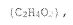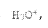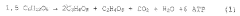How to Maximize Propionic Acid's Sustainability Impact?
JUL 3, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Propionic Acid Overview
Propionic acid is a versatile organic compound with the chemical formula C3H6O2. It is a naturally occurring carboxylic acid found in various sources, including dairy products and the digestive systems of ruminants. In its pure form, propionic acid is a colorless liquid with a pungent odor, similar to that of acetic acid but with a slightly oily texture.
The production of propionic acid has seen significant growth in recent years, driven by its wide range of applications across multiple industries. Traditionally, it has been synthesized through petrochemical processes, primarily using ethylene and carbon monoxide as raw materials. However, there is an increasing focus on developing more sustainable production methods to align with global environmental goals.
In the food industry, propionic acid serves as a crucial preservative, inhibiting the growth of mold and bacteria in various products, particularly baked goods. Its effectiveness in extending shelf life has made it an indispensable ingredient in food preservation. Beyond food applications, propionic acid plays a vital role in the pharmaceutical sector, where it is used as a precursor for various medications and as an excipient in drug formulations.
The agricultural sector also benefits from propionic acid's properties. It is widely used as a feed preservative for livestock, helping to prevent spoilage and maintain nutritional value. Additionally, its antimicrobial properties make it an effective treatment for animal hides and other agricultural products.
In the chemical industry, propionic acid serves as a building block for the synthesis of various compounds, including plastics, herbicides, and artificial flavorings. Its versatility in chemical reactions has led to its incorporation in numerous industrial processes, contributing to the production of a wide array of consumer and industrial goods.
The global market for propionic acid has been steadily expanding, with projections indicating continued growth in the coming years. This growth is attributed to increasing demand across its diverse application areas, as well as the development of new uses in emerging industries. As sustainability becomes a more pressing concern, there is a growing interest in exploring bio-based production methods for propionic acid, which could potentially reduce its environmental footprint and enhance its appeal in environmentally conscious markets.
Understanding the current landscape of propionic acid production and use is crucial for identifying opportunities to maximize its sustainability impact. By examining its production processes, applications, and market trends, we can begin to explore innovative approaches to enhance the environmental profile of this important chemical compound while maintaining its economic viability and functional benefits across various industries.
The production of propionic acid has seen significant growth in recent years, driven by its wide range of applications across multiple industries. Traditionally, it has been synthesized through petrochemical processes, primarily using ethylene and carbon monoxide as raw materials. However, there is an increasing focus on developing more sustainable production methods to align with global environmental goals.
In the food industry, propionic acid serves as a crucial preservative, inhibiting the growth of mold and bacteria in various products, particularly baked goods. Its effectiveness in extending shelf life has made it an indispensable ingredient in food preservation. Beyond food applications, propionic acid plays a vital role in the pharmaceutical sector, where it is used as a precursor for various medications and as an excipient in drug formulations.
The agricultural sector also benefits from propionic acid's properties. It is widely used as a feed preservative for livestock, helping to prevent spoilage and maintain nutritional value. Additionally, its antimicrobial properties make it an effective treatment for animal hides and other agricultural products.
In the chemical industry, propionic acid serves as a building block for the synthesis of various compounds, including plastics, herbicides, and artificial flavorings. Its versatility in chemical reactions has led to its incorporation in numerous industrial processes, contributing to the production of a wide array of consumer and industrial goods.
The global market for propionic acid has been steadily expanding, with projections indicating continued growth in the coming years. This growth is attributed to increasing demand across its diverse application areas, as well as the development of new uses in emerging industries. As sustainability becomes a more pressing concern, there is a growing interest in exploring bio-based production methods for propionic acid, which could potentially reduce its environmental footprint and enhance its appeal in environmentally conscious markets.
Understanding the current landscape of propionic acid production and use is crucial for identifying opportunities to maximize its sustainability impact. By examining its production processes, applications, and market trends, we can begin to explore innovative approaches to enhance the environmental profile of this important chemical compound while maintaining its economic viability and functional benefits across various industries.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for propionic acid has been steadily increasing due to its versatile applications across various industries. The global propionic acid market size was valued at approximately $1.5 billion in 2020 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 3.5% from 2021 to 2028. This growth is primarily driven by the rising demand for food preservatives and animal feed additives.
