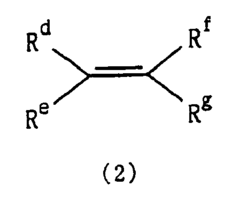
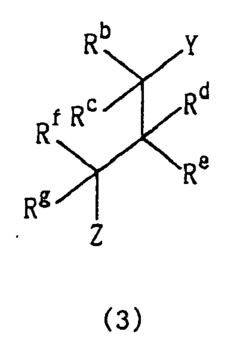
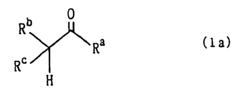
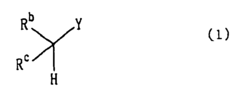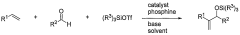Alkyl Pioneering Modern Materials Science
JUL 15, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Alkyl Materials Evolution
The evolution of alkyl materials in modern materials science represents a significant journey of innovation and discovery. This progression has been marked by several key milestones that have shaped our understanding and application of these versatile compounds.
In the early stages of alkyl materials research, scientists primarily focused on simple, linear alkyl chains. These basic structures formed the foundation for understanding the fundamental properties of alkyl compounds, such as their hydrophobicity and reactivity. As research progressed, the complexity of alkyl structures under investigation increased, leading to the exploration of branched and cyclic alkyl compounds.
The 1950s and 1960s saw a surge in polymer science, with alkyl groups playing a crucial role in the development of new synthetic materials. The introduction of alkyl side chains to polymer backbones led to the creation of materials with enhanced flexibility, durability, and chemical resistance. This period marked a significant leap forward in the practical applications of alkyl chemistry in materials science.
The advent of advanced analytical techniques in the 1970s and 1980s, such as nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy and mass spectrometry, allowed for more detailed characterization of alkyl compounds. This technological progress enabled researchers to study the structure-property relationships of alkyl materials with unprecedented precision, leading to more targeted and efficient material design.
In the 1990s and early 2000s, the focus shifted towards the development of functional alkyl materials. Scientists began incorporating alkyl groups into more complex molecular architectures, such as dendrimers and supramolecular assemblies. This era saw the emergence of alkyl-based materials with specific functionalities, including self-healing properties, stimuli-responsiveness, and controlled drug delivery capabilities.
The turn of the millennium brought about a renewed interest in sustainable and bio-based alkyl materials. Researchers began exploring the potential of renewable resources as precursors for alkyl compounds, aligning with the growing emphasis on green chemistry and environmental sustainability. This shift has led to the development of bio-derived alkyl materials with properties comparable to their petrochemical-based counterparts.
Most recently, the field has witnessed a convergence of alkyl materials science with nanotechnology. The manipulation of alkyl structures at the nanoscale has opened up new possibilities for creating materials with unique properties, such as enhanced catalytic activity, improved energy storage capabilities, and advanced sensing abilities. This integration of alkyl chemistry with nanoscience represents the cutting edge of modern materials research and promises to yield innovative solutions for a wide range of technological challenges.
In the early stages of alkyl materials research, scientists primarily focused on simple, linear alkyl chains. These basic structures formed the foundation for understanding the fundamental properties of alkyl compounds, such as their hydrophobicity and reactivity. As research progressed, the complexity of alkyl structures under investigation increased, leading to the exploration of branched and cyclic alkyl compounds.
The 1950s and 1960s saw a surge in polymer science, with alkyl groups playing a crucial role in the development of new synthetic materials. The introduction of alkyl side chains to polymer backbones led to the creation of materials with enhanced flexibility, durability, and chemical resistance. This period marked a significant leap forward in the practical applications of alkyl chemistry in materials science.
The advent of advanced analytical techniques in the 1970s and 1980s, such as nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy and mass spectrometry, allowed for more detailed characterization of alkyl compounds. This technological progress enabled researchers to study the structure-property relationships of alkyl materials with unprecedented precision, leading to more targeted and efficient material design.
In the 1990s and early 2000s, the focus shifted towards the development of functional alkyl materials. Scientists began incorporating alkyl groups into more complex molecular architectures, such as dendrimers and supramolecular assemblies. This era saw the emergence of alkyl-based materials with specific functionalities, including self-healing properties, stimuli-responsiveness, and controlled drug delivery capabilities.
