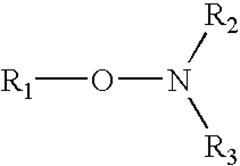
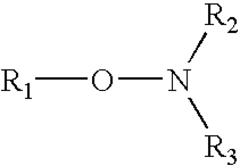
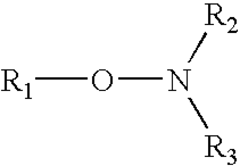
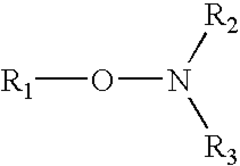
How to Enhance Alkyl Stability in Reactive Conditions?
JUL 15, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Alkyl Stability Enhancement: Background and Objectives
Alkyl stability enhancement in reactive conditions has become a critical focus in various chemical processes, particularly in the fields of organic synthesis, pharmaceuticals, and materials science. The evolution of this technology can be traced back to the early 20th century when researchers first began to explore the fundamental principles of organic chemistry and chemical bonding. Over the decades, significant advancements have been made in understanding the factors that influence alkyl stability and developing strategies to improve it.
The primary objective of enhancing alkyl stability is to maintain the structural integrity and reactivity of alkyl groups under challenging reactive conditions. This is crucial for numerous applications, including the synthesis of complex organic molecules, the development of more efficient catalysts, and the creation of advanced materials with improved performance characteristics. By increasing the stability of alkyl groups, researchers aim to expand the scope of chemical transformations, improve reaction yields, and enable the synthesis of previously inaccessible compounds.
Recent technological trends in this field have focused on several key areas. One significant trend is the development of novel protecting group strategies that can shield alkyl groups from undesired reactions while allowing for selective transformations. Another important direction is the exploration of transition metal-catalyzed reactions that can selectively activate and functionalize alkyl groups without compromising their stability. Additionally, there has been growing interest in the application of computational chemistry and machine learning techniques to predict and optimize alkyl stability under various reactive conditions.
The expected technological goals in this domain are multifaceted. Researchers aim to develop universal methods for enhancing alkyl stability that can be applied across a wide range of chemical environments. This includes the creation of new reagents and catalysts specifically designed to stabilize alkyl groups, as well as the optimization of reaction conditions to minimize unwanted side reactions. Furthermore, there is a push towards the development of in situ monitoring techniques that can provide real-time information on alkyl stability during reactions, enabling more precise control and optimization of chemical processes.
As the field continues to evolve, interdisciplinary approaches are becoming increasingly important. Collaborations between organic chemists, materials scientists, and computational experts are driving innovation and leading to novel solutions for enhancing alkyl stability. The ultimate goal is to establish a comprehensive toolkit of strategies and methodologies that can be readily applied to address stability challenges in diverse chemical contexts, paving the way for more efficient and sustainable chemical processes across industries.
The primary objective of enhancing alkyl stability is to maintain the structural integrity and reactivity of alkyl groups under challenging reactive conditions. This is crucial for numerous applications, including the synthesis of complex organic molecules, the development of more efficient catalysts, and the creation of advanced materials with improved performance characteristics. By increasing the stability of alkyl groups, researchers aim to expand the scope of chemical transformations, improve reaction yields, and enable the synthesis of previously inaccessible compounds.
Recent technological trends in this field have focused on several key areas. One significant trend is the development of novel protecting group strategies that can shield alkyl groups from undesired reactions while allowing for selective transformations. Another important direction is the exploration of transition metal-catalyzed reactions that can selectively activate and functionalize alkyl groups without compromising their stability. Additionally, there has been growing interest in the application of computational chemistry and machine learning techniques to predict and optimize alkyl stability under various reactive conditions.
The expected technological goals in this domain are multifaceted. Researchers aim to develop universal methods for enhancing alkyl stability that can be applied across a wide range of chemical environments. This includes the creation of new reagents and catalysts specifically designed to stabilize alkyl groups, as well as the optimization of reaction conditions to minimize unwanted side reactions. Furthermore, there is a push towards the development of in situ monitoring techniques that can provide real-time information on alkyl stability during reactions, enabling more precise control and optimization of chemical processes.
