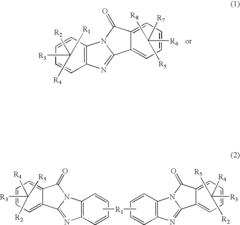
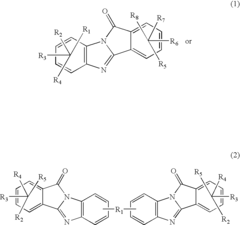
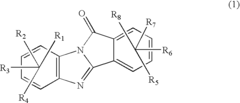
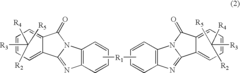
Potential of Alkyl Compounds in Circular Economies
JUL 15, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Alkyl Compounds in Circular Economy: Background and Objectives
Alkyl compounds have emerged as a focal point in the pursuit of circular economies, representing a significant shift in how we approach resource utilization and waste management. These organic molecules, characterized by their carbon-hydrogen bonds, are ubiquitous in various industries, from petrochemicals to pharmaceuticals. The circular economy concept, which aims to eliminate waste and maximize resource efficiency, has found a promising ally in alkyl compounds due to their versatility and potential for recycling and reuse.
The historical context of alkyl compounds traces back to the early days of organic chemistry, with their importance growing exponentially with the rise of the petrochemical industry in the 20th century. As global awareness of environmental issues and resource scarcity has increased, the focus has shifted towards finding sustainable alternatives to traditional linear economic models. This shift has placed alkyl compounds at the forefront of circular economy strategies, given their potential to be derived from renewable sources and their capacity for chemical transformation and recycling.
The primary objective of exploring alkyl compounds in circular economies is to develop closed-loop systems where these compounds can be continuously recycled, repurposed, or biodegraded without generating persistent waste. This aligns with the broader goals of reducing dependency on fossil fuels, minimizing environmental impact, and creating more sustainable industrial processes. By leveraging the chemical properties of alkyl compounds, researchers and industries aim to design products and processes that are inherently more circular, from production to end-of-life management.
One of the key technological trends in this field is the development of bio-based alkyl compounds, derived from renewable feedstocks such as plant oils or waste biomass. This approach not only reduces reliance on petroleum-based sources but also offers potential carbon neutrality. Another significant trend is the advancement in chemical recycling technologies, which allow for the breakdown of complex alkyl-based polymers into their constituent monomers or other valuable chemical intermediates, enabling true circularity in plastic and polymer industries.
The evolution of alkyl compounds in circular economies is closely tied to advancements in green chemistry principles, catalysis, and process intensification. These technological developments aim to enhance the efficiency of alkyl compound transformations, reduce energy consumption, and minimize the generation of by-products. Furthermore, the integration of digital technologies and artificial intelligence is expected to play a crucial role in optimizing the lifecycle management of alkyl compounds within circular economy frameworks.
The historical context of alkyl compounds traces back to the early days of organic chemistry, with their importance growing exponentially with the rise of the petrochemical industry in the 20th century. As global awareness of environmental issues and resource scarcity has increased, the focus has shifted towards finding sustainable alternatives to traditional linear economic models. This shift has placed alkyl compounds at the forefront of circular economy strategies, given their potential to be derived from renewable sources and their capacity for chemical transformation and recycling.
The primary objective of exploring alkyl compounds in circular economies is to develop closed-loop systems where these compounds can be continuously recycled, repurposed, or biodegraded without generating persistent waste. This aligns with the broader goals of reducing dependency on fossil fuels, minimizing environmental impact, and creating more sustainable industrial processes. By leveraging the chemical properties of alkyl compounds, researchers and industries aim to design products and processes that are inherently more circular, from production to end-of-life management.
One of the key technological trends in this field is the development of bio-based alkyl compounds, derived from renewable feedstocks such as plant oils or waste biomass. This approach not only reduces reliance on petroleum-based sources but also offers potential carbon neutrality. Another significant trend is the advancement in chemical recycling technologies, which allow for the breakdown of complex alkyl-based polymers into their constituent monomers or other valuable chemical intermediates, enabling true circularity in plastic and polymer industries.
The evolution of alkyl compounds in circular economies is closely tied to advancements in green chemistry principles, catalysis, and process intensification. These technological developments aim to enhance the efficiency of alkyl compound transformations, reduce energy consumption, and minimize the generation of by-products. Furthermore, the integration of digital technologies and artificial intelligence is expected to play a crucial role in optimizing the lifecycle management of alkyl compounds within circular economy frameworks.
