PMSM applications in ergonomic exoskeletons
AUG 15, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
PMSM in Exoskeletons: Background and Objectives
Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSMs) have emerged as a pivotal technology in the development of ergonomic exoskeletons, marking a significant advancement in the field of human augmentation and rehabilitation. The evolution of PMSMs in exoskeleton applications can be traced back to the early 2000s when researchers began exploring more efficient and compact actuator solutions for wearable robotic systems.
The primary objective of integrating PMSMs into exoskeletons is to enhance human performance and mobility while minimizing energy consumption and system weight. This technology aims to provide precise torque control, high power density, and improved efficiency compared to traditional motor technologies. The development of PMSM-driven exoskeletons has been driven by the growing demand for assistive devices in healthcare, industrial, and military sectors.
Over the past two decades, the application of PMSMs in exoskeletons has witnessed several key milestones. Initially, the focus was on proving the concept of using these motors in wearable robotic systems. As the technology matured, efforts shifted towards optimizing motor design for specific exoskeleton applications, including lower limb assistance, upper body support, and full-body augmentation.
The technological trajectory of PMSMs in exoskeletons has been characterized by continuous improvements in power-to-weight ratio, control algorithms, and integration with advanced sensors and materials. Recent advancements have focused on developing more compact and lightweight PMSM designs, as well as enhancing their adaptability to various user requirements and environmental conditions.
Current research and development efforts are aimed at addressing several critical challenges in PMSM-based exoskeleton systems. These include further reducing motor size and weight without compromising performance, improving energy efficiency to extend operational time, and developing more sophisticated control strategies for seamless human-machine interaction.
Looking ahead, the future of PMSM applications in ergonomic exoskeletons is expected to be shaped by emerging trends such as the integration of artificial intelligence for adaptive control, the use of advanced materials for motor construction, and the development of modular exoskeleton designs that can be customized for different applications and user needs.
As the field continues to evolve, the ultimate goal remains to create exoskeleton systems that are not only powerful and efficient but also comfortable, intuitive to use, and capable of seamlessly augmenting human capabilities across a wide range of activities and environments. The ongoing advancements in PMSM technology are poised to play a crucial role in realizing this vision and revolutionizing the way humans interact with assistive and augmentative robotic systems.
The primary objective of integrating PMSMs into exoskeletons is to enhance human performance and mobility while minimizing energy consumption and system weight. This technology aims to provide precise torque control, high power density, and improved efficiency compared to traditional motor technologies. The development of PMSM-driven exoskeletons has been driven by the growing demand for assistive devices in healthcare, industrial, and military sectors.
Over the past two decades, the application of PMSMs in exoskeletons has witnessed several key milestones. Initially, the focus was on proving the concept of using these motors in wearable robotic systems. As the technology matured, efforts shifted towards optimizing motor design for specific exoskeleton applications, including lower limb assistance, upper body support, and full-body augmentation.
The technological trajectory of PMSMs in exoskeletons has been characterized by continuous improvements in power-to-weight ratio, control algorithms, and integration with advanced sensors and materials. Recent advancements have focused on developing more compact and lightweight PMSM designs, as well as enhancing their adaptability to various user requirements and environmental conditions.
Current research and development efforts are aimed at addressing several critical challenges in PMSM-based exoskeleton systems. These include further reducing motor size and weight without compromising performance, improving energy efficiency to extend operational time, and developing more sophisticated control strategies for seamless human-machine interaction.
Looking ahead, the future of PMSM applications in ergonomic exoskeletons is expected to be shaped by emerging trends such as the integration of artificial intelligence for adaptive control, the use of advanced materials for motor construction, and the development of modular exoskeleton designs that can be customized for different applications and user needs.
As the field continues to evolve, the ultimate goal remains to create exoskeleton systems that are not only powerful and efficient but also comfortable, intuitive to use, and capable of seamlessly augmenting human capabilities across a wide range of activities and environments. The ongoing advancements in PMSM technology are poised to play a crucial role in realizing this vision and revolutionizing the way humans interact with assistive and augmentative robotic systems.
Market Analysis for Ergonomic Exoskeletons
The market for ergonomic exoskeletons has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing awareness of workplace safety and the need to reduce musculoskeletal disorders among workers. The global ergonomic exoskeleton market is expected to expand rapidly, with projections indicating substantial growth over the next decade.
