The Evolution of Fuel Delivery Systems in 2JZ Engines
AUG 5, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
2JZ Engine Fuel System Evolution and Objectives
The 2JZ engine, renowned for its robustness and performance potential, has undergone significant evolution in its fuel delivery systems since its inception. This technological progression reflects broader trends in automotive engineering, particularly the drive towards improved efficiency, power output, and emissions control.
Initially introduced in the early 1990s, the 2JZ engine featured a relatively advanced fuel injection system for its time. The original configuration utilized a sequential multi-port fuel injection system, which represented a substantial improvement over earlier carbureted designs. This system allowed for precise fuel metering to each cylinder, enhancing both performance and fuel economy.
As environmental regulations became more stringent and performance demands increased, Toyota engineers focused on refining the fuel delivery system. The introduction of variable valve timing (VVT-i) in later iterations of the 2JZ engine complemented the fuel injection system, allowing for more dynamic control over the engine's breathing and fuel consumption characteristics.
One of the key objectives in the evolution of the 2JZ's fuel system was to achieve a balance between high-performance capabilities and everyday drivability. This led to the development of more sophisticated engine management systems that could adjust fuel delivery based on a wider range of parameters, including engine load, temperature, and atmospheric conditions.
The aftermarket community has played a significant role in pushing the boundaries of the 2JZ's fuel delivery capabilities. Modifications such as larger fuel injectors, high-flow fuel pumps, and custom fuel rails became common among enthusiasts seeking to extract maximum performance from the engine. These aftermarket developments often informed and influenced subsequent factory improvements.
Recent technological advancements have opened new possibilities for further enhancing the 2JZ's fuel delivery system. Direct injection technology, while not originally implemented in the 2JZ, represents a potential avenue for future development or retrofitting. This technology offers the promise of even more precise fuel control, potentially unlocking additional power and efficiency gains.
The ongoing objective in fuel system evolution for the 2JZ engine remains centered on maximizing power output while simultaneously improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions. As automotive technology continues to advance, there is potential for integrating more advanced fuel delivery solutions, such as combined port and direct injection systems or even alternative fuel compatibility, ensuring the 2JZ's relevance in an increasingly eco-conscious automotive landscape.
Initially introduced in the early 1990s, the 2JZ engine featured a relatively advanced fuel injection system for its time. The original configuration utilized a sequential multi-port fuel injection system, which represented a substantial improvement over earlier carbureted designs. This system allowed for precise fuel metering to each cylinder, enhancing both performance and fuel economy.
As environmental regulations became more stringent and performance demands increased, Toyota engineers focused on refining the fuel delivery system. The introduction of variable valve timing (VVT-i) in later iterations of the 2JZ engine complemented the fuel injection system, allowing for more dynamic control over the engine's breathing and fuel consumption characteristics.
One of the key objectives in the evolution of the 2JZ's fuel system was to achieve a balance between high-performance capabilities and everyday drivability. This led to the development of more sophisticated engine management systems that could adjust fuel delivery based on a wider range of parameters, including engine load, temperature, and atmospheric conditions.
The aftermarket community has played a significant role in pushing the boundaries of the 2JZ's fuel delivery capabilities. Modifications such as larger fuel injectors, high-flow fuel pumps, and custom fuel rails became common among enthusiasts seeking to extract maximum performance from the engine. These aftermarket developments often informed and influenced subsequent factory improvements.
Recent technological advancements have opened new possibilities for further enhancing the 2JZ's fuel delivery system. Direct injection technology, while not originally implemented in the 2JZ, represents a potential avenue for future development or retrofitting. This technology offers the promise of even more precise fuel control, potentially unlocking additional power and efficiency gains.
The ongoing objective in fuel system evolution for the 2JZ engine remains centered on maximizing power output while simultaneously improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions. As automotive technology continues to advance, there is potential for integrating more advanced fuel delivery solutions, such as combined port and direct injection systems or even alternative fuel compatibility, ensuring the 2JZ's relevance in an increasingly eco-conscious automotive landscape.
