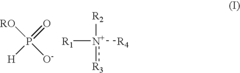How to Foster Green Development Through Alkyl Chemistry?
JUL 15, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Alkyl Chemistry Background and Green Goals
Alkyl chemistry has been a cornerstone of organic synthesis for over a century, playing a crucial role in the development of various industries, including pharmaceuticals, materials science, and energy production. The field has evolved from basic carbon-carbon bond formation to sophisticated methodologies that enable the creation of complex molecular structures. However, as global awareness of environmental issues has grown, the focus has shifted towards more sustainable practices in chemical synthesis.
The green chemistry movement, initiated in the 1990s, has significantly influenced the trajectory of alkyl chemistry. This paradigm shift aims to design chemical products and processes that reduce or eliminate the use and generation of hazardous substances. In the context of alkyl chemistry, this translates to developing more efficient, less toxic, and environmentally benign methods for carbon-carbon bond formation and functionalization.
One of the primary goals in fostering green development through alkyl chemistry is to minimize waste production and energy consumption. Traditional alkylation reactions often require stoichiometric amounts of reagents, leading to significant waste generation. Modern approaches seek to employ catalytic systems that can achieve high atom economy and reduce byproduct formation. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on utilizing renewable feedstocks as starting materials for alkyl chemistry, moving away from petroleum-based resources.
Another critical objective is the development of safer reaction conditions. Many conventional alkylation processes involve the use of harsh reagents or extreme temperatures and pressures. Green alkyl chemistry aims to design reactions that can proceed under mild conditions, ideally at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. This not only enhances safety but also reduces energy requirements, aligning with sustainable development principles.
Water-based reactions and the use of green solvents represent another frontier in environmentally friendly alkyl chemistry. Replacing toxic organic solvents with water or bio-derived alternatives can significantly reduce the environmental impact of chemical processes. Furthermore, the exploration of solvent-free reactions and solid-state chemistry offers promising avenues for sustainable alkylation methodologies.
The integration of biocatalysis and enzymatic processes into alkyl chemistry is an emerging trend that holds great potential for green development. Enzymes can catalyze highly selective transformations under mild conditions, often with water as the reaction medium. This approach not only aligns with green chemistry principles but also opens up new possibilities for stereoselective alkylations that are challenging to achieve through traditional methods.
In conclusion, the evolution of alkyl chemistry towards greener practices is driven by the need to address global environmental challenges while maintaining industrial productivity. The goals of this transformation encompass waste reduction, energy efficiency, safer processes, and the utilization of renewable resources. As research in this field progresses, it promises to deliver innovative solutions that balance chemical utility with ecological responsibility, paving the way for a more sustainable future in organic synthesis and industrial chemistry.
The green chemistry movement, initiated in the 1990s, has significantly influenced the trajectory of alkyl chemistry. This paradigm shift aims to design chemical products and processes that reduce or eliminate the use and generation of hazardous substances. In the context of alkyl chemistry, this translates to developing more efficient, less toxic, and environmentally benign methods for carbon-carbon bond formation and functionalization.
One of the primary goals in fostering green development through alkyl chemistry is to minimize waste production and energy consumption. Traditional alkylation reactions often require stoichiometric amounts of reagents, leading to significant waste generation. Modern approaches seek to employ catalytic systems that can achieve high atom economy and reduce byproduct formation. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on utilizing renewable feedstocks as starting materials for alkyl chemistry, moving away from petroleum-based resources.
Another critical objective is the development of safer reaction conditions. Many conventional alkylation processes involve the use of harsh reagents or extreme temperatures and pressures. Green alkyl chemistry aims to design reactions that can proceed under mild conditions, ideally at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. This not only enhances safety but also reduces energy requirements, aligning with sustainable development principles.
Water-based reactions and the use of green solvents represent another frontier in environmentally friendly alkyl chemistry. Replacing toxic organic solvents with water or bio-derived alternatives can significantly reduce the environmental impact of chemical processes. Furthermore, the exploration of solvent-free reactions and solid-state chemistry offers promising avenues for sustainable alkylation methodologies.
