Novel cooling gels for enhancing PMSM efficiency
AUG 15, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
PMSM Cooling Evolution
The evolution of cooling systems for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSMs) has been a critical factor in enhancing their efficiency and performance over the years. Initially, PMSMs relied on simple air cooling methods, which were sufficient for low-power applications but became inadequate as motor power densities increased.
In the 1980s and 1990s, liquid cooling systems began to emerge as a more effective solution for high-power PMSMs. These systems utilized coolant channels within the motor housing to dissipate heat more efficiently. This advancement allowed for higher power densities and improved overall motor performance.
The early 2000s saw the introduction of oil spray cooling techniques. This method involved spraying oil directly onto the motor windings, providing better thermal management and allowing for even higher power densities. However, the complexity of oil spray systems and potential maintenance issues limited their widespread adoption.
As environmental concerns grew, the focus shifted towards more sustainable cooling solutions. In the mid-2000s, water jacket cooling systems gained popularity. These systems offered a balance between cooling efficiency and environmental friendliness, using water as the primary coolant circulating through channels in the motor housing.
The late 2000s and early 2010s witnessed the development of advanced thermal management materials. Heat pipes and phase change materials were integrated into PMSM designs, offering passive cooling solutions that could complement active cooling systems.
In recent years, the trend has moved towards hybrid cooling solutions that combine multiple techniques. For instance, some designs incorporate both liquid cooling and heat pipe technology to maximize heat dissipation. This approach has proven particularly effective in high-performance applications such as electric vehicles.
The latest frontier in PMSM cooling evolution is the exploration of novel cooling gels. These gels offer promising potential for enhancing PMSM efficiency by providing superior thermal conductivity and conforming to complex motor geometries. Unlike traditional liquid coolants, cooling gels can be applied directly to motor components, ensuring more uniform heat distribution and potentially reducing the need for complex cooling channels.
As we look to the future, the evolution of PMSM cooling systems is likely to continue focusing on innovative materials and smart thermal management strategies. The integration of sensors and adaptive cooling systems that can respond to real-time thermal loads is an area of active research, promising further improvements in PMSM efficiency and reliability.
In the 1980s and 1990s, liquid cooling systems began to emerge as a more effective solution for high-power PMSMs. These systems utilized coolant channels within the motor housing to dissipate heat more efficiently. This advancement allowed for higher power densities and improved overall motor performance.
The early 2000s saw the introduction of oil spray cooling techniques. This method involved spraying oil directly onto the motor windings, providing better thermal management and allowing for even higher power densities. However, the complexity of oil spray systems and potential maintenance issues limited their widespread adoption.
As environmental concerns grew, the focus shifted towards more sustainable cooling solutions. In the mid-2000s, water jacket cooling systems gained popularity. These systems offered a balance between cooling efficiency and environmental friendliness, using water as the primary coolant circulating through channels in the motor housing.
The late 2000s and early 2010s witnessed the development of advanced thermal management materials. Heat pipes and phase change materials were integrated into PMSM designs, offering passive cooling solutions that could complement active cooling systems.
In recent years, the trend has moved towards hybrid cooling solutions that combine multiple techniques. For instance, some designs incorporate both liquid cooling and heat pipe technology to maximize heat dissipation. This approach has proven particularly effective in high-performance applications such as electric vehicles.
The latest frontier in PMSM cooling evolution is the exploration of novel cooling gels. These gels offer promising potential for enhancing PMSM efficiency by providing superior thermal conductivity and conforming to complex motor geometries. Unlike traditional liquid coolants, cooling gels can be applied directly to motor components, ensuring more uniform heat distribution and potentially reducing the need for complex cooling channels.
As we look to the future, the evolution of PMSM cooling systems is likely to continue focusing on innovative materials and smart thermal management strategies. The integration of sensors and adaptive cooling systems that can respond to real-time thermal loads is an area of active research, promising further improvements in PMSM efficiency and reliability.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for novel cooling gels to enhance Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor (PMSM) efficiency is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and the push for more energy-efficient industrial applications. As automotive manufacturers and industrial sectors seek to improve the performance and longevity of their electric motors, the need for advanced thermal management solutions has become paramount.
