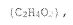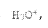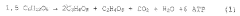How to Address Technical Challenges in Propionic Acid Research?
JUL 3, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Propionic Acid Research Background and Objectives
Propionic acid research has a rich history dating back to the mid-19th century when it was first isolated from dairy products. Over the years, this organic compound has gained significant importance in various industries, including food preservation, pharmaceuticals, and agriculture. The evolution of propionic acid research has been driven by the growing demand for sustainable and eco-friendly alternatives in these sectors.
The primary objective of current propionic acid research is to address the technical challenges associated with its production, purification, and application. One of the key goals is to develop more efficient and cost-effective production methods, particularly through biotechnological approaches. This includes optimizing fermentation processes, exploring novel microbial strains, and enhancing product yield and purity.
Another crucial aim is to expand the application spectrum of propionic acid and its derivatives. Researchers are investigating its potential in biodegradable plastics, animal feed additives, and as a building block for various chemical syntheses. The focus is on leveraging the unique properties of propionic acid to create innovative solutions for emerging market needs.
Environmental considerations play a significant role in shaping the research landscape. There is a growing emphasis on developing green production methods that minimize waste and energy consumption. This aligns with the global trend towards sustainable industrial practices and circular economy principles.
The technical challenges in propionic acid research are multifaceted. They include improving the efficiency of separation and purification processes, enhancing the stability of propionic acid-based products, and addressing issues related to corrosion in production equipment. Researchers are also working on overcoming the limitations of traditional petrochemical-based production methods by exploring renewable feedstocks and bio-based production routes.
In recent years, there has been a notable shift towards interdisciplinary approaches in propionic acid research. This involves combining expertise from microbiology, chemical engineering, materials science, and biotechnology to tackle complex challenges. The integration of advanced technologies such as metabolic engineering, synthetic biology, and process intensification is expected to drive significant breakthroughs in the field.
As the research progresses, there is a growing need for collaboration between academia and industry to bridge the gap between laboratory discoveries and commercial applications. This synergy is crucial for addressing real-world challenges and accelerating the development of innovative propionic acid-based solutions.
The primary objective of current propionic acid research is to address the technical challenges associated with its production, purification, and application. One of the key goals is to develop more efficient and cost-effective production methods, particularly through biotechnological approaches. This includes optimizing fermentation processes, exploring novel microbial strains, and enhancing product yield and purity.
Another crucial aim is to expand the application spectrum of propionic acid and its derivatives. Researchers are investigating its potential in biodegradable plastics, animal feed additives, and as a building block for various chemical syntheses. The focus is on leveraging the unique properties of propionic acid to create innovative solutions for emerging market needs.
Environmental considerations play a significant role in shaping the research landscape. There is a growing emphasis on developing green production methods that minimize waste and energy consumption. This aligns with the global trend towards sustainable industrial practices and circular economy principles.
The technical challenges in propionic acid research are multifaceted. They include improving the efficiency of separation and purification processes, enhancing the stability of propionic acid-based products, and addressing issues related to corrosion in production equipment. Researchers are also working on overcoming the limitations of traditional petrochemical-based production methods by exploring renewable feedstocks and bio-based production routes.
In recent years, there has been a notable shift towards interdisciplinary approaches in propionic acid research. This involves combining expertise from microbiology, chemical engineering, materials science, and biotechnology to tackle complex challenges. The integration of advanced technologies such as metabolic engineering, synthetic biology, and process intensification is expected to drive significant breakthroughs in the field.
As the research progresses, there is a growing need for collaboration between academia and industry to bridge the gap between laboratory discoveries and commercial applications. This synergy is crucial for addressing real-world challenges and accelerating the development of innovative propionic acid-based solutions.
Market Analysis for Propionic Acid Applications
The global propionic acid market has been experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand across various industries. The food and beverage sector remains the largest consumer of propionic acid, primarily due to its widespread use as a preservative in baked goods, dairy products, and animal feed. The compound's ability to inhibit mold growth and extend shelf life makes it an essential ingredient in food preservation.
