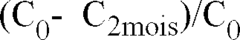Sodium Alginate: A Catalyst for Cosmetic Stabilization
JUL 14, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Sodium Alginate Overview
Sodium alginate, a versatile polysaccharide derived from brown seaweed, has gained significant attention in the cosmetic industry due to its remarkable stabilizing properties. This natural polymer, composed of mannuronic and guluronic acid units, exhibits unique characteristics that make it an invaluable ingredient in various cosmetic formulations.
The history of sodium alginate dates back to the 1880s when it was first discovered by British chemist E.C.C. Stanford. However, its potential in cosmetics was not fully realized until the mid-20th century. Since then, extensive research has been conducted to explore its multifaceted applications in the beauty and personal care sector.
One of the key attributes of sodium alginate is its ability to form stable gels in the presence of divalent cations, particularly calcium ions. This property, known as ionic gelation, allows for the creation of highly structured and stable cosmetic products. The resulting gel network can effectively suspend and stabilize other ingredients, preventing separation and ensuring product consistency over time.
In addition to its gelling capabilities, sodium alginate demonstrates excellent film-forming properties. When applied to the skin, it forms a protective barrier that helps retain moisture and shield against environmental stressors. This characteristic has made it a popular choice in skincare formulations, particularly in products designed for sensitive or dry skin types.
The thickening and emulsifying properties of sodium alginate further contribute to its widespread use in cosmetics. It can enhance the viscosity and texture of various formulations, ranging from lotions and creams to gels and masks. By stabilizing emulsions, sodium alginate helps create smooth, homogeneous products with improved shelf life and sensory appeal.
Recent advancements in cosmetic technology have led to the development of innovative applications for sodium alginate. For instance, it has been utilized in the creation of biodegradable microbeads for exfoliating products, offering an environmentally friendly alternative to synthetic microplastics. Furthermore, its compatibility with a wide range of active ingredients has made it an ideal carrier for controlled release systems in advanced skincare formulations.
The increasing demand for natural and sustainable cosmetic ingredients has further propelled the popularity of sodium alginate. As a renewable resource derived from seaweed, it aligns with the growing consumer preference for eco-friendly beauty products. This trend has encouraged cosmetic manufacturers to explore new ways of incorporating sodium alginate into their formulations, driving innovation in product development and expanding its potential applications.
The history of sodium alginate dates back to the 1880s when it was first discovered by British chemist E.C.C. Stanford. However, its potential in cosmetics was not fully realized until the mid-20th century. Since then, extensive research has been conducted to explore its multifaceted applications in the beauty and personal care sector.
One of the key attributes of sodium alginate is its ability to form stable gels in the presence of divalent cations, particularly calcium ions. This property, known as ionic gelation, allows for the creation of highly structured and stable cosmetic products. The resulting gel network can effectively suspend and stabilize other ingredients, preventing separation and ensuring product consistency over time.
In addition to its gelling capabilities, sodium alginate demonstrates excellent film-forming properties. When applied to the skin, it forms a protective barrier that helps retain moisture and shield against environmental stressors. This characteristic has made it a popular choice in skincare formulations, particularly in products designed for sensitive or dry skin types.
The thickening and emulsifying properties of sodium alginate further contribute to its widespread use in cosmetics. It can enhance the viscosity and texture of various formulations, ranging from lotions and creams to gels and masks. By stabilizing emulsions, sodium alginate helps create smooth, homogeneous products with improved shelf life and sensory appeal.
Recent advancements in cosmetic technology have led to the development of innovative applications for sodium alginate. For instance, it has been utilized in the creation of biodegradable microbeads for exfoliating products, offering an environmentally friendly alternative to synthetic microplastics. Furthermore, its compatibility with a wide range of active ingredients has made it an ideal carrier for controlled release systems in advanced skincare formulations.
