Ozonation: Materials Compatibility, Elastomer Selection And Corrosion Controls
SEP 18, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ozonation Technology Background and Objectives
Ozonation technology has evolved significantly since its discovery in the mid-19th century when Christian Friedrich Schönbein first identified ozone in 1839. The deliberate application of ozone for water treatment began in the late 1800s, with the first full-scale municipal ozonation system implemented in Nice, France in 1906. Over the decades, ozonation has transitioned from an experimental technique to a mainstream treatment technology across various industries including water purification, wastewater treatment, food processing, and healthcare.
The evolution of ozonation technology has been characterized by continuous improvements in ozone generation efficiency, application methods, and monitoring systems. Early ozone generators utilized corona discharge technology, which has been refined to achieve higher concentrations and energy efficiency. More recent developments include the emergence of electrolytic ozone generation and advanced plasma systems, which offer advantages in specific applications.
Current technological trends in ozonation focus on addressing the critical challenges of materials compatibility, elastomer selection, and corrosion control. These aspects have become increasingly important as ozonation systems are deployed in more diverse and demanding environments, requiring materials that can withstand ozone's highly oxidative properties while maintaining operational integrity and safety.
The primary objective of modern ozonation technology development is to optimize the balance between effective oxidation performance and system durability. This includes identifying and developing materials that resist degradation when exposed to ozone, particularly elastomers used in seals, gaskets, and flexible connections that are especially vulnerable to ozone attack.
Another key goal is the advancement of corrosion control strategies to protect metal components in ozonation systems. This involves both the development of inherently resistant materials and the implementation of protective measures such as coatings, cathodic protection, and strategic system design to minimize corrosion risks.
Research objectives also include the standardization of materials testing protocols specifically for ozone applications, as traditional compatibility testing may not adequately predict performance under ozone exposure. The industry aims to establish comprehensive guidelines for material selection based on factors including ozone concentration, exposure duration, temperature, pressure, and the presence of other chemicals.
The technological trajectory points toward integrated system designs that consider materials compatibility from the outset rather than as an afterthought. This holistic approach seeks to extend equipment lifespan, reduce maintenance requirements, improve safety profiles, and ultimately lower the total cost of ownership for ozonation systems across all application sectors.
The evolution of ozonation technology has been characterized by continuous improvements in ozone generation efficiency, application methods, and monitoring systems. Early ozone generators utilized corona discharge technology, which has been refined to achieve higher concentrations and energy efficiency. More recent developments include the emergence of electrolytic ozone generation and advanced plasma systems, which offer advantages in specific applications.
Current technological trends in ozonation focus on addressing the critical challenges of materials compatibility, elastomer selection, and corrosion control. These aspects have become increasingly important as ozonation systems are deployed in more diverse and demanding environments, requiring materials that can withstand ozone's highly oxidative properties while maintaining operational integrity and safety.
The primary objective of modern ozonation technology development is to optimize the balance between effective oxidation performance and system durability. This includes identifying and developing materials that resist degradation when exposed to ozone, particularly elastomers used in seals, gaskets, and flexible connections that are especially vulnerable to ozone attack.
Another key goal is the advancement of corrosion control strategies to protect metal components in ozonation systems. This involves both the development of inherently resistant materials and the implementation of protective measures such as coatings, cathodic protection, and strategic system design to minimize corrosion risks.
Research objectives also include the standardization of materials testing protocols specifically for ozone applications, as traditional compatibility testing may not adequately predict performance under ozone exposure. The industry aims to establish comprehensive guidelines for material selection based on factors including ozone concentration, exposure duration, temperature, pressure, and the presence of other chemicals.
The technological trajectory points toward integrated system designs that consider materials compatibility from the outset rather than as an afterthought. This holistic approach seeks to extend equipment lifespan, reduce maintenance requirements, improve safety profiles, and ultimately lower the total cost of ownership for ozonation systems across all application sectors.
Market Applications and Demand Analysis for Ozonation Systems
The global ozonation systems market has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing concerns over water quality and stringent environmental regulations. The market value reached approximately $1.2 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 6.8% through 2028. This growth trajectory is primarily fueled by the expanding applications of ozonation technology across various industries.
Water treatment remains the dominant application sector, accounting for over 40% of the total market share. Municipal water treatment facilities worldwide are increasingly adopting ozonation systems as a more effective alternative to traditional chlorination methods. This shift is particularly evident in developed regions like North America and Europe, where aging water infrastructure is being upgraded to meet higher quality standards and address emerging contaminants.
The industrial sector represents another substantial market segment, with applications spanning food and beverage processing, pharmaceuticals, and chemical manufacturing. In the food and beverage industry, ozonation systems are increasingly utilized for disinfection, shelf-life extension, and odor control. The pharmaceutical sector employs ozonation for water purification in production processes and sterilization applications, driving demand for specialized ozonation equipment with enhanced materials compatibility.
Healthcare applications have shown remarkable growth, particularly following the COVID-19 pandemic, which highlighted the importance of advanced disinfection technologies. Hospitals and medical facilities are investing in ozonation systems for room disinfection, medical waste treatment, and laundry sanitization, creating a specialized market segment with unique material requirements to withstand frequent ozone exposure.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead the market, collectively accounting for approximately 60% of global demand. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as the fastest-growing market, with China, India, and Southeast Asian countries investing heavily in water treatment infrastructure and industrial applications of ozonation technology.
