2JZ Engine Tuning for Emissions Compliance
AUG 5, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
2JZ Engine Evolution
The 2JZ engine, initially introduced by Toyota in 1991, has undergone significant evolution over the years, particularly in response to increasingly stringent emissions regulations. This iconic inline-six engine, known for its robustness and tuning potential, has faced numerous challenges in maintaining its performance while meeting modern environmental standards.
In its early iterations, the 2JZ engine was primarily focused on delivering high performance with less emphasis on emissions control. The original 2JZ-GE and 2JZ-GTE variants were designed to produce substantial power outputs, with the turbocharged GTE version capable of generating up to 320 horsepower in stock form. These engines utilized relatively simple emissions control systems by today's standards, primarily relying on catalytic converters and basic engine management systems.
As emissions regulations tightened globally throughout the 1990s and 2000s, Toyota was compelled to refine the 2JZ engine design. This led to the introduction of more advanced fuel injection systems, improved engine control units (ECUs), and enhanced catalytic converter technologies. The integration of variable valve timing (VVT-i) in later models marked a significant step forward in balancing performance with emissions compliance.
The tuning community's approach to the 2JZ engine has also evolved in response to emissions requirements. Early modifications often focused solely on increasing power output, sometimes at the expense of emissions control. However, as regulations became more stringent, tuners have had to develop more sophisticated strategies to maintain performance while staying within legal emissions limits.
Recent developments in 2JZ engine tuning have seen a shift towards cleaner burning fuel systems, including the adoption of E85 ethanol blends and more precise fuel injection mapping. Advanced aftermarket ECUs now allow for finer control over fuel and ignition timing, enabling tuners to optimize engine performance while minimizing harmful emissions.
The advent of OBD-II (On-Board Diagnostics II) systems has further influenced 2JZ engine evolution, requiring tuners to ensure that modifications do not trigger emissions-related fault codes. This has led to the development of specialized tuning software and hardware that can work in harmony with OBD-II systems while still allowing for performance enhancements.
Looking towards the future, the 2JZ engine faces new challenges in an era of increasing electrification and ever-tightening emissions standards. While its fundamental design remains highly regarded, continued evolution will likely involve the integration of hybrid technologies, more advanced materials, and cutting-edge emissions control systems to ensure its relevance in a changing automotive landscape.
In its early iterations, the 2JZ engine was primarily focused on delivering high performance with less emphasis on emissions control. The original 2JZ-GE and 2JZ-GTE variants were designed to produce substantial power outputs, with the turbocharged GTE version capable of generating up to 320 horsepower in stock form. These engines utilized relatively simple emissions control systems by today's standards, primarily relying on catalytic converters and basic engine management systems.
As emissions regulations tightened globally throughout the 1990s and 2000s, Toyota was compelled to refine the 2JZ engine design. This led to the introduction of more advanced fuel injection systems, improved engine control units (ECUs), and enhanced catalytic converter technologies. The integration of variable valve timing (VVT-i) in later models marked a significant step forward in balancing performance with emissions compliance.
The tuning community's approach to the 2JZ engine has also evolved in response to emissions requirements. Early modifications often focused solely on increasing power output, sometimes at the expense of emissions control. However, as regulations became more stringent, tuners have had to develop more sophisticated strategies to maintain performance while staying within legal emissions limits.
Recent developments in 2JZ engine tuning have seen a shift towards cleaner burning fuel systems, including the adoption of E85 ethanol blends and more precise fuel injection mapping. Advanced aftermarket ECUs now allow for finer control over fuel and ignition timing, enabling tuners to optimize engine performance while minimizing harmful emissions.
The advent of OBD-II (On-Board Diagnostics II) systems has further influenced 2JZ engine evolution, requiring tuners to ensure that modifications do not trigger emissions-related fault codes. This has led to the development of specialized tuning software and hardware that can work in harmony with OBD-II systems while still allowing for performance enhancements.
Looking towards the future, the 2JZ engine faces new challenges in an era of increasing electrification and ever-tightening emissions standards. While its fundamental design remains highly regarded, continued evolution will likely involve the integration of hybrid technologies, more advanced materials, and cutting-edge emissions control systems to ensure its relevance in a changing automotive landscape.
