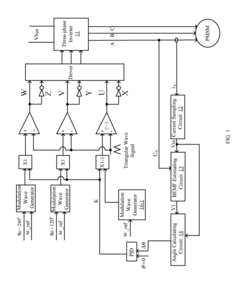
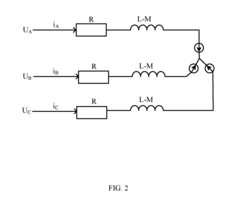
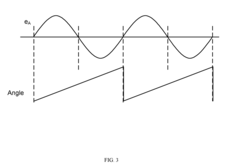
PMSM modeling in virtual prototyping environments
AUG 15, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
PMSM Modeling Background and Objectives
Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSM) have emerged as a critical component in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and renewable energy. The evolution of PMSM technology has been driven by the increasing demand for high-efficiency, compact, and reliable electric motors. Virtual prototyping environments have become essential tools in the development and optimization of PMSM designs, offering significant advantages in terms of cost reduction and time-to-market.
The history of PMSM modeling can be traced back to the early 1970s when the first theoretical models were developed. However, it wasn't until the 1990s that virtual prototyping environments began to play a significant role in PMSM design and analysis. The advent of powerful computing systems and advanced simulation software has since revolutionized the field, enabling more accurate and comprehensive modeling techniques.
The primary objective of PMSM modeling in virtual prototyping environments is to create accurate digital representations of the motor's behavior under various operating conditions. This includes simulating electromagnetic fields, thermal characteristics, mechanical dynamics, and control systems. By doing so, engineers can predict motor performance, optimize designs, and identify potential issues before physical prototypes are built.
One of the key trends in PMSM modeling is the integration of multi-physics simulations. This approach combines electromagnetic, thermal, and mechanical analyses to provide a more holistic understanding of motor behavior. Additionally, there is a growing focus on developing high-fidelity models that can accurately represent non-linear effects and transient phenomena, which are crucial for predicting motor performance in real-world applications.
The advancement of artificial intelligence and machine learning techniques has also begun to influence PMSM modeling. These technologies are being leveraged to enhance model accuracy, reduce computation time, and enable more efficient optimization processes. Furthermore, the increasing complexity of electric vehicle powertrains and industrial automation systems has driven the need for more sophisticated PMSM models that can simulate interactions with other components in the overall system.
Looking ahead, the field of PMSM modeling in virtual prototyping environments is expected to continue evolving. Key areas of development include real-time simulation capabilities, improved model parameterization techniques, and the integration of big data analytics for model validation and refinement. These advancements will be crucial in supporting the design of next-generation electric motors that meet increasingly stringent performance, efficiency, and reliability requirements across various industries.
The history of PMSM modeling can be traced back to the early 1970s when the first theoretical models were developed. However, it wasn't until the 1990s that virtual prototyping environments began to play a significant role in PMSM design and analysis. The advent of powerful computing systems and advanced simulation software has since revolutionized the field, enabling more accurate and comprehensive modeling techniques.
The primary objective of PMSM modeling in virtual prototyping environments is to create accurate digital representations of the motor's behavior under various operating conditions. This includes simulating electromagnetic fields, thermal characteristics, mechanical dynamics, and control systems. By doing so, engineers can predict motor performance, optimize designs, and identify potential issues before physical prototypes are built.
One of the key trends in PMSM modeling is the integration of multi-physics simulations. This approach combines electromagnetic, thermal, and mechanical analyses to provide a more holistic understanding of motor behavior. Additionally, there is a growing focus on developing high-fidelity models that can accurately represent non-linear effects and transient phenomena, which are crucial for predicting motor performance in real-world applications.
The advancement of artificial intelligence and machine learning techniques has also begun to influence PMSM modeling. These technologies are being leveraged to enhance model accuracy, reduce computation time, and enable more efficient optimization processes. Furthermore, the increasing complexity of electric vehicle powertrains and industrial automation systems has driven the need for more sophisticated PMSM models that can simulate interactions with other components in the overall system.
Looking ahead, the field of PMSM modeling in virtual prototyping environments is expected to continue evolving. Key areas of development include real-time simulation capabilities, improved model parameterization techniques, and the integration of big data analytics for model validation and refinement. These advancements will be crucial in supporting the design of next-generation electric motors that meet increasingly stringent performance, efficiency, and reliability requirements across various industries.