In the automotive sector, the global EV market is projected to expand rapidly, with estimates suggesting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 20% in the coming years. This growth directly translates to an increased demand for high-performance PMSMs and, consequently, innovative cooling solutions. The ability of novel cooling gels to enhance PMSM efficiency addresses a critical need in this expanding market, as improved motor efficiency directly impacts vehicle range and overall performance.
Industrial applications, including robotics, manufacturing equipment, and renewable energy systems, are also contributing to the rising demand for efficient PMSMs and their cooling solutions. The industrial motor market, which heavily utilizes PMSMs, is expected to grow steadily, further driving the need for advanced thermal management technologies.
Energy efficiency regulations and environmental concerns are additional factors fueling the market demand for PMSM cooling innovations. Governments worldwide are implementing stricter energy efficiency standards, compelling manufacturers to invest in technologies that can improve motor performance while reducing energy consumption. Novel cooling gels offer a promising solution to meet these regulatory requirements and sustainability goals.
The market for PMSM cooling solutions is also influenced by the trend towards miniaturization and increased power density in electric motors. As manufacturers strive to develop more compact and powerful motors, the challenge of effective heat dissipation becomes more pronounced. This creates a substantial opportunity for innovative cooling gel technologies that can manage higher heat loads in confined spaces.
Furthermore, the demand for these cooling gels extends beyond new motor production. The retrofit and upgrade market for existing PMSMs represents a significant opportunity, as operators seek to improve the efficiency and lifespan of their current motor systems without complete replacements.
In terms of regional demand, major automotive and industrial hubs in Asia, Europe, and North America are expected to be the primary markets for novel PMSM cooling gels. However, emerging economies with growing manufacturing sectors and increasing EV adoption are also likely to contribute to market growth in the coming years.
In the automotive sector, the global EV market is projected to expand rapidly, with estimates suggesting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 20% in the coming years. This growth directly translates to an increased demand for high-performance PMSMs and, consequently, innovative cooling solutions. The ability of novel cooling gels to enhance PMSM efficiency addresses a critical need in this expanding market, as improved motor efficiency directly impacts vehicle range and overall performance.
Industrial applications, including robotics, manufacturing equipment, and renewable energy systems, are also contributing to the rising demand for efficient PMSMs and their cooling solutions. The industrial motor market, which heavily utilizes PMSMs, is expected to grow steadily, further driving the need for advanced thermal management technologies.
Energy efficiency regulations and environmental concerns are additional factors fueling the market demand for PMSM cooling innovations. Governments worldwide are implementing stricter energy efficiency standards, compelling manufacturers to invest in technologies that can improve motor performance while reducing energy consumption. Novel cooling gels offer a promising solution to meet these regulatory requirements and sustainability goals.
The market for PMSM cooling solutions is also influenced by the trend towards miniaturization and increased power density in electric motors. As manufacturers strive to develop more compact and powerful motors, the challenge of effective heat dissipation becomes more pronounced. This creates a substantial opportunity for innovative cooling gel technologies that can manage higher heat loads in confined spaces.
Furthermore, the demand for these cooling gels extends beyond new motor production. The retrofit and upgrade market for existing PMSMs represents a significant opportunity, as operators seek to improve the efficiency and lifespan of their current motor systems without complete replacements.
In terms of regional demand, major automotive and industrial hubs in Asia, Europe, and North America are expected to be the primary markets for novel PMSM cooling gels. However, emerging economies with growing manufacturing sectors and increasing EV adoption are also likely to contribute to market growth in the coming years.
Cooling Gel Challenges
The development of novel cooling gels for enhancing Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor (PMSM) efficiency faces several significant challenges. These obstacles span across material science, thermal management, and practical implementation domains, requiring innovative solutions to overcome.
One of the primary challenges lies in the formulation of cooling gels with optimal thermal conductivity. While traditional cooling methods often rely on liquid or air-based systems, gels offer unique properties that could potentially improve heat dissipation. However, achieving the right balance between thermal conductivity and viscosity poses a significant hurdle. The gel must be sufficiently fluid to conform to motor components yet stable enough to maintain consistent contact and heat transfer properties over time.
Another critical challenge is the long-term stability of cooling gels under the harsh operating conditions of PMSMs. These motors often experience high temperatures, vibrations, and electromagnetic fields. Developing a gel that can withstand these conditions without degrading or losing its thermal management capabilities is crucial. This includes resistance to thermal cycling, chemical stability, and maintaining consistent performance over the motor's lifespan.