The integration of biocatalysis and enzymatic processes into alkyl chemistry is an emerging trend that holds great potential for green development. Enzymes can catalyze highly selective transformations under mild conditions, often with water as the reaction medium. This approach not only aligns with green chemistry principles but also opens up new possibilities for stereoselective alkylations that are challenging to achieve through traditional methods.
In conclusion, the evolution of alkyl chemistry towards greener practices is driven by the need to address global environmental challenges while maintaining industrial productivity. The goals of this transformation encompass waste reduction, energy efficiency, safer processes, and the utilization of renewable resources. As research in this field progresses, it promises to deliver innovative solutions that balance chemical utility with ecological responsibility, paving the way for a more sustainable future in organic synthesis and industrial chemistry.
Market Demand for Green Alkyl Products
The market demand for green alkyl products has been steadily increasing in recent years, driven by growing environmental concerns and stricter regulations across various industries. This trend is particularly evident in sectors such as personal care, cleaning products, and industrial applications, where consumers and businesses alike are seeking more sustainable alternatives to traditional petrochemical-based products.
In the personal care industry, there is a significant shift towards natural and eco-friendly ingredients. Green alkyl products, derived from renewable sources such as plant oils and fats, are gaining traction as alternatives to synthetic surfactants and emollients. These bio-based alkyl compounds offer similar performance characteristics to their petrochemical counterparts while boasting improved biodegradability and reduced environmental impact.
The cleaning products sector has also witnessed a surge in demand for green alkyl-based formulations. Consumers are increasingly opting for household cleaners, laundry detergents, and dishwashing liquids that contain plant-derived surfactants and solvents. This shift is driven by concerns over water pollution and the desire to reduce reliance on fossil fuel-based ingredients.
Industrial applications, including lubricants, plasticizers, and polymer additives, are another area where green alkyl products are finding growing acceptance. Companies are exploring bio-based alternatives to traditional petroleum-derived alkyl compounds to improve their sustainability profiles and meet increasingly stringent environmental regulations.
The market for green alkyl products is expected to continue its upward trajectory, with several factors contributing to this growth. Firstly, increasing consumer awareness of environmental issues and the desire for sustainable products are driving demand across various end-use sectors. Secondly, government initiatives and regulations promoting the use of bio-based chemicals are creating a favorable market environment for green alkyl products.
Furthermore, technological advancements in the production of green alkyl compounds are improving their cost-competitiveness and performance characteristics, making them more attractive to manufacturers. As research and development efforts continue to enhance the properties and expand the applications of these sustainable alternatives, their market penetration is likely to accelerate.
However, challenges remain in fully realizing the market potential of green alkyl products. These include the need for further improvements in production efficiency to achieve cost parity with conventional petrochemical-based alternatives, as well as addressing any performance gaps that may exist in certain applications. Additionally, ensuring a stable and sustainable supply chain for the renewable feedstocks used in green alkyl production is crucial for long-term market growth.
In the personal care industry, there is a significant shift towards natural and eco-friendly ingredients. Green alkyl products, derived from renewable sources such as plant oils and fats, are gaining traction as alternatives to synthetic surfactants and emollients. These bio-based alkyl compounds offer similar performance characteristics to their petrochemical counterparts while boasting improved biodegradability and reduced environmental impact.
The cleaning products sector has also witnessed a surge in demand for green alkyl-based formulations. Consumers are increasingly opting for household cleaners, laundry detergents, and dishwashing liquids that contain plant-derived surfactants and solvents. This shift is driven by concerns over water pollution and the desire to reduce reliance on fossil fuel-based ingredients.
Industrial applications, including lubricants, plasticizers, and polymer additives, are another area where green alkyl products are finding growing acceptance. Companies are exploring bio-based alternatives to traditional petroleum-derived alkyl compounds to improve their sustainability profiles and meet increasingly stringent environmental regulations.