The increasing demand for natural and sustainable cosmetic ingredients has further propelled the popularity of sodium alginate. As a renewable resource derived from seaweed, it aligns with the growing consumer preference for eco-friendly beauty products. This trend has encouraged cosmetic manufacturers to explore new ways of incorporating sodium alginate into their formulations, driving innovation in product development and expanding its potential applications.
Cosmetic Market Trends
The global cosmetics market has been experiencing steady growth, driven by increasing consumer awareness, rising disposable incomes, and a growing emphasis on personal appearance and self-care. In recent years, the market has shown a significant shift towards natural and organic products, with consumers becoming more conscious of the ingredients used in their skincare and beauty routines.
The demand for multifunctional cosmetic products has surged, with consumers seeking products that offer multiple benefits such as anti-aging, sun protection, and hydration in a single formulation. This trend has led to an increased focus on innovative ingredients and formulations that can deliver these diverse benefits effectively.
Sustainability has emerged as a key factor influencing consumer choices in the cosmetics industry. Brands are increasingly adopting eco-friendly packaging, sustainable sourcing practices, and cruelty-free production methods to appeal to environmentally conscious consumers. This shift has created new opportunities for ingredients like sodium alginate, which is derived from natural sources and aligns with the clean beauty movement.
The rise of social media and influencer marketing has significantly impacted cosmetic market trends, driving rapid changes in consumer preferences and accelerating product lifecycles. This has led to a need for agile product development and formulation processes that can quickly adapt to evolving market demands.
Personalization has become a major trend in the cosmetics industry, with consumers seeking products tailored to their specific skin types, concerns, and preferences. This has led to the development of customizable cosmetic formulations and the integration of technology to provide personalized skincare recommendations.
The Asia-Pacific region has emerged as a key growth driver for the global cosmetics market, with increasing urbanization, rising middle-class populations, and changing lifestyles contributing to the surge in demand. This regional shift has influenced product development strategies, with many brands focusing on ingredients and formulations that cater to Asian skin types and beauty preferences.
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated certain trends in the cosmetics market, such as the increased focus on skincare and self-care products, as well as the growth of e-commerce channels for cosmetic purchases. These shifts have created new opportunities for ingredients like sodium alginate, which can enhance product stability and shelf life, crucial factors in the context of online retail and extended storage periods.
The demand for multifunctional cosmetic products has surged, with consumers seeking products that offer multiple benefits such as anti-aging, sun protection, and hydration in a single formulation. This trend has led to an increased focus on innovative ingredients and formulations that can deliver these diverse benefits effectively.
Sustainability has emerged as a key factor influencing consumer choices in the cosmetics industry. Brands are increasingly adopting eco-friendly packaging, sustainable sourcing practices, and cruelty-free production methods to appeal to environmentally conscious consumers. This shift has created new opportunities for ingredients like sodium alginate, which is derived from natural sources and aligns with the clean beauty movement.
The rise of social media and influencer marketing has significantly impacted cosmetic market trends, driving rapid changes in consumer preferences and accelerating product lifecycles. This has led to a need for agile product development and formulation processes that can quickly adapt to evolving market demands.
Personalization has become a major trend in the cosmetics industry, with consumers seeking products tailored to their specific skin types, concerns, and preferences. This has led to the development of customizable cosmetic formulations and the integration of technology to provide personalized skincare recommendations.
The Asia-Pacific region has emerged as a key growth driver for the global cosmetics market, with increasing urbanization, rising middle-class populations, and changing lifestyles contributing to the surge in demand. This regional shift has influenced product development strategies, with many brands focusing on ingredients and formulations that cater to Asian skin types and beauty preferences.
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated certain trends in the cosmetics market, such as the increased focus on skincare and self-care products, as well as the growth of e-commerce channels for cosmetic purchases. These shifts have created new opportunities for ingredients like sodium alginate, which can enhance product stability and shelf life, crucial factors in the context of online retail and extended storage periods.