Market Analysis for Alkyl Compounds in Sustainable Industries
The market for alkyl compounds in sustainable industries is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing focus on circular economies and environmental sustainability. As industries seek to reduce their carbon footprint and embrace more eco-friendly practices, alkyl compounds have emerged as versatile and promising materials with diverse applications across various sectors.
In the chemical industry, alkyl compounds are finding increased use in the production of biodegradable plastics and sustainable packaging materials. This shift is largely driven by consumer demand for environmentally friendly products and stricter regulations on single-use plastics. The market for bio-based alkyl compounds in this sector is expected to grow substantially over the next decade, as manufacturers seek alternatives to traditional petroleum-based plastics.
The agricultural sector represents another key market for alkyl compounds, particularly in the development of sustainable pesticides and fertilizers. These compounds offer improved biodegradability and reduced environmental impact compared to conventional agrochemicals. As global agriculture trends towards more sustainable practices, the demand for alkyl-based agricultural products is projected to increase significantly.
In the energy sector, alkyl compounds are gaining traction in the development of next-generation biofuels and lubricants. These sustainable alternatives offer improved performance characteristics while reducing environmental impact. The market for alkyl-based biofuels is expected to expand rapidly, driven by government mandates for renewable energy sources and the automotive industry's shift towards cleaner fuel options.
The personal care and cosmetics industry is also embracing alkyl compounds as key ingredients in natural and organic product formulations. Consumers are increasingly seeking products with minimal environmental impact, driving demand for sustainable, plant-derived alkyl compounds in this sector.
Furthermore, the textile industry is exploring the use of alkyl compounds in the development of sustainable fibers and fabric treatments. These innovations aim to reduce the environmental footprint of textile production while improving product performance and durability.
As the global push for sustainability intensifies, the market for alkyl compounds in circular economies is expected to continue its upward trajectory. However, challenges remain, including the need for cost-effective production methods and the development of more efficient recycling technologies for alkyl-based products. Overcoming these hurdles will be crucial in fully realizing the potential of alkyl compounds in sustainable industries and accelerating the transition towards a more circular economy.
In the chemical industry, alkyl compounds are finding increased use in the production of biodegradable plastics and sustainable packaging materials. This shift is largely driven by consumer demand for environmentally friendly products and stricter regulations on single-use plastics. The market for bio-based alkyl compounds in this sector is expected to grow substantially over the next decade, as manufacturers seek alternatives to traditional petroleum-based plastics.
The agricultural sector represents another key market for alkyl compounds, particularly in the development of sustainable pesticides and fertilizers. These compounds offer improved biodegradability and reduced environmental impact compared to conventional agrochemicals. As global agriculture trends towards more sustainable practices, the demand for alkyl-based agricultural products is projected to increase significantly.
In the energy sector, alkyl compounds are gaining traction in the development of next-generation biofuels and lubricants. These sustainable alternatives offer improved performance characteristics while reducing environmental impact. The market for alkyl-based biofuels is expected to expand rapidly, driven by government mandates for renewable energy sources and the automotive industry's shift towards cleaner fuel options.
The personal care and cosmetics industry is also embracing alkyl compounds as key ingredients in natural and organic product formulations. Consumers are increasingly seeking products with minimal environmental impact, driving demand for sustainable, plant-derived alkyl compounds in this sector.
Furthermore, the textile industry is exploring the use of alkyl compounds in the development of sustainable fibers and fabric treatments. These innovations aim to reduce the environmental footprint of textile production while improving product performance and durability.
As the global push for sustainability intensifies, the market for alkyl compounds in circular economies is expected to continue its upward trajectory. However, challenges remain, including the need for cost-effective production methods and the development of more efficient recycling technologies for alkyl-based products. Overcoming these hurdles will be crucial in fully realizing the potential of alkyl compounds in sustainable industries and accelerating the transition towards a more circular economy.
Current Challenges in Alkyl Compound Recycling and Reuse
The recycling and reuse of alkyl compounds face several significant challenges in the context of circular economies. One of the primary obstacles is the chemical stability of these compounds, which often makes them resistant to conventional recycling methods. Many alkyl compounds are designed for durability and long-term use, making them difficult to break down into their constituent parts without significant energy input or chemical processing.
Another major challenge is the contamination of alkyl compounds during their lifecycle. As these compounds are used in various applications, they often become mixed with other substances or degraded by environmental factors. This contamination can make it challenging to separate and purify the alkyl compounds for reuse, requiring advanced separation techniques that may be energy-intensive or cost-prohibitive.