In recent years, there has been a notable surge in demand for propionic acid in the pharmaceutical and personal care industries. Its antimicrobial properties have led to increased adoption in the production of various medications and cosmetic products. Additionally, the growing awareness of hygiene and sanitation has further boosted the use of propionic acid in disinfectants and cleaning agents.
The agricultural sector presents a significant growth opportunity for propionic acid applications. As the global population continues to rise, there is an increasing need for efficient food preservation methods and improved animal feed. Propionic acid's role in preventing spoilage and enhancing feed efficiency positions it as a crucial component in addressing these challenges.
Environmental concerns and sustainability initiatives have also influenced the propionic acid market. The shift towards bio-based chemicals has led to the development of green production methods for propionic acid, using renewable resources such as biomass and agricultural waste. This trend is expected to drive further market growth and open up new applications in eco-friendly products.
Geographically, North America and Europe have traditionally been the largest consumers of propionic acid, owing to their well-established food and pharmaceutical industries. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a rapidly growing market, fueled by increasing industrialization, population growth, and rising disposable incomes. Countries like China and India are expected to be key drivers of demand in the coming years.
The market for propionic acid is characterized by a high degree of consolidation, with a few major players dominating the global supply. This concentration has led to concerns about price volatility and supply chain stability. As a result, there is growing interest in developing alternative production methods and expanding manufacturing capabilities to meet the increasing demand.
In conclusion, the propionic acid market shows promising growth potential across various sectors, with food preservation, pharmaceuticals, and agriculture leading the way. The industry's focus on sustainable production methods and expanding applications in emerging markets suggests a positive outlook for the future of propionic acid research and development.
In recent years, there has been a notable surge in demand for propionic acid in the pharmaceutical and personal care industries. Its antimicrobial properties have led to increased adoption in the production of various medications and cosmetic products. Additionally, the growing awareness of hygiene and sanitation has further boosted the use of propionic acid in disinfectants and cleaning agents.
The agricultural sector presents a significant growth opportunity for propionic acid applications. As the global population continues to rise, there is an increasing need for efficient food preservation methods and improved animal feed. Propionic acid's role in preventing spoilage and enhancing feed efficiency positions it as a crucial component in addressing these challenges.
Environmental concerns and sustainability initiatives have also influenced the propionic acid market. The shift towards bio-based chemicals has led to the development of green production methods for propionic acid, using renewable resources such as biomass and agricultural waste. This trend is expected to drive further market growth and open up new applications in eco-friendly products.
Geographically, North America and Europe have traditionally been the largest consumers of propionic acid, owing to their well-established food and pharmaceutical industries. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a rapidly growing market, fueled by increasing industrialization, population growth, and rising disposable incomes. Countries like China and India are expected to be key drivers of demand in the coming years.
The market for propionic acid is characterized by a high degree of consolidation, with a few major players dominating the global supply. This concentration has led to concerns about price volatility and supply chain stability. As a result, there is growing interest in developing alternative production methods and expanding manufacturing capabilities to meet the increasing demand.
In conclusion, the propionic acid market shows promising growth potential across various sectors, with food preservation, pharmaceuticals, and agriculture leading the way. The industry's focus on sustainable production methods and expanding applications in emerging markets suggests a positive outlook for the future of propionic acid research and development.
Current Challenges in Propionic Acid Production
Propionic acid production faces several significant challenges that hinder its widespread industrial application and commercial viability. One of the primary obstacles is the low yield and productivity of current fermentation processes. Traditional methods struggle to achieve high concentrations of propionic acid, typically resulting in yields below 30 g/L. This limitation is largely due to product inhibition, where the accumulation of propionic acid in the fermentation broth inhibits further microbial growth and production.
Another critical challenge is the high cost of downstream processing, particularly in the separation and purification stages. The recovery of propionic acid from fermentation broths is complex and energy-intensive, often requiring multiple steps such as filtration, extraction, and distillation. These processes significantly contribute to the overall production costs, making bio-based propionic acid less competitive compared to its petrochemical counterpart.
