Insights into Hypochlorous Acid's Industrial Safety Applications
AUG 4, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
HOCl Safety Tech Evolution
The evolution of hypochlorous acid (HOCl) safety technology in industrial applications has been marked by significant milestones and advancements over the years. Initially discovered in the early 19th century, HOCl's potential as a disinfectant and sanitizer was not fully realized until much later. The timeline of HOCl safety tech evolution can be traced through several key stages.
In the early 20th century, the first industrial applications of HOCl began to emerge, primarily in water treatment and sanitation. During this period, the focus was on developing stable production methods and understanding the basic safety parameters of HOCl use. The 1920s and 1930s saw increased research into HOCl's antimicrobial properties, leading to its adoption in healthcare settings for wound care and sterilization.
The mid-20th century marked a significant leap in HOCl technology with the development of electrolytic cells for on-site generation. This innovation addressed the stability issues of HOCl solutions and allowed for more controlled and efficient production. The 1960s and 1970s witnessed a surge in research on HOCl's effectiveness against various pathogens, expanding its potential applications in food safety and industrial cleaning.
The late 20th century brought about a renewed interest in HOCl as an environmentally friendly alternative to harsh chemical disinfectants. Advancements in production technology, such as membrane electrolysis, improved the purity and consistency of HOCl solutions. This period also saw the development of more sophisticated delivery systems, including foggers and electrostatic sprayers, enhancing the efficiency and coverage of HOCl applications in large-scale industrial settings.
The turn of the 21st century heralded a new era in HOCl safety technology. Improved analytical techniques allowed for more precise monitoring of HOCl concentrations and efficacy. The advent of nanotechnology led to the development of stabilized HOCl formulations with extended shelf life, addressing one of the primary challenges in HOCl utilization. Additionally, the integration of IoT and smart sensors in HOCl generation and application systems has enabled real-time monitoring and automated dosing, significantly enhancing safety and efficiency in industrial settings.
Recent years have seen a focus on optimizing HOCl production for specific industrial applications. Tailored HOCl solutions with precise pH levels and concentrations have been developed for various sectors, including food processing, healthcare, and water treatment. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated research and development in HOCl technology, particularly in air and surface disinfection applications.
Looking ahead, the evolution of HOCl safety technology is likely to continue with a focus on sustainability, efficiency, and versatility. Emerging trends include the development of hybrid systems combining HOCl with other disinfection technologies, such as UV light or ozone, for enhanced efficacy. Additionally, ongoing research into the long-term effects of HOCl exposure and its interaction with various materials is expected to further refine safety protocols and application methodologies in industrial settings.
In the early 20th century, the first industrial applications of HOCl began to emerge, primarily in water treatment and sanitation. During this period, the focus was on developing stable production methods and understanding the basic safety parameters of HOCl use. The 1920s and 1930s saw increased research into HOCl's antimicrobial properties, leading to its adoption in healthcare settings for wound care and sterilization.
The mid-20th century marked a significant leap in HOCl technology with the development of electrolytic cells for on-site generation. This innovation addressed the stability issues of HOCl solutions and allowed for more controlled and efficient production. The 1960s and 1970s witnessed a surge in research on HOCl's effectiveness against various pathogens, expanding its potential applications in food safety and industrial cleaning.
The late 20th century brought about a renewed interest in HOCl as an environmentally friendly alternative to harsh chemical disinfectants. Advancements in production technology, such as membrane electrolysis, improved the purity and consistency of HOCl solutions. This period also saw the development of more sophisticated delivery systems, including foggers and electrostatic sprayers, enhancing the efficiency and coverage of HOCl applications in large-scale industrial settings.
The turn of the 21st century heralded a new era in HOCl safety technology. Improved analytical techniques allowed for more precise monitoring of HOCl concentrations and efficacy. The advent of nanotechnology led to the development of stabilized HOCl formulations with extended shelf life, addressing one of the primary challenges in HOCl utilization. Additionally, the integration of IoT and smart sensors in HOCl generation and application systems has enabled real-time monitoring and automated dosing, significantly enhancing safety and efficiency in industrial settings.