Stabilization Challenges
Sodium alginate, a versatile polysaccharide derived from brown algae, has gained significant attention in the cosmetic industry for its stabilizing properties. However, its application in cosmetic formulations presents several challenges that researchers and manufacturers must address to ensure product efficacy and stability.
One of the primary stabilization challenges associated with sodium alginate is its sensitivity to pH fluctuations. The polymer's stability and functionality can be significantly affected by changes in the pH of the cosmetic formulation. In acidic environments, sodium alginate may undergo partial hydrolysis, leading to a reduction in its viscosity and stabilizing capabilities. Conversely, in highly alkaline conditions, the polymer may experience excessive swelling, potentially compromising the texture and consistency of the final product.
Another critical challenge is the interaction of sodium alginate with multivalent cations, particularly calcium ions. While this interaction can be beneficial in certain applications, such as creating gel-like structures, it can also lead to undesired precipitation or gelation in cosmetic formulations. This phenomenon can result in texture inconsistencies, reduced shelf life, and compromised product performance.
The molecular weight distribution of sodium alginate also poses a stabilization challenge. Variations in molecular weight can significantly impact the polymer's rheological properties, affecting the viscosity and flow characteristics of the cosmetic product. Achieving a consistent and optimal molecular weight distribution is crucial for maintaining the desired texture and stability of the formulation across different batches.
Temperature sensitivity is another factor that complicates the use of sodium alginate in cosmetics. Extreme temperatures, both high and low, can alter the polymer's structure and functionality. High temperatures may lead to degradation of the alginate chains, while low temperatures can cause phase separation or gelation, particularly in aqueous systems.
Furthermore, the compatibility of sodium alginate with other ingredients in cosmetic formulations presents a significant challenge. Interactions with certain preservatives, active ingredients, or other stabilizers can potentially reduce the effectiveness of sodium alginate or lead to undesired chemical reactions. Ensuring compatibility while maintaining the desired product attributes requires careful formulation and extensive stability testing.
The processing and incorporation of sodium alginate into cosmetic formulations also present technical challenges. Achieving uniform dispersion and hydration of the polymer without forming lumps or aggregates can be difficult, especially in large-scale production. Improper dispersion can lead to inconsistent product texture and reduced stabilizing efficiency.
Lastly, the natural origin of sodium alginate, while appealing from a marketing perspective, introduces variability in its composition and properties. Factors such as the source of the algae, harvesting conditions, and extraction methods can influence the quality and consistency of the sodium alginate used in cosmetic applications. This variability necessitates rigorous quality control measures to ensure consistent product performance and stability across different batches and formulations.
One of the primary stabilization challenges associated with sodium alginate is its sensitivity to pH fluctuations. The polymer's stability and functionality can be significantly affected by changes in the pH of the cosmetic formulation. In acidic environments, sodium alginate may undergo partial hydrolysis, leading to a reduction in its viscosity and stabilizing capabilities. Conversely, in highly alkaline conditions, the polymer may experience excessive swelling, potentially compromising the texture and consistency of the final product.
Another critical challenge is the interaction of sodium alginate with multivalent cations, particularly calcium ions. While this interaction can be beneficial in certain applications, such as creating gel-like structures, it can also lead to undesired precipitation or gelation in cosmetic formulations. This phenomenon can result in texture inconsistencies, reduced shelf life, and compromised product performance.
The molecular weight distribution of sodium alginate also poses a stabilization challenge. Variations in molecular weight can significantly impact the polymer's rheological properties, affecting the viscosity and flow characteristics of the cosmetic product. Achieving a consistent and optimal molecular weight distribution is crucial for maintaining the desired texture and stability of the formulation across different batches.
Temperature sensitivity is another factor that complicates the use of sodium alginate in cosmetics. Extreme temperatures, both high and low, can alter the polymer's structure and functionality. High temperatures may lead to degradation of the alginate chains, while low temperatures can cause phase separation or gelation, particularly in aqueous systems.