Market Demand for Virtual PMSM Prototyping
The market demand for virtual PMSM (Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor) prototyping has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by the increasing adoption of electric vehicles, renewable energy systems, and industrial automation. This surge in demand is primarily fueled by the automotive industry's shift towards electrification, with major manufacturers investing heavily in electric vehicle development.
Virtual prototyping environments for PMSM modeling offer substantial cost and time savings compared to traditional physical prototyping methods. They allow engineers to simulate and optimize motor designs before building physical prototypes, reducing development cycles and improving overall efficiency. This has led to a growing interest from both large corporations and small-to-medium enterprises in adopting virtual PMSM prototyping tools.
The aerospace and defense sectors are also contributing to the market demand, as they seek more efficient and lightweight electric propulsion systems. Virtual PMSM prototyping enables these industries to develop and test advanced motor designs for aircraft and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) without the need for expensive physical prototypes.
In the renewable energy sector, the demand for virtual PMSM prototyping is driven by the need to optimize wind turbine generators and improve their efficiency. As wind energy continues to grow as a significant source of clean power, manufacturers are increasingly turning to virtual prototyping to develop more efficient and reliable PMSM designs for their turbines.
The industrial automation sector is another key driver of market demand for virtual PMSM prototyping. As factories and manufacturing plants strive for greater energy efficiency and precision control, the need for optimized PMSM designs in robotics, conveyor systems, and other automated equipment has grown substantially.
Market analysts predict that the global virtual prototyping market, including PMSM modeling, will continue to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 15% in the coming years. This growth is expected to be particularly strong in regions with a high concentration of automotive and industrial manufacturing, such as North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific.
The increasing complexity of PMSM designs, coupled with the need for faster time-to-market and reduced development costs, is expected to further drive the demand for advanced virtual prototyping solutions. As a result, software vendors and engineering service providers are investing in the development of more sophisticated modeling tools and simulation environments to meet this growing market need.
Virtual prototyping environments for PMSM modeling offer substantial cost and time savings compared to traditional physical prototyping methods. They allow engineers to simulate and optimize motor designs before building physical prototypes, reducing development cycles and improving overall efficiency. This has led to a growing interest from both large corporations and small-to-medium enterprises in adopting virtual PMSM prototyping tools.
The aerospace and defense sectors are also contributing to the market demand, as they seek more efficient and lightweight electric propulsion systems. Virtual PMSM prototyping enables these industries to develop and test advanced motor designs for aircraft and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) without the need for expensive physical prototypes.
In the renewable energy sector, the demand for virtual PMSM prototyping is driven by the need to optimize wind turbine generators and improve their efficiency. As wind energy continues to grow as a significant source of clean power, manufacturers are increasingly turning to virtual prototyping to develop more efficient and reliable PMSM designs for their turbines.
The industrial automation sector is another key driver of market demand for virtual PMSM prototyping. As factories and manufacturing plants strive for greater energy efficiency and precision control, the need for optimized PMSM designs in robotics, conveyor systems, and other automated equipment has grown substantially.
Market analysts predict that the global virtual prototyping market, including PMSM modeling, will continue to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 15% in the coming years. This growth is expected to be particularly strong in regions with a high concentration of automotive and industrial manufacturing, such as North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific.
The increasing complexity of PMSM designs, coupled with the need for faster time-to-market and reduced development costs, is expected to further drive the demand for advanced virtual prototyping solutions. As a result, software vendors and engineering service providers are investing in the development of more sophisticated modeling tools and simulation environments to meet this growing market need.
Current Challenges in PMSM Virtual Modeling
Virtual prototyping of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSM) has become increasingly important in modern motor design and development. However, several challenges persist in accurately modeling these complex systems in virtual environments. One of the primary difficulties lies in capturing the nonlinear magnetic behavior of permanent magnets and core materials. The B-H curves of these materials are inherently nonlinear, and their accurate representation in virtual models is crucial for precise performance prediction.
