impact. This has led to the development of biodegradable and phosphate-free formulations that maintain cleaning efficacy in hard water without compromising on environmental sustainability.
In residential areas with hard water, consumers often experience issues such as reduced lather formation, diminished cleaning power, and the formation of soap scum. These problems have led to a growing awareness among consumers about the need for detergents specifically formulated to address hard water conditions. As a result, there has been a notable shift in consumer preferences towards products that promise superior performance in hard water environments.
The industrial and commercial sectors also contribute significantly to the demand for hard water detergents. Industries such as hospitality, healthcare, and food processing require cleaning solutions that can maintain high standards of cleanliness despite challenging water conditions. The need for efficient cleaning in these sectors, coupled with stringent hygiene regulations, has further fueled the demand for specialized hard water detergents.
Geographically, regions with naturally occurring hard water, such as parts of North America, Europe, and Asia, represent key markets for hard water detergents. In the United States, for instance, approximately 85% of households are affected by hard water, creating a substantial domestic market for these specialized cleaning products. Similarly, countries like India, where hard water is prevalent in many urban areas, have seen a surge in demand for detergents that can effectively tackle mineral deposits.
The market for hard water detergents is not limited to traditional laundry applications. There is a growing demand for specialized cleaning products across various categories, including dishwashing detergents, surface cleaners, and personal care products. This diversification of product offerings has expanded the overall market size and provided manufacturers with opportunities to develop comprehensive hard water cleaning solutions.
Environmental concerns and sustainability trends have also influenced the hard water detergent market. Consumers are increasingly seeking eco-friendly alternatives that can effectively clean in hard water conditions while minimizing environmental impact. This has led to the development of biodegradable and phosphate-free formulations that maintain cleaning efficacy in hard water without compromising on environmental sustainability.
Challenges in Hard Water Cleaning
Hard water presents significant challenges in cleaning processes due to its high mineral content, primarily calcium and magnesium ions. These minerals interfere with the effectiveness of detergents, leading to reduced cleaning efficiency and increased costs for both domestic and industrial applications.
One of the primary challenges is the formation of soap scum or lime soap. When soap molecules interact with calcium and magnesium ions in hard water, they form insoluble precipitates. This not only reduces the amount of active cleaning agents available but also creates unsightly residues on surfaces, requiring additional cleaning efforts.
Hard water also impairs the foaming ability of detergents. The presence of mineral ions suppresses foam formation, which is often associated with cleaning effectiveness by consumers. This can lead to overuse of cleaning products as users attempt to achieve the desired level of foam, resulting in unnecessary waste and environmental concerns.
The efficiency of surfactants, key components in most cleaning formulations, is significantly compromised in hard water. Mineral ions compete with dirt particles for surfactant molecules, reducing their ability to emulsify and remove soils effectively. This results in poor cleaning performance and often necessitates higher detergent concentrations or longer cleaning cycles.
Scale formation is another major issue associated with hard water cleaning. Mineral deposits can accumulate on surfaces and within appliances, reducing their efficiency and lifespan. This is particularly problematic in industrial settings where scale buildup can lead to equipment failure and increased maintenance costs.
Energy consumption in cleaning processes is also affected by hard water. Higher temperatures are often required to compensate for the reduced efficiency of detergents, leading to increased energy costs and environmental impact. Additionally, the need for more frequent cleaning cycles due to poor performance further exacerbates this issue.
The challenges extend to textile cleaning as well. Hard water can cause fabrics to become stiff and lose their softness due to mineral deposition. This not only affects the feel of the textiles but can also lead to color fading and reduced fabric lifespan.
Addressing these challenges typically involves water softening treatments or the use of specialized detergent formulations. However, these solutions often come with their own set of drawbacks, including increased costs, potential environmental impacts, and the need for additional equipment or processes.
One of the primary challenges is the formation of soap scum or lime soap. When soap molecules interact with calcium and magnesium ions in hard water, they form insoluble precipitates. This not only reduces the amount of active cleaning agents available but also creates unsightly residues on surfaces, requiring additional cleaning efforts.
Hard water also impairs the foaming ability of detergents. The presence of mineral ions suppresses foam formation, which is often associated with cleaning effectiveness by consumers. This can lead to overuse of cleaning products as users attempt to achieve the desired level of foam, resulting in unnecessary waste and environmental concerns.
