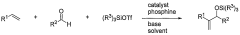Alkyl Compounds and Their Vital Roles in Future Chemistry
JUL 15, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Alkyl Compounds Overview and Research Objectives
Alkyl compounds, a fundamental class of organic molecules, have been at the forefront of chemical research for decades. These compounds, characterized by their carbon-hydrogen bonds, form the backbone of numerous organic substances and play crucial roles in various chemical processes. The evolution of alkyl compound research has been marked by significant breakthroughs in synthesis, analysis, and application, shaping the landscape of modern chemistry.
The historical trajectory of alkyl compound research spans from early structural elucidation to advanced functional group manipulations. Initially, scientists focused on understanding the basic properties and reactivity of simple alkanes, alkenes, and alkynes. As analytical techniques improved, researchers delved deeper into the complexities of alkyl compound behavior, uncovering intricate reaction mechanisms and stereochemical implications.
In recent years, the field has witnessed a surge in interest due to the potential applications of alkyl compounds in emerging technologies. From advanced materials to pharmaceutical development, these versatile molecules continue to demonstrate their significance across multiple industries. The ability to fine-tune the properties of alkyl compounds through structural modifications has opened new avenues for innovation in fields such as nanotechnology, energy storage, and sustainable chemistry.
The primary objective of current research on alkyl compounds is to explore their untapped potential in addressing global challenges. This includes developing more efficient and environmentally friendly synthetic routes, investigating novel applications in renewable energy technologies, and harnessing their properties for advanced drug delivery systems. Additionally, researchers aim to uncover new reaction pathways that could revolutionize industrial processes, making them more sustainable and cost-effective.
Another critical focus is the exploration of alkyl compounds in the context of green chemistry. As the world moves towards more sustainable practices, there is a growing emphasis on developing alkyl-based materials that are biodegradable, recyclable, and have minimal environmental impact. This shift aligns with the broader goals of reducing carbon footprints and promoting circular economy principles in chemical manufacturing.
The future of alkyl compound research is poised to be transformative, with interdisciplinary collaborations driving innovation. By combining insights from organic synthesis, computational chemistry, and materials science, researchers aim to unlock new functionalities and applications for these versatile molecules. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in predicting alkyl compound behavior and designing novel structures is expected to accelerate discovery and optimization processes significantly.
The historical trajectory of alkyl compound research spans from early structural elucidation to advanced functional group manipulations. Initially, scientists focused on understanding the basic properties and reactivity of simple alkanes, alkenes, and alkynes. As analytical techniques improved, researchers delved deeper into the complexities of alkyl compound behavior, uncovering intricate reaction mechanisms and stereochemical implications.
In recent years, the field has witnessed a surge in interest due to the potential applications of alkyl compounds in emerging technologies. From advanced materials to pharmaceutical development, these versatile molecules continue to demonstrate their significance across multiple industries. The ability to fine-tune the properties of alkyl compounds through structural modifications has opened new avenues for innovation in fields such as nanotechnology, energy storage, and sustainable chemistry.
The primary objective of current research on alkyl compounds is to explore their untapped potential in addressing global challenges. This includes developing more efficient and environmentally friendly synthetic routes, investigating novel applications in renewable energy technologies, and harnessing their properties for advanced drug delivery systems. Additionally, researchers aim to uncover new reaction pathways that could revolutionize industrial processes, making them more sustainable and cost-effective.
Another critical focus is the exploration of alkyl compounds in the context of green chemistry. As the world moves towards more sustainable practices, there is a growing emphasis on developing alkyl-based materials that are biodegradable, recyclable, and have minimal environmental impact. This shift aligns with the broader goals of reducing carbon footprints and promoting circular economy principles in chemical manufacturing.
The future of alkyl compound research is poised to be transformative, with interdisciplinary collaborations driving innovation. By combining insights from organic synthesis, computational chemistry, and materials science, researchers aim to unlock new functionalities and applications for these versatile molecules. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in predicting alkyl compound behavior and designing novel structures is expected to accelerate discovery and optimization processes significantly.
Market Analysis for Alkyl Compound Applications
The global market for alkyl compounds is experiencing significant growth, driven by their versatile applications across various industries. The chemical sector, in particular, is witnessing a surge in demand for these compounds due to their crucial role in the synthesis of numerous products. Alkyl compounds serve as essential building blocks in the production of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, polymers, and specialty chemicals.