Another significant challenge is the accurate modeling of eddy current losses in the rotor and stator. These losses are frequency-dependent and can significantly impact motor efficiency, especially at high speeds. Current virtual modeling techniques often struggle to accurately predict these losses, leading to discrepancies between simulated and real-world performance.
The thermal behavior of PMSMs presents another modeling hurdle. Heat generation and dissipation within the motor affect its performance and lifespan, but accurately simulating these thermal dynamics in a virtual environment remains challenging. This is particularly true when considering the complex geometries of modern motor designs and the various cooling methods employed.
Mechanical aspects of PMSM operation, such as vibration and acoustic noise, also pose significant modeling challenges. These phenomena are influenced by electromagnetic forces, mechanical design, and manufacturing tolerances, making their accurate prediction in virtual environments a complex task.
Furthermore, the integration of power electronics and control systems with the PMSM model adds another layer of complexity. Accurately simulating the interactions between the motor, inverter, and control algorithms in a unified virtual environment is essential for predicting real-world performance but remains a significant challenge.
The multi-physics nature of PMSM operation compounds these challenges. Electromagnetic, thermal, mechanical, and control aspects are all interrelated, and their coupled effects must be considered for accurate modeling. However, creating a comprehensive multi-physics model that captures all these interactions while maintaining computational efficiency is a formidable task.
Lastly, the validation of virtual PMSM models against real-world data remains a persistent challenge. Discrepancies between simulated and measured results often arise due to manufacturing variations, material property uncertainties, and simplifications in the modeling process. Bridging this gap between virtual prototypes and physical motors is crucial for improving the reliability and accuracy of PMSM virtual modeling techniques.
Another significant challenge is the accurate modeling of eddy current losses in the rotor and stator. These losses are frequency-dependent and can significantly impact motor efficiency, especially at high speeds. Current virtual modeling techniques often struggle to accurately predict these losses, leading to discrepancies between simulated and real-world performance.
The thermal behavior of PMSMs presents another modeling hurdle. Heat generation and dissipation within the motor affect its performance and lifespan, but accurately simulating these thermal dynamics in a virtual environment remains challenging. This is particularly true when considering the complex geometries of modern motor designs and the various cooling methods employed.
Mechanical aspects of PMSM operation, such as vibration and acoustic noise, also pose significant modeling challenges. These phenomena are influenced by electromagnetic forces, mechanical design, and manufacturing tolerances, making their accurate prediction in virtual environments a complex task.
Furthermore, the integration of power electronics and control systems with the PMSM model adds another layer of complexity. Accurately simulating the interactions between the motor, inverter, and control algorithms in a unified virtual environment is essential for predicting real-world performance but remains a significant challenge.
The multi-physics nature of PMSM operation compounds these challenges. Electromagnetic, thermal, mechanical, and control aspects are all interrelated, and their coupled effects must be considered for accurate modeling. However, creating a comprehensive multi-physics model that captures all these interactions while maintaining computational efficiency is a formidable task.
Lastly, the validation of virtual PMSM models against real-world data remains a persistent challenge. Discrepancies between simulated and measured results often arise due to manufacturing variations, material property uncertainties, and simplifications in the modeling process. Bridging this gap between virtual prototypes and physical motors is crucial for improving the reliability and accuracy of PMSM virtual modeling techniques.
Existing PMSM Virtual Prototyping Solutions
01 Control and optimization of PMSM
Advanced control strategies and optimization techniques for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSM) to improve performance, efficiency, and reliability. This includes methods for precise speed and torque control, sensorless control algorithms, and adaptive control systems to enhance motor operation under various conditions.- Control and optimization of PMSM: Various control strategies and optimization techniques are employed to enhance the performance of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors. These may include advanced control algorithms, sensorless control methods, and efficiency optimization techniques to improve motor operation and energy efficiency.
- PMSM design and construction: Innovations in the design and construction of PMSMs focus on improving motor characteristics such as power density, torque output, and thermal management. This includes advancements in magnet arrangements, rotor and stator designs, and material selection for enhanced performance.
- PMSM applications in electric vehicles: PMSMs are widely used in electric vehicle powertrains due to their high efficiency and power density. Research in this area focuses on optimizing motor performance for automotive applications, including improving torque characteristics and reducing cogging torque.