The efficiency of surfactants, key components in most cleaning formulations, is significantly compromised in hard water. Mineral ions compete with dirt particles for surfactant molecules, reducing their ability to emulsify and remove soils effectively. This results in poor cleaning performance and often necessitates higher detergent concentrations or longer cleaning cycles.
Scale formation is another major issue associated with hard water cleaning. Mineral deposits can accumulate on surfaces and within appliances, reducing their efficiency and lifespan. This is particularly problematic in industrial settings where scale buildup can lead to equipment failure and increased maintenance costs.
Energy consumption in cleaning processes is also affected by hard water. Higher temperatures are often required to compensate for the reduced efficiency of detergents, leading to increased energy costs and environmental impact. Additionally, the need for more frequent cleaning cycles due to poor performance further exacerbates this issue.
The challenges extend to textile cleaning as well. Hard water can cause fabrics to become stiff and lose their softness due to mineral deposition. This not only affects the feel of the textiles but can also lead to color fading and reduced fabric lifespan.
Addressing these challenges typically involves water softening treatments or the use of specialized detergent formulations. However, these solutions often come with their own set of drawbacks, including increased costs, potential environmental impacts, and the need for additional equipment or processes.
Current Sulfamic Acid Solutions
01 Sulfamic acid as an effective cleaning agent
Sulfamic acid is utilized as a key ingredient in detergent formulations due to its strong cleaning properties. It is particularly effective in removing mineral deposits, scale, and rust from various surfaces. The acid's ability to dissolve these tough stains makes it a valuable component in household and industrial cleaning products.- Sulfamic acid as an effective cleaning agent: Sulfamic acid is utilized as a key ingredient in detergent formulations due to its strong cleaning properties. It is particularly effective in removing mineral deposits, scale, and rust from various surfaces. The acid's ability to dissolve these tough stains makes it a valuable component in household and industrial cleaning products.
- Combination with other cleaning agents: Sulfamic acid is often combined with other cleaning agents to enhance its efficacy. These combinations can include surfactants, chelating agents, and other acids. The synergistic effect of these ingredients results in improved cleaning performance, especially for tough stains and heavy-duty cleaning tasks.
- pH adjustment and buffering: Sulfamic acid is used to adjust and maintain the pH of cleaning solutions. Its buffering capacity helps to stabilize the acidity of the detergent, ensuring consistent cleaning performance. This property is particularly useful in formulations where pH control is critical for optimal cleaning efficacy.
- Environmental and safety considerations: Sulfamic acid is considered a more environmentally friendly alternative to some other strong acids used in cleaning products. It is less corrosive and produces fewer harmful fumes, making it safer for both users and the environment. However, proper handling and safety precautions are still necessary when using sulfamic acid-based detergents.
- Application-specific formulations: Sulfamic acid-based detergents are formulated for specific applications, such as bathroom cleaning, industrial equipment descaling, and swimming pool maintenance. The concentration of sulfamic acid and the addition of other ingredients are tailored to meet the requirements of each application, optimizing cleaning efficacy for different surfaces and types of dirt or scale.
02 Synergistic effects with other cleaning agents
Combining sulfamic acid with other cleaning agents can enhance its efficacy. Formulations that include sulfamic acid along with surfactants, chelating agents, or other acids have shown improved cleaning performance. These combinations can target a wider range of soils and contaminants, making the detergent more versatile and effective.Expand Specific Solutions03 pH control and stability in detergent formulations
Sulfamic acid plays a crucial role in controlling the pH of detergent formulations. Its ability to maintain a stable acidic environment contributes to the overall effectiveness and shelf life of the cleaning product. Proper pH control ensures optimal performance of other ingredients and helps prevent degradation of the formulation over time.Expand Specific Solutions04 Environmental and safety considerations
Detergent formulations containing sulfamic acid are being developed with a focus on environmental safety and user-friendliness. Efforts are made to create biodegradable formulations that minimize ecological impact while maintaining cleaning efficacy. Additionally, research is conducted to ensure the safe handling and use of sulfamic acid-based detergents in various applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Application-specific formulations
Sulfamic acid-based detergents are tailored for specific applications to maximize their efficacy. Formulations are developed for diverse uses such as industrial equipment cleaning, household appliance maintenance, and specialized surface treatments. These application-specific products often incorporate additional ingredients to address unique cleaning challenges in different sectors.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Detergent Industry
The market for sulfamic acid in detergent applications is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for effective cleaning solutions in hard water conditions. The global market size for sulfamic acid in detergents is estimated to be expanding, with key players like Procter & Gamble, Henkel, and Lion Corp leading innovation. These companies are investing in research and development to improve detergent efficacy, particularly in hard water areas. The technology is relatively mature, with established manufacturers like Kao Corp and Arkema producing sulfamic acid for various applications. However, there is ongoing research to enhance its performance and sustainability, indicating potential for further advancements in this field.