In the pharmaceutical industry, alkyl compounds are extensively used in the synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and drug intermediates. The growing focus on personalized medicine and the development of novel therapeutic agents are expected to further boost the demand for alkyl compounds in this sector. Additionally, the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases and the expanding geriatric population worldwide are contributing to the growth of the pharmaceutical market, indirectly driving the demand for alkyl compounds.
The agrochemical industry is another significant consumer of alkyl compounds, utilizing them in the production of pesticides, herbicides, and fertilizers. As global food demand continues to rise, there is a growing need for efficient crop protection and yield enhancement solutions, which is expected to fuel the demand for alkyl compounds in this sector. Moreover, the shift towards sustainable and eco-friendly agricultural practices is driving innovation in the development of new alkyl-based agrochemical formulations.
The polymer industry is also a major consumer of alkyl compounds, employing them as monomers, initiators, and modifiers in the production of various plastics and synthetic materials. The increasing demand for lightweight and durable materials in automotive, construction, and packaging industries is driving the growth of the polymer market, consequently boosting the demand for alkyl compounds.
In the specialty chemicals sector, alkyl compounds find applications in the production of surfactants, lubricants, and additives for various industrial processes. The growing emphasis on sustainability and environmental regulations is driving the development of bio-based alkyl compounds, opening up new opportunities in this market segment.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific is expected to dominate the alkyl compounds market, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and economic growth in countries like China and India. North America and Europe are also significant markets, with a strong presence of pharmaceutical and specialty chemical industries. The Middle East and Africa region is anticipated to witness substantial growth in the coming years, primarily due to the expansion of the petrochemical industry.
In the pharmaceutical industry, alkyl compounds are extensively used in the synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and drug intermediates. The growing focus on personalized medicine and the development of novel therapeutic agents are expected to further boost the demand for alkyl compounds in this sector. Additionally, the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases and the expanding geriatric population worldwide are contributing to the growth of the pharmaceutical market, indirectly driving the demand for alkyl compounds.
The agrochemical industry is another significant consumer of alkyl compounds, utilizing them in the production of pesticides, herbicides, and fertilizers. As global food demand continues to rise, there is a growing need for efficient crop protection and yield enhancement solutions, which is expected to fuel the demand for alkyl compounds in this sector. Moreover, the shift towards sustainable and eco-friendly agricultural practices is driving innovation in the development of new alkyl-based agrochemical formulations.
The polymer industry is also a major consumer of alkyl compounds, employing them as monomers, initiators, and modifiers in the production of various plastics and synthetic materials. The increasing demand for lightweight and durable materials in automotive, construction, and packaging industries is driving the growth of the polymer market, consequently boosting the demand for alkyl compounds.
In the specialty chemicals sector, alkyl compounds find applications in the production of surfactants, lubricants, and additives for various industrial processes. The growing emphasis on sustainability and environmental regulations is driving the development of bio-based alkyl compounds, opening up new opportunities in this market segment.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific is expected to dominate the alkyl compounds market, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and economic growth in countries like China and India. North America and Europe are also significant markets, with a strong presence of pharmaceutical and specialty chemical industries. The Middle East and Africa region is anticipated to witness substantial growth in the coming years, primarily due to the expansion of the petrochemical industry.
Current Challenges in Alkyl Compound Synthesis
The synthesis of alkyl compounds faces several significant challenges in modern chemistry. One of the primary obstacles is the development of efficient and selective methods for carbon-carbon bond formation. Traditional approaches often require harsh conditions, multiple steps, or expensive catalysts, limiting their applicability in large-scale production and green chemistry initiatives.
Another major challenge lies in controlling the stereochemistry of alkyl compounds. Stereoselective synthesis is crucial for many applications, particularly in pharmaceutical and fine chemical industries. However, achieving high levels of stereoselectivity while maintaining reaction efficiency remains a complex task, especially for compounds with multiple chiral centers.
The activation of unreactive C-H bonds in alkyl compounds presents another frontier in synthetic chemistry. While significant progress has been made in aromatic C-H functionalization, extending these methodologies to sp3 carbons in alkyl chains is still challenging. This limitation hinders the direct functionalization of readily available hydrocarbons and the late-stage modification of complex molecules.