Market for Tuned 2JZ
The market for tuned 2JZ engines has experienced significant growth and evolution over the past decades, driven by enthusiasts' demand for high-performance vehicles and the engine's reputation for reliability and power potential. Initially popularized by the Toyota Supra, the 2JZ engine has become a staple in the aftermarket tuning industry, with applications extending beyond its original platform.
The primary market segments for tuned 2JZ engines include performance car enthusiasts, drag racing competitors, drift racing participants, and custom car builders. These segments have shown consistent demand for 2JZ engines due to their robust design and ability to handle substantial power increases. The aftermarket industry supporting 2JZ tuning has flourished, offering a wide range of performance parts and services.
In recent years, there has been a noticeable shift in market dynamics. As emissions regulations have become more stringent globally, the demand for emissions-compliant 2JZ tuning solutions has increased. This trend is particularly evident in regions with strict vehicle inspection and emissions testing requirements. Tuning shops and parts manufacturers have responded by developing products and services that balance performance enhancements with emissions compliance.
The market size for tuned 2JZ engines and related services is substantial, though precise figures are challenging to quantify due to the fragmented nature of the aftermarket industry. However, industry reports suggest that the global automotive aftermarket, which includes engine tuning, is valued in the hundreds of billions of dollars annually, with a significant portion attributed to performance enhancements for popular engines like the 2JZ.
Geographically, the market for tuned 2JZ engines is strongest in North America, Japan, and parts of Europe, where car culture and motorsports have a strong presence. However, emerging markets in Southeast Asia and the Middle East have shown rapid growth in recent years, driven by increasing disposable incomes and a growing car enthusiast culture.
The future market outlook for tuned 2JZ engines remains positive, albeit with some challenges. The increasing age of 2JZ-equipped vehicles and the shift towards electric and hybrid powertrains in new vehicles pose potential threats to market growth. However, the engine's legendary status and the continued interest in classic and retro vehicles suggest that demand will persist in the foreseeable future.
To address emissions compliance concerns, the market is likely to see an increase in demand for advanced engine management systems, cleaner-burning fuel systems, and more efficient turbocharger setups. This shift presents opportunities for innovative companies to develop new products and services that cater to both performance enthusiasts and regulatory requirements.
The primary market segments for tuned 2JZ engines include performance car enthusiasts, drag racing competitors, drift racing participants, and custom car builders. These segments have shown consistent demand for 2JZ engines due to their robust design and ability to handle substantial power increases. The aftermarket industry supporting 2JZ tuning has flourished, offering a wide range of performance parts and services.
In recent years, there has been a noticeable shift in market dynamics. As emissions regulations have become more stringent globally, the demand for emissions-compliant 2JZ tuning solutions has increased. This trend is particularly evident in regions with strict vehicle inspection and emissions testing requirements. Tuning shops and parts manufacturers have responded by developing products and services that balance performance enhancements with emissions compliance.
The market size for tuned 2JZ engines and related services is substantial, though precise figures are challenging to quantify due to the fragmented nature of the aftermarket industry. However, industry reports suggest that the global automotive aftermarket, which includes engine tuning, is valued in the hundreds of billions of dollars annually, with a significant portion attributed to performance enhancements for popular engines like the 2JZ.
Geographically, the market for tuned 2JZ engines is strongest in North America, Japan, and parts of Europe, where car culture and motorsports have a strong presence. However, emerging markets in Southeast Asia and the Middle East have shown rapid growth in recent years, driven by increasing disposable incomes and a growing car enthusiast culture.
The future market outlook for tuned 2JZ engines remains positive, albeit with some challenges. The increasing age of 2JZ-equipped vehicles and the shift towards electric and hybrid powertrains in new vehicles pose potential threats to market growth. However, the engine's legendary status and the continued interest in classic and retro vehicles suggest that demand will persist in the foreseeable future.
To address emissions compliance concerns, the market is likely to see an increase in demand for advanced engine management systems, cleaner-burning fuel systems, and more efficient turbocharger setups. This shift presents opportunities for innovative companies to develop new products and services that cater to both performance enthusiasts and regulatory requirements.
Emissions Challenges
The 2JZ engine, renowned for its robust design and performance potential, faces significant challenges in meeting modern emissions standards. As environmental regulations become increasingly stringent, tuning this iconic powerplant for emissions compliance has become a complex task that requires careful consideration of multiple factors.
