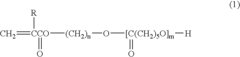
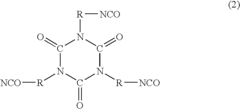
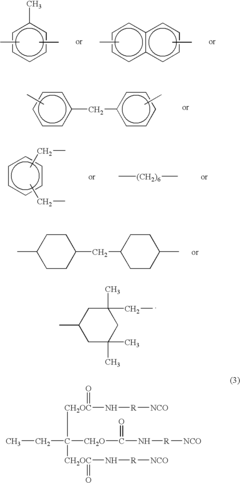
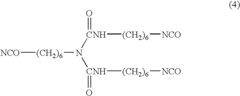
Acrylic Resin vs Melamine Crosslinked Systems: Surface Durability
OCT 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Resin Systems Background and Performance Objectives
Surface coating systems have evolved significantly over the past century, with acrylic resins and melamine crosslinked systems emerging as two dominant technologies in applications requiring superior surface durability. Acrylic resins, first developed in the 1930s, gained commercial prominence in the 1950s due to their exceptional weatherability and optical clarity. Melamine formaldehyde resins, discovered in the early 20th century, became widely adopted in the 1940s for their excellent hardness and chemical resistance properties when crosslinked.
The technological evolution of these resin systems has been driven by increasing demands for performance in diverse environmental conditions. Acrylic resins have progressed from simple homopolymers to sophisticated copolymer systems incorporating functional monomers that enhance specific properties. Similarly, melamine systems have evolved from basic formaldehyde adducts to complex crosslinking agents with modified reactivity profiles and reduced formaldehyde emissions.
Current market trends indicate a growing preference for high-performance coating systems that deliver extended service life while meeting increasingly stringent environmental regulations. This has accelerated development in both resin technologies, with particular focus on enhancing scratch resistance, chemical resistance, and UV stability without compromising other performance attributes.
The primary performance objectives for modern surface coating systems center around four key parameters: mechanical durability (scratch and abrasion resistance), chemical resistance, weatherability (UV and moisture resistance), and aesthetic longevity. Secondary but increasingly important objectives include environmental sustainability, reduced volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and compatibility with various application methods and substrates.
For industrial applications, the performance threshold typically requires resistance to at least 2,000 cycles in Taber abrasion testing, chemical resistance to common household cleaners without visible damage, and color stability after 2,000 hours of accelerated weathering. Consumer expectations have risen substantially, with market research indicating willingness to pay premium prices for coatings that maintain their appearance for 5+ years in demanding environments.
The technological trajectory suggests continued refinement of hybrid systems that leverage the strengths of both acrylic and melamine technologies. Recent innovations include nano-composite modifications, self-healing capabilities, and smart coatings that respond to environmental stimuli. These developments aim to address the fundamental challenge of balancing hardness with flexibility – a persistent trade-off in coating formulation that directly impacts long-term durability performance.
The technological evolution of these resin systems has been driven by increasing demands for performance in diverse environmental conditions. Acrylic resins have progressed from simple homopolymers to sophisticated copolymer systems incorporating functional monomers that enhance specific properties. Similarly, melamine systems have evolved from basic formaldehyde adducts to complex crosslinking agents with modified reactivity profiles and reduced formaldehyde emissions.
Current market trends indicate a growing preference for high-performance coating systems that deliver extended service life while meeting increasingly stringent environmental regulations. This has accelerated development in both resin technologies, with particular focus on enhancing scratch resistance, chemical resistance, and UV stability without compromising other performance attributes.
The primary performance objectives for modern surface coating systems center around four key parameters: mechanical durability (scratch and abrasion resistance), chemical resistance, weatherability (UV and moisture resistance), and aesthetic longevity. Secondary but increasingly important objectives include environmental sustainability, reduced volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and compatibility with various application methods and substrates.