As the field continues to evolve, interdisciplinary approaches are becoming increasingly important. Collaborations between organic chemists, materials scientists, and computational experts are driving innovation and leading to novel solutions for enhancing alkyl stability. The ultimate goal is to establish a comprehensive toolkit of strategies and methodologies that can be readily applied to address stability challenges in diverse chemical contexts, paving the way for more efficient and sustainable chemical processes across industries.
Market Demand for Stable Alkyl Compounds
The market demand for stable alkyl compounds has been steadily increasing across various industries due to their versatile applications and unique properties. In the chemical industry, these compounds play a crucial role as intermediates in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and specialty chemicals. The pharmaceutical sector, in particular, has shown a growing need for stable alkyl compounds in drug development and manufacturing processes, where maintaining molecular integrity under reactive conditions is paramount.
The petrochemical industry also represents a significant market for stable alkyl compounds, utilizing them in the production of lubricants, fuel additives, and polymer stabilizers. As the automotive and aerospace sectors continue to advance, the demand for high-performance lubricants and additives that can withstand extreme temperatures and pressures has surged, driving the need for more stable alkyl compounds.
In the field of materials science, stable alkyl compounds are increasingly sought after for their potential in developing advanced polymers and composites. These materials find applications in electronics, construction, and renewable energy technologies, where stability under varying environmental conditions is essential. The growing emphasis on sustainable and eco-friendly products has also led to increased research and development efforts focused on bio-based stable alkyl compounds, opening new market opportunities in the green chemistry sector.
The global market for stable alkyl compounds is projected to experience substantial growth in the coming years, driven by technological advancements and expanding applications across industries. Emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to contribute significantly to this growth, as their industrial sectors expand and modernize. Additionally, the increasing focus on quality and performance in consumer products has created new demand for stable alkyl compounds in personal care and household products.
Despite the positive market outlook, challenges such as stringent environmental regulations and the need for cost-effective production methods continue to shape the industry landscape. Manufacturers are investing in research and development to address these challenges, focusing on enhancing the stability and reactivity of alkyl compounds while minimizing environmental impact. This ongoing innovation is expected to further drive market growth and open new avenues for application in emerging technologies.
The petrochemical industry also represents a significant market for stable alkyl compounds, utilizing them in the production of lubricants, fuel additives, and polymer stabilizers. As the automotive and aerospace sectors continue to advance, the demand for high-performance lubricants and additives that can withstand extreme temperatures and pressures has surged, driving the need for more stable alkyl compounds.
In the field of materials science, stable alkyl compounds are increasingly sought after for their potential in developing advanced polymers and composites. These materials find applications in electronics, construction, and renewable energy technologies, where stability under varying environmental conditions is essential. The growing emphasis on sustainable and eco-friendly products has also led to increased research and development efforts focused on bio-based stable alkyl compounds, opening new market opportunities in the green chemistry sector.
The global market for stable alkyl compounds is projected to experience substantial growth in the coming years, driven by technological advancements and expanding applications across industries. Emerging economies in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to contribute significantly to this growth, as their industrial sectors expand and modernize. Additionally, the increasing focus on quality and performance in consumer products has created new demand for stable alkyl compounds in personal care and household products.
Despite the positive market outlook, challenges such as stringent environmental regulations and the need for cost-effective production methods continue to shape the industry landscape. Manufacturers are investing in research and development to address these challenges, focusing on enhancing the stability and reactivity of alkyl compounds while minimizing environmental impact. This ongoing innovation is expected to further drive market growth and open new avenues for application in emerging technologies.
Current Challenges in Alkyl Stability under Reactive Conditions
The stability of alkyl groups under reactive conditions presents significant challenges in various chemical processes, particularly in organic synthesis and industrial applications. One of the primary issues is the susceptibility of alkyl groups to oxidation, especially in the presence of strong oxidizing agents or elevated temperatures. This vulnerability can lead to undesired side reactions, compromising the integrity of the target molecules and reducing overall yield.