The integration of cooling gels into existing PMSM designs presents another set of challenges. Current motor designs may not be optimized for gel-based cooling systems, requiring potential redesigns or adaptations. This includes considerations for gel application methods, ensuring uniform coverage of critical components, and preventing gel migration during operation. Additionally, the added weight and potential impact on motor dynamics must be carefully evaluated and mitigated.
Scalability and cost-effectiveness of cooling gel solutions also pose significant challenges. For widespread adoption in PMSM applications, the cooling gel technology must be scalable for mass production while remaining economically viable. This involves optimizing material costs, developing efficient manufacturing processes, and ensuring that the performance benefits justify the additional expenses.
Environmental and safety considerations add another layer of complexity to the development of novel cooling gels. The materials used must comply with increasingly stringent environmental regulations, be non-toxic, and pose no risk in case of leakage or disposal. Balancing these requirements with performance characteristics presents a significant challenge in material selection and formulation.
Lastly, the challenge of quantifying and validating the performance improvements offered by cooling gels in real-world PMSM applications is substantial. Developing standardized testing methodologies, conducting comprehensive field trials, and accurately measuring the impact on motor efficiency across various operating conditions are essential steps. This validation process is crucial for gaining industry acceptance and demonstrating the technology's value proposition.
One of the primary challenges lies in the formulation of cooling gels with optimal thermal conductivity. While traditional cooling methods often rely on liquid or air-based systems, gels offer unique properties that could potentially improve heat dissipation. However, achieving the right balance between thermal conductivity and viscosity poses a significant hurdle. The gel must be sufficiently fluid to conform to motor components yet stable enough to maintain consistent contact and heat transfer properties over time.
Another critical challenge is the long-term stability of cooling gels under the harsh operating conditions of PMSMs. These motors often experience high temperatures, vibrations, and electromagnetic fields. Developing a gel that can withstand these conditions without degrading or losing its thermal management capabilities is crucial. This includes resistance to thermal cycling, chemical stability, and maintaining consistent performance over the motor's lifespan.
The integration of cooling gels into existing PMSM designs presents another set of challenges. Current motor designs may not be optimized for gel-based cooling systems, requiring potential redesigns or adaptations. This includes considerations for gel application methods, ensuring uniform coverage of critical components, and preventing gel migration during operation. Additionally, the added weight and potential impact on motor dynamics must be carefully evaluated and mitigated.
Scalability and cost-effectiveness of cooling gel solutions also pose significant challenges. For widespread adoption in PMSM applications, the cooling gel technology must be scalable for mass production while remaining economically viable. This involves optimizing material costs, developing efficient manufacturing processes, and ensuring that the performance benefits justify the additional expenses.
Environmental and safety considerations add another layer of complexity to the development of novel cooling gels. The materials used must comply with increasingly stringent environmental regulations, be non-toxic, and pose no risk in case of leakage or disposal. Balancing these requirements with performance characteristics presents a significant challenge in material selection and formulation.
Lastly, the challenge of quantifying and validating the performance improvements offered by cooling gels in real-world PMSM applications is substantial. Developing standardized testing methodologies, conducting comprehensive field trials, and accurately measuring the impact on motor efficiency across various operating conditions are essential steps. This validation process is crucial for gaining industry acceptance and demonstrating the technology's value proposition.
Current Cooling Solutions
01 Composition of cooling gels
Cooling gels typically contain a combination of ingredients that provide a cooling sensation when applied to the skin. These may include menthol, camphor, or other cooling agents, along with a gel base that allows for easy application and absorption. The efficiency of cooling gels can be enhanced by optimizing the concentration and combination of these active ingredients.- Composition of cooling gels: Cooling gels typically contain a combination of water, cooling agents, and gelling agents. The efficiency of these gels can be improved by optimizing the ratio of these components and incorporating additional ingredients such as menthol or other natural cooling compounds. The gel base provides a smooth application and helps in the even distribution of the cooling agents.
- Application methods for enhanced cooling efficiency: The efficiency of cooling gels can be improved through various application methods. These may include using specialized applicators, incorporating the gel into wearable devices, or developing multi-layer systems that provide sustained cooling effects. The method of application can significantly impact the gel's performance and duration of cooling.
