How to Strategize Isocyanate Market Entry Points?
JUL 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Isocyanate Market Overview and Objectives
The isocyanate market has experienced significant growth and transformation over the past decades, driven by increasing demand across various industries. Isocyanates, primarily used in the production of polyurethanes, have become integral components in numerous applications, including construction, automotive, furniture, and electronics. The market's evolution has been characterized by technological advancements, shifting consumer preferences, and stringent environmental regulations.
The global isocyanate market is projected to continue its upward trajectory, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 6% expected over the next five years. This growth is largely attributed to the expanding construction and automotive sectors in emerging economies, as well as the rising demand for energy-efficient materials in developed nations. The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and India, is anticipated to be the primary driver of market expansion due to rapid industrialization and urbanization.
Key objectives for market entry in the isocyanate sector include identifying niche segments with high growth potential, developing sustainable and eco-friendly production processes, and establishing strategic partnerships with end-users and distributors. Companies aiming to enter this market must focus on innovation to address environmental concerns and meet increasingly stringent regulations regarding volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions and health hazards associated with isocyanate exposure.
Another crucial objective is to optimize production costs and ensure a stable supply chain, given the volatility of raw material prices and potential disruptions in global trade. Diversification of product portfolios to include both aromatic and aliphatic isocyanates can help companies cater to a broader range of applications and mitigate risks associated with market fluctuations.
Market entrants should also prioritize research and development efforts to improve product performance, reduce environmental impact, and explore novel applications. This may involve investing in bio-based isocyanates or developing isocyanate-free alternatives to address growing environmental concerns and capitalize on the shift towards sustainable materials.
Understanding regional market dynamics and tailoring strategies accordingly is essential for successful market entry. For instance, while developed markets may focus on high-performance and specialty isocyanates, emerging markets might prioritize cost-effective solutions for mass-market applications. Additionally, companies should consider vertical integration or strategic alliances to secure raw material supplies and enhance their competitive position in the value chain.
The global isocyanate market is projected to continue its upward trajectory, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 6% expected over the next five years. This growth is largely attributed to the expanding construction and automotive sectors in emerging economies, as well as the rising demand for energy-efficient materials in developed nations. The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and India, is anticipated to be the primary driver of market expansion due to rapid industrialization and urbanization.
Key objectives for market entry in the isocyanate sector include identifying niche segments with high growth potential, developing sustainable and eco-friendly production processes, and establishing strategic partnerships with end-users and distributors. Companies aiming to enter this market must focus on innovation to address environmental concerns and meet increasingly stringent regulations regarding volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions and health hazards associated with isocyanate exposure.
Another crucial objective is to optimize production costs and ensure a stable supply chain, given the volatility of raw material prices and potential disruptions in global trade. Diversification of product portfolios to include both aromatic and aliphatic isocyanates can help companies cater to a broader range of applications and mitigate risks associated with market fluctuations.
Market entrants should also prioritize research and development efforts to improve product performance, reduce environmental impact, and explore novel applications. This may involve investing in bio-based isocyanates or developing isocyanate-free alternatives to address growing environmental concerns and capitalize on the shift towards sustainable materials.
Understanding regional market dynamics and tailoring strategies accordingly is essential for successful market entry. For instance, while developed markets may focus on high-performance and specialty isocyanates, emerging markets might prioritize cost-effective solutions for mass-market applications. Additionally, companies should consider vertical integration or strategic alliances to secure raw material supplies and enhance their competitive position in the value chain.
Global Demand Analysis for Isocyanates
The global demand for isocyanates has been steadily increasing, driven by the growth of various end-use industries such as construction, automotive, and furniture. The market is primarily dominated by two types of isocyanates: toluene diisocyanate (TDI) and methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI). These chemicals are essential components in the production of polyurethanes, which find applications in a wide range of products including foams, coatings, adhesives, and elastomers.
In recent years, the Asia-Pacific region has emerged as the largest consumer of isocyanates, accounting for a significant portion of global demand. This is largely attributed to the rapid industrialization and urbanization in countries like China and India, coupled with the expansion of manufacturing sectors. The construction industry, in particular, has been a major driver of isocyanate demand in this region, with increasing investments in infrastructure development and residential projects.