Market Demand for High-Performance Fuel Systems
The market demand for high-performance fuel systems in the context of 2JZ engines has experienced significant growth over the past decades. This demand is primarily driven by automotive enthusiasts, racing teams, and performance-oriented vehicle manufacturers seeking to maximize the potential of these legendary powerplants.
The 2JZ engine, particularly the 2JZ-GTE variant, has gained a cult following due to its robust design and exceptional tuning potential. As a result, there has been a consistent demand for advanced fuel delivery systems capable of supporting increased horsepower outputs. This market segment has expanded beyond the original equipment manufacturer (OEM) specifications, with aftermarket companies developing increasingly sophisticated fuel system components.
One of the key factors driving market demand is the pursuit of higher power outputs. As tuners and enthusiasts push the boundaries of engine performance, traditional fuel systems often become a bottleneck. This has led to a growing market for upgraded fuel pumps, larger fuel injectors, and high-flow fuel rails specifically designed for the 2JZ platform.
Another significant aspect of market demand is the need for reliability and consistency in fuel delivery. High-performance applications, especially in motorsports, require fuel systems that can maintain stable fuel pressure and flow rates under extreme conditions. This has spurred the development of advanced fuel pressure regulators, surge tanks, and fuel line systems tailored to the unique requirements of heavily modified 2JZ engines.
The rise of ethanol-based fuels, particularly E85, has also influenced market demand. Many 2JZ enthusiasts are turning to these alternative fuels for their cooling properties and increased octane ratings. This shift has created a niche market for fuel systems components compatible with ethanol blends, including corrosion-resistant fuel lines and specialized fuel pumps.
Furthermore, the global nature of the automotive performance industry has expanded the market for 2JZ fuel system components. With the engine's popularity spanning across continents, there is a growing international demand for high-quality, performance-oriented fuel delivery solutions. This has led to the emergence of specialized manufacturers and distributors catering to this global market.
The integration of modern engine management systems with advanced fuel delivery components has also become a crucial aspect of market demand. Enthusiasts and professional tuners alike seek fuel systems that can seamlessly interface with programmable ECUs, allowing for precise fuel control and optimization across various operating conditions.
In conclusion, the market demand for high-performance fuel systems in 2JZ engines continues to evolve, driven by the relentless pursuit of power, reliability, and efficiency. As technology advances and new fuels emerge, this market segment is expected to remain dynamic, offering opportunities for innovation and specialization in the automotive aftermarket industry.
The 2JZ engine, particularly the 2JZ-GTE variant, has gained a cult following due to its robust design and exceptional tuning potential. As a result, there has been a consistent demand for advanced fuel delivery systems capable of supporting increased horsepower outputs. This market segment has expanded beyond the original equipment manufacturer (OEM) specifications, with aftermarket companies developing increasingly sophisticated fuel system components.
One of the key factors driving market demand is the pursuit of higher power outputs. As tuners and enthusiasts push the boundaries of engine performance, traditional fuel systems often become a bottleneck. This has led to a growing market for upgraded fuel pumps, larger fuel injectors, and high-flow fuel rails specifically designed for the 2JZ platform.
Another significant aspect of market demand is the need for reliability and consistency in fuel delivery. High-performance applications, especially in motorsports, require fuel systems that can maintain stable fuel pressure and flow rates under extreme conditions. This has spurred the development of advanced fuel pressure regulators, surge tanks, and fuel line systems tailored to the unique requirements of heavily modified 2JZ engines.
The rise of ethanol-based fuels, particularly E85, has also influenced market demand. Many 2JZ enthusiasts are turning to these alternative fuels for their cooling properties and increased octane ratings. This shift has created a niche market for fuel systems components compatible with ethanol blends, including corrosion-resistant fuel lines and specialized fuel pumps.
Furthermore, the global nature of the automotive performance industry has expanded the market for 2JZ fuel system components. With the engine's popularity spanning across continents, there is a growing international demand for high-quality, performance-oriented fuel delivery solutions. This has led to the emergence of specialized manufacturers and distributors catering to this global market.