The turn of the millennium brought about a renewed interest in sustainable and bio-based alkyl materials. Researchers began exploring the potential of renewable resources as precursors for alkyl compounds, aligning with the growing emphasis on green chemistry and environmental sustainability. This shift has led to the development of bio-derived alkyl materials with properties comparable to their petrochemical-based counterparts.
Most recently, the field has witnessed a convergence of alkyl materials science with nanotechnology. The manipulation of alkyl structures at the nanoscale has opened up new possibilities for creating materials with unique properties, such as enhanced catalytic activity, improved energy storage capabilities, and advanced sensing abilities. This integration of alkyl chemistry with nanoscience represents the cutting edge of modern materials research and promises to yield innovative solutions for a wide range of technological challenges.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for alkyl-based materials in modern materials science has been experiencing significant growth in recent years. This surge is primarily driven by the increasing need for advanced materials with enhanced properties across various industries. The automotive sector, in particular, has shown a strong appetite for lightweight and durable materials that can improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. Alkyl-based polymers and composites offer promising solutions in this regard, leading to a robust demand from car manufacturers and their suppliers.
In the electronics industry, the miniaturization trend and the push for more efficient devices have created a substantial market for alkyl-based materials. These materials are crucial in developing flexible electronics, organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), and advanced semiconductor packaging. The growing consumer electronics market, coupled with the rapid expansion of 5G technology, is expected to further boost the demand for these innovative materials.
The construction sector is another major consumer of alkyl-based materials, particularly in the form of high-performance coatings and sealants. As sustainability becomes a key focus in building design and construction, there is an increasing demand for materials that can enhance energy efficiency and durability. Alkyl-based materials offer superior weathering resistance and thermal insulation properties, making them highly sought after in this industry.
In the healthcare and medical devices sector, the demand for biocompatible and sterilizable materials is driving the adoption of alkyl-based polymers. These materials are being used in a wide range of applications, from drug delivery systems to implantable devices, due to their versatility and compatibility with biological systems. The aging population in many developed countries and the growing emphasis on personalized medicine are expected to sustain this demand in the coming years.
The packaging industry is also contributing significantly to the market demand for alkyl-based materials. With the rise of e-commerce and the need for sustainable packaging solutions, there is a growing interest in materials that can provide both protection and environmental friendliness. Alkyl-based biodegradable plastics and barrier coatings are gaining traction in this sector, driven by consumer preferences and regulatory pressures.
As environmental concerns continue to shape market dynamics, there is an increasing focus on developing bio-based and recyclable alkyl materials. This trend is creating new opportunities in the market, particularly for companies that can innovate in the area of sustainable materials science. The circular economy concept is influencing research and development efforts, potentially leading to new market segments for alkyl-based materials that align with these principles.
In the electronics industry, the miniaturization trend and the push for more efficient devices have created a substantial market for alkyl-based materials. These materials are crucial in developing flexible electronics, organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), and advanced semiconductor packaging. The growing consumer electronics market, coupled with the rapid expansion of 5G technology, is expected to further boost the demand for these innovative materials.
The construction sector is another major consumer of alkyl-based materials, particularly in the form of high-performance coatings and sealants. As sustainability becomes a key focus in building design and construction, there is an increasing demand for materials that can enhance energy efficiency and durability. Alkyl-based materials offer superior weathering resistance and thermal insulation properties, making them highly sought after in this industry.
In the healthcare and medical devices sector, the demand for biocompatible and sterilizable materials is driving the adoption of alkyl-based polymers. These materials are being used in a wide range of applications, from drug delivery systems to implantable devices, due to their versatility and compatibility with biological systems. The aging population in many developed countries and the growing emphasis on personalized medicine are expected to sustain this demand in the coming years.
The packaging industry is also contributing significantly to the market demand for alkyl-based materials. With the rise of e-commerce and the need for sustainable packaging solutions, there is a growing interest in materials that can provide both protection and environmental friendliness. Alkyl-based biodegradable plastics and barrier coatings are gaining traction in this sector, driven by consumer preferences and regulatory pressures.