In the food and beverage industry, propionic acid is widely used as a preservative due to its antimicrobial properties. With the growing consumer preference for natural and clean-label products, there is an increasing demand for propionic acid as a safer alternative to synthetic preservatives. The bakery sector, in particular, has shown significant growth in the use of propionic acid to extend the shelf life of bread and other baked goods.
The animal feed industry represents another major market for propionic acid. As the global population continues to grow, so does the demand for meat and dairy products. Propionic acid is used as a mold inhibitor in animal feed, helping to prevent spoilage and improve feed efficiency. The increasing focus on animal health and nutrition is expected to further drive the demand for propionic acid in this sector.
Emerging applications in the pharmaceutical and personal care industries are also contributing to the market growth. Propionic acid is used in the production of various pharmaceuticals and as a pH adjuster in personal care products. The growing awareness of personal hygiene and health, especially in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, is likely to boost demand in these sectors.
From a sustainability perspective, there is a growing interest in bio-based propionic acid. As industries strive to reduce their carbon footprint, the demand for sustainable alternatives to petrochemical-derived propionic acid is increasing. This trend aligns with the global shift towards circular economy principles and presents an opportunity for innovation in production methods.
Geographically, Asia Pacific is expected to be the fastest-growing market for propionic acid, driven by rapid industrialization, population growth, and increasing disposable incomes. North America and Europe remain significant markets, with a focus on high-quality, sustainable products.
The market demand analysis indicates a positive outlook for propionic acid, with sustainability being a key driver for future growth. To maximize its sustainability impact, industry players need to focus on developing eco-friendly production methods, exploring renewable feedstocks, and enhancing the efficiency of existing applications. This approach will not only meet the growing market demand but also align with global sustainability goals.
In the food and beverage industry, propionic acid is widely used as a preservative due to its antimicrobial properties. With the growing consumer preference for natural and clean-label products, there is an increasing demand for propionic acid as a safer alternative to synthetic preservatives. The bakery sector, in particular, has shown significant growth in the use of propionic acid to extend the shelf life of bread and other baked goods.
The animal feed industry represents another major market for propionic acid. As the global population continues to grow, so does the demand for meat and dairy products. Propionic acid is used as a mold inhibitor in animal feed, helping to prevent spoilage and improve feed efficiency. The increasing focus on animal health and nutrition is expected to further drive the demand for propionic acid in this sector.
Emerging applications in the pharmaceutical and personal care industries are also contributing to the market growth. Propionic acid is used in the production of various pharmaceuticals and as a pH adjuster in personal care products. The growing awareness of personal hygiene and health, especially in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, is likely to boost demand in these sectors.
From a sustainability perspective, there is a growing interest in bio-based propionic acid. As industries strive to reduce their carbon footprint, the demand for sustainable alternatives to petrochemical-derived propionic acid is increasing. This trend aligns with the global shift towards circular economy principles and presents an opportunity for innovation in production methods.
Geographically, Asia Pacific is expected to be the fastest-growing market for propionic acid, driven by rapid industrialization, population growth, and increasing disposable incomes. North America and Europe remain significant markets, with a focus on high-quality, sustainable products.
The market demand analysis indicates a positive outlook for propionic acid, with sustainability being a key driver for future growth. To maximize its sustainability impact, industry players need to focus on developing eco-friendly production methods, exploring renewable feedstocks, and enhancing the efficiency of existing applications. This approach will not only meet the growing market demand but also align with global sustainability goals.
Sustainability Challenges
Propionic acid production and utilization face several sustainability challenges that need to be addressed to maximize its positive environmental impact. One of the primary concerns is the current reliance on fossil fuel-based feedstocks for its production. The conventional method of producing propionic acid involves the oxidation of propanol, which is derived from petroleum. This dependency on non-renewable resources contributes to carbon emissions and environmental degradation.
Another significant challenge is the energy-intensive nature of propionic acid production processes. Traditional manufacturing methods require high temperatures and pressures, leading to substantial energy consumption and associated greenhouse gas emissions. The optimization of these processes to reduce energy requirements while maintaining production efficiency is a critical area for improvement.