The integration of modern engine management systems with advanced fuel delivery components has also become a crucial aspect of market demand. Enthusiasts and professional tuners alike seek fuel systems that can seamlessly interface with programmable ECUs, allowing for precise fuel control and optimization across various operating conditions.
In conclusion, the market demand for high-performance fuel systems in 2JZ engines continues to evolve, driven by the relentless pursuit of power, reliability, and efficiency. As technology advances and new fuels emerge, this market segment is expected to remain dynamic, offering opportunities for innovation and specialization in the automotive aftermarket industry.
Current State and Challenges in 2JZ Fuel Delivery
The 2JZ engine, renowned for its robustness and performance potential, has seen significant advancements in its fuel delivery systems over the years. Currently, the stock 2JZ fuel system employs a combination of port fuel injection and direct injection, depending on the specific model and year of production. This dual-injection system allows for improved fuel atomization and more precise control over the air-fuel mixture, resulting in enhanced combustion efficiency and power output.
Despite its advanced design, the 2JZ fuel delivery system faces several challenges in meeting modern performance demands and emission standards. One of the primary issues is the limitation of the stock fuel injectors, which may struggle to provide sufficient fuel flow for high-performance applications. This becomes particularly evident when enthusiasts modify their engines for increased power output, often necessitating upgrades to larger capacity injectors or supplementary fuel systems.
Another challenge lies in the fuel pressure regulation. The stock fuel pressure regulator may not maintain optimal pressure levels under high-demand scenarios, potentially leading to fuel starvation or inconsistent fuel delivery. This can result in power fluctuations and potential engine damage, especially in heavily modified setups.
The fuel pump capacity also presents a bottleneck in high-performance applications. While adequate for stock power levels, the OEM fuel pump often falls short when supporting significant power increases. This limitation can lead to lean conditions under high load, potentially causing engine damage or failure.
Compatibility issues arise when integrating modern fuel management systems with the 2JZ's original electronic control unit (ECU). Aftermarket ECUs and fuel management solutions often require extensive tuning and calibration to work seamlessly with the engine's unique characteristics, presenting a challenge for both tuners and enthusiasts.
Environmental concerns and stricter emission regulations pose another significant challenge. The 2JZ's fuel delivery system, while efficient for its time, may struggle to meet increasingly stringent emission standards without substantial modifications. This necessitates the development of cleaner-burning fuel delivery solutions that maintain performance while reducing harmful emissions.
Lastly, the aging infrastructure of older 2JZ engines presents durability concerns. Fuel system components such as lines, fittings, and seals may degrade over time, leading to potential fuel leaks or system failures. This necessitates careful maintenance and periodic replacement of critical components to ensure long-term reliability and safety.
Despite its advanced design, the 2JZ fuel delivery system faces several challenges in meeting modern performance demands and emission standards. One of the primary issues is the limitation of the stock fuel injectors, which may struggle to provide sufficient fuel flow for high-performance applications. This becomes particularly evident when enthusiasts modify their engines for increased power output, often necessitating upgrades to larger capacity injectors or supplementary fuel systems.
Another challenge lies in the fuel pressure regulation. The stock fuel pressure regulator may not maintain optimal pressure levels under high-demand scenarios, potentially leading to fuel starvation or inconsistent fuel delivery. This can result in power fluctuations and potential engine damage, especially in heavily modified setups.
The fuel pump capacity also presents a bottleneck in high-performance applications. While adequate for stock power levels, the OEM fuel pump often falls short when supporting significant power increases. This limitation can lead to lean conditions under high load, potentially causing engine damage or failure.
Compatibility issues arise when integrating modern fuel management systems with the 2JZ's original electronic control unit (ECU). Aftermarket ECUs and fuel management solutions often require extensive tuning and calibration to work seamlessly with the engine's unique characteristics, presenting a challenge for both tuners and enthusiasts.
Environmental concerns and stricter emission regulations pose another significant challenge. The 2JZ's fuel delivery system, while efficient for its time, may struggle to meet increasingly stringent emission standards without substantial modifications. This necessitates the development of cleaner-burning fuel delivery solutions that maintain performance while reducing harmful emissions.