The selection and development of suitable microbial strains present another hurdle. While Propionibacterium species are the primary producers of propionic acid, they exhibit slow growth rates and limited tolerance to acidic conditions. This necessitates careful pH control during fermentation, adding to process complexity and operational costs. Furthermore, genetic engineering efforts to improve strain performance have shown limited success due to the complex metabolic pathways involved in propionic acid biosynthesis.
Substrate utilization efficiency is an additional concern in propionic acid production. Many current processes rely on expensive carbon sources, such as glucose or glycerol. The ability to efficiently convert low-cost, renewable feedstocks like lignocellulosic biomass or industrial by-products into propionic acid remains a significant challenge. This limitation not only affects the economic feasibility of production but also impacts the sustainability profile of the process.
The formation of by-products during fermentation further complicates propionic acid production. Acetic acid, in particular, is often produced alongside propionic acid, reducing overall yield and necessitating additional separation steps. Developing strategies to minimize by-product formation or to efficiently separate and valorize these co-products is crucial for improving process economics.
Lastly, scaling up laboratory-scale fermentation processes to industrial levels presents its own set of challenges. Issues such as maintaining consistent product quality, managing heat transfer in large bioreactors, and optimizing process parameters for continuous operation need to be addressed. The lack of robust, large-scale demonstration projects has hindered the widespread adoption of bio-based propionic acid production technologies in industry.
Another critical challenge is the high cost of downstream processing, particularly in the separation and purification stages. The recovery of propionic acid from fermentation broths is complex and energy-intensive, often requiring multiple steps such as filtration, extraction, and distillation. These processes significantly contribute to the overall production costs, making bio-based propionic acid less competitive compared to its petrochemical counterpart.
The selection and development of suitable microbial strains present another hurdle. While Propionibacterium species are the primary producers of propionic acid, they exhibit slow growth rates and limited tolerance to acidic conditions. This necessitates careful pH control during fermentation, adding to process complexity and operational costs. Furthermore, genetic engineering efforts to improve strain performance have shown limited success due to the complex metabolic pathways involved in propionic acid biosynthesis.
Substrate utilization efficiency is an additional concern in propionic acid production. Many current processes rely on expensive carbon sources, such as glucose or glycerol. The ability to efficiently convert low-cost, renewable feedstocks like lignocellulosic biomass or industrial by-products into propionic acid remains a significant challenge. This limitation not only affects the economic feasibility of production but also impacts the sustainability profile of the process.
The formation of by-products during fermentation further complicates propionic acid production. Acetic acid, in particular, is often produced alongside propionic acid, reducing overall yield and necessitating additional separation steps. Developing strategies to minimize by-product formation or to efficiently separate and valorize these co-products is crucial for improving process economics.
Lastly, scaling up laboratory-scale fermentation processes to industrial levels presents its own set of challenges. Issues such as maintaining consistent product quality, managing heat transfer in large bioreactors, and optimizing process parameters for continuous operation need to be addressed. The lack of robust, large-scale demonstration projects has hindered the widespread adoption of bio-based propionic acid production technologies in industry.
Existing Production Methods for Propionic Acid
01 Production methods of propionic acid
Various methods are employed for the production of propionic acid, including fermentation processes, chemical synthesis, and catalytic reactions. These methods aim to improve yield, efficiency, and purity of the final product. Some approaches involve the use of specific microorganisms or catalysts to facilitate the conversion of raw materials into propionic acid.- Production methods of propionic acid: Various methods are employed for the production of propionic acid, including fermentation processes, chemical synthesis, and catalytic reactions. These methods often involve the use of specific microorganisms, catalysts, or chemical precursors to efficiently produce propionic acid on an industrial scale.
- Applications of propionic acid in food preservation: Propionic acid is widely used as a food preservative due to its antimicrobial properties. It is effective in preventing mold growth and extending the shelf life of various food products, particularly in baked goods, dairy products, and animal feed.