Water usage and wastewater management also pose sustainability challenges in propionic acid production. The fermentation and purification processes often involve significant water consumption and generate wastewater that requires treatment before disposal. Developing more water-efficient production methods and implementing effective water recycling systems are essential steps towards enhancing the sustainability profile of propionic acid.
The use of chemical catalysts in propionic acid synthesis presents additional environmental concerns. Many catalysts used in industrial processes contain heavy metals or other potentially harmful substances. The disposal or recycling of these catalysts can lead to soil and water contamination if not managed properly. Finding greener alternatives or developing more efficient catalyst recovery methods is crucial for improving the overall sustainability of propionic acid production.
Transportation and distribution of propionic acid also contribute to its environmental footprint. As a bulk chemical, it is often transported over long distances, resulting in significant fuel consumption and emissions. Optimizing logistics networks and exploring localized production options could help mitigate these impacts.
Furthermore, the end-of-life management of products containing propionic acid presents sustainability challenges. Improper disposal or inadequate recycling of these products can lead to environmental pollution and resource waste. Developing effective recycling technologies and implementing circular economy principles in the propionic acid value chain are essential for maximizing its sustainability impact.
Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach, involving technological innovations, process optimizations, and policy interventions. By focusing on sustainable feedstock alternatives, energy-efficient production methods, water conservation, green chemistry principles, and circular economy strategies, the propionic acid industry can significantly enhance its sustainability profile and contribute positively to global environmental goals.
Another significant challenge is the energy-intensive nature of propionic acid production processes. Traditional manufacturing methods require high temperatures and pressures, leading to substantial energy consumption and associated greenhouse gas emissions. The optimization of these processes to reduce energy requirements while maintaining production efficiency is a critical area for improvement.
Water usage and wastewater management also pose sustainability challenges in propionic acid production. The fermentation and purification processes often involve significant water consumption and generate wastewater that requires treatment before disposal. Developing more water-efficient production methods and implementing effective water recycling systems are essential steps towards enhancing the sustainability profile of propionic acid.
The use of chemical catalysts in propionic acid synthesis presents additional environmental concerns. Many catalysts used in industrial processes contain heavy metals or other potentially harmful substances. The disposal or recycling of these catalysts can lead to soil and water contamination if not managed properly. Finding greener alternatives or developing more efficient catalyst recovery methods is crucial for improving the overall sustainability of propionic acid production.
Transportation and distribution of propionic acid also contribute to its environmental footprint. As a bulk chemical, it is often transported over long distances, resulting in significant fuel consumption and emissions. Optimizing logistics networks and exploring localized production options could help mitigate these impacts.
Furthermore, the end-of-life management of products containing propionic acid presents sustainability challenges. Improper disposal or inadequate recycling of these products can lead to environmental pollution and resource waste. Developing effective recycling technologies and implementing circular economy principles in the propionic acid value chain are essential for maximizing its sustainability impact.
Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach, involving technological innovations, process optimizations, and policy interventions. By focusing on sustainable feedstock alternatives, energy-efficient production methods, water conservation, green chemistry principles, and circular economy strategies, the propionic acid industry can significantly enhance its sustainability profile and contribute positively to global environmental goals.
Current Sustainable Solutions
01 Sustainable production methods
Innovative approaches to produce propionic acid using renewable resources and environmentally friendly processes. These methods aim to reduce the carbon footprint and improve the overall sustainability of propionic acid production, potentially including bio-based feedstocks or waste valorization techniques.- Sustainable production methods: Innovative approaches to produce propionic acid using renewable resources and environmentally friendly processes. These methods aim to reduce the carbon footprint and increase the sustainability of propionic acid production, potentially through fermentation of biomass or utilization of waste streams.
- Environmental impact reduction: Techniques and systems designed to minimize the environmental impact of propionic acid production and use. This includes waste reduction strategies, energy-efficient processes, and methods to capture and reuse byproducts, contributing to a more sustainable industry.
- Applications in sustainable agriculture: Use of propionic acid in sustainable agricultural practices, such as organic farming and eco-friendly pest control. This includes formulations and methods that leverage propionic acid's properties to enhance crop protection and preservation while minimizing environmental impact.
