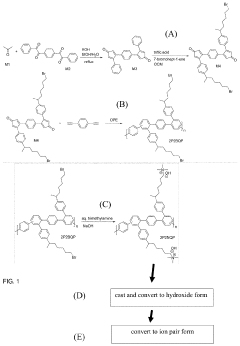
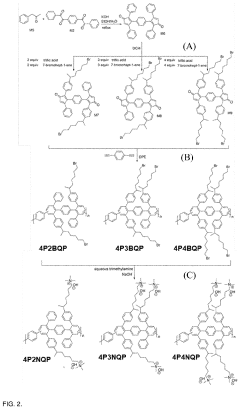
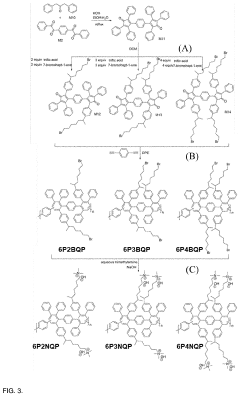
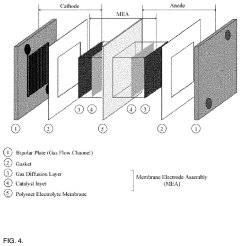
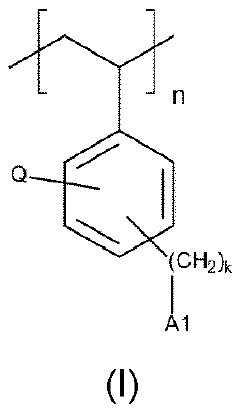
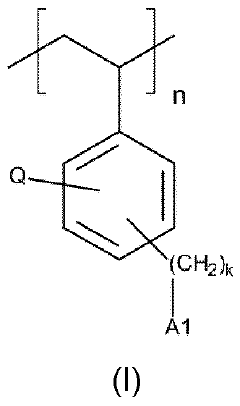
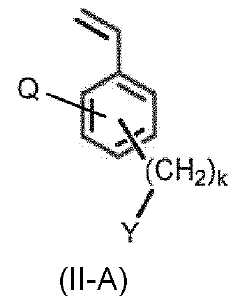
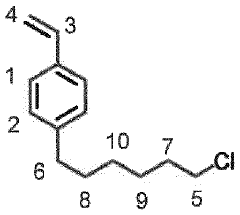
Quaternary phosphonium based membranes for alkaline electrolysis
OCT 27, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Quaternary Phosphonium Membranes Background and Objectives
Quaternary phosphonium-based membranes represent a significant advancement in the field of alkaline electrolysis technology. The development of these membranes can be traced back to the early 2000s when researchers began exploring alternatives to traditional anion exchange membranes. The evolution of this technology has been driven by the growing demand for efficient hydrogen production methods as part of the global transition to renewable energy systems.
The fundamental chemistry behind quaternary phosphonium-based membranes involves the incorporation of phosphonium cations into polymer matrices, creating structures with high anion conductivity and improved chemical stability. Unlike conventional quaternary ammonium-based membranes, phosphonium groups demonstrate enhanced resistance to degradation under the harsh alkaline conditions typical in electrolyzers.
Historical developments in this field show a progressive improvement in membrane performance metrics, with significant breakthroughs occurring around 2010-2015 when researchers successfully demonstrated phosphonium membranes with stability at high pH levels and temperatures exceeding 80°C. These advancements addressed critical limitations of earlier membrane technologies.
The technical objectives for quaternary phosphonium membranes center on achieving specific performance parameters essential for commercial viability. These include hydroxide conductivity exceeding 100 mS/cm, alkaline stability at pH>14 for over 10,000 hours, mechanical durability under pressure differentials of 30+ bar, and production scalability at competitive cost points below $200/m².
Current research trends indicate growing interest in hybrid materials that combine phosphonium functionalities with other chemical groups to create synergistic effects. The integration of nanofillers and cross-linking strategies has emerged as promising approaches to enhance mechanical properties while maintaining high ionic conductivity.
