Sodium Alginate Innovations in Personal Care Industry
JUL 14, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Alginate Evolution
Sodium alginate, derived from brown seaweed, has undergone significant evolution in its applications within the personal care industry. Initially discovered in the 1880s, alginate's journey began as a food additive and industrial material. However, its unique properties soon caught the attention of cosmetic formulators, marking the beginning of its transformation in personal care.
In the 1950s, alginate found its first major application in the personal care sector as a thickening agent in creams and lotions. Its ability to form stable gels and emulsions made it an ideal ingredient for improving product texture and stability. This period marked the initial phase of alginate's evolution, focusing primarily on its functional properties.
The 1970s and 1980s saw a shift towards understanding alginate's skin benefits. Researchers discovered its moisturizing and film-forming properties, leading to its incorporation in more sophisticated skincare formulations. This era also witnessed the development of advanced extraction and purification techniques, resulting in higher quality sodium alginate suitable for cosmetic use.
The 1990s brought about a revolution in alginate technology with the introduction of nanoparticle delivery systems. Sodium alginate's ability to encapsulate active ingredients and facilitate controlled release opened up new possibilities in targeted skincare treatments. This innovation significantly expanded alginate's role from a mere thickener to a crucial component in advanced skincare formulations.
The turn of the millennium saw alginate evolving into a multifunctional ingredient. Its natural origin aligned perfectly with the growing consumer demand for clean and green beauty products. Formulators began exploring alginate's potential in natural preservative systems, leveraging its antimicrobial properties to reduce the need for synthetic preservatives.
In recent years, the evolution of sodium alginate has taken a more sustainable direction. With increasing concerns about environmental impact, researchers have focused on developing eco-friendly extraction methods and exploring ways to utilize alginate byproducts. This has led to the concept of "zero-waste" alginate production, where every part of the seaweed is utilized, enhancing the ingredient's sustainability profile.
The latest frontier in alginate evolution is its role in smart and responsive skincare formulations. Scientists are developing alginate-based hydrogels that can respond to environmental stimuli such as pH, temperature, or light. These advanced materials promise to deliver a new generation of personalized skincare products that adapt to individual skin conditions and environmental factors.
As we look to the future, the evolution of sodium alginate in personal care continues to accelerate. Emerging research is exploring its potential in microbiome-friendly formulations and its synergistic effects with other natural ingredients. The ongoing evolution of this versatile ingredient promises to bring even more innovative and sustainable solutions to the personal care industry.
In the 1950s, alginate found its first major application in the personal care sector as a thickening agent in creams and lotions. Its ability to form stable gels and emulsions made it an ideal ingredient for improving product texture and stability. This period marked the initial phase of alginate's evolution, focusing primarily on its functional properties.
The 1970s and 1980s saw a shift towards understanding alginate's skin benefits. Researchers discovered its moisturizing and film-forming properties, leading to its incorporation in more sophisticated skincare formulations. This era also witnessed the development of advanced extraction and purification techniques, resulting in higher quality sodium alginate suitable for cosmetic use.
The 1990s brought about a revolution in alginate technology with the introduction of nanoparticle delivery systems. Sodium alginate's ability to encapsulate active ingredients and facilitate controlled release opened up new possibilities in targeted skincare treatments. This innovation significantly expanded alginate's role from a mere thickener to a crucial component in advanced skincare formulations.
The turn of the millennium saw alginate evolving into a multifunctional ingredient. Its natural origin aligned perfectly with the growing consumer demand for clean and green beauty products. Formulators began exploring alginate's potential in natural preservative systems, leveraging its antimicrobial properties to reduce the need for synthetic preservatives.
In recent years, the evolution of sodium alginate has taken a more sustainable direction. With increasing concerns about environmental impact, researchers have focused on developing eco-friendly extraction methods and exploring ways to utilize alginate byproducts. This has led to the concept of "zero-waste" alginate production, where every part of the seaweed is utilized, enhancing the ingredient's sustainability profile.
The latest frontier in alginate evolution is its role in smart and responsive skincare formulations. Scientists are developing alginate-based hydrogels that can respond to environmental stimuli such as pH, temperature, or light. These advanced materials promise to deliver a new generation of personalized skincare products that adapt to individual skin conditions and environmental factors.