The diversity of alkyl compounds used in different industries also presents a significant hurdle. Each type of alkyl compound may require a specific recycling or reuse process, making it difficult to develop standardized recycling systems. This diversity can lead to inefficiencies in collection and sorting processes, as well as increased costs for recycling facilities that need to handle multiple types of alkyl compounds.
Environmental concerns also pose challenges to the recycling and reuse of alkyl compounds. Some of these compounds can be toxic or harmful to ecosystems if not properly managed during the recycling process. Ensuring that recycling methods do not release harmful substances into the environment is crucial but can add complexity and cost to recycling operations.
Economic factors play a significant role in the challenges faced by alkyl compound recycling. The cost of collecting, sorting, and processing these compounds for reuse can be high, especially when compared to the cost of producing new alkyl compounds from virgin materials. This economic imbalance can discourage investment in recycling infrastructure and technologies.
Technological limitations also hinder the efficient recycling of alkyl compounds. Current recycling technologies may not be able to fully restore the properties of recycled alkyl compounds to their original state, limiting their potential applications in high-performance or sensitive uses. Developing new technologies that can effectively recycle alkyl compounds while maintaining their desirable properties is an ongoing challenge.
Regulatory frameworks and policy support for alkyl compound recycling are often inadequate or inconsistent across different regions. This lack of standardization can create barriers to the development of large-scale recycling initiatives and hinder the growth of markets for recycled alkyl compounds.
Another major challenge is the contamination of alkyl compounds during their lifecycle. As these compounds are used in various applications, they often become mixed with other substances or degraded by environmental factors. This contamination can make it challenging to separate and purify the alkyl compounds for reuse, requiring advanced separation techniques that may be energy-intensive or cost-prohibitive.
The diversity of alkyl compounds used in different industries also presents a significant hurdle. Each type of alkyl compound may require a specific recycling or reuse process, making it difficult to develop standardized recycling systems. This diversity can lead to inefficiencies in collection and sorting processes, as well as increased costs for recycling facilities that need to handle multiple types of alkyl compounds.
Environmental concerns also pose challenges to the recycling and reuse of alkyl compounds. Some of these compounds can be toxic or harmful to ecosystems if not properly managed during the recycling process. Ensuring that recycling methods do not release harmful substances into the environment is crucial but can add complexity and cost to recycling operations.
Economic factors play a significant role in the challenges faced by alkyl compound recycling. The cost of collecting, sorting, and processing these compounds for reuse can be high, especially when compared to the cost of producing new alkyl compounds from virgin materials. This economic imbalance can discourage investment in recycling infrastructure and technologies.
Technological limitations also hinder the efficient recycling of alkyl compounds. Current recycling technologies may not be able to fully restore the properties of recycled alkyl compounds to their original state, limiting their potential applications in high-performance or sensitive uses. Developing new technologies that can effectively recycle alkyl compounds while maintaining their desirable properties is an ongoing challenge.
Regulatory frameworks and policy support for alkyl compound recycling are often inadequate or inconsistent across different regions. This lack of standardization can create barriers to the development of large-scale recycling initiatives and hinder the growth of markets for recycled alkyl compounds.
Existing Circular Solutions for Alkyl Compounds
01 Synthesis of alkyl compounds
Various methods for synthesizing alkyl compounds are described, including reactions involving alkyl halides, alcohols, and other precursors. These processes often involve catalysts and specific reaction conditions to produce desired alkyl compounds efficiently.- Synthesis of alkyl compounds: Various methods for synthesizing alkyl compounds are described, including reactions involving alkyl halides, alcohols, and other precursors. These processes often involve catalysts and specific reaction conditions to produce desired alkyl derivatives.
- Applications of alkyl compounds in industry: Alkyl compounds find diverse applications in industrial processes, such as in the production of lubricants, plasticizers, and surfactants. They are also used as intermediates in the synthesis of more complex organic molecules.
- Alkyl compounds in polymer chemistry: Alkyl groups play a crucial role in polymer chemistry, influencing properties such as solubility, melting point, and mechanical strength. They are used in the production of various polymers and copolymers for different applications.
- Environmental and safety considerations of alkyl compounds: The use and handling of alkyl compounds often require specific safety measures due to their potential flammability and reactivity. Environmental impact assessments and regulations govern their production, use, and disposal to minimize ecological risks.
- Analytical methods for alkyl compounds: Various analytical techniques are employed to characterize and quantify alkyl compounds, including gas chromatography, mass spectrometry, and spectroscopic methods. These techniques are crucial for quality control and research in industries utilizing alkyl compounds.
