Polyvinyl Acetate in Healthcare Adhesives: Safety and Innovations
JUL 30, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
PVAc in Healthcare: Background and Objectives
Polyvinyl acetate (PVAc) has emerged as a significant material in healthcare adhesives, with a history dating back to the early 20th century. Initially developed for industrial applications, PVAc's unique properties have led to its widespread adoption in medical and healthcare settings. The evolution of PVAc in healthcare adhesives has been driven by the increasing demand for safe, effective, and versatile bonding solutions in medical devices, wound care, and drug delivery systems.
The primary objective of utilizing PVAc in healthcare adhesives is to provide a biocompatible, non-toxic, and easily applicable bonding agent that meets the stringent requirements of medical applications. PVAc offers excellent adhesion to various substrates, including skin, while maintaining flexibility and moisture resistance. These characteristics make it particularly suitable for use in transdermal patches, wound dressings, and surgical tapes.
In recent years, the focus on PVAc in healthcare has shifted towards enhancing its performance and addressing specific medical needs. Researchers and manufacturers are exploring ways to improve PVAc's antimicrobial properties, reduce skin irritation, and increase its durability in challenging environments such as high-moisture areas of the body. Additionally, there is a growing interest in developing PVAc-based adhesives that can facilitate controlled drug release, potentially revolutionizing drug delivery methods.
The technological trajectory of PVAc in healthcare adhesives is closely aligned with broader trends in medical technology, including the push for personalized medicine and minimally invasive treatments. As such, current research aims to create smart PVAc adhesives that can respond to physiological changes, monitor patient health, or deliver medications on-demand. These innovations could significantly impact patient care and treatment outcomes across various medical specialties.
Safety considerations remain paramount in the development and application of PVAc-based healthcare adhesives. Regulatory bodies worldwide have established strict guidelines for the use of adhesives in medical products, necessitating rigorous testing and validation processes. The ongoing challenge for researchers and manufacturers is to balance the adhesive performance of PVAc with its biocompatibility and safety profile, ensuring that it meets or exceeds regulatory standards while providing optimal functionality in diverse healthcare applications.
As we look to the future, the continued evolution of PVAc in healthcare adhesives is expected to play a crucial role in advancing medical technologies. The potential for creating multifunctional adhesives that not only bond effectively but also contribute actively to patient care represents an exciting frontier in healthcare innovation. This trajectory underscores the importance of ongoing research and development in PVAc-based adhesives, with the ultimate goal of improving patient outcomes and expanding the possibilities of medical treatment.
The primary objective of utilizing PVAc in healthcare adhesives is to provide a biocompatible, non-toxic, and easily applicable bonding agent that meets the stringent requirements of medical applications. PVAc offers excellent adhesion to various substrates, including skin, while maintaining flexibility and moisture resistance. These characteristics make it particularly suitable for use in transdermal patches, wound dressings, and surgical tapes.
In recent years, the focus on PVAc in healthcare has shifted towards enhancing its performance and addressing specific medical needs. Researchers and manufacturers are exploring ways to improve PVAc's antimicrobial properties, reduce skin irritation, and increase its durability in challenging environments such as high-moisture areas of the body. Additionally, there is a growing interest in developing PVAc-based adhesives that can facilitate controlled drug release, potentially revolutionizing drug delivery methods.
The technological trajectory of PVAc in healthcare adhesives is closely aligned with broader trends in medical technology, including the push for personalized medicine and minimally invasive treatments. As such, current research aims to create smart PVAc adhesives that can respond to physiological changes, monitor patient health, or deliver medications on-demand. These innovations could significantly impact patient care and treatment outcomes across various medical specialties.
Safety considerations remain paramount in the development and application of PVAc-based healthcare adhesives. Regulatory bodies worldwide have established strict guidelines for the use of adhesives in medical products, necessitating rigorous testing and validation processes. The ongoing challenge for researchers and manufacturers is to balance the adhesive performance of PVAc with its biocompatibility and safety profile, ensuring that it meets or exceeds regulatory standards while providing optimal functionality in diverse healthcare applications.