Another major challenge is the potential for alkyl groups to undergo rearrangement or elimination reactions under certain conditions. These transformations can be triggered by acidic or basic environments, high temperatures, or the presence of specific catalysts. Such reactions often result in the formation of unwanted byproducts, making it difficult to maintain the desired molecular structure and purity of the final product.
The stability of alkyl groups is also affected by their position within the molecule and the nature of adjacent functional groups. For instance, primary alkyl groups are generally more stable than tertiary ones, which are prone to carbocation formation and subsequent reactions. Additionally, the presence of electron-withdrawing or electron-donating groups in proximity to the alkyl moiety can significantly influence its reactivity and stability.
In many cases, the challenge lies in balancing the reactivity required for desired transformations with the need to preserve the alkyl group's integrity. This is particularly evident in multi-step syntheses, where the alkyl group must survive several reaction conditions before reaching the final product stage. The cumulative effect of exposure to various reagents and conditions throughout the synthetic pathway can lead to gradual degradation or modification of the alkyl group.
Furthermore, the stability of alkyl groups under reactive conditions is often compromised by the presence of radical species. Free radicals can initiate chain reactions that lead to the cleavage of carbon-carbon bonds or the abstraction of hydrogen atoms from alkyl groups, resulting in their degradation or transformation. This is especially problematic in polymerization processes and in the presence of peroxides or other radical initiators.
The challenge of maintaining alkyl stability extends to heterogeneous reaction environments as well. In scenarios involving phase transfer or interfacial reactions, the stability of alkyl groups can be affected by factors such as solvent effects, surface interactions, and mass transfer limitations. These complexities add another layer of difficulty in predicting and controlling the behavior of alkyl groups under reactive conditions.
Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach, combining innovative synthetic strategies, careful selection of reaction conditions, and the development of novel protecting group methodologies. The ongoing research in this area aims to enhance our understanding of the fundamental factors affecting alkyl stability and to devise more robust methods for preserving these important structural elements in complex chemical transformations.
Another major challenge is the potential for alkyl groups to undergo rearrangement or elimination reactions under certain conditions. These transformations can be triggered by acidic or basic environments, high temperatures, or the presence of specific catalysts. Such reactions often result in the formation of unwanted byproducts, making it difficult to maintain the desired molecular structure and purity of the final product.
The stability of alkyl groups is also affected by their position within the molecule and the nature of adjacent functional groups. For instance, primary alkyl groups are generally more stable than tertiary ones, which are prone to carbocation formation and subsequent reactions. Additionally, the presence of electron-withdrawing or electron-donating groups in proximity to the alkyl moiety can significantly influence its reactivity and stability.
In many cases, the challenge lies in balancing the reactivity required for desired transformations with the need to preserve the alkyl group's integrity. This is particularly evident in multi-step syntheses, where the alkyl group must survive several reaction conditions before reaching the final product stage. The cumulative effect of exposure to various reagents and conditions throughout the synthetic pathway can lead to gradual degradation or modification of the alkyl group.
Furthermore, the stability of alkyl groups under reactive conditions is often compromised by the presence of radical species. Free radicals can initiate chain reactions that lead to the cleavage of carbon-carbon bonds or the abstraction of hydrogen atoms from alkyl groups, resulting in their degradation or transformation. This is especially problematic in polymerization processes and in the presence of peroxides or other radical initiators.
The challenge of maintaining alkyl stability extends to heterogeneous reaction environments as well. In scenarios involving phase transfer or interfacial reactions, the stability of alkyl groups can be affected by factors such as solvent effects, surface interactions, and mass transfer limitations. These complexities add another layer of difficulty in predicting and controlling the behavior of alkyl groups under reactive conditions.
Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach, combining innovative synthetic strategies, careful selection of reaction conditions, and the development of novel protecting group methodologies. The ongoing research in this area aims to enhance our understanding of the fundamental factors affecting alkyl stability and to devise more robust methods for preserving these important structural elements in complex chemical transformations.
Existing Methods for Enhancing Alkyl Stability
01 Thermal stability of alkyl groups
Alkyl groups exhibit varying degrees of thermal stability depending on their structure and bonding. Longer chain alkyl groups generally show higher thermal stability compared to shorter chains. The presence of branching can also affect thermal stability, with more branched structures often being less stable at high temperatures.- Thermal stability of alkyl groups: Alkyl groups exhibit varying degrees of thermal stability depending on their structure and bonding. Longer chain alkyl groups generally show higher thermal stability compared to shorter chains. The presence of branching can also affect thermal stability. Understanding these factors is crucial for applications in high-temperature environments.
- Chemical stability of alkyl substituents: The chemical stability of alkyl groups is influenced by their position on the molecule and the surrounding chemical environment. Tertiary alkyl groups are generally more stable than primary or secondary ones. Factors such as steric hindrance and electronic effects play a role in determining the overall chemical stability of alkyl substituents.
- Alkyl group stability in polymers: In polymer chemistry, the stability of alkyl groups affects the overall properties of the material. Alkyl side chains can influence the polymer's thermal and mechanical properties, as well as its resistance to degradation. The length and arrangement of alkyl groups in the polymer backbone or as pendant groups can be tailored to achieve desired stability characteristics.
- Stabilization of alkyl groups in catalysts: Alkyl groups play a crucial role in many catalytic systems, and their stability is essential for maintaining catalyst performance. Various strategies can be employed to enhance the stability of alkyl groups in catalysts, including the use of supporting materials, ligand design, and controlling reaction conditions. Stable alkyl groups contribute to improved catalyst longevity and efficiency.
- Environmental factors affecting alkyl group stability: External factors such as temperature, pressure, pH, and the presence of reactive species can significantly impact the stability of alkyl groups. Understanding these environmental influences is crucial for predicting and controlling the behavior of alkyl-containing compounds in various applications, including industrial processes and environmental remediation.
02 Chemical stability of alkyl groups in different environments
The chemical stability of alkyl groups can be influenced by the surrounding environment. Factors such as pH, presence of oxidizing or reducing agents, and exposure to light can affect their stability. In some cases, protective measures or stabilizing additives may be used to enhance the chemical stability of alkyl-containing compounds.Expand Specific Solutions03 Alkyl group stability in polymers and materials
Alkyl groups play a crucial role in the stability of various polymers and materials. Their presence can affect properties such as heat resistance, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength. The stability of alkyl groups in these contexts is often related to their ability to resist degradation and maintain the overall integrity of the material.Expand Specific Solutions04 Stabilization techniques for alkyl-containing compounds
Various techniques can be employed to enhance the stability of alkyl-containing compounds. These may include the use of antioxidants, UV stabilizers, or other additives that protect against degradation. Additionally, structural modifications or the incorporation of specific functional groups can improve the overall stability of alkyl-containing molecules.Expand Specific Solutions05 Alkyl group stability in catalytic processes
The stability of alkyl groups is an important consideration in catalytic processes. Certain catalysts may promote the cleavage or rearrangement of alkyl groups, while others may help maintain their stability. Understanding the behavior of alkyl groups under various catalytic conditions is crucial for optimizing reaction outcomes and product yields.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Alkyl Chemistry and Stabilization
The competition landscape for enhancing alkyl stability in reactive conditions is characterized by a mature market with significant players across the chemical and petrochemical industries. Major companies like BASF, Sinopec, and Henkel are actively involved in research and development in this area. The market size is substantial, driven by the widespread application of alkyl compounds in various industrial processes. Technologically, the field is well-developed, with ongoing innovations focused on improving stability and efficiency. Companies such as China Petroleum & Chemical Corp., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, and Nippon Shokubai are at the forefront, leveraging their extensive research capabilities to develop advanced solutions. The competitive landscape is further enriched by contributions from research institutions like the Institute of Process Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, indicating a collaborative approach to technological advancement in this domain.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has developed advanced alkylation technologies to enhance alkyl stability in reactive conditions. Their approach involves using ionic liquid catalysts in alkylation processes, which significantly improves the stability of alkyl groups[1]. This method allows for better control of reaction conditions and reduces side reactions that can degrade alkyl compounds. Sinopec has also implemented a solid acid catalyst technology for alkylation, which operates at lower temperatures and pressures, further enhancing alkyl stability[2]. Additionally, they have explored the use of supercritical fluid extraction techniques to isolate and stabilize alkyl compounds in complex mixtures, improving their resistance to degradation in reactive environments[3].
