Ozonation: Advanced Oxidation (O₃/H₂O₂/UV), Radical Yields And By-Product Control
SEP 18, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ozonation Technology Evolution and Objectives
Ozonation technology has evolved significantly since its initial application in water treatment during the late 19th century. Originally implemented for disinfection purposes in Europe, ozonation has transformed into a sophisticated advanced oxidation process (AOP) with multifaceted applications across various industries. The evolution trajectory demonstrates a shift from simple disinfection to complex treatment systems capable of addressing emerging contaminants and micropollutants that conventional treatment methods fail to remove effectively.
The 1970s marked a pivotal turning point with the discovery of disinfection by-products (DBPs) in chlorinated water, prompting researchers to explore alternative treatment methods. This led to increased interest in ozonation as a primary or complementary treatment process. By the 1980s, researchers began investigating the combination of ozone with hydrogen peroxide (O₃/H₂O₂), which significantly enhanced oxidation efficiency through increased hydroxyl radical formation.
The 1990s witnessed the integration of ultraviolet (UV) radiation with ozonation systems, creating more powerful treatment configurations (O₃/UV and O₃/H₂O₂/UV). These combinations demonstrated superior performance in degrading recalcitrant compounds through synergistic effects. Concurrently, advancements in ozone generation technology, including the development of more energy-efficient corona discharge systems and electrolytic ozone generators, reduced operational costs and improved accessibility.
Recent technological developments have focused on optimizing radical yields while minimizing harmful by-product formation. The identification of ozonation by-products, including bromate, aldehydes, and carboxylic acids, has driven research toward developing strategies for their control and mitigation. Modern ozonation systems now incorporate sophisticated monitoring and control mechanisms that adjust treatment parameters in real-time based on water quality characteristics.
The primary objectives of current ozonation technology research include enhancing treatment efficiency while reducing energy consumption, developing more selective oxidation processes for specific contaminants, minimizing by-product formation, and integrating ozonation with other treatment technologies in hybrid systems. Researchers are particularly focused on improving hydroxyl radical yield through catalyst development and optimizing reaction conditions.
Future technological goals include the development of sustainable ozonation systems with reduced environmental footprints, advanced process control algorithms utilizing artificial intelligence for optimized operation, and the creation of modular, scalable systems suitable for decentralized applications. Additionally, there is growing interest in exploring the potential of ozonation for addressing emerging contaminants of concern, including pharmaceuticals, personal care products, and microplastics.
The 1970s marked a pivotal turning point with the discovery of disinfection by-products (DBPs) in chlorinated water, prompting researchers to explore alternative treatment methods. This led to increased interest in ozonation as a primary or complementary treatment process. By the 1980s, researchers began investigating the combination of ozone with hydrogen peroxide (O₃/H₂O₂), which significantly enhanced oxidation efficiency through increased hydroxyl radical formation.
The 1990s witnessed the integration of ultraviolet (UV) radiation with ozonation systems, creating more powerful treatment configurations (O₃/UV and O₃/H₂O₂/UV). These combinations demonstrated superior performance in degrading recalcitrant compounds through synergistic effects. Concurrently, advancements in ozone generation technology, including the development of more energy-efficient corona discharge systems and electrolytic ozone generators, reduced operational costs and improved accessibility.
Recent technological developments have focused on optimizing radical yields while minimizing harmful by-product formation. The identification of ozonation by-products, including bromate, aldehydes, and carboxylic acids, has driven research toward developing strategies for their control and mitigation. Modern ozonation systems now incorporate sophisticated monitoring and control mechanisms that adjust treatment parameters in real-time based on water quality characteristics.
The primary objectives of current ozonation technology research include enhancing treatment efficiency while reducing energy consumption, developing more selective oxidation processes for specific contaminants, minimizing by-product formation, and integrating ozonation with other treatment technologies in hybrid systems. Researchers are particularly focused on improving hydroxyl radical yield through catalyst development and optimizing reaction conditions.
Future technological goals include the development of sustainable ozonation systems with reduced environmental footprints, advanced process control algorithms utilizing artificial intelligence for optimized operation, and the creation of modular, scalable systems suitable for decentralized applications. Additionally, there is growing interest in exploring the potential of ozonation for addressing emerging contaminants of concern, including pharmaceuticals, personal care products, and microplastics.