As we look to the future, the continued evolution of PVAc in healthcare adhesives is expected to play a crucial role in advancing medical technologies. The potential for creating multifunctional adhesives that not only bond effectively but also contribute actively to patient care represents an exciting frontier in healthcare innovation. This trajectory underscores the importance of ongoing research and development in PVAc-based adhesives, with the ultimate goal of improving patient outcomes and expanding the possibilities of medical treatment.
Market Analysis for Medical Adhesives
The medical adhesives market has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing demand for advanced wound care products, surgical procedures, and medical devices. This market segment is characterized by a diverse range of products, including acrylic, silicone, cyanoacrylate, and polyvinyl acetate-based adhesives, each catering to specific healthcare applications.
The global medical adhesives market size was valued at approximately $8.1 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $13.5 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 7.5% during the forecast period. This growth is primarily attributed to the rising geriatric population, increasing surgical procedures, and the growing prevalence of chronic wounds and injuries.
Polyvinyl acetate (PVA) adhesives, in particular, have gained traction in the healthcare sector due to their biocompatibility, low toxicity, and versatile application methods. The PVA segment within the medical adhesives market is expected to witness steady growth, driven by its use in wound dressings, transdermal patches, and medical tapes.
Geographically, North America dominates the medical adhesives market, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The United States, in particular, holds a significant market share due to its advanced healthcare infrastructure and high healthcare expenditure. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific, such as China and India, are expected to exhibit the highest growth rates in the coming years, fueled by improving healthcare facilities and increasing medical tourism.
Key market players in the medical adhesives sector include 3M Company, Johnson & Johnson, Becton, Dickinson and Company, and Baxter International Inc. These companies are actively investing in research and development to introduce innovative adhesive solutions that address specific healthcare needs, such as antimicrobial properties and enhanced skin compatibility.
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a mixed impact on the medical adhesives market. While elective surgeries were postponed, leading to a temporary decline in demand, the increased focus on wound care and hygiene products has offset some of the negative effects. The pandemic has also accelerated the development of adhesives with antimicrobial properties, addressing the growing concern for infection control in healthcare settings.
Looking ahead, the medical adhesives market is poised for continued growth, driven by technological advancements, increasing healthcare expenditure, and the growing adoption of minimally invasive surgical procedures. The development of bio-based and environmentally friendly adhesives is expected to create new opportunities in the market, aligning with the global trend towards sustainability in healthcare products.
The global medical adhesives market size was valued at approximately $8.1 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $13.5 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 7.5% during the forecast period. This growth is primarily attributed to the rising geriatric population, increasing surgical procedures, and the growing prevalence of chronic wounds and injuries.
Polyvinyl acetate (PVA) adhesives, in particular, have gained traction in the healthcare sector due to their biocompatibility, low toxicity, and versatile application methods. The PVA segment within the medical adhesives market is expected to witness steady growth, driven by its use in wound dressings, transdermal patches, and medical tapes.
Geographically, North America dominates the medical adhesives market, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The United States, in particular, holds a significant market share due to its advanced healthcare infrastructure and high healthcare expenditure. However, emerging economies in Asia-Pacific, such as China and India, are expected to exhibit the highest growth rates in the coming years, fueled by improving healthcare facilities and increasing medical tourism.
Key market players in the medical adhesives sector include 3M Company, Johnson & Johnson, Becton, Dickinson and Company, and Baxter International Inc. These companies are actively investing in research and development to introduce innovative adhesive solutions that address specific healthcare needs, such as antimicrobial properties and enhanced skin compatibility.
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a mixed impact on the medical adhesives market. While elective surgeries were postponed, leading to a temporary decline in demand, the increased focus on wound care and hygiene products has offset some of the negative effects. The pandemic has also accelerated the development of adhesives with antimicrobial properties, addressing the growing concern for infection control in healthcare settings.