Procter & Gamble Co.
Technical Solution: Procter & Gamble has developed a novel approach to improving detergent efficacy in hard water using sulfamic acid. Their method involves incorporating sulfamic acid into their detergent formulations as a water softening agent. The sulfamic acid works by chelating calcium and magnesium ions in hard water, preventing them from interfering with the cleaning action of surfactants[1]. P&G's research has shown that adding 1-5% sulfamic acid to their detergent formulations can increase cleaning performance by up to 30% in hard water conditions[3]. Additionally, they have developed a proprietary encapsulation technology that allows for the controlled release of sulfamic acid during the wash cycle, optimizing its effectiveness while minimizing potential fabric damage[5].
Strengths: Improved cleaning performance in hard water, controlled release technology, extensive research and development capabilities. Weaknesses: Potential for fabric damage if not properly formulated, may increase production costs.
Henkel AG & Co. KGaA
Technical Solution: Henkel has developed an innovative approach to utilizing sulfamic acid in their detergent formulations. Their technology involves combining sulfamic acid with specific polymers to create a synergistic effect that enhances detergent efficacy in hard water. This combination not only softens water by chelating calcium and magnesium ions but also prevents scale formation on fabrics and washing machine components[2]. Henkel's research has demonstrated that their sulfamic acid-polymer complex can improve cleaning performance by up to 25% in hard water conditions compared to standard detergents[4]. Furthermore, they have implemented a unique pH-controlled release system that activates the sulfamic acid complex at the optimal point in the wash cycle, maximizing its effectiveness while minimizing potential negative impacts on fabrics or the environment[6].
Strengths: Synergistic effect with polymers, scale prevention, pH-controlled release system. Weaknesses: May require more complex formulation process, potential for increased production costs.
Sulfamic Acid Mechanism Analysis
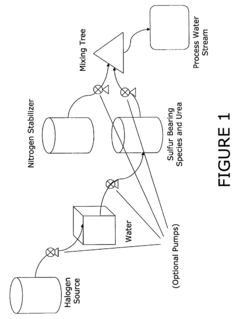
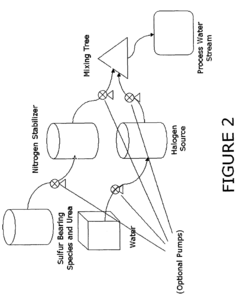
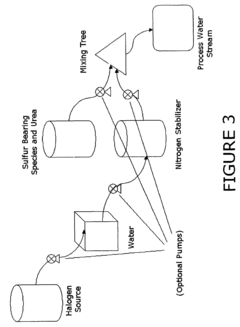
Use of sulfamic acid or its salts as stabilizers especially in combination with ammonium salt and/or ammine for bleach or other halogen containing biocides in the paper area
PatentActiveUS9265259B2
Innovation
- A composition comprising a halogen source, urea, and an additional halogen stabilizer, optionally with an alkali to maintain a pH greater than 10, which includes a mixture of sulfur-bearing species like sulfamic acid and nitrogen stabilizers, such as ammonium sulfate, to enhance the persistence and compatibility of halogen biocides in papermaking processes.