North America and Europe follow as the second and third largest markets for isocyanates, respectively. These regions have well-established automotive and furniture industries, which continue to drive demand for polyurethane-based products. The automotive sector, in particular, has been adopting lightweight materials to improve fuel efficiency, leading to increased use of polyurethane components.
The global isocyanate market has shown resilience despite challenges such as volatile raw material prices and environmental concerns. The industry has been focusing on developing eco-friendly alternatives and improving production processes to address these issues. Bio-based isocyanates, for instance, are gaining traction as sustainable options, although their market share remains relatively small compared to conventional isocyanates.
Looking ahead, the demand for isocyanates is expected to continue its upward trajectory. Emerging applications in sectors such as electronics, medical devices, and renewable energy are likely to create new growth opportunities. Additionally, the ongoing trend of urbanization in developing countries is anticipated to sustain the demand for construction and automotive applications, which remain the primary consumers of isocyanate-based products.
However, market entry strategies must consider regional variations in demand patterns, regulatory landscapes, and competitive dynamics. While Asia-Pacific offers significant growth potential, it also presents challenges in terms of intense competition and price sensitivity. Mature markets like North America and Europe, on the other hand, may require a focus on innovation and value-added products to gain market share.
In recent years, the Asia-Pacific region has emerged as the largest consumer of isocyanates, accounting for a significant portion of global demand. This is largely attributed to the rapid industrialization and urbanization in countries like China and India, coupled with the expansion of manufacturing sectors. The construction industry, in particular, has been a major driver of isocyanate demand in this region, with increasing investments in infrastructure development and residential projects.
North America and Europe follow as the second and third largest markets for isocyanates, respectively. These regions have well-established automotive and furniture industries, which continue to drive demand for polyurethane-based products. The automotive sector, in particular, has been adopting lightweight materials to improve fuel efficiency, leading to increased use of polyurethane components.
The global isocyanate market has shown resilience despite challenges such as volatile raw material prices and environmental concerns. The industry has been focusing on developing eco-friendly alternatives and improving production processes to address these issues. Bio-based isocyanates, for instance, are gaining traction as sustainable options, although their market share remains relatively small compared to conventional isocyanates.
Looking ahead, the demand for isocyanates is expected to continue its upward trajectory. Emerging applications in sectors such as electronics, medical devices, and renewable energy are likely to create new growth opportunities. Additionally, the ongoing trend of urbanization in developing countries is anticipated to sustain the demand for construction and automotive applications, which remain the primary consumers of isocyanate-based products.
However, market entry strategies must consider regional variations in demand patterns, regulatory landscapes, and competitive dynamics. While Asia-Pacific offers significant growth potential, it also presents challenges in terms of intense competition and price sensitivity. Mature markets like North America and Europe, on the other hand, may require a focus on innovation and value-added products to gain market share.
Current Challenges in Isocyanate Production
The isocyanate production industry faces several significant challenges that impact market dynamics and entry strategies. One of the primary issues is the volatility of raw material prices, particularly for key feedstocks like toluene and benzene. These fluctuations can significantly affect production costs and profit margins, making it difficult for manufacturers to maintain consistent pricing and market positioning.
Environmental and safety concerns pose another major challenge. Isocyanates are known for their potential health hazards and environmental impact, leading to increasingly stringent regulations worldwide. Producers must invest heavily in safety measures, emission control technologies, and waste management systems to comply with these regulations, which can substantially increase operational costs and create barriers to entry for new market players.
The energy-intensive nature of isocyanate production processes presents additional challenges. With growing emphasis on sustainability and carbon footprint reduction, manufacturers face pressure to optimize energy efficiency and explore alternative production methods. This necessitates significant research and development investments, which can be prohibitive for smaller companies or new entrants.
Market concentration and established supply chains also create obstacles for new entrants. The isocyanate market is dominated by a few large multinational corporations with vertically integrated operations. These companies benefit from economies of scale, established distribution networks, and long-term customer relationships, making it challenging for new players to gain a foothold in the market.