A key market trend is the increasing demand for ozone-resistant materials and components that can withstand prolonged exposure to this highly oxidative agent. This has created a parallel market for specialized elastomers, corrosion-resistant metals, and protective coatings designed specifically for ozonation systems. Manufacturers who can provide comprehensive solutions addressing both ozonation effectiveness and materials compatibility are gaining competitive advantage in this evolving marketplace.
Consumer awareness regarding water quality and environmental sustainability is further driving market growth, with residential ozonation systems for swimming pools, spas, and point-of-use water treatment representing a small but rapidly expanding market segment with annual growth rates exceeding 10%.
Water treatment remains the dominant application sector, accounting for over 40% of the total market share. Municipal water treatment facilities worldwide are increasingly adopting ozonation systems as a more effective alternative to traditional chlorination methods. This shift is particularly evident in developed regions like North America and Europe, where aging water infrastructure is being upgraded to meet higher quality standards and address emerging contaminants.
The industrial sector represents another substantial market segment, with applications spanning food and beverage processing, pharmaceuticals, and chemical manufacturing. In the food and beverage industry, ozonation systems are increasingly utilized for disinfection, shelf-life extension, and odor control. The pharmaceutical sector employs ozonation for water purification in production processes and sterilization applications, driving demand for specialized ozonation equipment with enhanced materials compatibility.
Healthcare applications have shown remarkable growth, particularly following the COVID-19 pandemic, which highlighted the importance of advanced disinfection technologies. Hospitals and medical facilities are investing in ozonation systems for room disinfection, medical waste treatment, and laundry sanitization, creating a specialized market segment with unique material requirements to withstand frequent ozone exposure.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead the market, collectively accounting for approximately 60% of global demand. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as the fastest-growing market, with China, India, and Southeast Asian countries investing heavily in water treatment infrastructure and industrial applications of ozonation technology.
A key market trend is the increasing demand for ozone-resistant materials and components that can withstand prolonged exposure to this highly oxidative agent. This has created a parallel market for specialized elastomers, corrosion-resistant metals, and protective coatings designed specifically for ozonation systems. Manufacturers who can provide comprehensive solutions addressing both ozonation effectiveness and materials compatibility are gaining competitive advantage in this evolving marketplace.
Consumer awareness regarding water quality and environmental sustainability is further driving market growth, with residential ozonation systems for swimming pools, spas, and point-of-use water treatment representing a small but rapidly expanding market segment with annual growth rates exceeding 10%.
Current Challenges in Materials Compatibility with Ozone
Despite significant advancements in ozonation technology, material compatibility remains one of the most critical challenges in ozone-based applications. Ozone's highly oxidative nature (redox potential of 2.07V) creates a hostile environment for many conventional materials, leading to accelerated degradation, structural failure, and system contamination. This fundamental incompatibility limits the widespread adoption of ozonation technologies across various industries.
Elastomeric materials present particular vulnerability to ozone attack. Common elastomers such as natural rubber, SBR (Styrene-Butadiene Rubber), and many nitrile compounds undergo rapid degradation when exposed to ozone, exhibiting characteristic cracking, hardening, and loss of mechanical properties. This degradation occurs primarily through the scission of carbon-carbon double bonds, creating ozonides that subsequently decompose into carbonyl compounds, leading to chain breakage and material failure.
Metallic components face equally significant challenges, with ozone-induced corrosion affecting even traditionally corrosion-resistant materials. Aluminum alloys, certain stainless steel grades, and copper-based materials all demonstrate vulnerability to ozone exposure, particularly in humid environments where ozone can generate highly reactive hydroxyl radicals. The resulting corrosion not only compromises structural integrity but can introduce metal ions into the treated medium, potentially creating secondary contamination issues.
The concentration-dependent nature of ozone compatibility further complicates material selection. Materials that perform adequately at low ozone concentrations (0.1-1 ppm) may fail catastrophically at the higher concentrations (5-15%) used in industrial applications. This non-linear relationship between concentration and degradation rate creates significant engineering challenges in designing systems with appropriate safety margins.
Temperature effects compound these challenges, as ozone's reactivity increases substantially with temperature. Materials that demonstrate acceptable compatibility at ambient conditions may experience accelerated degradation at elevated temperatures, necessitating complex thermal management strategies in ozone-generating equipment and distribution systems.
The interface between different materials presents additional compatibility concerns. Galvanic corrosion can occur at metal-metal junctions in the presence of ozone and moisture, while elastomer-metal interfaces often become failure points due to differential degradation rates. These junction failures are particularly problematic in sealing applications, where they can lead to system leakage and ozone release.
Current testing methodologies for ozone compatibility remain inadequate for predicting long-term performance. Accelerated aging tests often fail to replicate real-world conditions accurately, while standardized testing protocols specific to ozone applications are limited. This testing gap creates significant uncertainty in material selection and system design, often leading to conservative over-engineering or unexpected failures.