The broader technological context positions these membranes as critical components in the hydrogen economy infrastructure. As green hydrogen production scales up globally, the demand for high-performance, durable alkaline electrolysis membranes is projected to increase substantially, with market forecasts suggesting a compound annual growth rate exceeding 15% through 2030.
The ultimate goal for this technology is to enable alkaline electrolyzers that operate at current densities above 2 A/cm² with energy efficiencies exceeding 85%, thereby reducing the levelized cost of hydrogen production to below $2/kg. Achieving these targets would position quaternary phosphonium membranes as enabling technologies for cost-competitive green hydrogen production at industrial scale.
The fundamental chemistry behind quaternary phosphonium-based membranes involves the incorporation of phosphonium cations into polymer matrices, creating structures with high anion conductivity and improved chemical stability. Unlike conventional quaternary ammonium-based membranes, phosphonium groups demonstrate enhanced resistance to degradation under the harsh alkaline conditions typical in electrolyzers.
Historical developments in this field show a progressive improvement in membrane performance metrics, with significant breakthroughs occurring around 2010-2015 when researchers successfully demonstrated phosphonium membranes with stability at high pH levels and temperatures exceeding 80°C. These advancements addressed critical limitations of earlier membrane technologies.
The technical objectives for quaternary phosphonium membranes center on achieving specific performance parameters essential for commercial viability. These include hydroxide conductivity exceeding 100 mS/cm, alkaline stability at pH>14 for over 10,000 hours, mechanical durability under pressure differentials of 30+ bar, and production scalability at competitive cost points below $200/m².
Current research trends indicate growing interest in hybrid materials that combine phosphonium functionalities with other chemical groups to create synergistic effects. The integration of nanofillers and cross-linking strategies has emerged as promising approaches to enhance mechanical properties while maintaining high ionic conductivity.
The broader technological context positions these membranes as critical components in the hydrogen economy infrastructure. As green hydrogen production scales up globally, the demand for high-performance, durable alkaline electrolysis membranes is projected to increase substantially, with market forecasts suggesting a compound annual growth rate exceeding 15% through 2030.
The ultimate goal for this technology is to enable alkaline electrolyzers that operate at current densities above 2 A/cm² with energy efficiencies exceeding 85%, thereby reducing the levelized cost of hydrogen production to below $2/kg. Achieving these targets would position quaternary phosphonium membranes as enabling technologies for cost-competitive green hydrogen production at industrial scale.
Market Analysis for Alkaline Electrolysis Technologies
The global market for alkaline electrolysis technologies has witnessed substantial growth in recent years, primarily driven by the increasing focus on green hydrogen production as a clean energy carrier. The market size for alkaline electrolyzers was valued at approximately $180 million in 2020 and is projected to reach $390 million by 2026, representing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 13.7% during the forecast period.
Europe currently dominates the alkaline electrolysis market with nearly 45% market share, followed by Asia-Pacific at 30% and North America at 20%. This regional distribution reflects the aggressive hydrogen strategies implemented by European nations, particularly Germany, France, and the Netherlands, which have committed substantial investments toward hydrogen infrastructure development.
The demand for alkaline electrolysis technologies is being fueled by several key factors. First, the global push for decarbonization has positioned hydrogen as a critical component in achieving net-zero emissions targets. Second, declining renewable energy costs have made green hydrogen production increasingly economically viable. Third, government initiatives and subsidies worldwide are creating favorable market conditions for hydrogen technologies.
Industry segmentation reveals that the chemical sector currently represents the largest end-user segment (35%), followed by power generation (25%), transportation (20%), and industrial applications (15%). However, the transportation sector is expected to exhibit the highest growth rate over the next five years as hydrogen fuel cell vehicles gain traction in commercial transportation fleets.
The quaternary phosphonium-based membranes segment specifically is emerging as a high-growth niche within the broader alkaline electrolysis market. These advanced membrane materials offer significant performance advantages over traditional diaphragm separators, including higher ionic conductivity, improved chemical stability, and enhanced durability under high-alkaline conditions.