Furthermore, the compatibility of sodium alginate with other ingredients in cosmetic formulations presents a significant challenge. Interactions with certain preservatives, active ingredients, or other stabilizers can potentially reduce the effectiveness of sodium alginate or lead to undesired chemical reactions. Ensuring compatibility while maintaining the desired product attributes requires careful formulation and extensive stability testing.
The processing and incorporation of sodium alginate into cosmetic formulations also present technical challenges. Achieving uniform dispersion and hydration of the polymer without forming lumps or aggregates can be difficult, especially in large-scale production. Improper dispersion can lead to inconsistent product texture and reduced stabilizing efficiency.
Lastly, the natural origin of sodium alginate, while appealing from a marketing perspective, introduces variability in its composition and properties. Factors such as the source of the algae, harvesting conditions, and extraction methods can influence the quality and consistency of the sodium alginate used in cosmetic applications. This variability necessitates rigorous quality control measures to ensure consistent product performance and stability across different batches and formulations.
Current Stabilization
01 Stabilization of sodium alginate in pharmaceutical formulations
Sodium alginate is used as a stabilizer in various pharmaceutical formulations. It helps to improve the stability and consistency of drug formulations, particularly in liquid and semi-solid preparations. The stabilizing properties of sodium alginate are attributed to its ability to form gels and increase viscosity, which can prevent sedimentation and phase separation in suspensions and emulsions.- Stabilization of sodium alginate in pharmaceutical formulations: Sodium alginate is used as a stabilizer in various pharmaceutical formulations. It helps to improve the stability and consistency of drug formulations, particularly in liquid or semi-solid preparations. The stabilizing properties of sodium alginate are utilized to enhance the shelf life and maintain the efficacy of pharmaceutical products.
- Sodium alginate as a stabilizer in food and beverage products: Sodium alginate is widely used as a stabilizer in the food and beverage industry. It helps to improve texture, prevent separation, and maintain the consistency of various products. Its stabilizing properties are particularly useful in dairy products, sauces, and beverages, where it helps to create a smooth and uniform texture.
- Stabilization of emulsions and suspensions using sodium alginate: Sodium alginate is effective in stabilizing emulsions and suspensions. It acts as an emulsifier and thickening agent, helping to prevent the separation of oil and water phases in emulsions. In suspensions, it helps to keep particles evenly distributed throughout the liquid medium, preventing sedimentation or aggregation.
- Use of sodium alginate in wound dressings and medical applications: Sodium alginate is used in wound dressings and various medical applications due to its stabilizing and gel-forming properties. It helps to maintain a moist environment for wound healing, absorb exudates, and provide a protective barrier. The stability of sodium alginate gels is crucial for their effectiveness in these applications.
- Stabilization of sodium alginate in cosmetic formulations: Sodium alginate is utilized as a stabilizer in cosmetic formulations. It helps to improve the texture, consistency, and stability of various cosmetic products such as creams, lotions, and gels. The stabilizing properties of sodium alginate contribute to the overall quality and shelf life of cosmetic preparations.
02 Sodium alginate in food and beverage applications
Sodium alginate is widely used in the food and beverage industry as a stabilizer and thickening agent. It helps to improve texture, prevent syneresis, and enhance the overall stability of various food products. In beverages, it can be used to stabilize emulsions, suspend particles, and create unique textures.Expand Specific Solutions03 Sodium alginate in cosmetic formulations
In cosmetic products, sodium alginate is used as a stabilizer and thickening agent. It helps to improve the texture and stability of creams, lotions, and gels. Sodium alginate can also form protective films on the skin, contributing to moisturization and improved product performance.Expand Specific Solutions04 Sodium alginate in wound dressings and medical applications
Sodium alginate is utilized in wound dressings and various medical applications due to its biocompatibility and ability to form hydrogels. In wound care, it helps to maintain a moist environment, absorb exudates, and promote healing. The stabilization of sodium alginate in these applications is crucial for ensuring consistent performance and shelf-life.Expand Specific Solutions05 Stabilization techniques for sodium alginate solutions
Various techniques are employed to stabilize sodium alginate solutions and improve their long-term stability. These may include pH adjustment, addition of preservatives, use of chelating agents, and optimization of storage conditions. Proper stabilization is essential for maintaining the functional properties of sodium alginate in different applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The sodium alginate market for cosmetic stabilization is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for natural and sustainable ingredients in personal care products. The market size is expanding, with projections indicating significant growth potential in the coming years. Technologically, sodium alginate is well-established, but ongoing research focuses on enhancing its functionality and applications. Key players like L'Oréal, Beiersdorf, and Shiseido are investing in R&D to develop innovative formulations, while companies such as Shandong Jiejing Group and COSMAX are specializing in production and supply. The competitive landscape is diverse, with both global cosmetic giants and specialized ingredient manufacturers vying for market share.