Market Analysis for Advanced Oxidation Processes
The global market for Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs) has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing water scarcity concerns and stringent environmental regulations. The market value reached approximately $6.5 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.8% through 2030, potentially reaching $12.3 billion by the end of the forecast period.
Ozonation-based advanced oxidation technologies, particularly those combining O₃ with H₂O₂ and UV, represent the largest segment within the AOP market, accounting for roughly 38% of the total market share. This dominance stems from their proven efficacy in removing persistent organic pollutants and emerging contaminants of concern, including pharmaceuticals, personal care products, and industrial chemicals.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead the market adoption of advanced oxidation technologies, collectively representing over 60% of global installations. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as the fastest-growing market with a CAGR exceeding 9%, primarily driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and increasingly stringent wastewater treatment regulations in countries like China, India, and South Korea.
By application segment, municipal water treatment currently dominates the market with approximately 45% share, followed by industrial wastewater treatment at 35%. The remaining 20% is distributed across specialized applications including groundwater remediation, air purification, and food processing. Within industrial applications, the chemical, pharmaceutical, and textile sectors represent the largest end-users of ozonation and advanced oxidation technologies.
A key market driver is the growing concern over micropollutants and emerging contaminants that conventional treatment methods fail to address effectively. Regulatory frameworks such as the EU Water Framework Directive and the US EPA's Contaminant Candidate List have created substantial market pull for advanced treatment technologies capable of addressing these challenges.
Cost considerations remain a significant market restraint, with capital expenditure for advanced oxidation systems typically 30-50% higher than conventional treatment alternatives. However, technological advancements are gradually reducing implementation costs, with recent innovations focusing on energy efficiency, catalyst development, and process optimization to improve the economic feasibility of these systems.
The competitive landscape features both established water treatment companies and specialized technology providers. Major players include Xylem, Suez, Veolia, Evoqua Water Technologies, and Ozonia, collectively holding approximately 65% market share. The market is also witnessing increased activity from emerging players focused on specific technological innovations in catalyst design, reactor configuration, and process control systems for optimizing radical yields and minimizing harmful by-product formation.
Ozonation-based advanced oxidation technologies, particularly those combining O₃ with H₂O₂ and UV, represent the largest segment within the AOP market, accounting for roughly 38% of the total market share. This dominance stems from their proven efficacy in removing persistent organic pollutants and emerging contaminants of concern, including pharmaceuticals, personal care products, and industrial chemicals.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead the market adoption of advanced oxidation technologies, collectively representing over 60% of global installations. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as the fastest-growing market with a CAGR exceeding 9%, primarily driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and increasingly stringent wastewater treatment regulations in countries like China, India, and South Korea.
By application segment, municipal water treatment currently dominates the market with approximately 45% share, followed by industrial wastewater treatment at 35%. The remaining 20% is distributed across specialized applications including groundwater remediation, air purification, and food processing. Within industrial applications, the chemical, pharmaceutical, and textile sectors represent the largest end-users of ozonation and advanced oxidation technologies.
A key market driver is the growing concern over micropollutants and emerging contaminants that conventional treatment methods fail to address effectively. Regulatory frameworks such as the EU Water Framework Directive and the US EPA's Contaminant Candidate List have created substantial market pull for advanced treatment technologies capable of addressing these challenges.
Cost considerations remain a significant market restraint, with capital expenditure for advanced oxidation systems typically 30-50% higher than conventional treatment alternatives. However, technological advancements are gradually reducing implementation costs, with recent innovations focusing on energy efficiency, catalyst development, and process optimization to improve the economic feasibility of these systems.
The competitive landscape features both established water treatment companies and specialized technology providers. Major players include Xylem, Suez, Veolia, Evoqua Water Technologies, and Ozonia, collectively holding approximately 65% market share. The market is also witnessing increased activity from emerging players focused on specific technological innovations in catalyst design, reactor configuration, and process control systems for optimizing radical yields and minimizing harmful by-product formation.
Current Challenges in Ozonation and Advanced Oxidation
Despite significant advancements in ozonation and advanced oxidation processes (AOPs), several critical challenges continue to impede their widespread implementation and optimal performance. One fundamental challenge lies in the unpredictable formation of potentially harmful disinfection by-products (DBPs), particularly bromate in bromide-containing waters, which presents significant health concerns and regulatory compliance issues. The complex water matrix effects significantly influence oxidation efficiency, with natural organic matter (NOM) and various inorganic constituents acting as radical scavengers, thereby reducing treatment effectiveness and increasing operational costs.