Looking ahead, the medical adhesives market is poised for continued growth, driven by technological advancements, increasing healthcare expenditure, and the growing adoption of minimally invasive surgical procedures. The development of bio-based and environmentally friendly adhesives is expected to create new opportunities in the market, aligning with the global trend towards sustainability in healthcare products.
PVAc Safety Challenges in Healthcare
Polyvinyl acetate (PVAc) has been widely used in healthcare adhesives due to its versatility and effectiveness. However, its application in medical settings presents several safety challenges that need to be addressed. One of the primary concerns is the potential for allergic reactions in patients. While PVAc is generally considered non-toxic, some individuals may develop sensitivities or allergies to the compound or its additives, leading to skin irritation, rashes, or more severe allergic responses.
Another significant safety challenge is the risk of infection associated with PVAc-based adhesives. In healthcare settings, maintaining a sterile environment is crucial, and any adhesive used must not compromise this sterility. PVAc adhesives may create micro-environments that can harbor bacteria or other pathogens, potentially leading to healthcare-associated infections. This risk is particularly pronounced in wound care applications or when used near surgical sites.
The long-term effects of PVAc exposure in healthcare settings are also a concern. While acute toxicity is low, the cumulative effects of prolonged exposure to PVAc and its degradation products are not fully understood. This is especially relevant for healthcare workers who may have frequent contact with these adhesives over extended periods.
Biocompatibility is another critical safety challenge. PVAc-based adhesives must be compatible with human tissues and not cause adverse reactions when in direct contact with the body. This includes ensuring that the adhesive does not leach harmful substances into the body or interfere with the natural healing processes.
The stability and degradation of PVAc adhesives in various healthcare environments pose additional safety concerns. Exposure to bodily fluids, temperature fluctuations, and sterilization processes can affect the adhesive's integrity and performance. This may lead to premature failure of medical devices or dressings, potentially compromising patient care and safety.
Environmental and disposal considerations also present challenges. As healthcare facilities strive to reduce their environmental impact, the safe disposal of PVAc-containing medical waste becomes increasingly important. Proper protocols must be developed to handle and dispose of these materials without causing harm to the environment or human health.
Addressing these safety challenges requires ongoing research and innovation in PVAc formulations and applications. This includes developing hypoallergenic variants, improving antimicrobial properties, enhancing biocompatibility, and creating more environmentally friendly disposal methods. As the healthcare industry continues to evolve, so too must the safety standards and practices surrounding the use of PVAc in medical adhesives.
Another significant safety challenge is the risk of infection associated with PVAc-based adhesives. In healthcare settings, maintaining a sterile environment is crucial, and any adhesive used must not compromise this sterility. PVAc adhesives may create micro-environments that can harbor bacteria or other pathogens, potentially leading to healthcare-associated infections. This risk is particularly pronounced in wound care applications or when used near surgical sites.
The long-term effects of PVAc exposure in healthcare settings are also a concern. While acute toxicity is low, the cumulative effects of prolonged exposure to PVAc and its degradation products are not fully understood. This is especially relevant for healthcare workers who may have frequent contact with these adhesives over extended periods.
Biocompatibility is another critical safety challenge. PVAc-based adhesives must be compatible with human tissues and not cause adverse reactions when in direct contact with the body. This includes ensuring that the adhesive does not leach harmful substances into the body or interfere with the natural healing processes.
The stability and degradation of PVAc adhesives in various healthcare environments pose additional safety concerns. Exposure to bodily fluids, temperature fluctuations, and sterilization processes can affect the adhesive's integrity and performance. This may lead to premature failure of medical devices or dressings, potentially compromising patient care and safety.
