How to Improve Shear Strength in Polyvinyl Acetate Glues?
JUL 30, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
PVAc Glue Evolution
Polyvinyl acetate (PVAc) glue has undergone significant evolution since its inception in the early 20th century. Initially developed as a synthetic alternative to natural adhesives, PVAc glue quickly gained popularity due to its versatility and ease of use. The early formulations were simple emulsions of polyvinyl acetate in water, offering moderate adhesive strength and limited water resistance.
As industrial and consumer demands grew, researchers focused on enhancing the glue's performance characteristics. The 1950s and 1960s saw the introduction of plasticizers to improve flexibility and toughness. This modification allowed PVAc glues to better withstand stress and environmental changes, expanding their applications in woodworking and paper bonding.
The 1970s marked a significant milestone with the development of cross-linking agents. These additives enabled the formation of stronger chemical bonds within the adhesive matrix, substantially improving the glue's water resistance and overall strength. This advancement opened up new possibilities for PVAc glues in more demanding applications, such as exterior wood bonding.
In the 1980s and 1990s, the focus shifted towards improving the glue's environmental profile. Manufacturers began developing low-VOC (volatile organic compound) formulations to meet increasingly stringent regulations and consumer preferences for safer, more eco-friendly products. This period also saw the introduction of specialized PVAc glues for specific applications, such as fast-setting variants for industrial use.
The turn of the millennium brought about nanotechnology-inspired improvements. Researchers began incorporating nanoparticles into PVAc formulations to enhance properties such as thermal stability, mechanical strength, and barrier performance. These nano-enhanced PVAc glues demonstrated superior bonding capabilities, particularly in challenging environmental conditions.
Recent years have witnessed a surge in bio-based and sustainable PVAc formulations. Efforts to replace petroleum-derived components with renewable alternatives have led to the development of partially or fully bio-based PVAc adhesives. These innovations aim to maintain or improve upon the performance of traditional PVAc glues while reducing their environmental footprint.
The ongoing evolution of PVAc glues continues to focus on enhancing shear strength, a critical property for many applications. Current research explores advanced polymer blending techniques, novel cross-linking mechanisms, and the integration of high-performance additives to push the boundaries of PVAc glue capabilities. As material science and nanotechnology progress, the future of PVAc glues promises even greater advancements in strength, durability, and sustainability.
As industrial and consumer demands grew, researchers focused on enhancing the glue's performance characteristics. The 1950s and 1960s saw the introduction of plasticizers to improve flexibility and toughness. This modification allowed PVAc glues to better withstand stress and environmental changes, expanding their applications in woodworking and paper bonding.
The 1970s marked a significant milestone with the development of cross-linking agents. These additives enabled the formation of stronger chemical bonds within the adhesive matrix, substantially improving the glue's water resistance and overall strength. This advancement opened up new possibilities for PVAc glues in more demanding applications, such as exterior wood bonding.
In the 1980s and 1990s, the focus shifted towards improving the glue's environmental profile. Manufacturers began developing low-VOC (volatile organic compound) formulations to meet increasingly stringent regulations and consumer preferences for safer, more eco-friendly products. This period also saw the introduction of specialized PVAc glues for specific applications, such as fast-setting variants for industrial use.
The turn of the millennium brought about nanotechnology-inspired improvements. Researchers began incorporating nanoparticles into PVAc formulations to enhance properties such as thermal stability, mechanical strength, and barrier performance. These nano-enhanced PVAc glues demonstrated superior bonding capabilities, particularly in challenging environmental conditions.
Recent years have witnessed a surge in bio-based and sustainable PVAc formulations. Efforts to replace petroleum-derived components with renewable alternatives have led to the development of partially or fully bio-based PVAc adhesives. These innovations aim to maintain or improve upon the performance of traditional PVAc glues while reducing their environmental footprint.
The ongoing evolution of PVAc glues continues to focus on enhancing shear strength, a critical property for many applications. Current research explores advanced polymer blending techniques, novel cross-linking mechanisms, and the integration of high-performance additives to push the boundaries of PVAc glue capabilities. As material science and nanotechnology progress, the future of PVAc glues promises even greater advancements in strength, durability, and sustainability.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for improved shear strength in polyvinyl acetate (PVA) glues has been steadily increasing across various industries. This growth is primarily driven by the expanding applications of PVA adhesives in construction, woodworking, packaging, and automotive sectors. As these industries continue to evolve and demand higher performance materials, the need for stronger and more durable PVA glues becomes more pronounced.