The market for green alkyl products is expected to continue its upward trajectory, with several factors contributing to this growth. Firstly, increasing consumer awareness of environmental issues and the desire for sustainable products are driving demand across various end-use sectors. Secondly, government initiatives and regulations promoting the use of bio-based chemicals are creating a favorable market environment for green alkyl products.
Furthermore, technological advancements in the production of green alkyl compounds are improving their cost-competitiveness and performance characteristics, making them more attractive to manufacturers. As research and development efforts continue to enhance the properties and expand the applications of these sustainable alternatives, their market penetration is likely to accelerate.
However, challenges remain in fully realizing the market potential of green alkyl products. These include the need for further improvements in production efficiency to achieve cost parity with conventional petrochemical-based alternatives, as well as addressing any performance gaps that may exist in certain applications. Additionally, ensuring a stable and sustainable supply chain for the renewable feedstocks used in green alkyl production is crucial for long-term market growth.
Current State and Challenges in Green Alkyl Chemistry
Green alkyl chemistry has made significant strides in recent years, but it still faces numerous challenges in its quest for sustainable development. The current state of this field is characterized by a growing emphasis on eco-friendly processes and products, driven by increasing environmental concerns and regulatory pressures.
One of the primary advancements in green alkyl chemistry is the development of more efficient catalysts that enable reactions to occur under milder conditions, reducing energy consumption and waste generation. These catalysts often incorporate transition metals or enzymes, allowing for highly selective transformations with minimal by-product formation.
Another area of progress is the utilization of renewable feedstocks as alternatives to petroleum-based starting materials. Biomass-derived alkyl compounds, such as those obtained from plant oils or lignocellulosic materials, are increasingly being explored as sustainable sources for various chemical processes.
Despite these advancements, several challenges persist in the field of green alkyl chemistry. One major hurdle is the scalability of green processes. Many environmentally friendly reactions that work well in laboratory settings face difficulties when scaled up to industrial production levels, often due to increased costs or reduced efficiency.
The development of truly sustainable solvents remains a significant challenge. While progress has been made in using water, supercritical CO2, and ionic liquids as green alternatives, finding solvents that are both environmentally benign and universally applicable across various alkyl chemistry processes is still an ongoing effort.
Another obstacle is the limited availability and higher cost of some bio-based feedstocks compared to their petroleum-derived counterparts. This economic barrier often hinders the widespread adoption of greener alkylation processes in industry.
The synthesis of complex alkyl compounds using green methodologies also presents challenges. Many traditional routes rely on multi-step processes with poor atom economy, and developing greener alternatives that maintain high yields and selectivity is an active area of research.
Lastly, the assessment of the overall environmental impact of green alkyl chemistry processes remains a complex task. Life cycle analyses are crucial to ensure that seemingly green alternatives do not lead to unintended negative consequences in other areas of the production chain or product lifecycle.
In conclusion, while green alkyl chemistry has made significant progress, it continues to face multifaceted challenges. Overcoming these obstacles will require continued innovation in catalyst design, process engineering, and feedstock development, as well as a holistic approach to sustainability assessment.
One of the primary advancements in green alkyl chemistry is the development of more efficient catalysts that enable reactions to occur under milder conditions, reducing energy consumption and waste generation. These catalysts often incorporate transition metals or enzymes, allowing for highly selective transformations with minimal by-product formation.
Another area of progress is the utilization of renewable feedstocks as alternatives to petroleum-based starting materials. Biomass-derived alkyl compounds, such as those obtained from plant oils or lignocellulosic materials, are increasingly being explored as sustainable sources for various chemical processes.
Despite these advancements, several challenges persist in the field of green alkyl chemistry. One major hurdle is the scalability of green processes. Many environmentally friendly reactions that work well in laboratory settings face difficulties when scaled up to industrial production levels, often due to increased costs or reduced efficiency.
The development of truly sustainable solvents remains a significant challenge. While progress has been made in using water, supercritical CO2, and ionic liquids as green alternatives, finding solvents that are both environmentally benign and universally applicable across various alkyl chemistry processes is still an ongoing effort.