- Biodegradable materials development: Incorporation of propionic acid in the development of biodegradable materials and products. This involves creating sustainable alternatives to conventional plastics and other materials, potentially reducing long-term environmental pollution.
- Circular economy integration: Strategies to integrate propionic acid production and use into circular economy models. This includes recycling and upcycling processes, as well as the development of closed-loop systems that maximize resource efficiency and minimize waste throughout the product lifecycle.
02 Environmental impact reduction
Techniques and technologies focused on minimizing the environmental impact of propionic acid production and use. This may include improved waste management, reduced emissions, and enhanced energy efficiency in manufacturing processes, contributing to a more sustainable industry.Expand Specific Solutions03 Applications in sustainable products
Utilization of propionic acid in the development of eco-friendly and sustainable products. This could involve its use as a preservative in organic foods, as a component in biodegradable plastics, or in other applications that promote sustainability across various industries.Expand Specific Solutions04 Lifecycle assessment and circular economy
Studies and methodologies for assessing the full lifecycle impact of propionic acid, from production to end-use and disposal. This includes strategies for implementing circular economy principles, such as recycling and upcycling of propionic acid-containing products.Expand Specific Solutions05 Regulatory and policy implications
Analysis of regulatory frameworks and policy measures related to the sustainable production and use of propionic acid. This may include discussions on environmental standards, sustainability certifications, and incentives for adopting more sustainable practices in the propionic acid industry.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The propionic acid sustainability market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for eco-friendly preservatives and green chemicals. The global market size is expanding, with projections indicating significant growth potential in the coming years. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with key players like BASF, Dow, and Arkema leading innovation in sustainable production methods. Academic institutions such as Nanjing Tech University and The Ohio State University are contributing to research and development efforts. Emerging companies like Kemin Industries and Techfields Biochemical are also making strides in developing novel sustainable processes, indicating a competitive and dynamic landscape.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF has developed a sustainable production process for propionic acid using renewable resources. Their approach involves fermenting biomass-derived sugars using proprietary microorganisms. The process achieves high yields and selectivity, reducing energy consumption and waste generation compared to traditional petrochemical routes[1]. BASF has also implemented advanced purification techniques, such as membrane separation and crystallization, to obtain high-purity propionic acid suitable for various applications[2]. Additionally, they have integrated their propionic acid production with existing biorefinery concepts, creating synergies and improving overall resource efficiency[3].
Strengths: Renewable feedstock, reduced carbon footprint, integration with existing infrastructure. Weaknesses: Potentially higher production costs compared to petrochemical routes, dependence on biomass availability.
Arkema France SA
Technical Solution: Arkema has focused on maximizing propionic acid's sustainability impact through innovative applications and process improvements. They have developed a bio-based propionic acid production process using glycerol, a byproduct of biodiesel production, as a feedstock[10]. This approach not only utilizes a renewable resource but also contributes to the circular economy by valorizing waste streams. Arkema has also implemented advanced oxidation technologies to treat process effluents, reducing the environmental impact of production[11]. Furthermore, they have explored the use of propionic acid in eco-friendly coatings and adhesives, expanding its role in sustainable material solutions[12].
Strengths: Utilization of biodiesel byproducts, circular economy approach, applications in sustainable materials. Weaknesses: Dependence on biodiesel industry dynamics, potential limitations in production scale.
Innovative Technologies
Method for Improving Acid tolerance of Propionibacterium acdipropionici
PatentInactiveUS20140178952A1
Innovation
- Adding arginine and/or aspartic acid to the culture medium during the cultivation of Propionibacterium acdipropionici to enhance acid tolerance and propionic acid productivity.
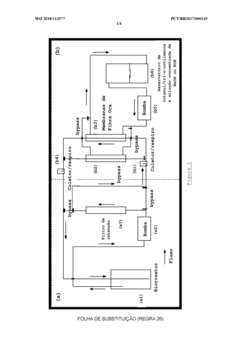
Fermentative process and integrated system for producing organic acids
PatentWO2018112577A1
Innovation
- A continuous fermentation process using Propionibacterium acidipropionici bacteria coupled with a perstration system employing hollow fiber membranes and tri-n-octylamine for efficient acid extraction, minimizing solvent use and maintaining pH stability.