Strengths: Innovative use of ionic liquids and solid acid catalysts improves reaction control and reduces side reactions. The supercritical fluid extraction technique offers enhanced isolation and stabilization of alkyl compounds. Weaknesses: Implementation may require significant infrastructure changes and high initial investment costs.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF Corp. has developed a multi-faceted approach to enhance alkyl stability in reactive conditions. Their strategy includes the use of novel stabilizers and antioxidants specifically designed for alkyl compounds[4]. These additives work by intercepting free radicals and preventing chain reactions that lead to degradation. BASF has also pioneered the development of alkyl-modified polymers with improved thermal and chemical resistance[5]. These polymers incorporate alkyl groups into their structure in a way that shields them from reactive species. Furthermore, BASF has introduced advanced encapsulation technologies that create protective barriers around alkyl compounds, significantly increasing their stability in harsh environments[6]. This approach allows for the controlled release of alkyl compounds in reactive conditions while maintaining their integrity.
Strengths: Comprehensive approach combining stabilizers, modified polymers, and encapsulation technologies. Offers solutions for a wide range of applications and reactive environments. Weaknesses: May require complex formulation processes and could potentially alter the properties of the final product.
Innovative Approaches to Alkyl Stabilization
Method of stabilizing aqueous cationic polymers
PatentActiveUS7868071B2
Innovation
- The addition of non-aldehyde, low molecular weight, non-ionic, water-soluble organic stabilizing compounds, such as tertiary amines and urea, in combination with water-soluble inorganic complexing metal salts, to inhibit reactions between high molecular weight polymer molecules, thereby enhancing storage stability without compromising wet strength efficiency.
Stabilized coenzyme solutions for determining dehydrogenase activity
PatentInactiveUS7300769B2
Innovation
- An aqueous solution containing a coenzyme for hydrogen-transferring enzymes, such as NAD or NADP, with organic compounds or salts having a pKa value between 1.5 and 6.0, and hydroxylamine derivatives, along with complexing agents like EDTA, is used to stabilize the solution, maintaining stability over extended periods and preventing degradation products from inhibiting enzyme activity.
Environmental Impact of Alkyl Stabilization Processes
The environmental impact of alkyl stabilization processes is a critical consideration in the development and implementation of technologies aimed at enhancing alkyl stability in reactive conditions. These processes, while essential for various industrial applications, can have significant implications for the environment if not properly managed.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with alkyl stabilization is the potential release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during the process. VOCs can contribute to air pollution and the formation of ground-level ozone, which can have detrimental effects on human health and ecosystems. The use of certain stabilizing agents, particularly those containing heavy metals or persistent organic pollutants, may lead to soil and water contamination if not properly handled or disposed of.
Energy consumption is another important factor to consider. Many alkyl stabilization processes require high temperatures or pressures, resulting in substantial energy usage and associated greenhouse gas emissions. This energy-intensive nature contributes to the overall carbon footprint of the industry and raises concerns about climate change impacts.
Waste generation is a significant issue in alkyl stabilization processes. The production of byproducts and spent stabilizing agents can lead to hazardous waste streams that require specialized treatment and disposal methods. Improper management of these wastes can result in long-term environmental contamination and ecological damage.