Energy consumption remains a substantial barrier, particularly for UV-based AOPs, which require significant electrical input, making these processes less economically viable for large-scale applications. This challenge is compounded by the difficulty in achieving optimal radical yields across varying water qualities and operational conditions, necessitating sophisticated process control systems that many facilities lack.
Process integration presents another significant hurdle, as incorporating ozonation and AOPs into existing treatment trains requires careful consideration of upstream and downstream processes to avoid negative interactions. The optimization of multiple parameters simultaneously—including pH, temperature, catalyst dosage, and oxidant concentrations—demands advanced modeling capabilities and real-time monitoring systems that are not yet standardized across the industry.
Catalyst development for heterogeneous AOPs faces challenges related to stability, reusability, and potential leaching of metals into treated water. Additionally, the formation of transformation products during treatment processes remains poorly understood, with limited analytical methods available for comprehensive identification and quantification of these compounds.
Scale-up issues persist when transitioning from laboratory to full-scale implementation, with significant discrepancies often observed between bench-scale results and real-world performance. This is particularly problematic for reactor design and hydraulic optimization in large facilities.
Regulatory frameworks have not kept pace with technological advancements, creating uncertainty regarding compliance requirements for emerging contaminants and treatment technologies. This regulatory gap hampers investment and adoption of innovative solutions.
Finally, the lack of standardized methods for performance evaluation and comparison between different AOP technologies makes it difficult for utilities and industries to make informed decisions about technology selection and implementation strategies, further slowing the adoption of these promising treatment approaches.
Energy consumption remains a substantial barrier, particularly for UV-based AOPs, which require significant electrical input, making these processes less economically viable for large-scale applications. This challenge is compounded by the difficulty in achieving optimal radical yields across varying water qualities and operational conditions, necessitating sophisticated process control systems that many facilities lack.
Process integration presents another significant hurdle, as incorporating ozonation and AOPs into existing treatment trains requires careful consideration of upstream and downstream processes to avoid negative interactions. The optimization of multiple parameters simultaneously—including pH, temperature, catalyst dosage, and oxidant concentrations—demands advanced modeling capabilities and real-time monitoring systems that are not yet standardized across the industry.
Catalyst development for heterogeneous AOPs faces challenges related to stability, reusability, and potential leaching of metals into treated water. Additionally, the formation of transformation products during treatment processes remains poorly understood, with limited analytical methods available for comprehensive identification and quantification of these compounds.
Scale-up issues persist when transitioning from laboratory to full-scale implementation, with significant discrepancies often observed between bench-scale results and real-world performance. This is particularly problematic for reactor design and hydraulic optimization in large facilities.
Regulatory frameworks have not kept pace with technological advancements, creating uncertainty regarding compliance requirements for emerging contaminants and treatment technologies. This regulatory gap hampers investment and adoption of innovative solutions.
Finally, the lack of standardized methods for performance evaluation and comparison between different AOP technologies makes it difficult for utilities and industries to make informed decisions about technology selection and implementation strategies, further slowing the adoption of these promising treatment approaches.
Mainstream O₃/H₂O₂/UV Integration Solutions
01 Radical yield enhancement in ozonation processes
Various methods can be employed to enhance radical yields during ozonation processes, which improves the efficiency of contaminant degradation. These methods include catalyst addition, pH adjustment, and combining ozone with UV radiation or hydrogen peroxide. Enhanced radical production leads to more effective oxidation of pollutants and reduces treatment time. The optimization of these parameters is crucial for maximizing the hydroxyl radical yield while minimizing energy consumption.- Optimization of radical yields in ozonation processes: Various methods can be employed to optimize the generation of hydroxyl radicals during ozonation processes. These include adjusting operational parameters such as pH, temperature, and ozone dosage to enhance radical formation. Additionally, catalysts can be incorporated to promote the decomposition of ozone into hydroxyl radicals, which are more reactive oxidizing species. These optimization strategies improve the efficiency of contaminant degradation while minimizing energy consumption in advanced oxidation processes.
- By-product control strategies in advanced oxidation processes: Controlling by-products formed during advanced oxidation processes is crucial for ensuring water quality. This can be achieved through process optimization, selective oxidation pathways, and post-treatment methods. Monitoring and controlling reaction conditions such as pH, temperature, and oxidant concentration helps minimize the formation of harmful by-products. Sequential treatment approaches combining different oxidation methods with biological or physical treatments can effectively remove intermediates and final by-products from treated water.