Elastomeric materials present particular vulnerability to ozone attack. Common elastomers such as natural rubber, SBR (Styrene-Butadiene Rubber), and many nitrile compounds undergo rapid degradation when exposed to ozone, exhibiting characteristic cracking, hardening, and loss of mechanical properties. This degradation occurs primarily through the scission of carbon-carbon double bonds, creating ozonides that subsequently decompose into carbonyl compounds, leading to chain breakage and material failure.
Metallic components face equally significant challenges, with ozone-induced corrosion affecting even traditionally corrosion-resistant materials. Aluminum alloys, certain stainless steel grades, and copper-based materials all demonstrate vulnerability to ozone exposure, particularly in humid environments where ozone can generate highly reactive hydroxyl radicals. The resulting corrosion not only compromises structural integrity but can introduce metal ions into the treated medium, potentially creating secondary contamination issues.
The concentration-dependent nature of ozone compatibility further complicates material selection. Materials that perform adequately at low ozone concentrations (0.1-1 ppm) may fail catastrophically at the higher concentrations (5-15%) used in industrial applications. This non-linear relationship between concentration and degradation rate creates significant engineering challenges in designing systems with appropriate safety margins.
Temperature effects compound these challenges, as ozone's reactivity increases substantially with temperature. Materials that demonstrate acceptable compatibility at ambient conditions may experience accelerated degradation at elevated temperatures, necessitating complex thermal management strategies in ozone-generating equipment and distribution systems.
The interface between different materials presents additional compatibility concerns. Galvanic corrosion can occur at metal-metal junctions in the presence of ozone and moisture, while elastomer-metal interfaces often become failure points due to differential degradation rates. These junction failures are particularly problematic in sealing applications, where they can lead to system leakage and ozone release.
Current testing methodologies for ozone compatibility remain inadequate for predicting long-term performance. Accelerated aging tests often fail to replicate real-world conditions accurately, while standardized testing protocols specific to ozone applications are limited. This testing gap creates significant uncertainty in material selection and system design, often leading to conservative over-engineering or unexpected failures.
Existing Solutions for Elastomer Selection in Ozone Environments
01 Ozone-resistant elastomer materials selection
Specific elastomers demonstrate superior resistance to ozone degradation and are suitable for applications involving ozonation processes. Materials such as EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer), fluoroelastomers like Viton, and certain silicone compounds maintain their integrity when exposed to ozone. These elastomers can be used in gaskets, seals, and other components in ozonation systems to ensure longevity and prevent leakage or failure due to material degradation.- Ozone-resistant elastomer materials for sealing applications: Specific elastomer materials demonstrate superior resistance to ozone degradation, making them suitable for sealing applications in ozonation systems. These materials include fluoroelastomers (FKM), ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM), and certain silicone compounds that maintain their physical properties when exposed to ozone. The selection of appropriate elastomers is critical for ensuring long-term system integrity and preventing leaks in equipment that handles ozone or ozonated water.
- Corrosion-resistant metal alloys for ozone equipment: Specific metal alloys have been developed to withstand the highly oxidative environment created by ozone. Stainless steel grades such as 316L and titanium alloys demonstrate excellent resistance to ozone-induced corrosion. These materials are particularly important for components like reaction chambers, piping systems, and valves that come into direct contact with ozone gas or ozonated water. Proper selection of these corrosion-resistant alloys significantly extends equipment lifespan and reduces maintenance requirements in ozonation systems.
- Protective coatings and surface treatments for ozone applications: Various protective coatings and surface treatments can enhance the ozone resistance of base materials. These include fluoropolymer coatings, ceramic-based linings, and specialized passivation treatments that create a protective oxide layer on metal surfaces. These coatings provide an additional barrier against ozone attack, particularly for components where using fully ozone-resistant materials would be cost-prohibitive or impractical. The application of these protective layers significantly improves material compatibility with ozone environments.
- Monitoring and control systems for ozone-induced corrosion: Advanced monitoring and control systems have been developed to detect and mitigate ozone-induced corrosion in real-time. These systems utilize electrochemical sensors, ultrasonic thickness gauges, and specialized software algorithms to track material degradation. By continuously monitoring key parameters such as redox potential, pH levels, and material thickness, these systems can automatically adjust ozone levels or trigger maintenance alerts before critical failure occurs, thereby extending equipment life and ensuring operational safety.
- Material compatibility testing methods for ozonation systems: Standardized testing protocols have been established to evaluate material compatibility with ozone environments. These methods include accelerated aging tests, stress-strain analysis under ozone exposure, and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy to quantify corrosion rates. By subjecting candidate materials to controlled ozone concentrations under various operating conditions, engineers can accurately predict long-term performance and make informed material selection decisions for specific ozonation applications, ensuring system reliability and safety.