As environmental concerns continue to shape market dynamics, there is an increasing focus on developing bio-based and recyclable alkyl materials. This trend is creating new opportunities in the market, particularly for companies that can innovate in the area of sustainable materials science. The circular economy concept is influencing research and development efforts, potentially leading to new market segments for alkyl-based materials that align with these principles.
Current Challenges
The field of alkyl research in modern materials science faces several significant challenges that hinder its progress and potential applications. One of the primary obstacles is the complexity of alkyl structures and their interactions with other materials. The vast diversity of alkyl compounds, ranging from simple linear chains to complex branched structures, makes it difficult to predict and control their behavior in various material systems.
Another major challenge lies in the synthesis and production of alkyl-based materials. While traditional methods exist, they often involve energy-intensive processes, the use of hazardous chemicals, or produce unwanted by-products. Developing more efficient, sustainable, and scalable production methods remains a critical area of focus for researchers in this field.
The stability and durability of alkyl-containing materials pose additional challenges. Many alkyl compounds are susceptible to degradation under various environmental conditions, such as exposure to heat, light, or oxidizing agents. This vulnerability limits their long-term performance and applicability in certain industries, particularly those requiring materials with extended lifespans or exposure to harsh environments.
Furthermore, the environmental impact of alkyl-based materials is a growing concern. As the world moves towards more sustainable practices, there is increasing pressure to develop biodegradable or recyclable alkyl materials. However, achieving this goal without compromising the desirable properties of these materials remains a significant challenge.
In the realm of characterization and analysis, researchers face difficulties in accurately measuring and predicting the properties of alkyl-containing materials. The complex interactions between alkyl groups and other components in a material system often lead to unexpected behaviors that are challenging to model or simulate accurately. This limitation hampers the design and optimization of new materials with tailored properties.
The integration of alkyl-based materials into existing manufacturing processes and technologies presents another set of challenges. Many industries have established production methods and equipment that may not be compatible with the unique properties of alkyl materials. Adapting these processes or developing new ones that can effectively incorporate alkyl-based components requires significant investment and innovation.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape surrounding alkyl materials, particularly in emerging applications such as nanotechnology or biomedical devices, is still evolving. Navigating the complex and sometimes uncertain regulatory requirements for new alkyl-based materials can be a significant hurdle for researchers and companies looking to bring innovative products to market.
Another major challenge lies in the synthesis and production of alkyl-based materials. While traditional methods exist, they often involve energy-intensive processes, the use of hazardous chemicals, or produce unwanted by-products. Developing more efficient, sustainable, and scalable production methods remains a critical area of focus for researchers in this field.
The stability and durability of alkyl-containing materials pose additional challenges. Many alkyl compounds are susceptible to degradation under various environmental conditions, such as exposure to heat, light, or oxidizing agents. This vulnerability limits their long-term performance and applicability in certain industries, particularly those requiring materials with extended lifespans or exposure to harsh environments.
Furthermore, the environmental impact of alkyl-based materials is a growing concern. As the world moves towards more sustainable practices, there is increasing pressure to develop biodegradable or recyclable alkyl materials. However, achieving this goal without compromising the desirable properties of these materials remains a significant challenge.
In the realm of characterization and analysis, researchers face difficulties in accurately measuring and predicting the properties of alkyl-containing materials. The complex interactions between alkyl groups and other components in a material system often lead to unexpected behaviors that are challenging to model or simulate accurately. This limitation hampers the design and optimization of new materials with tailored properties.
The integration of alkyl-based materials into existing manufacturing processes and technologies presents another set of challenges. Many industries have established production methods and equipment that may not be compatible with the unique properties of alkyl materials. Adapting these processes or developing new ones that can effectively incorporate alkyl-based components requires significant investment and innovation.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape surrounding alkyl materials, particularly in emerging applications such as nanotechnology or biomedical devices, is still evolving. Navigating the complex and sometimes uncertain regulatory requirements for new alkyl-based materials can be a significant hurdle for researchers and companies looking to bring innovative products to market.