- Temperature-responsive cooling gel systems: Advanced cooling gels can be designed to respond to temperature changes, providing more efficient cooling when needed. These systems may incorporate phase-change materials or thermoresponsive polymers that adjust their properties based on skin or environmental temperature, ensuring optimal cooling efficiency.
- Nanotechnology in cooling gel formulations: The use of nanotechnology in cooling gel formulations can significantly enhance their efficiency. Nanoparticles can improve the stability of the gel, increase the surface area for heat transfer, and allow for better penetration of cooling agents into the skin. This results in more effective and longer-lasting cooling effects.
- Eco-friendly and sustainable cooling gel solutions: Developing eco-friendly and sustainable cooling gels is becoming increasingly important. These formulations may use biodegradable ingredients, natural cooling agents, and environmentally friendly packaging. The focus is on maintaining high cooling efficiency while reducing environmental impact and improving sustainability.
02 Application methods for improved efficiency
The efficiency of cooling gels can be improved through various application methods. These may include using specialized applicators, incorporating the gel into wearable devices, or developing novel delivery systems that enhance the cooling effect and prolong its duration. Proper application techniques can significantly impact the overall effectiveness of the cooling gel.Expand Specific Solutions03 Temperature regulation mechanisms
Efficient cooling gels often incorporate advanced temperature regulation mechanisms. These may include phase-change materials, thermoelectric elements, or other technologies that help maintain a consistent cooling effect over an extended period. Such mechanisms can improve the overall efficiency and user experience of cooling gel products.Expand Specific Solutions04 Integration with medical devices
Cooling gels can be integrated into various medical devices to enhance their efficiency in therapeutic applications. This integration may involve incorporating cooling gels into bandages, wraps, or other medical apparatus to provide targeted cooling for pain relief, inflammation reduction, or post-operative care. The combination of cooling gels with medical devices can improve overall treatment efficacy.Expand Specific Solutions05 Nanotechnology in cooling gel formulations
The use of nanotechnology in cooling gel formulations can significantly improve their efficiency. Nanoparticles or nanostructures can be incorporated into the gel to enhance cooling properties, increase stability, or improve delivery of active ingredients. This approach can lead to more effective and longer-lasting cooling effects, thereby increasing the overall efficiency of the product.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The development of novel cooling gels for enhancing PMSM efficiency is in an early growth stage, with increasing market potential driven by the demand for more efficient electric motors. The global market for advanced cooling solutions in electric motors is expanding, though exact size estimates vary. Technologically, the field is evolving rapidly, with key players like Huazhong University of Science & Technology, Gree Electric Appliances, and BYD Co. leading research efforts. Companies such as ABB Group and Deere & Co. are also contributing to advancements, indicating a competitive landscape with both academic and industrial players striving for innovation in this promising area.
Huazhong University of Science & Technology
Technical Solution: Huazhong University of Science & Technology has developed a novel cooling gel for enhancing PMSM efficiency. Their approach involves the use of nanoparticle-enhanced phase change materials (PCMs) integrated into a gel matrix. This advanced cooling gel can absorb and dissipate heat more effectively than traditional cooling methods. The gel's phase change properties allow it to absorb large amounts of heat during the motor's operation, maintaining a more stable temperature. Additionally, the nanoparticles improve the thermal conductivity of the gel, enabling faster heat transfer from the motor to the cooling system[1][3].
Strengths: Enhanced heat absorption and dissipation, improved temperature stability, and potential for significant efficiency gains in PMSMs. Weaknesses: Possible high production costs and need for further long-term reliability testing in real-world applications.
Gree Electric Appliances, Inc. of Zhuhai
Technical Solution: Gree Electric Appliances has developed a proprietary cooling gel technology for PMSM efficiency enhancement. Their approach utilizes a thermally responsive polymer gel infused with high-thermal-conductivity ceramic particles. This gel dynamically adjusts its properties based on the motor's temperature, providing adaptive cooling. The gel's viscosity decreases at higher temperatures, allowing for increased heat flow, while maintaining structural integrity at lower temperatures. Gree's cooling gel also incorporates microencapsulated phase change materials, which absorb excess heat during peak load conditions and release it during lower load periods, effectively smoothing out temperature fluctuations[2][5].