02 Corrosion control strategies for ozonation systems
Various methods can be employed to mitigate corrosion in ozonation systems. These include the use of corrosion-resistant materials such as stainless steel grades 316L and 904L, titanium alloys, or specialized coatings. Additionally, implementing cathodic protection systems, maintaining optimal pH levels, and utilizing corrosion inhibitors can significantly extend the service life of equipment exposed to ozone. Regular monitoring and maintenance protocols are essential to detect early signs of corrosion and prevent system failures.Expand Specific Solutions03 Advanced material compatibility testing for ozone applications
Specialized testing methodologies have been developed to evaluate material compatibility with ozone. These include accelerated aging tests, ozone chamber exposure tests, and mechanical property retention analysis after ozone exposure. Such testing helps in selecting appropriate materials for specific ozonation applications and predicting their service life. The testing protocols often involve exposing materials to elevated ozone concentrations under controlled temperature and humidity conditions to simulate long-term exposure effects in a shorter timeframe.Expand Specific Solutions04 Composite and engineered materials for ozone resistance
Innovative composite and engineered materials have been developed specifically for ozone-rich environments. These include fluoropolymer composites, ceramic-reinforced polymers, and specially formulated plastic compounds with ozone-resistant additives. Such materials combine the beneficial properties of multiple components to achieve superior ozone resistance while maintaining other desirable characteristics such as flexibility, strength, or electrical properties. These engineered materials find applications in critical components of ozonation systems where standard materials would rapidly degrade.Expand Specific Solutions05 System design considerations for ozone compatibility
Proper system design plays a crucial role in ensuring material compatibility in ozonation processes. This includes minimizing exposure of sensitive materials to ozone through strategic component placement, implementing effective sealing systems, incorporating adequate ventilation to prevent ozone accumulation, and designing for easy replacement of components subject to degradation. Additionally, the integration of monitoring systems to detect material failure and automated shutdown mechanisms can prevent catastrophic failures in ozonation systems.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Manufacturers and Suppliers in Ozone-Compatible Materials
Ozonation technology for materials compatibility and corrosion control is currently in a mature development stage, with a growing market driven by water treatment and industrial applications. The global market shows steady expansion as environmental regulations tighten worldwide. Technologically, significant advancements have been made in elastomer selection and corrosion-resistant materials. Leading players demonstrate varying levels of expertise: Toyota Motor Corp. and BMW focus on automotive applications; Solvay, Henkel, and PPG Industries lead in chemical solutions; while research institutions like Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft, Southwest Research Institute, and Industrial Technology Research Institute drive innovation through collaborative R&D. Academic players including Harvard College and Hokkaido University contribute fundamental research, creating a competitive landscape balanced between industrial implementation and ongoing scientific advancement.
PPG Industries Ohio, Inc.
Technical Solution: PPG has pioneered advanced coating technologies specifically engineered for ozone resistance in industrial applications. Their approach combines specialized polymer chemistry with corrosion inhibiting additives to create multi-functional protective systems. PPG's elastomer compatibility research has identified optimal material combinations for various exposure scenarios, resulting in their ENVIROCRON® series that maintains integrity even under severe ozone conditions. Their materials selection framework evaluates elastomers across five key parameters: ozone concentration tolerance, temperature range stability, mechanical property retention, chemical compatibility, and long-term aging characteristics. For corrosion control, PPG has developed proprietary barrier coatings that prevent ozone penetration to metal substrates while simultaneously neutralizing any ozone molecules that breach the primary barrier. Their testing protocols have demonstrated that properly selected elastomer-coating combinations can maintain performance for over 10,000 hours in environments with ozone concentrations up to 200 ppm. PPG's solutions are particularly valuable in outdoor applications where UV exposure accelerates ozone-related degradation through synergistic effects.
Strengths: Comprehensive protection against both ozone degradation and UV-accelerated damage; extensive testing under real-world conditions; solutions available for both new equipment and retrofitting existing systems. Weaknesses: Some coating systems require specialized application equipment; potential compatibility issues with certain substrate materials; performance may degrade in extremely high temperature environments.
Solvay SA
Technical Solution: Solvay has developed advanced fluoroelastomer compounds specifically designed for ozone resistance in industrial applications. Their technology utilizes perfluoroelastomers (FFKM) with modified polymer chains that resist oxidative degradation when exposed to ozone. The company's proprietary cross-linking systems create stable carbon-fluorine bonds that remain intact even under high ozone concentrations (up to 500 ppm). Solvay's materials compatibility research has led to the development of their Tecnoflon® series, which combines ozone resistance with excellent chemical resistance across a wide temperature range (-40°C to 230°C). Their corrosion control approach integrates specialized additives into the elastomer matrix that act as ozone scavengers, neutralizing ozone molecules before they can attack the polymer backbone. Additionally, Solvay has pioneered surface treatment technologies that create protective barriers against ozone penetration while maintaining the elastomer's mechanical properties.
Strengths: Superior ozone resistance even at high concentrations; excellent temperature range performance; comprehensive material compatibility with various chemicals and fluids. Weaknesses: Higher cost compared to conventional elastomers; more complex processing requirements; potential limitations in extreme low-temperature applications requiring high flexibility.