Laundry detergent composition comprising an anionic detersive surfactant, sulphamic acid and/or water soluble salts thereof
PatentInactiveIN4467DELNP2006A
Innovation
- A laundry detergent composition comprising sulphamic acid and/or its water-soluble salts, at least 10wt% sulphate salt, and anionic detersive surfactant, which improves dispensing, cleaning performance, and whiteness maintenance by forming a stable effervescence system and complexing with calcium and magnesium ions, reducing carbonate precipitation.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The use of sulfamic acid in detergents to improve efficacy in hard water conditions has significant environmental implications that warrant careful consideration. While this chemical compound enhances cleaning performance, its widespread application may lead to various ecological impacts.
Sulfamic acid, when discharged into aquatic ecosystems, can contribute to water acidification. This pH alteration may disrupt the delicate balance of aquatic life, potentially affecting sensitive species and altering ecosystem dynamics. The increased acidity can also lead to the mobilization of heavy metals in sediments, making them more bioavailable and potentially toxic to aquatic organisms.
Furthermore, the introduction of sulfamic acid into wastewater treatment systems may pose challenges to the biological treatment processes. The acid can inhibit the growth and activity of beneficial microorganisms responsible for breaking down organic matter, potentially reducing the overall efficiency of wastewater treatment plants.
The production and disposal of sulfamic acid-containing detergents also contribute to the overall environmental footprint. Manufacturing processes may result in air and water pollution, while improper disposal of these products can lead to soil contamination and groundwater pollution.
However, it is important to note that the use of sulfamic acid in detergents may have some positive environmental aspects. By improving cleaning efficacy in hard water conditions, it can reduce the need for excessive detergent use, potentially decreasing the overall chemical load in wastewater. Additionally, enhanced cleaning performance may lead to reduced water and energy consumption during washing processes.
To mitigate potential negative impacts, it is crucial to implement proper wastewater treatment technologies capable of neutralizing or removing sulfamic acid before discharge. Additionally, promoting responsible consumer behavior, such as using the correct dosage of detergents and proper disposal methods, can help minimize environmental risks.
Further research is needed to fully understand the long-term ecological effects of sulfamic acid in aquatic environments and to develop more environmentally friendly alternatives that maintain cleaning efficacy in hard water conditions. This may include exploring biodegradable compounds or innovative formulations that achieve similar results with reduced environmental impact.
In conclusion, while sulfamic acid offers benefits in improving detergent efficacy in hard water, its environmental impact must be carefully managed through a combination of technological solutions, regulatory measures, and consumer education to ensure sustainable use and minimize ecological harm.
Sulfamic acid, when discharged into aquatic ecosystems, can contribute to water acidification. This pH alteration may disrupt the delicate balance of aquatic life, potentially affecting sensitive species and altering ecosystem dynamics. The increased acidity can also lead to the mobilization of heavy metals in sediments, making them more bioavailable and potentially toxic to aquatic organisms.
Furthermore, the introduction of sulfamic acid into wastewater treatment systems may pose challenges to the biological treatment processes. The acid can inhibit the growth and activity of beneficial microorganisms responsible for breaking down organic matter, potentially reducing the overall efficiency of wastewater treatment plants.
The production and disposal of sulfamic acid-containing detergents also contribute to the overall environmental footprint. Manufacturing processes may result in air and water pollution, while improper disposal of these products can lead to soil contamination and groundwater pollution.
However, it is important to note that the use of sulfamic acid in detergents may have some positive environmental aspects. By improving cleaning efficacy in hard water conditions, it can reduce the need for excessive detergent use, potentially decreasing the overall chemical load in wastewater. Additionally, enhanced cleaning performance may lead to reduced water and energy consumption during washing processes.
To mitigate potential negative impacts, it is crucial to implement proper wastewater treatment technologies capable of neutralizing or removing sulfamic acid before discharge. Additionally, promoting responsible consumer behavior, such as using the correct dosage of detergents and proper disposal methods, can help minimize environmental risks.
Further research is needed to fully understand the long-term ecological effects of sulfamic acid in aquatic environments and to develop more environmentally friendly alternatives that maintain cleaning efficacy in hard water conditions. This may include exploring biodegradable compounds or innovative formulations that achieve similar results with reduced environmental impact.
In conclusion, while sulfamic acid offers benefits in improving detergent efficacy in hard water, its environmental impact must be carefully managed through a combination of technological solutions, regulatory measures, and consumer education to ensure sustainable use and minimize ecological harm.