Sustainability concerns also pose challenges in alkyl compound synthesis. Many current methods rely on petroleum-derived starting materials and generate significant waste. Developing greener alternatives that utilize renewable feedstocks and adhere to the principles of atom economy is a pressing need in the field.
The synthesis of highly functionalized and complex alkyl compounds remains challenging due to the potential for undesired side reactions and functional group incompatibilities. Protecting group strategies are often required, leading to longer synthetic routes and reduced overall efficiency. Developing methods that tolerate a wide range of functional groups would greatly streamline the synthesis of complex alkyl-based molecules.
Scalability is another critical issue in alkyl compound synthesis. Many novel methodologies developed in academic laboratories face difficulties when scaled up for industrial production. Addressing issues such as heat and mass transfer, reagent availability, and process safety on larger scales is essential for the practical application of new synthetic methods.
Lastly, the development of catalytic systems that can selectively functionalize specific positions in alkyl chains remains a significant challenge. While directed functionalization strategies have shown promise, achieving site-selectivity in the absence of directing groups, particularly in complex molecules, is still an area of active research and development in the field of alkyl compound synthesis.
Another major challenge lies in controlling the stereochemistry of alkyl compounds. Stereoselective synthesis is crucial for many applications, particularly in pharmaceutical and fine chemical industries. However, achieving high levels of stereoselectivity while maintaining reaction efficiency remains a complex task, especially for compounds with multiple chiral centers.
The activation of unreactive C-H bonds in alkyl compounds presents another frontier in synthetic chemistry. While significant progress has been made in aromatic C-H functionalization, extending these methodologies to sp3 carbons in alkyl chains is still challenging. This limitation hinders the direct functionalization of readily available hydrocarbons and the late-stage modification of complex molecules.
Sustainability concerns also pose challenges in alkyl compound synthesis. Many current methods rely on petroleum-derived starting materials and generate significant waste. Developing greener alternatives that utilize renewable feedstocks and adhere to the principles of atom economy is a pressing need in the field.
The synthesis of highly functionalized and complex alkyl compounds remains challenging due to the potential for undesired side reactions and functional group incompatibilities. Protecting group strategies are often required, leading to longer synthetic routes and reduced overall efficiency. Developing methods that tolerate a wide range of functional groups would greatly streamline the synthesis of complex alkyl-based molecules.
Scalability is another critical issue in alkyl compound synthesis. Many novel methodologies developed in academic laboratories face difficulties when scaled up for industrial production. Addressing issues such as heat and mass transfer, reagent availability, and process safety on larger scales is essential for the practical application of new synthetic methods.
Lastly, the development of catalytic systems that can selectively functionalize specific positions in alkyl chains remains a significant challenge. While directed functionalization strategies have shown promise, achieving site-selectivity in the absence of directing groups, particularly in complex molecules, is still an area of active research and development in the field of alkyl compound synthesis.
State-of-the-Art Alkyl Compound Synthesis Methods
01 Synthesis of alkyl compounds
Various methods for synthesizing alkyl compounds are described, including reactions involving alkyl halides, alcohols, and other precursors. These processes often involve catalysts and specific reaction conditions to produce desired alkyl compounds efficiently.- Synthesis of alkyl compounds: Various methods for synthesizing alkyl compounds are described, including reactions involving alkyl halides, alcohols, and other precursors. These processes often involve catalysts and specific reaction conditions to produce desired alkyl compounds efficiently.
- Applications of alkyl compounds in industry: Alkyl compounds find diverse applications in industries such as petrochemicals, polymers, and pharmaceuticals. They are used as intermediates, solvents, and raw materials for the production of various products, including plastics, lubricants, and specialty chemicals.
- Alkyl compounds in organic synthesis: Alkyl compounds play a crucial role in organic synthesis as building blocks and reagents. They are utilized in various reactions, including alkylation, substitution, and elimination, to create more complex organic molecules and functional materials.
- Purification and characterization of alkyl compounds: Techniques for purifying and characterizing alkyl compounds are discussed, including distillation, chromatography, and spectroscopic methods. These processes are essential for ensuring the quality and purity of alkyl compounds for various applications and research purposes.
