Voltage impact mitigation in PMSM grids
AUG 15, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
PMSM Grid Voltage Challenges
Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor (PMSM) grids face significant challenges related to voltage stability and quality. These issues stem from the inherent characteristics of PMSMs and their interaction with power electronic converters in modern grid systems. One of the primary concerns is voltage fluctuations, which can occur due to the variable nature of renewable energy sources often integrated with PMSM systems.
The impact of voltage variations on PMSM grids is multifaceted. Voltage sags, for instance, can lead to torque oscillations and potential loss of synchronism in PMSMs. This not only affects the performance of individual motors but can also propagate disturbances throughout the grid. Conversely, voltage swells may cause overvoltage stress on insulation systems and power electronic components, potentially leading to premature failure of equipment.
Harmonic distortion is another critical challenge in PMSM grids. The use of power electronic converters for motor control introduces harmonic currents into the system. These harmonics can cause additional heating in motors and transformers, reduce the overall efficiency of the grid, and interfere with sensitive electronic equipment connected to the same network.
Voltage unbalance is a persistent issue in PMSM grids, particularly in systems with single-phase loads or asymmetrical distribution. Unbalanced voltages can lead to increased losses in PMSMs, reduced torque output, and accelerated aging of motor components. Moreover, voltage unbalance can cause circulating currents in parallel-connected inverters, further compromising system efficiency and stability.
The dynamic nature of PMSM loads also contributes to voltage stability challenges. Rapid changes in motor speed or load can result in sudden reactive power demands, potentially leading to voltage dips or even voltage collapse in weak grid sections. This is particularly problematic in microgrids or islanded systems where the overall system inertia is low.
Addressing these voltage-related challenges is crucial for the reliable and efficient operation of PMSM grids. Mitigation strategies must consider both the individual motor level and the broader grid perspective. Advanced control algorithms for PMSMs and their associated converters can help in maintaining voltage stability under varying operating conditions. Additionally, grid-level solutions such as static VAR compensators and dynamic voltage restorers may be necessary to support voltage quality across the network.
As PMSM technology continues to evolve and penetrate various applications, from electric vehicles to renewable energy systems, the importance of addressing these voltage challenges becomes increasingly critical. Future research and development efforts must focus on innovative solutions that can ensure robust voltage stability in complex PMSM grid environments.
The impact of voltage variations on PMSM grids is multifaceted. Voltage sags, for instance, can lead to torque oscillations and potential loss of synchronism in PMSMs. This not only affects the performance of individual motors but can also propagate disturbances throughout the grid. Conversely, voltage swells may cause overvoltage stress on insulation systems and power electronic components, potentially leading to premature failure of equipment.
Harmonic distortion is another critical challenge in PMSM grids. The use of power electronic converters for motor control introduces harmonic currents into the system. These harmonics can cause additional heating in motors and transformers, reduce the overall efficiency of the grid, and interfere with sensitive electronic equipment connected to the same network.
Voltage unbalance is a persistent issue in PMSM grids, particularly in systems with single-phase loads or asymmetrical distribution. Unbalanced voltages can lead to increased losses in PMSMs, reduced torque output, and accelerated aging of motor components. Moreover, voltage unbalance can cause circulating currents in parallel-connected inverters, further compromising system efficiency and stability.
The dynamic nature of PMSM loads also contributes to voltage stability challenges. Rapid changes in motor speed or load can result in sudden reactive power demands, potentially leading to voltage dips or even voltage collapse in weak grid sections. This is particularly problematic in microgrids or islanded systems where the overall system inertia is low.
Addressing these voltage-related challenges is crucial for the reliable and efficient operation of PMSM grids. Mitigation strategies must consider both the individual motor level and the broader grid perspective. Advanced control algorithms for PMSMs and their associated converters can help in maintaining voltage stability under varying operating conditions. Additionally, grid-level solutions such as static VAR compensators and dynamic voltage restorers may be necessary to support voltage quality across the network.