L'Oréal SA
Technical Solution: L'Oréal has developed an innovative approach to using sodium alginate in cosmetic formulations. Their research focuses on creating a stable emulsion system that incorporates sodium alginate as a natural thickening and stabilizing agent. The company has patented a method that combines sodium alginate with specific oil-phase components to form a robust gel network[1]. This network enhances the stability of water-in-oil emulsions, particularly in sunscreen formulations. L'Oréal's technique involves precise control of the alginate's molecular weight and concentration, which allows for customized texture and viscosity in various cosmetic products[2]. Additionally, they have explored the synergistic effects of sodium alginate with other natural polymers to create multifunctional stabilizing systems that offer improved sensory properties and long-lasting effects[3].
Strengths: Utilizes natural, sustainable ingredients; Provides excellent stability in various formulations; Offers customizable textures. Weaknesses: May require specialized processing techniques; Potential for higher production costs compared to synthetic stabilizers.
Beiersdorf AG
Technical Solution: Beiersdorf AG has developed a proprietary technology leveraging sodium alginate for advanced skincare formulations. Their approach focuses on creating a "smart" delivery system that utilizes the responsive properties of sodium alginate to environmental stimuli[4]. The company has engineered a method to encapsulate active ingredients within sodium alginate-based microspheres, which can release their contents in response to changes in pH or ion concentration on the skin[5]. This technology allows for targeted and controlled delivery of sensitive ingredients, such as vitamins or peptides. Beiersdorf has also explored the combination of sodium alginate with specific proteins to create biomimetic films that enhance skin barrier function and provide long-lasting hydration[6]. Their research extends to developing sodium alginate-based hydrogels that can adapt to skin movement, ensuring comfort and prolonged efficacy of topical treatments.
Strengths: Enables targeted delivery of active ingredients; Provides responsive and adaptive formulations. Weaknesses: May have limitations in certain product types; Requires sophisticated formulation expertise.
Alginate Innovations
Cosmetic and/or dermatological use of a composition containing at least one oxidation-sensitive hydrophilic active stabilised by at least one polymer or copolymer of maleic anhydride
PatentInactiveEP1374849A1
Innovation
- A composition containing ascorbic acid or its derivatives combined with maleic anhydride copolymers in an aqueous phase, which stabilizes the active ingredient and enhances its depigmenting and whitening effects by inhibiting tyrosinase and melanocyte dendricity.
Compositions and methods for reducing the transmissivity of illnesses using an oral delivery system
PatentPendingUS20240165191A1
Innovation
- A composition comprising silver in colloidal or nanoparticle form, combined with glycyrrhizic acid, quercetin, and other antimicrobial agents like xylitol, ascorbic acid, curcumin, and eucalyptol, is administered as a nasal spray, mouthwash, or bronchial aerosol to inhibit viral replication and reduce microbial attachment, providing both prophylactic and therapeutic benefits.
Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance is a critical aspect of sodium alginate's use in cosmetic stabilization. As a naturally derived ingredient, sodium alginate generally enjoys a favorable regulatory status across major global markets. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recognizes sodium alginate as Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) for use in food and cosmetic products. This classification allows for its widespread application in cosmetic formulations without significant regulatory hurdles.