Technological advancements and process innovations are critical for maintaining competitiveness in isocyanate production. However, developing and implementing new technologies requires substantial capital investment and expertise. Smaller companies or new entrants may struggle to keep pace with these advancements, potentially limiting their ability to compete effectively in the market.
Capacity management presents another challenge in the isocyanate industry. Balancing production capacity with market demand is crucial for maintaining profitability. Overcapacity can lead to price pressures and reduced margins, while undercapacity may result in lost market opportunities. This delicate balance is particularly challenging in a market characterized by cyclical demand patterns and global economic fluctuations.
Lastly, the complexity of the isocyanate supply chain and logistics poses significant challenges. The transportation and storage of isocyanates require specialized equipment and handling procedures due to their reactive nature and potential hazards. This complexity adds to the overall cost of production and distribution, creating additional barriers for new market entrants and smaller players in the industry.
Environmental and safety concerns pose another major challenge. Isocyanates are known for their potential health hazards and environmental impact, leading to increasingly stringent regulations worldwide. Producers must invest heavily in safety measures, emission control technologies, and waste management systems to comply with these regulations, which can substantially increase operational costs and create barriers to entry for new market players.
The energy-intensive nature of isocyanate production processes presents additional challenges. With growing emphasis on sustainability and carbon footprint reduction, manufacturers face pressure to optimize energy efficiency and explore alternative production methods. This necessitates significant research and development investments, which can be prohibitive for smaller companies or new entrants.
Market concentration and established supply chains also create obstacles for new entrants. The isocyanate market is dominated by a few large multinational corporations with vertically integrated operations. These companies benefit from economies of scale, established distribution networks, and long-term customer relationships, making it challenging for new players to gain a foothold in the market.
Technological advancements and process innovations are critical for maintaining competitiveness in isocyanate production. However, developing and implementing new technologies requires substantial capital investment and expertise. Smaller companies or new entrants may struggle to keep pace with these advancements, potentially limiting their ability to compete effectively in the market.
Capacity management presents another challenge in the isocyanate industry. Balancing production capacity with market demand is crucial for maintaining profitability. Overcapacity can lead to price pressures and reduced margins, while undercapacity may result in lost market opportunities. This delicate balance is particularly challenging in a market characterized by cyclical demand patterns and global economic fluctuations.
Lastly, the complexity of the isocyanate supply chain and logistics poses significant challenges. The transportation and storage of isocyanates require specialized equipment and handling procedures due to their reactive nature and potential hazards. This complexity adds to the overall cost of production and distribution, creating additional barriers for new market entrants and smaller players in the industry.
Existing Market Entry Strategies
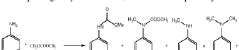
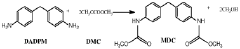
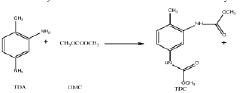
01 Synthesis and properties of isocyanates
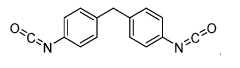
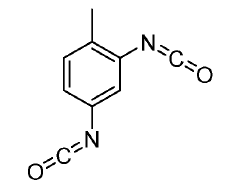
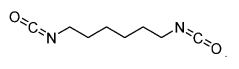
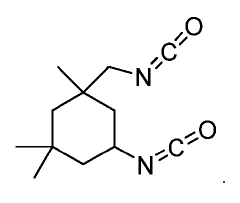
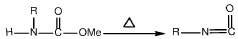
Isocyanates are a class of highly reactive compounds characterized by the -NCO functional group. They are widely used in the production of polyurethanes and other polymeric materials. The synthesis of isocyanates often involves the reaction of amines with phosgene or other carbonyl-containing compounds. Their properties, such as reactivity and stability, are crucial for various industrial applications.- Synthesis and modification of isocyanates: This category focuses on methods for synthesizing isocyanates and modifying their chemical structure. It includes processes for producing various types of isocyanates, such as aliphatic and aromatic isocyanates, as well as techniques for altering their properties through chemical modifications.
- Isocyanate-based polymers and coatings: This point covers the use of isocyanates in the production of polymers and coatings. It includes the development of polyurethanes, polyureas, and other isocyanate-based materials for applications in various industries, such as automotive, construction, and electronics.