Key industries driving the demand for ergonomic exoskeletons include manufacturing, construction, healthcare, and logistics. In the manufacturing sector, exoskeletons are being adopted to assist workers in tasks involving repetitive motions, heavy lifting, and awkward postures. The construction industry is leveraging exoskeletons to enhance worker safety and productivity in physically demanding environments.
Healthcare applications are emerging as a promising market segment, with exoskeletons being used to assist medical professionals during long surgeries and to aid in patient rehabilitation. The logistics and warehousing sector is also showing increased interest in exoskeletons to improve efficiency and reduce worker fatigue in material handling operations.
Geographically, North America and Europe are currently the leading markets for ergonomic exoskeletons, owing to stringent workplace safety regulations and higher adoption rates of advanced technologies. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth, driven by rapid industrialization and increasing focus on worker well-being in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea.
The market is characterized by a mix of established players and innovative startups. Major companies are investing heavily in research and development to improve exoskeleton technology, focusing on aspects such as weight reduction, enhanced mobility, and integration of smart features. Collaborations between exoskeleton manufacturers and end-user industries are becoming more common, leading to customized solutions for specific applications.
Despite the positive outlook, several factors are influencing market dynamics. The high initial cost of exoskeletons remains a barrier to widespread adoption, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises. Additionally, there are challenges related to user acceptance, ergonomic design, and the need for standardization in the industry.
Looking ahead, the integration of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSM) in ergonomic exoskeletons is expected to drive further market growth. PMSMs offer advantages such as high power density, improved efficiency, and precise control, which are crucial for enhancing the performance and usability of exoskeletons. This technological advancement is likely to expand the application scope of ergonomic exoskeletons and contribute to market expansion in the coming years.
Key industries driving the demand for ergonomic exoskeletons include manufacturing, construction, healthcare, and logistics. In the manufacturing sector, exoskeletons are being adopted to assist workers in tasks involving repetitive motions, heavy lifting, and awkward postures. The construction industry is leveraging exoskeletons to enhance worker safety and productivity in physically demanding environments.
Healthcare applications are emerging as a promising market segment, with exoskeletons being used to assist medical professionals during long surgeries and to aid in patient rehabilitation. The logistics and warehousing sector is also showing increased interest in exoskeletons to improve efficiency and reduce worker fatigue in material handling operations.
Geographically, North America and Europe are currently the leading markets for ergonomic exoskeletons, owing to stringent workplace safety regulations and higher adoption rates of advanced technologies. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth, driven by rapid industrialization and increasing focus on worker well-being in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea.
The market is characterized by a mix of established players and innovative startups. Major companies are investing heavily in research and development to improve exoskeleton technology, focusing on aspects such as weight reduction, enhanced mobility, and integration of smart features. Collaborations between exoskeleton manufacturers and end-user industries are becoming more common, leading to customized solutions for specific applications.
Despite the positive outlook, several factors are influencing market dynamics. The high initial cost of exoskeletons remains a barrier to widespread adoption, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises. Additionally, there are challenges related to user acceptance, ergonomic design, and the need for standardization in the industry.
Looking ahead, the integration of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSM) in ergonomic exoskeletons is expected to drive further market growth. PMSMs offer advantages such as high power density, improved efficiency, and precise control, which are crucial for enhancing the performance and usability of exoskeletons. This technological advancement is likely to expand the application scope of ergonomic exoskeletons and contribute to market expansion in the coming years.
PMSM Technology: Current State and Challenges
Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSMs) have emerged as a promising technology for ergonomic exoskeletons, offering significant advantages in terms of power density, efficiency, and control precision. However, the current state of PMSM technology in this application faces several challenges that need to be addressed for wider adoption and improved performance.
One of the primary challenges is the optimization of power-to-weight ratio. While PMSMs generally offer high power density, further improvements are necessary to meet the stringent weight requirements of wearable exoskeletons. Researchers are exploring advanced magnetic materials and innovative motor designs to enhance power output without significantly increasing motor mass.
Thermal management remains a critical issue, particularly in compact exoskeleton designs where space for cooling systems is limited. Overheating can lead to reduced efficiency and potential damage to motor components. Current efforts focus on developing more efficient cooling strategies and materials with better heat dissipation properties.
Control complexity is another significant challenge. PMSMs require sophisticated control algorithms to achieve optimal performance, especially in the dynamic and unpredictable environments typical of exoskeleton use. Researchers are working on adaptive control systems that can quickly respond to changing loads and user movements, ensuring smooth and natural operation.