Recent years have seen a focus on optimizing HOCl production for specific industrial applications. Tailored HOCl solutions with precise pH levels and concentrations have been developed for various sectors, including food processing, healthcare, and water treatment. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated research and development in HOCl technology, particularly in air and surface disinfection applications.
Looking ahead, the evolution of HOCl safety technology is likely to continue with a focus on sustainability, efficiency, and versatility. Emerging trends include the development of hybrid systems combining HOCl with other disinfection technologies, such as UV light or ozone, for enhanced efficacy. Additionally, ongoing research into the long-term effects of HOCl exposure and its interaction with various materials is expected to further refine safety protocols and application methodologies in industrial settings.
Industrial Demand Analysis
The industrial demand for hypochlorous acid (HOCl) in safety applications has been steadily increasing due to its effectiveness as a disinfectant and sanitizer. This growth is driven by several factors, including heightened awareness of hygiene and safety standards across various industries, the need for eco-friendly and non-toxic cleaning solutions, and the versatility of HOCl in addressing a wide range of pathogens.
In the healthcare sector, there is a significant demand for HOCl-based products for surface disinfection, wound care, and sterilization of medical equipment. Hospitals, clinics, and long-term care facilities are adopting HOCl solutions to combat healthcare-associated infections and maintain stringent hygiene protocols. The ongoing global health challenges have further accelerated this trend, with healthcare providers seeking reliable and fast-acting disinfectants.
The food and beverage industry represents another major market for HOCl applications. Food processing plants, restaurants, and commercial kitchens are increasingly using HOCl for sanitizing food contact surfaces, equipment, and even fresh produce. The ability of HOCl to effectively eliminate foodborne pathogens without leaving harmful residues aligns well with the industry's focus on food safety and quality assurance.
Water treatment is an emerging area of industrial demand for HOCl. Municipal water suppliers and industrial facilities are exploring HOCl as an alternative to traditional chlorine-based disinfection methods. The lower environmental impact and reduced formation of disinfection by-products make HOCl an attractive option for ensuring safe drinking water and treating industrial wastewater.
In the agriculture sector, HOCl is gaining traction for crop protection and post-harvest treatment. Farmers and food distributors are using HOCl solutions to extend the shelf life of produce, control plant diseases, and sanitize agricultural equipment. The demand in this sector is driven by the push for reduced chemical usage and the need for solutions that do not compromise food quality or safety.
The transportation industry, particularly in the wake of recent global events, has shown increased interest in HOCl-based disinfection systems. Airlines, public transit authorities, and shipping companies are implementing HOCl fogging and spraying systems to sanitize vehicles and passenger areas, addressing concerns about the spread of pathogens in enclosed spaces.
As industries continue to prioritize safety and sustainability, the demand for HOCl in industrial applications is expected to grow. This trend is supported by ongoing research into new applications and delivery methods for HOCl, as well as improvements in production technology that are making HOCl more accessible and cost-effective for industrial use.
In the healthcare sector, there is a significant demand for HOCl-based products for surface disinfection, wound care, and sterilization of medical equipment. Hospitals, clinics, and long-term care facilities are adopting HOCl solutions to combat healthcare-associated infections and maintain stringent hygiene protocols. The ongoing global health challenges have further accelerated this trend, with healthcare providers seeking reliable and fast-acting disinfectants.
The food and beverage industry represents another major market for HOCl applications. Food processing plants, restaurants, and commercial kitchens are increasingly using HOCl for sanitizing food contact surfaces, equipment, and even fresh produce. The ability of HOCl to effectively eliminate foodborne pathogens without leaving harmful residues aligns well with the industry's focus on food safety and quality assurance.
Water treatment is an emerging area of industrial demand for HOCl. Municipal water suppliers and industrial facilities are exploring HOCl as an alternative to traditional chlorine-based disinfection methods. The lower environmental impact and reduced formation of disinfection by-products make HOCl an attractive option for ensuring safe drinking water and treating industrial wastewater.