One of the primary challenges is reducing nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions, which are particularly high in high-performance engines like the 2JZ. The engine's ability to withstand high boost pressures and generate substantial power often results in elevated combustion temperatures, leading to increased NOx formation. Addressing this issue while maintaining the engine's performance characteristics requires advanced tuning strategies and potentially the integration of additional emissions control technologies.
Hydrocarbon (HC) emissions present another significant hurdle. The 2JZ's large displacement and potential for incomplete combustion, especially during cold starts or under certain operating conditions, can lead to elevated HC levels. Tuners must optimize fuel injection timing and duration to ensure more complete combustion across all operating ranges, a task that becomes increasingly complex when balancing performance goals with emissions targets.
Carbon monoxide (CO) emissions, while generally lower in gasoline engines compared to diesel, still pose a challenge for high-performance tuning. The rich fuel mixtures often favored for maximum power output can lead to increased CO production. Achieving the delicate balance between optimal air-fuel ratios for performance and those required for emissions compliance demands sophisticated engine management systems and precise tuning.
Particulate matter (PM) emissions, traditionally more associated with diesel engines, are becoming a concern for high-performance gasoline engines as well. Direct injection systems, which are sometimes employed in modern 2JZ-based builds, can contribute to increased PM emissions. Addressing this issue may require modifications to injection strategies or the addition of particulate filters, which can impact engine performance and responsiveness.
The implementation of On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD-II) systems adds another layer of complexity to emissions-compliant tuning. Ensuring that all emissions-related systems function within specified parameters and do not trigger fault codes while maintaining high performance is a delicate balancing act. Tuners must navigate the intricacies of OBD-II systems to avoid triggering check engine lights or entering limp modes due to emissions-related issues.
Furthermore, the global nature of emissions regulations presents challenges for 2JZ enthusiasts worldwide. Different regions have varying standards and testing procedures, requiring tuners to develop market-specific solutions. This can lead to increased complexity in engine management software and hardware configurations, potentially limiting the interchangeability of parts and tunes across different markets.
One of the primary challenges is reducing nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions, which are particularly high in high-performance engines like the 2JZ. The engine's ability to withstand high boost pressures and generate substantial power often results in elevated combustion temperatures, leading to increased NOx formation. Addressing this issue while maintaining the engine's performance characteristics requires advanced tuning strategies and potentially the integration of additional emissions control technologies.
Hydrocarbon (HC) emissions present another significant hurdle. The 2JZ's large displacement and potential for incomplete combustion, especially during cold starts or under certain operating conditions, can lead to elevated HC levels. Tuners must optimize fuel injection timing and duration to ensure more complete combustion across all operating ranges, a task that becomes increasingly complex when balancing performance goals with emissions targets.
Carbon monoxide (CO) emissions, while generally lower in gasoline engines compared to diesel, still pose a challenge for high-performance tuning. The rich fuel mixtures often favored for maximum power output can lead to increased CO production. Achieving the delicate balance between optimal air-fuel ratios for performance and those required for emissions compliance demands sophisticated engine management systems and precise tuning.
Particulate matter (PM) emissions, traditionally more associated with diesel engines, are becoming a concern for high-performance gasoline engines as well. Direct injection systems, which are sometimes employed in modern 2JZ-based builds, can contribute to increased PM emissions. Addressing this issue may require modifications to injection strategies or the addition of particulate filters, which can impact engine performance and responsiveness.
The implementation of On-Board Diagnostics II (OBD-II) systems adds another layer of complexity to emissions-compliant tuning. Ensuring that all emissions-related systems function within specified parameters and do not trigger fault codes while maintaining high performance is a delicate balancing act. Tuners must navigate the intricacies of OBD-II systems to avoid triggering check engine lights or entering limp modes due to emissions-related issues.
Furthermore, the global nature of emissions regulations presents challenges for 2JZ enthusiasts worldwide. Different regions have varying standards and testing procedures, requiring tuners to develop market-specific solutions. This can lead to increased complexity in engine management software and hardware configurations, potentially limiting the interchangeability of parts and tunes across different markets.