Critical Patents and Research on Ozone-Resistant Materials
An ozone-resistant polyurethane composition and associated method of production
PatentInactiveUS20130303668A1
Innovation
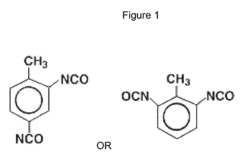
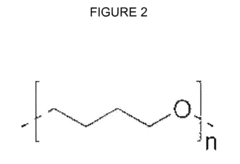
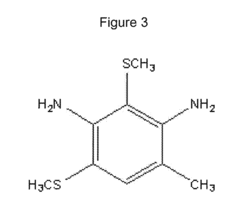
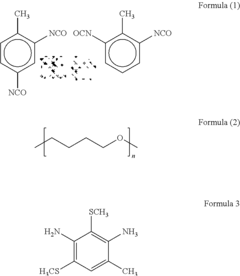
- A polyurethane composition comprising toluene diisocyanate, polytetramethylene ether glycol, 6-methyl-2,4-bis(methylthio)phenylene-1,3-diamine, and benzophenone or benzotriazole is developed, which provides excellent ozone resistance and durability, maintaining hardness and preventing cracking even at high ozone concentrations up to 8 ppm.
Ozonized biochar: phosphorus sustainability and sand soilization
PatentInactiveUS20190002764A1
Innovation
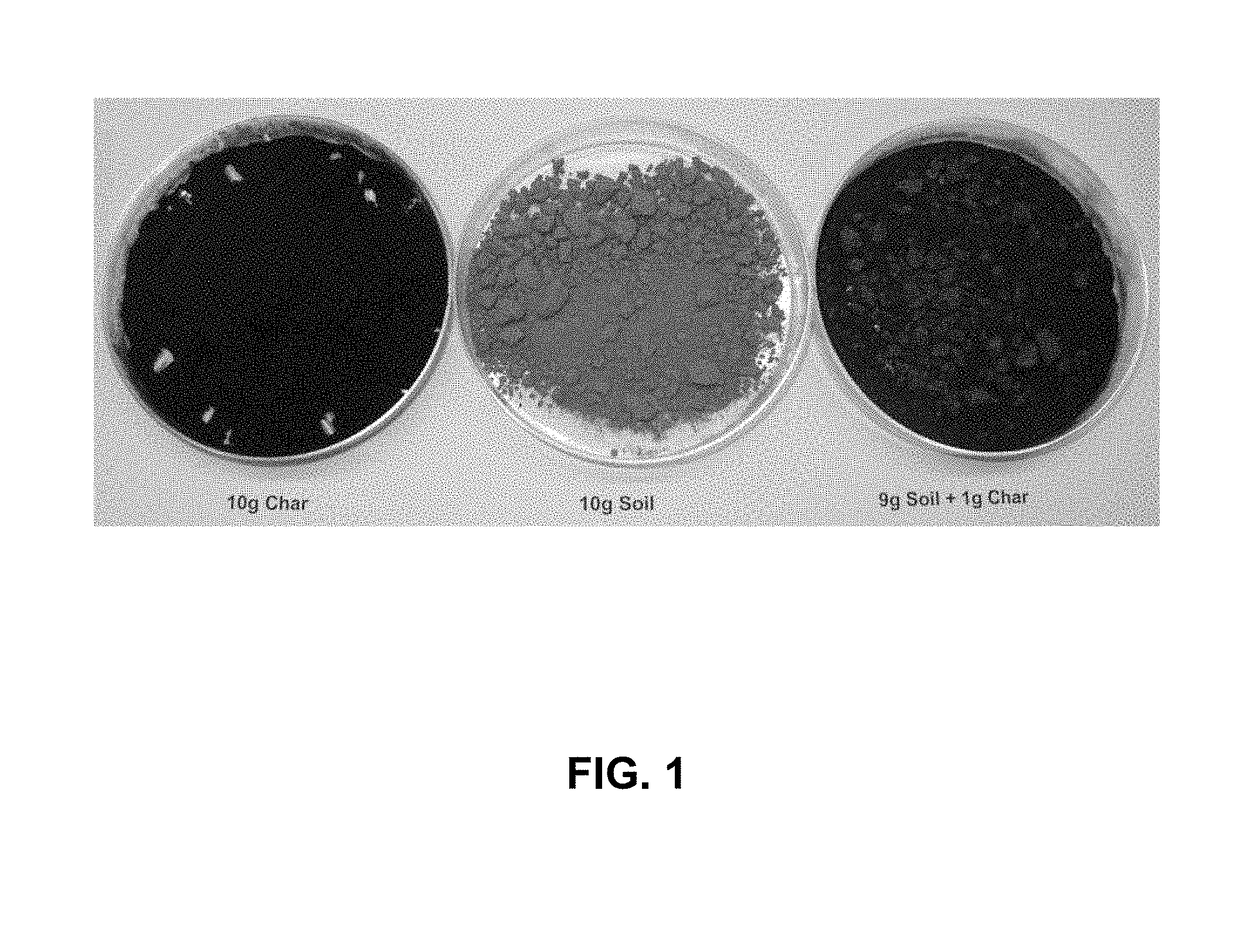
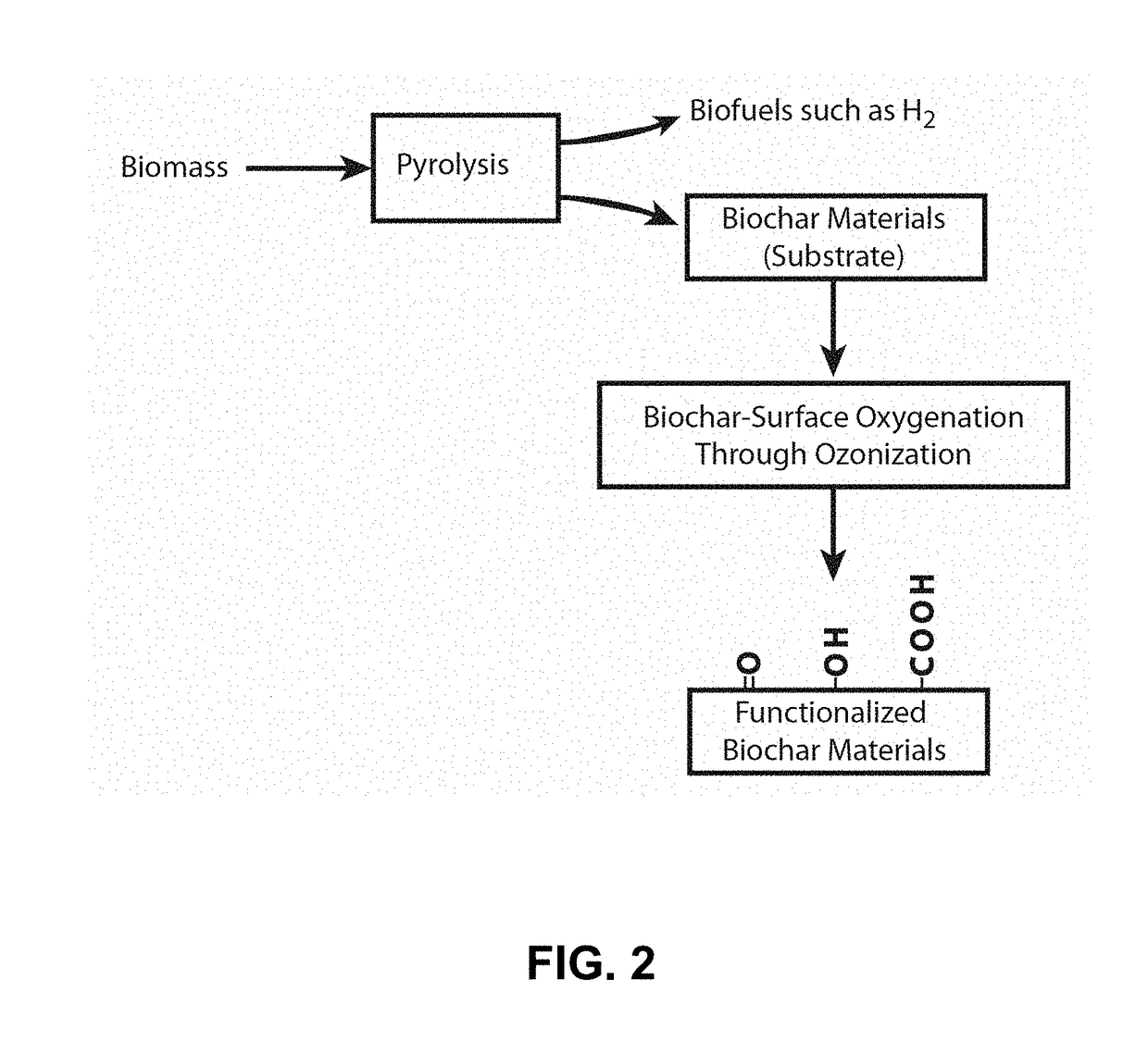
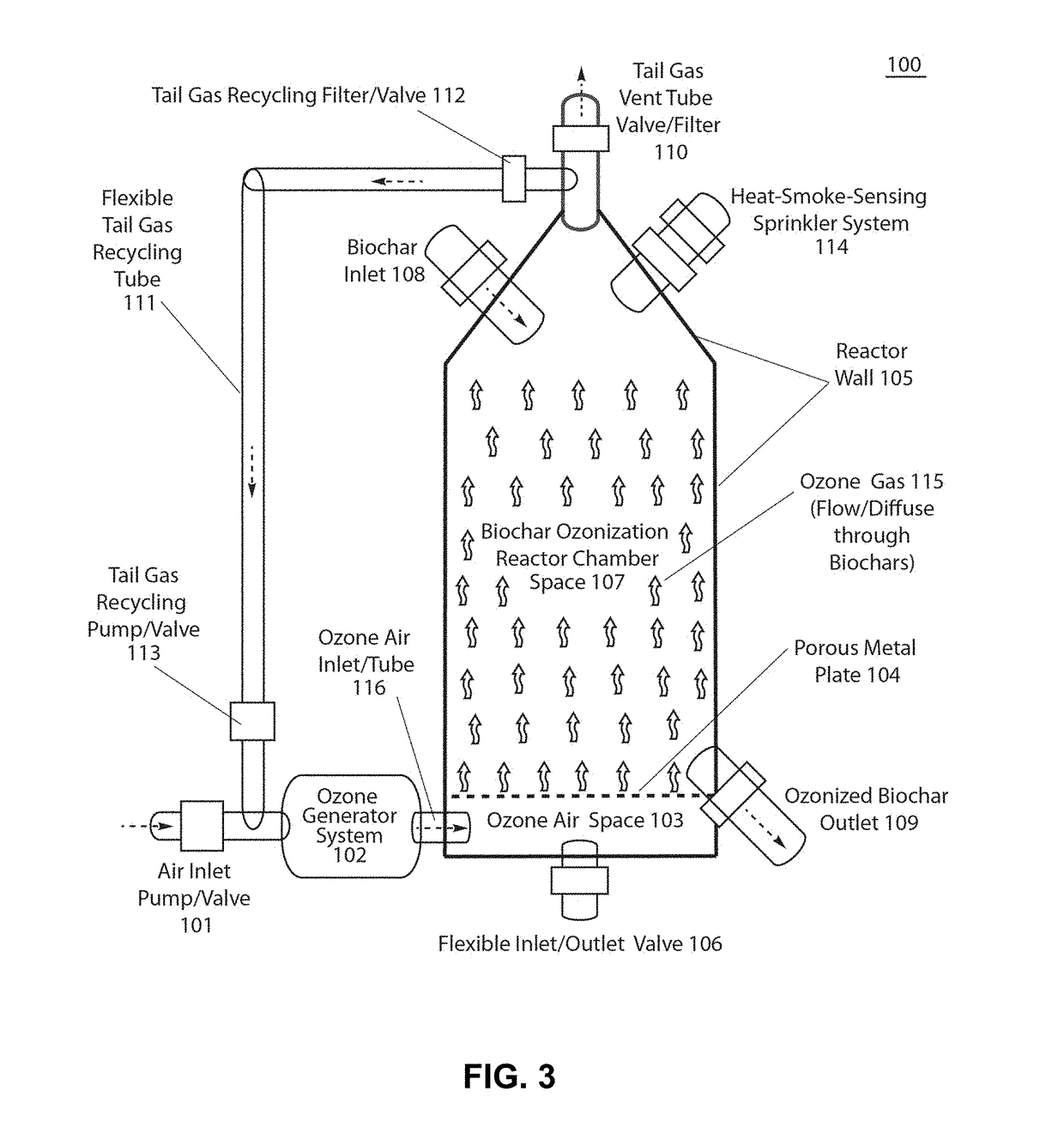
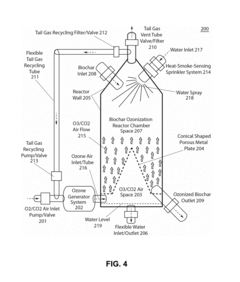
- A method involving sonication and ozonization of biochar to create surface-oxygenated biochar compositions with enhanced cation exchange capacity, optimized pH, and reduced toxicity, using a biochar sonication-ozonization treatment reactor system that contacts biochar with an ozone-containing gas stream to oxygenate the surface, destroy toxins, and produce a biochar composition suitable for phosphorus solubilization and filtration applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