02 Applications of alkyl compounds in industrial processes
Alkyl compounds find diverse applications in industrial processes, such as in the production of polymers, lubricants, and surfactants. They are also used as intermediates in the synthesis of more complex organic molecules and pharmaceutical compounds.Expand Specific Solutions03 Alkyl compounds in fuel and energy applications
Alkyl compounds play a significant role in fuel and energy applications. They are used as additives to improve fuel performance, reduce emissions, and enhance combustion efficiency in various types of engines and power generation systems.Expand Specific Solutions04 Environmental and safety considerations of alkyl compounds
The use and handling of alkyl compounds often require careful consideration of environmental and safety factors. This includes proper storage, transportation, and disposal methods, as well as measures to prevent environmental contamination and ensure worker safety during production and use.Expand Specific Solutions05 Alkyl compounds in personal care and cosmetic products
Alkyl compounds are utilized in various personal care and cosmetic products due to their emollient, surfactant, and solvent properties. They contribute to the formulation of skincare products, hair care items, and other cosmetic applications, enhancing product performance and stability.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Alkyl Compound Circular Economy
The market for alkyl compounds in circular economies is in its early growth stage, with increasing interest driven by sustainability goals and regulatory pressures. The market size is expanding as industries seek eco-friendly alternatives to traditional petrochemicals. Technological maturity varies across different applications, with some alkyl compounds already commercialized while others are still in development. Companies like Croda International Plc and Genomatica, Inc. are leading innovation in bio-based alkyl compounds, while established petrochemical players such as Sinopec Shanghai Petrochemical Co., Ltd. and Arkema, Inc. are adapting their portfolios to include more sustainable options. Research institutions like Massachusetts Institute of Technology and Northwestern University are contributing to advancing the field through fundamental research and collaborative industry partnerships.
Sinopec Shanghai Petrochemical Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Sinopec Shanghai Petrochemical Co., Ltd. has been exploring the potential of alkyl compounds in circular economies through various initiatives. They have developed a proprietary technology for producing bio-based ethylene and propylene, key building blocks for many alkyl compounds, from biomass feedstocks[1]. The company has also invested in chemical recycling technologies to convert plastic waste back into valuable alkyl compounds and other chemical intermediates[2]. Sinopec's circular economy approach includes the development of biodegradable plastics using alkyl-based monomers, which can be composted at end-of-life[3]. Additionally, they are researching catalytic processes to efficiently convert CO2 into useful alkyl compounds, contributing to carbon capture and utilization efforts[4].
Strengths: Large-scale production capabilities, integrated value chain from feedstock to end products. Weaknesses: Heavy reliance on traditional petrochemical processes, slower transition to fully renewable sources compared to some competitors.
Arkema, Inc.
Technical Solution: Arkema has developed innovative alkyl-based compounds for circular economies, focusing on bio-based and recyclable materials. Their Rilsan® polyamide 11, derived from castor oil, is 100% bio-based and offers high performance in various applications[1]. They've also introduced Pebax® Rnew, a thermoplastic elastomer partially derived from renewable resources[2]. Arkema's circular economy strategy includes developing products with recycled content, such as their Elium® recyclable thermoplastic resin for wind turbine blades[3]. The company is investing in chemical recycling technologies to convert end-of-life plastics back into high-quality raw materials[4].
Strengths: Strong focus on renewable resources and recyclability, diverse product portfolio. Weaknesses: Dependency on specific bio-based feedstocks, potential scalability challenges for some circular technologies.
