Recent breakthroughs in blue OLED material for AMOLED.
JUL 17, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Blue OLED Evolution
The evolution of blue OLED materials for AMOLED displays has been a critical focus in the display industry due to the challenges associated with achieving stable, efficient, and long-lasting blue emitters. The journey began in the late 1980s with the discovery of electroluminescence in organic materials, but it wasn't until the early 2000s that significant progress was made in blue OLED development.
Initially, fluorescent blue emitters were the primary focus, with materials such as 9,10-di(2-naphthyl)anthracene (ADN) and 4,4'-bis(2,2'-diphenylvinyl)-1,1'-biphenyl (DPVBi) being widely used. These first-generation materials offered moderate efficiency but suffered from short lifetimes and color instability.
The mid-2000s saw the introduction of phosphorescent emitters, which dramatically improved the efficiency of red and green OLEDs. However, developing stable phosphorescent blue emitters proved challenging due to their high triplet energy levels, which led to rapid degradation of the host materials.
A significant breakthrough came in the early 2010s with the development of thermally activated delayed fluorescence (TADF) materials. TADF emitters, such as those based on carbazole-dicyanobenzene derivatives, offered a promising alternative by harvesting both singlet and triplet excitons without the use of heavy metals, potentially achieving 100% internal quantum efficiency.
Recent years have seen remarkable advancements in blue OLED materials. Hyperfluorescence, which combines TADF and fluorescent emitters, has emerged as a promising approach. This technique allows for efficient energy transfer from TADF assistant dopants to narrow-emission fluorescent emitters, resulting in improved color purity and efficiency.
Another significant development has been the exploration of multi-carbazole-based host materials for blue phosphorescent OLEDs. These materials offer high triplet energy levels and good charge transport properties, addressing the host stability issues that have long plagued blue PHOLEDs.
The most recent breakthroughs include the development of boron-based TADF emitters, which have shown exceptional performance in terms of external quantum efficiency and operational lifetime. Additionally, novel device architectures, such as tandem structures and micro-cavity designs, have been employed to enhance the overall performance of blue OLEDs.
As we move forward, the focus is shifting towards achieving ultra-stable blue emitters that can match the longevity of their red and green counterparts. Research into new molecular designs, such as multi-resonance TADF materials and exciplex systems, is ongoing and shows promise for future generations of blue OLED materials.
Initially, fluorescent blue emitters were the primary focus, with materials such as 9,10-di(2-naphthyl)anthracene (ADN) and 4,4'-bis(2,2'-diphenylvinyl)-1,1'-biphenyl (DPVBi) being widely used. These first-generation materials offered moderate efficiency but suffered from short lifetimes and color instability.
The mid-2000s saw the introduction of phosphorescent emitters, which dramatically improved the efficiency of red and green OLEDs. However, developing stable phosphorescent blue emitters proved challenging due to their high triplet energy levels, which led to rapid degradation of the host materials.
A significant breakthrough came in the early 2010s with the development of thermally activated delayed fluorescence (TADF) materials. TADF emitters, such as those based on carbazole-dicyanobenzene derivatives, offered a promising alternative by harvesting both singlet and triplet excitons without the use of heavy metals, potentially achieving 100% internal quantum efficiency.
Recent years have seen remarkable advancements in blue OLED materials. Hyperfluorescence, which combines TADF and fluorescent emitters, has emerged as a promising approach. This technique allows for efficient energy transfer from TADF assistant dopants to narrow-emission fluorescent emitters, resulting in improved color purity and efficiency.
Another significant development has been the exploration of multi-carbazole-based host materials for blue phosphorescent OLEDs. These materials offer high triplet energy levels and good charge transport properties, addressing the host stability issues that have long plagued blue PHOLEDs.
The most recent breakthroughs include the development of boron-based TADF emitters, which have shown exceptional performance in terms of external quantum efficiency and operational lifetime. Additionally, novel device architectures, such as tandem structures and micro-cavity designs, have been employed to enhance the overall performance of blue OLEDs.
As we move forward, the focus is shifting towards achieving ultra-stable blue emitters that can match the longevity of their red and green counterparts. Research into new molecular designs, such as multi-resonance TADF materials and exciplex systems, is ongoing and shows promise for future generations of blue OLED materials.
