Alkyl Compounds: Innovations in Chemical Synthesis
JUL 15, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Alkyl Compound Synthesis Background and Objectives
Alkyl compounds have been a cornerstone of organic chemistry for over a century, playing crucial roles in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and materials science. The synthesis of these compounds has evolved significantly since the early days of organic chemistry, with each advancement opening new possibilities for creating complex molecules and improving industrial processes.
The field of alkyl compound synthesis has its roots in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, with pioneering work by chemists such as Victor Grignard and Edward Frankland. These early discoveries laid the foundation for modern organometallic chemistry and paved the way for more sophisticated synthetic methods. As the field progressed, the development of new catalysts, reagents, and reaction conditions has continually expanded the toolkit available to chemists for creating carbon-carbon bonds and manipulating alkyl groups.
In recent decades, the focus of innovation in alkyl compound synthesis has shifted towards more sustainable and efficient processes. This change has been driven by increasing environmental concerns and the need for greener chemistry practices. Researchers are now exploring novel catalytic systems, including transition metal catalysts and organocatalysts, that can facilitate alkyl compound synthesis under milder conditions and with reduced waste generation.
The advent of computational chemistry and high-throughput screening techniques has accelerated the pace of innovation in this field. These tools allow researchers to predict reaction outcomes, design new catalysts, and optimize reaction conditions with unprecedented speed and accuracy. As a result, the discovery of new synthetic methodologies for alkyl compounds has become more systematic and data-driven.
The objectives of current research in alkyl compound synthesis are multifaceted. Firstly, there is a strong emphasis on developing more selective and atom-economical reactions, which can produce complex alkyl structures with minimal side products. Secondly, researchers are striving to create methods that utilize readily available and renewable starting materials, moving away from petroleum-based feedstocks. Thirdly, there is a push towards developing scalable processes that can be easily translated from laboratory settings to industrial production.
Looking ahead, the field of alkyl compound synthesis is poised for further breakthroughs. Emerging areas such as photoredox catalysis, electrochemistry, and flow chemistry are opening new avenues for alkyl compound synthesis under unconventional conditions. These innovative approaches promise to expand the scope of accessible molecules and potentially revolutionize industrial processes for alkyl compound production.
The field of alkyl compound synthesis has its roots in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, with pioneering work by chemists such as Victor Grignard and Edward Frankland. These early discoveries laid the foundation for modern organometallic chemistry and paved the way for more sophisticated synthetic methods. As the field progressed, the development of new catalysts, reagents, and reaction conditions has continually expanded the toolkit available to chemists for creating carbon-carbon bonds and manipulating alkyl groups.
In recent decades, the focus of innovation in alkyl compound synthesis has shifted towards more sustainable and efficient processes. This change has been driven by increasing environmental concerns and the need for greener chemistry practices. Researchers are now exploring novel catalytic systems, including transition metal catalysts and organocatalysts, that can facilitate alkyl compound synthesis under milder conditions and with reduced waste generation.
The advent of computational chemistry and high-throughput screening techniques has accelerated the pace of innovation in this field. These tools allow researchers to predict reaction outcomes, design new catalysts, and optimize reaction conditions with unprecedented speed and accuracy. As a result, the discovery of new synthetic methodologies for alkyl compounds has become more systematic and data-driven.
The objectives of current research in alkyl compound synthesis are multifaceted. Firstly, there is a strong emphasis on developing more selective and atom-economical reactions, which can produce complex alkyl structures with minimal side products. Secondly, researchers are striving to create methods that utilize readily available and renewable starting materials, moving away from petroleum-based feedstocks. Thirdly, there is a push towards developing scalable processes that can be easily translated from laboratory settings to industrial production.
Looking ahead, the field of alkyl compound synthesis is poised for further breakthroughs. Emerging areas such as photoredox catalysis, electrochemistry, and flow chemistry are opening new avenues for alkyl compound synthesis under unconventional conditions. These innovative approaches promise to expand the scope of accessible molecules and potentially revolutionize industrial processes for alkyl compound production.
Market Analysis for Alkyl Compounds
The global market for alkyl compounds has been experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing demand across various industries. These versatile organic compounds find applications in sectors such as pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, personal care products, and industrial solvents. The pharmaceutical industry, in particular, has been a significant contributor to the market expansion, with alkyl compounds serving as crucial intermediates in the synthesis of numerous drugs and active pharmaceutical ingredients.