For industrial applications, the performance threshold typically requires resistance to at least 2,000 cycles in Taber abrasion testing, chemical resistance to common household cleaners without visible damage, and color stability after 2,000 hours of accelerated weathering. Consumer expectations have risen substantially, with market research indicating willingness to pay premium prices for coatings that maintain their appearance for 5+ years in demanding environments.
The technological trajectory suggests continued refinement of hybrid systems that leverage the strengths of both acrylic and melamine technologies. Recent innovations include nano-composite modifications, self-healing capabilities, and smart coatings that respond to environmental stimuli. These developments aim to address the fundamental challenge of balancing hardness with flexibility – a persistent trade-off in coating formulation that directly impacts long-term durability performance.
Market Analysis for Durable Surface Coating Materials
The global market for durable surface coating materials has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing demand across multiple industries including automotive, construction, furniture, and electronics. The combined market value for high-performance coating materials reached approximately $29.7 billion in 2022, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate of 5.8% through 2028.
Within this market, acrylic resin and melamine crosslinked systems represent two dominant technologies competing for market share in applications requiring superior surface durability. Acrylic-based coatings currently hold approximately 38% of the high-performance coating market, valued at $11.3 billion, while melamine crosslinked systems account for roughly 27%, representing $8 billion in market value.
Consumer preferences are increasingly shifting toward products with extended lifespans and reduced maintenance requirements, particularly in premium market segments. This trend has intensified competition between these two coating technologies, with manufacturers investing heavily in research and development to enhance durability performance metrics including scratch resistance, chemical resistance, and UV stability.
Regional analysis reveals distinct market patterns, with North America and Europe showing stronger preference for acrylic systems due to stricter environmental regulations limiting formaldehyde emissions associated with some melamine formulations. Conversely, Asia-Pacific markets continue to favor melamine crosslinked systems due to their lower cost structure and established manufacturing infrastructure, though this is gradually changing as environmental standards tighten globally.
End-user segmentation indicates that furniture manufacturers represent the largest consumer group for both technologies at 31% of total consumption, followed by building materials at 24%, automotive applications at 19%, and consumer electronics at 14%. The remaining 12% is distributed across various specialty applications including marine, aerospace, and medical equipment.
Price sensitivity analysis reveals interesting dynamics between these competing technologies. While melamine systems typically offer a 15-20% cost advantage in raw material pricing, this gap narrows when considering total lifecycle costs including application processes, curing requirements, and long-term performance. Premium market segments demonstrate willingness to pay 25-30% price premiums for coatings that can demonstrate superior durability metrics, particularly in scratch resistance and UV stability.
Market forecasts suggest that environmental considerations will increasingly influence market share distribution, with water-based acrylic systems gaining advantage as regulatory frameworks continue to evolve toward stricter VOC and formaldehyde emission standards. However, innovations in melamine chemistry aimed at reducing environmental impact while maintaining performance characteristics may counterbalance this trend in coming years.
Within this market, acrylic resin and melamine crosslinked systems represent two dominant technologies competing for market share in applications requiring superior surface durability. Acrylic-based coatings currently hold approximately 38% of the high-performance coating market, valued at $11.3 billion, while melamine crosslinked systems account for roughly 27%, representing $8 billion in market value.
Consumer preferences are increasingly shifting toward products with extended lifespans and reduced maintenance requirements, particularly in premium market segments. This trend has intensified competition between these two coating technologies, with manufacturers investing heavily in research and development to enhance durability performance metrics including scratch resistance, chemical resistance, and UV stability.
Regional analysis reveals distinct market patterns, with North America and Europe showing stronger preference for acrylic systems due to stricter environmental regulations limiting formaldehyde emissions associated with some melamine formulations. Conversely, Asia-Pacific markets continue to favor melamine crosslinked systems due to their lower cost structure and established manufacturing infrastructure, though this is gradually changing as environmental standards tighten globally.