Water usage and potential water pollution are additional environmental considerations. Some stabilization processes may require large volumes of water, potentially straining local water resources. Furthermore, the discharge of process water containing residual chemicals or byproducts can impact aquatic ecosystems if not adequately treated.
To mitigate these environmental impacts, researchers and industry professionals are exploring more sustainable approaches to alkyl stabilization. Green chemistry principles are being applied to develop less toxic and more environmentally friendly stabilizing agents. Process optimization techniques are being employed to reduce energy consumption and minimize waste generation. Closed-loop systems and recycling technologies are being implemented to recover and reuse materials, reducing the overall environmental footprint of these processes.
Regulatory frameworks and environmental standards play a crucial role in driving the adoption of more sustainable practices in alkyl stabilization. Stricter emissions controls, waste management regulations, and energy efficiency requirements are pushing the industry towards cleaner technologies and more responsible environmental stewardship.
As the focus on sustainability intensifies, life cycle assessments are becoming increasingly important in evaluating the environmental impact of alkyl stabilization processes. These comprehensive analyses consider the entire life cycle of the products and processes, from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal, providing valuable insights for improving environmental performance and guiding future research and development efforts in this field.
One of the primary environmental concerns associated with alkyl stabilization is the potential release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during the process. VOCs can contribute to air pollution and the formation of ground-level ozone, which can have detrimental effects on human health and ecosystems. The use of certain stabilizing agents, particularly those containing heavy metals or persistent organic pollutants, may lead to soil and water contamination if not properly handled or disposed of.
Energy consumption is another important factor to consider. Many alkyl stabilization processes require high temperatures or pressures, resulting in substantial energy usage and associated greenhouse gas emissions. This energy-intensive nature contributes to the overall carbon footprint of the industry and raises concerns about climate change impacts.
Waste generation is a significant issue in alkyl stabilization processes. The production of byproducts and spent stabilizing agents can lead to hazardous waste streams that require specialized treatment and disposal methods. Improper management of these wastes can result in long-term environmental contamination and ecological damage.
Water usage and potential water pollution are additional environmental considerations. Some stabilization processes may require large volumes of water, potentially straining local water resources. Furthermore, the discharge of process water containing residual chemicals or byproducts can impact aquatic ecosystems if not adequately treated.
To mitigate these environmental impacts, researchers and industry professionals are exploring more sustainable approaches to alkyl stabilization. Green chemistry principles are being applied to develop less toxic and more environmentally friendly stabilizing agents. Process optimization techniques are being employed to reduce energy consumption and minimize waste generation. Closed-loop systems and recycling technologies are being implemented to recover and reuse materials, reducing the overall environmental footprint of these processes.
Regulatory frameworks and environmental standards play a crucial role in driving the adoption of more sustainable practices in alkyl stabilization. Stricter emissions controls, waste management regulations, and energy efficiency requirements are pushing the industry towards cleaner technologies and more responsible environmental stewardship.
As the focus on sustainability intensifies, life cycle assessments are becoming increasingly important in evaluating the environmental impact of alkyl stabilization processes. These comprehensive analyses consider the entire life cycle of the products and processes, from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal, providing valuable insights for improving environmental performance and guiding future research and development efforts in this field.
Safety Considerations in Alkyl Stability Enhancement
Enhancing alkyl stability in reactive conditions necessitates a comprehensive approach to safety considerations. The inherent reactivity of alkyl groups, particularly in the presence of oxidizing agents or extreme temperatures, poses significant risks that must be carefully managed throughout the research and development process.
One of the primary safety concerns is the potential for uncontrolled reactions, which can lead to rapid pressure buildup, thermal runaway, or even explosions. To mitigate these risks, it is crucial to implement robust engineering controls, such as pressure relief systems, temperature monitoring devices, and emergency shutdown mechanisms. These systems should be designed to automatically respond to deviations from safe operating parameters, ensuring rapid intervention in the event of unexpected reactivity.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) plays a vital role in safeguarding researchers and operators working with alkyl compounds. Specialized chemical-resistant gloves, face shields, and protective clothing should be mandatory when handling these materials. Additionally, proper ventilation systems, including fume hoods and local exhaust ventilation, are essential to prevent the accumulation of potentially harmful vapors or gases that may be generated during reactions involving alkyl groups.