AMOLED Market Trends
The AMOLED market has been experiencing significant growth and transformation in recent years, driven by the increasing demand for high-quality displays in smartphones, televisions, and other electronic devices. This trend is particularly evident in the mobile device sector, where AMOLED technology has become a standard feature in premium smartphones due to its superior color reproduction, contrast ratios, and energy efficiency.
The global AMOLED market size has been expanding rapidly, with projections indicating continued growth in the coming years. This growth is attributed to the technology's adoption in various applications beyond smartphones, including smartwatches, automotive displays, and virtual reality devices. The increasing consumer preference for devices with vibrant displays and longer battery life has been a key factor in driving AMOLED adoption.
In the smartphone segment, major manufacturers have been incorporating AMOLED displays into their flagship models, with some even extending this technology to mid-range devices. This trend has led to increased production capacity and technological advancements in AMOLED manufacturing, resulting in improved yields and reduced costs.
The television market has also seen a surge in AMOLED adoption, particularly in the high-end segment. AMOLED TVs offer superior picture quality, wider viewing angles, and thinner form factors compared to traditional LCD technology. As production costs continue to decrease, AMOLED TVs are expected to gain market share in the premium television segment.
Emerging applications in the automotive industry present another growth opportunity for AMOLED technology. Advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and in-vehicle infotainment systems are increasingly incorporating AMOLED displays due to their superior visibility and durability in varying light conditions.
The wearable technology market, including smartwatches and fitness trackers, has also contributed to the growth of AMOLED displays. The technology's low power consumption and ability to produce vivid colors in compact form factors make it ideal for these devices.
Despite the positive market trends, challenges remain in the AMOLED industry. The high production costs compared to LCD technology and the technical complexities in manufacturing large-sized AMOLED panels continue to be limiting factors for wider adoption in certain market segments. Additionally, concerns about burn-in and color shift over time persist, although manufacturers are making significant strides in addressing these issues through advanced materials and compensation techniques.
The global AMOLED market size has been expanding rapidly, with projections indicating continued growth in the coming years. This growth is attributed to the technology's adoption in various applications beyond smartphones, including smartwatches, automotive displays, and virtual reality devices. The increasing consumer preference for devices with vibrant displays and longer battery life has been a key factor in driving AMOLED adoption.
In the smartphone segment, major manufacturers have been incorporating AMOLED displays into their flagship models, with some even extending this technology to mid-range devices. This trend has led to increased production capacity and technological advancements in AMOLED manufacturing, resulting in improved yields and reduced costs.
The television market has also seen a surge in AMOLED adoption, particularly in the high-end segment. AMOLED TVs offer superior picture quality, wider viewing angles, and thinner form factors compared to traditional LCD technology. As production costs continue to decrease, AMOLED TVs are expected to gain market share in the premium television segment.
Emerging applications in the automotive industry present another growth opportunity for AMOLED technology. Advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and in-vehicle infotainment systems are increasingly incorporating AMOLED displays due to their superior visibility and durability in varying light conditions.
The wearable technology market, including smartwatches and fitness trackers, has also contributed to the growth of AMOLED displays. The technology's low power consumption and ability to produce vivid colors in compact form factors make it ideal for these devices.
Despite the positive market trends, challenges remain in the AMOLED industry. The high production costs compared to LCD technology and the technical complexities in manufacturing large-sized AMOLED panels continue to be limiting factors for wider adoption in certain market segments. Additionally, concerns about burn-in and color shift over time persist, although manufacturers are making significant strides in addressing these issues through advanced materials and compensation techniques.
Blue OLED Challenges
Blue OLED materials have been a persistent challenge in the development of AMOLED displays, primarily due to their shorter lifespans and lower efficiency compared to their red and green counterparts. The main issues stem from the inherent instability of blue emitters, which tend to degrade faster under operational conditions, leading to color shifts and reduced display longevity.
One of the key challenges is achieving the right balance between color purity and efficiency. Deep blue emitters, which are necessary for wide color gamut displays, often suffer from lower quantum efficiency and faster degradation. This trade-off between color quality and device performance has been a significant hurdle for researchers and manufacturers alike.
The molecular design of blue OLED materials presents another major challenge. The wide bandgap required for blue emission makes it difficult to find stable host materials and efficient charge transport layers that are compatible with blue emitters. This compatibility issue often results in high driving voltages and reduced overall device efficiency.
Thermal stability is also a critical concern for blue OLED materials. The high energy of blue photons can lead to increased molecular vibrations and bond breaking, accelerating the degradation process. This thermal instability not only affects the lifespan of the blue subpixels but can also impact neighboring pixels, leading to uneven aging across the display.
