How to Optimize Alkyl Reactions for Enhanced Yield?
JUL 15, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Alkyl Reaction Optimization Background and Objectives
Alkyl reactions have been a cornerstone of organic synthesis for decades, playing a crucial role in the production of various chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and materials. The optimization of these reactions for enhanced yield has become increasingly important as industries strive for greater efficiency and sustainability in their processes.
The evolution of alkyl reaction technology can be traced back to the early 20th century, with significant advancements made in the understanding of reaction mechanisms and the development of new catalysts. Over time, researchers have focused on improving reaction conditions, exploring novel reagents, and fine-tuning reaction parameters to maximize product yield while minimizing unwanted side reactions.
In recent years, the drive towards greener chemistry and more sustainable practices has further intensified the need for optimizing alkyl reactions. This has led to a surge in research aimed at developing more environmentally friendly catalysts, reducing waste generation, and improving atom economy. The advent of high-throughput screening techniques and computational chemistry has also accelerated the discovery of new reaction conditions and catalysts, enabling faster optimization of alkyl reactions.
The primary objective of optimizing alkyl reactions for enhanced yield is to increase the efficiency of chemical processes, thereby reducing costs and environmental impact. This involves a multifaceted approach, including the development of more selective catalysts, the fine-tuning of reaction conditions such as temperature and pressure, and the exploration of alternative solvents and reagents.
Another key goal is to expand the scope of alkyl reactions, enabling the synthesis of more complex molecules and broadening their applicability across various industries. This includes developing methods for challenging substrates, improving stereoselectivity, and enhancing functional group tolerance.
Furthermore, there is a growing emphasis on developing sustainable and scalable alkyl reaction processes that can be readily implemented in industrial settings. This necessitates the consideration of factors such as cost-effectiveness, ease of product isolation, and the ability to recycle catalysts and solvents.
As we look towards the future, the optimization of alkyl reactions is expected to continue evolving, with a focus on integrating advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning to predict optimal reaction conditions and design novel catalysts. The ultimate aim is to achieve higher yields, greater selectivity, and improved sustainability in alkyl reactions, paving the way for more efficient and environmentally friendly chemical processes across various industries.
The evolution of alkyl reaction technology can be traced back to the early 20th century, with significant advancements made in the understanding of reaction mechanisms and the development of new catalysts. Over time, researchers have focused on improving reaction conditions, exploring novel reagents, and fine-tuning reaction parameters to maximize product yield while minimizing unwanted side reactions.
In recent years, the drive towards greener chemistry and more sustainable practices has further intensified the need for optimizing alkyl reactions. This has led to a surge in research aimed at developing more environmentally friendly catalysts, reducing waste generation, and improving atom economy. The advent of high-throughput screening techniques and computational chemistry has also accelerated the discovery of new reaction conditions and catalysts, enabling faster optimization of alkyl reactions.
The primary objective of optimizing alkyl reactions for enhanced yield is to increase the efficiency of chemical processes, thereby reducing costs and environmental impact. This involves a multifaceted approach, including the development of more selective catalysts, the fine-tuning of reaction conditions such as temperature and pressure, and the exploration of alternative solvents and reagents.
Another key goal is to expand the scope of alkyl reactions, enabling the synthesis of more complex molecules and broadening their applicability across various industries. This includes developing methods for challenging substrates, improving stereoselectivity, and enhancing functional group tolerance.
Furthermore, there is a growing emphasis on developing sustainable and scalable alkyl reaction processes that can be readily implemented in industrial settings. This necessitates the consideration of factors such as cost-effectiveness, ease of product isolation, and the ability to recycle catalysts and solvents.
As we look towards the future, the optimization of alkyl reactions is expected to continue evolving, with a focus on integrating advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning to predict optimal reaction conditions and design novel catalysts. The ultimate aim is to achieve higher yields, greater selectivity, and improved sustainability in alkyl reactions, paving the way for more efficient and environmentally friendly chemical processes across various industries.