Energy efficiency is a constant concern, particularly for battery-powered exoskeletons. While PMSMs are inherently efficient, there is ongoing research to further reduce energy losses, especially at low speeds and during start-stop operations common in exoskeleton applications.
Durability and reliability under varied operating conditions pose additional challenges. Exoskeletons may be subjected to impacts, vibrations, and environmental factors that can affect motor performance and longevity. Developing robust motor designs and protective enclosures that do not significantly add to the overall weight is an active area of research.
Cost remains a barrier to widespread adoption. The high-quality materials and precision manufacturing required for PMSMs contribute to elevated production costs. Efforts are underway to identify cost-effective manufacturing processes and alternative materials that maintain performance while reducing expenses.
Lastly, the integration of PMSMs with other exoskeleton components, such as sensors, controllers, and power sources, presents ongoing challenges. Achieving seamless integration while maintaining compact design and minimizing electromagnetic interference is crucial for optimal exoskeleton performance.
Despite these challenges, the field is rapidly advancing. Innovations in materials science, control theory, and manufacturing techniques are continually pushing the boundaries of PMSM technology in ergonomic exoskeletons, promising more efficient, powerful, and user-friendly devices in the future.
One of the primary challenges is the optimization of power-to-weight ratio. While PMSMs generally offer high power density, further improvements are necessary to meet the stringent weight requirements of wearable exoskeletons. Researchers are exploring advanced magnetic materials and innovative motor designs to enhance power output without significantly increasing motor mass.
Thermal management remains a critical issue, particularly in compact exoskeleton designs where space for cooling systems is limited. Overheating can lead to reduced efficiency and potential damage to motor components. Current efforts focus on developing more efficient cooling strategies and materials with better heat dissipation properties.
Control complexity is another significant challenge. PMSMs require sophisticated control algorithms to achieve optimal performance, especially in the dynamic and unpredictable environments typical of exoskeleton use. Researchers are working on adaptive control systems that can quickly respond to changing loads and user movements, ensuring smooth and natural operation.
Energy efficiency is a constant concern, particularly for battery-powered exoskeletons. While PMSMs are inherently efficient, there is ongoing research to further reduce energy losses, especially at low speeds and during start-stop operations common in exoskeleton applications.
Durability and reliability under varied operating conditions pose additional challenges. Exoskeletons may be subjected to impacts, vibrations, and environmental factors that can affect motor performance and longevity. Developing robust motor designs and protective enclosures that do not significantly add to the overall weight is an active area of research.
Cost remains a barrier to widespread adoption. The high-quality materials and precision manufacturing required for PMSMs contribute to elevated production costs. Efforts are underway to identify cost-effective manufacturing processes and alternative materials that maintain performance while reducing expenses.
Lastly, the integration of PMSMs with other exoskeleton components, such as sensors, controllers, and power sources, presents ongoing challenges. Achieving seamless integration while maintaining compact design and minimizing electromagnetic interference is crucial for optimal exoskeleton performance.
Despite these challenges, the field is rapidly advancing. Innovations in materials science, control theory, and manufacturing techniques are continually pushing the boundaries of PMSM technology in ergonomic exoskeletons, promising more efficient, powerful, and user-friendly devices in the future.
PMSM Integration Solutions for Exoskeletons
01 Motor design and structure
Innovations in PMSM design focus on improving efficiency and performance. This includes optimizing the arrangement of permanent magnets, enhancing rotor and stator configurations, and developing novel winding techniques. These advancements aim to increase power density, reduce cogging torque, and improve overall motor efficiency.- Motor design and structure: Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSMs) have unique design features and structural elements that contribute to their efficiency and performance. These may include specific rotor configurations, stator designs, and magnet arrangements to optimize power output and reduce losses.
- Control systems and algorithms: Advanced control systems and algorithms are crucial for optimizing PMSM performance. These may include sensorless control techniques, adaptive control strategies, and advanced modulation methods to improve efficiency, reduce torque ripple, and enhance overall motor operation.
- Efficiency improvement techniques: Various techniques are employed to improve the efficiency of PMSMs, such as optimizing magnetic circuit design, reducing core losses, and implementing energy recovery systems. These improvements can lead to higher power density and better overall performance in applications ranging from electric vehicles to industrial machinery.
- Thermal management and cooling systems: Effective thermal management is essential for maintaining PMSM performance and longevity. This includes innovative cooling systems, heat dissipation techniques, and temperature monitoring methods to prevent overheating and ensure optimal operation under various load conditions.