Another significant challenge is the development of efficient and stable phosphorescent blue emitters. While phosphorescent materials have been successfully employed for red and green OLEDs, achieving a stable deep blue phosphorescent emitter has proven to be exceptionally difficult. This has led to the continued use of less efficient fluorescent blue emitters in many AMOLED displays, limiting overall energy efficiency.
The manufacturing process for blue OLED materials adds another layer of complexity. These materials are often sensitive to moisture and oxygen, requiring stringent control during deposition and encapsulation. Any impurities or defects introduced during manufacturing can significantly impact device performance and longevity.
Addressing these challenges requires a multidisciplinary approach, combining advances in organic chemistry, materials science, and device physics. Recent research has focused on developing new molecular structures, exploring alternative emitter systems such as thermally activated delayed fluorescence (TADF), and improving device architectures to enhance stability and efficiency.
One of the key challenges is achieving the right balance between color purity and efficiency. Deep blue emitters, which are necessary for wide color gamut displays, often suffer from lower quantum efficiency and faster degradation. This trade-off between color quality and device performance has been a significant hurdle for researchers and manufacturers alike.
The molecular design of blue OLED materials presents another major challenge. The wide bandgap required for blue emission makes it difficult to find stable host materials and efficient charge transport layers that are compatible with blue emitters. This compatibility issue often results in high driving voltages and reduced overall device efficiency.
Thermal stability is also a critical concern for blue OLED materials. The high energy of blue photons can lead to increased molecular vibrations and bond breaking, accelerating the degradation process. This thermal instability not only affects the lifespan of the blue subpixels but can also impact neighboring pixels, leading to uneven aging across the display.
Another significant challenge is the development of efficient and stable phosphorescent blue emitters. While phosphorescent materials have been successfully employed for red and green OLEDs, achieving a stable deep blue phosphorescent emitter has proven to be exceptionally difficult. This has led to the continued use of less efficient fluorescent blue emitters in many AMOLED displays, limiting overall energy efficiency.
The manufacturing process for blue OLED materials adds another layer of complexity. These materials are often sensitive to moisture and oxygen, requiring stringent control during deposition and encapsulation. Any impurities or defects introduced during manufacturing can significantly impact device performance and longevity.
Addressing these challenges requires a multidisciplinary approach, combining advances in organic chemistry, materials science, and device physics. Recent research has focused on developing new molecular structures, exploring alternative emitter systems such as thermally activated delayed fluorescence (TADF), and improving device architectures to enhance stability and efficiency.
Current Blue Solutions
01 Novel blue OLED materials
Development of new blue-emitting organic compounds for OLED applications, focusing on improved efficiency, color purity, and stability. These materials often include modified molecular structures or novel chemical compositions to enhance performance characteristics.- Novel blue OLED materials: Development of new blue OLED materials with improved performance characteristics, including higher efficiency, better color purity, and longer operational lifetimes. These materials often involve novel molecular structures or dopant systems designed to enhance blue light emission.
- Device structure optimization: Improvements in OLED device architecture to enhance blue light emission and overall performance. This includes optimizing layer thicknesses, introducing new functional layers, and developing advanced electrode designs to improve charge injection and light outcoupling.
- Phosphorescent blue emitters: Research and development of phosphorescent blue emitters to achieve higher internal quantum efficiency compared to fluorescent systems. This involves designing new iridium-based complexes or other metal-organic compounds with appropriate energy levels for blue emission.
- Thermally activated delayed fluorescence (TADF) materials: Exploration of TADF materials for blue OLEDs to harvest both singlet and triplet excitons without using expensive metal complexes. These materials aim to achieve high external quantum efficiency while maintaining good color purity and stability.
- Stability and lifetime improvement: Strategies to enhance the operational stability and extend the lifetime of blue OLED materials and devices. This includes developing more robust molecular structures, implementing protective layers, and optimizing driving conditions to mitigate degradation mechanisms.