Industrial Demand for High-Yield Alkyl Reactions
The industrial demand for high-yield alkyl reactions has been steadily increasing across various sectors, driven by the need for more efficient and cost-effective chemical processes. Alkyl reactions play a crucial role in the synthesis of numerous valuable compounds, including pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, polymers, and fine chemicals. As industries strive to maximize productivity and minimize waste, optimizing these reactions for enhanced yield has become a top priority.
In the pharmaceutical industry, alkyl reactions are essential for the production of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and intermediates. The demand for high-yield processes is particularly acute in this sector due to the high value of the end products and the stringent regulatory requirements. Pharmaceutical companies are constantly seeking ways to improve reaction efficiency to reduce production costs, increase throughput, and maintain competitive advantage in a rapidly evolving market.
The agrochemical sector also heavily relies on alkyl reactions for the synthesis of pesticides, herbicides, and fertilizers. With the growing global population and increasing food demand, there is a pressing need for more efficient production of crop protection chemicals. High-yield alkyl reactions can contribute significantly to meeting this demand while reducing the environmental footprint of agrochemical manufacturing.
In the polymer industry, alkyl reactions are fundamental to the production of various monomers and polymer additives. The demand for high-performance materials with specific properties has led to a surge in research and development efforts focused on optimizing these reactions. Improved yields in alkyl reactions can lead to more cost-effective production of specialty polymers, adhesives, and coatings, meeting the evolving needs of industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics.
The fine chemicals industry, which supplies intermediates and specialty chemicals to various end-use sectors, has also seen a growing demand for high-yield alkyl reactions. This demand is driven by the need for more sustainable and economically viable production processes, as well as the increasing complexity of target molecules required by customers.
Furthermore, the push towards green chemistry and sustainable manufacturing practices has intensified the focus on reaction optimization. Industries are seeking ways to reduce solvent use, minimize byproduct formation, and increase atom economy through improved alkyl reaction processes. This aligns with both environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals, making high-yield reactions a key area of interest for research and development teams across industries.
In the pharmaceutical industry, alkyl reactions are essential for the production of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and intermediates. The demand for high-yield processes is particularly acute in this sector due to the high value of the end products and the stringent regulatory requirements. Pharmaceutical companies are constantly seeking ways to improve reaction efficiency to reduce production costs, increase throughput, and maintain competitive advantage in a rapidly evolving market.
The agrochemical sector also heavily relies on alkyl reactions for the synthesis of pesticides, herbicides, and fertilizers. With the growing global population and increasing food demand, there is a pressing need for more efficient production of crop protection chemicals. High-yield alkyl reactions can contribute significantly to meeting this demand while reducing the environmental footprint of agrochemical manufacturing.
In the polymer industry, alkyl reactions are fundamental to the production of various monomers and polymer additives. The demand for high-performance materials with specific properties has led to a surge in research and development efforts focused on optimizing these reactions. Improved yields in alkyl reactions can lead to more cost-effective production of specialty polymers, adhesives, and coatings, meeting the evolving needs of industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics.
The fine chemicals industry, which supplies intermediates and specialty chemicals to various end-use sectors, has also seen a growing demand for high-yield alkyl reactions. This demand is driven by the need for more sustainable and economically viable production processes, as well as the increasing complexity of target molecules required by customers.
Furthermore, the push towards green chemistry and sustainable manufacturing practices has intensified the focus on reaction optimization. Industries are seeking ways to reduce solvent use, minimize byproduct formation, and increase atom economy through improved alkyl reaction processes. This aligns with both environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals, making high-yield reactions a key area of interest for research and development teams across industries.