Environmental and disposal considerations also present challenges. As healthcare facilities strive to reduce their environmental impact, the safe disposal of PVAc-containing medical waste becomes increasingly important. Proper protocols must be developed to handle and dispose of these materials without causing harm to the environment or human health.
Addressing these safety challenges requires ongoing research and innovation in PVAc formulations and applications. This includes developing hypoallergenic variants, improving antimicrobial properties, enhancing biocompatibility, and creating more environmentally friendly disposal methods. As the healthcare industry continues to evolve, so too must the safety standards and practices surrounding the use of PVAc in medical adhesives.
Current PVAc Formulations for Medical Use
01 Safety considerations in polyvinyl acetate production
The production of polyvinyl acetate involves various safety considerations, including the handling of raw materials, controlling reaction conditions, and managing potential hazards. Proper safety protocols and equipment are essential to ensure worker safety and prevent accidents during the manufacturing process.- Safety considerations in polyvinyl acetate production: The production of polyvinyl acetate involves various safety considerations, including the handling of raw materials, controlling reaction conditions, and managing potential hazards. Proper safety protocols and equipment are essential to ensure worker safety and prevent accidents during the manufacturing process.
- Environmental impact and biodegradability: The environmental impact of polyvinyl acetate is an important aspect of its safety profile. Research has been conducted on improving its biodegradability and reducing its ecological footprint. Efforts are being made to develop more environmentally friendly formulations and disposal methods.
- Food contact and packaging applications: Polyvinyl acetate is used in various food contact and packaging applications. Safety assessments and regulations ensure its suitability for these purposes. Studies have been conducted to evaluate potential migration of substances from polyvinyl acetate-based materials into food and beverages.
- Toxicological studies and health effects: Toxicological studies have been performed to assess the potential health effects of polyvinyl acetate exposure. These studies evaluate acute and chronic toxicity, as well as potential carcinogenic, mutagenic, or reproductive effects. The results inform safety guidelines and occupational exposure limits.
- Safety improvements in polyvinyl acetate formulations: Ongoing research focuses on improving the safety profile of polyvinyl acetate formulations. This includes developing low-VOC (volatile organic compound) versions, reducing residual monomer content, and incorporating additives to enhance fire resistance or other safety properties.
02 Environmental impact and biodegradability
The environmental impact of polyvinyl acetate is an important safety consideration. Research focuses on developing more environmentally friendly formulations and improving the biodegradability of polyvinyl acetate-based products to reduce their long-term impact on ecosystems.Expand Specific Solutions03 Food contact safety and regulations
The safety of polyvinyl acetate in food contact applications is crucial. Regulations and standards govern the use of polyvinyl acetate in food packaging and other food-related applications to ensure consumer safety and prevent potential contamination.Expand Specific Solutions04 Toxicity and health effects
Studies on the toxicity and potential health effects of polyvinyl acetate are conducted to assess its safety for various applications. This includes evaluating short-term and long-term exposure risks, as well as investigating any potential allergenic or carcinogenic properties.Expand Specific Solutions05 Safe handling and disposal methods
Proper handling and disposal methods for polyvinyl acetate and its related products are essential for ensuring safety. This includes guidelines for storage, transportation, and waste management to minimize risks to human health and the environment.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Medical Adhesive Industry
The market for polyvinyl acetate in healthcare adhesives is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for advanced medical devices and wound care products. The global market size is estimated to be in the hundreds of millions of dollars, with steady expansion projected. Technologically, the field is moderately mature but continues to evolve, with innovations focused on improving biocompatibility, adhesion strength, and controlled drug release capabilities. Key players like Henkel, BASF, and Kuraray are investing in R&D to develop specialized formulations, while companies such as LTS LOHMANN and Sanyo Chemical are exploring novel applications in transdermal patches and superabsorbent polymers for medical use.