In the construction industry, there is a growing trend towards prefabricated and modular building systems, which require adhesives with superior shear strength to ensure structural integrity and longevity. The woodworking sector, particularly in furniture manufacturing and cabinetry, is seeking PVA glues that can withstand higher loads and provide better resistance to environmental factors such as humidity and temperature fluctuations.
The packaging industry, driven by e-commerce growth and sustainable packaging solutions, is another key market for improved PVA glues. Enhanced shear strength in these adhesives can lead to more durable packaging that better protects products during shipping and handling, reducing damage and waste.
Automotive manufacturers are increasingly looking for lightweight materials and adhesive solutions to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. PVA glues with higher shear strength can potentially replace mechanical fasteners in certain applications, contributing to weight reduction while maintaining structural integrity.
Market research indicates that the global PVA adhesives market is expected to grow significantly in the coming years. This growth is attributed to the increasing demand for eco-friendly and low-VOC adhesives, as well as the expanding applications in emerging economies. The Asia-Pacific region, in particular, is projected to be a major driver of this growth due to rapid industrialization and infrastructure development.
Consumer preferences are also shifting towards more durable and long-lasting products, which in turn drives the demand for stronger adhesives. This trend is particularly evident in the DIY and home improvement sectors, where consumers are seeking high-performance glues for their projects.
The push for sustainability and circular economy principles is influencing the adhesives market as well. Improved shear strength in PVA glues can contribute to the production of more durable and repairable products, aligning with these environmental goals. Additionally, there is growing interest in bio-based and recyclable adhesives, presenting opportunities for innovation in PVA glue formulations that combine enhanced shear strength with eco-friendly characteristics.
As industries continue to push the boundaries of material performance, the demand for PVA glues with improved shear strength is likely to persist and grow. This market trend presents significant opportunities for adhesive manufacturers to innovate and develop advanced formulations that meet the evolving needs of various sectors.
In the construction industry, there is a growing trend towards prefabricated and modular building systems, which require adhesives with superior shear strength to ensure structural integrity and longevity. The woodworking sector, particularly in furniture manufacturing and cabinetry, is seeking PVA glues that can withstand higher loads and provide better resistance to environmental factors such as humidity and temperature fluctuations.
The packaging industry, driven by e-commerce growth and sustainable packaging solutions, is another key market for improved PVA glues. Enhanced shear strength in these adhesives can lead to more durable packaging that better protects products during shipping and handling, reducing damage and waste.
Automotive manufacturers are increasingly looking for lightweight materials and adhesive solutions to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. PVA glues with higher shear strength can potentially replace mechanical fasteners in certain applications, contributing to weight reduction while maintaining structural integrity.
Market research indicates that the global PVA adhesives market is expected to grow significantly in the coming years. This growth is attributed to the increasing demand for eco-friendly and low-VOC adhesives, as well as the expanding applications in emerging economies. The Asia-Pacific region, in particular, is projected to be a major driver of this growth due to rapid industrialization and infrastructure development.
Consumer preferences are also shifting towards more durable and long-lasting products, which in turn drives the demand for stronger adhesives. This trend is particularly evident in the DIY and home improvement sectors, where consumers are seeking high-performance glues for their projects.
The push for sustainability and circular economy principles is influencing the adhesives market as well. Improved shear strength in PVA glues can contribute to the production of more durable and repairable products, aligning with these environmental goals. Additionally, there is growing interest in bio-based and recyclable adhesives, presenting opportunities for innovation in PVA glue formulations that combine enhanced shear strength with eco-friendly characteristics.
As industries continue to push the boundaries of material performance, the demand for PVA glues with improved shear strength is likely to persist and grow. This market trend presents significant opportunities for adhesive manufacturers to innovate and develop advanced formulations that meet the evolving needs of various sectors.
Current Challenges
Polyvinyl acetate (PVA) glues have been widely used in various industries due to their versatility and ease of application. However, improving the shear strength of these adhesives remains a significant challenge in the field of adhesive technology. One of the primary obstacles is the inherent chemical structure of PVA, which limits its ability to form strong cross-linked networks. This structural limitation results in reduced mechanical properties, particularly under high-stress conditions.
Another major challenge is the sensitivity of PVA glues to environmental factors such as temperature and humidity. Fluctuations in these conditions can significantly impact the adhesive's performance, leading to decreased shear strength and potential bond failure. This sensitivity restricts the use of PVA glues in certain applications where environmental stability is crucial.