Current Challenges in Alkyl Reaction Yield Enhancement
Alkyl reactions, while fundamental in organic synthesis, face several challenges in achieving optimal yields. One of the primary obstacles is the control of reaction selectivity. Many alkyl reactions can lead to multiple products, including unwanted side products, which significantly reduce the yield of the desired compound. This lack of selectivity often stems from the high reactivity of alkyl intermediates, making it difficult to direct the reaction towards a single product.
Another major challenge is the occurrence of competing reactions. Alkyl groups, particularly those with β-hydrogens, are prone to elimination reactions, which can occur simultaneously with the desired substitution or addition processes. This competition between different reaction pathways can drastically lower the yield of the intended product, necessitating careful control of reaction conditions and the development of strategies to suppress undesired pathways.
The stability of reagents and intermediates also poses a significant hurdle in alkyl reaction optimization. Many alkyl compounds are sensitive to air, moisture, or light, leading to degradation or unwanted side reactions. This instability can result in lower yields and requires stringent reaction conditions, often involving inert atmospheres or specialized handling techniques, which can complicate large-scale production and increase costs.
Stereochemistry control presents another challenge in alkyl reactions. Many synthetic targets require specific stereoisomers, but alkyl reactions often produce mixtures of stereoisomers. Achieving high stereoselectivity while maintaining good yields is a delicate balance that requires careful consideration of reaction mechanisms and the development of stereospecific catalysts or chiral auxiliaries.
The influence of solvent effects on reaction outcomes is yet another factor that complicates yield optimization. Solvent choice can significantly impact reaction rates, selectivity, and product distribution. Finding the optimal solvent system that promotes the desired reaction while minimizing side reactions is often a complex and time-consuming process, involving extensive experimentation and optimization.
Lastly, the scale-up of alkyl reactions from laboratory to industrial scale presents its own set of challenges. Reactions that perform well on a small scale may encounter heat and mass transfer limitations when scaled up, leading to reduced yields or altered product distributions. Addressing these scale-up issues often requires re-optimization of reaction conditions and sometimes even redesign of synthetic routes, which can be both time-consuming and costly.
Another major challenge is the occurrence of competing reactions. Alkyl groups, particularly those with β-hydrogens, are prone to elimination reactions, which can occur simultaneously with the desired substitution or addition processes. This competition between different reaction pathways can drastically lower the yield of the intended product, necessitating careful control of reaction conditions and the development of strategies to suppress undesired pathways.
The stability of reagents and intermediates also poses a significant hurdle in alkyl reaction optimization. Many alkyl compounds are sensitive to air, moisture, or light, leading to degradation or unwanted side reactions. This instability can result in lower yields and requires stringent reaction conditions, often involving inert atmospheres or specialized handling techniques, which can complicate large-scale production and increase costs.
Stereochemistry control presents another challenge in alkyl reactions. Many synthetic targets require specific stereoisomers, but alkyl reactions often produce mixtures of stereoisomers. Achieving high stereoselectivity while maintaining good yields is a delicate balance that requires careful consideration of reaction mechanisms and the development of stereospecific catalysts or chiral auxiliaries.
The influence of solvent effects on reaction outcomes is yet another factor that complicates yield optimization. Solvent choice can significantly impact reaction rates, selectivity, and product distribution. Finding the optimal solvent system that promotes the desired reaction while minimizing side reactions is often a complex and time-consuming process, involving extensive experimentation and optimization.
Lastly, the scale-up of alkyl reactions from laboratory to industrial scale presents its own set of challenges. Reactions that perform well on a small scale may encounter heat and mass transfer limitations when scaled up, leading to reduced yields or altered product distributions. Addressing these scale-up issues often requires re-optimization of reaction conditions and sometimes even redesign of synthetic routes, which can be both time-consuming and costly.