In recent years, the market has witnessed a shift towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly production methods for alkyl compounds. This trend is largely influenced by stringent environmental regulations and growing consumer awareness regarding eco-friendly products. As a result, manufacturers are investing in research and development to innovate greener synthesis processes, which is expected to shape the market landscape in the coming years.
The Asia-Pacific region has emerged as a key player in the alkyl compounds market, with China and India leading the growth. These countries have become major production hubs due to their robust chemical manufacturing infrastructure and relatively lower production costs. However, North America and Europe continue to maintain significant market shares, particularly in high-value applications such as specialty chemicals and pharmaceuticals.
The market for alkyl compounds is characterized by a high degree of fragmentation, with numerous small and medium-sized enterprises competing alongside multinational corporations. This competitive landscape has fostered innovation and product differentiation, leading to a diverse range of alkyl compounds tailored for specific end-use applications.
Looking ahead, the market is projected to continue its growth trajectory, with emerging applications in advanced materials and nanotechnology expected to create new opportunities. The increasing focus on bio-based alkyl compounds, derived from renewable resources, is anticipated to open up new market segments and attract environmentally conscious consumers.
However, the market also faces challenges, including volatility in raw material prices and stringent regulatory requirements. The fluctuating prices of petrochemical feedstocks, which are primary raw materials for alkyl compound synthesis, can significantly impact production costs and profit margins. Additionally, compliance with evolving environmental and safety regulations requires ongoing investments in process improvements and waste management systems.
In conclusion, the market for alkyl compounds presents a dynamic landscape with promising growth potential. The industry's ability to adapt to changing regulatory environments, invest in sustainable production methods, and develop innovative applications will be crucial in shaping its future trajectory and capitalizing on emerging opportunities.
In recent years, the market has witnessed a shift towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly production methods for alkyl compounds. This trend is largely influenced by stringent environmental regulations and growing consumer awareness regarding eco-friendly products. As a result, manufacturers are investing in research and development to innovate greener synthesis processes, which is expected to shape the market landscape in the coming years.
The Asia-Pacific region has emerged as a key player in the alkyl compounds market, with China and India leading the growth. These countries have become major production hubs due to their robust chemical manufacturing infrastructure and relatively lower production costs. However, North America and Europe continue to maintain significant market shares, particularly in high-value applications such as specialty chemicals and pharmaceuticals.
The market for alkyl compounds is characterized by a high degree of fragmentation, with numerous small and medium-sized enterprises competing alongside multinational corporations. This competitive landscape has fostered innovation and product differentiation, leading to a diverse range of alkyl compounds tailored for specific end-use applications.
Looking ahead, the market is projected to continue its growth trajectory, with emerging applications in advanced materials and nanotechnology expected to create new opportunities. The increasing focus on bio-based alkyl compounds, derived from renewable resources, is anticipated to open up new market segments and attract environmentally conscious consumers.
However, the market also faces challenges, including volatility in raw material prices and stringent regulatory requirements. The fluctuating prices of petrochemical feedstocks, which are primary raw materials for alkyl compound synthesis, can significantly impact production costs and profit margins. Additionally, compliance with evolving environmental and safety regulations requires ongoing investments in process improvements and waste management systems.
In conclusion, the market for alkyl compounds presents a dynamic landscape with promising growth potential. The industry's ability to adapt to changing regulatory environments, invest in sustainable production methods, and develop innovative applications will be crucial in shaping its future trajectory and capitalizing on emerging opportunities.
Current Challenges in Alkyl Synthesis
The synthesis of alkyl compounds faces several significant challenges in the current chemical landscape. One of the primary obstacles is the development of more efficient and selective methods for carbon-carbon bond formation. Traditional approaches often require harsh conditions, multiple steps, or expensive catalysts, leading to low yields and unwanted side products.
Environmental concerns pose another major challenge in alkyl synthesis. Many conventional methods rely on toxic reagents or generate substantial amounts of waste, conflicting with the principles of green chemistry. The need for more sustainable and eco-friendly synthetic routes has become increasingly urgent, driving researchers to explore alternative reagents and catalytic systems.