In the agriculture sector, HOCl is gaining traction for crop protection and post-harvest treatment. Farmers and food distributors are using HOCl solutions to extend the shelf life of produce, control plant diseases, and sanitize agricultural equipment. The demand in this sector is driven by the push for reduced chemical usage and the need for solutions that do not compromise food quality or safety.
The transportation industry, particularly in the wake of recent global events, has shown increased interest in HOCl-based disinfection systems. Airlines, public transit authorities, and shipping companies are implementing HOCl fogging and spraying systems to sanitize vehicles and passenger areas, addressing concerns about the spread of pathogens in enclosed spaces.
As industries continue to prioritize safety and sustainability, the demand for HOCl in industrial applications is expected to grow. This trend is supported by ongoing research into new applications and delivery methods for HOCl, as well as improvements in production technology that are making HOCl more accessible and cost-effective for industrial use.
HOCl Safety Challenges
Despite the numerous benefits of hypochlorous acid (HOCl) in industrial safety applications, several challenges persist in its widespread adoption and effective implementation. One of the primary concerns is the stability of HOCl solutions. The compound is known to degrade over time, especially when exposed to light, heat, or certain metals. This instability can lead to reduced efficacy and potentially compromise safety measures in industrial settings where consistent performance is crucial.
Another significant challenge lies in the production and storage of HOCl. The process of generating HOCl on-site often requires specialized equipment and precise control of pH levels. Maintaining the optimal pH range (typically between 5 and 6.5) is critical for maximizing the effectiveness of HOCl while minimizing the formation of less desirable chlorine species. This requirement for precise control can be difficult to achieve in diverse industrial environments, potentially leading to variations in product quality and effectiveness.
The potential for corrosion is another concern when using HOCl in industrial applications. While HOCl is generally less corrosive than many traditional chlorine-based disinfectants, it can still cause damage to certain materials, particularly metals, over time. This necessitates careful material selection for storage containers, application equipment, and surfaces that will come into regular contact with HOCl solutions.
Safety considerations also extend to the handling and application of HOCl. Although it is considered safer than many alternative disinfectants, proper training and protective equipment are still necessary to ensure worker safety. Inhalation of HOCl vapors or mist can cause respiratory irritation, and direct contact with concentrated solutions may lead to skin or eye irritation. Developing comprehensive safety protocols and ensuring strict adherence to them remains a challenge in various industrial settings.
Furthermore, the regulatory landscape surrounding HOCl usage in industrial safety applications can be complex and varies across different regions and industries. Compliance with evolving regulations and obtaining necessary approvals for new applications can be time-consuming and resource-intensive. This regulatory uncertainty can sometimes hinder innovation and slow down the adoption of HOCl-based solutions in new industrial sectors.
Lastly, there is an ongoing challenge in educating industry stakeholders about the benefits and proper use of HOCl. Overcoming misconceptions and resistance to change, especially in industries with long-established disinfection practices, requires sustained efforts in communication, demonstration, and training. Bridging the knowledge gap and fostering acceptance of HOCl as a viable, safe, and effective alternative to traditional methods remains a significant hurdle in expanding its industrial safety applications.
Another significant challenge lies in the production and storage of HOCl. The process of generating HOCl on-site often requires specialized equipment and precise control of pH levels. Maintaining the optimal pH range (typically between 5 and 6.5) is critical for maximizing the effectiveness of HOCl while minimizing the formation of less desirable chlorine species. This requirement for precise control can be difficult to achieve in diverse industrial environments, potentially leading to variations in product quality and effectiveness.
The potential for corrosion is another concern when using HOCl in industrial applications. While HOCl is generally less corrosive than many traditional chlorine-based disinfectants, it can still cause damage to certain materials, particularly metals, over time. This necessitates careful material selection for storage containers, application equipment, and surfaces that will come into regular contact with HOCl solutions.
