Acrylic Resin vs Epoxy-Modified Acrylates: Strength and Curing Speed
OCT 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Resin Technology Background and Objectives
Resin technology has evolved significantly over the past several decades, with acrylic resins and epoxy-modified acrylates emerging as critical materials in various industrial applications. The development of these resin systems can be traced back to the mid-20th century when polymer chemistry began to advance rapidly, enabling the creation of synthetic materials with tailored properties for specific applications.
Acrylic resins, primarily based on polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) and related acrylic monomers, gained prominence in the 1930s and have since become fundamental components in coatings, adhesives, dental materials, and optical applications. Their evolution has been driven by demands for improved weatherability, optical clarity, and processing characteristics.
Epoxy-modified acrylates represent a more recent technological advancement, emerging in the 1970s and 1980s as manufacturers sought to combine the rapid curing capabilities of acrylics with the superior mechanical strength and chemical resistance of epoxies. This hybrid technology addressed limitations in traditional acrylic systems while maintaining their desirable processing characteristics.
The technological trajectory has been shaped by increasing demands across multiple industries for materials that offer both rapid processing and enhanced performance properties. Automotive, electronics, construction, and medical sectors have all contributed to pushing the boundaries of what these resin systems can achieve.
Current research and development efforts focus on several key objectives. Primary among these is optimizing the balance between curing speed and mechanical strength—traditionally a challenging trade-off in polymer chemistry. Faster curing typically results in reduced cross-linking density and consequently lower mechanical properties, while higher strength often requires longer curing times or more aggressive curing conditions.
Additional objectives include enhancing environmental sustainability through reduced volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions, developing bio-based alternatives to petroleum-derived monomers, and improving energy efficiency in curing processes. The industry is also pursuing innovations in formulation technology to achieve consistent performance across varying environmental conditions.
The anticipated technological goals include developing resin systems that can cure completely within seconds while achieving tensile strengths exceeding 70 MPa, creating formulations that maintain performance integrity across temperature ranges from -40°C to 150°C, and designing systems with improved adhesion to difficult substrates without requiring extensive surface preparation.
Understanding the fundamental chemistry and performance characteristics of both acrylic resins and epoxy-modified acrylates is essential for identifying pathways to overcome current limitations and achieve next-generation performance benchmarks in strength and curing speed.
Acrylic resins, primarily based on polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) and related acrylic monomers, gained prominence in the 1930s and have since become fundamental components in coatings, adhesives, dental materials, and optical applications. Their evolution has been driven by demands for improved weatherability, optical clarity, and processing characteristics.
Epoxy-modified acrylates represent a more recent technological advancement, emerging in the 1970s and 1980s as manufacturers sought to combine the rapid curing capabilities of acrylics with the superior mechanical strength and chemical resistance of epoxies. This hybrid technology addressed limitations in traditional acrylic systems while maintaining their desirable processing characteristics.
The technological trajectory has been shaped by increasing demands across multiple industries for materials that offer both rapid processing and enhanced performance properties. Automotive, electronics, construction, and medical sectors have all contributed to pushing the boundaries of what these resin systems can achieve.
Current research and development efforts focus on several key objectives. Primary among these is optimizing the balance between curing speed and mechanical strength—traditionally a challenging trade-off in polymer chemistry. Faster curing typically results in reduced cross-linking density and consequently lower mechanical properties, while higher strength often requires longer curing times or more aggressive curing conditions.
Additional objectives include enhancing environmental sustainability through reduced volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions, developing bio-based alternatives to petroleum-derived monomers, and improving energy efficiency in curing processes. The industry is also pursuing innovations in formulation technology to achieve consistent performance across varying environmental conditions.
The anticipated technological goals include developing resin systems that can cure completely within seconds while achieving tensile strengths exceeding 70 MPa, creating formulations that maintain performance integrity across temperature ranges from -40°C to 150°C, and designing systems with improved adhesion to difficult substrates without requiring extensive surface preparation.
Understanding the fundamental chemistry and performance characteristics of both acrylic resins and epoxy-modified acrylates is essential for identifying pathways to overcome current limitations and achieve next-generation performance benchmarks in strength and curing speed.