Current Tuning Methods
01 Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) systems
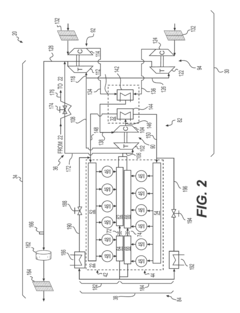
EGR systems are used to reduce nitrogen oxide emissions in 2JZ engines by recirculating a portion of the exhaust gas back into the combustion chamber. This lowers combustion temperatures and reduces the formation of NOx. Advanced EGR systems may include cooling mechanisms and precise control strategies to optimize emission reduction while maintaining engine performance.- Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) systems: EGR systems are used to reduce nitrogen oxide emissions in 2JZ engines by recirculating a portion of the exhaust gas back into the combustion chamber. This lowers combustion temperatures and reduces the formation of NOx. Advanced EGR systems may include cooling mechanisms and precise control strategies to optimize emission reduction while maintaining engine performance.
- Catalytic converters and aftertreatment systems: Catalytic converters and other aftertreatment systems are crucial for reducing harmful emissions from 2JZ engines. These systems may include three-way catalysts, diesel particulate filters, or selective catalytic reduction (SCR) technology to convert pollutants into less harmful substances before they are released into the atmosphere.
- Engine control unit (ECU) optimization: Advanced engine control strategies implemented through the ECU can significantly reduce emissions from 2JZ engines. This includes optimizing fuel injection timing, air-fuel ratio control, and ignition timing based on various sensor inputs and operating conditions to minimize the production of pollutants while maintaining engine efficiency.
- Fuel system improvements: Enhancements to the fuel system, such as high-pressure direct injection or dual fuel systems, can improve fuel atomization and combustion efficiency in 2JZ engines. These improvements lead to more complete combustion, reducing unburned hydrocarbons and particulate matter emissions.
- Turbocharger and air intake optimization: Optimizing the turbocharger system and air intake design can improve the air-fuel mixture and combustion efficiency in 2JZ engines. This may include variable geometry turbochargers, intercoolers, or advanced air filtration systems to enhance engine breathing and reduce emissions across various operating conditions.
02 Catalytic converters and aftertreatment systems
Catalytic converters and other aftertreatment systems are crucial for reducing harmful emissions from 2JZ engines. These systems may include three-way catalysts, diesel oxidation catalysts, or selective catalytic reduction (SCR) technology to convert pollutants into less harmful substances. Advanced sensors and control systems ensure optimal performance of these emission control devices.Expand Specific Solutions03 Engine management and control systems
Sophisticated engine management systems are employed to optimize fuel injection, ignition timing, and air-fuel ratios in 2JZ engines. These systems use various sensors and advanced algorithms to continuously adjust engine parameters, ensuring efficient combustion and minimizing emissions across different operating conditions.Expand Specific Solutions04 Fuel system improvements
Enhancements to the fuel system, such as high-pressure direct injection or advanced fuel atomization techniques, contribute to more complete combustion in 2JZ engines. These improvements result in reduced unburned hydrocarbons and particulate matter emissions. Precise fuel metering and spray patterns are crucial for emission control.Expand Specific Solutions05 Turbocharging and air intake optimization
Turbocharging and optimized air intake systems are used to improve the combustion efficiency of 2JZ engines. These technologies enhance air-fuel mixing, allowing for more complete combustion and reduced emissions. Variable geometry turbochargers and advanced intercooling systems may be employed to further improve performance and emissions across various engine speeds and loads.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Tuning Companies
The 2JZ Engine Tuning for Emissions Compliance market is in a mature stage, with established players like Toyota Motor Corp. and Honda Motor Co., Ltd. leading the way. The market size is significant, driven by increasing emissions regulations globally. Technologically, the field is advanced, with companies like Robert Bosch GmbH and Continental Automotive GmbH providing cutting-edge solutions. Major automakers such as Renault SA, Ford Global Technologies LLC, and General Motors LLC are actively investing in emissions-compliant engine tuning. Specialized firms like AVL List GmbH offer expertise in powertrain development and testing, contributing to the overall technological maturity of the sector.
Toyota Motor Corp.
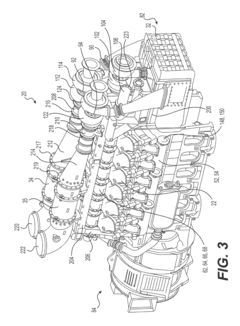
Technical Solution: Toyota has developed an advanced engine management system for the 2JZ engine to meet modern emissions standards while maintaining performance. This system incorporates direct fuel injection, variable valve timing, and a high-pressure common rail fuel system[1]. The engine control unit (ECU) uses sophisticated algorithms to optimize fuel injection timing and quantity based on real-time sensor data, ensuring efficient combustion and reduced emissions[2]. Toyota has also implemented a dual-stage exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system, which helps to lower nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions by recirculating a portion of the exhaust gases back into the combustion chamber[3]. Additionally, the company has integrated a close-coupled catalytic converter design to rapidly achieve light-off temperature, significantly reducing cold-start emissions[4].