The storage and handling of alkyl compounds and their precursors require careful consideration. These materials should be stored in cool, dry areas away from sources of heat, ignition, and incompatible substances. Proper labeling and segregation of chemicals are crucial to prevent accidental mixing and potential reactions. Furthermore, the use of inert atmospheres, such as nitrogen or argon, during storage and handling can significantly reduce the risk of unwanted oxidation or degradation.
Risk assessment and management protocols should be established and regularly updated to address the specific hazards associated with alkyl stability enhancement research. This includes conducting thorough hazard analyses for each experimental procedure, developing detailed standard operating procedures (SOPs), and implementing a robust incident reporting and investigation system.
Training and education are paramount in ensuring the safe execution of alkyl stability enhancement techniques. All personnel involved in the research should receive comprehensive training on the properties of alkyl compounds, potential hazards, proper handling techniques, and emergency response procedures. Regular refresher courses and safety drills should be conducted to maintain a high level of awareness and preparedness.
Environmental considerations must also be addressed when working to enhance alkyl stability. Proper waste management protocols should be implemented to ensure the safe disposal of reaction byproducts and unused materials. This may include neutralization procedures, specialized waste treatment facilities, or controlled incineration methods to minimize environmental impact and comply with regulatory requirements.
By integrating these safety considerations into the research and development process for enhancing alkyl stability in reactive conditions, organizations can significantly reduce the risks associated with this challenging area of chemistry while advancing the field's technological capabilities.
One of the primary safety concerns is the potential for uncontrolled reactions, which can lead to rapid pressure buildup, thermal runaway, or even explosions. To mitigate these risks, it is crucial to implement robust engineering controls, such as pressure relief systems, temperature monitoring devices, and emergency shutdown mechanisms. These systems should be designed to automatically respond to deviations from safe operating parameters, ensuring rapid intervention in the event of unexpected reactivity.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) plays a vital role in safeguarding researchers and operators working with alkyl compounds. Specialized chemical-resistant gloves, face shields, and protective clothing should be mandatory when handling these materials. Additionally, proper ventilation systems, including fume hoods and local exhaust ventilation, are essential to prevent the accumulation of potentially harmful vapors or gases that may be generated during reactions involving alkyl groups.
The storage and handling of alkyl compounds and their precursors require careful consideration. These materials should be stored in cool, dry areas away from sources of heat, ignition, and incompatible substances. Proper labeling and segregation of chemicals are crucial to prevent accidental mixing and potential reactions. Furthermore, the use of inert atmospheres, such as nitrogen or argon, during storage and handling can significantly reduce the risk of unwanted oxidation or degradation.
Risk assessment and management protocols should be established and regularly updated to address the specific hazards associated with alkyl stability enhancement research. This includes conducting thorough hazard analyses for each experimental procedure, developing detailed standard operating procedures (SOPs), and implementing a robust incident reporting and investigation system.
Training and education are paramount in ensuring the safe execution of alkyl stability enhancement techniques. All personnel involved in the research should receive comprehensive training on the properties of alkyl compounds, potential hazards, proper handling techniques, and emergency response procedures. Regular refresher courses and safety drills should be conducted to maintain a high level of awareness and preparedness.
Environmental considerations must also be addressed when working to enhance alkyl stability. Proper waste management protocols should be implemented to ensure the safe disposal of reaction byproducts and unused materials. This may include neutralization procedures, specialized waste treatment facilities, or controlled incineration methods to minimize environmental impact and comply with regulatory requirements.
By integrating these safety considerations into the research and development process for enhancing alkyl stability in reactive conditions, organizations can significantly reduce the risks associated with this challenging area of chemistry while advancing the field's technological capabilities.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!