Market Demand Analysis for High-Performance Adhesives
The high-performance adhesives market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing demand across multiple industries including automotive, construction, electronics, and medical devices. The global high-performance adhesives market was valued at approximately 9.4 billion USD in 2022 and is projected to reach 13.6 billion USD by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 6.3% during the forecast period.
Within this market, acrylic-based adhesives represent a substantial segment, accounting for roughly 27% of the total market share. The specific comparison between traditional acrylic resins and epoxy-modified acrylates is particularly relevant as industries increasingly demand adhesives with both rapid curing capabilities and superior strength properties.
The automotive industry remains one of the largest consumers of high-performance adhesives, with manufacturers seeking solutions that can reduce vehicle weight while maintaining structural integrity. The transition toward electric vehicles has further accelerated demand for specialized adhesives that can bond dissimilar materials while withstanding thermal cycling and vibration. In this context, epoxy-modified acrylates have gained significant traction due to their balanced performance profile.
Electronics manufacturing represents another critical market, where miniaturization trends and the proliferation of portable devices drive demand for adhesives that can cure quickly in production environments while providing long-term durability. Market research indicates that electronics manufacturers are willing to pay premium prices for adhesives that can reduce assembly time by 30% or more while maintaining reliability standards.
The construction sector's shift toward prefabricated and modular building systems has created new opportunities for high-performance adhesives. Contractors increasingly prefer solutions that offer rapid installation capabilities combined with long-term structural performance, particularly in applications exposed to environmental stressors.
Consumer preferences are also evolving, with sustainability becoming a key consideration. Market surveys indicate that 68% of industrial purchasers now consider environmental impact when selecting adhesive systems. This has created a growing niche for bio-based and low-VOC formulations that maintain performance characteristics comparable to traditional systems.
Regional analysis shows that North America and Europe currently dominate the high-performance adhesives market, though Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region with a projected CAGR of 7.8% through 2028. China and India are particularly notable markets due to their expanding manufacturing bases and increasing adoption of advanced assembly techniques.
The price sensitivity varies significantly by application, with aerospace and medical applications demonstrating the lowest price elasticity due to stringent performance requirements and regulatory considerations. Conversely, general industrial applications show greater price sensitivity, creating distinct market segments with different value propositions for acrylic resin and epoxy-modified acrylate systems.
Within this market, acrylic-based adhesives represent a substantial segment, accounting for roughly 27% of the total market share. The specific comparison between traditional acrylic resins and epoxy-modified acrylates is particularly relevant as industries increasingly demand adhesives with both rapid curing capabilities and superior strength properties.
The automotive industry remains one of the largest consumers of high-performance adhesives, with manufacturers seeking solutions that can reduce vehicle weight while maintaining structural integrity. The transition toward electric vehicles has further accelerated demand for specialized adhesives that can bond dissimilar materials while withstanding thermal cycling and vibration. In this context, epoxy-modified acrylates have gained significant traction due to their balanced performance profile.
Electronics manufacturing represents another critical market, where miniaturization trends and the proliferation of portable devices drive demand for adhesives that can cure quickly in production environments while providing long-term durability. Market research indicates that electronics manufacturers are willing to pay premium prices for adhesives that can reduce assembly time by 30% or more while maintaining reliability standards.
The construction sector's shift toward prefabricated and modular building systems has created new opportunities for high-performance adhesives. Contractors increasingly prefer solutions that offer rapid installation capabilities combined with long-term structural performance, particularly in applications exposed to environmental stressors.
Consumer preferences are also evolving, with sustainability becoming a key consideration. Market surveys indicate that 68% of industrial purchasers now consider environmental impact when selecting adhesive systems. This has created a growing niche for bio-based and low-VOC formulations that maintain performance characteristics comparable to traditional systems.
Regional analysis shows that North America and Europe currently dominate the high-performance adhesives market, though Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region with a projected CAGR of 7.8% through 2028. China and India are particularly notable markets due to their expanding manufacturing bases and increasing adoption of advanced assembly techniques.
The price sensitivity varies significantly by application, with aerospace and medical applications demonstrating the lowest price elasticity due to stringent performance requirements and regulatory considerations. Conversely, general industrial applications show greater price sensitivity, creating distinct market segments with different value propositions for acrylic resin and epoxy-modified acrylate systems.