Ozonation processes, while effective for water and air treatment, present significant environmental considerations that must be carefully evaluated in system design and operation. The environmental footprint of ozonation extends beyond its immediate application, encompassing raw material extraction for compatible materials, manufacturing processes, operational energy consumption, and end-of-life disposal considerations.
Energy consumption represents one of the most substantial environmental impacts of ozonation systems. The generation of ozone is inherently energy-intensive, requiring approximately 10-15 kWh per kilogram of ozone produced using conventional technologies. This energy requirement contributes significantly to the carbon footprint of ozonation processes, particularly when power sources are carbon-intensive. The selection of corrosion-resistant materials and compatible elastomers can influence operational efficiency, potentially reducing energy requirements through minimized maintenance and extended equipment lifespan.
Material selection for ozonation systems carries important sustainability implications. Highly ozone-resistant materials often include fluoropolymers and specialized stainless steels, which may have significant embodied energy and extraction impacts. The manufacturing processes for these specialized materials typically require more resources than conventional alternatives. However, their extended service life in ozone environments can offset initial environmental costs through reduced replacement frequency and system downtime.
Waste generation and management present additional environmental challenges. Degraded elastomers and corroded components require proper disposal, with some specialized materials presenting recycling difficulties. The environmental impact of these waste streams can be minimized through thoughtful material selection that balances ozone resistance with recyclability and biodegradability where appropriate. Emerging biobased elastomers with enhanced ozone resistance represent a promising development in this area.
The chemical byproducts of ozonation processes warrant careful consideration. While ozone itself decomposes rapidly to oxygen without persistent environmental residues, its reaction with certain compounds can generate bromates, aldehydes, and other potentially harmful byproducts. Material compatibility considerations must therefore extend to potential leaching of compounds that might react with ozone to form these byproducts. Proper material selection can minimize these risks while maintaining system integrity.
Water conservation aspects of ozonation systems relate directly to material compatibility and corrosion control. Systems designed with appropriate materials experience fewer leaks and failures, reducing water waste. Additionally, ozonation can enable water reuse applications that might otherwise be impractical, potentially offsetting the environmental impacts of the treatment process through conservation of this critical resource.