End-user segmentation indicates that furniture manufacturers represent the largest consumer group for both technologies at 31% of total consumption, followed by building materials at 24%, automotive applications at 19%, and consumer electronics at 14%. The remaining 12% is distributed across various specialty applications including marine, aerospace, and medical equipment.
Price sensitivity analysis reveals interesting dynamics between these competing technologies. While melamine systems typically offer a 15-20% cost advantage in raw material pricing, this gap narrows when considering total lifecycle costs including application processes, curing requirements, and long-term performance. Premium market segments demonstrate willingness to pay 25-30% price premiums for coatings that can demonstrate superior durability metrics, particularly in scratch resistance and UV stability.
Market forecasts suggest that environmental considerations will increasingly influence market share distribution, with water-based acrylic systems gaining advantage as regulatory frameworks continue to evolve toward stricter VOC and formaldehyde emission standards. However, innovations in melamine chemistry aimed at reducing environmental impact while maintaining performance characteristics may counterbalance this trend in coming years.
Current Technical Challenges in Surface Durability Systems
Surface durability remains a critical challenge in coating systems, with acrylic resin and melamine crosslinked systems representing two predominant technologies with distinct performance characteristics. Current technical challenges primarily revolve around balancing durability with environmental compliance and cost-effectiveness.
The inherent chemical structure limitations of acrylic resins present significant hurdles. While offering excellent UV resistance and color stability, pure acrylic systems typically demonstrate inferior scratch and chemical resistance compared to melamine crosslinked alternatives. This performance gap becomes particularly evident in high-traffic commercial environments where surface abrasion is constant.
Melamine crosslinked systems, conversely, excel in hardness and chemical resistance but face challenges in weatherability and yellowing upon prolonged UV exposure. The formaldehyde emissions associated with melamine chemistry also present regulatory compliance issues as global environmental standards become increasingly stringent.
Crosslinking efficiency remains problematic across both systems. Acrylic resins often require specialized catalysts or elevated curing temperatures to achieve optimal crosslinking density, limiting their application in temperature-sensitive substrates. Melamine systems, while more reactive, can suffer from over-crosslinking, resulting in brittleness and reduced impact resistance over time.
Water resistance presents another significant technical barrier. Hydrolytic stability of the crosslinked network, particularly at the interface between different polymer domains, often deteriorates under prolonged moisture exposure. This manifests as whitening, delamination, or loss of gloss in finished surfaces.
Adhesion to diverse substrates continues to challenge formulators, especially when considering the expanding range of composite and engineered materials entering the market. The surface tension mismatch between coating and substrate often necessitates specialized primers or surface treatments, adding complexity and cost to finishing systems.
Recent advances in nanotechnology have introduced potential solutions through incorporation of nanoparticles to enhance surface properties. However, dispersion stability and compatibility with existing resin systems remain problematic, with agglomeration leading to optical clarity issues and inconsistent performance.
Manufacturing consistency presents additional challenges, with batch-to-batch variations in raw materials significantly impacting final coating performance. The sensitivity of crosslinking reactions to minor fluctuations in temperature, humidity, and catalyst concentration makes quality control exceptionally demanding.
Cost pressures further complicate technical development, as high-performance additives and specialty monomers necessary for enhanced durability significantly impact formulation economics, limiting widespread commercial adoption of cutting-edge solutions.
The inherent chemical structure limitations of acrylic resins present significant hurdles. While offering excellent UV resistance and color stability, pure acrylic systems typically demonstrate inferior scratch and chemical resistance compared to melamine crosslinked alternatives. This performance gap becomes particularly evident in high-traffic commercial environments where surface abrasion is constant.
Melamine crosslinked systems, conversely, excel in hardness and chemical resistance but face challenges in weatherability and yellowing upon prolonged UV exposure. The formaldehyde emissions associated with melamine chemistry also present regulatory compliance issues as global environmental standards become increasingly stringent.