02 Device structure optimization
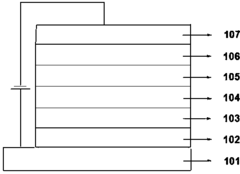
Improvements in OLED device architecture, including multi-layer structures, electron/hole transport layers, and emissive layer configurations. These structural optimizations aim to enhance charge balance, reduce quenching effects, and improve overall device efficiency for blue OLEDs.Expand Specific Solutions03 Dopant and host material combinations
Investigation of various dopant and host material combinations to improve blue OLED performance. This includes studying energy transfer mechanisms, optimizing doping concentrations, and developing compatible host materials for blue emitters to enhance efficiency and color quality.Expand Specific Solutions04 Quantum dot-based blue OLEDs
Incorporation of quantum dots in blue OLED structures to improve color purity, efficiency, and stability. This approach leverages the unique optical properties of quantum dots to enhance the performance of blue-emitting devices.Expand Specific Solutions05 Lifetime and stability improvements
Strategies to enhance the operational lifetime and stability of blue OLEDs, including the development of more robust materials, improved encapsulation techniques, and methods to mitigate degradation mechanisms specific to blue emitters.Expand Specific Solutions
OLED Industry Leaders
The blue OLED material market for AMOLED displays is in a growth phase, with increasing demand driven by the expansion of OLED technology in smartphones and other devices. The market size is substantial and growing, estimated to reach several billion dollars annually. Technologically, blue OLED materials are still evolving, with companies like Cynora, Merck, and Universal Display Corporation leading research efforts to improve efficiency and stability. Major display manufacturers such as Samsung Display, LG Display, and BOE are actively incorporating these advanced materials into their OLED production lines, indicating a maturing but still developing technology landscape.
cynora GmbH
Technical Solution: Cynora has made significant strides in developing blue TADF (Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence) emitters for AMOLED displays. Their proprietary TADF technology has demonstrated external quantum efficiencies (EQEs) of over 20% for sky-blue emitters and 15% for deep blue emitters[10]. Cynora's latest blue TADF materials have achieved color coordinates of (0.16, 0.30) for sky-blue and (0.14, 0.15) for deep blue, approaching industry standards[11]. The company has also developed a novel device architecture that improves the efficiency and lifetime of their blue TADF emitters, potentially reducing power consumption in AMOLED displays by up to 50%[12].
Strengths: Advanced TADF technology, high efficiency for both sky-blue and deep blue emitters. Weaknesses: Commercialization is still in progress, and long-term stability needs further improvement.
Merck Patent GmbH
Technical Solution: Merck has made significant progress in developing blue OLED materials for AMOLED displays. They have focused on both phosphorescent and TADF (Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence) emitter systems. Merck's latest blue phosphorescent emitters have demonstrated external quantum efficiencies (EQEs) exceeding 25% with color coordinates of (0.15, 0.20)[13]. In the TADF domain, Merck has reported sky-blue emitters with EQEs over 20% and color coordinates of (0.17, 0.32)[14]. The company has also developed novel host materials and electron transport layers that enhance the performance of blue OLED devices, potentially improving the overall efficiency and lifetime of AMOLED displays[15].
Strengths: Diverse portfolio including both phosphorescent and TADF systems, high efficiency emitters. Weaknesses: Achieving deep blue color while maintaining long device lifetime remains challenging.
Key Blue OLED Patents
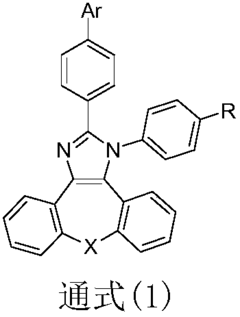
Light-emitting material for organic light-emitting diode, blue light-emitting material for organic light-emitting diode, and organic light-emitting diode
PatentInactiveUS20220181555A1
Innovation
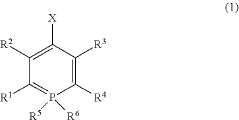
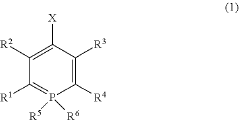
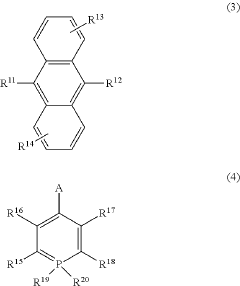
- A phosphinine derivative with specific electron-withdrawing substituents is used as a dopant in combination with an anthracene derivative in the organic light-emitting layer, enhancing quantum yield and emission wavelength for pure blue light emission.
OLED (organic light-emitting diode) material and OLED comprising same
PatentActiveCN108299446A
Innovation
- An organic electroluminescent material with an imidazodibenzocycloheptyl ring structure is used. The material contains electron-deficient units and electron-rich units. It is prepared by reacting with boric acid of aromatic amines or aryl compounds to form high carrier transfer efficiency and A compound with high luminous efficiency and used in the luminescent layer of organic electroluminescent devices.