As we look to the future, the evolution of sodium alginate in personal care continues to accelerate. Emerging research is exploring its potential in microbiome-friendly formulations and its synergistic effects with other natural ingredients. The ongoing evolution of this versatile ingredient promises to bring even more innovative and sustainable solutions to the personal care industry.
Personal Care Market
The personal care market has experienced significant growth and transformation in recent years, driven by changing consumer preferences, technological advancements, and increasing awareness of health and wellness. This market encompasses a wide range of products, including skincare, haircare, oral care, and cosmetics, with a growing emphasis on natural and sustainable solutions.
Sodium alginate, a versatile biopolymer derived from brown seaweed, has emerged as a key ingredient in various personal care formulations. Its unique properties, such as thickening, stabilizing, and film-forming capabilities, make it particularly valuable in this industry. The increasing demand for natural and eco-friendly ingredients has further boosted the adoption of sodium alginate in personal care products.
The global personal care market size was valued at approximately $450 billion in 2020 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 5% from 2021 to 2026. This growth is attributed to factors such as rising disposable incomes, urbanization, and a growing middle-class population in emerging economies. Additionally, the increasing focus on self-care and personal grooming, particularly among millennials and Gen Z consumers, has fueled market expansion.
Within the personal care market, skincare remains the largest segment, accounting for nearly 40% of the total market share. The haircare segment follows closely, with oral care and color cosmetics also contributing significantly to the overall market value. Sodium alginate finds applications across these segments, particularly in skincare and haircare products, where its moisturizing and texturizing properties are highly valued.
The trend towards natural and organic products has been a major driver in the personal care industry, with consumers increasingly seeking products free from synthetic chemicals and harmful additives. This shift has created a favorable environment for ingredients like sodium alginate, which aligns well with the clean beauty movement. The market for natural and organic personal care products is expected to grow at a CAGR of over 9% through 2026, outpacing the overall market growth.
Sustainability has also become a crucial factor in the personal care market, with consumers demanding environmentally friendly products and packaging. Sodium alginate's biodegradability and renewable sourcing make it an attractive option for brands looking to enhance their sustainability credentials. This aligns with the broader industry trend towards circular economy principles and reduced environmental impact.
The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated certain trends in the personal care market, such as the increased focus on hygiene and self-care routines. This has led to a surge in demand for hand sanitizers, soaps, and other personal hygiene products, many of which incorporate sodium alginate for its gel-forming and stabilizing properties.
Sodium alginate, a versatile biopolymer derived from brown seaweed, has emerged as a key ingredient in various personal care formulations. Its unique properties, such as thickening, stabilizing, and film-forming capabilities, make it particularly valuable in this industry. The increasing demand for natural and eco-friendly ingredients has further boosted the adoption of sodium alginate in personal care products.
The global personal care market size was valued at approximately $450 billion in 2020 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 5% from 2021 to 2026. This growth is attributed to factors such as rising disposable incomes, urbanization, and a growing middle-class population in emerging economies. Additionally, the increasing focus on self-care and personal grooming, particularly among millennials and Gen Z consumers, has fueled market expansion.
Within the personal care market, skincare remains the largest segment, accounting for nearly 40% of the total market share. The haircare segment follows closely, with oral care and color cosmetics also contributing significantly to the overall market value. Sodium alginate finds applications across these segments, particularly in skincare and haircare products, where its moisturizing and texturizing properties are highly valued.
The trend towards natural and organic products has been a major driver in the personal care industry, with consumers increasingly seeking products free from synthetic chemicals and harmful additives. This shift has created a favorable environment for ingredients like sodium alginate, which aligns well with the clean beauty movement. The market for natural and organic personal care products is expected to grow at a CAGR of over 9% through 2026, outpacing the overall market growth.
Sustainability has also become a crucial factor in the personal care market, with consumers demanding environmentally friendly products and packaging. Sodium alginate's biodegradability and renewable sourcing make it an attractive option for brands looking to enhance their sustainability credentials. This aligns with the broader industry trend towards circular economy principles and reduced environmental impact.
The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated certain trends in the personal care market, such as the increased focus on hygiene and self-care routines. This has led to a surge in demand for hand sanitizers, soaps, and other personal hygiene products, many of which incorporate sodium alginate for its gel-forming and stabilizing properties.