Existing Alkyl Solutions
01 Synthesis of alkyl compounds
Various methods for synthesizing alkyl compounds are described, including reactions involving alkyl halides, alcohols, and other precursors. These processes often involve catalysts and specific reaction conditions to achieve desired alkyl products.- Synthesis of alkyl compounds: Various methods for synthesizing alkyl compounds are described, including reactions involving alkyl halides, alcohols, and other precursors. These processes often involve catalysts and specific reaction conditions to achieve desired alkyl products.
- Applications of alkyl compounds in industry: Alkyl compounds find diverse applications in industrial processes, such as in the production of lubricants, plasticizers, and surfactants. They are also used as intermediates in the synthesis of more complex organic molecules.
- Alkyl compounds in polymer chemistry: Alkyl groups play a crucial role in polymer chemistry, influencing properties such as solubility, melting point, and mechanical strength. They are used in the synthesis of various polymers and copolymers for different applications.
- Environmental and safety considerations of alkyl compounds: The environmental impact and safety aspects of alkyl compounds are addressed, including their biodegradability, toxicity, and potential for bioaccumulation. Methods for safe handling, storage, and disposal are also discussed.
- Analytical methods for alkyl compounds: Various analytical techniques are employed for the identification, quantification, and characterization of alkyl compounds. These methods include chromatography, spectroscopy, and mass spectrometry, which are essential for quality control and research purposes.
02 Applications of alkyl compounds in industry
Alkyl compounds find diverse applications in industrial processes, such as in the production of lubricants, plasticizers, and surfactants. They are also used as intermediates in the synthesis of more complex organic molecules.Expand Specific Solutions03 Alkyl compounds in polymer chemistry
Alkyl groups play a crucial role in polymer chemistry, influencing properties such as solubility, melting point, and reactivity. They are often incorporated into polymer structures to modify their characteristics for specific applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Purification and characterization of alkyl compounds
Various techniques are employed for the purification and characterization of alkyl compounds, including distillation, chromatography, and spectroscopic methods. These processes are essential for ensuring the quality and purity of alkyl products.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental and safety considerations of alkyl compounds
The use and handling of alkyl compounds often require specific safety measures due to their potential flammability and reactivity. Environmental concerns related to the production and disposal of these compounds are also addressed in various patents.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The research on alkyl pioneering modern materials science is in a dynamic growth phase, with a rapidly expanding market and evolving technological landscape. The global market size for advanced materials is projected to reach significant figures in the coming years, driven by increasing demand across various industries. The technology's maturity varies across different applications, with some areas more developed than others. Key players like Dow Global Technologies, BASF Corp., and Akzo Nobel Chemicals International BV are at the forefront of innovation, leveraging their extensive R&D capabilities. Academic institutions such as MIT and EPFL are contributing fundamental research, while companies like Sanofi and Perstorp AB are exploring applications in pharmaceuticals and specialty chemicals, respectively. This diverse ecosystem of players is driving the field forward, with collaborations between industry and academia accelerating progress.
Dow Global Technologies LLC
Technical Solution: Dow Global Technologies LLC has been at the forefront of alkyl research in modern materials science. Their approach involves developing novel alkyl-based polymers with enhanced properties. They have pioneered the use of controlled radical polymerization techniques to synthesize well-defined alkyl-containing block copolymers[1]. These materials exhibit improved thermal stability and mechanical properties compared to conventional polymers. Dow has also developed alkyl-functionalized nanoparticles for advanced composite materials, which show increased dispersion and interfacial adhesion in polymer matrices[2]. Their research extends to sustainable alkyl-based materials, focusing on bio-derived monomers and environmentally friendly synthesis routes[3].
Strengths: Extensive expertise in polymer science, strong R&D capabilities, and a wide range of industrial applications. Weaknesses: High development costs and potential regulatory challenges for new materials.
Akzo Nobel Chemicals International BV
Technical Solution: Akzo Nobel has been actively researching alkyl-based materials for various applications. They have developed alkyl-modified waterborne coatings with improved durability and chemical resistance[8]. Their research includes the synthesis of novel alkyl-functional resins for high-performance industrial coatings[9]. Akzo Nobel has also explored the use of alkyl-silane chemistry for surface modification, enhancing the properties of materials such as textiles and construction materials[10]. Additionally, they have investigated alkyl-based self-healing materials, which show promise in extending the lifespan of coatings and adhesives[11].
