Ozonation: Ozone Generation—Corona Discharge, Feed Gas Drying And Power Efficiency
SEP 18, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Ozone Generation Technology Background and Objectives
Ozone generation technology has evolved significantly since its discovery in the early 19th century by Christian Friedrich Schönbein. Initially recognized for its distinctive odor and oxidizing properties, ozone has transitioned from a laboratory curiosity to an essential component in various industrial applications, including water treatment, air purification, food processing, and medical sterilization. The development trajectory has been marked by continuous improvements in generation efficiency, system reliability, and application versatility.
Corona discharge technology emerged as the predominant method for commercial ozone generation in the mid-20th century, offering advantages in scalability and production consistency compared to earlier UV-based methods. This approach utilizes electrical discharge across a dielectric barrier to convert oxygen molecules into ozone, achieving significantly higher concentrations and production rates necessary for industrial applications.
The technical evolution of corona discharge systems has focused on three critical aspects: electrode design optimization, dielectric material advancement, and power supply efficiency. Early systems suffered from rapid electrode degradation, inconsistent ozone production, and excessive energy consumption, limiting their practical application and economic viability.
Feed gas preparation, particularly drying processes, represents another crucial development area in ozone generation technology. The presence of moisture in feed gas significantly impacts ozone production efficiency and system longevity. Historical approaches ranged from simple refrigeration drying to more sophisticated desiccant and membrane technologies, each presenting distinct trade-offs between effectiveness, energy consumption, and operational complexity.
Power efficiency has emerged as perhaps the most significant challenge in modern ozone generation systems. Traditional corona discharge systems typically convert only 10-20% of input energy into ozone production, with the remainder dissipated as heat. This inefficiency has driven research into advanced power supply designs, including high-frequency converters, resonant circuits, and precision control systems that optimize discharge characteristics.
The primary objective of current research and development efforts is to create ozone generation systems that maximize production efficiency while minimizing energy consumption. Specific technical goals include achieving energy conversion efficiencies exceeding 30%, reducing cooling requirements, extending electrode and dielectric lifespans beyond 10,000 operating hours, and developing intelligent control systems that dynamically optimize operating parameters based on environmental conditions and application requirements.
Additional objectives include miniaturization for point-of-use applications, integration with renewable energy sources to reduce carbon footprint, and development of hybrid systems that combine corona discharge with other technologies to address specific application challenges in emerging markets such as semiconductor manufacturing, advanced oxidation processes, and medical therapies.
Corona discharge technology emerged as the predominant method for commercial ozone generation in the mid-20th century, offering advantages in scalability and production consistency compared to earlier UV-based methods. This approach utilizes electrical discharge across a dielectric barrier to convert oxygen molecules into ozone, achieving significantly higher concentrations and production rates necessary for industrial applications.
The technical evolution of corona discharge systems has focused on three critical aspects: electrode design optimization, dielectric material advancement, and power supply efficiency. Early systems suffered from rapid electrode degradation, inconsistent ozone production, and excessive energy consumption, limiting their practical application and economic viability.
Feed gas preparation, particularly drying processes, represents another crucial development area in ozone generation technology. The presence of moisture in feed gas significantly impacts ozone production efficiency and system longevity. Historical approaches ranged from simple refrigeration drying to more sophisticated desiccant and membrane technologies, each presenting distinct trade-offs between effectiveness, energy consumption, and operational complexity.
Power efficiency has emerged as perhaps the most significant challenge in modern ozone generation systems. Traditional corona discharge systems typically convert only 10-20% of input energy into ozone production, with the remainder dissipated as heat. This inefficiency has driven research into advanced power supply designs, including high-frequency converters, resonant circuits, and precision control systems that optimize discharge characteristics.
The primary objective of current research and development efforts is to create ozone generation systems that maximize production efficiency while minimizing energy consumption. Specific technical goals include achieving energy conversion efficiencies exceeding 30%, reducing cooling requirements, extending electrode and dielectric lifespans beyond 10,000 operating hours, and developing intelligent control systems that dynamically optimize operating parameters based on environmental conditions and application requirements.
Additional objectives include miniaturization for point-of-use applications, integration with renewable energy sources to reduce carbon footprint, and development of hybrid systems that combine corona discharge with other technologies to address specific application challenges in emerging markets such as semiconductor manufacturing, advanced oxidation processes, and medical therapies.