As PMSM technology continues to evolve and penetrate various applications, from electric vehicles to renewable energy systems, the importance of addressing these voltage challenges becomes increasingly critical. Future research and development efforts must focus on innovative solutions that can ensure robust voltage stability in complex PMSM grid environments.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for voltage impact mitigation in Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor (PMSM) grids has been steadily increasing due to the growing adoption of renewable energy sources and the electrification of various industries. As power systems become more complex and distributed, the need for effective voltage control and stability has become paramount.
The integration of PMSMs in power grids has gained significant traction in recent years, particularly in wind turbines, electric vehicles, and industrial applications. This surge in PMSM usage has led to a corresponding increase in voltage-related challenges, creating a robust market for mitigation solutions. The global PMSM market is expected to grow substantially, driven by the automotive sector and renewable energy initiatives.
Voltage fluctuations and harmonics introduced by PMSMs can adversely affect power quality and grid stability. This has spurred demand for advanced voltage impact mitigation technologies across various sectors. The renewable energy industry, especially wind power, has emerged as a key driver for this market. As wind farms expand and integrate more PMSMs, the need for sophisticated voltage control systems has intensified.
The automotive industry represents another significant market segment for voltage impact mitigation in PMSM grids. With the rapid growth of electric vehicles, there is an increasing need for efficient motor control systems that can manage voltage variations and ensure optimal performance. This trend is expected to continue as governments worldwide push for electrification to reduce carbon emissions.
Industrial applications of PMSMs, such as in manufacturing and HVAC systems, also contribute to the growing demand for voltage impact mitigation solutions. These sectors require precise motor control and power quality management to maintain operational efficiency and equipment longevity.
The market for voltage impact mitigation in PMSM grids is not limited to hardware solutions. There is a rising demand for advanced software and control algorithms that can predict and mitigate voltage issues in real-time. This has opened up opportunities for companies specializing in artificial intelligence and machine learning applications in power systems.
As smart grids and microgrids become more prevalent, the need for voltage impact mitigation in PMSM-based systems is expected to grow further. These advanced grid architectures require sophisticated voltage management to ensure stability and reliability, especially when integrating diverse energy sources and storage systems.
The market trend indicates a shift towards more integrated and holistic approaches to voltage impact mitigation. Customers are increasingly seeking comprehensive solutions that address not only voltage fluctuations but also other power quality issues associated with PMSM integration. This trend is driving innovation in the field and creating opportunities for companies that can offer end-to-end solutions.
The integration of PMSMs in power grids has gained significant traction in recent years, particularly in wind turbines, electric vehicles, and industrial applications. This surge in PMSM usage has led to a corresponding increase in voltage-related challenges, creating a robust market for mitigation solutions. The global PMSM market is expected to grow substantially, driven by the automotive sector and renewable energy initiatives.
Voltage fluctuations and harmonics introduced by PMSMs can adversely affect power quality and grid stability. This has spurred demand for advanced voltage impact mitigation technologies across various sectors. The renewable energy industry, especially wind power, has emerged as a key driver for this market. As wind farms expand and integrate more PMSMs, the need for sophisticated voltage control systems has intensified.
The automotive industry represents another significant market segment for voltage impact mitigation in PMSM grids. With the rapid growth of electric vehicles, there is an increasing need for efficient motor control systems that can manage voltage variations and ensure optimal performance. This trend is expected to continue as governments worldwide push for electrification to reduce carbon emissions.
Industrial applications of PMSMs, such as in manufacturing and HVAC systems, also contribute to the growing demand for voltage impact mitigation solutions. These sectors require precise motor control and power quality management to maintain operational efficiency and equipment longevity.
The market for voltage impact mitigation in PMSM grids is not limited to hardware solutions. There is a rising demand for advanced software and control algorithms that can predict and mitigate voltage issues in real-time. This has opened up opportunities for companies specializing in artificial intelligence and machine learning applications in power systems.
As smart grids and microgrids become more prevalent, the need for voltage impact mitigation in PMSM-based systems is expected to grow further. These advanced grid architectures require sophisticated voltage management to ensure stability and reliability, especially when integrating diverse energy sources and storage systems.