- Use of propionic acid in pharmaceutical industry: Propionic acid and its derivatives find applications in the pharmaceutical industry. They are used in the synthesis of various drugs, as intermediates in the production of active pharmaceutical ingredients, and in some cases, as therapeutic agents themselves.
- Environmental and safety considerations in propionic acid handling: The handling and storage of propionic acid require specific safety measures due to its corrosive nature and potential environmental impact. Proper containment, neutralization techniques, and waste management strategies are essential for safe industrial use of propionic acid.
- Purification and quality control of propionic acid: Various methods are employed for the purification and quality control of propionic acid to meet industrial standards. These may include distillation techniques, chromatographic methods, and spectroscopic analyses to ensure the purity and consistency of the final product.
02 Applications of propionic acid in food preservation
Propionic acid is widely used as a food preservative due to its antimicrobial properties. It is effective in inhibiting the growth of mold and certain bacteria, thereby extending the shelf life of various food products. The acid and its salts are commonly added to baked goods, dairy products, and animal feed to prevent spoilage and maintain quality.Expand Specific Solutions03 Propionic acid derivatives and their uses
Derivatives of propionic acid, such as esters and salts, have diverse applications in industries including pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and agriculture. These compounds are synthesized through various chemical processes and can exhibit different properties compared to the parent acid. Some derivatives are used as intermediates in the production of other chemicals or as active ingredients in different formulations.Expand Specific Solutions04 Environmental and safety considerations in propionic acid handling
The production, storage, and use of propionic acid require careful consideration of environmental and safety factors. This includes developing methods for waste treatment, implementing proper handling procedures, and designing equipment to minimize exposure risks. Efforts are made to reduce environmental impact and ensure worker safety in facilities dealing with propionic acid.Expand Specific Solutions05 Analytical methods for propionic acid detection and quantification
Various analytical techniques are employed for the detection and quantification of propionic acid in different matrices. These methods include chromatography, spectroscopy, and electrochemical analysis. The development of accurate and sensitive analytical procedures is crucial for quality control in industries using propionic acid and for research purposes.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Propionic Acid Industry
The propionic acid research field is in a growth phase, with increasing market demand driven by its applications in food preservation, pharmaceuticals, and agriculture. The global market size is projected to expand significantly in the coming years. Technologically, the field is advancing, with companies like Nippon Shokubai, China Petroleum & Chemical Corp., and LG Chem leading innovations. These firms are focusing on improving production efficiency, developing bio-based routes, and exploring new applications. Universities such as Jiangnan University and The Ohio State University are contributing to fundamental research, while industry players like Dow Chemical and Cargill are investing in commercial-scale production and sustainable processes.
Nippon Shokubai Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Nippon Shokubai has developed a novel catalytic process for propionic acid production using ethylene and carbon monoxide as raw materials. Their approach utilizes a palladium-based catalyst system with high selectivity, achieving yields of up to 95% [1]. The company has also implemented advanced purification techniques, including reactive distillation, to enhance product quality and reduce energy consumption in the separation process [3]. Additionally, Nippon Shokubai has explored the use of bio-based feedstocks, such as lactic acid, as an alternative route to propionic acid, aligning with sustainability goals [5].
Strengths: High yield and selectivity, energy-efficient purification, exploration of sustainable feedstocks. Weaknesses: Potential high costs of palladium catalyst, dependence on petrochemical feedstocks for main process.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has made significant advancements in propionic acid production through their oxidation of propionaldehyde process. They have developed a highly efficient cobalt-manganese catalyst system that operates at moderate temperatures and pressures, achieving conversion rates of over 98% [2]. Sinopec has also implemented an integrated production system that utilizes propylene from their refinery operations as a starting material, creating a more cost-effective and streamlined process [4]. Furthermore, the company has invested in advanced process control systems and real-time monitoring technologies to optimize reaction conditions and maintain product quality [6].
Strengths: High conversion rates, integrated production system, advanced process control. Weaknesses: Reliance on fossil fuel-based feedstocks, potential environmental concerns related to oxidation process.