Strengths: Proven reliability of the 2JZ platform, extensive experience in emissions compliance, and strong R&D capabilities. Weaknesses: Potential increased complexity and cost of the engine system, and challenges in maintaining the 2JZ's legendary performance while meeting stricter emissions standards.
Robert Bosch GmbH
Technical Solution: Bosch has developed a comprehensive emissions control solution for the 2JZ engine, focusing on advanced fuel injection and exhaust aftertreatment technologies. Their system utilizes high-precision piezoelectric injectors capable of multiple injections per cycle, allowing for more precise fuel control and reduced emissions[5]. Bosch's latest generation of engine control units (ECUs) incorporates machine learning algorithms to continuously optimize engine performance and emissions in real-time[6]. The company has also developed a selective catalytic reduction (SCR) system specifically tailored for high-performance engines like the 2JZ, which can reduce NOx emissions by up to 95%[7]. Furthermore, Bosch's particulate filter technology has been adapted to work efficiently with the 2JZ's high exhaust temperatures, effectively capturing soot particles without significantly impacting engine performance[8].
Strengths: Cutting-edge fuel injection technology, extensive experience in emissions control systems, and strong partnerships with major automakers. Weaknesses: Potential high cost of implementation and the need for regular maintenance of complex aftertreatment systems.
Innovative Tuning Tech
Engine system for emissions compliance
PatentActiveUS9845722B2
Innovation
- The engine system incorporates a turbocharger arrangement with high-pressure and low-pressure turbochargers of equal size, positioned adjacent to an air cooling system, with a mixing duct and after-treatment system located at the drive end, reducing ducting and component complexity, and allowing for easier maintenance.
Emissions Regulations
Emissions regulations for automotive engines have become increasingly stringent over the past few decades, driven by growing concerns about air quality and environmental impact. These regulations vary across different regions and countries, but generally aim to reduce harmful emissions such as carbon monoxide (CO), nitrogen oxides (NOx), hydrocarbons (HC), and particulate matter (PM).
In the context of 2JZ engine tuning, compliance with emissions regulations presents a significant challenge. The 2JZ engine, known for its robust design and high-performance potential, was originally developed in an era with less stringent emissions standards. As regulations have evolved, tuners must now balance performance enhancements with emissions control.
Key regulatory bodies influencing emissions standards include the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States, the European Union's Euro emissions standards, and Japan's emission standards set by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism. These organizations continually update their requirements, pushing manufacturers and tuners to develop more advanced emission control technologies.
For 2JZ engine tuning, meeting modern emissions standards often requires a multi-faceted approach. This may include optimizing fuel injection systems, implementing advanced engine management systems, and integrating catalytic converters designed to handle higher exhaust temperatures and flow rates associated with performance tuning.
One of the primary challenges in emissions-compliant tuning is maintaining the engine's power output while reducing pollutants. This often involves precise adjustments to air-fuel ratios, ignition timing, and exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) systems. Additionally, the use of higher-quality fuels and lubricants can play a crucial role in reducing emissions without sacrificing performance.
Emissions testing procedures have also become more comprehensive, with many regions now implementing real-world driving emissions (RDE) tests in addition to laboratory-based assessments. This shift has further complicated the tuning process, as engines must now perform efficiently across a wider range of operating conditions.
As emissions regulations continue to tighten, the future of 2JZ engine tuning will likely involve more advanced technologies such as variable valve timing, direct injection, and possibly even hybrid systems to meet stringent standards while preserving the engine's legendary performance capabilities.
In the context of 2JZ engine tuning, compliance with emissions regulations presents a significant challenge. The 2JZ engine, known for its robust design and high-performance potential, was originally developed in an era with less stringent emissions standards. As regulations have evolved, tuners must now balance performance enhancements with emissions control.
Key regulatory bodies influencing emissions standards include the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States, the European Union's Euro emissions standards, and Japan's emission standards set by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism. These organizations continually update their requirements, pushing manufacturers and tuners to develop more advanced emission control technologies.