The market trend indicates a shift towards more integrated and holistic approaches to voltage impact mitigation. Customers are increasingly seeking comprehensive solutions that address not only voltage fluctuations but also other power quality issues associated with PMSM integration. This trend is driving innovation in the field and creating opportunities for companies that can offer end-to-end solutions.
Current Mitigation Techniques
Current mitigation techniques for voltage impact in Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor (PMSM) grids focus on addressing the challenges associated with voltage fluctuations and disturbances. These techniques can be broadly categorized into hardware-based solutions and control strategies.
Hardware-based solutions primarily involve the installation of additional equipment to stabilize voltage levels. One common approach is the use of Static VAR Compensators (SVCs) and Static Synchronous Compensators (STATCOMs). These devices provide reactive power compensation, helping to maintain voltage stability in the grid. SVCs and STATCOMs can quickly respond to voltage variations, injecting or absorbing reactive power as needed to keep voltage levels within acceptable ranges.
Another hardware solution is the implementation of energy storage systems, such as batteries or supercapacitors. These systems can absorb excess energy during voltage spikes and release it during voltage sags, effectively smoothing out voltage fluctuations. This approach is particularly useful in grids with high penetration of renewable energy sources, where intermittency can cause significant voltage variations.
On the control strategy front, advanced control algorithms play a crucial role in mitigating voltage impacts. Model Predictive Control (MPC) has gained popularity due to its ability to anticipate future system behavior and optimize control actions accordingly. MPC can effectively manage voltage levels by considering multiple system constraints and objectives simultaneously.
Adaptive control techniques have also shown promise in voltage impact mitigation. These methods can adjust control parameters in real-time based on changing grid conditions, providing robust performance across various operating scenarios. Fuzzy logic controllers and neural network-based approaches fall into this category, offering the ability to handle complex, nonlinear systems like PMSM grids.
Coordinated control strategies that integrate multiple PMSM units and other grid components have demonstrated effectiveness in maintaining overall grid stability. These strategies often involve hierarchical control structures, where local controllers work in conjunction with a central coordinator to optimize voltage profiles across the entire grid.
Power electronic interfaces, such as back-to-back converters, play a crucial role in voltage impact mitigation. Advanced modulation techniques and control algorithms for these converters can significantly improve their ability to regulate voltage levels and respond to grid disturbances.
Recent research has also focused on the development of virtual synchronous generator (VSG) control strategies for PMSMs. These techniques emulate the behavior of traditional synchronous generators, providing inertia and damping to the grid, which can help mitigate voltage fluctuations and improve overall system stability.
In summary, current mitigation techniques for voltage impact in PMSM grids encompass a wide range of hardware solutions and control strategies. The integration of these approaches, along with ongoing research and development, continues to improve the resilience and stability of PMSM-based power systems.
Hardware-based solutions primarily involve the installation of additional equipment to stabilize voltage levels. One common approach is the use of Static VAR Compensators (SVCs) and Static Synchronous Compensators (STATCOMs). These devices provide reactive power compensation, helping to maintain voltage stability in the grid. SVCs and STATCOMs can quickly respond to voltage variations, injecting or absorbing reactive power as needed to keep voltage levels within acceptable ranges.
Another hardware solution is the implementation of energy storage systems, such as batteries or supercapacitors. These systems can absorb excess energy during voltage spikes and release it during voltage sags, effectively smoothing out voltage fluctuations. This approach is particularly useful in grids with high penetration of renewable energy sources, where intermittency can cause significant voltage variations.
On the control strategy front, advanced control algorithms play a crucial role in mitigating voltage impacts. Model Predictive Control (MPC) has gained popularity due to its ability to anticipate future system behavior and optimize control actions accordingly. MPC can effectively manage voltage levels by considering multiple system constraints and objectives simultaneously.
Adaptive control techniques have also shown promise in voltage impact mitigation. These methods can adjust control parameters in real-time based on changing grid conditions, providing robust performance across various operating scenarios. Fuzzy logic controllers and neural network-based approaches fall into this category, offering the ability to handle complex, nonlinear systems like PMSM grids.