Another obstacle is the limited availability and higher cost of some bio-based feedstocks compared to their petroleum-derived counterparts. This economic barrier often hinders the widespread adoption of greener alkylation processes in industry.
The synthesis of complex alkyl compounds using green methodologies also presents challenges. Many traditional routes rely on multi-step processes with poor atom economy, and developing greener alternatives that maintain high yields and selectivity is an active area of research.
Lastly, the assessment of the overall environmental impact of green alkyl chemistry processes remains a complex task. Life cycle analyses are crucial to ensure that seemingly green alternatives do not lead to unintended negative consequences in other areas of the production chain or product lifecycle.
In conclusion, while green alkyl chemistry has made significant progress, it continues to face multifaceted challenges. Overcoming these obstacles will require continued innovation in catalyst design, process engineering, and feedstock development, as well as a holistic approach to sustainability assessment.
Existing Green Alkyl Synthesis Solutions
01 Alkyl-based chemical synthesis and modifications
This category focuses on the synthesis and modification of alkyl compounds, including various chemical reactions and processes involving alkyl groups. It encompasses the creation of new alkyl-based materials and the alteration of existing compounds through alkylation or other related chemical transformations.- Alkyl-based chemical reactions and synthesis: This category focuses on various chemical reactions and synthesis methods involving alkyl groups. It includes processes for creating alkyl compounds, modifying existing molecules with alkyl groups, and studying the reactivity of alkyl-containing substances. These reactions are fundamental in organic chemistry and have applications in pharmaceuticals, materials science, and industrial processes.
- Alkyl-modified materials and coatings: This area explores the use of alkyl groups to modify materials and create specialized coatings. By incorporating alkyl chains into polymers, surfaces, or nanoparticles, researchers can alter properties such as hydrophobicity, chemical resistance, and surface energy. These modifications have applications in areas like water-repellent fabrics, anti-fouling coatings, and advanced composite materials.
- Alkyl-based surfactants and emulsifiers: This category covers the development and application of alkyl-based surfactants and emulsifiers. These compounds, which typically contain both hydrophilic and hydrophobic (alkyl) portions, are crucial in formulating stable emulsions, detergents, and personal care products. Research in this area focuses on optimizing alkyl chain length and structure for specific applications and improving the environmental profile of these substances.
- Alkyl-functionalized catalysts and enzymes: This field involves the modification of catalysts and enzymes with alkyl groups to enhance their performance or specificity. By attaching alkyl chains to these biomolecules or synthetic catalysts, researchers can alter their solubility, stability, and catalytic properties. This approach is particularly relevant in biocatalysis, green chemistry, and the development of more efficient industrial processes.
- Analytical methods for alkyl compounds: This area focuses on developing and improving analytical techniques for detecting, quantifying, and characterizing alkyl compounds. It includes spectroscopic methods, chromatography, mass spectrometry, and other advanced analytical approaches tailored for alkyl-containing molecules. These methods are crucial for quality control in industries, environmental monitoring, and research in organic chemistry and related fields.
02 Applications of alkyl compounds in electronic devices
Alkyl chemistry plays a significant role in the development and improvement of electronic devices. This includes the use of alkyl-based materials in semiconductors, display technologies, and other electronic components. The unique properties of alkyl compounds contribute to enhanced performance and functionality in various electronic applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Alkyl-based materials in biotechnology and medical applications
This category explores the use of alkyl compounds in biotechnology and medical fields. It includes the development of alkyl-based drug delivery systems, biocompatible materials, and diagnostic tools. The chemical properties of alkyl groups are leveraged to create innovative solutions for various medical and biological challenges.Expand Specific Solutions04 Environmental applications of alkyl chemistry
Alkyl chemistry finds applications in environmental science and technology. This includes the development of alkyl-based materials for pollution control, water treatment, and sustainable chemical processes. The focus is on utilizing alkyl compounds to address environmental challenges and promote eco-friendly solutions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Analytical techniques in alkyl chemistry
This category covers analytical methods and techniques specifically developed or adapted for the study of alkyl compounds. It includes spectroscopic methods, chromatography techniques, and other analytical approaches used to characterize, identify, and quantify alkyl-based materials in various contexts.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Green Alkyl Chemistry Industry
The green development through alkyl chemistry is in an emerging stage, with growing market potential driven by sustainability demands. The technology is still evolving, with varying levels of maturity across different applications. Key players like Shell Oil Co., BASF Corp., and China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. are investing in research and development to advance alkyl-based green technologies. Academic institutions such as the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences and Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics are contributing to fundamental research. The competitive landscape is diverse, with both established petrochemical companies and specialized firms like Global Bioenergies SA exploring innovative approaches to sustainable alkyl chemistry applications.