The water resistance of PVA glues also presents a considerable challenge. While some formulations offer improved water resistance, many PVA adhesives still struggle to maintain their shear strength when exposed to moisture or high humidity environments. This limitation narrows the range of applications where PVA glues can be effectively utilized, particularly in outdoor or high-moisture settings.
Furthermore, the aging characteristics of PVA glues pose a long-term challenge. Over time, these adhesives may experience a reduction in shear strength due to various factors, including polymer degradation and loss of plasticizers. This aging process can lead to decreased bond durability and potential failure in long-term applications.
The compatibility of PVA glues with different substrate materials is another area of concern. While these adhesives perform well with porous materials like wood, they often struggle to achieve high shear strength on non-porous or low-energy surfaces. This limitation restricts their use in certain industrial applications and necessitates the development of specialized formulations or surface treatments.
Additionally, the curing time of PVA glues can be a challenge in fast-paced manufacturing environments. Although some quick-setting formulations exist, many PVA adhesives require extended curing periods to achieve optimal shear strength. This prolonged curing time can impact production efficiency and limit the adhesive's suitability for certain high-speed assembly processes.
Lastly, the balance between shear strength and other desirable properties, such as flexibility and toughness, presents a complex challenge. Efforts to enhance shear strength often come at the expense of other important characteristics, necessitating careful formulation adjustments to achieve an optimal balance of properties for specific applications.
Another major challenge is the sensitivity of PVA glues to environmental factors such as temperature and humidity. Fluctuations in these conditions can significantly impact the adhesive's performance, leading to decreased shear strength and potential bond failure. This sensitivity restricts the use of PVA glues in certain applications where environmental stability is crucial.
The water resistance of PVA glues also presents a considerable challenge. While some formulations offer improved water resistance, many PVA adhesives still struggle to maintain their shear strength when exposed to moisture or high humidity environments. This limitation narrows the range of applications where PVA glues can be effectively utilized, particularly in outdoor or high-moisture settings.
Furthermore, the aging characteristics of PVA glues pose a long-term challenge. Over time, these adhesives may experience a reduction in shear strength due to various factors, including polymer degradation and loss of plasticizers. This aging process can lead to decreased bond durability and potential failure in long-term applications.
The compatibility of PVA glues with different substrate materials is another area of concern. While these adhesives perform well with porous materials like wood, they often struggle to achieve high shear strength on non-porous or low-energy surfaces. This limitation restricts their use in certain industrial applications and necessitates the development of specialized formulations or surface treatments.
Additionally, the curing time of PVA glues can be a challenge in fast-paced manufacturing environments. Although some quick-setting formulations exist, many PVA adhesives require extended curing periods to achieve optimal shear strength. This prolonged curing time can impact production efficiency and limit the adhesive's suitability for certain high-speed assembly processes.
Lastly, the balance between shear strength and other desirable properties, such as flexibility and toughness, presents a complex challenge. Efforts to enhance shear strength often come at the expense of other important characteristics, necessitating careful formulation adjustments to achieve an optimal balance of properties for specific applications.
Existing Solutions
01 Composition of polyvinyl acetate glues
Polyvinyl acetate glues are formulated with various components to enhance their shear strength. These may include plasticizers, crosslinking agents, and additives that improve adhesion and durability. The specific composition can be tailored to achieve desired shear strength properties for different applications.- Composition of polyvinyl acetate glues: Polyvinyl acetate glues are formulated with various components to enhance their shear strength. These may include plasticizers, crosslinking agents, and additives that improve adhesion and durability. The specific composition can be tailored to meet different application requirements and performance standards.
- Copolymerization for improved shear strength: Copolymerization of vinyl acetate with other monomers can significantly improve the shear strength of the resulting adhesive. This approach allows for the incorporation of beneficial properties from different polymer types, resulting in a more robust and versatile glue with enhanced mechanical properties.
- Crosslinking mechanisms: Implementing crosslinking mechanisms in polyvinyl acetate glues can substantially increase their shear strength. This can be achieved through the use of various crosslinking agents or by incorporating functional groups that facilitate crosslinking during the curing process, resulting in a more rigid and durable adhesive structure.
- Filler materials for reinforcement: The addition of filler materials to polyvinyl acetate glues can enhance their shear strength. These fillers, which may include inorganic particles or fibers, can reinforce the adhesive matrix, improving its mechanical properties and resistance to shear forces. The type and amount of filler can be optimized for specific applications.