Technical Challenges in Acrylic and Epoxy-Modified Resins
The current landscape of acrylic resin and epoxy-modified acrylate technologies presents several significant technical challenges that impact their industrial applications. Traditional acrylic resins offer excellent weatherability and optical clarity but suffer from inherent brittleness and limited adhesion to certain substrates. Meanwhile, epoxy-modified acrylates demonstrate superior strength and adhesion but face issues with yellowing under UV exposure and often exhibit slower curing speeds.
One of the primary technical hurdles involves balancing curing speed with mechanical properties. Accelerating the curing process of epoxy-modified acrylates typically results in increased internal stress within the polymer matrix, leading to potential cracking and reduced impact resistance. Conversely, traditional acrylic resins can cure rapidly but often cannot achieve the cross-linking density necessary for high-strength applications.
Thermal stability presents another significant challenge, particularly for epoxy-modified systems. While these materials offer excellent mechanical properties at room temperature, their performance can degrade significantly at elevated temperatures above 150°C, limiting their use in high-temperature environments. Acrylic resins generally maintain better dimensional stability across temperature ranges but sacrifice ultimate strength.
Moisture sensitivity remains problematic for both material systems. Epoxy-modified acrylates can absorb atmospheric moisture during curing, potentially causing cloudiness, reduced adhesion, and compromised mechanical properties. Traditional acrylics, while less hygroscopic, still face challenges with water permeability that can affect long-term durability in humid environments.
Shrinkage during polymerization represents a persistent technical obstacle, particularly for high-solid content formulations. Acrylic resins typically exhibit volumetric shrinkage of 10-15% during curing, creating internal stresses that can lead to warping and dimensional instability. Epoxy-modified systems show reduced shrinkage (typically 2-8%) but often at the cost of extended cure times.
Compatibility issues between the epoxy and acrylic components in hybrid systems create formulation challenges. Phase separation during storage or application can lead to inconsistent performance and reduced shelf life. Achieving homogeneous mixtures requires sophisticated compatibilizers and stabilizers that add complexity and cost to formulations.
The development of photoinitiators that function effectively across both chemistries remains technically challenging. Current initiator systems often favor either the acrylic or epoxy component, resulting in uneven cure profiles and potentially compromised mechanical properties in the final polymer network.
One of the primary technical hurdles involves balancing curing speed with mechanical properties. Accelerating the curing process of epoxy-modified acrylates typically results in increased internal stress within the polymer matrix, leading to potential cracking and reduced impact resistance. Conversely, traditional acrylic resins can cure rapidly but often cannot achieve the cross-linking density necessary for high-strength applications.
Thermal stability presents another significant challenge, particularly for epoxy-modified systems. While these materials offer excellent mechanical properties at room temperature, their performance can degrade significantly at elevated temperatures above 150°C, limiting their use in high-temperature environments. Acrylic resins generally maintain better dimensional stability across temperature ranges but sacrifice ultimate strength.
Moisture sensitivity remains problematic for both material systems. Epoxy-modified acrylates can absorb atmospheric moisture during curing, potentially causing cloudiness, reduced adhesion, and compromised mechanical properties. Traditional acrylics, while less hygroscopic, still face challenges with water permeability that can affect long-term durability in humid environments.
Shrinkage during polymerization represents a persistent technical obstacle, particularly for high-solid content formulations. Acrylic resins typically exhibit volumetric shrinkage of 10-15% during curing, creating internal stresses that can lead to warping and dimensional instability. Epoxy-modified systems show reduced shrinkage (typically 2-8%) but often at the cost of extended cure times.
Compatibility issues between the epoxy and acrylic components in hybrid systems create formulation challenges. Phase separation during storage or application can lead to inconsistent performance and reduced shelf life. Achieving homogeneous mixtures requires sophisticated compatibilizers and stabilizers that add complexity and cost to formulations.
The development of photoinitiators that function effectively across both chemistries remains technically challenging. Current initiator systems often favor either the acrylic or epoxy component, resulting in uneven cure profiles and potentially compromised mechanical properties in the final polymer network.