Safety considerations also extend to the handling and application of HOCl. Although it is considered safer than many alternative disinfectants, proper training and protective equipment are still necessary to ensure worker safety. Inhalation of HOCl vapors or mist can cause respiratory irritation, and direct contact with concentrated solutions may lead to skin or eye irritation. Developing comprehensive safety protocols and ensuring strict adherence to them remains a challenge in various industrial settings.
Furthermore, the regulatory landscape surrounding HOCl usage in industrial safety applications can be complex and varies across different regions and industries. Compliance with evolving regulations and obtaining necessary approvals for new applications can be time-consuming and resource-intensive. This regulatory uncertainty can sometimes hinder innovation and slow down the adoption of HOCl-based solutions in new industrial sectors.
Lastly, there is an ongoing challenge in educating industry stakeholders about the benefits and proper use of HOCl. Overcoming misconceptions and resistance to change, especially in industries with long-established disinfection practices, requires sustained efforts in communication, demonstration, and training. Bridging the knowledge gap and fostering acceptance of HOCl as a viable, safe, and effective alternative to traditional methods remains a significant hurdle in expanding its industrial safety applications.
Current HOCl Solutions
01 Production methods of hypochlorous acid
Various methods are employed to produce hypochlorous acid, including electrolysis of salt solutions, chemical reactions involving chlorine and water, and controlled mixing of precursor chemicals. These production methods aim to create stable and effective hypochlorous acid solutions for different applications.- Production methods of hypochlorous acid: Various methods are employed to produce hypochlorous acid, including electrolysis of salt solutions, chemical reactions involving chlorine and water, and controlled mixing of precursor chemicals. These production methods aim to create stable and effective hypochlorous acid solutions for different applications.
- Antimicrobial applications of hypochlorous acid: Hypochlorous acid is widely used as an antimicrobial agent in various fields, including healthcare, food processing, and water treatment. Its effectiveness against a broad spectrum of pathogens, combined with its low toxicity to humans, makes it a valuable disinfectant and sanitizer.
- Stabilization techniques for hypochlorous acid solutions: Researchers have developed various stabilization techniques to prolong the shelf life and maintain the efficacy of hypochlorous acid solutions. These methods may involve pH adjustment, addition of stabilizing agents, or specialized packaging to prevent degradation and ensure consistent performance over time.
- Medical and therapeutic uses of hypochlorous acid: Hypochlorous acid has found applications in medical and therapeutic settings, including wound care, eye care, and respiratory treatments. Its ability to effectively kill pathogens while being gentle on human tissues makes it suitable for various medical applications.
- Environmental and industrial applications of hypochlorous acid: Hypochlorous acid is utilized in environmental remediation and industrial processes due to its strong oxidizing properties. Applications include water treatment, air purification, and surface decontamination in various industries, offering an eco-friendly alternative to harsher chemicals.
02 Antimicrobial applications of hypochlorous acid
Hypochlorous acid is widely used as an antimicrobial agent in various fields, including healthcare, food processing, and water treatment. Its effectiveness against a broad spectrum of pathogens, combined with its low toxicity to humans, makes it a valuable disinfectant and sanitizer.Expand Specific Solutions03 Stabilization and formulation of hypochlorous acid solutions
Techniques for stabilizing hypochlorous acid solutions are crucial for maintaining their efficacy over time. This includes pH adjustment, addition of stabilizing agents, and specialized packaging methods to prevent degradation and ensure a longer shelf life for hypochlorous acid products.Expand Specific Solutions04 Medical and therapeutic uses of hypochlorous acid
Hypochlorous acid finds applications in various medical and therapeutic contexts, including wound care, dermatological treatments, and respiratory therapies. Its natural occurrence in the human immune system and its gentle yet effective antimicrobial properties make it suitable for these medical applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and industrial applications of hypochlorous acid
Hypochlorous acid is utilized in environmental remediation, industrial cleaning, and agricultural practices. Its eco-friendly nature and effectiveness in removing contaminants and pathogens make it a preferred choice in these sectors, contributing to sustainable and safe practices.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The industrial safety applications of hypochlorous acid are in a growth phase, with increasing market size driven by rising awareness of its effectiveness and safety. The global market for hypochlorous acid is projected to expand significantly in the coming years. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with companies like Fluid Energy Group Ltd. and Aquaox, Inc. leading innovation in production methods and application technologies. Established players such as Tokuyama Corp. and Mitsui Chemicals, Inc. are leveraging their expertise to develop new formulations and expand market reach. Emerging companies like WIAB WATER INNOVATION AB and Guangzhou Taidaoan Medical Technology Co., Ltd. are introducing novel applications, particularly in healthcare and sanitation sectors, indicating a maturing but still evolving technological landscape.