Market Analysis for Ozonation Applications
The global ozonation market has witnessed substantial growth in recent years, driven primarily by increasing water treatment needs and growing environmental concerns. The market value for ozone technology reached approximately $1.2 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 7.3% through 2028, with corona discharge technology accounting for over 65% of the total market share.
Water treatment remains the dominant application sector, representing nearly 70% of the total ozonation market. Municipal water treatment facilities are increasingly adopting ozone systems to replace traditional chlorination methods due to ozone's superior disinfection capabilities without harmful byproducts. The industrial wastewater treatment segment is experiencing the fastest growth rate at 8.5% annually, as stringent environmental regulations force industries to implement advanced oxidation processes.
The healthcare and pharmaceutical sectors constitute an emerging market for ozonation technology, with applications in sterilization and advanced oxidation processes for pharmaceutical waste treatment. This segment is expected to grow at 9.2% annually as healthcare facilities seek alternatives to chemical sterilization methods.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead the ozonation market with combined market share of 58%, attributed to strict water quality regulations and established infrastructure. However, the Asia-Pacific region is demonstrating the most rapid growth at 10.1% annually, driven by industrialization, urbanization, and increasing government investments in water treatment infrastructure in China, India, and Southeast Asian countries.
Energy efficiency has emerged as a critical factor influencing market adoption. Traditional corona discharge systems consume significant energy, with power costs representing 30-40% of operational expenses. Recent technological innovations focusing on power efficiency improvements have reduced energy consumption by 15-25%, significantly enhancing the cost-effectiveness of ozonation systems and expanding their market potential.
The feed gas drying component represents a substantial portion of system costs, with approximately 20% of initial capital expenditure allocated to gas preparation systems. Market analysis indicates growing demand for integrated systems that optimize both power consumption and gas preparation, with potential for 30% reduction in operational costs through these improvements.
Market forecasts suggest that innovations in corona discharge efficiency and feed gas optimization will be key differentiators for manufacturers, with customers increasingly prioritizing total cost of ownership over initial capital expenditure. This trend is expected to drive further research and development in power-efficient ozone generation technologies over the next decade.
Water treatment remains the dominant application sector, representing nearly 70% of the total ozonation market. Municipal water treatment facilities are increasingly adopting ozone systems to replace traditional chlorination methods due to ozone's superior disinfection capabilities without harmful byproducts. The industrial wastewater treatment segment is experiencing the fastest growth rate at 8.5% annually, as stringent environmental regulations force industries to implement advanced oxidation processes.
The healthcare and pharmaceutical sectors constitute an emerging market for ozonation technology, with applications in sterilization and advanced oxidation processes for pharmaceutical waste treatment. This segment is expected to grow at 9.2% annually as healthcare facilities seek alternatives to chemical sterilization methods.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently lead the ozonation market with combined market share of 58%, attributed to strict water quality regulations and established infrastructure. However, the Asia-Pacific region is demonstrating the most rapid growth at 10.1% annually, driven by industrialization, urbanization, and increasing government investments in water treatment infrastructure in China, India, and Southeast Asian countries.
Energy efficiency has emerged as a critical factor influencing market adoption. Traditional corona discharge systems consume significant energy, with power costs representing 30-40% of operational expenses. Recent technological innovations focusing on power efficiency improvements have reduced energy consumption by 15-25%, significantly enhancing the cost-effectiveness of ozonation systems and expanding their market potential.
The feed gas drying component represents a substantial portion of system costs, with approximately 20% of initial capital expenditure allocated to gas preparation systems. Market analysis indicates growing demand for integrated systems that optimize both power consumption and gas preparation, with potential for 30% reduction in operational costs through these improvements.
Market forecasts suggest that innovations in corona discharge efficiency and feed gas optimization will be key differentiators for manufacturers, with customers increasingly prioritizing total cost of ownership over initial capital expenditure. This trend is expected to drive further research and development in power-efficient ozone generation technologies over the next decade.
Corona Discharge Technology: Current Status and Challenges
Corona discharge technology represents the most widely adopted method for industrial ozone generation, accounting for approximately 90% of all commercial ozone production systems. This technology utilizes the principle of electrical discharge across a dielectric-filled gap to generate non-equilibrium plasma, which efficiently converts oxygen molecules into ozone. Despite its widespread adoption, corona discharge systems face several significant technical challenges that limit their efficiency and application scope.