Life Cycle Assessment
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) plays a crucial role in maximizing the sustainability impact of propionic acid production and utilization. This comprehensive approach evaluates the environmental impacts associated with all stages of propionic acid's life cycle, from raw material extraction to disposal or recycling. By conducting a thorough LCA, stakeholders can identify hotspots of environmental burden and opportunities for improvement throughout the value chain.
The LCA process for propionic acid typically begins with a clear definition of the system boundaries and functional unit. This may include the production of raw materials, such as propanol or ethanol, the fermentation or chemical synthesis process, purification steps, packaging, distribution, use phase, and end-of-life management. The functional unit could be defined as a specific quantity of propionic acid produced or a particular application of the acid.
Data collection is a critical step in the LCA process. This involves gathering information on energy consumption, water usage, emissions, and waste generation at each stage of the life cycle. For propionic acid, special attention should be given to the fermentation process if using biological production methods, or to the chemical synthesis route if using petrochemical feedstocks. The choice of production method can significantly impact the overall sustainability profile.
Once data is collected, impact assessment methods are applied to translate the inventory data into potential environmental impacts. Common impact categories for propionic acid LCA include global warming potential, acidification, eutrophication, water depletion, and fossil resource depletion. The results of this assessment can highlight which stages of the life cycle contribute most significantly to different environmental impacts.
Interpretation of LCA results is crucial for identifying improvement opportunities. For propionic acid, this may involve exploring alternative feedstocks, optimizing fermentation conditions, improving energy efficiency in production processes, or developing more sustainable packaging solutions. The LCA can also inform decisions on transportation modes and distances, as well as end-of-life management strategies.
Comparative LCAs can be particularly valuable in maximizing propionic acid's sustainability impact. By comparing different production routes, feedstocks, or applications, stakeholders can make informed decisions that minimize overall environmental burden. For instance, comparing bio-based propionic acid production to petrochemical routes can provide insights into the potential benefits and trade-offs of each approach.
To enhance the credibility and usefulness of the LCA, it is important to conduct sensitivity and uncertainty analyses. These analyses can help identify which parameters have the greatest influence on the results and where data quality improvements are most needed. This information can guide future research and development efforts to maximize the sustainability of propionic acid production and use.
The LCA process for propionic acid typically begins with a clear definition of the system boundaries and functional unit. This may include the production of raw materials, such as propanol or ethanol, the fermentation or chemical synthesis process, purification steps, packaging, distribution, use phase, and end-of-life management. The functional unit could be defined as a specific quantity of propionic acid produced or a particular application of the acid.
Data collection is a critical step in the LCA process. This involves gathering information on energy consumption, water usage, emissions, and waste generation at each stage of the life cycle. For propionic acid, special attention should be given to the fermentation process if using biological production methods, or to the chemical synthesis route if using petrochemical feedstocks. The choice of production method can significantly impact the overall sustainability profile.
Once data is collected, impact assessment methods are applied to translate the inventory data into potential environmental impacts. Common impact categories for propionic acid LCA include global warming potential, acidification, eutrophication, water depletion, and fossil resource depletion. The results of this assessment can highlight which stages of the life cycle contribute most significantly to different environmental impacts.
Interpretation of LCA results is crucial for identifying improvement opportunities. For propionic acid, this may involve exploring alternative feedstocks, optimizing fermentation conditions, improving energy efficiency in production processes, or developing more sustainable packaging solutions. The LCA can also inform decisions on transportation modes and distances, as well as end-of-life management strategies.
Comparative LCAs can be particularly valuable in maximizing propionic acid's sustainability impact. By comparing different production routes, feedstocks, or applications, stakeholders can make informed decisions that minimize overall environmental burden. For instance, comparing bio-based propionic acid production to petrochemical routes can provide insights into the potential benefits and trade-offs of each approach.
To enhance the credibility and usefulness of the LCA, it is important to conduct sensitivity and uncertainty analyses. These analyses can help identify which parameters have the greatest influence on the results and where data quality improvements are most needed. This information can guide future research and development efforts to maximize the sustainability of propionic acid production and use.