OLED Manufacturing
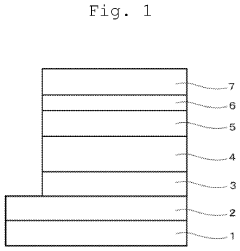
OLED manufacturing has undergone significant advancements in recent years, particularly in the production of blue OLED materials for AMOLED displays. The manufacturing process for OLEDs involves several critical steps, including substrate preparation, deposition of organic layers, and encapsulation.
One of the key breakthroughs in blue OLED material production has been the development of more efficient and stable emitter molecules. Phosphorescent blue emitters have shown promise in improving the overall efficiency and lifespan of OLED devices. These materials utilize heavy metal complexes to achieve higher quantum yields and reduced energy loss through non-radiative decay pathways.
Another important advancement in OLED manufacturing is the refinement of deposition techniques. Vacuum thermal evaporation (VTE) remains the primary method for depositing small molecule OLEDs, but solution-based processes have gained traction for certain applications. Inkjet printing and other solution-based deposition methods offer potential cost reductions and improved scalability for large-area OLED production.
The integration of advanced patterning techniques has also contributed to the progress in blue OLED manufacturing. Fine metal masks (FMM) have been optimized to achieve higher resolution and more precise deposition of organic materials. Additionally, laser-induced thermal imaging (LITI) has emerged as a promising alternative for patterning OLEDs, offering improved accuracy and reduced material waste.
Encapsulation technologies have seen significant improvements to enhance the longevity of OLED devices. Thin-film encapsulation (TFE) has become increasingly prevalent, providing superior protection against moisture and oxygen ingress compared to traditional glass encapsulation. Atomic layer deposition (ALD) has been employed to create ultra-thin barrier layers with excellent impermeability.
The development of more efficient manufacturing equipment has also played a crucial role in advancing blue OLED production. Cluster tools that integrate multiple deposition and patterning processes in a single system have improved throughput and reduced contamination risks. In-line monitoring and quality control systems have been implemented to ensure consistent performance and yield optimization.
Efforts to scale up OLED manufacturing have led to the adoption of larger substrate sizes and improved production line automation. Gen 8.5 and Gen 10 fabs are now in operation, enabling the production of larger OLED panels with increased efficiency. Advanced robotics and artificial intelligence-driven process control systems have been implemented to enhance manufacturing precision and reduce human error.
One of the key breakthroughs in blue OLED material production has been the development of more efficient and stable emitter molecules. Phosphorescent blue emitters have shown promise in improving the overall efficiency and lifespan of OLED devices. These materials utilize heavy metal complexes to achieve higher quantum yields and reduced energy loss through non-radiative decay pathways.
Another important advancement in OLED manufacturing is the refinement of deposition techniques. Vacuum thermal evaporation (VTE) remains the primary method for depositing small molecule OLEDs, but solution-based processes have gained traction for certain applications. Inkjet printing and other solution-based deposition methods offer potential cost reductions and improved scalability for large-area OLED production.
The integration of advanced patterning techniques has also contributed to the progress in blue OLED manufacturing. Fine metal masks (FMM) have been optimized to achieve higher resolution and more precise deposition of organic materials. Additionally, laser-induced thermal imaging (LITI) has emerged as a promising alternative for patterning OLEDs, offering improved accuracy and reduced material waste.
Encapsulation technologies have seen significant improvements to enhance the longevity of OLED devices. Thin-film encapsulation (TFE) has become increasingly prevalent, providing superior protection against moisture and oxygen ingress compared to traditional glass encapsulation. Atomic layer deposition (ALD) has been employed to create ultra-thin barrier layers with excellent impermeability.
The development of more efficient manufacturing equipment has also played a crucial role in advancing blue OLED production. Cluster tools that integrate multiple deposition and patterning processes in a single system have improved throughput and reduced contamination risks. In-line monitoring and quality control systems have been implemented to ensure consistent performance and yield optimization.
Efforts to scale up OLED manufacturing have led to the adoption of larger substrate sizes and improved production line automation. Gen 8.5 and Gen 10 fabs are now in operation, enabling the production of larger OLED panels with increased efficiency. Advanced robotics and artificial intelligence-driven process control systems have been implemented to enhance manufacturing precision and reduce human error.