The current state-of-the-art corona discharge generators typically achieve energy efficiency between 10-25%, with laboratory prototypes reaching up to 30% under optimal conditions. This relatively low efficiency remains a major limitation, as approximately 70-90% of input energy is lost as heat rather than being utilized for ozone production. The heat generation necessitates complex cooling systems that increase both capital and operational costs.
Feed gas quality presents another critical challenge. Corona discharge systems require extremely dry gas inputs (typically with dew points below -60°C) to prevent nitric acid formation and electrode corrosion. Conventional desiccant-based drying systems add significant energy costs, accounting for up to 15% of the total system energy consumption. Recent advancements in membrane technology and pressure swing adsorption have improved drying efficiency but remain energy-intensive.
Electrode design and materials constitute ongoing research areas. Traditional stainless steel and aluminum electrodes suffer from oxidation and degradation in the aggressive ozone environment. Advanced ceramic-coated electrodes and boron-doped diamond electrodes have shown promising durability improvements but at substantially higher manufacturing costs. The dielectric barrier materials, typically glass or ceramic, also face degradation issues that limit system lifespan.
Power supply technology represents another challenge area. Modern corona discharge systems utilize medium-frequency (400-1000 Hz) power supplies that improve efficiency compared to older line-frequency systems. However, high-frequency (>10 kHz) and pulsed power supplies, which theoretically offer higher efficiency, face practical implementation challenges related to power electronics reliability and electromagnetic interference.
Scale-up limitations also restrict industrial applications. As system capacity increases, maintaining uniform discharge characteristics becomes increasingly difficult, leading to reduced efficiency and increased heat generation in larger systems. This creates a technical ceiling that limits the maximum practical size of individual ozone generators, necessitating modular approaches for large-scale applications.
Environmental factors further complicate implementation. Corona discharge systems produce trace amounts of nitrogen oxides when using air as feed gas, potentially requiring additional treatment systems. Additionally, the high voltage requirements (typically 10-30 kV) create safety concerns and necessitate specialized installation and maintenance protocols.
The current state-of-the-art corona discharge generators typically achieve energy efficiency between 10-25%, with laboratory prototypes reaching up to 30% under optimal conditions. This relatively low efficiency remains a major limitation, as approximately 70-90% of input energy is lost as heat rather than being utilized for ozone production. The heat generation necessitates complex cooling systems that increase both capital and operational costs.
Feed gas quality presents another critical challenge. Corona discharge systems require extremely dry gas inputs (typically with dew points below -60°C) to prevent nitric acid formation and electrode corrosion. Conventional desiccant-based drying systems add significant energy costs, accounting for up to 15% of the total system energy consumption. Recent advancements in membrane technology and pressure swing adsorption have improved drying efficiency but remain energy-intensive.
Electrode design and materials constitute ongoing research areas. Traditional stainless steel and aluminum electrodes suffer from oxidation and degradation in the aggressive ozone environment. Advanced ceramic-coated electrodes and boron-doped diamond electrodes have shown promising durability improvements but at substantially higher manufacturing costs. The dielectric barrier materials, typically glass or ceramic, also face degradation issues that limit system lifespan.
Power supply technology represents another challenge area. Modern corona discharge systems utilize medium-frequency (400-1000 Hz) power supplies that improve efficiency compared to older line-frequency systems. However, high-frequency (>10 kHz) and pulsed power supplies, which theoretically offer higher efficiency, face practical implementation challenges related to power electronics reliability and electromagnetic interference.
Scale-up limitations also restrict industrial applications. As system capacity increases, maintaining uniform discharge characteristics becomes increasingly difficult, leading to reduced efficiency and increased heat generation in larger systems. This creates a technical ceiling that limits the maximum practical size of individual ozone generators, necessitating modular approaches for large-scale applications.
Environmental factors further complicate implementation. Corona discharge systems produce trace amounts of nitrogen oxides when using air as feed gas, potentially requiring additional treatment systems. Additionally, the high voltage requirements (typically 10-30 kV) create safety concerns and necessitate specialized installation and maintenance protocols.