Shell Oil Co.
Technical Solution: Shell has made significant strides in fostering green development through alkyl chemistry. The company has focused on developing more sustainable alkylation processes, including the implementation of their proprietary NEXALKYLATION™ technology. This solid catalyst alkylation process eliminates the use of liquid acids, reducing environmental and safety risks associated with traditional alkylation methods[10]. Shell has also invested in bio-based feedstocks for alkyl chemistry, exploring the production of renewable alkyl-based chemicals from biomass sources. Their research includes the development of bio-based lubricants and surfactants with improved biodegradability profiles[11]. Furthermore, Shell has implemented energy efficiency measures in their alkylation units, utilizing heat integration and advanced process control systems to reduce overall energy consumption and carbon footprint[12].
Strengths: Global presence, strong R&D capabilities, and diverse energy portfolio. Weaknesses: Balancing traditional oil and gas operations with green initiatives, potential public perception challenges.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF has developed a comprehensive approach to foster green development through alkyl chemistry. Their strategy includes the use of bio-based feedstocks, such as renewable raw materials, to produce alkyl-based chemicals. They have implemented a circular economy model, focusing on recycling and upcycling alkyl-based products[1]. BASF has also invested in catalytic processes that reduce energy consumption and increase selectivity in alkyl chemistry reactions. Their proprietary PolyTHF® technology, based on alkyl chemistry, enables the production of biodegradable plastics with reduced environmental impact[2]. Additionally, BASF has developed water-based alkyd resins that significantly reduce volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions in coatings and adhesives[3].
Strengths: Extensive R&D capabilities, global presence, and diverse product portfolio. Weaknesses: High capital investment required for green technologies, potential regulatory challenges in different markets.
Core Innovations in Green Alkyl Chemistry
Green chemistry method for one-pot synthesis of biologically active 1,1-di-, tri-, and tetra-substituted alkanes
PatentPendingIN202211031721A
Innovation
- A metal-free, one-pot synthesis method using Brønsted Acid Mediated Brønsted Acid Catalyzed Friedel Crafts Alkylation/arylation with feedstock aldehydes and ketones, employing a mixed solvent system and a super acidic system generated by fluoroalcohols and Brønsted acid catalysts like p-toluenesulfonic acid, allowing for the synthesis of symmetrical and unsymmetrical alkanes under ambient conditions.
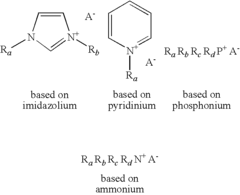
Alkyl H-phosphonates of N,N′-dialkylimidazoliums and of quaternary ammoniums and uses thereof
PatentInactiveUS8309736B2
Innovation
- A novel single-step synthesis method for salts associating an ammonium cation with an alkyl H-phosphonate anion, conducted in the absence of organic solvents, which results in room temperature ionic liquids (RTILHPAs) that are thermally stable, non-volatile, and non-flammable, with low viscosity and enhanced solvent properties.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental impact assessment of alkyl chemistry in fostering green development is a critical aspect that requires thorough examination. Alkyl compounds, widely used in various industries, have significant implications for the environment throughout their lifecycle. The production processes often involve energy-intensive reactions and the use of potentially hazardous raw materials, which can lead to greenhouse gas emissions and the generation of toxic by-products.