- Integration of ozonation with other treatment technologies: Combining ozonation with other treatment technologies creates synergistic effects that enhance contaminant removal while controlling by-product formation. Hybrid systems incorporating ozonation with biological treatment, membrane filtration, or activated carbon adsorption can effectively remove both parent compounds and transformation products. These integrated approaches provide more complete treatment, addressing limitations of individual technologies and improving overall process efficiency and effectiveness for complex water matrices.
- Reactor design for improved radical generation and by-product control: Advanced reactor designs can significantly enhance radical generation efficiency and by-product control in ozonation processes. Innovations include optimized gas-liquid contact systems, specialized mixing chambers, and reactor configurations that improve mass transfer and reaction kinetics. Some designs incorporate multiple treatment zones, allowing for staged oxidation that can better control reaction pathways and resulting by-products. These engineering approaches maximize treatment effectiveness while minimizing energy consumption and unwanted by-product formation.
- Monitoring and control systems for advanced oxidation processes: Sophisticated monitoring and control systems are essential for optimizing radical yields and managing by-product formation in advanced oxidation processes. These systems employ real-time sensors to measure key parameters such as oxidant concentration, pH, and organic matter content. Automated feedback control mechanisms adjust process conditions based on these measurements to maintain optimal treatment efficiency. Advanced analytics and predictive modeling help operators anticipate treatment challenges and proactively adjust parameters to ensure consistent performance and by-product control.
02 By-product control strategies in advanced oxidation processes
Controlling by-products formed during advanced oxidation processes is essential for ensuring treated water safety. Strategies include selective radical generation, process parameter optimization, and sequential treatment approaches. Monitoring and adjusting reaction conditions such as pH, temperature, and oxidant dosage can significantly reduce harmful by-product formation. Additionally, incorporating scavenger compounds or quenching agents at specific stages of the treatment process can help control unwanted oxidation pathways.Expand Specific Solutions03 Reactor design for optimized ozonation efficiency
Specialized reactor designs can significantly improve ozonation efficiency and control by-product formation. These designs focus on enhancing mass transfer between ozone and water, optimizing contact time, and ensuring uniform distribution of oxidants. Features such as multi-stage reactors, advanced diffusion systems, and turbulence-inducing components help maximize radical formation while minimizing energy consumption. Properly designed reactors also facilitate better control of reaction conditions, leading to more predictable by-product profiles.Expand Specific Solutions04 Integration of multiple advanced oxidation technologies
Combining multiple advanced oxidation technologies creates synergistic effects that enhance radical yields and improve by-product control. Hybrid systems such as ozone/UV, ozone/hydrogen peroxide, and ozone/catalysis can achieve higher degradation efficiencies than single processes. These integrated approaches allow for more complete mineralization of contaminants, reducing the formation of persistent by-products. The complementary nature of different oxidation mechanisms helps overcome limitations of individual technologies and provides more robust treatment solutions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Monitoring and control systems for advanced oxidation processes
Advanced monitoring and control systems are essential for optimizing radical yields and managing by-product formation in real-time. These systems utilize sensors, analyzers, and automated feedback mechanisms to continuously adjust process parameters based on water quality and treatment objectives. Real-time monitoring of oxidation-reduction potential, dissolved ozone, and key water quality parameters enables precise dosing control and process optimization. Intelligent control algorithms can predict by-product formation pathways and adjust treatment conditions accordingly.Expand Specific Solutions
Industry Leaders in Advanced Oxidation Technologies
The ozonation and advanced oxidation technologies market is currently in a growth phase, characterized by increasing adoption across water treatment, industrial processes, and environmental remediation sectors. The global market size for advanced oxidation technologies is expanding rapidly, projected to reach significant valuation due to stringent environmental regulations and growing water scarcity concerns. Technologically, the field shows varying maturity levels, with companies like Toshiba, Evoqua Water Technologies, and Mitsubishi Electric leading with established commercial solutions, while research institutions such as Harbin Institute of Technology and University of Washington are advancing fundamental understanding of radical chemistry and by-product formation. Industrial players including Sinopec, McWong Environmental, and OZOMAX are implementing these technologies at scale, focusing on optimizing O₃/H₂O₂/UV combinations for improved efficiency and reduced by-product formation.