Lastly, the aging infrastructure of older 2JZ engines presents durability concerns. Fuel system components such as lines, fittings, and seals may degrade over time, leading to potential fuel leaks or system failures. This necessitates careful maintenance and periodic replacement of critical components to ensure long-term reliability and safety.
Existing 2JZ Fuel System Upgrade Solutions
01 Direct fuel injection systems
Direct fuel injection systems are used in 2JZ engines to improve fuel efficiency and performance. These systems inject fuel directly into the combustion chamber, allowing for precise control over fuel delivery and timing. This results in better atomization of fuel, improved combustion, and reduced emissions.- Direct fuel injection systems: Direct fuel injection systems are used in 2JZ engines to improve fuel efficiency and performance. These systems inject fuel directly into the combustion chamber, allowing for precise control over fuel delivery timing and quantity. This results in better fuel atomization, improved combustion, and reduced emissions.
- High-pressure fuel pumps: 2JZ engines utilize high-pressure fuel pumps to deliver fuel at the required pressure for direct injection systems. These pumps are capable of generating pressures up to several thousand PSI, ensuring optimal fuel atomization and distribution within the combustion chamber.
- Fuel rail and injector design: The fuel rail and injector design in 2JZ engines are crucial for proper fuel distribution. The fuel rail maintains consistent pressure across all injectors, while the injectors are designed to deliver precise amounts of fuel in a fine spray pattern. This design helps optimize fuel atomization and combustion efficiency.
- Electronic fuel management systems: 2JZ engines incorporate advanced electronic fuel management systems that control fuel delivery based on various engine parameters. These systems use sensors to monitor factors such as engine speed, load, and temperature, adjusting fuel delivery in real-time to optimize performance and efficiency.
- Fuel pressure regulation: Fuel pressure regulation is essential in 2JZ engines to maintain consistent fuel delivery across various operating conditions. Pressure regulators are used to control fuel pressure in the system, ensuring optimal fuel atomization and preventing issues such as fuel starvation or over-fueling.
02 High-pressure fuel pumps
High-pressure fuel pumps are essential components in 2JZ engine fuel delivery systems. These pumps are designed to deliver fuel at high pressures required for direct injection systems. They ensure consistent fuel supply under various operating conditions, contributing to improved engine performance and fuel efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions03 Fuel rail and injector design
The fuel rail and injector design play a crucial role in the fuel delivery system of 2JZ engines. Advanced fuel rails distribute fuel evenly to all injectors, while precisely engineered injectors ensure optimal fuel atomization and spray pattern. This combination contributes to efficient combustion and improved engine performance.Expand Specific Solutions04 Electronic fuel control systems
Electronic fuel control systems are utilized in 2JZ engines to manage fuel delivery accurately. These systems use various sensors and an engine control unit (ECU) to monitor engine conditions and adjust fuel delivery in real-time. This results in optimized fuel consumption, improved performance, and reduced emissions across different operating conditions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Fuel pressure regulation
Fuel pressure regulation is a critical aspect of 2JZ engine fuel delivery systems. Advanced pressure regulators maintain consistent fuel pressure across various engine loads and speeds. This ensures optimal fuel atomization and delivery, contributing to improved engine performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions control.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in 2JZ Engine Aftermarket Industry
The evolution of fuel delivery systems in 2JZ engines represents a mature technology within the automotive industry. The market for these systems is relatively stable, with a focus on refinement and optimization rather than revolutionary changes. Key players like Ford Global Technologies LLC, Robert Bosch GmbH, and Continental Automotive GmbH have established strong positions in this field, leveraging their extensive R&D capabilities and industry experience. The technology's maturity is evident in the incremental improvements made by these companies, focusing on enhancing efficiency, performance, and emissions control. While the market size for 2JZ engine fuel delivery systems is niche compared to broader automotive technologies, it remains significant for specialized applications and enthusiast markets.