Feed Gas Drying Solutions and Implementation
01 Electrode design optimization for ozone generation
Optimizing electrode design is crucial for improving ozone generation efficiency. This includes using specialized materials, geometries, and surface treatments that enhance electron discharge while minimizing energy consumption. Advanced electrode configurations can significantly reduce power requirements while maintaining or increasing ozone output. Some designs incorporate cooling systems to prevent efficiency losses due to heat generation during operation.- Electrode design optimization for ozone generation: Optimizing electrode design is crucial for improving ozone generation efficiency. This includes using specialized materials, geometries, and configurations that enhance electron discharge while minimizing energy consumption. Advanced electrode designs can significantly reduce power requirements while maintaining or increasing ozone production rates. Innovations in this area focus on surface treatments, spacing optimization, and novel electrode shapes that maximize the electric field distribution.
- Power supply and electrical control systems: Sophisticated power supply and electrical control systems play a vital role in ozone generation efficiency. These systems include high-frequency inverters, pulse width modulation techniques, and intelligent power management algorithms that optimize energy delivery to the ozone generator. By precisely controlling voltage, current, and frequency parameters, these systems can significantly reduce power consumption while maintaining optimal ozone output levels under varying operating conditions.
- Cooling and thermal management techniques: Effective cooling and thermal management are essential for maintaining high efficiency in ozone generation systems. Excessive heat reduces ozone production efficiency and increases power consumption. Advanced cooling techniques include liquid cooling systems, heat exchangers, and thermally optimized designs that efficiently dissipate heat from critical components. Proper thermal management ensures stable operation at optimal temperatures, significantly improving the power efficiency of the ozone generation process.
- Feed gas preparation and treatment: The composition and quality of feed gas significantly impact ozone generation efficiency. Advanced gas preparation techniques include moisture removal, oxygen concentration enhancement, and contaminant filtration systems that optimize the gas stream before it enters the ozone generator. By providing high-purity feed gas with controlled humidity levels, these systems reduce the energy required for ozone production and extend the operational life of the generator components.
- Hybrid and combined technology approaches: Hybrid and combined technology approaches integrate multiple ozone generation methods or complementary technologies to achieve higher efficiency. These systems may combine different discharge types, incorporate catalytic elements, or integrate renewable energy sources to power ozone generation. By leveraging the strengths of various technologies while mitigating their individual limitations, these hybrid approaches can significantly improve overall power efficiency and reduce operational costs in ozone production.
02 Power supply and electrical discharge optimization
Efficient power supply systems are essential for improving ozone generation efficiency. This includes using high-frequency power supplies, pulse width modulation techniques, and optimized voltage control systems. Advanced electrical discharge methods can create more uniform plasma fields that produce ozone with less energy input. Some systems incorporate intelligent power management that adjusts electrical parameters based on operational conditions to maintain optimal efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions03 Cooling and thermal management systems
Effective thermal management significantly improves ozone generation efficiency by preventing performance degradation at higher temperatures. Advanced cooling systems using water, air, or other media help maintain optimal operating temperatures. Some designs incorporate heat exchangers or thermal isolation techniques to prevent heat transfer between components. Maintaining lower operating temperatures extends equipment lifespan while reducing energy consumption per unit of ozone produced.Expand Specific Solutions04 Gas flow and mixture optimization
Optimizing the flow rate, pressure, and composition of feed gases significantly impacts ozone generation efficiency. Precise control of oxygen concentration, humidity levels, and contaminants in the input gas stream can substantially reduce power consumption. Some systems incorporate gas pre-treatment, specialized flow channels, or turbulence-inducing structures to enhance ozone formation. Advanced gas mixture techniques can achieve higher ozone concentrations while using less energy.Expand Specific Solutions05 Monitoring and control systems for efficiency optimization
Intelligent monitoring and control systems can significantly improve ozone generation efficiency through real-time adjustments. These systems use sensors to monitor key parameters such as temperature, gas flow, power consumption, and ozone output. Advanced algorithms optimize operational parameters based on current conditions and production requirements. Some systems incorporate predictive maintenance capabilities to prevent efficiency losses due to component degradation over time.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Manufacturers and Research Institutions
Ozonation technology for water treatment is currently in a growth phase, with the market expanding due to increasing water quality regulations and industrial demand. The global ozone generation market is estimated to reach significant scale as applications diversify across municipal water treatment, industrial processes, and healthcare. Technologically, corona discharge remains the dominant method, with companies like Mitsubishi Electric, Toshiba, and Evoqua Water Technologies leading innovation in power efficiency and feed gas drying techniques. Air Products & Chemicals and OZOMAX have made notable advances in gas preparation systems, while academic institutions like Tsinghua University and Zhejiang University contribute research on electrode materials and discharge optimization. The competitive landscape shows established industrial players focusing on energy efficiency improvements while newer entrants target specialized applications with compact, modular designs.