The European Union, through its Cosmetic Regulation (EC) No. 1223/2009, also permits the use of sodium alginate in cosmetic products. The European Commission's database of cosmetic ingredients, CosIng, lists sodium alginate with no specific restrictions, further facilitating its incorporation into a wide range of cosmetic products within the EU market.
In Japan, sodium alginate is approved by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare for use in cosmetics and is listed in the Japanese Standards of Cosmetic Ingredients (JSCI). This approval ensures its compliance with Japanese regulatory requirements, allowing for its use in cosmetic formulations sold in the Japanese market.
However, manufacturers must be aware of specific regulations regarding product claims and labeling when using sodium alginate in cosmetic formulations. For instance, in the United States, if a product containing sodium alginate makes any drug claims, it may be subject to additional regulatory scrutiny and potentially classified as a drug rather than a cosmetic.
Globally, the International Nomenclature of Cosmetic Ingredients (INCI) recognizes sodium alginate, providing a standardized naming convention for ingredient lists on cosmetic products. This standardization aids in regulatory compliance across different markets and enhances transparency for consumers.
While sodium alginate is generally well-regarded by regulatory bodies, formulators must still adhere to good manufacturing practices (GMP) and ensure that the final product meets all safety and quality standards. This includes conducting appropriate stability testing, preservative efficacy testing, and safety assessments of the complete formulation.
As sustainability becomes an increasingly important factor in regulatory considerations, sodium alginate's natural origin from brown seaweed may provide additional advantages. Many regulatory bodies are encouraging the use of sustainable and naturally derived ingredients, which aligns well with sodium alginate's profile.
In conclusion, the regulatory landscape for sodium alginate in cosmetic stabilization is largely favorable, with widespread acceptance across major global markets. However, cosmetic manufacturers must remain vigilant in monitoring any changes in regulations and ensure compliance with specific regional requirements, particularly regarding product claims and overall formulation safety.
The European Union, through its Cosmetic Regulation (EC) No. 1223/2009, also permits the use of sodium alginate in cosmetic products. The European Commission's database of cosmetic ingredients, CosIng, lists sodium alginate with no specific restrictions, further facilitating its incorporation into a wide range of cosmetic products within the EU market.
In Japan, sodium alginate is approved by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare for use in cosmetics and is listed in the Japanese Standards of Cosmetic Ingredients (JSCI). This approval ensures its compliance with Japanese regulatory requirements, allowing for its use in cosmetic formulations sold in the Japanese market.
However, manufacturers must be aware of specific regulations regarding product claims and labeling when using sodium alginate in cosmetic formulations. For instance, in the United States, if a product containing sodium alginate makes any drug claims, it may be subject to additional regulatory scrutiny and potentially classified as a drug rather than a cosmetic.
Globally, the International Nomenclature of Cosmetic Ingredients (INCI) recognizes sodium alginate, providing a standardized naming convention for ingredient lists on cosmetic products. This standardization aids in regulatory compliance across different markets and enhances transparency for consumers.
While sodium alginate is generally well-regarded by regulatory bodies, formulators must still adhere to good manufacturing practices (GMP) and ensure that the final product meets all safety and quality standards. This includes conducting appropriate stability testing, preservative efficacy testing, and safety assessments of the complete formulation.
As sustainability becomes an increasingly important factor in regulatory considerations, sodium alginate's natural origin from brown seaweed may provide additional advantages. Many regulatory bodies are encouraging the use of sustainable and naturally derived ingredients, which aligns well with sodium alginate's profile.
In conclusion, the regulatory landscape for sodium alginate in cosmetic stabilization is largely favorable, with widespread acceptance across major global markets. However, cosmetic manufacturers must remain vigilant in monitoring any changes in regulations and ensure compliance with specific regional requirements, particularly regarding product claims and overall formulation safety.