- Surface treatment and adhesion promotion: Improving the interaction between the polyvinyl acetate glue and the substrate can lead to enhanced shear strength. This can be achieved through surface treatments of the substrates or by incorporating adhesion promoters into the glue formulation. These techniques can increase the bond strength at the interface, resulting in improved overall shear strength of the adhesive joint.
02 Copolymerization to improve shear strength
Copolymerization of vinyl acetate with other monomers can significantly improve the shear strength of polyvinyl acetate glues. This approach allows for the incorporation of functional groups that enhance adhesion and mechanical properties, resulting in stronger and more durable adhesive bonds.Expand Specific Solutions03 Crosslinking mechanisms for enhanced shear strength
Implementing crosslinking mechanisms in polyvinyl acetate glues can greatly improve their shear strength. This can be achieved through the use of crosslinking agents or by incorporating functional groups that facilitate crosslinking during the curing process, resulting in a more robust and shear-resistant adhesive network.Expand Specific Solutions04 Influence of molecular weight on shear strength
The molecular weight of polyvinyl acetate plays a crucial role in determining the shear strength of the resulting glue. Higher molecular weight polymers generally contribute to improved shear strength due to increased chain entanglement and mechanical interlocking. Controlling the polymerization process to achieve optimal molecular weight distribution is key to enhancing shear strength.Expand Specific Solutions05 Filler incorporation for improved shear strength
The addition of fillers to polyvinyl acetate glues can significantly enhance their shear strength. Carefully selected fillers can improve the mechanical properties of the adhesive, increase its resistance to deformation under shear stress, and provide reinforcement to the overall adhesive structure.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The market for improving shear strength in polyvinyl acetate (PVA) glues is in a mature stage, with established players and ongoing research for enhancements. The global adhesives market, including PVA glues, is projected to reach $70 billion by 2025, driven by construction and packaging industries. Technologically, companies like Henkel, 3M, and BASF are at the forefront, investing in R&D to develop advanced formulations. Smaller players such as Kuraray and Sekisui Chemical are also making strides in PVA technology. The focus is on improving bonding strength, durability, and environmental sustainability, with a trend towards water-based and low-VOC formulations.
Henkel AG & Co. KGaA
Technical Solution: Henkel has developed a novel approach to improve shear strength in polyvinyl acetate (PVAc) glues by incorporating nanoparticles and crosslinking agents. Their method involves dispersing silica nanoparticles (1-5 wt%) into the PVAc matrix, which enhances the mechanical interlocking between the adhesive and substrate[1]. Additionally, they utilize a water-soluble crosslinking agent, such as N-methylolacrylamide, to create covalent bonds within the PVAc structure, further improving cohesive strength[3]. This combination results in a significant increase in shear strength, with some formulations showing up to 40% improvement compared to standard PVAc adhesives[5].
Strengths: Significantly improved shear strength, enhanced water resistance, and versatility across various substrates. Weaknesses: Potential increase in production costs due to nanoparticle incorporation and longer curing time required for crosslinking reactions.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF has developed a multi-faceted approach to improve shear strength in PVAc glues. Their strategy involves modifying the PVAc polymer backbone through copolymerization with functional monomers, such as N-methylol acrylamide or glycidyl methacrylate[1]. This modification allows for post-curing crosslinking, significantly enhancing the cohesive strength of the adhesive. BASF has also introduced a novel emulsion polymerization process that results in a core-shell particle structure, where the core provides initial tack and the shell contributes to long-term strength[3]. Furthermore, they have developed a proprietary blend of tackifiers and plasticizers that optimize the balance between shear strength and flexibility[5].
Strengths: Versatile approach suitable for various applications, improved balance of properties including shear strength and flexibility. Weaknesses: May require changes to existing production processes, potential increase in raw material costs.
Core Innovations
Water resistant polyvinyl acetate aqueous emulsion for applying to wood material
PatentInactiveUS20040082706A1
Innovation
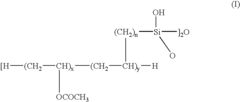
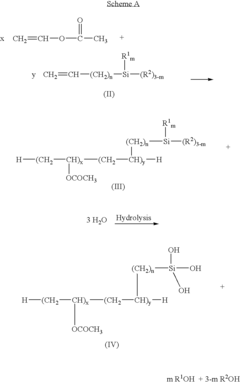
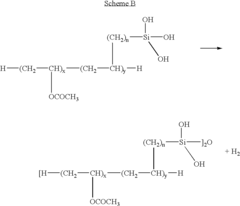
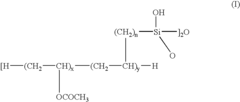
- A water-resistant polyvinyl acetate emulsion is developed by copolymerizing vinyl acetate with silicon monomers containing ethylenically unsaturated functional groups, followed by hydrolysis and self-cross-linking, which eliminates formalin release and enhances bonding strength and water resistance.