- Fault detection and diagnosis in PMSM: Developing robust fault detection and diagnosis methods for PMSMs is crucial for ensuring reliable operation. This includes techniques for identifying and mitigating issues such as demagnetization, winding faults, and bearing failures to improve motor longevity and system reliability.
- Integration of PMSM with power electronics: Advancements in the integration of PMSMs with power electronic systems focus on improving overall system efficiency and performance. This includes developments in inverter design, control strategies for motor-drive systems, and optimization of power flow between the motor and power electronics.
02 PMSM design and construction
Innovative approaches in the design and construction of PMSMs, focusing on improved magnetic circuit configurations, rotor and stator designs, and material selection. These advancements aim to enhance power density, reduce cogging torque, and increase overall motor efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions03 Thermal management in PMSM
Techniques for effective thermal management in PMSMs to prevent overheating and maintain optimal performance. This includes novel cooling systems, heat dissipation methods, and temperature monitoring strategies to extend motor life and maintain efficiency under high-load conditions.Expand Specific Solutions04 PMSM for electric vehicle applications
Specialized PMSM designs and control strategies tailored for electric vehicle (EV) applications. This encompasses high-efficiency motors, regenerative braking systems, and integrated motor-drive units optimized for automotive use, focusing on range extension and performance improvement in EVs.Expand Specific Solutions05 Fault diagnosis and reliability enhancement in PMSM
Development of fault detection, diagnosis, and tolerance methods for PMSMs to improve reliability and maintenance. This includes real-time monitoring systems, predictive maintenance algorithms, and fault-tolerant control strategies to ensure continuous operation and minimize downtime in critical applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in PMSM Simulation Software
The PMSM modeling in virtual prototyping environments market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for efficient electric motors in various industries. The market size is expanding, with a projected CAGR of around 8-10% over the next five years. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with companies like Intel Corp. and Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. leading innovation in simulation software and hardware integration. Coventor, Inc. and Siemens AG are also key players, offering specialized MEMS simulation tools and comprehensive digital twin solutions, respectively. The technology's maturity is moderate, with ongoing research at institutions like the University of Southern California and Central South University pushing boundaries in accuracy and computational efficiency.
Intel Corp.
Technical Solution: Intel Corp. has developed PMSM modeling capabilities within their virtual prototyping ecosystem, focusing on the integration of motor models with their processor and FPGA platforms. Their approach leverages high-performance computing to enable real-time simulation of PMSM behavior, particularly for applications in robotics and autonomous systems. Intel's solution incorporates machine learning techniques to enhance model accuracy and adaptability, allowing for rapid iteration in motor design and control strategy development[5]. The company has also implemented hardware-in-the-loop (HIL) simulation capabilities, enabling seamless transition from virtual prototyping to physical testing of motor control systems[6].
Strengths: Integration with Intel's hardware platforms, real-time simulation capabilities, and advanced machine learning techniques. Weaknesses: Potential limitations in detailed electromagnetic modeling compared to specialized motor simulation tools.
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Huawei Technologies has developed PMSM modeling solutions as part of their broader efforts in virtual prototyping for industrial automation and electric vehicle applications. Their approach focuses on creating scalable and efficient models that can be deployed across various computing platforms, from edge devices to cloud-based systems. Huawei's PMSM modeling technique incorporates artificial intelligence to improve model accuracy and adaptability, particularly in predicting motor performance under varying environmental conditions[7]. The company has also implemented advanced optimization algorithms within their virtual prototyping environment, enabling rapid design iterations and performance improvements for PMSM-based systems[8].
Strengths: Scalable modeling solutions, AI-enhanced accuracy, and integration with Huawei's broader IoT ecosystem. Weaknesses: Relatively new entrant in the field compared to established industrial automation companies.
Core Innovations in PMSM Modeling Algorithms
Method for adapting the control parameters of an electric traction machine being a permanent magnetic synchronous motor
PatentActiveUS11870374B2
Innovation
- A method that involves estimating the linked magnetic flux as a function of current, combining it with the permanent magnet flux, and adapting control parameters to optimize PMSM operation, including current control, by performing standstill characterization and retardation tests to determine flux characteristics and no-load power losses.