Energy consumption represents one of the most substantial environmental impacts of ozonation systems. The generation of ozone is inherently energy-intensive, requiring approximately 10-15 kWh per kilogram of ozone produced using conventional technologies. This energy requirement contributes significantly to the carbon footprint of ozonation processes, particularly when power sources are carbon-intensive. The selection of corrosion-resistant materials and compatible elastomers can influence operational efficiency, potentially reducing energy requirements through minimized maintenance and extended equipment lifespan.
Material selection for ozonation systems carries important sustainability implications. Highly ozone-resistant materials often include fluoropolymers and specialized stainless steels, which may have significant embodied energy and extraction impacts. The manufacturing processes for these specialized materials typically require more resources than conventional alternatives. However, their extended service life in ozone environments can offset initial environmental costs through reduced replacement frequency and system downtime.
Waste generation and management present additional environmental challenges. Degraded elastomers and corroded components require proper disposal, with some specialized materials presenting recycling difficulties. The environmental impact of these waste streams can be minimized through thoughtful material selection that balances ozone resistance with recyclability and biodegradability where appropriate. Emerging biobased elastomers with enhanced ozone resistance represent a promising development in this area.
The chemical byproducts of ozonation processes warrant careful consideration. While ozone itself decomposes rapidly to oxygen without persistent environmental residues, its reaction with certain compounds can generate bromates, aldehydes, and other potentially harmful byproducts. Material compatibility considerations must therefore extend to potential leaching of compounds that might react with ozone to form these byproducts. Proper material selection can minimize these risks while maintaining system integrity.
Water conservation aspects of ozonation systems relate directly to material compatibility and corrosion control. Systems designed with appropriate materials experience fewer leaks and failures, reducing water waste. Additionally, ozonation can enable water reuse applications that might otherwise be impractical, potentially offsetting the environmental impacts of the treatment process through conservation of this critical resource.
Regulatory Standards and Compliance Requirements
Ozone treatment systems are subject to stringent regulatory frameworks that vary across regions and industries. The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has established comprehensive guidelines under the Safe Drinking Water Act, specifying maximum contaminant levels for disinfection byproducts resulting from ozonation processes. These regulations mandate regular monitoring and reporting of ozone concentration levels, reaction byproducts, and system performance metrics to ensure public safety.
In the European Union, the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) enforces REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals) regulations that impact material selection for ozonation systems. These standards specifically address the compatibility of materials with oxidizing agents and establish limits for chemical migration from system components into treated water or air.
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has developed ISO 13959 and ISO 23500 series, which provide guidelines for water treatment systems including ozonation in healthcare applications. These standards outline specific requirements for materials that can withstand prolonged exposure to ozone without degradation or leaching of harmful substances.
For industrial applications, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has established permissible exposure limits (PEL) for ozone at 0.1 ppm (parts per million) over an 8-hour time-weighted average. This necessitates robust material selection and corrosion control measures to prevent system leakage and ensure workplace safety.
Material certification requirements vary by application sector. NSF International certification is often required for components used in drinking water treatment systems, while FDA compliance is necessary for food processing applications. These certifications evaluate both the chemical resistance of materials to ozone and their potential for releasing harmful substances under oxidative stress.
Compliance documentation for ozonation systems typically includes material compatibility testing results, corrosion rate data, and elastomer performance metrics under specified ozone concentrations. Manufacturers must maintain detailed records demonstrating that their material selections meet the applicable standards for the intended application environment.
Recent regulatory trends indicate increasing scrutiny of long-term material performance in ozonation systems, with particular focus on microplastic generation from degrading elastomers and the potential for metal ion leaching from corroded components. Several jurisdictions are implementing more stringent lifecycle assessment requirements for system components, necessitating improved predictive models for material degradation under ozone exposure.
In the European Union, the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) enforces REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals) regulations that impact material selection for ozonation systems. These standards specifically address the compatibility of materials with oxidizing agents and establish limits for chemical migration from system components into treated water or air.
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has developed ISO 13959 and ISO 23500 series, which provide guidelines for water treatment systems including ozonation in healthcare applications. These standards outline specific requirements for materials that can withstand prolonged exposure to ozone without degradation or leaching of harmful substances.
For industrial applications, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has established permissible exposure limits (PEL) for ozone at 0.1 ppm (parts per million) over an 8-hour time-weighted average. This necessitates robust material selection and corrosion control measures to prevent system leakage and ensure workplace safety.
Material certification requirements vary by application sector. NSF International certification is often required for components used in drinking water treatment systems, while FDA compliance is necessary for food processing applications. These certifications evaluate both the chemical resistance of materials to ozone and their potential for releasing harmful substances under oxidative stress.
Compliance documentation for ozonation systems typically includes material compatibility testing results, corrosion rate data, and elastomer performance metrics under specified ozone concentrations. Manufacturers must maintain detailed records demonstrating that their material selections meet the applicable standards for the intended application environment.
Recent regulatory trends indicate increasing scrutiny of long-term material performance in ozonation systems, with particular focus on microplastic generation from degrading elastomers and the potential for metal ion leaching from corroded components. Several jurisdictions are implementing more stringent lifecycle assessment requirements for system components, necessitating improved predictive models for material degradation under ozone exposure.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!