However, recent advancements in alkyl chemistry have shown promising potential for mitigating these environmental concerns. Green chemistry principles are being increasingly applied to alkyl synthesis, focusing on atom economy, waste reduction, and the use of renewable feedstocks. These approaches not only reduce the environmental footprint of production but also contribute to the overall sustainability of the chemical industry.
The application of alkyl compounds in end products also plays a crucial role in environmental impact. Many alkyl-based materials, such as biodegradable plastics and environmentally friendly lubricants, offer improved end-of-life scenarios compared to traditional petrochemical alternatives. These innovations contribute to reduced plastic pollution and decreased reliance on fossil fuel-derived products.
Water and soil contamination risks associated with alkyl compounds are being addressed through the development of more environmentally benign alternatives and improved waste management strategies. Advanced treatment technologies and stricter regulations are helping to minimize the release of harmful alkyl substances into ecosystems.
The life cycle assessment (LCA) of alkyl chemistry reveals both challenges and opportunities for green development. While some alkyl compounds may have negative environmental impacts during production or disposal, others demonstrate net positive effects when considering their entire lifecycle. For instance, certain alkyl-based materials used in renewable energy technologies or energy-efficient products can offset their initial environmental costs through long-term benefits.
Efforts to foster green development through alkyl chemistry also extend to the realm of catalysis. Novel alkyl-based catalysts are being developed to facilitate more efficient and environmentally friendly chemical processes. These catalysts often enable reactions to occur under milder conditions, reducing energy consumption and minimizing the formation of unwanted by-products.
In conclusion, the environmental impact assessment of alkyl chemistry in the context of green development reveals a complex landscape of challenges and opportunities. While historical practices have raised environmental concerns, ongoing research and innovation in this field are paving the way for more sustainable chemical processes and products. The continued focus on green alkyl chemistry holds promise for significantly reducing the environmental footprint of various industries and contributing to a more sustainable future.
However, recent advancements in alkyl chemistry have shown promising potential for mitigating these environmental concerns. Green chemistry principles are being increasingly applied to alkyl synthesis, focusing on atom economy, waste reduction, and the use of renewable feedstocks. These approaches not only reduce the environmental footprint of production but also contribute to the overall sustainability of the chemical industry.
The application of alkyl compounds in end products also plays a crucial role in environmental impact. Many alkyl-based materials, such as biodegradable plastics and environmentally friendly lubricants, offer improved end-of-life scenarios compared to traditional petrochemical alternatives. These innovations contribute to reduced plastic pollution and decreased reliance on fossil fuel-derived products.
Water and soil contamination risks associated with alkyl compounds are being addressed through the development of more environmentally benign alternatives and improved waste management strategies. Advanced treatment technologies and stricter regulations are helping to minimize the release of harmful alkyl substances into ecosystems.
The life cycle assessment (LCA) of alkyl chemistry reveals both challenges and opportunities for green development. While some alkyl compounds may have negative environmental impacts during production or disposal, others demonstrate net positive effects when considering their entire lifecycle. For instance, certain alkyl-based materials used in renewable energy technologies or energy-efficient products can offset their initial environmental costs through long-term benefits.
Efforts to foster green development through alkyl chemistry also extend to the realm of catalysis. Novel alkyl-based catalysts are being developed to facilitate more efficient and environmentally friendly chemical processes. These catalysts often enable reactions to occur under milder conditions, reducing energy consumption and minimizing the formation of unwanted by-products.
In conclusion, the environmental impact assessment of alkyl chemistry in the context of green development reveals a complex landscape of challenges and opportunities. While historical practices have raised environmental concerns, ongoing research and innovation in this field are paving the way for more sustainable chemical processes and products. The continued focus on green alkyl chemistry holds promise for significantly reducing the environmental footprint of various industries and contributing to a more sustainable future.