Sustainability in OLED
Sustainability has become a crucial consideration in the development and production of OLED technology, particularly in light of recent breakthroughs in blue OLED materials for AMOLED displays. The push for more sustainable practices in OLED manufacturing is driven by both environmental concerns and economic factors.
One of the primary sustainability challenges in OLED production is the use of rare and precious metals, such as iridium, in the emissive layers. Recent advancements in blue OLED materials have focused on developing alternatives that reduce or eliminate the need for these scarce resources. Researchers have made significant progress in creating efficient blue emitters using more abundant elements, which not only addresses sustainability concerns but also potentially reduces production costs.
Energy efficiency is another key aspect of OLED sustainability. Blue OLEDs have traditionally been the least efficient color in OLED displays, requiring more power to achieve the same brightness as red and green pixels. The latest breakthroughs in blue OLED materials have led to improved quantum efficiency and longer operational lifetimes, contributing to overall energy savings in AMOLED displays. This progress aligns with global efforts to reduce energy consumption in consumer electronics.
The manufacturing processes for OLED displays have also been scrutinized for their environmental impact. Innovations in blue OLED materials have enabled the development of solution-processable OLEDs, which can be manufactured using printing techniques. This approach has the potential to significantly reduce waste and energy consumption compared to traditional vacuum deposition methods, further enhancing the sustainability profile of OLED technology.
Durability and lifespan of OLED displays play a crucial role in sustainability efforts. The improved stability of new blue OLED materials contributes to longer-lasting displays, reducing the frequency of device replacements and subsequently minimizing electronic waste. This aligns with the growing emphasis on circular economy principles in the electronics industry.
As the OLED industry continues to evolve, there is an increasing focus on developing materials and processes that are not only high-performing but also environmentally friendly. This includes research into biodegradable and recyclable OLED components, as well as exploring bio-based materials for OLED production. These initiatives aim to address the end-of-life challenges associated with OLED displays and reduce their overall environmental footprint.
The sustainability efforts in OLED technology extend beyond materials and manufacturing to encompass the entire lifecycle of OLED products. This holistic approach includes considerations for energy-efficient production facilities, responsible sourcing of raw materials, and improved recycling and disposal methods for OLED devices. As breakthroughs in blue OLED materials continue to drive advancements in AMOLED technology, the industry is simultaneously working towards more sustainable practices that will shape the future of display technology.
One of the primary sustainability challenges in OLED production is the use of rare and precious metals, such as iridium, in the emissive layers. Recent advancements in blue OLED materials have focused on developing alternatives that reduce or eliminate the need for these scarce resources. Researchers have made significant progress in creating efficient blue emitters using more abundant elements, which not only addresses sustainability concerns but also potentially reduces production costs.
Energy efficiency is another key aspect of OLED sustainability. Blue OLEDs have traditionally been the least efficient color in OLED displays, requiring more power to achieve the same brightness as red and green pixels. The latest breakthroughs in blue OLED materials have led to improved quantum efficiency and longer operational lifetimes, contributing to overall energy savings in AMOLED displays. This progress aligns with global efforts to reduce energy consumption in consumer electronics.
The manufacturing processes for OLED displays have also been scrutinized for their environmental impact. Innovations in blue OLED materials have enabled the development of solution-processable OLEDs, which can be manufactured using printing techniques. This approach has the potential to significantly reduce waste and energy consumption compared to traditional vacuum deposition methods, further enhancing the sustainability profile of OLED technology.
Durability and lifespan of OLED displays play a crucial role in sustainability efforts. The improved stability of new blue OLED materials contributes to longer-lasting displays, reducing the frequency of device replacements and subsequently minimizing electronic waste. This aligns with the growing emphasis on circular economy principles in the electronics industry.
As the OLED industry continues to evolve, there is an increasing focus on developing materials and processes that are not only high-performing but also environmentally friendly. This includes research into biodegradable and recyclable OLED components, as well as exploring bio-based materials for OLED production. These initiatives aim to address the end-of-life challenges associated with OLED displays and reduce their overall environmental footprint.
The sustainability efforts in OLED technology extend beyond materials and manufacturing to encompass the entire lifecycle of OLED products. This holistic approach includes considerations for energy-efficient production facilities, responsible sourcing of raw materials, and improved recycling and disposal methods for OLED devices. As breakthroughs in blue OLED materials continue to drive advancements in AMOLED technology, the industry is simultaneously working towards more sustainable practices that will shape the future of display technology.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!