Innovative Approaches in Alkyl Compound Upcycling
Catalytic reactions involving alkenes
PatentInactiveUS20090216025A1
Innovation
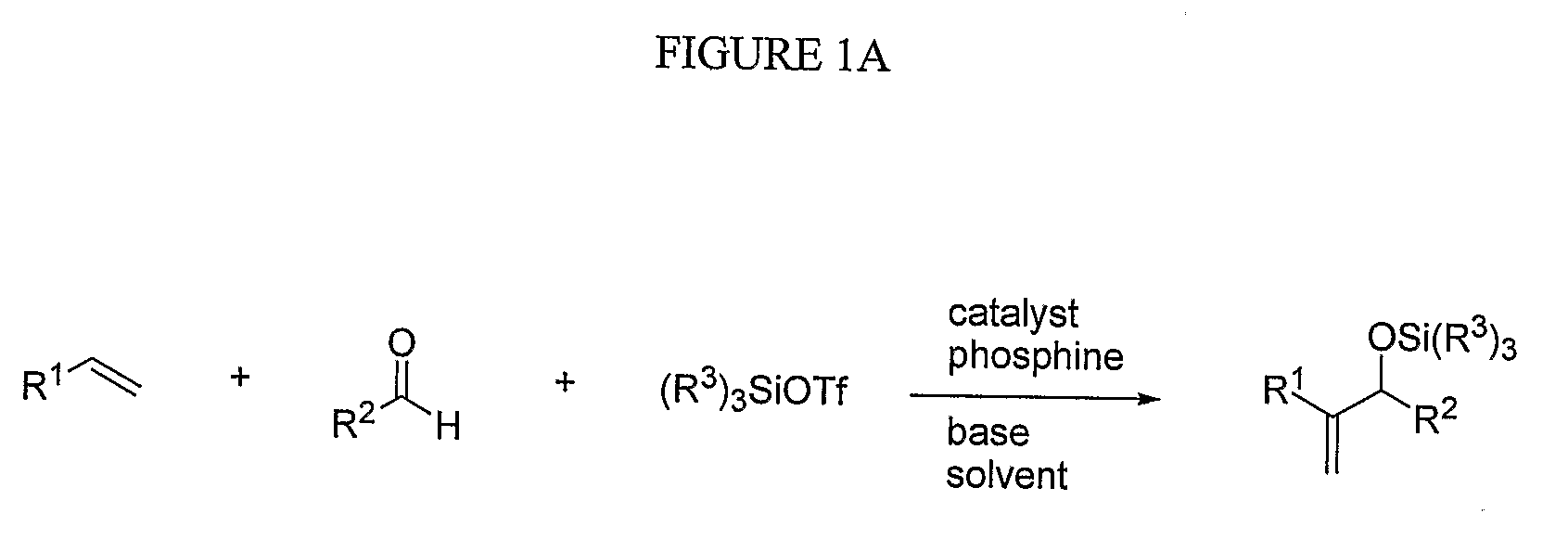
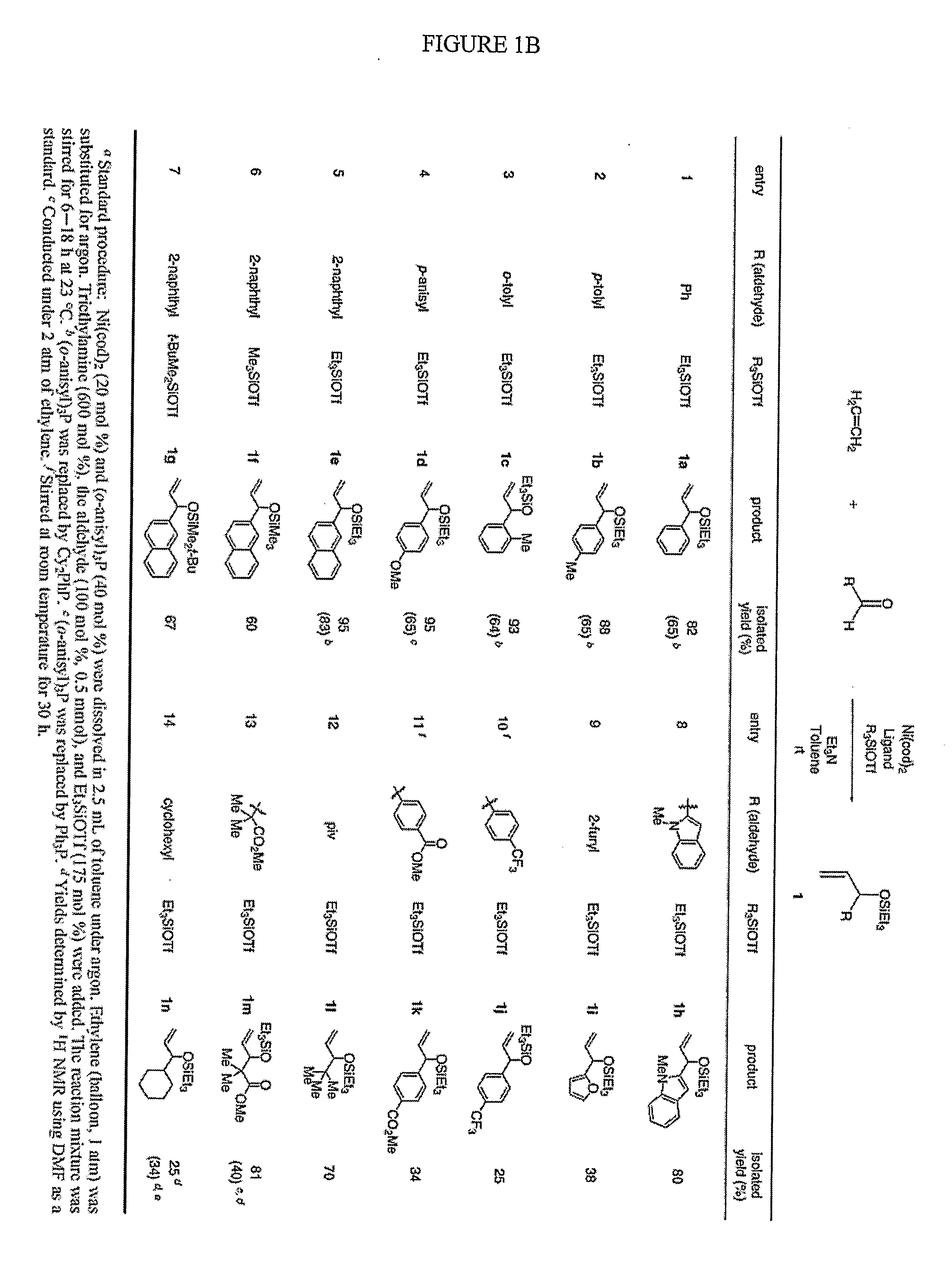
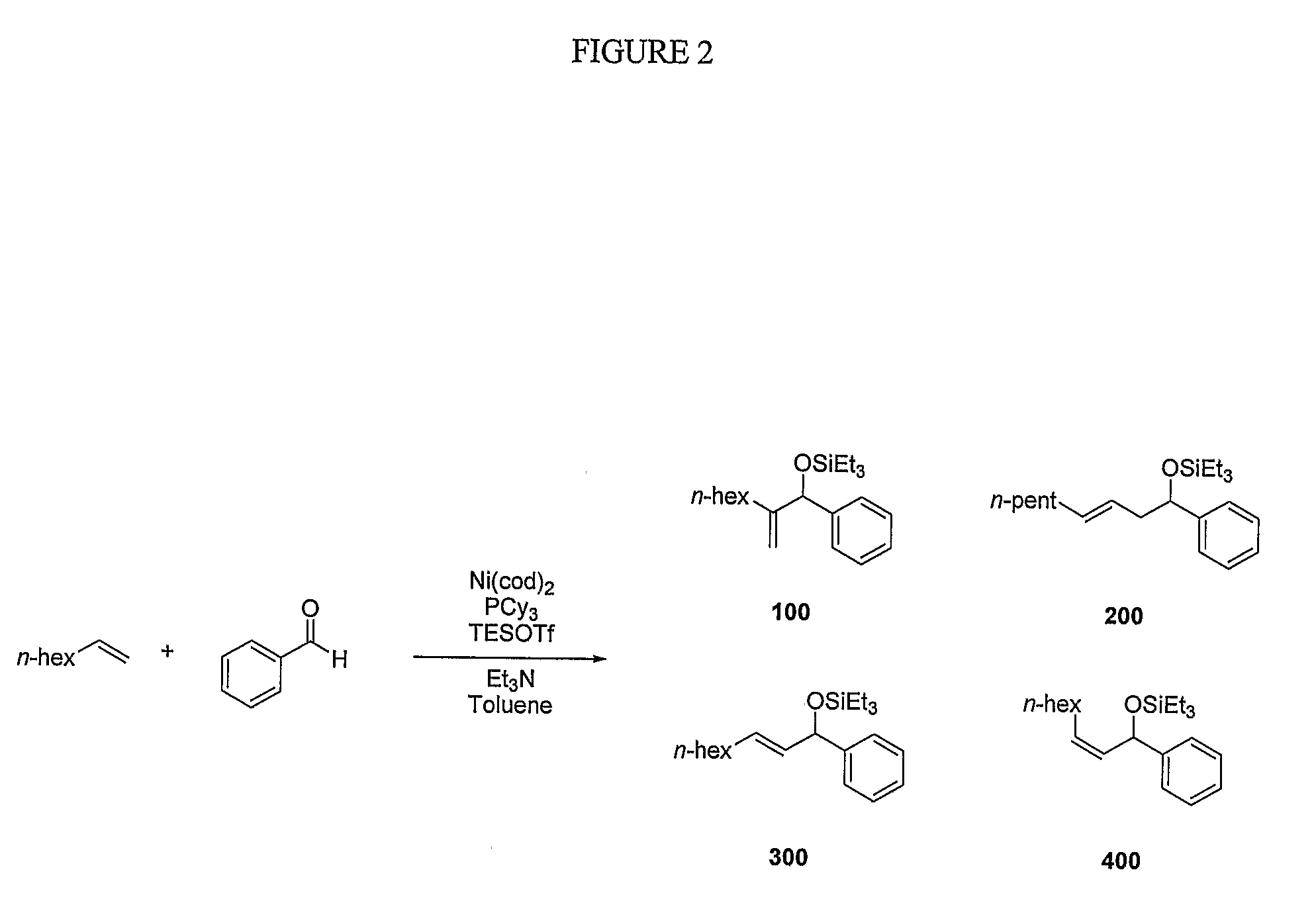
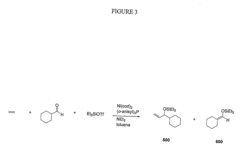
- A nickel-catalyzed method using a catalyst system comprising a nickel-containing compound, a phosphorus-containing ligand, a silicon-containing compound, and a base, which facilitates the coupling of alkenes and aldehydes to form allylic alcohols or their precursors, such as silyl ethers, under mild conditions, allowing for the use of alpha-olefins and avoiding the need for stoichiometric nickel.