Policy and Regulatory Framework for Green Chemistry
The policy and regulatory framework for green chemistry plays a crucial role in fostering sustainable development through alkyl chemistry. Governments worldwide are increasingly recognizing the importance of promoting environmentally friendly practices in the chemical industry, leading to the implementation of various policies and regulations.
One of the key aspects of this framework is the establishment of comprehensive guidelines for the design, manufacture, and use of chemical products that reduce or eliminate the generation of hazardous substances. These guidelines often emphasize the principles of green chemistry, such as atom economy, waste prevention, and the use of renewable feedstocks. By incorporating these principles into regulatory frameworks, policymakers aim to encourage the development of safer and more sustainable alkyl chemistry processes.
Many countries have introduced legislation that mandates the reduction of harmful emissions and waste from chemical manufacturing processes. For instance, the European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation requires companies to assess and manage the risks associated with the chemicals they produce or import. This regulation has had a significant impact on the alkyl chemistry sector, pushing companies to invest in greener alternatives and more sustainable production methods.
In addition to regulatory measures, governments are also implementing incentive programs to promote green chemistry research and development. These programs often include tax credits, grants, and subsidies for companies that invest in eco-friendly technologies or develop innovative green chemistry solutions. Such incentives have been particularly effective in encouraging small and medium-sized enterprises to adopt more sustainable practices in alkyl chemistry.
The policy framework also extends to education and training initiatives. Many countries are incorporating green chemistry principles into their academic curricula and professional development programs. This approach aims to create a workforce that is well-versed in sustainable chemistry practices and capable of driving innovation in the field of alkyl chemistry.
International cooperation plays a vital role in shaping the global policy landscape for green chemistry. Organizations such as the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development) and the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) are working to harmonize green chemistry standards and promote best practices across borders. These efforts help create a level playing field for companies operating in different countries and facilitate the global adoption of sustainable alkyl chemistry practices.
As the field of green chemistry continues to evolve, policymakers are faced with the challenge of keeping regulations up-to-date with the latest technological advancements. This requires ongoing collaboration between government agencies, industry stakeholders, and academic institutions to ensure that policies remain effective and relevant in promoting sustainable development through alkyl chemistry.
One of the key aspects of this framework is the establishment of comprehensive guidelines for the design, manufacture, and use of chemical products that reduce or eliminate the generation of hazardous substances. These guidelines often emphasize the principles of green chemistry, such as atom economy, waste prevention, and the use of renewable feedstocks. By incorporating these principles into regulatory frameworks, policymakers aim to encourage the development of safer and more sustainable alkyl chemistry processes.
Many countries have introduced legislation that mandates the reduction of harmful emissions and waste from chemical manufacturing processes. For instance, the European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation requires companies to assess and manage the risks associated with the chemicals they produce or import. This regulation has had a significant impact on the alkyl chemistry sector, pushing companies to invest in greener alternatives and more sustainable production methods.
In addition to regulatory measures, governments are also implementing incentive programs to promote green chemistry research and development. These programs often include tax credits, grants, and subsidies for companies that invest in eco-friendly technologies or develop innovative green chemistry solutions. Such incentives have been particularly effective in encouraging small and medium-sized enterprises to adopt more sustainable practices in alkyl chemistry.
The policy framework also extends to education and training initiatives. Many countries are incorporating green chemistry principles into their academic curricula and professional development programs. This approach aims to create a workforce that is well-versed in sustainable chemistry practices and capable of driving innovation in the field of alkyl chemistry.
International cooperation plays a vital role in shaping the global policy landscape for green chemistry. Organizations such as the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development) and the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) are working to harmonize green chemistry standards and promote best practices across borders. These efforts help create a level playing field for companies operating in different countries and facilitate the global adoption of sustainable alkyl chemistry practices.
As the field of green chemistry continues to evolve, policymakers are faced with the challenge of keeping regulations up-to-date with the latest technological advancements. This requires ongoing collaboration between government agencies, industry stakeholders, and academic institutions to ensure that policies remain effective and relevant in promoting sustainable development through alkyl chemistry.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!