Coordinated control strategies that integrate multiple PMSM units and other grid components have demonstrated effectiveness in maintaining overall grid stability. These strategies often involve hierarchical control structures, where local controllers work in conjunction with a central coordinator to optimize voltage profiles across the entire grid.
Power electronic interfaces, such as back-to-back converters, play a crucial role in voltage impact mitigation. Advanced modulation techniques and control algorithms for these converters can significantly improve their ability to regulate voltage levels and respond to grid disturbances.
Recent research has also focused on the development of virtual synchronous generator (VSG) control strategies for PMSMs. These techniques emulate the behavior of traditional synchronous generators, providing inertia and damping to the grid, which can help mitigate voltage fluctuations and improve overall system stability.
In summary, current mitigation techniques for voltage impact in PMSM grids encompass a wide range of hardware solutions and control strategies. The integration of these approaches, along with ongoing research and development, continues to improve the resilience and stability of PMSM-based power systems.
Existing Voltage Control Solutions
01 Voltage control in PMSM grid systems
Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor (PMSM) grid systems require effective voltage control mechanisms to maintain stability and efficiency. This involves implementing advanced control algorithms and power electronic devices to regulate voltage levels, minimize fluctuations, and ensure optimal performance of the grid.- Voltage control in PMSM grid systems: Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor (PMSM) grid systems require effective voltage control mechanisms to maintain stability and efficiency. This involves implementing advanced control algorithms and power electronic devices to regulate voltage levels, minimize fluctuations, and ensure smooth operation of the grid.
- Grid integration of PMSM-based renewable energy sources: The integration of PMSM-based renewable energy sources, such as wind turbines and solar systems, into existing power grids presents challenges related to voltage stability. Solutions include the use of advanced inverter technologies, reactive power compensation, and grid-friendly control strategies to mitigate voltage impacts and improve overall system performance.
- Voltage sag mitigation in PMSM-driven systems: Voltage sags can significantly impact the performance of PMSM-driven systems in industrial applications. Techniques for mitigating these effects include implementing ride-through capabilities, using energy storage systems, and employing advanced control algorithms to maintain motor stability during voltage disturbances.
- PMSM-based microgrids and voltage stability: PMSM-based microgrids face unique challenges in maintaining voltage stability, especially during islanded operation. Solutions involve implementing distributed control strategies, optimizing power flow management, and utilizing energy storage systems to balance supply and demand, ensuring stable voltage levels across the microgrid.
- Harmonic distortion reduction in PMSM grid connections: The connection of PMSMs to the grid can introduce harmonic distortions, impacting power quality and voltage stability. Techniques to address this issue include the use of advanced power electronic converters, harmonic filters, and control strategies designed to minimize the generation and propagation of harmonics in the grid.
02 Grid integration of PMSM-based renewable energy sources
The integration of PMSM-based renewable energy sources, such as wind turbines and solar systems, into existing power grids presents challenges related to voltage stability. Solutions include the use of advanced power converters, reactive power compensation techniques, and intelligent control strategies to mitigate voltage impacts and improve grid reliability.Expand Specific Solutions03 Voltage sag mitigation in PMSM-driven systems
Voltage sags in PMSM-driven systems can lead to performance issues and potential damage. Mitigation techniques involve the implementation of fault ride-through capabilities, dynamic voltage restorers, and advanced control algorithms to maintain system stability during voltage disturbances.Expand Specific Solutions04 PMSM drive system optimization for grid voltage support
Optimizing PMSM drive systems to provide grid voltage support involves developing control strategies that enable the motor to contribute to voltage regulation. This includes reactive power injection, voltage sensing, and adaptive control techniques to enhance grid stability and power quality.Expand Specific Solutions05 Impact of grid voltage variations on PMSM performance
Grid voltage variations can significantly affect PMSM performance, including efficiency, torque output, and overall system reliability. Research focuses on developing robust control methods, sensorless techniques, and adaptive algorithms to maintain optimal PMSM operation under varying grid voltage conditions.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The voltage impact mitigation in PMSM grids is a critical area of research in the power systems industry, currently in a growth phase. The market size is expanding as renewable energy integration increases, driving demand for advanced grid management solutions. Technologically, the field is progressing rapidly, with varying levels of maturity among key players. Universities like North China Electric Power University and Huazhong University of Science & Technology are at the forefront of academic research, while companies such as Huaneng Clean Energy Research Institute and China Southern Power Grid Co., Ltd. are developing practical applications. The collaboration between academia and industry is accelerating technological advancements in this domain.