Photoconductive members
PatentActiveUS7514192B2
Innovation
- Development of layered photoconductive imaging members using bis(tetrahalophenyl)biphenylbisimidazole or tetrahalobenzamidazolebenzene dimers, which are sensitive to blue light wavelengths between 350 to 450 nanometers, with a photogenerating layer deposited on a supporting substrate, enabling tunable electrical properties and stable performance.
Environmental Impact Assessment of Alkyl Compound Lifecycles
The environmental impact assessment of alkyl compound lifecycles is crucial for understanding their potential in circular economies. These compounds, widely used in various industries, have significant implications throughout their lifecycle stages.
Production of alkyl compounds often involves energy-intensive processes and the use of non-renewable resources. The extraction and refining of petroleum-based feedstocks contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and potential soil and water contamination. However, advancements in green chemistry are leading to more sustainable production methods, such as bio-based alkyl compounds derived from renewable resources.
During the use phase, alkyl compounds demonstrate diverse environmental impacts depending on their specific applications. In some cases, they contribute to improved energy efficiency and reduced emissions, particularly in lubricants and fuel additives. Conversely, certain alkyl compounds may pose risks of environmental contamination through leaching or volatilization, especially in consumer products and industrial processes.
End-of-life management of alkyl compounds presents both challenges and opportunities for circular economies. Traditional disposal methods, such as incineration or landfilling, can lead to air pollution and soil contamination. However, emerging recycling technologies are enabling the recovery and reuse of these compounds, reducing waste and conserving resources.
The persistence and bioaccumulation potential of some alkyl compounds raise concerns about long-term environmental effects. Certain long-chain alkyl compounds have been found to persist in ecosystems, potentially impacting wildlife and human health. This has led to increased regulatory scrutiny and the development of more environmentally friendly alternatives.
Water systems are particularly vulnerable to alkyl compound pollution. Runoff from agricultural and industrial sites can introduce these compounds into aquatic ecosystems, affecting water quality and aquatic life. Advanced wastewater treatment technologies are being developed to remove alkyl compounds more effectively, but their widespread implementation remains a challenge.
In the context of circular economies, the lifecycle assessment of alkyl compounds highlights the need for holistic approaches. This includes designing products for easier recycling, implementing closed-loop manufacturing processes, and developing more efficient recovery methods. Such strategies can significantly reduce the environmental footprint of alkyl compounds and enhance their role in sustainable economic models.
Production of alkyl compounds often involves energy-intensive processes and the use of non-renewable resources. The extraction and refining of petroleum-based feedstocks contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and potential soil and water contamination. However, advancements in green chemistry are leading to more sustainable production methods, such as bio-based alkyl compounds derived from renewable resources.
During the use phase, alkyl compounds demonstrate diverse environmental impacts depending on their specific applications. In some cases, they contribute to improved energy efficiency and reduced emissions, particularly in lubricants and fuel additives. Conversely, certain alkyl compounds may pose risks of environmental contamination through leaching or volatilization, especially in consumer products and industrial processes.
End-of-life management of alkyl compounds presents both challenges and opportunities for circular economies. Traditional disposal methods, such as incineration or landfilling, can lead to air pollution and soil contamination. However, emerging recycling technologies are enabling the recovery and reuse of these compounds, reducing waste and conserving resources.
The persistence and bioaccumulation potential of some alkyl compounds raise concerns about long-term environmental effects. Certain long-chain alkyl compounds have been found to persist in ecosystems, potentially impacting wildlife and human health. This has led to increased regulatory scrutiny and the development of more environmentally friendly alternatives.