Fluid Energy Group Ltd.
Technical Solution: Fluid Energy Group has pioneered the development of stabilized hypochlorous acid solutions for industrial applications. Their patented formulation, known as AIHOL, maintains the efficacy of HOCl for extended periods, addressing the traditional stability issues associated with hypochlorous acid[3]. The company's technology allows for the production of HOCl solutions with concentrations up to 500 ppm, which remain stable for up to two years when stored properly. Fluid Energy Group's AIHOL is particularly effective in oil and gas operations, where it is used for microbial control in hydraulic fracturing and produced water treatment[4].
Strengths: Long-term stability of HOCl solutions; Proven effectiveness in challenging industrial environments; Reduced environmental impact compared to traditional biocides. Weaknesses: May require specialized handling and storage procedures; Potentially higher cost compared to unstabilized HOCl solutions.
Aquaox, Inc.
Technical Solution: Aquaox has developed a proprietary electrochemical activation (ECA) technology for producing hypochlorous acid (HOCl) on-site. Their system generates a stable form of HOCl with a pH range of 6.5-7.5, which is highly effective for disinfection while being safe for human contact. The company's ECA devices can produce HOCl solutions with concentrations ranging from 10-1000 ppm, suitable for various industrial applications[1]. Aquaox's technology allows for the production of HOCl without the need for hazardous chemical storage or transportation, enhancing overall safety in industrial settings[2].
Strengths: On-site production eliminates chemical storage risks; Stable HOCl formulation enhances efficacy and shelf-life; Scalable solution for various industrial needs. Weaknesses: Requires initial investment in ECA equipment; Ongoing maintenance of electrolysis cells may be necessary.
HOCl Safety Innovations
Stabilized hypohalous acid solutions
PatentActiveUS20190151449A1
Innovation
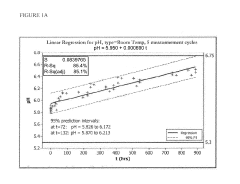
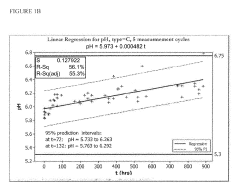
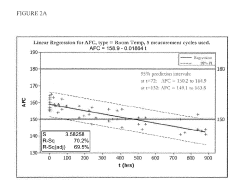
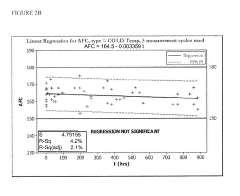
- A stabilized hypohalous acid solution with a stabilizing amount of dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC) such as bicarbonate or carbonate, maintaining an available free chlorine (AFC) content of 10 to 10,000 ppm and a pH of 4.0 to 7.5, which is prepared by electrolysis of saline and stabilized for at least one month, allowing for longer shelf life and reduced irritation.