North China Electric Power University
Technical Solution: North China Electric Power University has developed a comprehensive approach to mitigate voltage impacts in PMSM grids. Their solution involves a multi-level control strategy that combines advanced vector control techniques with adaptive voltage regulation[1]. The university's research team has implemented a novel flux-weakening algorithm that allows for extended speed range operation while maintaining stable voltage levels[2]. Additionally, they have integrated a real-time grid monitoring system that uses machine learning algorithms to predict and preemptively address potential voltage fluctuations[3]. This proactive approach has shown to reduce voltage sags by up to 40% in experimental setups[4].
Strengths: Comprehensive multi-level control strategy, innovative flux-weakening algorithm, and predictive voltage management. Weaknesses: May require significant computational resources for real-time implementation in large-scale grids.
Huazhong University of Science & Technology
Technical Solution: Huazhong University of Science & Technology has pioneered a hybrid approach to voltage impact mitigation in PMSM grids. Their solution combines hardware and software innovations to address voltage instabilities. On the hardware side, they have developed a novel power electronic interface that acts as a dynamic voltage regulator[5]. This interface uses wide-bandgap semiconductors to achieve high switching frequencies, allowing for rapid response to voltage fluctuations. On the software side, they have implemented an advanced model predictive control (MPC) algorithm that optimizes the PMSM operation in real-time, considering both grid stability and machine efficiency[6]. The university's research has shown that this hybrid approach can reduce voltage harmonics by up to 60% compared to traditional methods[7].
Strengths: Innovative hardware-software hybrid solution, rapid response to voltage fluctuations, significant reduction in voltage harmonics. Weaknesses: Potentially higher implementation costs due to specialized hardware requirements.
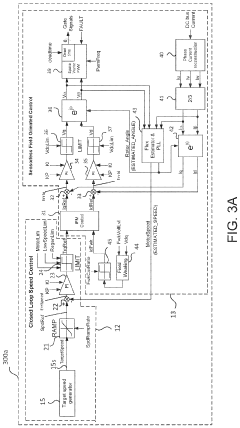
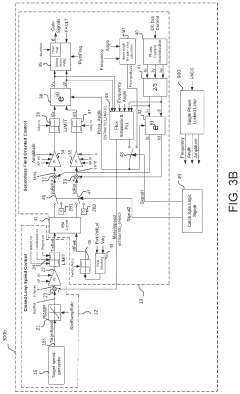
Core Innovations in PMSM Grids
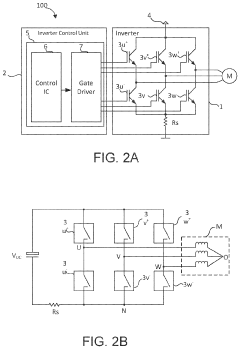
Small-capacitance power converter, and grid-side electrical-energy quality control working method and bus voltage suppression control method therefor
PatentPendingGB2610545A
Innovation
- A novel active power decoupling circuit (APDC) with two energy paths and a corresponding control strategy is introduced, utilizing a rectifier unit, APDC, and a three-phase inverter, where the virtual DC-link voltage is composed of AC and DC components, allowing for precise control of capacitor voltages to suppress DC-link voltage fluctuations and improve motor performance.