Stereoselective synthesis of alkyl compounds remains a formidable challenge, particularly in the creation of complex molecules with multiple chiral centers. Controlling the stereochemistry of reactions to produce specific isomers with high enantioselectivity is crucial for many applications, especially in the pharmaceutical industry.
The scalability of alkyl synthesis processes presents another significant hurdle. Many laboratory-scale methods fail to translate effectively to industrial production due to issues such as heat transfer limitations, mixing problems, or the impracticality of using certain reagents or catalysts on a large scale. Developing robust and scalable processes is essential for the commercial viability of new synthetic routes.
Another challenge lies in the functionalization of unactivated alkyl groups. While methods for functionalizing activated positions (e.g., adjacent to carbonyl groups) are well-established, selective modification of inert C-H bonds in alkyl chains remains difficult. This limitation hinders the direct transformation of readily available hydrocarbons into more valuable products.
The synthesis of highly branched or sterically hindered alkyl compounds poses unique challenges due to increased steric effects and reduced reactivity. Developing methods to overcome these limitations and access structurally diverse alkyl scaffolds is crucial for expanding the chemical space available to synthetic chemists.
Lastly, the integration of alkyl synthesis with emerging technologies, such as flow chemistry and automated synthesis platforms, presents both opportunities and challenges. While these technologies offer potential advantages in terms of efficiency and reproducibility, adapting traditional alkyl synthesis methods to these new paradigms often requires significant optimization and re-engineering of reaction conditions.
Environmental concerns pose another major challenge in alkyl synthesis. Many conventional methods rely on toxic reagents or generate substantial amounts of waste, conflicting with the principles of green chemistry. The need for more sustainable and eco-friendly synthetic routes has become increasingly urgent, driving researchers to explore alternative reagents and catalytic systems.
Stereoselective synthesis of alkyl compounds remains a formidable challenge, particularly in the creation of complex molecules with multiple chiral centers. Controlling the stereochemistry of reactions to produce specific isomers with high enantioselectivity is crucial for many applications, especially in the pharmaceutical industry.
The scalability of alkyl synthesis processes presents another significant hurdle. Many laboratory-scale methods fail to translate effectively to industrial production due to issues such as heat transfer limitations, mixing problems, or the impracticality of using certain reagents or catalysts on a large scale. Developing robust and scalable processes is essential for the commercial viability of new synthetic routes.
Another challenge lies in the functionalization of unactivated alkyl groups. While methods for functionalizing activated positions (e.g., adjacent to carbonyl groups) are well-established, selective modification of inert C-H bonds in alkyl chains remains difficult. This limitation hinders the direct transformation of readily available hydrocarbons into more valuable products.
The synthesis of highly branched or sterically hindered alkyl compounds poses unique challenges due to increased steric effects and reduced reactivity. Developing methods to overcome these limitations and access structurally diverse alkyl scaffolds is crucial for expanding the chemical space available to synthetic chemists.
Lastly, the integration of alkyl synthesis with emerging technologies, such as flow chemistry and automated synthesis platforms, presents both opportunities and challenges. While these technologies offer potential advantages in terms of efficiency and reproducibility, adapting traditional alkyl synthesis methods to these new paradigms often requires significant optimization and re-engineering of reaction conditions.
State-of-the-Art Alkyl Synthesis Techniques
01 Synthesis of alkyl compounds
Various methods for synthesizing alkyl compounds are described, including reactions involving alkyl halides, alcohols, and other precursors. These processes often involve catalysts and specific reaction conditions to produce desired alkyl compounds efficiently.- Synthesis of alkyl compounds: Various methods for synthesizing alkyl compounds are described, including reactions involving alkyl halides, alcohols, and other precursors. These processes often involve catalysts and specific reaction conditions to produce desired alkyl derivatives.
- Applications of alkyl compounds in industry: Alkyl compounds find diverse applications in industrial processes, such as in the production of polymers, lubricants, and surfactants. They are also used as intermediates in the synthesis of more complex organic molecules.
- Alkyl compounds in pharmaceutical formulations: Certain alkyl compounds are utilized in pharmaceutical formulations as active ingredients, excipients, or as part of drug delivery systems. These compounds can enhance drug solubility, stability, or bioavailability.