- Environmental and safety considerations of alkyl compounds: The environmental impact and safety aspects of alkyl compounds are addressed, including their toxicity, flammability, and potential for environmental contamination. Proper handling, storage, and disposal methods are discussed to minimize risks associated with these compounds.
02 Applications of alkyl compounds in industry
Alkyl compounds find diverse applications in industrial processes, such as in the production of plastics, lubricants, and surfactants. They are also used as intermediates in the synthesis of more complex organic molecules and pharmaceuticals.Expand Specific Solutions03 Alkyl compounds in polymer chemistry
Alkyl compounds play a crucial role in polymer chemistry, serving as monomers or modifying agents in the production of various polymeric materials. They can influence the properties of the resulting polymers, such as flexibility, durability, and chemical resistance.Expand Specific Solutions04 Purification and characterization of alkyl compounds
Techniques for purifying and characterizing alkyl compounds are discussed, including distillation, chromatography, and spectroscopic methods. These processes are essential for ensuring the quality and purity of alkyl compounds for various applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and safety considerations of alkyl compounds
The environmental impact and safety aspects of alkyl compounds are addressed, including their biodegradability, toxicity, and potential for bioaccumulation. Proper handling, storage, and disposal methods are discussed to minimize risks associated with these compounds.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Alkyl Compound Research
The research on alkyl compounds and their roles in future chemistry is at a mature stage, with significant market potential and ongoing innovation. The industry is characterized by a mix of established players and emerging companies, indicating a competitive landscape. Major pharmaceutical and chemical companies like Novartis AG, Eli Lilly & Co., and BASF Corp. are actively involved, leveraging their extensive R&D capabilities. Academic institutions such as MIT and the Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry contribute to fundamental research, while specialized firms like Novomer, Inc. focus on innovative applications. The market is driven by increasing demand for sustainable and high-performance materials across various sectors, including pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and industrial chemicals.
Sinopec Shanghai Petrochemical Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Sinopec Shanghai Petrochemical Co., Ltd. has been actively researching alkyl compounds, particularly in the context of petrochemical processes and fuel additives. The company has developed a novel alkylation technology that improves the octane rating of gasoline while reducing sulfur content[2]. This process utilizes a solid acid catalyst, which offers advantages over traditional liquid acid catalysts in terms of safety and environmental impact. Sinopec has also made strides in the production of long-chain alkyl benzene (LAB), a key intermediate for biodegradable detergents[4]. Their research includes the optimization of LAB production through improved catalytic systems and process intensification, resulting in higher yields and reduced energy consumption[6].
Strengths: Strong integration with upstream oil and gas operations, significant market share in Asia. Weaknesses: Relatively limited global presence compared to some competitors, potential challenges in transitioning to more sustainable technologies.
Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Technical Solution: MIT has been at the forefront of fundamental research on alkyl compounds, with a focus on developing new synthetic methodologies and exploring novel applications. The institute's researchers have made significant advancements in C-H activation chemistry, enabling the direct functionalization of alkyl groups with unprecedented selectivity[2]. MIT's work on photoredox catalysis has opened new avenues for alkyl radical generation and subsequent transformations, leading to more efficient and environmentally friendly synthetic routes[4]. The institute has also been pioneering research in the field of alkyl-based organic electronics, developing novel materials for flexible and printable electronic devices[6]. Additionally, MIT's interdisciplinary approach has led to breakthroughs in understanding the role of alkyl compounds in biological systems, particularly in lipid signaling and membrane dynamics[8].
Strengths: Cutting-edge research facilities, interdisciplinary collaboration, and a strong track record of innovation. Weaknesses: As an academic institution, may face challenges in scaling up technologies for industrial applications.
Breakthrough Innovations in Alkyl Chemistry
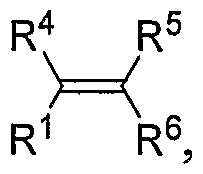
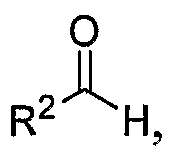
Catalytic reactions involving alkenes
PatentWO2007027752A1
Innovation
- A nickel-catalyzed method involving a catalyst system with a Group 9, 10, or 11 metal, using a nickel-containing compound, a phosphorus-containing ligand, a silicon-containing compound, and a base, such as dicyclohexylphenylphosphine or tri(ortho-anisyl)phosphine, to facilitate the coupling of alkenes and aldehydes, forming allylic alcohols or their precursors like silyl ethers in a one-pot reaction.