Mitsubishi Electric Corp.
Technical Solution: Mitsubishi Electric has developed advanced corona discharge ozone generation systems that utilize ceramic dielectric materials and specialized electrode designs to enhance ozone production efficiency. Their technology employs a multi-layer dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) configuration that optimizes the electric field distribution across the discharge gap, resulting in more uniform plasma formation and higher ozone yields. The company has implemented sophisticated feed gas drying systems using molecular sieve technology that can achieve dew points below -70°C, significantly improving ozone production efficiency by eliminating moisture that would otherwise react with ozone. Their power supply systems incorporate high-frequency inverter technology operating at 10-20 kHz, which reduces power losses and improves energy transfer to the discharge gap. Mitsubishi's systems also feature advanced thermal management through water cooling circuits that maintain optimal discharge temperatures, preventing thermal degradation of ozone and extending equipment lifespan.
Strengths: Superior energy efficiency with reported power consumption reductions of 20-30% compared to conventional systems; excellent reliability with electrode designs that resist degradation; and comprehensive system integration capabilities. Weaknesses: Higher initial capital costs compared to simpler systems; requires specialized maintenance expertise; and larger physical footprint for complete integrated systems.
Evoqua Water Technologies LLC
Technical Solution: Evoqua has pioneered modular ozone generation systems based on advanced corona discharge technology specifically optimized for water treatment applications. Their systems feature proprietary electrode designs with specialized coatings that enhance discharge stability and reduce electrode degradation over time. For feed gas preparation, Evoqua employs a multi-stage drying process incorporating both refrigeration and desiccant technologies, achieving moisture content below 20 ppm in the feed gas. This comprehensive approach to gas drying significantly extends the operational life of their generators while maximizing ozone production efficiency. Their power supply systems utilize digital signal processing (DSP) controlled inverters that dynamically adjust power parameters based on real-time monitoring of discharge conditions, optimizing energy consumption across varying operational demands. Evoqua's systems also incorporate intelligent cooling systems that precisely control discharge gap temperatures to maximize ozone yield while minimizing energy consumption.
Strengths: Highly optimized for water treatment applications with turnkey integration capabilities; excellent scalability from small to large installations; and advanced control systems that provide precise ozone dosing. Weaknesses: Systems are primarily designed for water treatment rather than industrial gas applications; higher operational complexity requiring trained operators; and relatively high maintenance requirements for the gas drying components.
Power Efficiency Innovations in Corona Discharge Systems
Ozone Generation System
PatentInactiveUS20220259044A1
Innovation
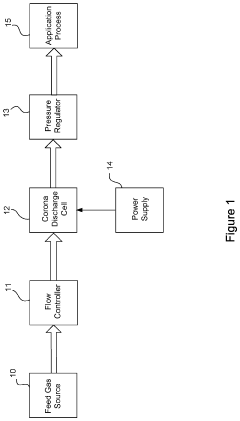
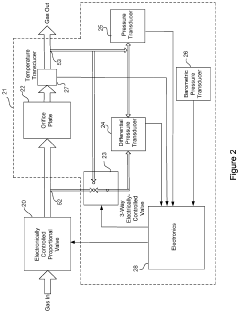
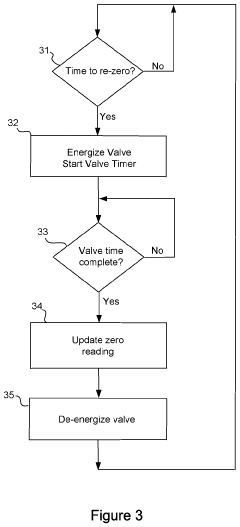
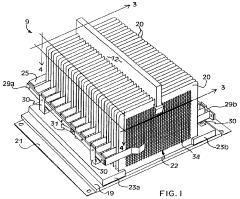
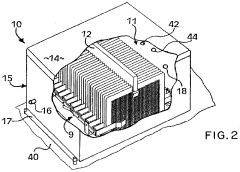
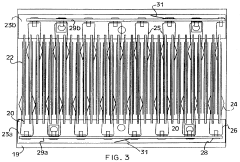
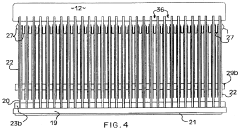
- An ozone generation system with a corona discharge cell, a flow controller using an orifice plate and electrically controlled valve to maintain constant flow, and a pressure regulator with a flexible diaphragm to isolate cell pressure from application process pressures, allowing for independent control and accurate ozone supply.