Multi-chambered storage and delivery container
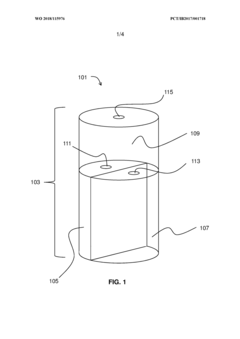
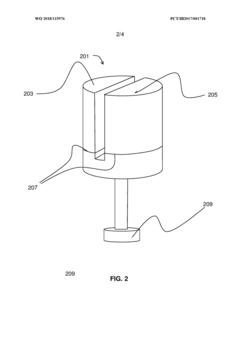
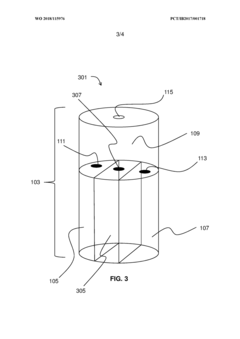
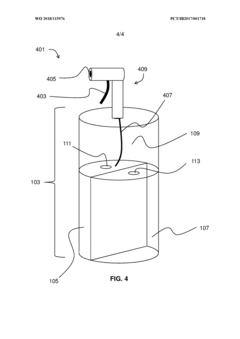
PatentWO2018115976A1
Innovation
- A multi-chambered container system that separates and stabilizes the components for producing hypochlorous acid, using one-way valves and buffering agents to maintain a stable pH and prevent air exposure, allowing for on-site preparation and long-term storage of hypochlorous acid compositions, which are substantially free of chloride and metal ions.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of hypochlorous acid (HOCl) in industrial safety applications is a critical consideration for sustainable practices. HOCl, known for its potent disinfecting properties, offers a more eco-friendly alternative to traditional chemical disinfectants. Its decomposition into harmless byproducts, primarily water and salt, significantly reduces the environmental footprint compared to harsher chemicals.
In water treatment applications, HOCl's effectiveness in pathogen elimination contributes to improved water quality without introducing harmful residues into aquatic ecosystems. This is particularly important in industrial processes where large volumes of water are treated and discharged. The reduced chemical load in effluents helps maintain the ecological balance of receiving water bodies.
Air quality is another area where HOCl demonstrates environmental benefits. When used in air purification systems, it effectively neutralizes airborne pathogens and odors without releasing volatile organic compounds (VOCs) or other pollutants. This makes it an ideal choice for indoor air quality management in industrial settings, contributing to healthier work environments and reduced atmospheric pollution.
The production of HOCl through electrolysis of salt water is an energy-efficient process with minimal environmental impact. Compared to the manufacturing of complex chemical disinfectants, HOCl production requires less energy and fewer raw materials, aligning with principles of green chemistry and sustainable industrial practices.
In terms of waste management, the use of HOCl reduces the volume of hazardous waste generated in industrial cleaning and disinfection processes. Its rapid breakdown means that excess HOCl does not persist in the environment, minimizing the risk of accumulation in soil or water systems. This characteristic is particularly valuable in industries where frequent disinfection is necessary, such as food processing or healthcare facilities.
The biodegradability of HOCl also contributes to its positive environmental profile. Unlike many synthetic disinfectants that can persist in the environment for extended periods, HOCl quickly breaks down into non-toxic components. This rapid degradation reduces the potential for long-term environmental contamination and ecosystem disruption.
However, it's important to note that while HOCl offers significant environmental advantages, its production and use still require careful management. Proper dosing and application techniques are essential to maximize efficacy while minimizing unnecessary environmental exposure. Additionally, the salt used in HOCl production should be sourced responsibly to avoid negative impacts on salt-producing ecosystems.
In water treatment applications, HOCl's effectiveness in pathogen elimination contributes to improved water quality without introducing harmful residues into aquatic ecosystems. This is particularly important in industrial processes where large volumes of water are treated and discharged. The reduced chemical load in effluents helps maintain the ecological balance of receiving water bodies.
Air quality is another area where HOCl demonstrates environmental benefits. When used in air purification systems, it effectively neutralizes airborne pathogens and odors without releasing volatile organic compounds (VOCs) or other pollutants. This makes it an ideal choice for indoor air quality management in industrial settings, contributing to healthier work environments and reduced atmospheric pollution.
The production of HOCl through electrolysis of salt water is an energy-efficient process with minimal environmental impact. Compared to the manufacturing of complex chemical disinfectants, HOCl production requires less energy and fewer raw materials, aligning with principles of green chemistry and sustainable industrial practices.