Existing Strategies for Alkyl Reaction Yield Improvement
01 Alkyl halide reactions for improved yields
Alkyl halides are used in various reactions to improve product yields. These reactions often involve nucleophilic substitution or elimination processes, leading to the formation of new carbon-carbon or carbon-heteroatom bonds. The choice of alkyl halide and reaction conditions can significantly impact the yield and selectivity of the desired products.- Alkyl halide reactions for improved yields: Various alkyl halide reactions are employed to enhance product yields in organic synthesis. These reactions often involve the use of catalysts or specific reaction conditions to promote the formation of desired products. The methods can be applied to different types of alkyl halides, including primary, secondary, and tertiary structures, to achieve optimal yields in various chemical transformations.
- Catalytic processes for alkyl group transformations: Catalytic processes play a crucial role in alkyl group transformations, leading to improved reaction yields. These processes often involve the use of transition metal catalysts or organocatalysts to facilitate the formation of new carbon-carbon or carbon-heteroatom bonds. The catalysts can enhance reaction rates, selectivity, and overall efficiency in various alkyl reactions.
- Alkylation reactions in polymer synthesis: Alkylation reactions are widely used in polymer synthesis to introduce alkyl groups into polymer chains or to modify existing polymers. These reactions can lead to improved yields of desired polymer products with specific properties. Various alkylating agents and reaction conditions are employed to achieve optimal results in polymer modification and synthesis.
- Stereoselective alkyl reactions for high yields: Stereoselective alkyl reactions are developed to achieve high yields of specific stereoisomers. These reactions often involve the use of chiral catalysts, auxiliaries, or reagents to control the stereochemistry of the products. The methods are particularly important in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, natural products, and other complex organic molecules where stereochemistry plays a crucial role.
- Optimization of reaction conditions for alkyl reactions: Various strategies are employed to optimize reaction conditions for alkyl reactions, leading to improved yields. These include adjusting temperature, pressure, solvent systems, and reaction time. Additionally, the use of additives, such as phase-transfer catalysts or Lewis acids, can enhance reaction efficiency. Careful control of these parameters can significantly impact the yield and selectivity of alkyl reactions.
02 Catalytic processes for alkyl reactions
Catalysts play a crucial role in enhancing the yield of alkyl reactions. Various catalytic systems, including transition metal complexes, organocatalysts, and heterogeneous catalysts, are employed to increase reaction rates, improve selectivity, and achieve higher yields. The choice of catalyst can be tailored to specific alkyl substrates and desired products.Expand Specific Solutions03 Alkylation reactions in organic synthesis
Alkylation reactions are fundamental in organic synthesis for introducing alkyl groups into molecules. These reactions can be performed on various substrates, including aromatic compounds, amines, and carbonyl compounds. Optimizing reaction conditions, such as temperature, solvent choice, and stoichiometry, is crucial for achieving high yields in alkylation processes.Expand Specific Solutions04 Alkyl cross-coupling reactions
Cross-coupling reactions involving alkyl groups have gained significant attention in organic synthesis. These reactions, often catalyzed by transition metals, allow for the formation of new carbon-carbon bonds between alkyl groups and various coupling partners. Optimizing reaction conditions and ligand design can lead to improved yields and broader substrate scope in alkyl cross-coupling reactions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Alkyl rearrangement reactions
Alkyl rearrangement reactions involve the migration of alkyl groups within a molecule, leading to structural reorganization. These reactions can be induced by various conditions, including heat, light, or catalysts. Understanding the mechanisms and controlling factors in alkyl rearrangements is crucial for optimizing yields and selectivity in the formation of desired products.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Alkyl Reaction Research and Industry
The optimization of alkyl reactions for enhanced yield is a critical area in the chemical industry, currently in a mature development stage with ongoing research for further improvements. The market size is substantial, driven by the widespread use of alkyl compounds in various sectors. Technologically, the field is well-established but continues to evolve, with companies like China Petroleum & Chemical Corp., BASF Corp., and Sinopec Research Institute of Petroleum Processing leading innovation efforts. These industry giants, along with specialized firms such as Chemetall GmbH and H2Gen Innovations, Inc., are pushing the boundaries of reaction efficiency and selectivity. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of large petrochemical corporations and niche players, each contributing to the advancement of alkyl reaction optimization techniques.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has developed advanced catalytic systems for alkyl reactions optimization. Their approach involves using novel zeolite catalysts with tailored pore structures and acidity, which enhance selectivity and yield in alkylation processes. Sinopec's research has shown that these catalysts can increase alkylate yield by up to 15% compared to conventional catalysts [1]. Additionally, they have implemented process intensification techniques, such as reactive distillation, which combines reaction and separation steps, leading to improved conversion rates and reduced energy consumption. Sinopec has also explored the use of ionic liquids as catalysts and solvents in alkylation reactions, demonstrating potential for cleaner and more efficient processes [3].