Circular Economy Integration
Integrating propionic acid production into circular economy models presents significant opportunities for maximizing its sustainability impact. By adopting closed-loop systems, industries can reduce waste, conserve resources, and minimize environmental footprints associated with propionic acid manufacturing and utilization.
One key approach is the valorization of organic waste streams as feedstock for propionic acid production. Agricultural residues, food processing byproducts, and other biomass sources can be fermented to yield propionic acid, effectively upcycling waste materials into valuable chemicals. This not only diverts organic waste from landfills but also reduces reliance on fossil-based feedstocks traditionally used in propionic acid synthesis.
Implementing cascading use principles can further enhance sustainability. Propionic acid and its derivatives can be designed for multiple life cycles, with each subsequent use maintaining or increasing the overall value. For instance, propionic acid used as a food preservative could later be recovered and repurposed for industrial applications or as a precursor for other chemicals, maximizing resource efficiency.
Developing efficient recycling and recovery technologies is crucial for circular economy integration. Advanced separation techniques, such as membrane filtration or solvent extraction, can be employed to reclaim propionic acid from waste streams or spent products. These recovered materials can then be reintroduced into production processes, creating closed-loop systems that minimize resource inputs and waste outputs.
Collaborative industrial symbiosis presents another avenue for circular economy integration. By establishing partnerships between propionic acid producers and industries that generate suitable waste streams or can utilize byproducts, resource efficiency can be optimized across value chains. This approach not only reduces waste but also creates new economic opportunities and strengthens regional circular economy networks.
Digitalization and smart manufacturing technologies can play a crucial role in enabling circular economy practices for propionic acid. Real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and data-driven optimization can minimize waste generation, improve process efficiency, and extend equipment lifespans. Additionally, blockchain and other traceability solutions can enhance transparency and accountability throughout the circular value chain.
By embracing these circular economy principles, the propionic acid industry can significantly enhance its sustainability profile. This shift not only addresses environmental concerns but also offers potential economic benefits through improved resource utilization and the creation of new value streams. As regulatory pressures and consumer demand for sustainable products continue to grow, circular economy integration will become increasingly critical for the long-term viability and competitiveness of propionic acid production.
One key approach is the valorization of organic waste streams as feedstock for propionic acid production. Agricultural residues, food processing byproducts, and other biomass sources can be fermented to yield propionic acid, effectively upcycling waste materials into valuable chemicals. This not only diverts organic waste from landfills but also reduces reliance on fossil-based feedstocks traditionally used in propionic acid synthesis.
Implementing cascading use principles can further enhance sustainability. Propionic acid and its derivatives can be designed for multiple life cycles, with each subsequent use maintaining or increasing the overall value. For instance, propionic acid used as a food preservative could later be recovered and repurposed for industrial applications or as a precursor for other chemicals, maximizing resource efficiency.
Developing efficient recycling and recovery technologies is crucial for circular economy integration. Advanced separation techniques, such as membrane filtration or solvent extraction, can be employed to reclaim propionic acid from waste streams or spent products. These recovered materials can then be reintroduced into production processes, creating closed-loop systems that minimize resource inputs and waste outputs.
Collaborative industrial symbiosis presents another avenue for circular economy integration. By establishing partnerships between propionic acid producers and industries that generate suitable waste streams or can utilize byproducts, resource efficiency can be optimized across value chains. This approach not only reduces waste but also creates new economic opportunities and strengthens regional circular economy networks.
Digitalization and smart manufacturing technologies can play a crucial role in enabling circular economy practices for propionic acid. Real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and data-driven optimization can minimize waste generation, improve process efficiency, and extend equipment lifespans. Additionally, blockchain and other traceability solutions can enhance transparency and accountability throughout the circular value chain.
By embracing these circular economy principles, the propionic acid industry can significantly enhance its sustainability profile. This shift not only addresses environmental concerns but also offers potential economic benefits through improved resource utilization and the creation of new value streams. As regulatory pressures and consumer demand for sustainable products continue to grow, circular economy integration will become increasingly critical for the long-term viability and competitiveness of propionic acid production.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!