Technical Hurdles
Despite the widespread use of sodium alginate in the personal care industry, several technical hurdles still exist that limit its full potential. One of the primary challenges is the stability of sodium alginate in various formulations. When exposed to certain pH levels or ionic environments, sodium alginate can undergo undesired gelation or precipitation, compromising the product's texture and efficacy. This instability can lead to inconsistencies in product performance and shelf life, particularly in complex formulations containing multiple active ingredients.
Another significant hurdle is the control of viscosity and rheological properties. While sodium alginate's thickening ability is valuable, achieving precise and consistent viscosity across different batches and formulations can be challenging. This variability can affect the sensory attributes of personal care products, potentially impacting consumer acceptance and product efficacy.
The molecular weight distribution of sodium alginate also presents technical difficulties. Different molecular weight fractions can significantly influence the material's properties, including its gelling characteristics and film-forming abilities. Controlling and standardizing the molecular weight distribution during production and processing remains a challenge, affecting the reproducibility of product performance.
Compatibility with other ingredients in personal care formulations is another area of concern. Sodium alginate can interact unpredictably with certain active ingredients, preservatives, or other polymers, potentially leading to reduced efficacy or undesired changes in product texture. This limitation restricts the range of ingredients that can be effectively combined with sodium alginate in a single formulation.
The bioavailability and skin penetration of active ingredients in sodium alginate-based formulations also present challenges. While sodium alginate can form protective films on the skin, this property may inadvertently hinder the absorption of beneficial compounds. Balancing the barrier properties of sodium alginate with the need for effective delivery of active ingredients requires careful formulation and often involves complex delivery systems.
Lastly, the sourcing and quality control of sodium alginate pose ongoing challenges. As a natural polymer derived from seaweed, sodium alginate can exhibit batch-to-batch variations in its properties. Ensuring consistent quality and purity across different sources and production batches is crucial for maintaining product performance and safety standards in the personal care industry.
Another significant hurdle is the control of viscosity and rheological properties. While sodium alginate's thickening ability is valuable, achieving precise and consistent viscosity across different batches and formulations can be challenging. This variability can affect the sensory attributes of personal care products, potentially impacting consumer acceptance and product efficacy.
The molecular weight distribution of sodium alginate also presents technical difficulties. Different molecular weight fractions can significantly influence the material's properties, including its gelling characteristics and film-forming abilities. Controlling and standardizing the molecular weight distribution during production and processing remains a challenge, affecting the reproducibility of product performance.
Compatibility with other ingredients in personal care formulations is another area of concern. Sodium alginate can interact unpredictably with certain active ingredients, preservatives, or other polymers, potentially leading to reduced efficacy or undesired changes in product texture. This limitation restricts the range of ingredients that can be effectively combined with sodium alginate in a single formulation.
The bioavailability and skin penetration of active ingredients in sodium alginate-based formulations also present challenges. While sodium alginate can form protective films on the skin, this property may inadvertently hinder the absorption of beneficial compounds. Balancing the barrier properties of sodium alginate with the need for effective delivery of active ingredients requires careful formulation and often involves complex delivery systems.
Lastly, the sourcing and quality control of sodium alginate pose ongoing challenges. As a natural polymer derived from seaweed, sodium alginate can exhibit batch-to-batch variations in its properties. Ensuring consistent quality and purity across different sources and production batches is crucial for maintaining product performance and safety standards in the personal care industry.
Current Applications
01 Use of sodium alginate in cosmetic formulations
Sodium alginate is widely used in cosmetic formulations due to its thickening, stabilizing, and film-forming properties. It can improve the texture and consistency of various cosmetic products, including creams, lotions, and gels. Sodium alginate also helps in moisture retention, making it beneficial for skincare products.- Use of sodium alginate in cosmetic formulations: Sodium alginate is widely used in cosmetic formulations due to its thickening, stabilizing, and film-forming properties. It can improve the texture and consistency of various cosmetic products, including creams, lotions, and gels. Sodium alginate also helps in moisture retention, making it beneficial for skincare products.
- Sodium alginate in drug delivery systems: Sodium alginate is utilized in pharmaceutical applications, particularly in drug delivery systems. It can form hydrogels that encapsulate drugs, allowing for controlled release. This property makes it useful in developing oral, topical, and injectable drug formulations with improved bioavailability and targeted delivery.