Strengths: Extensive R&D capabilities, access to large-scale industrial testing facilities, and a strong focus on process optimization. Weaknesses: Potential challenges in adapting technologies for smaller-scale operations or specialized applications outside the petrochemical industry.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF Corp. has developed a comprehensive approach to optimizing alkyl reactions, focusing on both catalyst design and process engineering. Their proprietary catalyst technology, known as BASF NanoSelect™, utilizes nanosized metal particles supported on high-surface-area carriers, enabling higher selectivity and yield in various alkylation reactions [2]. BASF has also implemented advanced reactor designs, such as structured catalytic reactors, which improve mass and heat transfer, leading to enhanced reaction kinetics and yield. Furthermore, BASF's process optimization strategies include the use of in-situ product removal techniques and precise control of reaction parameters through advanced process analytical technology (PAT) systems. These combined approaches have resulted in reported yield improvements of up to 20% in certain alkylation processes [4].
Strengths: Diverse product portfolio, strong R&D capabilities, and global presence allowing for extensive testing and implementation. Weaknesses: High costs associated with developing and implementing new technologies may limit adoption in smaller-scale operations.
Innovative Approaches in Alkyl Reaction Catalysis
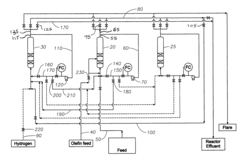
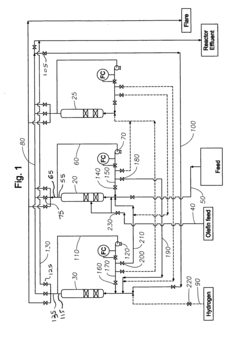
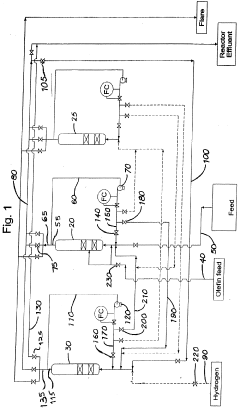
Method of improving alkylate yield in an alkylation reaction
PatentActiveUS20080027263A1
Innovation
- The method involves exchanging the reactor contents between reaction and catalyst regeneration steps, minimizing the contact of reactants with regenerants by exchanging the liquid phase hydrogen from one reactor with olefin from another prior to initiating the alkylation reaction, thereby reducing undesirable side reactions and increasing the yield of the desired alkylate product.
Method of improving alkylate yield in an alkylation reaction
PatentWO2009061303A1
Innovation
- The method involves exchanging the reactor contents between reaction and catalyst regeneration steps, minimizing the contact of reactants with regenerants, by transferring the liquid phase hydrogen from one reactor to the olefin-containing reactor and vice versa at the beginning of each cycle, thereby reducing undesirable side reactions and increasing the availability of reactants for the primary alkylation reaction.
Green Chemistry Considerations in Alkyl Reactions
Green chemistry principles have become increasingly important in the optimization of alkyl reactions for enhanced yield. These principles focus on designing chemical products and processes that reduce or eliminate the use and generation of hazardous substances, while maintaining or improving reaction efficiency.