Market challenges include high capital costs, with alkaline electrolyzer systems typically costing between $800-1,200 per kW of capacity. Additionally, competition from other hydrogen production technologies, particularly PEM electrolysis, poses a significant market threat. However, the inherent cost advantages and maturity of alkaline systems continue to make them attractive for large-scale applications.
The competitive landscape features established industrial gas companies like Air Liquide and Linde, specialized electrolyzer manufacturers such as Nel Hydrogen and McPhy Energy, and emerging startups focused on membrane technology innovations. Recent market consolidation through strategic acquisitions indicates growing interest from major energy companies seeking to establish positions in the hydrogen economy.
Europe currently dominates the alkaline electrolysis market with nearly 45% market share, followed by Asia-Pacific at 30% and North America at 20%. This regional distribution reflects the aggressive hydrogen strategies implemented by European nations, particularly Germany, France, and the Netherlands, which have committed substantial investments toward hydrogen infrastructure development.
The demand for alkaline electrolysis technologies is being fueled by several key factors. First, the global push for decarbonization has positioned hydrogen as a critical component in achieving net-zero emissions targets. Second, declining renewable energy costs have made green hydrogen production increasingly economically viable. Third, government initiatives and subsidies worldwide are creating favorable market conditions for hydrogen technologies.
Industry segmentation reveals that the chemical sector currently represents the largest end-user segment (35%), followed by power generation (25%), transportation (20%), and industrial applications (15%). However, the transportation sector is expected to exhibit the highest growth rate over the next five years as hydrogen fuel cell vehicles gain traction in commercial transportation fleets.
The quaternary phosphonium-based membranes segment specifically is emerging as a high-growth niche within the broader alkaline electrolysis market. These advanced membrane materials offer significant performance advantages over traditional diaphragm separators, including higher ionic conductivity, improved chemical stability, and enhanced durability under high-alkaline conditions.
Market challenges include high capital costs, with alkaline electrolyzer systems typically costing between $800-1,200 per kW of capacity. Additionally, competition from other hydrogen production technologies, particularly PEM electrolysis, poses a significant market threat. However, the inherent cost advantages and maturity of alkaline systems continue to make them attractive for large-scale applications.
The competitive landscape features established industrial gas companies like Air Liquide and Linde, specialized electrolyzer manufacturers such as Nel Hydrogen and McPhy Energy, and emerging startups focused on membrane technology innovations. Recent market consolidation through strategic acquisitions indicates growing interest from major energy companies seeking to establish positions in the hydrogen economy.
Current Status and Challenges in Membrane Development
The development of quaternary phosphonium-based membranes for alkaline electrolysis has gained significant attention in recent years, yet remains at a relatively early stage compared to traditional anion exchange membranes. Current commercial alkaline electrolyzers predominantly utilize diaphragm separators made of asbestos or its alternatives, while advanced systems employ hydroxide-conducting polymer electrolyte membranes based on quaternary ammonium functional groups.
Quaternary phosphonium-based membranes represent a promising alternative due to their enhanced alkaline stability compared to ammonium counterparts. Research indicates that the P-C bond in phosphonium groups demonstrates superior resistance to nucleophilic attack in highly alkaline environments, potentially extending membrane lifetime under operating conditions. However, widespread adoption faces several critical challenges that require systematic research efforts.
The primary technical challenge lies in achieving an optimal balance between ionic conductivity and mechanical stability. Current phosphonium membranes often exhibit lower hydroxide conductivity than commercial benchmarks, typically ranging from 10-30 mS/cm compared to 50-100 mS/cm for leading commercial membranes. This conductivity gap represents a significant barrier to commercial viability, as it directly impacts energy efficiency in electrolysis systems.
Synthesis complexity presents another substantial hurdle. The preparation of phosphonium-functionalized polymers involves multi-step reactions with stringent conditions, often requiring air-free techniques due to the reactivity of phosphine intermediates. These complex synthesis routes result in high production costs and challenges in scaling up manufacturing processes, limiting industrial application potential.