Therapeutic compounds
PatentWO2010019536A1
Innovation
- Development of novel compounds with specific structural features, including organic acid functional groups, amides, esters, and tetrazolyl functional groups, which can reduce intraocular pressure, treat glaucoma, and promote hair growth and appearance by increasing hair length, density, and improving color and shine.
Environmental Impact of Alkyl Compounds
The environmental impact of alkyl compounds is a critical consideration in the field of chemistry, particularly as we look towards future applications and developments. These compounds, characterized by their carbon-hydrogen bonds, are ubiquitous in nature and widely used in industrial processes, making their environmental footprint a subject of significant concern.
Alkyl compounds can have both direct and indirect effects on the environment. When released into the atmosphere, many volatile alkyl compounds contribute to the formation of photochemical smog, a major air pollution issue in urban areas. This process occurs when alkyl compounds react with nitrogen oxides in the presence of sunlight, leading to the production of ground-level ozone and other harmful secondary pollutants. The resulting smog can have detrimental effects on human health, plant life, and overall air quality.
In aquatic environments, alkyl compounds pose a different set of challenges. Some alkyl-based substances, particularly those with longer carbon chains, exhibit low water solubility and tend to accumulate in sediments and aquatic organisms. This bioaccumulation can lead to long-term ecological impacts, affecting the health of aquatic ecosystems and potentially entering the food chain. Moreover, certain alkyl compounds have been identified as endocrine disruptors, interfering with the hormonal systems of wildlife and potentially humans.
The persistence of alkyl compounds in the environment is another area of concern. Many of these substances are resistant to natural degradation processes, leading to their long-term presence in ecosystems. This persistence can result in prolonged exposure for organisms and ecosystems, potentially causing chronic effects that may not be immediately apparent but could have significant long-term consequences.
However, it's important to note that not all environmental impacts of alkyl compounds are negative. Some alkyl-based substances play crucial roles in natural biochemical processes and are essential components of living organisms. Furthermore, in the field of green chemistry, researchers are exploring the use of certain alkyl compounds as environmentally friendly alternatives to more harmful substances. For instance, some alkyl-based solvents are being developed as replacements for traditional organic solvents, offering reduced toxicity and improved biodegradability.
As we look to the future of chemistry, addressing the environmental impact of alkyl compounds will be crucial. This involves not only mitigating the negative effects of existing compounds but also developing new, more environmentally benign alkyl-based substances. Research into biodegradable alkyl compounds, improved methods for their containment and disposal, and the development of more efficient chemical processes that minimize the release of these compounds into the environment are all key areas of focus.
Alkyl compounds can have both direct and indirect effects on the environment. When released into the atmosphere, many volatile alkyl compounds contribute to the formation of photochemical smog, a major air pollution issue in urban areas. This process occurs when alkyl compounds react with nitrogen oxides in the presence of sunlight, leading to the production of ground-level ozone and other harmful secondary pollutants. The resulting smog can have detrimental effects on human health, plant life, and overall air quality.
In aquatic environments, alkyl compounds pose a different set of challenges. Some alkyl-based substances, particularly those with longer carbon chains, exhibit low water solubility and tend to accumulate in sediments and aquatic organisms. This bioaccumulation can lead to long-term ecological impacts, affecting the health of aquatic ecosystems and potentially entering the food chain. Moreover, certain alkyl compounds have been identified as endocrine disruptors, interfering with the hormonal systems of wildlife and potentially humans.
The persistence of alkyl compounds in the environment is another area of concern. Many of these substances are resistant to natural degradation processes, leading to their long-term presence in ecosystems. This persistence can result in prolonged exposure for organisms and ecosystems, potentially causing chronic effects that may not be immediately apparent but could have significant long-term consequences.
However, it's important to note that not all environmental impacts of alkyl compounds are negative. Some alkyl-based substances play crucial roles in natural biochemical processes and are essential components of living organisms. Furthermore, in the field of green chemistry, researchers are exploring the use of certain alkyl compounds as environmentally friendly alternatives to more harmful substances. For instance, some alkyl-based solvents are being developed as replacements for traditional organic solvents, offering reduced toxicity and improved biodegradability.