- Environmental impact and biodegradation of alkyl compounds: Research on the environmental fate and biodegradation of alkyl compounds is conducted to assess their impact on ecosystems. Studies focus on developing eco-friendly alternatives and improving the biodegradability of alkyl-based products.
- Alkyl compounds in material science: Alkyl compounds play a role in material science, particularly in the development of advanced materials with specific properties. They are used in the synthesis of novel polymers, coatings, and composite materials with tailored characteristics.
02 Applications of alkyl compounds in industry
Alkyl compounds find diverse applications in industrial processes, such as in the production of lubricants, plasticizers, and surfactants. They are also used as intermediates in the synthesis of more complex organic molecules and polymers.Expand Specific Solutions03 Alkyl compounds in pharmaceutical formulations
Alkyl compounds play a role in pharmaceutical formulations, serving as excipients, solubilizers, or active pharmaceutical ingredients. They can enhance drug delivery, improve stability, or contribute to the therapeutic effect of medications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Environmental impact and biodegradability of alkyl compounds
Research focuses on the environmental impact of alkyl compounds, including their biodegradability and potential toxicity. Efforts are made to develop more environmentally friendly alkyl compounds and assess their lifecycle in ecosystems.Expand Specific Solutions05 Alkyl compounds in material science
Alkyl compounds are utilized in material science for modifying surface properties, enhancing material performance, and developing new materials with specific characteristics. They play a role in creating hydrophobic coatings, improving polymer properties, and developing advanced composites.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Chemical Synthesis Industry
The field of chemical synthesis of alkyl compounds is in a mature stage of development, with ongoing innovations driving market growth. The global market for alkyl compounds is substantial, estimated to be in the billions of dollars, with applications spanning pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and industrial sectors. Technologically, the field is well-established but continues to evolve, with major players like Novartis AG, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd., and Sanofi leading research efforts. Academic institutions such as MIT and Northwestern University contribute significantly to fundamental research. Companies like Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd. and Mitsubishi Gas Chemical Co., Inc. are advancing industrial applications, while smaller firms like Landos Biopharma, Inc. focus on niche innovations, particularly in pharmaceutical applications.
Novartis AG
Technical Solution: Novartis AG has developed innovative approaches in the chemical synthesis of alkyl compounds, focusing on sustainable and efficient methods. They have implemented a novel catalytic system for alkylation reactions, utilizing transition metal catalysts to achieve high selectivity and yield[1]. Their process incorporates green chemistry principles, reducing waste and energy consumption. Novartis has also pioneered the use of continuous flow chemistry for alkyl compound synthesis, allowing for better control of reaction parameters and improved scalability[3]. Additionally, they have explored photocatalytic methods for C-H alkylation, enabling the formation of complex alkyl structures under mild conditions[5].
Strengths: High efficiency, reduced environmental impact, and scalability. Weaknesses: Potentially higher initial costs for specialized equipment and catalyst development.
F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.
Technical Solution: F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd. has made significant advancements in the chemical synthesis of alkyl compounds, particularly in the pharmaceutical context. They have developed a novel approach to C-C bond formation using photoredox catalysis, enabling the synthesis of complex alkyl structures with high functional group tolerance[2]. Roche has also implemented automated synthesis platforms for rapid alkyl compound library generation, accelerating drug discovery processes[4]. Their innovations include the use of biocatalysis for stereoselective alkylation reactions, leveraging engineered enzymes to achieve high enantioselectivity in alkyl compound synthesis[6]. Furthermore, Roche has explored the application of artificial intelligence in predicting optimal reaction conditions for alkyl compound synthesis, streamlining process development[8].
Strengths: High precision in stereoselective synthesis, rapid compound library generation, and integration of cutting-edge technologies. Weaknesses: Potential limitations in large-scale production of some specialized methods.
Breakthrough Innovations in Alkyl Synthesis
A process for the palladium-catalyzed coupling of terminal alkynes with aryl tosylates
PatentInactiveEP2176203A1
Innovation
- A palladium-catalyzed coupling process using a bidentate ligand and a protic solvent, which allows for the direct, mild, and regioselective synthesis of aryl-1-alkynes from aryl tosylates and terminal alkynes, eliminating the need for slow alkyne addition and toxic solvents, and enabling the preparation of a wide variety of substituted aryl-1-alkynes.