Current Formulation Approaches and Solutions
01 Epoxy-modified acrylate compositions for enhanced strength
Epoxy-modified acrylate resins can be formulated to provide superior mechanical strength properties. These compositions typically combine the flexibility of acrylic polymers with the durability and adhesion properties of epoxy resins. The modification of acrylic resins with epoxy groups creates cross-linking sites that enhance tensile strength, impact resistance, and overall structural integrity. These formulations are particularly valuable in applications requiring high mechanical performance while maintaining the processing advantages of acrylic systems.- Epoxy-modified acrylate compositions for enhanced strength: Epoxy-modified acrylate resins can be formulated to provide superior mechanical strength properties compared to conventional acrylic resins. These compositions typically incorporate epoxy functional groups into the acrylic backbone, creating a hybrid polymer with improved tensile strength, impact resistance, and adhesion. The cross-linking between epoxy and acrylic components creates a more rigid and durable polymer network that maintains flexibility while offering enhanced structural integrity for various applications.
- Photoinitiators and curing accelerators for rapid polymerization: Specialized photoinitiators and curing accelerators can significantly improve the curing speed of acrylic and epoxy-modified acrylate systems. These additives initiate and propagate the polymerization reaction when exposed to specific wavelengths of light or thermal energy. By carefully selecting and optimizing the concentration of these components, manufacturers can achieve rapid curing times while maintaining the desired mechanical properties. Advanced photoinitiator systems may include synergistic combinations that enhance both the speed and depth of cure in thick sections.
- Dual-cure systems combining UV and thermal curing mechanisms: Dual-cure systems incorporate both UV-activated and thermally-activated curing mechanisms to optimize both curing speed and final strength properties. These formulations typically contain photoinitiators for rapid initial curing under UV light, followed by thermal curing agents that complete the polymerization process. This approach allows for quick handling strength development followed by complete curing that maximizes mechanical properties. The dual-cure approach is particularly valuable for complex geometries or applications where UV light penetration may be limited.
- Reactive diluents for viscosity control and crosslinking enhancement: Reactive diluents can be incorporated into epoxy-modified acrylate formulations to reduce viscosity while contributing to the crosslinking network. These functional monomers improve processing characteristics and allow for higher solid content formulations without compromising curing speed. By selecting reactive diluents with complementary functionality, formulators can enhance both the curing kinetics and final mechanical properties of the cured material. The proper balance of reactive diluents can optimize flow properties during application while ensuring rapid cure response and high strength development.
- Nanoparticle reinforcement for mechanical property enhancement: The incorporation of nanoparticles into acrylic and epoxy-modified acrylate systems can significantly enhance mechanical strength while maintaining or improving cure speed. Nanofillers such as silica, alumina, or carbon-based materials create reinforced polymer composites with superior hardness, abrasion resistance, and dimensional stability. These nanocomposites often exhibit improved heat resistance and reduced shrinkage during curing. The surface modification of nanoparticles ensures proper dispersion and chemical compatibility with the resin system, maximizing the reinforcement effect without negatively impacting cure kinetics.
02 Curing accelerators and catalysts for rapid polymerization
Various catalysts and accelerators can be incorporated into acrylic and epoxy-modified acrylate formulations to significantly reduce curing time. These include photoinitiators for UV-curing systems, thermal initiators, and metal-based catalysts that facilitate faster polymerization reactions. The selection of appropriate accelerator systems allows for rapid curing even at lower temperatures, which is beneficial for heat-sensitive substrates. Optimized catalyst combinations can achieve complete curing in minutes rather than hours while maintaining the desired mechanical properties of the final product.Expand Specific Solutions03 Hybrid resin systems with dual-cure mechanisms
Hybrid systems combining acrylic resins with epoxy-modified acrylates can utilize dual-cure mechanisms to optimize both curing speed and final strength properties. These formulations typically employ both free-radical and cationic polymerization pathways, allowing for initial rapid curing followed by post-curing processes that develop maximum strength. The synergistic effect between the different polymer networks creates materials with enhanced thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical properties compared to single-component systems.Expand Specific Solutions04 Functional additives for strength enhancement
Various functional additives can be incorporated into acrylic and epoxy-modified acrylate formulations to enhance mechanical strength. These include reinforcing fillers such as silica nanoparticles, glass fibers, and carbon-based materials that improve tensile strength and impact resistance. Cross-linking enhancers and reactive diluents can also be added to optimize the polymer network structure. Additionally, coupling agents improve the interface between organic and inorganic components, resulting in superior mechanical properties in the cured material.Expand Specific Solutions05 Environmental factors affecting curing and strength
Environmental conditions significantly impact both the curing speed and final strength properties of acrylic and epoxy-modified acrylate systems. Factors such as humidity, temperature, oxygen inhibition, and substrate characteristics can affect polymerization kinetics and network formation. Formulations can be optimized to perform under specific environmental conditions by incorporating moisture-scavenging additives, oxygen inhibition suppressants, or temperature-responsive catalysts. Understanding these environmental influences allows for the development of robust formulations that maintain consistent performance across varying application conditions.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players and Competitive Landscape
The acrylic resin versus epoxy-modified acrylates market is currently in a mature growth phase, with increasing demand driven by construction, automotive, and electronics applications. The global market size is estimated at $9-10 billion, growing at 4-5% annually. In terms of technical maturity, epoxy-modified acrylates are gaining traction due to superior strength-to-curing speed ratio. Key players include DIC Corp. and Nippon Shokubai leading in traditional acrylics, while Kukdo Chemical and Kaneka Corp. excel in epoxy-modified technologies. Mitsubishi Gas Chemical and Soken Chemical are advancing rapid-cure formulations, while Henkel and Sika Technology focus on high-strength applications. Japanese manufacturers like Teijin and Kuraray maintain significant market share through specialized formulations for industrial applications.