Driving circuit and driving method for permanent magnet synchronous motor
PatentActiveUS20170085196A1
Innovation
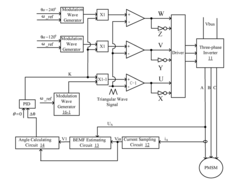
- A driving circuit and method that includes a current sampling circuit, back electromotive force (BEMF) circuit, and torque regulating circuit to estimate BEMF information and regulate the amplitude of a U-shaped modulation wave, allowing for maximum torque per ampere without a position sensor, using a sliding mode controller and PID regulator to synchronize rotor current with the modulation wave.
Integration with Digital Twin Technology
The integration of PMSM modeling with Digital Twin technology represents a significant advancement in virtual prototyping environments. This convergence enables real-time synchronization between physical permanent magnet synchronous motors and their digital counterparts, offering unprecedented insights into motor performance and behavior.
Digital Twin technology creates a virtual replica of the PMSM, continuously updated with real-world data from sensors and IoT devices. This dynamic model allows for accurate simulation and prediction of motor behavior under various operating conditions. By incorporating PMSM modeling into Digital Twin frameworks, engineers can optimize motor design, predict maintenance needs, and enhance overall system efficiency.
The integration process involves several key components. First, high-fidelity PMSM models are developed using advanced mathematical techniques, incorporating electromagnetic, thermal, and mechanical aspects. These models are then linked to real-time data streams from physical motors, ensuring the digital representation remains accurate and up-to-date.
Machine learning algorithms play a crucial role in this integration, continuously refining the digital model based on observed discrepancies between simulated and actual motor performance. This adaptive approach enhances the accuracy of predictions and enables the identification of subtle performance trends that may not be apparent through traditional modeling methods.
The combined PMSM-Digital Twin system offers numerous benefits for virtual prototyping. It allows for rapid iteration and testing of motor designs without the need for physical prototypes, significantly reducing development time and costs. Additionally, the system enables virtual commissioning, where control algorithms and system integration can be validated in a digital environment before deployment.
Furthermore, this integration facilitates predictive maintenance strategies by analyzing motor performance data in real-time and forecasting potential failures or degradation. This proactive approach minimizes downtime and extends the operational lifespan of PMSMs in various applications.
As the field of virtual prototyping continues to evolve, the integration of PMSM modeling with Digital Twin technology is expected to become increasingly sophisticated. Future developments may include enhanced multi-physics simulations, improved sensor technologies for more accurate data collection, and advanced AI algorithms for better predictive capabilities.
Digital Twin technology creates a virtual replica of the PMSM, continuously updated with real-world data from sensors and IoT devices. This dynamic model allows for accurate simulation and prediction of motor behavior under various operating conditions. By incorporating PMSM modeling into Digital Twin frameworks, engineers can optimize motor design, predict maintenance needs, and enhance overall system efficiency.
The integration process involves several key components. First, high-fidelity PMSM models are developed using advanced mathematical techniques, incorporating electromagnetic, thermal, and mechanical aspects. These models are then linked to real-time data streams from physical motors, ensuring the digital representation remains accurate and up-to-date.
Machine learning algorithms play a crucial role in this integration, continuously refining the digital model based on observed discrepancies between simulated and actual motor performance. This adaptive approach enhances the accuracy of predictions and enables the identification of subtle performance trends that may not be apparent through traditional modeling methods.
The combined PMSM-Digital Twin system offers numerous benefits for virtual prototyping. It allows for rapid iteration and testing of motor designs without the need for physical prototypes, significantly reducing development time and costs. Additionally, the system enables virtual commissioning, where control algorithms and system integration can be validated in a digital environment before deployment.
Furthermore, this integration facilitates predictive maintenance strategies by analyzing motor performance data in real-time and forecasting potential failures or degradation. This proactive approach minimizes downtime and extends the operational lifespan of PMSMs in various applications.
As the field of virtual prototyping continues to evolve, the integration of PMSM modeling with Digital Twin technology is expected to become increasingly sophisticated. Future developments may include enhanced multi-physics simulations, improved sensor technologies for more accurate data collection, and advanced AI algorithms for better predictive capabilities.