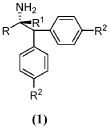
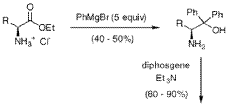
AN IMPROVED ASYMMETRIC SYNTHESIS OF alpha-(DIARYLMETHYL) ALKYL AMINES
PatentWO2019180627A1
Innovation
- A direct asymmetric synthesis method involving the reaction of lithiated diarylmethyl anion with Ellman's Imines, specifically using n-Butyl Lithium as a lithiating agent, which avoids toxic catalysts and solvents, and eliminates the need for additional purification steps, allowing for a scalable and cost-effective production of alpha-(diarylmethyl) alkyl amines.
Green Chemistry Approaches in Alkyl Synthesis
Green chemistry approaches in alkyl synthesis have gained significant attention in recent years due to their potential to reduce environmental impact and improve sustainability in chemical processes. These approaches focus on developing more efficient and environmentally friendly methods for synthesizing alkyl compounds, which are essential building blocks in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and materials science.
One of the key principles of green chemistry in alkyl synthesis is the use of renewable feedstocks. Researchers are exploring the utilization of biomass-derived starting materials, such as plant oils and sugars, as alternatives to petroleum-based resources. This shift towards bio-based feedstocks not only reduces reliance on fossil fuels but also contributes to the circular economy by valorizing waste materials.
Catalysis plays a crucial role in green alkyl synthesis, with emphasis on developing highly selective and efficient catalysts. Heterogeneous catalysts, in particular, have shown promise due to their ease of separation and potential for reuse. Recent advancements include the development of supported metal nanoparticles and metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) as catalysts for alkyl synthesis reactions, offering improved selectivity and reduced waste generation.
The use of alternative reaction media is another important aspect of green chemistry approaches in alkyl synthesis. Supercritical fluids, ionic liquids, and water have been explored as environmentally benign solvents to replace traditional organic solvents. These alternative media often provide unique reaction environments that can enhance reaction rates and selectivity while minimizing the generation of hazardous waste.
Process intensification techniques are being applied to alkyl synthesis to improve energy efficiency and reduce waste. Continuous flow reactors and microreactors have demonstrated advantages in terms of improved heat and mass transfer, leading to higher yields and reduced reaction times. These technologies also enable better control over reaction parameters, resulting in enhanced product quality and reduced byproduct formation.
Photochemical and electrochemical methods are emerging as promising green approaches for alkyl synthesis. These techniques often operate under mild conditions and can be powered by renewable energy sources, aligning with the principles of green chemistry. Recent developments in photoredox catalysis and electrocatalysis have opened new avenues for selective alkyl synthesis reactions with reduced environmental impact.
The integration of biocatalysis in alkyl synthesis represents another frontier in green chemistry. Enzymes and whole-cell biocatalysts offer high selectivity and can operate under mild conditions, often in aqueous media. Advances in protein engineering and directed evolution have expanded the scope of biocatalytic alkyl synthesis, enabling the production of complex molecules with minimal environmental footprint.
One of the key principles of green chemistry in alkyl synthesis is the use of renewable feedstocks. Researchers are exploring the utilization of biomass-derived starting materials, such as plant oils and sugars, as alternatives to petroleum-based resources. This shift towards bio-based feedstocks not only reduces reliance on fossil fuels but also contributes to the circular economy by valorizing waste materials.
Catalysis plays a crucial role in green alkyl synthesis, with emphasis on developing highly selective and efficient catalysts. Heterogeneous catalysts, in particular, have shown promise due to their ease of separation and potential for reuse. Recent advancements include the development of supported metal nanoparticles and metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) as catalysts for alkyl synthesis reactions, offering improved selectivity and reduced waste generation.
The use of alternative reaction media is another important aspect of green chemistry approaches in alkyl synthesis. Supercritical fluids, ionic liquids, and water have been explored as environmentally benign solvents to replace traditional organic solvents. These alternative media often provide unique reaction environments that can enhance reaction rates and selectivity while minimizing the generation of hazardous waste.
Process intensification techniques are being applied to alkyl synthesis to improve energy efficiency and reduce waste. Continuous flow reactors and microreactors have demonstrated advantages in terms of improved heat and mass transfer, leading to higher yields and reduced reaction times. These technologies also enable better control over reaction parameters, resulting in enhanced product quality and reduced byproduct formation.