Toshiba Corp.
Technical Solution: Toshiba has engineered an advanced ozonation system that leverages their expertise in electrical engineering and water treatment technologies. Their solution incorporates high-efficiency dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) ozone generators that achieve up to 20% concentration by weight while minimizing power consumption. Toshiba's integrated AOP approach combines ozone with hydrogen peroxide injection and their proprietary low-pressure UV systems to maximize hydroxyl radical generation. The technology features Toshiba's TOSBAC™ control system that employs machine learning algorithms to predict optimal treatment parameters based on influent water quality, reducing by-product formation while maintaining treatment efficacy. Their system incorporates specialized gas-liquid contactors designed to achieve over 95% ozone transfer efficiency, significantly reducing off-gas treatment requirements. Toshiba has developed a novel catalytic process that selectively targets bromide oxidation pathways, substantially reducing bromate formation during ozonation of bromide-containing waters. The company's technology includes real-time monitoring of by-product precursors and automated adjustment of treatment parameters to maintain compliance with increasingly stringent regulatory standards.
Strengths: Highly efficient ozone generation and transfer systems; advanced control algorithms optimizing treatment while minimizing by-products; specialized catalytic processes for bromate control. Weaknesses: Significant capital investment required; complex integration with existing infrastructure; higher energy requirements compared to conventional treatment methods.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has developed advanced ozonation technology specifically tailored for petrochemical wastewater treatment applications. Their system integrates ozone generation with catalytic processes to enhance hydroxyl radical formation while minimizing energy consumption. Sinopec's technology employs a multi-stage treatment approach where ozone is strategically introduced at different points in the treatment train to target specific contaminants while controlling by-product formation. Their process incorporates proprietary metal oxide catalysts that promote ozone decomposition into hydroxyl radicals while simultaneously adsorbing potential by-product precursors. The system features specialized gas-liquid contactors designed to handle high-strength industrial wastewaters with significant organic loading and potential scavengers. Sinopec has developed an integrated monitoring platform that tracks over 20 water quality parameters in real-time, allowing for dynamic adjustment of O₃/H₂O₂ ratios and UV intensity to optimize treatment efficiency. Their technology includes specialized pre-treatment processes that selectively remove radical scavengers like carbonates and bicarbonates, significantly improving the efficiency of the subsequent advanced oxidation process while reducing operating costs.
Strengths: Specialized design for high-strength industrial wastewaters; proprietary catalysts enhancing radical formation while controlling by-products; comprehensive monitoring and control systems. Weaknesses: High energy consumption; requires significant technical expertise to operate; potential for incomplete mineralization of certain recalcitrant compounds requiring additional treatment steps.
Critical Patents in Radical Yield Enhancement
Advanced oxidation processing method
PatentActiveJP2014131800A
Innovation
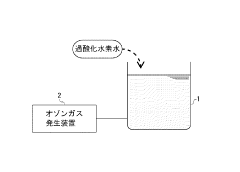
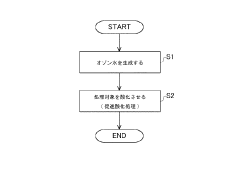
- The method involves adding an appropriate amount of hydrogen peroxide solution to ozone water at the initial stage, stopping the addition, and intermittently adding it during the treatment process, using a cheaper pump capable of regular interval operations.
Advanced oxidation treatment apparatus comprising electrolysis apparatus for molecular destruction, and advanced oxidation treatment method using same
PatentWO2021137459A1
Innovation
- A cyclic advanced oxidation treatment device and method combining an ozone oxidation reaction device, ultraviolet oxidation reaction device, ultrasonic treatment, and electrolysis device with a control unit for polarity conversion, which generates OH radicals and applies magnetic fields to efficiently decompose pollutants in a wastewater tank, allowing for simultaneous dissociation of ionic and covalent substances.
Environmental Impact Assessment of Oxidation By-Products
The environmental impact of oxidation by-products from advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) represents a critical consideration in water treatment applications. Ozonation and combined O₃/H₂O₂/UV treatments, while effective for contaminant degradation, generate various transformation products that may pose ecological and human health risks if not properly managed.