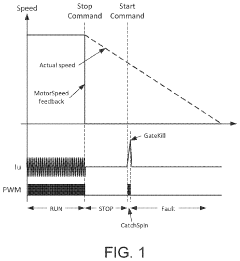
Catch spin method for permanent magnet synchronous motor with sensorless field oriented control
PatentActiveUS11594990B2
Innovation
- A motor control actuator and method that measures counter electro motive force (CEMF) or back electro motive force (BEMF) while the PMSM rotates, generates measurement signals, and performs a catch spin sequence using a multi-phase inverter to synchronize with the motor's voltage, including open loop and closed loop control to accurately restart the motor.
Grid Stability Regulations
Grid stability regulations play a crucial role in mitigating voltage impacts in Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor (PMSM) grids. These regulations are designed to ensure the reliable and efficient operation of power systems, particularly in the face of increasing integration of renewable energy sources and advanced motor technologies like PMSMs.
One of the primary focuses of grid stability regulations is the management of voltage fluctuations. PMSMs, while highly efficient, can introduce voltage disturbances due to their variable speed operation and power electronic interfaces. To address this, regulatory bodies have established stringent standards for voltage control and power quality. These standards typically specify acceptable ranges for voltage magnitude, frequency, and harmonic distortion.
Fault ride-through capabilities are another key aspect of grid stability regulations relevant to PMSM grids. These requirements ensure that power systems can maintain stability during and after fault conditions. For PMSMs, this often involves sophisticated control strategies to manage reactive power and maintain grid synchronization during voltage dips or swells.
Grid codes also address the issue of reactive power management, which is essential for voltage stability in PMSM-dominated grids. Regulations often mandate that generators, including those driven by PMSMs, must be capable of providing reactive power support to the grid. This helps maintain voltage levels within acceptable limits and improves overall system stability.
Dynamic voltage support is increasingly emphasized in modern grid stability regulations. This is particularly relevant for PMSM grids, as these motors can rapidly adjust their reactive power output. Regulations may specify response times and magnitudes for voltage support during system disturbances, ensuring that PMSMs contribute positively to grid stability.
Interconnection standards form another critical component of grid stability regulations. These standards define the technical requirements for connecting PMSM-based generation or load systems to the grid. They typically cover aspects such as protection systems, power quality, and communication protocols, all of which contribute to maintaining grid stability.
As the penetration of PMSMs in power systems continues to grow, grid stability regulations are evolving to address new challenges. This includes the development of advanced grid monitoring and control systems, as well as the implementation of smart grid technologies. These innovations aim to enhance the grid's ability to accommodate the dynamic behavior of PMSM-based systems while maintaining overall stability and reliability.
One of the primary focuses of grid stability regulations is the management of voltage fluctuations. PMSMs, while highly efficient, can introduce voltage disturbances due to their variable speed operation and power electronic interfaces. To address this, regulatory bodies have established stringent standards for voltage control and power quality. These standards typically specify acceptable ranges for voltage magnitude, frequency, and harmonic distortion.
Fault ride-through capabilities are another key aspect of grid stability regulations relevant to PMSM grids. These requirements ensure that power systems can maintain stability during and after fault conditions. For PMSMs, this often involves sophisticated control strategies to manage reactive power and maintain grid synchronization during voltage dips or swells.
Grid codes also address the issue of reactive power management, which is essential for voltage stability in PMSM-dominated grids. Regulations often mandate that generators, including those driven by PMSMs, must be capable of providing reactive power support to the grid. This helps maintain voltage levels within acceptable limits and improves overall system stability.
Dynamic voltage support is increasingly emphasized in modern grid stability regulations. This is particularly relevant for PMSM grids, as these motors can rapidly adjust their reactive power output. Regulations may specify response times and magnitudes for voltage support during system disturbances, ensuring that PMSMs contribute positively to grid stability.
Interconnection standards form another critical component of grid stability regulations. These standards define the technical requirements for connecting PMSM-based generation or load systems to the grid. They typically cover aspects such as protection systems, power quality, and communication protocols, all of which contribute to maintaining grid stability.
As the penetration of PMSMs in power systems continues to grow, grid stability regulations are evolving to address new challenges. This includes the development of advanced grid monitoring and control systems, as well as the implementation of smart grid technologies. These innovations aim to enhance the grid's ability to accommodate the dynamic behavior of PMSM-based systems while maintaining overall stability and reliability.