Sustainability Impact
The use of sodium alginate in cosmetic formulations has significant implications for sustainability in the beauty industry. As a natural, biodegradable polymer derived from brown seaweed, sodium alginate offers a more environmentally friendly alternative to synthetic stabilizers and emulsifiers. Its renewable sourcing aligns with the growing consumer demand for sustainable and natural ingredients in personal care products.
The cultivation and harvesting of seaweed for alginate production can contribute to marine ecosystem health when managed responsibly. Seaweed farms can act as carbon sinks, absorbing CO2 from the atmosphere and helping to mitigate climate change. Additionally, these farms can provide habitats for marine life and help reduce ocean acidification. However, it is crucial to ensure sustainable harvesting practices to prevent overexploitation of seaweed resources.
From a manufacturing perspective, the production of sodium alginate generally requires less energy and generates fewer harmful byproducts compared to the synthesis of many petroleum-based stabilizers. This can lead to a reduced carbon footprint for cosmetic products that incorporate sodium alginate. Furthermore, the biodegradability of alginate-based formulations means they are less likely to persist in the environment after use, potentially reducing the accumulation of microplastics in water systems.
The multifunctional nature of sodium alginate in cosmetic formulations can also contribute to sustainability efforts. Its ability to act as a thickener, emulsifier, and stabilizer may allow formulators to reduce the number of ingredients in a product, simplifying supply chains and potentially decreasing packaging requirements. This streamlining can lead to more efficient resource use and reduced waste throughout the product lifecycle.
However, it is important to consider the potential environmental impacts of increased sodium alginate demand. Sustainable seaweed farming practices must be implemented to prevent ecosystem disruption and ensure long-term viability. Additionally, the transportation of seaweed and alginate products should be optimized to minimize the carbon footprint associated with their global distribution.
As the cosmetics industry continues to prioritize sustainability, sodium alginate's role as a natural, versatile, and eco-friendly ingredient is likely to expand. Its use can support brands in meeting consumer expectations for green beauty products while potentially improving their overall environmental performance. Future research and development efforts may focus on enhancing the efficiency of alginate extraction and processing methods to further improve its sustainability profile.
The cultivation and harvesting of seaweed for alginate production can contribute to marine ecosystem health when managed responsibly. Seaweed farms can act as carbon sinks, absorbing CO2 from the atmosphere and helping to mitigate climate change. Additionally, these farms can provide habitats for marine life and help reduce ocean acidification. However, it is crucial to ensure sustainable harvesting practices to prevent overexploitation of seaweed resources.
From a manufacturing perspective, the production of sodium alginate generally requires less energy and generates fewer harmful byproducts compared to the synthesis of many petroleum-based stabilizers. This can lead to a reduced carbon footprint for cosmetic products that incorporate sodium alginate. Furthermore, the biodegradability of alginate-based formulations means they are less likely to persist in the environment after use, potentially reducing the accumulation of microplastics in water systems.
The multifunctional nature of sodium alginate in cosmetic formulations can also contribute to sustainability efforts. Its ability to act as a thickener, emulsifier, and stabilizer may allow formulators to reduce the number of ingredients in a product, simplifying supply chains and potentially decreasing packaging requirements. This streamlining can lead to more efficient resource use and reduced waste throughout the product lifecycle.
However, it is important to consider the potential environmental impacts of increased sodium alginate demand. Sustainable seaweed farming practices must be implemented to prevent ecosystem disruption and ensure long-term viability. Additionally, the transportation of seaweed and alginate products should be optimized to minimize the carbon footprint associated with their global distribution.
As the cosmetics industry continues to prioritize sustainability, sodium alginate's role as a natural, versatile, and eco-friendly ingredient is likely to expand. Its use can support brands in meeting consumer expectations for green beauty products while potentially improving their overall environmental performance. Future research and development efforts may focus on enhancing the efficiency of alginate extraction and processing methods to further improve its sustainability profile.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!