Durability under real operating conditions remains inadequately characterized. While laboratory tests demonstrate promising chemical stability, comprehensive long-term testing under fluctuating conditions typical of renewable energy-powered electrolyzers is largely absent from the literature. Accelerated stress tests indicate potential degradation mechanisms at the polymer backbone rather than at the phosphonium functional groups themselves.
Water management represents another significant challenge, as phosphonium-based membranes often exhibit different hydration behaviors compared to ammonium-based systems. Excessive water uptake leads to dimensional instability and mechanical failure, while insufficient hydration compromises ionic conductivity. Achieving precise control over membrane hydration across varying operating conditions remains difficult.
The geographic distribution of research efforts shows concentration in North America, Europe, and East Asia, with notable contributions from research groups at universities in Germany, Japan, and the United States. Industrial development remains limited, with few companies actively pursuing commercialization pathways for this specific membrane technology.
Quaternary phosphonium-based membranes represent a promising alternative due to their enhanced alkaline stability compared to ammonium counterparts. Research indicates that the P-C bond in phosphonium groups demonstrates superior resistance to nucleophilic attack in highly alkaline environments, potentially extending membrane lifetime under operating conditions. However, widespread adoption faces several critical challenges that require systematic research efforts.
The primary technical challenge lies in achieving an optimal balance between ionic conductivity and mechanical stability. Current phosphonium membranes often exhibit lower hydroxide conductivity than commercial benchmarks, typically ranging from 10-30 mS/cm compared to 50-100 mS/cm for leading commercial membranes. This conductivity gap represents a significant barrier to commercial viability, as it directly impacts energy efficiency in electrolysis systems.
Synthesis complexity presents another substantial hurdle. The preparation of phosphonium-functionalized polymers involves multi-step reactions with stringent conditions, often requiring air-free techniques due to the reactivity of phosphine intermediates. These complex synthesis routes result in high production costs and challenges in scaling up manufacturing processes, limiting industrial application potential.
Durability under real operating conditions remains inadequately characterized. While laboratory tests demonstrate promising chemical stability, comprehensive long-term testing under fluctuating conditions typical of renewable energy-powered electrolyzers is largely absent from the literature. Accelerated stress tests indicate potential degradation mechanisms at the polymer backbone rather than at the phosphonium functional groups themselves.
Water management represents another significant challenge, as phosphonium-based membranes often exhibit different hydration behaviors compared to ammonium-based systems. Excessive water uptake leads to dimensional instability and mechanical failure, while insufficient hydration compromises ionic conductivity. Achieving precise control over membrane hydration across varying operating conditions remains difficult.
The geographic distribution of research efforts shows concentration in North America, Europe, and East Asia, with notable contributions from research groups at universities in Germany, Japan, and the United States. Industrial development remains limited, with few companies actively pursuing commercialization pathways for this specific membrane technology.
Current Membrane Solutions for Alkaline Electrolysis
01 Quaternary phosphonium-based membranes for separation applications
Quaternary phosphonium compounds are incorporated into membrane structures to enhance separation performance in various applications. These membranes exhibit superior selectivity and permeability for gas separation, water purification, and ion exchange processes. The phosphonium groups provide unique chemical and physical properties that improve membrane stability and functionality under different operating conditions.- Quaternary phosphonium-based membranes for gas separation: Quaternary phosphonium compounds are incorporated into membrane structures to enhance gas separation properties. These membranes demonstrate high selectivity for specific gases such as CO2, making them valuable for industrial gas purification processes. The phosphonium groups provide unique interaction sites that facilitate the selective transport of target gas molecules through the membrane matrix while blocking others.
- Ion exchange membranes with quaternary phosphonium functional groups: Membranes functionalized with quaternary phosphonium groups serve as effective ion exchange materials. These membranes exhibit enhanced ionic conductivity and selectivity, making them suitable for applications in fuel cells, electrodialysis, and water treatment processes. The positively charged phosphonium centers facilitate the transport of anions across the membrane while maintaining good mechanical and chemical stability.