One key aspect of green chemistry in alkyl reactions is the use of safer solvents and reaction conditions. Traditional organic solvents are often toxic, flammable, and environmentally harmful. Researchers are exploring alternative solvents such as water, ionic liquids, and supercritical fluids, which can provide a more environmentally friendly medium for alkyl reactions. These green solvents can also enhance reaction rates and selectivity in some cases, contributing to improved yields.
Catalysis plays a crucial role in green chemistry approaches to alkyl reactions. The development of more efficient and selective catalysts can reduce energy requirements, minimize waste production, and improve overall reaction yields. Heterogeneous catalysts, in particular, offer advantages in terms of ease of separation and potential for reuse, aligning with green chemistry principles. Recent advances in nanocatalysis have shown promise in enhancing the efficiency of alkyl reactions while reducing environmental impact.
The use of renewable feedstocks is another important consideration in green alkyl reactions. Biomass-derived starting materials can provide a sustainable alternative to petroleum-based reagents. For example, the conversion of plant oils to alkyl esters for biodiesel production demonstrates the potential for green chemistry in large-scale alkyl reactions.
Atom economy, a fundamental principle of green chemistry, is particularly relevant to alkyl reactions. Designing reactions that incorporate most of the atoms from the reactants into the final product minimizes waste generation and improves overall efficiency. This approach often leads to simplified purification processes and reduced environmental impact.
Energy efficiency is a critical factor in optimizing alkyl reactions from a green chemistry perspective. The development of room-temperature reactions or the use of alternative energy sources, such as microwave irradiation or photochemistry, can significantly reduce the energy requirements of these processes. These methods not only contribute to sustainability but can also lead to faster reaction times and improved yields in many cases.
Waste reduction and in-process recycling are essential aspects of green chemistry in alkyl reactions. Implementing continuous flow processes, for instance, can allow for more efficient use of reagents and solvents, reducing waste generation. Additionally, developing methods for the recovery and reuse of catalysts and solvents can significantly improve the overall sustainability of alkyl reaction processes.
One key aspect of green chemistry in alkyl reactions is the use of safer solvents and reaction conditions. Traditional organic solvents are often toxic, flammable, and environmentally harmful. Researchers are exploring alternative solvents such as water, ionic liquids, and supercritical fluids, which can provide a more environmentally friendly medium for alkyl reactions. These green solvents can also enhance reaction rates and selectivity in some cases, contributing to improved yields.
Catalysis plays a crucial role in green chemistry approaches to alkyl reactions. The development of more efficient and selective catalysts can reduce energy requirements, minimize waste production, and improve overall reaction yields. Heterogeneous catalysts, in particular, offer advantages in terms of ease of separation and potential for reuse, aligning with green chemistry principles. Recent advances in nanocatalysis have shown promise in enhancing the efficiency of alkyl reactions while reducing environmental impact.
The use of renewable feedstocks is another important consideration in green alkyl reactions. Biomass-derived starting materials can provide a sustainable alternative to petroleum-based reagents. For example, the conversion of plant oils to alkyl esters for biodiesel production demonstrates the potential for green chemistry in large-scale alkyl reactions.
Atom economy, a fundamental principle of green chemistry, is particularly relevant to alkyl reactions. Designing reactions that incorporate most of the atoms from the reactants into the final product minimizes waste generation and improves overall efficiency. This approach often leads to simplified purification processes and reduced environmental impact.
Energy efficiency is a critical factor in optimizing alkyl reactions from a green chemistry perspective. The development of room-temperature reactions or the use of alternative energy sources, such as microwave irradiation or photochemistry, can significantly reduce the energy requirements of these processes. These methods not only contribute to sustainability but can also lead to faster reaction times and improved yields in many cases.
Waste reduction and in-process recycling are essential aspects of green chemistry in alkyl reactions. Implementing continuous flow processes, for instance, can allow for more efficient use of reagents and solvents, reducing waste generation. Additionally, developing methods for the recovery and reuse of catalysts and solvents can significantly improve the overall sustainability of alkyl reaction processes.