For 2JZ engine tuning, meeting modern emissions standards often requires a multi-faceted approach. This may include optimizing fuel injection systems, implementing advanced engine management systems, and integrating catalytic converters designed to handle higher exhaust temperatures and flow rates associated with performance tuning.
One of the primary challenges in emissions-compliant tuning is maintaining the engine's power output while reducing pollutants. This often involves precise adjustments to air-fuel ratios, ignition timing, and exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) systems. Additionally, the use of higher-quality fuels and lubricants can play a crucial role in reducing emissions without sacrificing performance.
Emissions testing procedures have also become more comprehensive, with many regions now implementing real-world driving emissions (RDE) tests in addition to laboratory-based assessments. This shift has further complicated the tuning process, as engines must now perform efficiently across a wider range of operating conditions.
As emissions regulations continue to tighten, the future of 2JZ engine tuning will likely involve more advanced technologies such as variable valve timing, direct injection, and possibly even hybrid systems to meet stringent standards while preserving the engine's legendary performance capabilities.
Eco-Friendly Tuning
Eco-friendly tuning for the 2JZ engine represents a significant shift in the approach to performance enhancement, focusing on balancing power output with environmental responsibility. This approach aims to optimize the engine's efficiency while minimizing harmful emissions, aligning with increasingly stringent global emissions standards.
One key aspect of eco-friendly tuning involves optimizing the engine's fuel injection system. By fine-tuning the fuel mapping and employing advanced injection strategies, it's possible to achieve a more complete combustion process. This not only improves fuel efficiency but also reduces the production of unburned hydrocarbons and carbon monoxide.
Another critical area is the implementation of advanced exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) systems. By recirculating a portion of the exhaust gases back into the combustion chamber, NOx emissions can be significantly reduced. Modern EGR systems, when properly calibrated, can achieve this without substantially compromising engine performance.
The use of low-friction components and coatings can also contribute to eco-friendly tuning. By reducing internal friction, less energy is lost as heat, improving overall efficiency and potentially reducing fuel consumption. This approach can include the use of lightweight pistons, low-friction piston rings, and specialized engine oil formulations.
Catalytic converter optimization is another crucial element in eco-friendly tuning. By selecting high-flow catalytic converters and precisely tuning the engine management system to work in harmony with these components, it's possible to maintain high performance while still meeting stringent emissions standards.
Advanced engine management systems play a pivotal role in eco-friendly tuning. These systems can continuously adjust various parameters such as ignition timing, fuel injection, and valve timing to optimize performance and emissions based on real-time operating conditions. The integration of machine learning algorithms can further enhance this capability, allowing the system to adapt and improve over time.
Lastly, the incorporation of mild hybrid technology can significantly contribute to eco-friendly performance. By integrating a small electric motor and battery system, the 2JZ engine can benefit from features like regenerative braking and electric boost, improving both efficiency and performance without compromising emissions compliance.
One key aspect of eco-friendly tuning involves optimizing the engine's fuel injection system. By fine-tuning the fuel mapping and employing advanced injection strategies, it's possible to achieve a more complete combustion process. This not only improves fuel efficiency but also reduces the production of unburned hydrocarbons and carbon monoxide.
Another critical area is the implementation of advanced exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) systems. By recirculating a portion of the exhaust gases back into the combustion chamber, NOx emissions can be significantly reduced. Modern EGR systems, when properly calibrated, can achieve this without substantially compromising engine performance.
The use of low-friction components and coatings can also contribute to eco-friendly tuning. By reducing internal friction, less energy is lost as heat, improving overall efficiency and potentially reducing fuel consumption. This approach can include the use of lightweight pistons, low-friction piston rings, and specialized engine oil formulations.
Catalytic converter optimization is another crucial element in eco-friendly tuning. By selecting high-flow catalytic converters and precisely tuning the engine management system to work in harmony with these components, it's possible to maintain high performance while still meeting stringent emissions standards.
Advanced engine management systems play a pivotal role in eco-friendly tuning. These systems can continuously adjust various parameters such as ignition timing, fuel injection, and valve timing to optimize performance and emissions based on real-time operating conditions. The integration of machine learning algorithms can further enhance this capability, allowing the system to adapt and improve over time.
Lastly, the incorporation of mild hybrid technology can significantly contribute to eco-friendly performance. By integrating a small electric motor and battery system, the 2JZ engine can benefit from features like regenerative braking and electric boost, improving both efficiency and performance without compromising emissions compliance.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!