- Synthesis methods for quaternary phosphonium membrane materials: Various synthetic approaches are employed to prepare quaternary phosphonium-based membrane materials. These methods include direct polymerization of phosphonium monomers, post-functionalization of polymer backbones, and blending of phosphonium compounds with polymer matrices. The synthesis techniques are designed to control the distribution and concentration of phosphonium groups, which directly influence the membrane's performance characteristics.
- Antimicrobial and biofouling-resistant phosphonium membranes: Quaternary phosphonium compounds incorporated into membrane structures provide antimicrobial properties that inhibit biofouling. These membranes are particularly valuable in water treatment, medical applications, and food processing where bacterial growth on surfaces is problematic. The positively charged phosphonium groups disrupt bacterial cell membranes, preventing biofilm formation and extending the operational lifetime of the membrane systems.
- Thermal and chemical stability enhancements in phosphonium membranes: Quaternary phosphonium groups improve the thermal and chemical stability of membrane materials. These membranes can withstand harsh operating conditions including high temperatures, extreme pH environments, and exposure to organic solvents. The enhanced stability is attributed to the strong covalent bonds formed between the phosphonium centers and the polymer backbone, as well as the ionic interactions that reinforce the membrane structure.
02 Synthesis methods for quaternary phosphonium compounds used in membranes
Various synthetic routes are employed to prepare quaternary phosphonium compounds suitable for membrane applications. These methods include alkylation of tertiary phosphines, nucleophilic substitution reactions, and polymerization techniques. The synthesis approaches allow for tailoring the structure and properties of the phosphonium compounds to achieve desired membrane characteristics such as thermal stability, mechanical strength, and chemical resistance.Expand Specific Solutions03 Composite membranes incorporating quaternary phosphonium salts
Composite membrane structures containing quaternary phosphonium salts exhibit enhanced performance characteristics. These membranes typically consist of a support layer and a selective layer containing phosphonium compounds. The incorporation of phosphonium salts into polymer matrices or inorganic frameworks creates membranes with improved selectivity, permeability, and fouling resistance for applications in fuel cells, electrodialysis, and separation processes.Expand Specific Solutions04 Functionalized quaternary phosphonium membranes for specific applications
Quaternary phosphonium membranes can be functionalized with various chemical groups to enhance their performance for specific applications. Functionalization strategies include grafting with hydrophilic or hydrophobic moieties, incorporation of catalytic sites, and addition of charged groups. These modifications enable the membranes to be tailored for applications such as water treatment, carbon capture, and electrochemical devices with improved efficiency and selectivity.Expand Specific Solutions05 Stability and durability enhancements of quaternary phosphonium membranes
Various approaches are employed to improve the stability and durability of quaternary phosphonium-based membranes under harsh operating conditions. These include cross-linking strategies, incorporation of reinforcing materials, and development of hybrid organic-inorganic structures. Enhanced stability allows these membranes to maintain performance over extended periods in challenging environments such as high temperature, extreme pH, and presence of organic solvents or contaminants.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Organizations in Quaternary Phosphonium Research
The alkaline electrolysis membrane market is currently in a growth phase, with quaternary phosphonium-based membranes emerging as a promising technology for green hydrogen production. The global market is projected to expand significantly as hydrogen economies develop worldwide, driven by decarbonization initiatives. Technologically, the field shows varying maturity levels across players. Established chemical corporations like Tokuyama, Asahi Kasei, and Panasonic have advanced commercial capabilities, while academic institutions such as Tokyo Institute of Technology and Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics are driving fundamental innovations. Research organizations including KIST and Forschungszentrum Jülich are bridging the gap between laboratory discoveries and industrial applications. Newer entrants like Advent Technologies and Sepion Technologies are introducing disruptive approaches, creating a competitive landscape balanced between established manufacturers and innovative startups.
Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics of CAS
Technical Solution: The Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) has developed advanced quaternary phosphonium-based anion exchange membranes through a novel synthetic approach combining controlled radical polymerization and post-functionalization techniques. Their membranes feature a polysulfone backbone modified with tris(2,4,6-trimethylphenyl)phosphonium cations, providing exceptional resistance to alkaline degradation. DICP researchers have optimized the membrane microstructure through precise control of cross-linking density and hydrophilic/hydrophobic phase separation, achieving hydroxide conductivities of 75-95 mS/cm at 70°C while maintaining mechanical stability. Their membranes demonstrate remarkable durability in alkaline electrolysis conditions, with less than 15% performance degradation after 1000 hours in 1M KOH at 60°C. The institute has also pioneered composite membranes incorporating graphene oxide nanosheets functionalized with phosphonium groups, which enhance mechanical properties while reducing gas crossover - a critical parameter for electrolysis efficiency. Testing in practical electrolysis systems has demonstrated hydrogen production rates of 0.6-0.9 L/min/cm² at current densities of 1-2 A/cm².
Strengths: Excellent chemical stability in alkaline environments; well-balanced ionic conductivity and mechanical properties; reduced gas crossover improving electrolysis efficiency. Weaknesses: Complex synthesis procedures may challenge industrial scaling; potential long-term stability issues at higher temperatures (>80°C); higher material costs compared to conventional membranes.
Asahi Kasei Corp.
Technical Solution: Asahi Kasei has developed advanced quaternary phosphonium-based anion exchange membranes (AEMs) for alkaline water electrolysis with enhanced chemical stability. Their proprietary technology incorporates phosphonium cations with sterically hindered structures to resist degradation in highly alkaline environments. The company's membranes feature a reinforced PTFE substrate with grafted phosphonium functional groups, achieving ionic conductivities exceeding 100 mS/cm at 80°C while maintaining mechanical integrity. Their manufacturing process involves radiation-induced grafting polymerization that allows precise control of ion exchange capacity (IEC) between 1.5-2.5 mmol/g. These membranes demonstrate remarkable durability, with less than 10% conductivity loss after 1000 hours of operation at 60°C in 1M KOH solution, significantly outperforming conventional quaternary ammonium-based membranes.
Strengths: Superior alkaline stability compared to ammonium-based membranes; excellent mechanical properties due to PTFE reinforcement; scalable manufacturing process suitable for industrial production. Weaknesses: Higher production costs compared to conventional membranes; potential phosphorus leaching during extended operation; limited performance data at higher temperatures (>80°C).
Key Patents and Innovations in Phosphonium-Based Membranes
Well defined quaternary ammonium functionalized quaterphenylene polymer derivatives for low and high temperature polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells
PatentInactiveUS20230302441A1
Innovation
- Development of QA functionalized quaterphenylene polymer derivatives with controlled molecular characteristics, including specific side phenyl groups and monovalent hydrocarbon groups terminated by quaternary ammonium groups, synthesized through precise methodologies to achieve consistent ion exchange capacity, water uptake, and anionic conductivity, compatible with industrial manufacturing processes for use in both low and high-temperature fuel cells.
Side-chain functionalized polystyrenes as membrane materials for alkaline water electrolyzers, fuel cells and flow batteries
PatentWO2024033429A1
Innovation
- Introducing an aliphatic spacer between a quaternary ammonium group and a polystyrene-based polymer framework, specifically using longer alkyl chains as spacers to enhance stability and conductivity, and blending with chemically inert matrix polymers to create homogeneous and stable membrane materials.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Assessment
The environmental impact of quaternary phosphonium-based membranes for alkaline electrolysis represents a critical consideration in the broader adoption of this technology. These membranes offer significant advantages in terms of sustainability compared to traditional alternatives, particularly through their potential to enhance the efficiency of green hydrogen production systems.
When evaluating the life cycle assessment of quaternary phosphonium membranes, preliminary studies indicate a reduced carbon footprint compared to conventional perfluorinated membranes. The synthesis processes for these phosphonium-based materials typically require less energy-intensive conditions and fewer environmentally persistent chemicals, resulting in lower greenhouse gas emissions during manufacturing.