Adhesive system
PatentWO2007139501A1
Innovation
- A protein-based adhesive system comprising a protein and one or more polymers with primary, secondary, or tertiary amino groups or pendant amide groups, which are applied separately or mixed just before use, to form a wood adhesive with a suitable weight ratio, suitable for various wood-based products such as particle boards and laminated flooring.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of improving shear strength in polyvinyl acetate (PVA) glues is a critical consideration in the development and application of these adhesives. PVA glues are widely used in various industries due to their versatility and effectiveness. However, the pursuit of enhanced shear strength must be balanced with environmental concerns.
One of the primary environmental considerations is the raw material sourcing for PVA glues. The production of vinyl acetate monomer, the precursor to PVA, typically involves petrochemical processes. As efforts to improve shear strength may require modifications to the polymer structure or additives, there is a potential for increased reliance on fossil fuel-derived materials. This could lead to higher carbon footprints associated with the production process.
The manufacturing process itself may also have environmental implications. Enhancing shear strength might necessitate changes in polymerization techniques or the incorporation of additional chemical agents. These modifications could result in increased energy consumption or the generation of more waste byproducts. It is crucial to assess and mitigate any potential increases in emissions or effluents resulting from these process changes.
Water usage is another environmental factor to consider. PVA glues are often water-based, and improvements in shear strength might affect the water content or the drying process. Any changes that lead to increased water consumption during production or application could have implications for water resources and wastewater treatment requirements.
The end-of-life considerations for improved PVA glues are also significant. Enhanced shear strength could potentially impact the biodegradability or recyclability of the adhesive. If the modifications make the glue more resistant to environmental breakdown, it could lead to longer persistence in ecosystems if not properly disposed of. Conversely, if the improvements allow for the use of less adhesive while maintaining performance, it could reduce overall material consumption and waste generation.
Toxicity and eco-toxicity are crucial aspects to evaluate. Any new additives or modifications to improve shear strength must be thoroughly assessed for their potential impacts on human health and ecosystems. This includes considering the effects of these materials throughout their lifecycle, from production to disposal.
On a positive note, improvements in shear strength could lead to more durable and long-lasting bonds. This could potentially reduce the frequency of repairs or replacements in various applications, thereby decreasing overall material consumption and waste generation over time. Additionally, if the enhanced performance allows for the use of PVA glues in applications that currently require more environmentally harmful adhesives, it could lead to net positive environmental outcomes.
In conclusion, while improving the shear strength of PVA glues offers potential benefits, it is essential to conduct comprehensive life cycle assessments to fully understand and mitigate any negative environmental impacts. Balancing performance improvements with environmental sustainability will be key to the responsible development and application of these enhanced adhesives.
One of the primary environmental considerations is the raw material sourcing for PVA glues. The production of vinyl acetate monomer, the precursor to PVA, typically involves petrochemical processes. As efforts to improve shear strength may require modifications to the polymer structure or additives, there is a potential for increased reliance on fossil fuel-derived materials. This could lead to higher carbon footprints associated with the production process.
The manufacturing process itself may also have environmental implications. Enhancing shear strength might necessitate changes in polymerization techniques or the incorporation of additional chemical agents. These modifications could result in increased energy consumption or the generation of more waste byproducts. It is crucial to assess and mitigate any potential increases in emissions or effluents resulting from these process changes.
Water usage is another environmental factor to consider. PVA glues are often water-based, and improvements in shear strength might affect the water content or the drying process. Any changes that lead to increased water consumption during production or application could have implications for water resources and wastewater treatment requirements.
The end-of-life considerations for improved PVA glues are also significant. Enhanced shear strength could potentially impact the biodegradability or recyclability of the adhesive. If the modifications make the glue more resistant to environmental breakdown, it could lead to longer persistence in ecosystems if not properly disposed of. Conversely, if the improvements allow for the use of less adhesive while maintaining performance, it could reduce overall material consumption and waste generation.