NIPPON STEEL Chemical & Material Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: NIPPON STEEL Chemical & Material has developed advanced epoxy-modified acrylic resin systems marketed under their NITOFLON® brand. Their technology focuses on optimizing the balance between cure speed and mechanical properties through precise control of the epoxy-to-acrylic ratio and innovative catalyst systems. Their research has demonstrated that incorporating specific epoxy functionalities into acrylic backbones can achieve cure times of under 3 minutes at 120°C while maintaining tensile strengths exceeding 70 MPa. The company's proprietary formulations utilize specialized photoinitiators that enable dual-cure mechanisms - initial UV curing followed by thermal post-cure for shadow areas. NIPPON STEEL's systems are particularly noted for their excellent adhesion to metal substrates, with lap shear strengths on steel substrates reaching 25-30 MPa. Their latest innovations include formulations with enhanced chemical resistance specifically designed for automotive and electronic applications where exposure to harsh environments is expected.
Strengths: Exceptional adhesion to metal substrates; excellent chemical and heat resistance; good balance of flexibility and strength. Weaknesses: Requires both UV and thermal curing for optimal performance; higher processing temperatures than pure acrylic systems; more complex application equipment needed compared to single-component systems.
Mitsubishi Gas Chemical Co., Inc.
Technical Solution: Mitsubishi Gas Chemical has developed innovative epoxy-acrylate hybrid resins under their ARONIX® product line. Their technology utilizes proprietary molecular design to create interpenetrating polymer networks (IPNs) that combine the rapid cure characteristics of acrylics with the superior mechanical properties of epoxies. Their research demonstrates cure speeds of 5-10 seconds under UV exposure for the acrylic component, while the epoxy network develops over 1-2 hours at ambient conditions. MGC's formulations achieve glass transition temperatures (Tg) exceeding 150°C after complete cure, significantly higher than conventional acrylic systems. The company has pioneered specialized coupling agents that improve the compatibility between the acrylic and epoxy phases, resulting in homogeneous materials with reduced internal stress. Their latest innovations include formulations with enhanced moisture resistance and thermal cycling durability specifically designed for semiconductor packaging applications.
Strengths: Excellent thermal stability and high glass transition temperatures; superior moisture resistance compared to pure acrylic systems; good dimensional stability after cure. Weaknesses: More complex processing requirements than single-component systems; higher cost than conventional materials; potential for stress development during cure of thicker sections.
Critical Patents and Technical Innovations
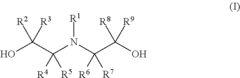
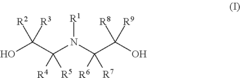
Epoxide (meth) acrylate composition
PatentInactiveUS8318870B2
Innovation
- A composition comprising a free-radically polymerizable monomer, a free-radical former, an epoxy resin with multiple epoxy groups, and a specific compound that allows immediate free-radical polymerization at room temperature without additional energy, enabling high early strength and complete curing without heat.