- Integration with power electronics: The integration of PMSMs with advanced power electronics is crucial for overall system performance. This includes the development of specialized inverters, power converters, and drive systems tailored to the unique characteristics of PMSMs, enabling better control, efficiency, and reliability in various applications.
02 Control systems and algorithms
Advanced control strategies are developed for PMSMs to enhance their performance and efficiency. These include sensorless control techniques, adaptive control algorithms, and improved vector control methods. Such systems aim to optimize motor operation under various load conditions and speeds, reducing energy consumption and improving dynamic response.Expand Specific Solutions03 Thermal management and cooling
Effective thermal management is crucial for PMSM performance and longevity. Innovations in this area include advanced cooling systems, heat-resistant materials, and improved thermal modeling techniques. These developments help to maintain optimal operating temperatures, prevent demagnetization, and extend motor lifespan.Expand Specific Solutions04 Integration with power electronics
The integration of PMSMs with advanced power electronics is a key area of development. This includes the design of compact, efficient inverters, improved power factor correction techniques, and the implementation of smart grid compatibility. Such integrations aim to enhance overall system efficiency and enable better control of motor performance.Expand Specific Solutions05 Application-specific optimizations
PMSMs are being optimized for specific applications such as electric vehicles, industrial automation, and renewable energy systems. These optimizations involve tailoring motor characteristics to meet specific requirements like high torque at low speeds, rapid acceleration, or operation in harsh environments. Such developments aim to improve the performance and efficiency of PMSMs in diverse applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in PMSM and Exoskeleton Industries
The PMSM applications in ergonomic exoskeletons market is in its growth stage, with increasing adoption across various industries. The global market size for exoskeletons is projected to reach several billion dollars by 2025, driven by demand in healthcare, industrial, and military sectors. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with companies like Ekso Bionics, Roam Robotics, and Honda Motor Co. leading innovation in lightweight, portable designs. Universities such as Zhejiang University and Georgia Tech are contributing to R&D efforts. While still evolving, the technology is becoming more mature, with commercial products available and ongoing improvements in power efficiency, control systems, and human-machine interfaces.
Ekso Bionics, Inc.
Technical Solution: Ekso Bionics has developed advanced PMSM-based exoskeletons for medical and industrial applications. Their EksoNR™ robotic exoskeleton utilizes precision-controlled PMSMs to provide gait training for patients with neurological conditions[1]. The system employs adaptive algorithms to adjust motor torque and speed based on the user's movement patterns, enhancing rehabilitation efficacy. Ekso Bionics has also implemented field-oriented control (FOC) techniques to optimize PMSM performance, resulting in smoother motion and improved energy efficiency[2]. Their industrial exoskeletons, such as the EksoVest, incorporate compact PMSMs with high torque-to-weight ratios, enabling workers to perform overhead tasks with reduced fatigue[3].
Strengths: Proven clinical efficacy, advanced control algorithms, and versatile applications in both medical and industrial sectors. Weaknesses: High initial cost and potential complexity in user training and maintenance.
Roam Robotics, Inc.
Technical Solution: Roam Robotics has pioneered lightweight, soft exoskeletons using PMSM technology for enhanced mobility and performance. Their Ascend™ smart knee orthosis employs compact PMSMs with high power density to provide assistive torque during various activities[4]. The system utilizes advanced sensors and machine learning algorithms to predict user intent and adjust motor output accordingly. Roam's innovative approach combines flexible materials with precision PMSM control, resulting in a more natural and comfortable user experience. The company has also developed a proprietary PMSM driver that optimizes motor efficiency across a wide range of operating conditions, extending battery life and improving overall system performance[5].
Strengths: Lightweight and comfortable design, advanced predictive algorithms, and versatile applications for both medical and recreational use. Weaknesses: Limited load-bearing capacity compared to rigid exoskeletons and potential challenges in durability of soft components.