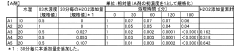
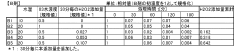
Primary oxidation by-products include bromate, formaldehyde, aldehydes, ketones, and carboxylic acids, with their formation mechanisms heavily dependent on source water quality parameters such as pH, alkalinity, and natural organic matter (NOM) concentration. Bromate formation, particularly concerning due to its classification as a potential human carcinogen, occurs when bromide-containing waters undergo ozonation, with formation rates accelerating at higher pH values and ozone doses.
Ecotoxicological studies indicate that certain oxidation by-products demonstrate acute and chronic toxicity to aquatic organisms at environmentally relevant concentrations. For instance, nitrosamines formed during ozonation of nitrogen-containing compounds have shown mutagenic properties in various test systems. The persistence of these by-products varies significantly, with some degrading rapidly while others remain stable in aquatic environments for extended periods, potentially accumulating in sediments or bioaccumulating in aquatic organisms.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide have established maximum contaminant levels for known by-products such as bromate (10 μg/L in both EU and US regulations), though many transformation products remain unregulated due to analytical challenges and insufficient toxicological data. This regulatory gap presents significant challenges for comprehensive risk assessment and management strategies.
Mitigation strategies for by-product formation include process optimization through precise control of oxidant dosage, reaction time, and pH conditions. Pre-treatment steps such as activated carbon filtration or biofiltration can reduce precursor compounds, while post-treatment biological filtration has demonstrated effectiveness in removing biodegradable oxidation by-products. Recent research indicates that sequential treatment combining ozonation with biological processes can reduce overall by-product formation by up to 60-80%.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies comparing different advanced oxidation technologies suggest that while O₃/H₂O₂/UV processes may generate concerning by-products, their overall environmental footprint may be lower than alternative treatment methods when considering energy consumption, chemical usage, and treatment efficacy. However, these assessments must incorporate local water quality parameters and treatment objectives for meaningful comparison.
Emerging analytical techniques, including high-resolution mass spectrometry coupled with effect-directed analysis, are enhancing our ability to identify previously unknown transformation products and assess their potential toxicity, addressing a critical knowledge gap in environmental impact assessment of oxidation processes.
Primary oxidation by-products include bromate, formaldehyde, aldehydes, ketones, and carboxylic acids, with their formation mechanisms heavily dependent on source water quality parameters such as pH, alkalinity, and natural organic matter (NOM) concentration. Bromate formation, particularly concerning due to its classification as a potential human carcinogen, occurs when bromide-containing waters undergo ozonation, with formation rates accelerating at higher pH values and ozone doses.
Ecotoxicological studies indicate that certain oxidation by-products demonstrate acute and chronic toxicity to aquatic organisms at environmentally relevant concentrations. For instance, nitrosamines formed during ozonation of nitrogen-containing compounds have shown mutagenic properties in various test systems. The persistence of these by-products varies significantly, with some degrading rapidly while others remain stable in aquatic environments for extended periods, potentially accumulating in sediments or bioaccumulating in aquatic organisms.
Regulatory frameworks worldwide have established maximum contaminant levels for known by-products such as bromate (10 μg/L in both EU and US regulations), though many transformation products remain unregulated due to analytical challenges and insufficient toxicological data. This regulatory gap presents significant challenges for comprehensive risk assessment and management strategies.
Mitigation strategies for by-product formation include process optimization through precise control of oxidant dosage, reaction time, and pH conditions. Pre-treatment steps such as activated carbon filtration or biofiltration can reduce precursor compounds, while post-treatment biological filtration has demonstrated effectiveness in removing biodegradable oxidation by-products. Recent research indicates that sequential treatment combining ozonation with biological processes can reduce overall by-product formation by up to 60-80%.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies comparing different advanced oxidation technologies suggest that while O₃/H₂O₂/UV processes may generate concerning by-products, their overall environmental footprint may be lower than alternative treatment methods when considering energy consumption, chemical usage, and treatment efficacy. However, these assessments must incorporate local water quality parameters and treatment objectives for meaningful comparison.
Emerging analytical techniques, including high-resolution mass spectrometry coupled with effect-directed analysis, are enhancing our ability to identify previously unknown transformation products and assess their potential toxicity, addressing a critical knowledge gap in environmental impact assessment of oxidation processes.
Regulatory Framework for Water Treatment Technologies
The regulatory landscape governing advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) like ozonation with O₃/H₂O₂/UV combinations has evolved significantly in response to growing water quality concerns and scientific understanding of disinfection by-products (DBPs). These regulations establish critical frameworks that water treatment facilities must navigate when implementing these technologies.