Strengths: Strong focus on sustainable chemistry, extensive experience in coatings technology. Weaknesses: Intense competition in the coatings market, potential raw material price fluctuations.
Innovative Alkyl Patents
Process for the preparation of organic compounds with manganese catalysts or the like
PatentInactiveEP1178031B1
Innovation
- A catalytic radical addition reaction process using a manganese compound and a cobalt compound in the presence of oxygen, which allows compounds with electron attractive groups to react with olefins, producing compounds with high selectivity and yield, including furanol derivatives.
Catalytic reactions involving alkenes
PatentWO2007027752A1
Innovation
- A nickel-catalyzed method involving a catalyst system with a Group 9, 10, or 11 metal, using a nickel-containing compound, a phosphorus-containing ligand, a silicon-containing compound, and a base, such as dicyclohexylphenylphosphine or tri(ortho-anisyl)phosphine, to facilitate the coupling of alkenes and aldehydes, forming allylic alcohols or their precursors like silyl ethers in a one-pot reaction.
Sustainability Aspects
Sustainability has become a crucial aspect in the development of modern materials science, particularly in the context of alkyl research. The focus on sustainability in this field addresses the growing concern for environmental impact, resource conservation, and long-term viability of materials and processes.
In the realm of alkyl-based materials, researchers are increasingly exploring bio-based alternatives to traditional petrochemical sources. This shift towards renewable feedstocks not only reduces dependence on fossil fuels but also contributes to the circular economy by utilizing waste streams from agriculture and forestry industries. The development of bio-based alkyl compounds offers a promising pathway for creating sustainable materials with reduced carbon footprints.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) has emerged as a vital tool in evaluating the sustainability of alkyl-derived materials. By analyzing the environmental impacts from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal, researchers can identify hotspots for improvement and optimize production processes. This holistic approach enables the development of more eco-friendly alkyl-based materials and guides decision-making in material selection and design.
Energy efficiency in the synthesis and processing of alkyl compounds is another key focus area for sustainability. Researchers are exploring novel catalytic systems and reaction pathways that require less energy input and generate fewer by-products. Green chemistry principles are being applied to develop safer, more efficient synthetic routes that minimize waste and reduce the use of hazardous substances.
The recyclability and biodegradability of alkyl-based materials are receiving increased attention in the quest for sustainable solutions. Efforts are being made to design materials that can be easily disassembled, recycled, or biodegraded at the end of their useful life. This approach not only reduces waste but also conserves valuable resources and minimizes environmental impact.
Water conservation and pollution prevention are critical sustainability aspects in alkyl research. Scientists are developing water-based processes and exploring solvent-free reactions to reduce water consumption and minimize the release of harmful chemicals into the environment. Additionally, advanced wastewater treatment technologies are being integrated into production processes to ensure responsible water management.
The integration of sustainability principles in alkyl research is driving innovation in material design and performance. By considering environmental factors alongside traditional performance metrics, researchers are developing multifunctional materials that offer both enhanced properties and reduced ecological footprints. This holistic approach is paving the way for a new generation of sustainable, high-performance materials that meet the demands of modern applications while addressing global sustainability challenges.
In the realm of alkyl-based materials, researchers are increasingly exploring bio-based alternatives to traditional petrochemical sources. This shift towards renewable feedstocks not only reduces dependence on fossil fuels but also contributes to the circular economy by utilizing waste streams from agriculture and forestry industries. The development of bio-based alkyl compounds offers a promising pathway for creating sustainable materials with reduced carbon footprints.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) has emerged as a vital tool in evaluating the sustainability of alkyl-derived materials. By analyzing the environmental impacts from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal, researchers can identify hotspots for improvement and optimize production processes. This holistic approach enables the development of more eco-friendly alkyl-based materials and guides decision-making in material selection and design.
Energy efficiency in the synthesis and processing of alkyl compounds is another key focus area for sustainability. Researchers are exploring novel catalytic systems and reaction pathways that require less energy input and generate fewer by-products. Green chemistry principles are being applied to develop safer, more efficient synthetic routes that minimize waste and reduce the use of hazardous substances.