Photochemical and electrochemical methods are emerging as promising green approaches for alkyl synthesis. These techniques often operate under mild conditions and can be powered by renewable energy sources, aligning with the principles of green chemistry. Recent developments in photoredox catalysis and electrocatalysis have opened new avenues for selective alkyl synthesis reactions with reduced environmental impact.
The integration of biocatalysis in alkyl synthesis represents another frontier in green chemistry. Enzymes and whole-cell biocatalysts offer high selectivity and can operate under mild conditions, often in aqueous media. Advances in protein engineering and directed evolution have expanded the scope of biocatalytic alkyl synthesis, enabling the production of complex molecules with minimal environmental footprint.
Economic Impact of Alkyl Synthesis Innovations
The economic impact of innovations in alkyl compound synthesis has been profound, reshaping industries and driving economic growth across multiple sectors. These advancements have significantly reduced production costs, leading to increased profitability for chemical manufacturers and downstream industries. The automotive sector, for instance, has benefited from more affordable and efficient fuel additives, enhancing engine performance and fuel economy.
In the pharmaceutical industry, novel alkyl synthesis methods have accelerated drug discovery processes and reduced manufacturing expenses. This has not only improved access to life-saving medications but also bolstered the competitiveness of pharmaceutical companies in global markets. The resulting economic gains have spurred further investment in research and development, creating a positive feedback loop of innovation and economic growth.
The agricultural sector has also experienced substantial economic benefits from alkyl synthesis innovations. More cost-effective production of pesticides and herbicides has improved crop yields and farm productivity, contributing to food security and rural economic development. Additionally, the emergence of bio-based alkyl compounds has opened new markets and revenue streams for agricultural producers, fostering the growth of the bioeconomy.
In the realm of materials science, advancements in alkyl synthesis have enabled the development of high-performance polymers and composites at lower costs. This has revolutionized manufacturing processes across industries, from aerospace to consumer electronics, driving efficiency gains and spurring product innovation. The resulting economic impact extends beyond direct cost savings to include job creation in emerging high-tech manufacturing sectors.
The environmental benefits of improved alkyl synthesis methods have also translated into economic advantages. More efficient and selective processes have reduced waste generation and energy consumption, aligning with global sustainability goals. This has not only lowered operational costs for companies but also positioned them favorably in increasingly environmentally conscious markets, enhancing their long-term economic viability.
Furthermore, the global trade in alkyl compounds and related products has expanded significantly due to these innovations. Countries with advanced chemical industries have strengthened their export positions, while emerging economies have found new opportunities for economic diversification and growth. This has contributed to the formation of complex, high-value global supply chains, fostering international economic interdependence and driving overall economic growth.
In the pharmaceutical industry, novel alkyl synthesis methods have accelerated drug discovery processes and reduced manufacturing expenses. This has not only improved access to life-saving medications but also bolstered the competitiveness of pharmaceutical companies in global markets. The resulting economic gains have spurred further investment in research and development, creating a positive feedback loop of innovation and economic growth.
The agricultural sector has also experienced substantial economic benefits from alkyl synthesis innovations. More cost-effective production of pesticides and herbicides has improved crop yields and farm productivity, contributing to food security and rural economic development. Additionally, the emergence of bio-based alkyl compounds has opened new markets and revenue streams for agricultural producers, fostering the growth of the bioeconomy.
In the realm of materials science, advancements in alkyl synthesis have enabled the development of high-performance polymers and composites at lower costs. This has revolutionized manufacturing processes across industries, from aerospace to consumer electronics, driving efficiency gains and spurring product innovation. The resulting economic impact extends beyond direct cost savings to include job creation in emerging high-tech manufacturing sectors.
The environmental benefits of improved alkyl synthesis methods have also translated into economic advantages. More efficient and selective processes have reduced waste generation and energy consumption, aligning with global sustainability goals. This has not only lowered operational costs for companies but also positioned them favorably in increasingly environmentally conscious markets, enhancing their long-term economic viability.
Furthermore, the global trade in alkyl compounds and related products has expanded significantly due to these innovations. Countries with advanced chemical industries have strengthened their export positions, while emerging economies have found new opportunities for economic diversification and growth. This has contributed to the formation of complex, high-value global supply chains, fostering international economic interdependence and driving overall economic growth.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!