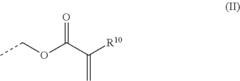
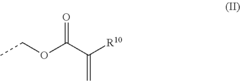
Resin composition
PatentWO2022019309A1
Innovation
- A novel composition combining an acrylic resin with an alicyclic epoxy resin, where the acrylic resin has acid groups and reactive groups that react with the epoxy resin, resulting in a modified epoxy resin with reduced viscosity and enhanced transparency, achieved through specific mixing and emulsification processes.
Environmental and Regulatory Considerations
The regulatory landscape surrounding adhesive materials has evolved significantly in recent years, with increasing focus on environmental impact and human health considerations. Acrylic resins and epoxy-modified acrylates face different regulatory challenges due to their distinct chemical compositions and emission profiles. Volatile Organic Compound (VOC) regulations particularly impact these materials, with traditional acrylic resins often containing higher VOC levels compared to newer epoxy-modified acrylate formulations.
In the European Union, the REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation imposes strict requirements on both material types, with particular scrutiny on bisphenol A (BPA) content in epoxy components. Similarly, the United States EPA has established guidelines under the Clean Air Act that affect manufacturing processes and application methods for both adhesive types.
Occupational health considerations represent another significant regulatory dimension. Epoxy-modified acrylates typically require more stringent handling protocols due to potential skin sensitization issues before curing. However, the faster curing speed of these hybrid materials reduces overall exposure time for workers, potentially offsetting some health concerns when properly managed.
From an environmental perspective, the lifecycle assessment of these materials reveals important distinctions. While acrylic resins generally demonstrate lower environmental impact during production, epoxy-modified acrylates often exhibit superior durability, potentially reducing replacement frequency and associated environmental costs. The extended service life of epoxy-modified products may contribute to lower overall environmental footprint despite higher initial production impacts.
Waste management considerations also differ significantly between these material types. Fully cured epoxy-modified acrylates typically present fewer leaching concerns in landfill environments compared to standard acrylic resins. However, the complex chemical structure of epoxy-modified materials can complicate recycling efforts, whereas certain acrylic resin formulations may be more amenable to recycling processes.
Industry certification systems increasingly recognize these distinctions, with green building standards like LEED and BREEAM awarding points based on VOC content, recyclability, and overall environmental impact. This regulatory environment has driven innovation toward water-based formulations in both material categories, though epoxy-modified acrylates have generally achieved greater technical success in maintaining performance properties while reducing environmental impact.
Recent regulatory trends indicate movement toward harmonized global standards for these materials, with particular emphasis on eliminating substances of very high concern (SVHCs) from formulations. Manufacturers increasingly must balance performance requirements against evolving regulatory constraints, driving continuous reformulation efforts and alternative chemistry development.
In the European Union, the REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals) regulation imposes strict requirements on both material types, with particular scrutiny on bisphenol A (BPA) content in epoxy components. Similarly, the United States EPA has established guidelines under the Clean Air Act that affect manufacturing processes and application methods for both adhesive types.
Occupational health considerations represent another significant regulatory dimension. Epoxy-modified acrylates typically require more stringent handling protocols due to potential skin sensitization issues before curing. However, the faster curing speed of these hybrid materials reduces overall exposure time for workers, potentially offsetting some health concerns when properly managed.
From an environmental perspective, the lifecycle assessment of these materials reveals important distinctions. While acrylic resins generally demonstrate lower environmental impact during production, epoxy-modified acrylates often exhibit superior durability, potentially reducing replacement frequency and associated environmental costs. The extended service life of epoxy-modified products may contribute to lower overall environmental footprint despite higher initial production impacts.
Waste management considerations also differ significantly between these material types. Fully cured epoxy-modified acrylates typically present fewer leaching concerns in landfill environments compared to standard acrylic resins. However, the complex chemical structure of epoxy-modified materials can complicate recycling efforts, whereas certain acrylic resin formulations may be more amenable to recycling processes.
Industry certification systems increasingly recognize these distinctions, with green building standards like LEED and BREEAM awarding points based on VOC content, recyclability, and overall environmental impact. This regulatory environment has driven innovation toward water-based formulations in both material categories, though epoxy-modified acrylates have generally achieved greater technical success in maintaining performance properties while reducing environmental impact.
Recent regulatory trends indicate movement toward harmonized global standards for these materials, with particular emphasis on eliminating substances of very high concern (SVHCs) from formulations. Manufacturers increasingly must balance performance requirements against evolving regulatory constraints, driving continuous reformulation efforts and alternative chemistry development.