The recyclability and biodegradability of alkyl-based materials are receiving increased attention in the quest for sustainable solutions. Efforts are being made to design materials that can be easily disassembled, recycled, or biodegraded at the end of their useful life. This approach not only reduces waste but also conserves valuable resources and minimizes environmental impact.
Water conservation and pollution prevention are critical sustainability aspects in alkyl research. Scientists are developing water-based processes and exploring solvent-free reactions to reduce water consumption and minimize the release of harmful chemicals into the environment. Additionally, advanced wastewater treatment technologies are being integrated into production processes to ensure responsible water management.
The integration of sustainability principles in alkyl research is driving innovation in material design and performance. By considering environmental factors alongside traditional performance metrics, researchers are developing multifunctional materials that offer both enhanced properties and reduced ecological footprints. This holistic approach is paving the way for a new generation of sustainable, high-performance materials that meet the demands of modern applications while addressing global sustainability challenges.
Regulatory Framework
The regulatory framework surrounding alkyl-based materials in modern materials science is complex and multifaceted, reflecting the diverse applications and potential impacts of these substances. Governments and international bodies have established comprehensive regulations to ensure the safe development, production, and use of alkyl compounds in various industries.
At the forefront of regulatory efforts is the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation in the European Union. REACH requires manufacturers and importers to register chemical substances, including alkyl compounds, and provide detailed information on their properties, hazards, and safe use. This regulation has significantly influenced global standards for chemical management and safety.
In the United States, the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) governs the introduction of new or already existing chemicals. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has the authority to require reporting, record-keeping, and testing of chemicals that may pose environmental or health risks. Alkyl compounds, depending on their specific properties and applications, may fall under various sections of TSCA.
The Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) has been widely adopted to standardize hazard communication for chemicals, including alkyl-based materials. This system ensures consistent labeling and safety data sheets across different countries, facilitating international trade and improving workplace safety.
Specific regulations also exist for alkyl compounds used in consumer products. For instance, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States regulates alkyl-based materials used in food packaging, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals. Similarly, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) assesses the safety of these materials in food contact applications.
Environmental regulations play a crucial role in managing the potential ecological impacts of alkyl compounds. The Clean Air Act and Clean Water Act in the United States set limits on emissions and discharges of various chemicals, including certain alkyl compounds. In Europe, the Water Framework Directive addresses water pollution, encompassing measures to control the release of hazardous substances, which may include specific alkyl-based materials.
As research in alkyl-based materials advances, regulatory frameworks are continuously evolving to address new findings and emerging risks. Regulatory bodies are increasingly focusing on the long-term environmental persistence and bioaccumulation potential of certain alkyl compounds. This has led to stricter controls on perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in many jurisdictions, with some countries implementing phase-outs or bans on specific PFAS compounds.
At the forefront of regulatory efforts is the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation in the European Union. REACH requires manufacturers and importers to register chemical substances, including alkyl compounds, and provide detailed information on their properties, hazards, and safe use. This regulation has significantly influenced global standards for chemical management and safety.
In the United States, the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) governs the introduction of new or already existing chemicals. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has the authority to require reporting, record-keeping, and testing of chemicals that may pose environmental or health risks. Alkyl compounds, depending on their specific properties and applications, may fall under various sections of TSCA.
The Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) has been widely adopted to standardize hazard communication for chemicals, including alkyl-based materials. This system ensures consistent labeling and safety data sheets across different countries, facilitating international trade and improving workplace safety.
Specific regulations also exist for alkyl compounds used in consumer products. For instance, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States regulates alkyl-based materials used in food packaging, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals. Similarly, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) assesses the safety of these materials in food contact applications.
Environmental regulations play a crucial role in managing the potential ecological impacts of alkyl compounds. The Clean Air Act and Clean Water Act in the United States set limits on emissions and discharges of various chemicals, including certain alkyl compounds. In Europe, the Water Framework Directive addresses water pollution, encompassing measures to control the release of hazardous substances, which may include specific alkyl-based materials.
As research in alkyl-based materials advances, regulatory frameworks are continuously evolving to address new findings and emerging risks. Regulatory bodies are increasingly focusing on the long-term environmental persistence and bioaccumulation potential of certain alkyl compounds. This has led to stricter controls on perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in many jurisdictions, with some countries implementing phase-outs or bans on specific PFAS compounds.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!