As we look to the future of chemistry, addressing the environmental impact of alkyl compounds will be crucial. This involves not only mitigating the negative effects of existing compounds but also developing new, more environmentally benign alkyl-based substances. Research into biodegradable alkyl compounds, improved methods for their containment and disposal, and the development of more efficient chemical processes that minimize the release of these compounds into the environment are all key areas of focus.
Regulatory Framework for Alkyl Compound Usage
The regulatory framework for alkyl compound usage has become increasingly complex and stringent in recent years, reflecting growing concerns about environmental and health impacts. At the international level, the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) has been instrumental in regulating certain alkyl compounds, particularly those with long-chain structures known for their persistence in the environment.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a crucial role in regulating alkyl compounds under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA). The TSCA requires manufacturers to submit premanufacture notices for new chemical substances, including novel alkyl compounds, allowing the EPA to assess potential risks before market entry. Additionally, the EPA has implemented the Significant New Use Rule (SNUR) for certain alkyl compounds, mandating notification and review of new applications that may pose environmental or health risks.
The European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation has set a global benchmark for chemical management, including alkyl compounds. Under REACH, companies must register chemical substances manufactured or imported in quantities over one tonne per year, providing detailed safety and environmental impact data. This process has led to the restriction or phase-out of several alkyl compounds deemed hazardous.
In Asia, countries like Japan and South Korea have established their own chemical regulatory systems. Japan's Chemical Substances Control Law (CSCL) and Korea's Act on Registration and Evaluation of Chemicals (K-REACH) both require rigorous safety assessments for new and existing chemical substances, including alkyl compounds.
Specific regulations have been implemented for certain classes of alkyl compounds. For instance, perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) have come under intense scrutiny due to their persistence and potential health effects. Many countries have introduced restrictions on PFAS in consumer products, with some moving towards complete bans.
The regulatory landscape also addresses the use of alkyl compounds in specific industries. In the food industry, regulations govern the use of alkyl-based food additives and packaging materials. The cosmetics industry faces stringent rules on the use of certain alkyl compounds in personal care products, particularly those with potential for bioaccumulation or endocrine disruption.
As research continues to unveil the complex interactions between alkyl compounds and biological systems, regulatory frameworks are likely to evolve. There is a growing trend towards more comprehensive, lifecycle-based approaches to chemical regulation, considering not only the immediate impacts but also long-term environmental fate and potential for bioaccumulation. This shift is driving innovation in green chemistry, pushing for the development of safer, more sustainable alkyl compounds and their alternatives.
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a crucial role in regulating alkyl compounds under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA). The TSCA requires manufacturers to submit premanufacture notices for new chemical substances, including novel alkyl compounds, allowing the EPA to assess potential risks before market entry. Additionally, the EPA has implemented the Significant New Use Rule (SNUR) for certain alkyl compounds, mandating notification and review of new applications that may pose environmental or health risks.
The European Union's REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation has set a global benchmark for chemical management, including alkyl compounds. Under REACH, companies must register chemical substances manufactured or imported in quantities over one tonne per year, providing detailed safety and environmental impact data. This process has led to the restriction or phase-out of several alkyl compounds deemed hazardous.
In Asia, countries like Japan and South Korea have established their own chemical regulatory systems. Japan's Chemical Substances Control Law (CSCL) and Korea's Act on Registration and Evaluation of Chemicals (K-REACH) both require rigorous safety assessments for new and existing chemical substances, including alkyl compounds.
Specific regulations have been implemented for certain classes of alkyl compounds. For instance, perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) have come under intense scrutiny due to their persistence and potential health effects. Many countries have introduced restrictions on PFAS in consumer products, with some moving towards complete bans.
The regulatory landscape also addresses the use of alkyl compounds in specific industries. In the food industry, regulations govern the use of alkyl-based food additives and packaging materials. The cosmetics industry faces stringent rules on the use of certain alkyl compounds in personal care products, particularly those with potential for bioaccumulation or endocrine disruption.
As research continues to unveil the complex interactions between alkyl compounds and biological systems, regulatory frameworks are likely to evolve. There is a growing trend towards more comprehensive, lifecycle-based approaches to chemical regulation, considering not only the immediate impacts but also long-term environmental fate and potential for bioaccumulation. This shift is driving innovation in green chemistry, pushing for the development of safer, more sustainable alkyl compounds and their alternatives.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!