Core PMSM Innovations for Exoskeleton Applications
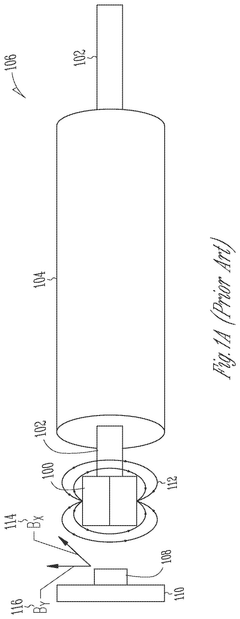
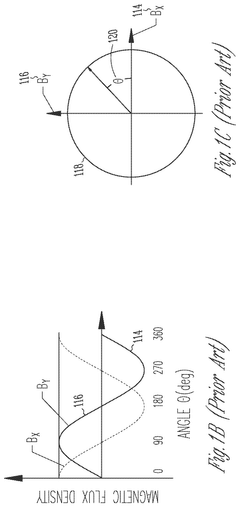
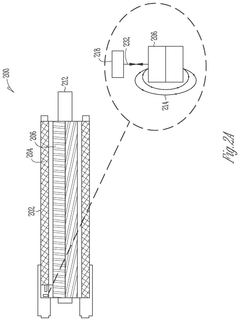
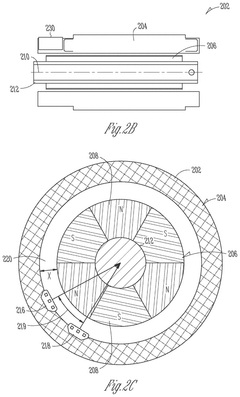
Permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM) integrated position sensing
PatentActiveUS12212257B2
Innovation
- The integration of analog magnetic flux sensors within the hollow cylindrical stator of the PMSM, arranged concentrically around the rotational axis at a constant mechanical angle relative to each other, allows for direct measurement of the magnetic flux from the rotor without external obstructions, enabling accurate rotor position sensing and reducing motor size and cost.
Safety Standards for Powered Exoskeletons
Safety standards for powered exoskeletons are crucial for ensuring the well-being of users and promoting the widespread adoption of this technology. These standards address various aspects of exoskeleton design, manufacturing, and operation to minimize risks and maximize benefits.
One of the primary safety considerations is the mechanical integrity of the exoskeleton. Standards typically require robust construction and materials that can withstand the intended loads and usage conditions. This includes specifications for structural strength, durability, and resistance to environmental factors such as moisture and temperature variations.
Electrical safety is another critical area covered by exoskeleton standards. Guidelines often mandate proper insulation, grounding, and protection against short circuits and overloads. For PMSM-driven exoskeletons, specific requirements may address the safe integration and operation of these motors, including thermal management and electromagnetic compatibility.
Human-machine interface safety is a key focus, given the close interaction between the user and the exoskeleton. Standards typically outline requirements for ergonomic design, ensuring that the device fits comfortably and does not cause undue strain or pressure points. They may also specify guidelines for adjustability to accommodate different user sizes and body types.
Control system safety is paramount, particularly for PMSM-driven exoskeletons. Standards often require fail-safe mechanisms, redundant systems, and robust software algorithms to prevent unintended movements or loss of control. This may include specifications for emergency stop functions, power loss handling, and system response times.
User training and operational safety procedures are typically addressed in exoskeleton standards. These guidelines outline the necessary information and training that must be provided to users, including proper donning and doffing procedures, operational limits, and potential hazards.
Environmental safety considerations are also included, specifying the conditions under which the exoskeleton can be safely operated. This may cover factors such as temperature ranges, humidity levels, and exposure to dust or other contaminants.
Lastly, standards often address the need for regular maintenance and inspection protocols to ensure ongoing safety. This includes guidelines for periodic checks, component replacement schedules, and documentation requirements for maintenance activities.
One of the primary safety considerations is the mechanical integrity of the exoskeleton. Standards typically require robust construction and materials that can withstand the intended loads and usage conditions. This includes specifications for structural strength, durability, and resistance to environmental factors such as moisture and temperature variations.
Electrical safety is another critical area covered by exoskeleton standards. Guidelines often mandate proper insulation, grounding, and protection against short circuits and overloads. For PMSM-driven exoskeletons, specific requirements may address the safe integration and operation of these motors, including thermal management and electromagnetic compatibility.
Human-machine interface safety is a key focus, given the close interaction between the user and the exoskeleton. Standards typically outline requirements for ergonomic design, ensuring that the device fits comfortably and does not cause undue strain or pressure points. They may also specify guidelines for adjustability to accommodate different user sizes and body types.
Control system safety is paramount, particularly for PMSM-driven exoskeletons. Standards often require fail-safe mechanisms, redundant systems, and robust software algorithms to prevent unintended movements or loss of control. This may include specifications for emergency stop functions, power loss handling, and system response times.
User training and operational safety procedures are typically addressed in exoskeleton standards. These guidelines outline the necessary information and training that must be provided to users, including proper donning and doffing procedures, operational limits, and potential hazards.