- Isocyanate curing and crosslinking agents: This category deals with the use of isocyanates as curing and crosslinking agents in various formulations. It includes their application in adhesives, sealants, and composite materials to improve mechanical properties, chemical resistance, and durability.
- Environmental and safety considerations for isocyanates: This point addresses the environmental impact and safety concerns associated with isocyanates. It covers topics such as reducing emissions, developing safer handling procedures, and creating more environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional isocyanate-based products.
- Novel applications of isocyanates: This category explores innovative uses of isocyanates beyond traditional applications. It includes their incorporation in advanced materials, such as shape-memory polymers, self-healing coatings, and functional nanocomposites, as well as their potential use in emerging technologies.
02 Applications of isocyanates in coatings and adhesives
Isocyanates play a significant role in the formulation of high-performance coatings and adhesives. They react with polyols to form polyurethanes, which offer excellent durability, chemical resistance, and adhesion properties. These materials find applications in automotive coatings, industrial finishes, and structural adhesives.Expand Specific Solutions03 Isocyanate-based foam production
Isocyanates are crucial components in the production of polyurethane foams. When combined with polyols and appropriate catalysts and blowing agents, they form flexible or rigid foams used in insulation, cushioning, and packaging applications. The foam properties can be tailored by adjusting the isocyanate and polyol formulations.Expand Specific Solutions04 Safety and handling of isocyanates
Due to their high reactivity, isocyanates require careful handling and safety precautions. Exposure can cause respiratory irritation and sensitization. Proper personal protective equipment, ventilation, and storage practices are essential when working with isocyanates. Regulations and guidelines have been established to ensure safe use in industrial settings.Expand Specific Solutions05 Isocyanate-free alternatives and sustainable approaches
With increasing environmental and health concerns, research is focused on developing isocyanate-free alternatives and more sustainable approaches. This includes the use of bio-based raw materials, non-isocyanate polyurethanes, and alternative crosslinking chemistries. These efforts aim to maintain the performance benefits of traditional isocyanate-based systems while reducing potential hazards and environmental impact.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Isocyanate Industry
The isocyanate market is in a mature growth phase, characterized by steady demand and established applications across various industries. The global market size is substantial, estimated to be over $20 billion annually, driven by robust growth in construction, automotive, and furniture sectors. Technologically, isocyanate production is well-developed, with major players like Wanhua Chemical, BASF, and Covestro leading innovation. These companies, along with others such as Asahi Kasei and Mitsui Chemicals, are focusing on developing more environmentally friendly and sustainable isocyanate products to meet evolving regulatory requirements and consumer preferences. Market entry strategies should consider regional demand patterns, raw material access, and potential partnerships with established players to navigate this competitive landscape.
Wanhua Chemical Group Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Wanhua Chemical Group has developed a comprehensive strategy for isocyanate market entry, focusing on vertical integration and product diversification. The company has invested heavily in research and development to create innovative isocyanate products, including MDI (Methylene Diphenyl Diisocyanate) and TDI (Toluene Diisocyanate). Wanhua has established world-class production facilities with advanced technologies, allowing for efficient and large-scale production[1]. Their approach includes expanding global reach through strategic partnerships and acquisitions, such as the purchase of Yantai Wanhua Polyurethanes Co., Ltd., which significantly increased their production capacity[2]. Additionally, Wanhua has focused on developing eco-friendly isocyanate products to meet growing environmental concerns, positioning themselves as a leader in sustainable chemical solutions[3].
Strengths: Vertical integration, large production capacity, and strong R&D capabilities. Weaknesses: Heavy reliance on the Chinese market and potential vulnerability to trade disputes.
BASF Corp.
Technical Solution: BASF's isocyanate market entry strategy centers on innovation and sustainability. The company has developed a range of high-performance isocyanate products, including their Lupranate® series for various applications. BASF has invested in bio-based isocyanates, aiming to reduce the carbon footprint of their products[4]. Their approach includes a strong focus on customer collaboration, offering tailored solutions and technical support. BASF has also implemented a global production network, with strategic locations in Europe, North America, and Asia, ensuring supply chain resilience and proximity to key markets[5]. The company's commitment to digitalization has led to the development of advanced process control systems and predictive maintenance in their isocyanate production facilities, improving efficiency and product quality[6].