At the international level, the World Health Organization (WHO) provides guidelines for drinking water quality that address ozonation by-products, particularly bromate formation when treating bromide-containing waters. These guidelines establish a provisional value of 10 μg/L for bromate, reflecting its classification as a potential human carcinogen. The WHO framework emphasizes a risk-based approach that balances microbial pathogen reduction against chemical by-product formation.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates ozonation and advanced oxidation processes through multiple mechanisms. The Safe Drinking Water Act (SDWA) establishes Maximum Contaminant Levels (MCLs) for various disinfection by-products, including the 10 μg/L limit for bromate. Additionally, the EPA's Disinfectants and Disinfection Byproducts Rules (D/DBPRs) specifically address the formation of halogenated by-products during oxidation processes, requiring monitoring and control strategies.
The European Union's Drinking Water Directive (98/83/EC, updated in 2020) similarly establishes parametric values for ozonation by-products, maintaining the 10 μg/L bromate standard. The directive further requires member states to implement risk assessment and risk management approaches throughout the water supply chain, with specific attention to advanced treatment processes like ozonation.
Regulatory frameworks increasingly incorporate the concept of Best Available Technologies (BAT) for controlling by-product formation. For ozonation and advanced oxidation, this includes requirements for process optimization, pH control, ammonia addition for bromate control, and proper UV dosing when combined with peroxide systems. Many jurisdictions now mandate water quality monitoring before and after treatment to verify by-product control effectiveness.
Emerging regulatory trends focus on unregulated contaminants of concern, including transformation products from pharmaceutical compounds and personal care products during advanced oxidation. The EPA's Contaminant Candidate List (CCL) and Unregulated Contaminant Monitoring Rule (UCMR) programs are developing frameworks to address these emerging concerns, potentially leading to future regulations specific to advanced oxidation applications.
Compliance with these regulatory frameworks requires water utilities to implement comprehensive monitoring strategies, maintain detailed operational records, and develop site-specific optimization protocols that balance pathogen inactivation against by-product formation, particularly when using combined O₃/H₂O₂/UV systems where radical yields and reaction pathways can significantly impact treatment outcomes.
At the international level, the World Health Organization (WHO) provides guidelines for drinking water quality that address ozonation by-products, particularly bromate formation when treating bromide-containing waters. These guidelines establish a provisional value of 10 μg/L for bromate, reflecting its classification as a potential human carcinogen. The WHO framework emphasizes a risk-based approach that balances microbial pathogen reduction against chemical by-product formation.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates ozonation and advanced oxidation processes through multiple mechanisms. The Safe Drinking Water Act (SDWA) establishes Maximum Contaminant Levels (MCLs) for various disinfection by-products, including the 10 μg/L limit for bromate. Additionally, the EPA's Disinfectants and Disinfection Byproducts Rules (D/DBPRs) specifically address the formation of halogenated by-products during oxidation processes, requiring monitoring and control strategies.
The European Union's Drinking Water Directive (98/83/EC, updated in 2020) similarly establishes parametric values for ozonation by-products, maintaining the 10 μg/L bromate standard. The directive further requires member states to implement risk assessment and risk management approaches throughout the water supply chain, with specific attention to advanced treatment processes like ozonation.
Regulatory frameworks increasingly incorporate the concept of Best Available Technologies (BAT) for controlling by-product formation. For ozonation and advanced oxidation, this includes requirements for process optimization, pH control, ammonia addition for bromate control, and proper UV dosing when combined with peroxide systems. Many jurisdictions now mandate water quality monitoring before and after treatment to verify by-product control effectiveness.
Emerging regulatory trends focus on unregulated contaminants of concern, including transformation products from pharmaceutical compounds and personal care products during advanced oxidation. The EPA's Contaminant Candidate List (CCL) and Unregulated Contaminant Monitoring Rule (UCMR) programs are developing frameworks to address these emerging concerns, potentially leading to future regulations specific to advanced oxidation applications.
Compliance with these regulatory frameworks requires water utilities to implement comprehensive monitoring strategies, maintain detailed operational records, and develop site-specific optimization protocols that balance pathogen inactivation against by-product formation, particularly when using combined O₃/H₂O₂/UV systems where radical yields and reaction pathways can significantly impact treatment outcomes.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!