Innovative Approaches in Propionic Acid Synthesis
Methods and processes for producing organic acids
PatentWO2009154624A1
Innovation
- Metabolically engineered mutant bacteria with disrupted acetate kinase and phosphotransacetylase genes are immobilized in a fibrous-bed bioreactor to increase acid tolerance and productivity, redirecting carbon flux for enhanced butyric acid and propionic acid production, achieving final concentrations above 50 g/L.
Fermentative process and integrated system for producing organic acids
PatentWO2018112577A1
Innovation
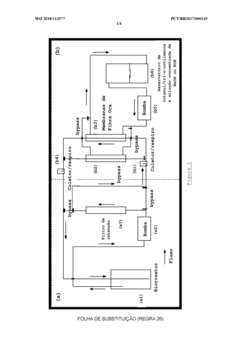
- A continuous fermentation process using Propionibacterium acidipropionici bacteria coupled with a perstration system employing hollow fiber membranes and tri-n-octylamine for efficient acid extraction, minimizing solvent use and maintaining pH stability.
Environmental Impact of Propionic Acid Production
The production of propionic acid has significant environmental implications that must be carefully considered and addressed. Traditional manufacturing processes, particularly those relying on petrochemical feedstocks, have been associated with substantial carbon emissions and energy consumption. These methods often involve the oxidation of propanol or the carbonylation of ethylene, both of which require high temperatures and pressures, leading to increased energy demands and greenhouse gas emissions.
Water pollution is another critical concern in propionic acid production. The process generates wastewater containing organic compounds and potentially harmful byproducts. If not properly treated, this effluent can lead to eutrophication and ecosystem disruption in local water bodies. Additionally, the use of catalysts in some production methods may result in heavy metal contamination, further exacerbating environmental risks.
Air quality is also affected by propionic acid manufacturing. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other air pollutants are often released during production, contributing to smog formation and potentially impacting human health in surrounding communities. The transportation and storage of raw materials and finished products can also lead to fugitive emissions, necessitating robust containment and handling protocols.
However, recent advancements in biotechnology offer promising alternatives with potentially lower environmental impacts. Fermentation-based production of propionic acid using renewable biomass feedstocks has gained attention as a more sustainable approach. This method can significantly reduce carbon footprint by utilizing agricultural waste or other renewable carbon sources. Furthermore, it operates under milder conditions, reducing energy requirements and associated emissions.
Life cycle assessments (LCAs) have been conducted to compare the environmental performance of traditional and bio-based propionic acid production methods. These studies generally indicate that bio-based routes can offer substantial reductions in greenhouse gas emissions and fossil resource depletion. However, they also highlight potential trade-offs, such as increased land and water use associated with biomass cultivation.
To mitigate environmental impacts, researchers and industry players are exploring various strategies. These include process intensification to improve energy efficiency, the development of more selective catalysts to reduce waste generation, and the implementation of closed-loop systems for water and solvent recycling. Additionally, there is growing interest in integrating propionic acid production with other biorefinery processes to maximize resource utilization and minimize waste.
As environmental regulations become more stringent globally, the propionic acid industry faces increasing pressure to adopt cleaner production technologies. This has spurred innovation in process design and waste management practices. Future research directions are likely to focus on further optimizing bio-based production methods, exploring novel feedstocks, and developing advanced separation and purification techniques to enhance overall environmental performance.
Water pollution is another critical concern in propionic acid production. The process generates wastewater containing organic compounds and potentially harmful byproducts. If not properly treated, this effluent can lead to eutrophication and ecosystem disruption in local water bodies. Additionally, the use of catalysts in some production methods may result in heavy metal contamination, further exacerbating environmental risks.
Air quality is also affected by propionic acid manufacturing. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other air pollutants are often released during production, contributing to smog formation and potentially impacting human health in surrounding communities. The transportation and storage of raw materials and finished products can also lead to fugitive emissions, necessitating robust containment and handling protocols.
However, recent advancements in biotechnology offer promising alternatives with potentially lower environmental impacts. Fermentation-based production of propionic acid using renewable biomass feedstocks has gained attention as a more sustainable approach. This method can significantly reduce carbon footprint by utilizing agricultural waste or other renewable carbon sources. Furthermore, it operates under milder conditions, reducing energy requirements and associated emissions.