Strengths: Global presence, strong brand reputation, and focus on sustainable solutions. Weaknesses: High operational costs and exposure to raw material price fluctuations.
Innovative Approaches in Isocyanate Synthesis
Flow chemistry synthesis of isocyanates
PatentWO2021119606A1
Innovation
- A continuous flow process involving the mixing of acyl hydrazides with nitrous acid to form acyl azides, followed by heating in the presence of an organic solvent to produce isocyanates through Curtius rearrangement, offering a safer and more scalable method for isocyanate synthesis.
A process for the synthesis of aromatic carbamates
PatentWO2018216036A1
Innovation
- A process using a binary or ternary mixed metal oxide catalyst, specifically Ce:Zr or Zn:Zr mixed metal oxides, to react amines with dialkyl carbonates at controlled temperatures and times, achieving high selectivity and conversion of aromatic carbamates with ease of catalyst recycling.
Regulatory Framework for Isocyanates
The regulatory framework for isocyanates plays a crucial role in shaping market entry strategies for companies looking to enter or expand their presence in the isocyanate industry. Globally, isocyanates are subject to stringent regulations due to their potential health and environmental impacts. In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has established specific standards for occupational exposure to isocyanates, including permissible exposure limits and requirements for personal protective equipment. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) also regulates isocyanates under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA), which mandates reporting, record-keeping, and testing requirements.
In the European Union, the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation governs the use and import of isocyanates. REACH requires manufacturers and importers to register substances and provide safety data, which can be a significant barrier for new market entrants. Additionally, the Classification, Labeling, and Packaging (CLP) Regulation sets specific requirements for the classification and labeling of isocyanate-containing products.
Asian markets, particularly China and Japan, have their own regulatory frameworks. China's Measures for Environmental Management of New Chemical Substances and Japan's Chemical Substances Control Law both require pre-market notification and risk assessment for new chemical substances, including isocyanates.
Companies seeking to enter the isocyanate market must navigate these complex regulatory landscapes, which often necessitate substantial investments in compliance and safety measures. This includes developing robust safety data sheets, implementing worker protection programs, and establishing systems for tracking and reporting chemical usage and emissions.
The regulatory framework also influences product development and marketing strategies. For instance, the growing emphasis on sustainable and eco-friendly products has led to increased regulation of certain isocyanates, prompting companies to invest in research and development of alternative formulations or application methods that reduce environmental impact and improve worker safety.
Furthermore, the regulatory landscape is dynamic, with ongoing efforts to harmonize standards across different regions and update regulations based on new scientific evidence. This requires companies to maintain vigilance and adaptability in their compliance strategies. Successful market entry often involves proactive engagement with regulatory bodies, industry associations, and stakeholders to stay ahead of regulatory changes and contribute to the development of industry standards.
In the European Union, the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation governs the use and import of isocyanates. REACH requires manufacturers and importers to register substances and provide safety data, which can be a significant barrier for new market entrants. Additionally, the Classification, Labeling, and Packaging (CLP) Regulation sets specific requirements for the classification and labeling of isocyanate-containing products.
Asian markets, particularly China and Japan, have their own regulatory frameworks. China's Measures for Environmental Management of New Chemical Substances and Japan's Chemical Substances Control Law both require pre-market notification and risk assessment for new chemical substances, including isocyanates.
Companies seeking to enter the isocyanate market must navigate these complex regulatory landscapes, which often necessitate substantial investments in compliance and safety measures. This includes developing robust safety data sheets, implementing worker protection programs, and establishing systems for tracking and reporting chemical usage and emissions.
The regulatory framework also influences product development and marketing strategies. For instance, the growing emphasis on sustainable and eco-friendly products has led to increased regulation of certain isocyanates, prompting companies to invest in research and development of alternative formulations or application methods that reduce environmental impact and improve worker safety.