In terms of waste management, the use of HOCl reduces the volume of hazardous waste generated in industrial cleaning and disinfection processes. Its rapid breakdown means that excess HOCl does not persist in the environment, minimizing the risk of accumulation in soil or water systems. This characteristic is particularly valuable in industries where frequent disinfection is necessary, such as food processing or healthcare facilities.
The biodegradability of HOCl also contributes to its positive environmental profile. Unlike many synthetic disinfectants that can persist in the environment for extended periods, HOCl quickly breaks down into non-toxic components. This rapid degradation reduces the potential for long-term environmental contamination and ecosystem disruption.
However, it's important to note that while HOCl offers significant environmental advantages, its production and use still require careful management. Proper dosing and application techniques are essential to maximize efficacy while minimizing unnecessary environmental exposure. Additionally, the salt used in HOCl production should be sourced responsibly to avoid negative impacts on salt-producing ecosystems.
Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance is a critical aspect of implementing hypochlorous acid (HOCl) in industrial safety applications. As the use of HOCl expands across various sectors, adherence to established guidelines and standards becomes increasingly important to ensure safe and effective utilization.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a crucial role in regulating HOCl as an antimicrobial agent. Under the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA), HOCl products must be registered with the EPA before they can be sold or distributed. This registration process involves rigorous testing to evaluate the product's efficacy, safety, and environmental impact.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) also provides guidelines for the safe handling and use of HOCl in workplace settings. These guidelines cover aspects such as proper storage, handling procedures, and personal protective equipment requirements for workers exposed to HOCl.
Internationally, the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) regulates the use of HOCl under the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation. Companies manufacturing or importing HOCl in quantities exceeding one tonne per year must register the substance and provide detailed safety information.
The food industry, in particular, faces stringent regulations regarding the use of HOCl as a sanitizer. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved HOCl for use in food processing and preparation under specific conditions. Similarly, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has evaluated the safety of HOCl for use in food production and processing.
Compliance with these regulations often requires extensive documentation, including safety data sheets, risk assessments, and standard operating procedures. Companies must also ensure that their HOCl products meet specific concentration and purity standards, as outlined by regulatory bodies.
As the industrial applications of HOCl continue to evolve, regulatory frameworks are likely to adapt. Staying informed about changes in regulations and proactively addressing compliance requirements is essential for companies operating in this space. This may involve regular audits, staff training, and updating safety protocols to align with the latest regulatory standards.
Furthermore, companies should consider voluntary compliance with industry-specific standards and best practices, such as those set by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) or sector-specific associations. These additional measures can enhance safety, improve product quality, and demonstrate a commitment to excellence beyond basic regulatory requirements.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a crucial role in regulating HOCl as an antimicrobial agent. Under the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA), HOCl products must be registered with the EPA before they can be sold or distributed. This registration process involves rigorous testing to evaluate the product's efficacy, safety, and environmental impact.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) also provides guidelines for the safe handling and use of HOCl in workplace settings. These guidelines cover aspects such as proper storage, handling procedures, and personal protective equipment requirements for workers exposed to HOCl.
Internationally, the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) regulates the use of HOCl under the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation. Companies manufacturing or importing HOCl in quantities exceeding one tonne per year must register the substance and provide detailed safety information.
The food industry, in particular, faces stringent regulations regarding the use of HOCl as a sanitizer. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved HOCl for use in food processing and preparation under specific conditions. Similarly, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has evaluated the safety of HOCl for use in food production and processing.
Compliance with these regulations often requires extensive documentation, including safety data sheets, risk assessments, and standard operating procedures. Companies must also ensure that their HOCl products meet specific concentration and purity standards, as outlined by regulatory bodies.
As the industrial applications of HOCl continue to evolve, regulatory frameworks are likely to adapt. Staying informed about changes in regulations and proactively addressing compliance requirements is essential for companies operating in this space. This may involve regular audits, staff training, and updating safety protocols to align with the latest regulatory standards.
Furthermore, companies should consider voluntary compliance with industry-specific standards and best practices, such as those set by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) or sector-specific associations. These additional measures can enhance safety, improve product quality, and demonstrate a commitment to excellence beyond basic regulatory requirements.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!