Life cycle assessments (LCAs) have been conducted to compare the environmental performance of traditional and bio-based propionic acid production methods. These studies generally indicate that bio-based routes can offer substantial reductions in greenhouse gas emissions and fossil resource depletion. However, they also highlight potential trade-offs, such as increased land and water use associated with biomass cultivation.
To mitigate environmental impacts, researchers and industry players are exploring various strategies. These include process intensification to improve energy efficiency, the development of more selective catalysts to reduce waste generation, and the implementation of closed-loop systems for water and solvent recycling. Additionally, there is growing interest in integrating propionic acid production with other biorefinery processes to maximize resource utilization and minimize waste.
As environmental regulations become more stringent globally, the propionic acid industry faces increasing pressure to adopt cleaner production technologies. This has spurred innovation in process design and waste management practices. Future research directions are likely to focus on further optimizing bio-based production methods, exploring novel feedstocks, and developing advanced separation and purification techniques to enhance overall environmental performance.
Regulatory Framework for Propionic Acid Industry
The regulatory framework for the propionic acid industry plays a crucial role in ensuring product safety, environmental protection, and fair market practices. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees the use of propionic acid in food applications, classifying it as Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) when used as a preservative. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates its industrial production and potential environmental impacts, while the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) sets workplace safety standards for handling this chemical.
In the European Union, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) evaluates the safety of propionic acid as a food additive, and its use is governed by Regulation (EC) No 1333/2008 on food additives. The Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation also applies to propionic acid production and import within the EU, requiring manufacturers and importers to register substances and provide safety information.
Globally, the Codex Alimentarius Commission, established by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO), provides international food standards that include guidelines for the use of propionic acid as a preservative. These standards often serve as a reference for countries developing their own regulations.
In Asia, countries like China and Japan have their own regulatory bodies overseeing the use of propionic acid. The National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) in China and the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare in Japan set standards for its use in food and pharmaceutical applications.
Regulatory compliance in the propionic acid industry extends beyond product safety to encompass environmental regulations. Many countries have implemented strict guidelines for waste management, emissions control, and sustainable production practices. For instance, the EU's Industrial Emissions Directive (IED) sets emission limits and mandates the use of Best Available Techniques (BAT) in chemical production processes, including those involving propionic acid.
As research in propionic acid advances, regulatory frameworks are expected to evolve. Emerging areas of focus include the development of bio-based production methods, which may lead to new regulations around feedstock sourcing and production processes. Additionally, as propionic acid finds applications in new industries, such as bioplastics or advanced materials, regulatory bodies may need to adapt their guidelines to address these novel uses.
In the European Union, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) evaluates the safety of propionic acid as a food additive, and its use is governed by Regulation (EC) No 1333/2008 on food additives. The Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation also applies to propionic acid production and import within the EU, requiring manufacturers and importers to register substances and provide safety information.
Globally, the Codex Alimentarius Commission, established by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO), provides international food standards that include guidelines for the use of propionic acid as a preservative. These standards often serve as a reference for countries developing their own regulations.
In Asia, countries like China and Japan have their own regulatory bodies overseeing the use of propionic acid. The National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) in China and the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare in Japan set standards for its use in food and pharmaceutical applications.
Regulatory compliance in the propionic acid industry extends beyond product safety to encompass environmental regulations. Many countries have implemented strict guidelines for waste management, emissions control, and sustainable production practices. For instance, the EU's Industrial Emissions Directive (IED) sets emission limits and mandates the use of Best Available Techniques (BAT) in chemical production processes, including those involving propionic acid.
As research in propionic acid advances, regulatory frameworks are expected to evolve. Emerging areas of focus include the development of bio-based production methods, which may lead to new regulations around feedstock sourcing and production processes. Additionally, as propionic acid finds applications in new industries, such as bioplastics or advanced materials, regulatory bodies may need to adapt their guidelines to address these novel uses.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!