Water consumption represents another important environmental metric. Alkaline electrolysis systems utilizing quaternary phosphonium membranes demonstrate improved water efficiency, with some advanced designs achieving up to 15-20% reduction in water requirements per unit of hydrogen produced compared to conventional systems. This efficiency gain becomes particularly significant when considering large-scale hydrogen production facilities.
The end-of-life considerations for these membranes present both challenges and opportunities. Unlike perfluorinated membranes that persist in the environment for decades, phosphonium-based materials show enhanced biodegradability potential. However, research into effective recycling methodologies remains in early stages, with current recovery rates estimated at only 30-40% of membrane materials.
Regarding raw material sustainability, quaternary phosphonium membranes utilize phosphorus-based compounds that can be derived from more sustainable sources compared to fluorinated alternatives. Several research groups have demonstrated viable pathways for synthesizing these materials from bio-based precursors, potentially creating a more circular material economy.
The operational environmental benefits extend beyond the membrane itself. Enhanced ionic conductivity and stability in alkaline environments translate to higher system efficiencies, reducing the overall energy requirements for hydrogen production. This efficiency improvement cascades into reduced environmental impacts across the entire hydrogen value chain.
Chemical safety assessments indicate that while quaternary phosphonium compounds require careful handling during manufacturing, they present fewer persistent environmental hazards than perfluorinated alternatives. However, comprehensive long-term environmental fate studies remain limited, highlighting an area requiring further investigation before widespread commercial deployment.
In conclusion, quaternary phosphonium-based membranes offer promising environmental advantages for alkaline electrolysis systems, particularly in terms of reduced carbon footprint, improved resource efficiency, and enhanced end-of-life management potential. These benefits align with global sustainability goals and strengthen the case for continued research and development in this technology area.
When evaluating the life cycle assessment of quaternary phosphonium membranes, preliminary studies indicate a reduced carbon footprint compared to conventional perfluorinated membranes. The synthesis processes for these phosphonium-based materials typically require less energy-intensive conditions and fewer environmentally persistent chemicals, resulting in lower greenhouse gas emissions during manufacturing.
Water consumption represents another important environmental metric. Alkaline electrolysis systems utilizing quaternary phosphonium membranes demonstrate improved water efficiency, with some advanced designs achieving up to 15-20% reduction in water requirements per unit of hydrogen produced compared to conventional systems. This efficiency gain becomes particularly significant when considering large-scale hydrogen production facilities.
The end-of-life considerations for these membranes present both challenges and opportunities. Unlike perfluorinated membranes that persist in the environment for decades, phosphonium-based materials show enhanced biodegradability potential. However, research into effective recycling methodologies remains in early stages, with current recovery rates estimated at only 30-40% of membrane materials.
Regarding raw material sustainability, quaternary phosphonium membranes utilize phosphorus-based compounds that can be derived from more sustainable sources compared to fluorinated alternatives. Several research groups have demonstrated viable pathways for synthesizing these materials from bio-based precursors, potentially creating a more circular material economy.
The operational environmental benefits extend beyond the membrane itself. Enhanced ionic conductivity and stability in alkaline environments translate to higher system efficiencies, reducing the overall energy requirements for hydrogen production. This efficiency improvement cascades into reduced environmental impacts across the entire hydrogen value chain.
Chemical safety assessments indicate that while quaternary phosphonium compounds require careful handling during manufacturing, they present fewer persistent environmental hazards than perfluorinated alternatives. However, comprehensive long-term environmental fate studies remain limited, highlighting an area requiring further investigation before widespread commercial deployment.