Henkel AG & Co. KGaA
Technical Solution: Henkel has developed innovative polyvinyl acetate (PVAc) formulations for healthcare adhesives, focusing on biocompatibility and skin-friendliness. Their advanced PVAc-based adhesives incorporate antimicrobial properties to reduce infection risks in medical applications[1]. Henkel's research has led to the creation of pressure-sensitive adhesives (PSAs) that combine PVAc with other polymers, resulting in improved adhesion strength and moisture resistance[2]. These adhesives are designed for various medical devices, including wound dressings, surgical tapes, and transdermal drug delivery systems. Henkel has also invested in enhancing the biodegradability of their PVAc adhesives, addressing environmental concerns in healthcare settings[3].
Strengths: Strong focus on biocompatibility and skin-friendliness, antimicrobial properties, and improved adhesion strength. Weaknesses: May face challenges in achieving optimal balance between adhesion and easy removal for sensitive skin applications.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF has made significant strides in developing PVAc-based healthcare adhesives with enhanced safety profiles. Their research focuses on reducing the presence of residual monomers and potentially harmful additives in PVAc formulations[4]. BASF's innovative approach includes the development of water-based PVAc adhesives that minimize the use of organic solvents, thereby reducing potential toxicity and environmental impact[5]. The company has also explored the incorporation of natural and biodegradable additives to improve the overall safety and sustainability of their healthcare adhesives. BASF's PVAc adhesives are designed for a wide range of medical applications, including ostomy care products, wound dressings, and medical tapes, with a particular emphasis on long-wear comfort and skin protection[6].
Strengths: Focus on reducing harmful additives and residual monomers, development of water-based formulations. Weaknesses: May face challenges in matching the performance of solvent-based adhesives in certain high-demand applications.
Innovations in PVAc Safety Enhancement
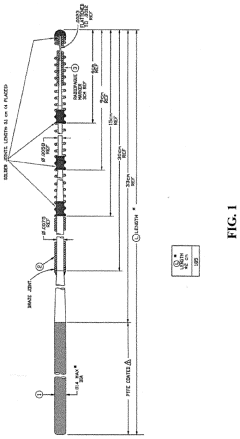
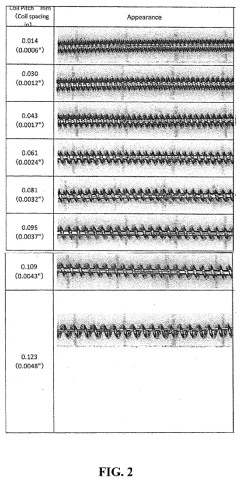
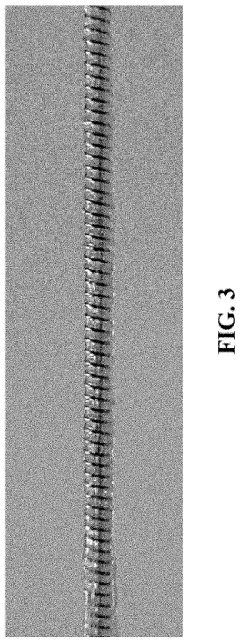
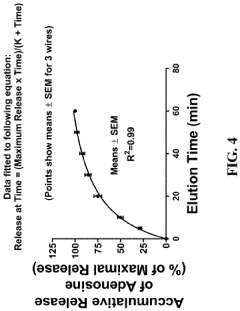
Medical devices for continuous delivery of therapeutic agents
PatentActiveUS20220288284A1
Innovation
- A hydrogel-coated guidewire with a therapeutic agent, such as adenosine, is developed, which releases the agent continuously when in contact with body fluids, providing localized treatment to improve tissue perfusion and prevent MVO by incorporating a polymer blend of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) and polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) that forms a stable coating on the guidewire, allowing for controlled drug release.
Adhesive
PatentWO2017057582A1
Innovation
- A modified polyvinyl acetal with an imine structure, combined with a reactive diluent and polymerization initiator, is used to create a liquid adhesive at room temperature, offering excellent adhesion to both organic and inorganic materials and improving handling properties by crosslinking and curing.