Energy Efficiency Considerations in PMSM Modeling
Energy efficiency is a critical consideration in the modeling of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSM) within virtual prototyping environments. The accurate representation of energy consumption and losses is essential for optimizing motor performance and reducing operational costs in various applications.
One of the primary factors affecting PMSM energy efficiency is the accurate modeling of core losses. These losses occur in the stator and rotor laminations due to hysteresis and eddy currents. Advanced modeling techniques, such as finite element analysis (FEA), can provide detailed insights into the magnetic field distribution and core loss distribution within the motor. By incorporating these models into virtual prototyping environments, engineers can optimize the lamination design and material selection to minimize core losses.
Copper losses, another significant source of energy inefficiency in PMSMs, arise from the resistance of the stator windings. Accurate modeling of these losses requires consideration of factors such as winding configuration, wire gauge, and temperature effects. Virtual prototyping environments can incorporate detailed thermal models to simulate the heat distribution within the motor, allowing for more precise estimation of copper losses under various operating conditions.
Mechanical losses, including friction and windage, also contribute to the overall energy efficiency of PMSMs. These losses can be modeled using empirical formulas or more advanced computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations. By integrating these models into the virtual prototyping environment, designers can optimize rotor geometry and bearing selection to minimize mechanical losses.
The efficiency of power electronics and control systems plays a crucial role in the overall energy performance of PMSM-based systems. Virtual prototyping environments should include models of inverters, converters, and control algorithms to accurately simulate the entire drivetrain. This holistic approach allows for the optimization of motor control strategies, such as field-oriented control or direct torque control, to maximize energy efficiency across different operating points.
Furthermore, the integration of energy efficiency considerations in PMSM modeling enables the exploration of advanced techniques such as loss minimization algorithms and optimal flux weakening strategies. These approaches can be simulated and refined within the virtual prototyping environment before implementation in physical prototypes, potentially leading to significant improvements in overall system efficiency.
By incorporating comprehensive energy efficiency models into virtual prototyping environments for PMSMs, engineers can conduct parametric studies and sensitivity analyses to identify the most influential factors affecting motor performance. This approach facilitates the development of more efficient motor designs, optimized for specific application requirements, while reducing the time and cost associated with physical prototyping and testing.
One of the primary factors affecting PMSM energy efficiency is the accurate modeling of core losses. These losses occur in the stator and rotor laminations due to hysteresis and eddy currents. Advanced modeling techniques, such as finite element analysis (FEA), can provide detailed insights into the magnetic field distribution and core loss distribution within the motor. By incorporating these models into virtual prototyping environments, engineers can optimize the lamination design and material selection to minimize core losses.
Copper losses, another significant source of energy inefficiency in PMSMs, arise from the resistance of the stator windings. Accurate modeling of these losses requires consideration of factors such as winding configuration, wire gauge, and temperature effects. Virtual prototyping environments can incorporate detailed thermal models to simulate the heat distribution within the motor, allowing for more precise estimation of copper losses under various operating conditions.
Mechanical losses, including friction and windage, also contribute to the overall energy efficiency of PMSMs. These losses can be modeled using empirical formulas or more advanced computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations. By integrating these models into the virtual prototyping environment, designers can optimize rotor geometry and bearing selection to minimize mechanical losses.
The efficiency of power electronics and control systems plays a crucial role in the overall energy performance of PMSM-based systems. Virtual prototyping environments should include models of inverters, converters, and control algorithms to accurately simulate the entire drivetrain. This holistic approach allows for the optimization of motor control strategies, such as field-oriented control or direct torque control, to maximize energy efficiency across different operating points.
Furthermore, the integration of energy efficiency considerations in PMSM modeling enables the exploration of advanced techniques such as loss minimization algorithms and optimal flux weakening strategies. These approaches can be simulated and refined within the virtual prototyping environment before implementation in physical prototypes, potentially leading to significant improvements in overall system efficiency.
By incorporating comprehensive energy efficiency models into virtual prototyping environments for PMSMs, engineers can conduct parametric studies and sensitivity analyses to identify the most influential factors affecting motor performance. This approach facilitates the development of more efficient motor designs, optimized for specific application requirements, while reducing the time and cost associated with physical prototyping and testing.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!