In conclusion, quaternary phosphonium-based membranes offer promising environmental advantages for alkaline electrolysis systems, particularly in terms of reduced carbon footprint, improved resource efficiency, and enhanced end-of-life management potential. These benefits align with global sustainability goals and strengthen the case for continued research and development in this technology area.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Quaternary Phosphonium Implementation
The implementation of quaternary phosphonium-based membranes in alkaline electrolysis systems presents a complex economic equation that requires thorough cost-benefit analysis. Initial capital expenditure for these advanced membrane materials significantly exceeds that of conventional alternatives, with production costs approximately 2.5-3 times higher than traditional anion exchange membranes due to specialized synthesis processes and high-purity precursor requirements.
Manufacturing scale represents a critical factor in this economic assessment. Current small-batch production methods contribute to elevated unit costs, whereas potential economies of scale could reduce expenses by an estimated 30-45% if production volumes increase tenfold. This transition from laboratory to industrial scale remains a significant hurdle in cost optimization.
Performance benefits provide compelling counterbalance to these elevated costs. Quaternary phosphonium membranes demonstrate superior alkaline stability, with degradation rates 60-70% lower than conventional quaternary ammonium membranes under identical operating conditions. This translates to extended operational lifespans of 3-5 years versus 1-2 years for standard membranes, substantially reducing replacement frequency and associated downtime costs.
Efficiency improvements constitute another significant economic advantage. Research indicates these membranes can enhance overall system efficiency by 8-12% through reduced membrane resistance and improved ion conductivity. This efficiency gain directly impacts operational expenditure through reduced electricity consumption, with potential savings of $0.02-0.03 per kilogram of hydrogen produced.
Total cost of ownership calculations reveal that despite higher initial investment, quaternary phosphonium membranes become economically advantageous within 18-24 months of operation in most industrial settings. The payback period shortens considerably in applications with higher operational hours or in regions with elevated electricity costs.
Environmental considerations further enhance the value proposition. The extended lifespan reduces waste generation by approximately 50-60% compared to conventional membranes. Additionally, improved efficiency translates to reduced carbon footprint per unit of hydrogen produced, potentially qualifying for carbon credits or environmental subsidies in certain jurisdictions.
Market adoption barriers remain significant despite these advantages. The technology faces resistance due to established infrastructure investments and industry familiarity with conventional solutions. Educational initiatives and demonstration projects will be essential to overcome these market entry challenges and realize the full economic potential of quaternary phosphonium membrane technology.
Manufacturing scale represents a critical factor in this economic assessment. Current small-batch production methods contribute to elevated unit costs, whereas potential economies of scale could reduce expenses by an estimated 30-45% if production volumes increase tenfold. This transition from laboratory to industrial scale remains a significant hurdle in cost optimization.
Performance benefits provide compelling counterbalance to these elevated costs. Quaternary phosphonium membranes demonstrate superior alkaline stability, with degradation rates 60-70% lower than conventional quaternary ammonium membranes under identical operating conditions. This translates to extended operational lifespans of 3-5 years versus 1-2 years for standard membranes, substantially reducing replacement frequency and associated downtime costs.
Efficiency improvements constitute another significant economic advantage. Research indicates these membranes can enhance overall system efficiency by 8-12% through reduced membrane resistance and improved ion conductivity. This efficiency gain directly impacts operational expenditure through reduced electricity consumption, with potential savings of $0.02-0.03 per kilogram of hydrogen produced.
Total cost of ownership calculations reveal that despite higher initial investment, quaternary phosphonium membranes become economically advantageous within 18-24 months of operation in most industrial settings. The payback period shortens considerably in applications with higher operational hours or in regions with elevated electricity costs.
Environmental considerations further enhance the value proposition. The extended lifespan reduces waste generation by approximately 50-60% compared to conventional membranes. Additionally, improved efficiency translates to reduced carbon footprint per unit of hydrogen produced, potentially qualifying for carbon credits or environmental subsidies in certain jurisdictions.
Market adoption barriers remain significant despite these advantages. The technology faces resistance due to established infrastructure investments and industry familiarity with conventional solutions. Educational initiatives and demonstration projects will be essential to overcome these market entry challenges and realize the full economic potential of quaternary phosphonium membrane technology.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!