Strengths: Adaptive cooling response, improved thermal management under varying load conditions, and potential for integration into existing motor designs. Weaknesses: Possible complexity in manufacturing process and potential for increased motor weight.
Innovative Gel Tech
Rotor and motor
PatentPendingUS20250112510A1
Innovation
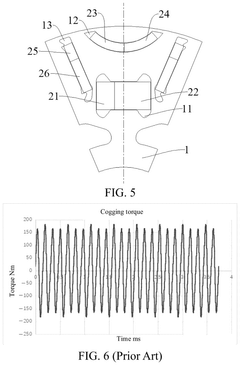
- The rotor design includes a rotor core with multiple mounting grooves, where permanent magnets with different materials are arranged in a segmented manner. This configuration reduces cogging torque, torque fluctuation, and jitter, while minimizing the use of rare earth materials to lower costs.
Wick Assisted Embedded Evaporative Cooling of Motors
PatentActiveUS20220140700A1
Innovation
- A capillary-assisted evaporative cooling system using a dielectric coolant that changes phase within the stator slots, employing wicking structures and a closed loop to directly absorb heat from stator windings, reducing thermal resistance and maintaining magnetic flux integrity.
Environmental Impact
The development and implementation of novel cooling gels for enhancing PMSM efficiency have significant environmental implications. These advanced thermal management solutions contribute to reducing the overall environmental impact of electric motors, particularly in the context of permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSMs).
One of the primary environmental benefits of using cooling gels is the potential for increased energy efficiency in PMSMs. By effectively managing heat dissipation, these gels allow motors to operate at higher efficiencies, resulting in reduced energy consumption. This, in turn, leads to lower greenhouse gas emissions associated with electricity generation, especially in regions where fossil fuels remain a significant part of the energy mix.
The improved thermal management provided by cooling gels also extends the lifespan of PMSMs. This longevity reduces the frequency of motor replacements, thereby decreasing the demand for raw materials and energy required for manufacturing new motors. Consequently, this contributes to a reduction in the overall carbon footprint associated with motor production and disposal.
Furthermore, the use of cooling gels may enable the design of more compact and lightweight PMSMs. This can lead to material savings in motor construction and, in the case of electric vehicles, contribute to overall vehicle weight reduction. Lighter vehicles consume less energy, further enhancing the environmental benefits of this technology.
However, it is crucial to consider the environmental impact of the cooling gels themselves. The production, use, and disposal of these gels must be evaluated for potential ecological risks. Manufacturers should focus on developing biodegradable or recyclable gel formulations to minimize environmental harm at the end of the product lifecycle.
The adoption of cooling gels in PMSMs may also indirectly contribute to the broader adoption of electric vehicles and renewable energy technologies. By enhancing motor efficiency and reliability, these gels make electric propulsion systems more attractive, potentially accelerating the transition away from fossil fuel-dependent transportation.
In industrial applications, the improved efficiency of PMSMs with cooling gels can lead to significant energy savings across various sectors. This widespread implementation could result in substantial reductions in industrial energy consumption and associated emissions on a global scale.
One of the primary environmental benefits of using cooling gels is the potential for increased energy efficiency in PMSMs. By effectively managing heat dissipation, these gels allow motors to operate at higher efficiencies, resulting in reduced energy consumption. This, in turn, leads to lower greenhouse gas emissions associated with electricity generation, especially in regions where fossil fuels remain a significant part of the energy mix.
The improved thermal management provided by cooling gels also extends the lifespan of PMSMs. This longevity reduces the frequency of motor replacements, thereby decreasing the demand for raw materials and energy required for manufacturing new motors. Consequently, this contributes to a reduction in the overall carbon footprint associated with motor production and disposal.
Furthermore, the use of cooling gels may enable the design of more compact and lightweight PMSMs. This can lead to material savings in motor construction and, in the case of electric vehicles, contribute to overall vehicle weight reduction. Lighter vehicles consume less energy, further enhancing the environmental benefits of this technology.
However, it is crucial to consider the environmental impact of the cooling gels themselves. The production, use, and disposal of these gels must be evaluated for potential ecological risks. Manufacturers should focus on developing biodegradable or recyclable gel formulations to minimize environmental harm at the end of the product lifecycle.