Toxicity and eco-toxicity are crucial aspects to evaluate. Any new additives or modifications to improve shear strength must be thoroughly assessed for their potential impacts on human health and ecosystems. This includes considering the effects of these materials throughout their lifecycle, from production to disposal.
On a positive note, improvements in shear strength could lead to more durable and long-lasting bonds. This could potentially reduce the frequency of repairs or replacements in various applications, thereby decreasing overall material consumption and waste generation over time. Additionally, if the enhanced performance allows for the use of PVA glues in applications that currently require more environmentally harmful adhesives, it could lead to net positive environmental outcomes.
In conclusion, while improving the shear strength of PVA glues offers potential benefits, it is essential to conduct comprehensive life cycle assessments to fully understand and mitigate any negative environmental impacts. Balancing performance improvements with environmental sustainability will be key to the responsible development and application of these enhanced adhesives.
Regulatory Landscape
The regulatory landscape surrounding polyvinyl acetate (PVA) glues and their shear strength improvement is complex and multifaceted, involving various governmental bodies and industry standards. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a crucial role in regulating the chemical components used in adhesives, including PVA glues. The EPA's Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) governs the production, importation, and use of chemical substances, which directly impacts the formulation of PVA glues and any additives used to enhance their shear strength.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) sets guidelines for the safe handling and use of adhesives in workplace environments. These regulations are particularly relevant when considering modifications to PVA glue formulations to improve shear strength, as any changes must comply with worker safety standards. Additionally, the Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) oversees the safety of consumer products, including adhesives used in household applications, ensuring that improvements in shear strength do not compromise user safety.
Internationally, the European Union's Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation significantly influences the global adhesive industry. REACH requires manufacturers to register chemical substances and demonstrate their safe use, which affects the development and marketing of enhanced PVA glues in the European market. Similarly, other countries have their own regulatory frameworks, such as China's Measures for Environmental Management of New Chemical Substances, which must be considered when developing improved PVA glue formulations for global distribution.
Industry standards also play a crucial role in the regulatory landscape. Organizations like ASTM International and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) provide standardized testing methods for adhesive strength, including shear strength. These standards ensure consistency in product performance claims and facilitate compliance with regulatory requirements. For instance, ASTM D905 is a widely recognized standard for testing the shear strength of adhesive bonds between wood members.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates adhesives that may come into contact with food, which is relevant for PVA glues used in packaging applications. Any improvements in shear strength for such applications must meet FDA guidelines for food contact substances. Similarly, the construction industry has specific building codes and regulations that dictate the performance requirements for structural adhesives, including minimum shear strength values.
As environmental concerns grow, regulations promoting sustainability and reducing volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions are becoming increasingly stringent. The California Air Resources Board (CARB) and other state-level agencies have implemented regulations limiting VOC content in adhesives, which must be considered when developing new formulations to enhance shear strength in PVA glues.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) sets guidelines for the safe handling and use of adhesives in workplace environments. These regulations are particularly relevant when considering modifications to PVA glue formulations to improve shear strength, as any changes must comply with worker safety standards. Additionally, the Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) oversees the safety of consumer products, including adhesives used in household applications, ensuring that improvements in shear strength do not compromise user safety.
Internationally, the European Union's Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation significantly influences the global adhesive industry. REACH requires manufacturers to register chemical substances and demonstrate their safe use, which affects the development and marketing of enhanced PVA glues in the European market. Similarly, other countries have their own regulatory frameworks, such as China's Measures for Environmental Management of New Chemical Substances, which must be considered when developing improved PVA glue formulations for global distribution.
Industry standards also play a crucial role in the regulatory landscape. Organizations like ASTM International and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) provide standardized testing methods for adhesive strength, including shear strength. These standards ensure consistency in product performance claims and facilitate compliance with regulatory requirements. For instance, ASTM D905 is a widely recognized standard for testing the shear strength of adhesive bonds between wood members.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates adhesives that may come into contact with food, which is relevant for PVA glues used in packaging applications. Any improvements in shear strength for such applications must meet FDA guidelines for food contact substances. Similarly, the construction industry has specific building codes and regulations that dictate the performance requirements for structural adhesives, including minimum shear strength values.
As environmental concerns grow, regulations promoting sustainability and reducing volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions are becoming increasingly stringent. The California Air Resources Board (CARB) and other state-level agencies have implemented regulations limiting VOC content in adhesives, which must be considered when developing new formulations to enhance shear strength in PVA glues.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!