Ford Global Technologies LLC
Technical Solution: Ford Global Technologies has developed an advanced fuel delivery system that could be applied to high-performance engines like the 2JZ. Their system features a combination of port and direct fuel injection, allowing for optimal fuel delivery across all engine speeds and loads[17]. The direct injection component operates at pressures up to 2,150 bar, enabling fine fuel atomization and precise metering[18]. Ford's system incorporates a twin-pump setup, with a low-pressure pump in the fuel tank and a high-pressure pump on the engine, ensuring consistent fuel supply under all conditions[19]. The engine control unit employs adaptive learning algorithms to continuously optimize fuel delivery based on driving style and environmental factors[20].
Strengths: Flexible fuel delivery strategy, good balance of performance and efficiency. Weaknesses: Increased system complexity may lead to higher production and maintenance costs.
Robert Bosch GmbH
Technical Solution: Robert Bosch GmbH has developed advanced fuel delivery systems for high-performance engines like the 2JZ. Their latest direct injection technology utilizes piezoelectric injectors capable of multiple injections per cycle, improving fuel atomization and combustion efficiency[1]. The system operates at pressures up to 2,500 bar, allowing for precise fuel metering and reduced emissions[2]. Bosch's engine control units (ECUs) integrate seamlessly with these injectors, utilizing adaptive learning algorithms to optimize fuel delivery based on real-time engine conditions[3]. This system also incorporates a high-pressure fuel pump with variable flow control, ensuring optimal fuel pressure across the entire RPM range[4].
Strengths: Precise fuel control, improved efficiency, and reduced emissions. Weaknesses: Higher cost and complexity compared to traditional systems, potential reliability issues with high-pressure components.
Innovative Fuel Delivery Technologies for 2JZ
Fuel delivery system
PatentActiveUS20160341152A1
Innovation
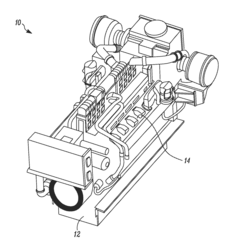
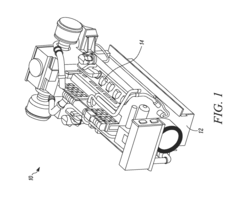
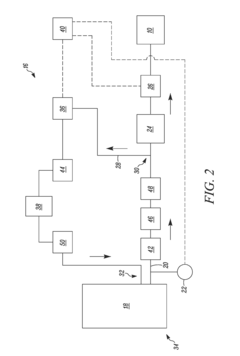
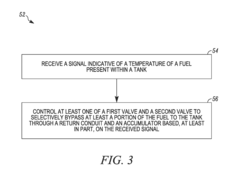
- A fuel delivery system with a temperature sensor, heat exchanger, valves, and an accumulator that selectively bypasses fuel to raise tank pressure by converting liquid LNG to vapor, eliminating the need for a separate boost pump.
Fuel delivery system for hand-held two-stroke cycle engines
PatentInactiveUS5682845A
Innovation
- A hybrid fuel delivery system combining a diaphragm carburetor for idle fuel control with a direct cylinder fuel injection system using a peristaltic type pump and fuel injector nozzle, operating only at part-throttle and wide open throttle conditions, to provide most engine fuel demand while maintaining engine lubrication without a separate oil system.
Emissions Regulations Impact on Fuel Systems
The evolution of fuel delivery systems in 2JZ engines has been significantly influenced by increasingly stringent emissions regulations. These regulations have driven continuous improvements in fuel system design, aiming to reduce harmful emissions while maintaining or enhancing engine performance.
In the early stages of 2JZ engine development, fuel delivery systems were primarily focused on providing adequate fuel supply for performance. However, as emissions standards became more stringent, manufacturers had to adapt their fuel systems to meet these new requirements. This led to the introduction of more precise fuel injection systems, replacing less efficient carburetor-based designs.
The implementation of electronic fuel injection (EFI) systems in 2JZ engines marked a significant milestone in emissions control. EFI allowed for more accurate fuel metering, resulting in improved combustion efficiency and reduced emissions. As regulations continued to tighten, manufacturers further refined these systems, incorporating advanced sensors and control units to optimize fuel delivery based on various engine parameters.