Environmental safety considerations are also included, specifying the conditions under which the exoskeleton can be safely operated. This may cover factors such as temperature ranges, humidity levels, and exposure to dust or other contaminants.
Lastly, standards often address the need for regular maintenance and inspection protocols to ensure ongoing safety. This includes guidelines for periodic checks, component replacement schedules, and documentation requirements for maintenance activities.
Energy Efficiency in PMSM-Driven Exoskeletons
Energy efficiency is a critical factor in the development and application of PMSM-driven exoskeletons. The use of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSMs) in ergonomic exoskeletons has shown significant potential for improving energy efficiency compared to other motor types. This is primarily due to their high power density, excellent torque-to-weight ratio, and superior control characteristics.
One of the key aspects of energy efficiency in PMSM-driven exoskeletons is the optimization of motor control strategies. Advanced control algorithms, such as field-oriented control (FOC) and model predictive control (MPC), have been implemented to maximize the motor's efficiency across various operating conditions. These control methods allow for precise torque and speed regulation, minimizing energy losses and improving overall system performance.
The design of the PMSM itself plays a crucial role in energy efficiency. Manufacturers have focused on developing high-performance magnetic materials and optimizing motor geometries to reduce core losses and improve power factor. Additionally, the integration of advanced power electronics, including efficient inverters and regenerative braking systems, has further enhanced the energy efficiency of exoskeleton systems.
Energy recovery mechanisms have been incorporated into PMSM-driven exoskeletons to harness and reuse energy that would otherwise be dissipated. During the deceleration or descending phases of movement, the PMSM can act as a generator, converting kinetic energy back into electrical energy. This regenerative braking capability significantly extends the operational time of battery-powered exoskeletons and reduces overall energy consumption.
The selection of appropriate gear ratios and transmission systems has also been optimized to ensure that PMSMs operate within their most efficient speed and torque ranges. This careful matching of motor characteristics with load requirements minimizes energy losses and improves the overall efficiency of the exoskeleton system.
Researchers have explored the use of lightweight materials and optimized structural designs to reduce the overall weight of exoskeletons, thereby decreasing the power requirements and improving energy efficiency. The integration of energy-efficient sensors and low-power electronics further contributes to reducing the overall energy consumption of the system.
Recent advancements in energy storage technologies, particularly in battery technology, have complemented the energy efficiency improvements in PMSM-driven exoskeletons. High-density, fast-charging batteries with improved cycle life have extended the operational range and reduced the downtime of exoskeleton systems, enhancing their practicality and efficiency in real-world applications.
One of the key aspects of energy efficiency in PMSM-driven exoskeletons is the optimization of motor control strategies. Advanced control algorithms, such as field-oriented control (FOC) and model predictive control (MPC), have been implemented to maximize the motor's efficiency across various operating conditions. These control methods allow for precise torque and speed regulation, minimizing energy losses and improving overall system performance.
The design of the PMSM itself plays a crucial role in energy efficiency. Manufacturers have focused on developing high-performance magnetic materials and optimizing motor geometries to reduce core losses and improve power factor. Additionally, the integration of advanced power electronics, including efficient inverters and regenerative braking systems, has further enhanced the energy efficiency of exoskeleton systems.
Energy recovery mechanisms have been incorporated into PMSM-driven exoskeletons to harness and reuse energy that would otherwise be dissipated. During the deceleration or descending phases of movement, the PMSM can act as a generator, converting kinetic energy back into electrical energy. This regenerative braking capability significantly extends the operational time of battery-powered exoskeletons and reduces overall energy consumption.
The selection of appropriate gear ratios and transmission systems has also been optimized to ensure that PMSMs operate within their most efficient speed and torque ranges. This careful matching of motor characteristics with load requirements minimizes energy losses and improves the overall efficiency of the exoskeleton system.
Researchers have explored the use of lightweight materials and optimized structural designs to reduce the overall weight of exoskeletons, thereby decreasing the power requirements and improving energy efficiency. The integration of energy-efficient sensors and low-power electronics further contributes to reducing the overall energy consumption of the system.
Recent advancements in energy storage technologies, particularly in battery technology, have complemented the energy efficiency improvements in PMSM-driven exoskeletons. High-density, fast-charging batteries with improved cycle life have extended the operational range and reduced the downtime of exoskeleton systems, enhancing their practicality and efficiency in real-world applications.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!