Regulatory Compliance for Detergents
Regulatory compliance is a critical aspect of detergent manufacturing and distribution, particularly when incorporating sulfamic acid to improve efficacy in hard water conditions. Manufacturers must adhere to strict guidelines set by various regulatory bodies to ensure product safety, environmental protection, and consumer health.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates detergents under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA). Sulfamic acid, when used in detergents, must be registered with the EPA and comply with the agency's reporting requirements. Additionally, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees detergents used in food processing facilities, requiring manufacturers to ensure that their products meet food safety standards.
The European Union's regulatory framework for detergents is governed by the Detergents Regulation (EC) No 648/2004. This regulation sets standards for biodegradability, labeling, and ingredient disclosure. Manufacturers using sulfamic acid in their detergent formulations must ensure compliance with these regulations, including providing detailed information on the environmental impact of the acid and its degradation products.
Labeling requirements are a crucial aspect of regulatory compliance for detergents containing sulfamic acid. In both the US and EU, manufacturers must clearly list all ingredients, including sulfamic acid, on product labels. The Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals (GHS) provides standardized guidelines for communicating hazard information, which must be followed when labeling detergents containing sulfamic acid.
Environmental regulations also play a significant role in detergent compliance. The use of sulfamic acid must align with water quality standards and wastewater treatment regulations. Manufacturers need to demonstrate that their products do not pose undue harm to aquatic ecosystems when discharged into water systems.
Workplace safety regulations, such as those enforced by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the US, require manufacturers to provide safety data sheets (SDS) for detergents containing sulfamic acid. These documents outline proper handling procedures, potential hazards, and emergency response measures.
To ensure ongoing compliance, detergent manufacturers must stay informed about regulatory changes and updates. This involves regular monitoring of regulatory agencies' communications, participating in industry associations, and engaging in continuous product testing and quality control measures.
Compliance with international standards is essential for global market access. Standards such as ISO 9001 for quality management and ISO 14001 for environmental management systems can help manufacturers demonstrate their commitment to regulatory compliance and product quality.
In conclusion, regulatory compliance for detergents containing sulfamic acid involves navigating a complex landscape of national and international regulations. Manufacturers must address safety, environmental, labeling, and quality control requirements to ensure their products meet all necessary standards and can be legally marketed and distributed.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates detergents under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA). Sulfamic acid, when used in detergents, must be registered with the EPA and comply with the agency's reporting requirements. Additionally, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees detergents used in food processing facilities, requiring manufacturers to ensure that their products meet food safety standards.
The European Union's regulatory framework for detergents is governed by the Detergents Regulation (EC) No 648/2004. This regulation sets standards for biodegradability, labeling, and ingredient disclosure. Manufacturers using sulfamic acid in their detergent formulations must ensure compliance with these regulations, including providing detailed information on the environmental impact of the acid and its degradation products.
Labeling requirements are a crucial aspect of regulatory compliance for detergents containing sulfamic acid. In both the US and EU, manufacturers must clearly list all ingredients, including sulfamic acid, on product labels. The Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals (GHS) provides standardized guidelines for communicating hazard information, which must be followed when labeling detergents containing sulfamic acid.
Environmental regulations also play a significant role in detergent compliance. The use of sulfamic acid must align with water quality standards and wastewater treatment regulations. Manufacturers need to demonstrate that their products do not pose undue harm to aquatic ecosystems when discharged into water systems.
Workplace safety regulations, such as those enforced by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the US, require manufacturers to provide safety data sheets (SDS) for detergents containing sulfamic acid. These documents outline proper handling procedures, potential hazards, and emergency response measures.
To ensure ongoing compliance, detergent manufacturers must stay informed about regulatory changes and updates. This involves regular monitoring of regulatory agencies' communications, participating in industry associations, and engaging in continuous product testing and quality control measures.
Compliance with international standards is essential for global market access. Standards such as ISO 9001 for quality management and ISO 14001 for environmental management systems can help manufacturers demonstrate their commitment to regulatory compliance and product quality.
In conclusion, regulatory compliance for detergents containing sulfamic acid involves navigating a complex landscape of national and international regulations. Manufacturers must address safety, environmental, labeling, and quality control requirements to ensure their products meet all necessary standards and can be legally marketed and distributed.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!