One of the key advancements driven by emissions regulations was the introduction of sequential fuel injection. This technology allowed for precise timing of fuel delivery to each cylinder, further improving combustion efficiency and reducing unburned fuel emissions. The 2JZ engine's fuel system evolved to incorporate this technology, resulting in better fuel economy and lower emissions without sacrificing performance.
Emissions regulations also pushed for the development of more sophisticated fuel pressure control systems. Variable fuel pressure regulators were introduced to maintain optimal fuel pressure across different operating conditions, ensuring efficient combustion and minimizing emissions. This technology became particularly important in turbocharged variants of the 2JZ engine, where fuel delivery needs to adapt to varying boost pressures.
The need to reduce evaporative emissions led to improvements in fuel tank and line designs. Enhanced sealing technologies and vapor recovery systems were implemented to minimize fuel vapor escape, addressing a significant source of hydrocarbon emissions. These changes affected not only the fuel delivery components but also the overall fuel system architecture in vehicles equipped with 2JZ engines.
As emissions standards continued to evolve, manufacturers had to focus on cold-start emissions, a critical phase for emissions control. This led to the development of more advanced fuel injectors capable of producing finer fuel atomization, especially during engine warm-up. The 2JZ engine's fuel system incorporated these improvements, resulting in reduced emissions during the critical cold-start period.
The impact of emissions regulations on 2JZ fuel systems also extended to the integration of on-board diagnostics (OBD) systems. These systems monitor fuel system performance and emissions-related components, alerting drivers to potential issues that could lead to increased emissions. This integration required further refinement of fuel system sensors and control algorithms to ensure accurate monitoring and reporting.
In the early stages of 2JZ engine development, fuel delivery systems were primarily focused on providing adequate fuel supply for performance. However, as emissions standards became more stringent, manufacturers had to adapt their fuel systems to meet these new requirements. This led to the introduction of more precise fuel injection systems, replacing less efficient carburetor-based designs.
The implementation of electronic fuel injection (EFI) systems in 2JZ engines marked a significant milestone in emissions control. EFI allowed for more accurate fuel metering, resulting in improved combustion efficiency and reduced emissions. As regulations continued to tighten, manufacturers further refined these systems, incorporating advanced sensors and control units to optimize fuel delivery based on various engine parameters.
One of the key advancements driven by emissions regulations was the introduction of sequential fuel injection. This technology allowed for precise timing of fuel delivery to each cylinder, further improving combustion efficiency and reducing unburned fuel emissions. The 2JZ engine's fuel system evolved to incorporate this technology, resulting in better fuel economy and lower emissions without sacrificing performance.
Emissions regulations also pushed for the development of more sophisticated fuel pressure control systems. Variable fuel pressure regulators were introduced to maintain optimal fuel pressure across different operating conditions, ensuring efficient combustion and minimizing emissions. This technology became particularly important in turbocharged variants of the 2JZ engine, where fuel delivery needs to adapt to varying boost pressures.
The need to reduce evaporative emissions led to improvements in fuel tank and line designs. Enhanced sealing technologies and vapor recovery systems were implemented to minimize fuel vapor escape, addressing a significant source of hydrocarbon emissions. These changes affected not only the fuel delivery components but also the overall fuel system architecture in vehicles equipped with 2JZ engines.
As emissions standards continued to evolve, manufacturers had to focus on cold-start emissions, a critical phase for emissions control. This led to the development of more advanced fuel injectors capable of producing finer fuel atomization, especially during engine warm-up. The 2JZ engine's fuel system incorporated these improvements, resulting in reduced emissions during the critical cold-start period.