- Sodium alginate in wound healing applications: Sodium alginate is employed in wound dressings and healing applications due to its biocompatibility and ability to maintain a moist wound environment. It can absorb wound exudates and form a protective gel, promoting faster healing and reducing the risk of infection. These properties make it valuable in advanced wound care products.
- Use of sodium alginate in food industry: In the food industry, sodium alginate is used as a thickening agent, stabilizer, and emulsifier. It can improve the texture and stability of various food products, including ice cream, sauces, and beverages. Sodium alginate is also used in molecular gastronomy for creating unique food textures and presentations.
- Sodium alginate in 3D bioprinting and tissue engineering: Sodium alginate is utilized in 3D bioprinting and tissue engineering applications due to its biocompatibility and ability to form hydrogels. It can be used as a bioink for printing cell-laden structures, supporting cell growth and differentiation. This makes it valuable in creating artificial tissues and organs for regenerative medicine.
02 Sodium alginate in drug delivery systems
Sodium alginate is utilized in pharmaceutical applications, particularly in drug delivery systems. It can form hydrogels that encapsulate drugs, allowing for controlled release. This property makes it useful in developing oral, topical, and injectable drug formulations with improved bioavailability and targeted delivery.Expand Specific Solutions03 Sodium alginate in wound healing applications
Sodium alginate is employed in wound dressings and healing applications due to its biocompatibility and ability to maintain a moist wound environment. It can absorb wound exudates and form a protective gel, promoting faster healing and reducing the risk of infection. These properties make it valuable in advanced wound care products.Expand Specific Solutions04 Use of sodium alginate in food industry
In the food industry, sodium alginate is used as a thickening agent, stabilizer, and emulsifier. It can improve the texture and stability of various food products, including ice cream, yogurt, and sauces. Sodium alginate is also used in molecular gastronomy for creating unique food textures and presentations.Expand Specific Solutions05 Sodium alginate in 3D bioprinting and tissue engineering
Sodium alginate plays a crucial role in 3D bioprinting and tissue engineering applications. Its ability to form hydrogels that can encapsulate cells makes it suitable for creating bioinks used in 3D bioprinting of tissue constructs. This technology has potential applications in regenerative medicine and drug testing platforms.Expand Specific Solutions
Industry Leaders
The sodium alginate market in the personal care industry is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing consumer demand for natural and sustainable ingredients. The market is in a mature stage but continues to expand due to innovative applications. Major players like Unilever, Colgate-Palmolive, and Momentive Performance Materials are investing in research and development to enhance product performance and diversify applications. The technology's maturity varies across different segments, with established uses in skincare and oral care, while newer applications in hair care and color cosmetics are still evolving. Companies are focusing on improving extraction methods and developing novel formulations to meet the growing demand for clean beauty products.
Unilever Plc
Technical Solution: Unilever has developed innovative sodium alginate-based formulations for personal care products, focusing on sustainable and natural ingredients. Their approach includes using sodium alginate as a thickening and stabilizing agent in hair care products, particularly in shampoos and conditioners. The company has also incorporated sodium alginate into their skincare lines, utilizing its moisture-retaining properties to create hydrating face masks and serums. Unilever's research has shown that sodium alginate can form a protective film on the skin, helping to lock in moisture and deliver active ingredients more effectively[1][3]. Additionally, they have explored the use of sodium alginate in oral care products, developing innovative toothpaste formulations that leverage its natural cleansing and remineralizing properties[2].
Strengths: Extensive R&D capabilities, global market presence, and a strong focus on sustainability. Weaknesses: Potential higher costs associated with natural ingredients and the need for consumer education on the benefits of sodium alginate in personal care products.
Momentive Performance Materials, Inc.
Technical Solution: Momentive has developed a range of sodium alginate-based products for the personal care industry, focusing on innovative textures and sensory experiences. Their technology combines sodium alginate with silicone chemistry to create unique hybrid materials that offer both the natural benefits of alginate and the performance advantages of silicones. These hybrid materials are used in various applications, including hair styling products that provide long-lasting hold with a natural feel, and skincare formulations that offer improved spreadability and a silky texture. Momentive's research has shown that these alginate-silicone hybrids can enhance the efficacy of active ingredients in skincare products by forming a breathable film on the skin surface[4][5]. The company has also developed sodium alginate-based encapsulation technologies for controlled release of fragrances and active ingredients in personal care formulations.