Continuous corona discharge ozone generation device
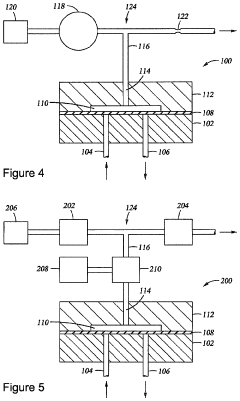
PatentInactiveUS5525310A
Innovation
- A corona discharge ozone generator with spring-biased wire mesh electrodes and ozone-resistant power cables, using lower voltage and air cooling, which increases ozone output per unit of power consumption and avoids the use of adhesives susceptible to ozone degradation.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
Ozone generation through corona discharge technology presents significant environmental implications that must be carefully considered in the context of sustainability. The process itself serves as an environmentally favorable alternative to chemical disinfection methods, particularly in water treatment applications, as it produces no persistent harmful byproducts when properly implemented. Ozone naturally decomposes back into oxygen, leaving no residual contaminants in treated water systems.
However, the environmental footprint of ozone generation systems extends beyond the immediate application. Energy consumption represents the most substantial environmental concern, as corona discharge systems typically require considerable electrical input. The carbon footprint of this energy usage directly correlates with the source of electricity powering these systems. Operations running on fossil fuel-derived electricity contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions, whereas renewable energy sources can substantially mitigate this impact.
Feed gas preparation, particularly the drying processes, introduces additional environmental considerations. Traditional desiccant-based drying systems require regular regeneration cycles that consume energy and potentially release waste heat. More advanced membrane drying technologies offer improved environmental performance but still contribute to the overall energy demand of the system. The production, transportation, and disposal of drying materials also factor into the life-cycle environmental assessment of ozone generation systems.
The manufacturing of corona discharge equipment itself involves resource extraction and industrial processes with associated environmental impacts. The specialized materials required for electrodes, dielectrics, and cooling systems each carry embedded carbon and resource footprints. Additionally, the refrigerants used in cooling systems for larger installations may have significant global warming potential if not properly managed throughout their lifecycle.
From a sustainability perspective, recent technological advancements have focused on improving the overall efficiency of corona discharge ozone generators. Enhanced electrode designs, optimized power supply systems, and more efficient feed gas preparation have collectively reduced the environmental impact per unit of ozone produced. These improvements align with broader sustainability goals by decreasing resource intensity while maintaining or improving performance.
The long-term environmental benefits of ozone technology must be weighed against these production impacts. When displacing chemical alternatives like chlorine-based disinfectants, ozone systems typically demonstrate favorable environmental profiles despite their energy requirements. The absence of chemical transportation, storage risks, and persistent disinfection byproducts represents significant environmental advantages that support the continued development and implementation of increasingly sustainable ozone generation technologies.
However, the environmental footprint of ozone generation systems extends beyond the immediate application. Energy consumption represents the most substantial environmental concern, as corona discharge systems typically require considerable electrical input. The carbon footprint of this energy usage directly correlates with the source of electricity powering these systems. Operations running on fossil fuel-derived electricity contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions, whereas renewable energy sources can substantially mitigate this impact.
Feed gas preparation, particularly the drying processes, introduces additional environmental considerations. Traditional desiccant-based drying systems require regular regeneration cycles that consume energy and potentially release waste heat. More advanced membrane drying technologies offer improved environmental performance but still contribute to the overall energy demand of the system. The production, transportation, and disposal of drying materials also factor into the life-cycle environmental assessment of ozone generation systems.
The manufacturing of corona discharge equipment itself involves resource extraction and industrial processes with associated environmental impacts. The specialized materials required for electrodes, dielectrics, and cooling systems each carry embedded carbon and resource footprints. Additionally, the refrigerants used in cooling systems for larger installations may have significant global warming potential if not properly managed throughout their lifecycle.
From a sustainability perspective, recent technological advancements have focused on improving the overall efficiency of corona discharge ozone generators. Enhanced electrode designs, optimized power supply systems, and more efficient feed gas preparation have collectively reduced the environmental impact per unit of ozone produced. These improvements align with broader sustainability goals by decreasing resource intensity while maintaining or improving performance.