Regulatory Framework for Medical Adhesives
The regulatory framework for medical adhesives, including those containing polyvinyl acetate, is a complex and evolving landscape designed to ensure patient safety and product efficacy. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a pivotal role in overseeing medical adhesives through its Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH). These products are typically classified as Class I or Class II medical devices, depending on their intended use and risk profile.
For Class I devices, which pose minimal potential harm, manufacturers must adhere to general controls, including good manufacturing practices and proper labeling. Class II devices, which may include more advanced adhesive formulations, are subject to special controls in addition to general controls. These special controls often involve performance standards, post-market surveillance, and specific labeling requirements.
The FDA's 510(k) premarket notification process is a common pathway for many medical adhesives to gain market approval. This process requires manufacturers to demonstrate that their product is substantially equivalent to a legally marketed predicate device in terms of safety and effectiveness. For novel adhesives or those with unique formulations, a more rigorous premarket approval (PMA) process may be necessary.
In the European Union, medical adhesives fall under the purview of the Medical Device Regulation (MDR), which replaced the previous Medical Device Directive in 2021. The MDR introduced more stringent requirements for clinical evidence, post-market surveillance, and traceability. Under this framework, medical adhesives are classified based on their intended use, duration of contact with the body, and potential risks.
International standards, such as ISO 10993 for biocompatibility testing, play a crucial role in the regulatory landscape. These standards provide guidelines for evaluating the biological safety of medical devices, including adhesives, and are often referenced by regulatory bodies worldwide.
Manufacturers must also consider specific regulations related to the chemical components of their adhesives. For instance, the use of polyvinyl acetate in healthcare adhesives may be subject to additional scrutiny due to potential concerns about residual monomers or degradation products. Regulatory bodies may require extensive toxicological data and risk assessments for such components.
As healthcare technology advances, regulatory frameworks are adapting to address emerging challenges. This includes considerations for combination products that incorporate adhesives with drugs or biologics, as well as the growing focus on sustainability and environmental impact of medical materials.
For Class I devices, which pose minimal potential harm, manufacturers must adhere to general controls, including good manufacturing practices and proper labeling. Class II devices, which may include more advanced adhesive formulations, are subject to special controls in addition to general controls. These special controls often involve performance standards, post-market surveillance, and specific labeling requirements.
The FDA's 510(k) premarket notification process is a common pathway for many medical adhesives to gain market approval. This process requires manufacturers to demonstrate that their product is substantially equivalent to a legally marketed predicate device in terms of safety and effectiveness. For novel adhesives or those with unique formulations, a more rigorous premarket approval (PMA) process may be necessary.
In the European Union, medical adhesives fall under the purview of the Medical Device Regulation (MDR), which replaced the previous Medical Device Directive in 2021. The MDR introduced more stringent requirements for clinical evidence, post-market surveillance, and traceability. Under this framework, medical adhesives are classified based on their intended use, duration of contact with the body, and potential risks.
International standards, such as ISO 10993 for biocompatibility testing, play a crucial role in the regulatory landscape. These standards provide guidelines for evaluating the biological safety of medical devices, including adhesives, and are often referenced by regulatory bodies worldwide.
Manufacturers must also consider specific regulations related to the chemical components of their adhesives. For instance, the use of polyvinyl acetate in healthcare adhesives may be subject to additional scrutiny due to potential concerns about residual monomers or degradation products. Regulatory bodies may require extensive toxicological data and risk assessments for such components.
As healthcare technology advances, regulatory frameworks are adapting to address emerging challenges. This includes considerations for combination products that incorporate adhesives with drugs or biologics, as well as the growing focus on sustainability and environmental impact of medical materials.
Environmental Impact of PVAc Adhesives
The environmental impact of Polyvinyl Acetate (PVAc) adhesives in healthcare applications is a critical consideration as the industry moves towards more sustainable practices. PVAc adhesives, while widely used due to their effectiveness and versatility, present both advantages and challenges from an environmental perspective.