Strengths: Unique combination of natural and synthetic technologies, diverse product portfolio. Weaknesses: Potential concerns from consumers seeking fully natural products, complexity in formulation process.
Key Alginate Patents
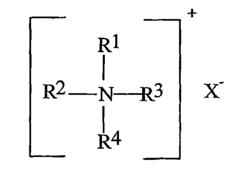
Composition comprising at least one alginate for use in treatment and/or prevention of overweight
PatentActiveUS20160015736A1
Innovation
- A reconstitutable composition combining low viscosity and high viscosity alginates, along with a suspending agent, to create a clear, palatable, and easily mixable aqueous diet product that forms a strong gel in the stomach, reducing caloric intake and promoting satiety.
Process for manufacture of personal care products utilizing a concentrate water phase
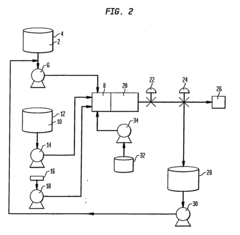
PatentInactiveEP1575695B1
Innovation
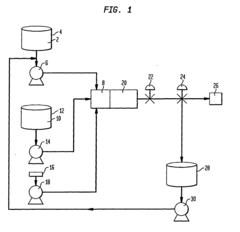
- A process involving a concentrated first water phase, a second phase (either oil or aqueous with surfactants), and a third phase of water, blended together in a small blending tube under high pressure and shear, significantly reducing equipment needs and mixing time.
Regulatory Landscape
The regulatory landscape for sodium alginate in the personal care industry is complex and dynamic, reflecting the growing emphasis on product safety and environmental sustainability. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates sodium alginate as a food additive and cosmetic ingredient. Under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, sodium alginate is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) for use in food products, which has facilitated its adoption in personal care formulations.
The European Union, through the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), has registered sodium alginate under the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation. This registration ensures that manufacturers and importers assess and manage the risks associated with sodium alginate, providing a framework for its safe use in personal care products across EU member states.
In Japan, the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare has approved sodium alginate for use in cosmetics under the Pharmaceutical Affairs Law. The ingredient is listed in the Japanese Standards of Cosmetic Ingredients (JSCI), which outlines the permitted uses and concentrations for cosmetic formulations.
Globally, the International Nomenclature of Cosmetic Ingredients (INCI) recognizes sodium alginate, facilitating its identification and use across different markets. This standardization has been crucial in promoting transparency and consistency in product labeling worldwide.
Environmental regulations are increasingly impacting the use of sodium alginate in personal care products. The biodegradability of alginate-based materials aligns well with the growing demand for sustainable and eco-friendly cosmetic ingredients. Regulatory bodies, such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States, are placing greater emphasis on the environmental impact of personal care products, including their ingredients and packaging.
Recent regulatory trends indicate a move towards stricter control of microplastics in cosmetics, which may indirectly benefit sodium alginate as a natural, biodegradable alternative. The European Union's proposed restriction on intentionally added microplastics in products, including personal care items, is expected to drive innovation in alginate-based formulations.
As sustainability becomes a key focus for regulators and consumers alike, the regulatory landscape is evolving to favor ingredients like sodium alginate. This shift is evident in the increasing number of certifications and standards for natural and organic cosmetics, such as COSMOS and NATRUE, which often include sodium alginate in their approved ingredient lists.
The European Union, through the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), has registered sodium alginate under the Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) regulation. This registration ensures that manufacturers and importers assess and manage the risks associated with sodium alginate, providing a framework for its safe use in personal care products across EU member states.
In Japan, the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare has approved sodium alginate for use in cosmetics under the Pharmaceutical Affairs Law. The ingredient is listed in the Japanese Standards of Cosmetic Ingredients (JSCI), which outlines the permitted uses and concentrations for cosmetic formulations.
Globally, the International Nomenclature of Cosmetic Ingredients (INCI) recognizes sodium alginate, facilitating its identification and use across different markets. This standardization has been crucial in promoting transparency and consistency in product labeling worldwide.
Environmental regulations are increasingly impacting the use of sodium alginate in personal care products. The biodegradability of alginate-based materials aligns well with the growing demand for sustainable and eco-friendly cosmetic ingredients. Regulatory bodies, such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States, are placing greater emphasis on the environmental impact of personal care products, including their ingredients and packaging.