Application-Specific Performance Benchmarking
Performance benchmarking across specific applications reveals significant differences between acrylic resins and epoxy-modified acrylates. In dental applications, epoxy-modified acrylates demonstrate superior compressive strength (350-420 MPa compared to traditional acrylics' 250-300 MPa) and reduced polymerization shrinkage (1.5-2.0% versus 6-8%), resulting in more durable restorations with improved marginal integrity.
For industrial adhesives, testing under standardized conditions (ASTM D1002) shows epoxy-modified acrylates achieving lap shear strengths of 18-25 MPa, outperforming conventional acrylics (10-15 MPa) in metal-to-metal bonding applications. This performance advantage becomes particularly pronounced in environments with temperature fluctuations between -40°C and 120°C.
In automotive manufacturing, impact resistance testing demonstrates epoxy-modified acrylates maintain 85% of their original strength after 1000 hours of accelerated weathering, while standard acrylics retain only 60-70%. However, production line integration benchmarks indicate conventional acrylics achieve functional handling strength in 30-45 seconds versus 60-90 seconds for epoxy-modified formulations.
Construction adhesive performance metrics reveal epoxy-modified acrylates provide superior long-term durability with 95% strength retention after water immersion testing (ASTM D870), compared to 75-80% for standard acrylics. This advantage is offset by installation efficiency metrics showing conventional acrylics allow for faster project completion in temperature-controlled environments.
Electronics assembly benchmarking demonstrates epoxy-modified acrylates maintain electrical insulation properties (>10^12 ohm-cm) after thermal cycling tests, while standard acrylics show degradation below 10^10 ohm-cm after equivalent testing. However, precision dispensing tests indicate conventional acrylics offer superior flow characteristics for automated manufacturing processes.
Medical device manufacturing comparisons show epoxy-modified acrylates achieving ISO 10993 biocompatibility standards with lower cytotoxicity profiles than many conventional acrylics. Sterilization resistance testing reveals epoxy-modified formulations maintain 92% of mechanical properties after gamma irradiation (25 kGy), compared to 78% retention for standard acrylics.
Cost-performance analysis across these applications indicates epoxy-modified acrylates typically command a 30-45% price premium but deliver 50-70% longer service life in high-stress applications, representing a favorable lifetime value proposition despite higher initial costs and longer curing requirements.
For industrial adhesives, testing under standardized conditions (ASTM D1002) shows epoxy-modified acrylates achieving lap shear strengths of 18-25 MPa, outperforming conventional acrylics (10-15 MPa) in metal-to-metal bonding applications. This performance advantage becomes particularly pronounced in environments with temperature fluctuations between -40°C and 120°C.
In automotive manufacturing, impact resistance testing demonstrates epoxy-modified acrylates maintain 85% of their original strength after 1000 hours of accelerated weathering, while standard acrylics retain only 60-70%. However, production line integration benchmarks indicate conventional acrylics achieve functional handling strength in 30-45 seconds versus 60-90 seconds for epoxy-modified formulations.
Construction adhesive performance metrics reveal epoxy-modified acrylates provide superior long-term durability with 95% strength retention after water immersion testing (ASTM D870), compared to 75-80% for standard acrylics. This advantage is offset by installation efficiency metrics showing conventional acrylics allow for faster project completion in temperature-controlled environments.
Electronics assembly benchmarking demonstrates epoxy-modified acrylates maintain electrical insulation properties (>10^12 ohm-cm) after thermal cycling tests, while standard acrylics show degradation below 10^10 ohm-cm after equivalent testing. However, precision dispensing tests indicate conventional acrylics offer superior flow characteristics for automated manufacturing processes.
Medical device manufacturing comparisons show epoxy-modified acrylates achieving ISO 10993 biocompatibility standards with lower cytotoxicity profiles than many conventional acrylics. Sterilization resistance testing reveals epoxy-modified formulations maintain 92% of mechanical properties after gamma irradiation (25 kGy), compared to 78% retention for standard acrylics.
Cost-performance analysis across these applications indicates epoxy-modified acrylates typically command a 30-45% price premium but deliver 50-70% longer service life in high-stress applications, representing a favorable lifetime value proposition despite higher initial costs and longer curing requirements.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!