The impact of emissions regulations on 2JZ fuel systems also extended to the integration of on-board diagnostics (OBD) systems. These systems monitor fuel system performance and emissions-related components, alerting drivers to potential issues that could lead to increased emissions. This integration required further refinement of fuel system sensors and control algorithms to ensure accurate monitoring and reporting.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Fuel System Upgrades
The cost-benefit analysis of fuel system upgrades for 2JZ engines reveals a complex interplay between performance gains and financial investments. Upgrading the fuel delivery system can significantly enhance engine output, but the associated costs must be carefully weighed against the potential benefits.
One of the primary advantages of upgrading the fuel system is the increased power potential. By improving fuel delivery, engines can support higher horsepower levels, often resulting in substantial performance gains. This is particularly relevant for enthusiasts and racers seeking to maximize their engine's capabilities. However, these performance improvements come at a price, both in terms of initial investment and ongoing maintenance costs.
The initial costs of upgrading a 2JZ engine's fuel system can be substantial. High-flow fuel injectors, an upgraded fuel pump, and a more robust fuel pressure regulator are among the essential components that may need replacement. Additionally, supporting modifications such as an upgraded ECU or fuel management system might be necessary to fully utilize the enhanced fuel delivery capabilities. These upgrades can range from moderate to significant expenses, depending on the quality and brand of components chosen.
On the benefit side, upgraded fuel systems often contribute to improved fuel efficiency when properly tuned. This can lead to long-term cost savings, especially for high-performance applications where fuel consumption is a significant factor. Moreover, a more precise fuel delivery system can result in cleaner combustion, potentially reducing engine wear and extending the lifespan of critical components.
Another consideration is the impact on vehicle resale value. While some buyers may appreciate and value performance upgrades, others might be deterred by extensively modified vehicles. This factor can influence the long-term financial implications of fuel system upgrades, particularly for those who frequently change vehicles.
Maintenance costs associated with upgraded fuel systems should also be factored into the analysis. High-performance components may require more frequent servicing or replacement, potentially increasing long-term ownership costs. However, these expenses may be offset by the improved reliability and performance of a well-designed fuel system upgrade.
In conclusion, the decision to upgrade a 2JZ engine's fuel system should be based on a careful evaluation of performance goals, budget constraints, and long-term ownership plans. While the potential for significant performance gains is attractive, the associated costs and ongoing commitments must be carefully considered to ensure that the upgrades align with the user's overall objectives and financial capabilities.
One of the primary advantages of upgrading the fuel system is the increased power potential. By improving fuel delivery, engines can support higher horsepower levels, often resulting in substantial performance gains. This is particularly relevant for enthusiasts and racers seeking to maximize their engine's capabilities. However, these performance improvements come at a price, both in terms of initial investment and ongoing maintenance costs.
The initial costs of upgrading a 2JZ engine's fuel system can be substantial. High-flow fuel injectors, an upgraded fuel pump, and a more robust fuel pressure regulator are among the essential components that may need replacement. Additionally, supporting modifications such as an upgraded ECU or fuel management system might be necessary to fully utilize the enhanced fuel delivery capabilities. These upgrades can range from moderate to significant expenses, depending on the quality and brand of components chosen.
On the benefit side, upgraded fuel systems often contribute to improved fuel efficiency when properly tuned. This can lead to long-term cost savings, especially for high-performance applications where fuel consumption is a significant factor. Moreover, a more precise fuel delivery system can result in cleaner combustion, potentially reducing engine wear and extending the lifespan of critical components.
Another consideration is the impact on vehicle resale value. While some buyers may appreciate and value performance upgrades, others might be deterred by extensively modified vehicles. This factor can influence the long-term financial implications of fuel system upgrades, particularly for those who frequently change vehicles.
Maintenance costs associated with upgraded fuel systems should also be factored into the analysis. High-performance components may require more frequent servicing or replacement, potentially increasing long-term ownership costs. However, these expenses may be offset by the improved reliability and performance of a well-designed fuel system upgrade.
In conclusion, the decision to upgrade a 2JZ engine's fuel system should be based on a careful evaluation of performance goals, budget constraints, and long-term ownership plans. While the potential for significant performance gains is attractive, the associated costs and ongoing commitments must be carefully considered to ensure that the upgrades align with the user's overall objectives and financial capabilities.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!