The long-term environmental benefits of ozone technology must be weighed against these production impacts. When displacing chemical alternatives like chlorine-based disinfectants, ozone systems typically demonstrate favorable environmental profiles despite their energy requirements. The absence of chemical transportation, storage risks, and persistent disinfection byproducts represents significant environmental advantages that support the continued development and implementation of increasingly sustainable ozone generation technologies.
Regulatory Framework for Ozonation Systems
The regulatory landscape for ozonation systems has evolved significantly over the past decades, reflecting growing awareness of both the benefits and potential risks associated with ozone technology. In the United States, the FDA has established specific regulations for ozone generators used in food processing and water treatment, requiring manufacturers to demonstrate compliance with safety standards and efficacy claims. Similarly, the EPA regulates ozonation systems under the Clean Air Act and Safe Drinking Water Act, establishing maximum ozone emission limits and treatment requirements.
The European Union maintains some of the world's most comprehensive regulatory frameworks for ozonation technology through the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) and the Biocidal Products Regulation (BPR). These regulations mandate rigorous safety assessments, technical documentation, and performance validation before ozonation systems can enter the market. Corona discharge ozone generators specifically must meet electrical safety standards outlined in the Low Voltage Directive (2014/35/EU) and Electromagnetic Compatibility Directive (2014/30/EU).
International standards organizations play a crucial role in harmonizing global requirements. The International Ozone Association (IOA) has developed technical guidelines that serve as reference points for many national regulations. ISO standards, particularly ISO 13959 for water quality and ISO 21911 for air quality monitoring in ozone applications, provide standardized testing methodologies and performance metrics that manufacturers must satisfy.
Feed gas drying systems in ozonation equipment face additional regulatory scrutiny due to their impact on energy consumption and operational efficiency. Energy efficiency regulations in various jurisdictions increasingly incorporate specific provisions for auxiliary systems in water treatment technologies, including desiccant dryers and refrigeration systems used in feed gas preparation for corona discharge generators.
Regulatory compliance documentation for ozonation systems typically requires comprehensive technical files including design specifications, risk assessments, performance data, and power efficiency metrics. Third-party certification from recognized bodies such as NSF International, UL, or TÜV is often necessary to demonstrate compliance with applicable standards and regulations.
Emerging regulatory trends indicate increasing focus on the environmental footprint of ozonation systems, with new frameworks emphasizing lifecycle assessment, energy optimization requirements, and limitations on byproduct formation. Several jurisdictions are developing specialized regulatory pathways for advanced oxidation processes that combine ozonation with other technologies, recognizing their unique operational characteristics and applications.
The European Union maintains some of the world's most comprehensive regulatory frameworks for ozonation technology through the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) and the Biocidal Products Regulation (BPR). These regulations mandate rigorous safety assessments, technical documentation, and performance validation before ozonation systems can enter the market. Corona discharge ozone generators specifically must meet electrical safety standards outlined in the Low Voltage Directive (2014/35/EU) and Electromagnetic Compatibility Directive (2014/30/EU).
International standards organizations play a crucial role in harmonizing global requirements. The International Ozone Association (IOA) has developed technical guidelines that serve as reference points for many national regulations. ISO standards, particularly ISO 13959 for water quality and ISO 21911 for air quality monitoring in ozone applications, provide standardized testing methodologies and performance metrics that manufacturers must satisfy.
Feed gas drying systems in ozonation equipment face additional regulatory scrutiny due to their impact on energy consumption and operational efficiency. Energy efficiency regulations in various jurisdictions increasingly incorporate specific provisions for auxiliary systems in water treatment technologies, including desiccant dryers and refrigeration systems used in feed gas preparation for corona discharge generators.
Regulatory compliance documentation for ozonation systems typically requires comprehensive technical files including design specifications, risk assessments, performance data, and power efficiency metrics. Third-party certification from recognized bodies such as NSF International, UL, or TÜV is often necessary to demonstrate compliance with applicable standards and regulations.
Emerging regulatory trends indicate increasing focus on the environmental footprint of ozonation systems, with new frameworks emphasizing lifecycle assessment, energy optimization requirements, and limitations on byproduct formation. Several jurisdictions are developing specialized regulatory pathways for advanced oxidation processes that combine ozonation with other technologies, recognizing their unique operational characteristics and applications.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!