Recent regulatory trends indicate a move towards stricter control of microplastics in cosmetics, which may indirectly benefit sodium alginate as a natural, biodegradable alternative. The European Union's proposed restriction on intentionally added microplastics in products, including personal care items, is expected to drive innovation in alginate-based formulations.
As sustainability becomes a key focus for regulators and consumers alike, the regulatory landscape is evolving to favor ingredients like sodium alginate. This shift is evident in the increasing number of certifications and standards for natural and organic cosmetics, such as COSMOS and NATRUE, which often include sodium alginate in their approved ingredient lists.
Sustainability Impact
The integration of sodium alginate innovations in the personal care industry has significant implications for sustainability. As a natural, biodegradable polymer derived from brown seaweed, sodium alginate offers a renewable alternative to synthetic ingredients, aligning with the growing consumer demand for eco-friendly products.
The use of sodium alginate in personal care formulations contributes to reducing the industry's reliance on petrochemical-based ingredients. This shift towards bio-based materials helps decrease the carbon footprint associated with product manufacturing and disposal. Furthermore, the biodegradability of sodium alginate ensures that it breaks down naturally in the environment, minimizing long-term ecological impact.
In terms of resource efficiency, sodium alginate extraction from seaweed presents a sustainable sourcing model. Seaweed cultivation requires minimal land use and does not compete with food crops for agricultural space. Additionally, seaweed farming can contribute to carbon sequestration and improve marine ecosystems, offering potential environmental benefits beyond the personal care industry.
The versatility of sodium alginate in personal care applications also supports sustainability efforts through product innovation. Its ability to form stable emulsions and gels allows for the development of multifunctional products, potentially reducing the number of separate items consumers need to purchase. This consolidation can lead to decreased packaging waste and lower transportation-related emissions.
From a circular economy perspective, sodium alginate's natural origin facilitates easier integration into closed-loop systems. Products containing sodium alginate are more likely to be compatible with existing composting and biodegradation processes, supporting end-of-life management strategies that minimize waste.
The water-retention properties of sodium alginate contribute to the formulation of more concentrated personal care products. This characteristic enables the creation of waterless or low-water formulations, addressing water scarcity concerns and reducing the weight of products during transportation, thereby lowering associated carbon emissions.
As the personal care industry faces increasing pressure to adopt sustainable practices, sodium alginate innovations offer a promising pathway. By incorporating this natural polymer, companies can enhance their sustainability profiles, meet regulatory requirements for eco-friendly ingredients, and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers. The continued research and development in sodium alginate applications are likely to unveil further sustainability benefits, reinforcing its role in the industry's transition towards more responsible and sustainable product offerings.
The use of sodium alginate in personal care formulations contributes to reducing the industry's reliance on petrochemical-based ingredients. This shift towards bio-based materials helps decrease the carbon footprint associated with product manufacturing and disposal. Furthermore, the biodegradability of sodium alginate ensures that it breaks down naturally in the environment, minimizing long-term ecological impact.
In terms of resource efficiency, sodium alginate extraction from seaweed presents a sustainable sourcing model. Seaweed cultivation requires minimal land use and does not compete with food crops for agricultural space. Additionally, seaweed farming can contribute to carbon sequestration and improve marine ecosystems, offering potential environmental benefits beyond the personal care industry.
The versatility of sodium alginate in personal care applications also supports sustainability efforts through product innovation. Its ability to form stable emulsions and gels allows for the development of multifunctional products, potentially reducing the number of separate items consumers need to purchase. This consolidation can lead to decreased packaging waste and lower transportation-related emissions.
From a circular economy perspective, sodium alginate's natural origin facilitates easier integration into closed-loop systems. Products containing sodium alginate are more likely to be compatible with existing composting and biodegradation processes, supporting end-of-life management strategies that minimize waste.
The water-retention properties of sodium alginate contribute to the formulation of more concentrated personal care products. This characteristic enables the creation of waterless or low-water formulations, addressing water scarcity concerns and reducing the weight of products during transportation, thereby lowering associated carbon emissions.
As the personal care industry faces increasing pressure to adopt sustainable practices, sodium alginate innovations offer a promising pathway. By incorporating this natural polymer, companies can enhance their sustainability profiles, meet regulatory requirements for eco-friendly ingredients, and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers. The continued research and development in sodium alginate applications are likely to unveil further sustainability benefits, reinforcing its role in the industry's transition towards more responsible and sustainable product offerings.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!