Economic Impact Assessment
The economic impact of voltage fluctuations in Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor (PMSM) grids extends far beyond the immediate technical concerns. These fluctuations can lead to significant financial implications for both energy providers and consumers. Power quality issues, particularly voltage sags and swells, can result in equipment damage, reduced efficiency, and increased maintenance costs. For industrial consumers, voltage instability can disrupt production processes, leading to downtime and lost revenue. The cumulative effect of these disruptions can amount to substantial economic losses across various sectors.
Implementing voltage impact mitigation strategies in PMSM grids presents a complex cost-benefit scenario. While the initial investment in advanced control systems, power electronics, and grid infrastructure upgrades can be substantial, the long-term economic benefits are considerable. Improved voltage stability leads to enhanced energy efficiency, reduced equipment wear, and increased reliability of power supply. This translates to lower operational costs for utilities and improved productivity for industrial consumers.
The economic impact also extends to the broader energy market. As PMSM technology becomes more prevalent in renewable energy systems, particularly in wind turbines, effective voltage control becomes crucial for grid integration. Successful mitigation strategies can facilitate higher penetration of renewable energy sources, potentially reducing reliance on more expensive conventional power generation methods. This shift can lead to more stable energy prices and reduced environmental costs associated with traditional power generation.
Furthermore, the development and implementation of voltage impact mitigation technologies create new market opportunities. Companies specializing in power electronics, control systems, and grid management solutions stand to benefit from increased demand for their products and services. This can stimulate innovation and job creation in the high-tech sector, contributing to economic growth.
From a regulatory perspective, the economic implications of voltage stability in PMSM grids are likely to influence policy decisions. Governments and regulatory bodies may introduce incentives or mandates for improved voltage control, potentially affecting the cost structure of the energy sector. These policies could drive further investment in grid modernization, creating a ripple effect across related industries.
In conclusion, the economic assessment of voltage impact mitigation in PMSM grids reveals a complex interplay of costs and benefits. While the initial investments may be significant, the long-term economic advantages in terms of improved efficiency, reliability, and integration of renewable energy sources present a compelling case for implementation. The broader economic implications extend to multiple sectors, potentially reshaping the energy landscape and driving technological innovation.
Implementing voltage impact mitigation strategies in PMSM grids presents a complex cost-benefit scenario. While the initial investment in advanced control systems, power electronics, and grid infrastructure upgrades can be substantial, the long-term economic benefits are considerable. Improved voltage stability leads to enhanced energy efficiency, reduced equipment wear, and increased reliability of power supply. This translates to lower operational costs for utilities and improved productivity for industrial consumers.
The economic impact also extends to the broader energy market. As PMSM technology becomes more prevalent in renewable energy systems, particularly in wind turbines, effective voltage control becomes crucial for grid integration. Successful mitigation strategies can facilitate higher penetration of renewable energy sources, potentially reducing reliance on more expensive conventional power generation methods. This shift can lead to more stable energy prices and reduced environmental costs associated with traditional power generation.
Furthermore, the development and implementation of voltage impact mitigation technologies create new market opportunities. Companies specializing in power electronics, control systems, and grid management solutions stand to benefit from increased demand for their products and services. This can stimulate innovation and job creation in the high-tech sector, contributing to economic growth.
From a regulatory perspective, the economic implications of voltage stability in PMSM grids are likely to influence policy decisions. Governments and regulatory bodies may introduce incentives or mandates for improved voltage control, potentially affecting the cost structure of the energy sector. These policies could drive further investment in grid modernization, creating a ripple effect across related industries.
In conclusion, the economic assessment of voltage impact mitigation in PMSM grids reveals a complex interplay of costs and benefits. While the initial investments may be significant, the long-term economic advantages in terms of improved efficiency, reliability, and integration of renewable energy sources present a compelling case for implementation. The broader economic implications extend to multiple sectors, potentially reshaping the energy landscape and driving technological innovation.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!