Water systems are particularly vulnerable to alkyl compound pollution. Runoff from agricultural and industrial sites can introduce these compounds into aquatic ecosystems, affecting water quality and aquatic life. Advanced wastewater treatment technologies are being developed to remove alkyl compounds more effectively, but their widespread implementation remains a challenge.
In the context of circular economies, the lifecycle assessment of alkyl compounds highlights the need for holistic approaches. This includes designing products for easier recycling, implementing closed-loop manufacturing processes, and developing more efficient recovery methods. Such strategies can significantly reduce the environmental footprint of alkyl compounds and enhance their role in sustainable economic models.
Policy Framework for Promoting Alkyl Compound Circularity
The development of a comprehensive policy framework is crucial for promoting the circularity of alkyl compounds in the context of circular economies. Such a framework should address multiple aspects, including regulatory measures, economic incentives, and collaborative initiatives.
Regulatory measures form the foundation of the policy framework. These should include mandatory recycling targets for alkyl compounds, extended producer responsibility (EPR) schemes, and strict regulations on the disposal of alkyl compound waste. Implementing these measures would encourage manufacturers to design products with recyclability in mind and take responsibility for the entire lifecycle of their products.
Economic incentives play a vital role in driving the adoption of circular practices for alkyl compounds. Governments can introduce tax breaks or subsidies for companies that incorporate recycled alkyl compounds into their production processes. Additionally, implementing a carbon pricing mechanism that accounts for the environmental impact of alkyl compound production and disposal can further incentivize circular practices.
Collaborative initiatives between government, industry, and research institutions are essential for fostering innovation in alkyl compound circularity. Establishing public-private partnerships to fund research and development of new recycling technologies can accelerate progress in this field. Furthermore, creating platforms for knowledge sharing and best practice exchange among stakeholders can promote the widespread adoption of circular economy principles in the alkyl compound industry.
Education and awareness programs should be integrated into the policy framework to ensure public understanding and support for alkyl compound circularity. This can include consumer education campaigns on proper disposal and recycling of products containing alkyl compounds, as well as training programs for industry professionals on circular economy practices.
To ensure the effectiveness of the policy framework, robust monitoring and enforcement mechanisms must be put in place. This includes regular audits of companies' compliance with recycling targets and EPR schemes, as well as penalties for non-compliance. Additionally, establishing a system for tracking the flow of alkyl compounds throughout their lifecycle can provide valuable data for policy refinement and improvement.
International cooperation is another crucial aspect of the policy framework. Given the global nature of supply chains and environmental challenges, harmonizing policies and standards across countries can facilitate the transition to a circular economy for alkyl compounds. This can involve bilateral agreements, participation in international forums, and alignment with global sustainability goals.
Regulatory measures form the foundation of the policy framework. These should include mandatory recycling targets for alkyl compounds, extended producer responsibility (EPR) schemes, and strict regulations on the disposal of alkyl compound waste. Implementing these measures would encourage manufacturers to design products with recyclability in mind and take responsibility for the entire lifecycle of their products.
Economic incentives play a vital role in driving the adoption of circular practices for alkyl compounds. Governments can introduce tax breaks or subsidies for companies that incorporate recycled alkyl compounds into their production processes. Additionally, implementing a carbon pricing mechanism that accounts for the environmental impact of alkyl compound production and disposal can further incentivize circular practices.
Collaborative initiatives between government, industry, and research institutions are essential for fostering innovation in alkyl compound circularity. Establishing public-private partnerships to fund research and development of new recycling technologies can accelerate progress in this field. Furthermore, creating platforms for knowledge sharing and best practice exchange among stakeholders can promote the widespread adoption of circular economy principles in the alkyl compound industry.
Education and awareness programs should be integrated into the policy framework to ensure public understanding and support for alkyl compound circularity. This can include consumer education campaigns on proper disposal and recycling of products containing alkyl compounds, as well as training programs for industry professionals on circular economy practices.
To ensure the effectiveness of the policy framework, robust monitoring and enforcement mechanisms must be put in place. This includes regular audits of companies' compliance with recycling targets and EPR schemes, as well as penalties for non-compliance. Additionally, establishing a system for tracking the flow of alkyl compounds throughout their lifecycle can provide valuable data for policy refinement and improvement.
International cooperation is another crucial aspect of the policy framework. Given the global nature of supply chains and environmental challenges, harmonizing policies and standards across countries can facilitate the transition to a circular economy for alkyl compounds. This can involve bilateral agreements, participation in international forums, and alignment with global sustainability goals.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!