Furthermore, the regulatory landscape is dynamic, with ongoing efforts to harmonize standards across different regions and update regulations based on new scientific evidence. This requires companies to maintain vigilance and adaptability in their compliance strategies. Successful market entry often involves proactive engagement with regulatory bodies, industry associations, and stakeholders to stay ahead of regulatory changes and contribute to the development of industry standards.
Environmental Impact Assessment
The environmental impact assessment of isocyanate production and usage is a critical consideration for market entry strategies. Isocyanates, widely used in the production of polyurethanes, have significant environmental implications throughout their lifecycle. The manufacturing process of isocyanates involves the use of hazardous chemicals and energy-intensive operations, contributing to air and water pollution if not properly managed.
Emissions from isocyanate production facilities can include volatile organic compounds (VOCs), particulate matter, and greenhouse gases. These emissions may lead to local air quality issues and contribute to global climate change. Water pollution is another concern, as the production process generates wastewater containing various contaminants that require proper treatment before discharge.
The use of isocyanates in end products also presents environmental challenges. Many polyurethane products are not biodegradable and can persist in the environment for extended periods. This persistence raises concerns about long-term accumulation in ecosystems and potential impacts on wildlife. Additionally, the disposal of isocyanate-containing products can release harmful substances if not handled correctly.
However, the industry has made significant strides in mitigating these environmental impacts. Advanced production technologies have been developed to reduce emissions and improve energy efficiency. Closed-loop systems and solvent recovery processes have been implemented to minimize waste and resource consumption. Furthermore, research into bio-based isocyanates and more environmentally friendly alternatives is ongoing, offering potential future solutions.
When strategizing market entry points, companies must consider the regulatory landscape surrounding isocyanate production and use. Environmental regulations vary by region, with some areas imposing strict controls on emissions, waste management, and product safety. Compliance with these regulations is essential for market access and can significantly impact operational costs and competitiveness.
Sustainability initiatives and corporate social responsibility are increasingly important factors in the isocyanate market. Companies that demonstrate a commitment to environmental stewardship may gain a competitive advantage. This can include investing in cleaner production technologies, developing eco-friendly product formulations, and implementing comprehensive recycling and waste management programs.
The environmental impact assessment should also consider the potential for positive contributions. Isocyanate-based products, such as insulation materials, can improve energy efficiency in buildings, potentially offsetting their environmental footprint through reduced energy consumption over their lifecycle. Balancing these positive impacts against the environmental costs of production and disposal is crucial for a comprehensive assessment.
Emissions from isocyanate production facilities can include volatile organic compounds (VOCs), particulate matter, and greenhouse gases. These emissions may lead to local air quality issues and contribute to global climate change. Water pollution is another concern, as the production process generates wastewater containing various contaminants that require proper treatment before discharge.
The use of isocyanates in end products also presents environmental challenges. Many polyurethane products are not biodegradable and can persist in the environment for extended periods. This persistence raises concerns about long-term accumulation in ecosystems and potential impacts on wildlife. Additionally, the disposal of isocyanate-containing products can release harmful substances if not handled correctly.
However, the industry has made significant strides in mitigating these environmental impacts. Advanced production technologies have been developed to reduce emissions and improve energy efficiency. Closed-loop systems and solvent recovery processes have been implemented to minimize waste and resource consumption. Furthermore, research into bio-based isocyanates and more environmentally friendly alternatives is ongoing, offering potential future solutions.
When strategizing market entry points, companies must consider the regulatory landscape surrounding isocyanate production and use. Environmental regulations vary by region, with some areas imposing strict controls on emissions, waste management, and product safety. Compliance with these regulations is essential for market access and can significantly impact operational costs and competitiveness.
Sustainability initiatives and corporate social responsibility are increasingly important factors in the isocyanate market. Companies that demonstrate a commitment to environmental stewardship may gain a competitive advantage. This can include investing in cleaner production technologies, developing eco-friendly product formulations, and implementing comprehensive recycling and waste management programs.
The environmental impact assessment should also consider the potential for positive contributions. Isocyanate-based products, such as insulation materials, can improve energy efficiency in buildings, potentially offsetting their environmental footprint through reduced energy consumption over their lifecycle. Balancing these positive impacts against the environmental costs of production and disposal is crucial for a comprehensive assessment.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!