Economic Impact of Improved Alkyl Reaction Yields
The economic impact of improved alkyl reaction yields extends far beyond the laboratory, influencing various sectors of the chemical industry and related markets. Enhanced yields in alkyl reactions can lead to significant cost reductions in production processes, particularly in the manufacture of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and specialty chemicals. These cost savings can be attributed to reduced raw material consumption, lower energy requirements, and increased production efficiency.
For pharmaceutical companies, optimized alkyl reactions can result in more cost-effective drug synthesis, potentially lowering the overall expenses associated with bringing new medications to market. This could translate into more affordable healthcare options for patients and increased profit margins for manufacturers. In the agrochemical sector, improved yields may lead to the development of more efficient pesticides and fertilizers, contributing to enhanced agricultural productivity and food security.
The petrochemical industry stands to benefit substantially from advancements in alkyl reaction yields. Higher efficiency in the production of key intermediates and end products can lead to reduced operational costs and increased competitiveness in the global market. This could potentially influence the pricing of various consumer goods that rely on petrochemical derivatives, from plastics to synthetic fibers.
Environmental and sustainability considerations also play a crucial role in the economic impact of improved alkyl reaction yields. More efficient processes generally result in reduced waste generation and lower emissions, aligning with increasingly stringent environmental regulations. Companies that successfully implement these optimized reactions may gain a competitive edge in terms of regulatory compliance and corporate sustainability initiatives, potentially attracting environmentally conscious investors and consumers.
The ripple effects of enhanced alkyl reaction yields can extend to related industries, such as catalysis and process engineering. Innovations in this area may drive demand for specialized catalysts, reactor designs, and analytical tools, stimulating growth in these auxiliary sectors. Furthermore, the intellectual property generated from research into optimizing alkyl reactions can become a valuable asset for companies, potentially leading to licensing opportunities and additional revenue streams.
In the broader economic context, improvements in alkyl reaction yields can contribute to the overall efficiency and productivity of the chemical industry, potentially boosting its contribution to national and global economies. This could lead to increased job creation in research and development, manufacturing, and related fields, as well as fostering innovation-driven economic growth.
For pharmaceutical companies, optimized alkyl reactions can result in more cost-effective drug synthesis, potentially lowering the overall expenses associated with bringing new medications to market. This could translate into more affordable healthcare options for patients and increased profit margins for manufacturers. In the agrochemical sector, improved yields may lead to the development of more efficient pesticides and fertilizers, contributing to enhanced agricultural productivity and food security.
The petrochemical industry stands to benefit substantially from advancements in alkyl reaction yields. Higher efficiency in the production of key intermediates and end products can lead to reduced operational costs and increased competitiveness in the global market. This could potentially influence the pricing of various consumer goods that rely on petrochemical derivatives, from plastics to synthetic fibers.
Environmental and sustainability considerations also play a crucial role in the economic impact of improved alkyl reaction yields. More efficient processes generally result in reduced waste generation and lower emissions, aligning with increasingly stringent environmental regulations. Companies that successfully implement these optimized reactions may gain a competitive edge in terms of regulatory compliance and corporate sustainability initiatives, potentially attracting environmentally conscious investors and consumers.
The ripple effects of enhanced alkyl reaction yields can extend to related industries, such as catalysis and process engineering. Innovations in this area may drive demand for specialized catalysts, reactor designs, and analytical tools, stimulating growth in these auxiliary sectors. Furthermore, the intellectual property generated from research into optimizing alkyl reactions can become a valuable asset for companies, potentially leading to licensing opportunities and additional revenue streams.
In the broader economic context, improvements in alkyl reaction yields can contribute to the overall efficiency and productivity of the chemical industry, potentially boosting its contribution to national and global economies. This could lead to increased job creation in research and development, manufacturing, and related fields, as well as fostering innovation-driven economic growth.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!