The adoption of cooling gels in PMSMs may also indirectly contribute to the broader adoption of electric vehicles and renewable energy technologies. By enhancing motor efficiency and reliability, these gels make electric propulsion systems more attractive, potentially accelerating the transition away from fossil fuel-dependent transportation.
In industrial applications, the improved efficiency of PMSMs with cooling gels can lead to significant energy savings across various sectors. This widespread implementation could result in substantial reductions in industrial energy consumption and associated emissions on a global scale.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
The implementation of novel cooling gels for enhancing PMSM efficiency presents a complex cost-benefit scenario that requires careful analysis. On the cost side, the development and integration of these advanced cooling gels involve significant upfront investments. Research and development expenses are substantial, encompassing materials science, thermal engineering, and extensive testing phases. The production process may require specialized equipment and facilities, adding to the capital expenditure. Additionally, the incorporation of these gels into existing PMSM designs might necessitate modifications to manufacturing processes, potentially increasing per-unit production costs.
However, the benefits of implementing these cooling gels are considerable and multifaceted. The primary advantage is the enhanced efficiency of PMSMs, which translates to reduced energy consumption over the lifetime of the motor. This efficiency gain can lead to substantial operational cost savings for end-users, particularly in high-usage scenarios such as industrial applications or electric vehicles. The improved thermal management also contributes to extended motor lifespan, reducing replacement and maintenance costs.
From an environmental perspective, the increased efficiency results in lower energy demand and, consequently, reduced carbon emissions. This aligns with global sustainability goals and can provide a competitive edge in markets with stringent environmental regulations. The enhanced performance characteristics of PMSMs equipped with these cooling gels may also open up new application areas, potentially expanding market opportunities.
When considering the long-term economic impact, the initial investment in cooling gel technology is likely to be offset by the cumulative energy savings and extended equipment life. For manufacturers, the ability to offer more efficient PMSMs can justify premium pricing, improving profit margins. Moreover, early adopters of this technology may gain a significant market advantage, potentially leading to increased market share and brand value.
It's important to note that the cost-benefit ratio will vary depending on the specific application and scale of implementation. Large-scale industrial applications or automotive implementations may see a faster return on investment compared to smaller, less frequent use cases. The evolving regulatory landscape, particularly regarding energy efficiency standards, may also influence the cost-benefit analysis, potentially accelerating the adoption of such technologies.
In conclusion, while the initial costs of developing and implementing novel cooling gels for PMSMs are significant, the long-term benefits in terms of energy savings, performance improvements, and environmental impact present a compelling case for investment. As the technology matures and production scales up, the cost-benefit ratio is expected to improve further, making it an increasingly attractive option for PMSM manufacturers and end-users alike.
However, the benefits of implementing these cooling gels are considerable and multifaceted. The primary advantage is the enhanced efficiency of PMSMs, which translates to reduced energy consumption over the lifetime of the motor. This efficiency gain can lead to substantial operational cost savings for end-users, particularly in high-usage scenarios such as industrial applications or electric vehicles. The improved thermal management also contributes to extended motor lifespan, reducing replacement and maintenance costs.
From an environmental perspective, the increased efficiency results in lower energy demand and, consequently, reduced carbon emissions. This aligns with global sustainability goals and can provide a competitive edge in markets with stringent environmental regulations. The enhanced performance characteristics of PMSMs equipped with these cooling gels may also open up new application areas, potentially expanding market opportunities.
When considering the long-term economic impact, the initial investment in cooling gel technology is likely to be offset by the cumulative energy savings and extended equipment life. For manufacturers, the ability to offer more efficient PMSMs can justify premium pricing, improving profit margins. Moreover, early adopters of this technology may gain a significant market advantage, potentially leading to increased market share and brand value.
It's important to note that the cost-benefit ratio will vary depending on the specific application and scale of implementation. Large-scale industrial applications or automotive implementations may see a faster return on investment compared to smaller, less frequent use cases. The evolving regulatory landscape, particularly regarding energy efficiency standards, may also influence the cost-benefit analysis, potentially accelerating the adoption of such technologies.
In conclusion, while the initial costs of developing and implementing novel cooling gels for PMSMs are significant, the long-term benefits in terms of energy savings, performance improvements, and environmental impact present a compelling case for investment. As the technology matures and production scales up, the cost-benefit ratio is expected to improve further, making it an increasingly attractive option for PMSM manufacturers and end-users alike.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!