One of the primary environmental benefits of PVAc adhesives is their water-based formulation. Unlike solvent-based alternatives, PVAc adhesives release minimal volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during application and curing. This characteristic significantly reduces air pollution and potential health risks associated with adhesive use in healthcare settings.
However, the production of PVAc adhesives does involve petrochemical-based raw materials, which contribute to carbon emissions and resource depletion. The manufacturing process requires energy-intensive polymerization reactions, potentially offsetting some of the environmental gains achieved during application.
Disposal of PVAc adhesives and products bonded with them presents another environmental challenge. While PVAc is not classified as hazardous waste in most jurisdictions, it is not biodegradable. This means that PVAc-bonded medical devices and packaging may persist in landfills for extended periods, contributing to long-term waste management issues.
Recent innovations in PVAc formulations have aimed to address these environmental concerns. Some manufacturers have developed bio-based PVAc adhesives, incorporating renewable resources to partially replace petroleum-derived components. These formulations can reduce the overall carbon footprint of the adhesive while maintaining performance characteristics crucial for healthcare applications.
Additionally, research into improving the end-of-life recyclability of PVAc-bonded products is ongoing. Efforts are being made to develop PVAc adhesives that can be more easily separated from substrates during recycling processes, potentially increasing the recyclability of medical devices and packaging.
Water consumption and wastewater generation during PVAc production and application are also environmental factors to consider. While water-based formulations are generally preferred over solvent-based alternatives, the industry is exploring ways to optimize water use and implement closed-loop systems to minimize environmental impact.
As healthcare facilities increasingly prioritize sustainability, the demand for eco-friendly adhesive solutions is growing. This has spurred innovation in PVAc technology, with a focus on reducing environmental impact throughout the product lifecycle. Future developments may include further improvements in biodegradability, increased use of renewable resources, and enhanced recyclability of PVAc-bonded healthcare products.
One of the primary environmental benefits of PVAc adhesives is their water-based formulation. Unlike solvent-based alternatives, PVAc adhesives release minimal volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during application and curing. This characteristic significantly reduces air pollution and potential health risks associated with adhesive use in healthcare settings.
However, the production of PVAc adhesives does involve petrochemical-based raw materials, which contribute to carbon emissions and resource depletion. The manufacturing process requires energy-intensive polymerization reactions, potentially offsetting some of the environmental gains achieved during application.
Disposal of PVAc adhesives and products bonded with them presents another environmental challenge. While PVAc is not classified as hazardous waste in most jurisdictions, it is not biodegradable. This means that PVAc-bonded medical devices and packaging may persist in landfills for extended periods, contributing to long-term waste management issues.
Recent innovations in PVAc formulations have aimed to address these environmental concerns. Some manufacturers have developed bio-based PVAc adhesives, incorporating renewable resources to partially replace petroleum-derived components. These formulations can reduce the overall carbon footprint of the adhesive while maintaining performance characteristics crucial for healthcare applications.
Additionally, research into improving the end-of-life recyclability of PVAc-bonded products is ongoing. Efforts are being made to develop PVAc adhesives that can be more easily separated from substrates during recycling processes, potentially increasing the recyclability of medical devices and packaging.
Water consumption and wastewater generation during PVAc production and application are also environmental factors to consider. While water-based formulations are generally preferred over solvent-based alternatives, the industry is exploring ways to optimize water use and implement closed-loop systems to minimize environmental impact.
As healthcare facilities increasingly prioritize sustainability, the demand for eco-friendly adhesive solutions is growing. This has spurred innovation in PVAc technology, with a focus on reducing environmental impact throughout the product lifecycle. Future developments may include further improvements in biodegradability, increased use of renewable resources, and enhanced recyclability of PVAc-bonded healthcare products.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!