Crosslinking efficiency remains problematic across both systems. Acrylic resins often require specialized catalysts or elevated curing temperatures to achieve optimal crosslinking density, limiting their application in temperature-sensitive substrates. Melamine systems, while more reactive, can suffer from over-crosslinking, resulting in brittleness and reduced impact resistance over time.
Water resistance presents another significant technical barrier. Hydrolytic stability of the crosslinked network, particularly at the interface between different polymer domains, often deteriorates under prolonged moisture exposure. This manifests as whitening, delamination, or loss of gloss in finished surfaces.
Adhesion to diverse substrates continues to challenge formulators, especially when considering the expanding range of composite and engineered materials entering the market. The surface tension mismatch between coating and substrate often necessitates specialized primers or surface treatments, adding complexity and cost to finishing systems.
Recent advances in nanotechnology have introduced potential solutions through incorporation of nanoparticles to enhance surface properties. However, dispersion stability and compatibility with existing resin systems remain problematic, with agglomeration leading to optical clarity issues and inconsistent performance.
Manufacturing consistency presents additional challenges, with batch-to-batch variations in raw materials significantly impacting final coating performance. The sensitivity of crosslinking reactions to minor fluctuations in temperature, humidity, and catalyst concentration makes quality control exceptionally demanding.
Cost pressures further complicate technical development, as high-performance additives and specialty monomers necessary for enhanced durability significantly impact formulation economics, limiting widespread commercial adoption of cutting-edge solutions.
Comparative Analysis of Acrylic and Melamine Crosslinked Solutions
01 Crosslinking mechanisms for improved surface durability
Acrylic resin and melamine crosslinked systems achieve enhanced surface durability through specific crosslinking mechanisms. The reaction between hydroxyl groups in acrylic resins and methylol groups in melamine formaldehyde creates strong covalent bonds that resist physical abrasion and chemical attack. This network structure provides excellent hardness, scratch resistance, and weatherability, making these systems ideal for protective coatings on various surfaces.- Formulation of acrylic-melamine coatings for enhanced durability: Acrylic resins crosslinked with melamine formaldehyde resins create durable surface coatings with excellent weathering resistance. The specific ratio of acrylic to melamine components significantly impacts the coating's hardness, flexibility, and overall durability. These systems typically incorporate hydroxyl-functional acrylic polymers that react with melamine crosslinkers under heat to form a tightly crosslinked network, resulting in surfaces with superior scratch and chemical resistance while maintaining good appearance properties.
- Additives for improving surface properties of crosslinked systems: Various additives can be incorporated into acrylic-melamine systems to enhance specific surface properties. UV absorbers and hindered amine light stabilizers (HALS) significantly improve weathering resistance and prevent surface degradation from sun exposure. Silicone additives and modified waxes enhance scratch resistance and surface slip properties. Nanomaterials such as silica and alumina particles can be dispersed in the coating to improve abrasion resistance while maintaining transparency. These additives work synergistically with the crosslinked polymer network to provide superior surface durability.
- Curing conditions and their impact on surface durability: The curing process significantly affects the surface durability of acrylic-melamine systems. Optimal temperature profiles and curing times ensure complete crosslinking while preventing defects. Catalyst selection and concentration influence reaction kinetics and the final network structure. Two-stage curing processes, with an initial lower temperature followed by higher temperature baking, can produce more uniform crosslinking and superior surface properties. Proper curing conditions minimize residual stresses in the coating, which otherwise could lead to cracking or reduced impact resistance over time.
- Modified acrylic and melamine resins for specialized applications: Chemical modifications to standard acrylic and melamine resins can enhance specific performance characteristics. Silicone-modified acrylics provide improved weather resistance and thermal stability. Partially methylated or butylated melamine resins offer better compatibility with acrylic polymers and enhanced flexibility. Core-shell acrylic polymers with engineered hardness gradients can improve impact resistance while maintaining surface hardness. These modified resins enable formulators to tailor coatings for specific end-use requirements while maintaining excellent surface durability.
- Testing and evaluation methods for surface durability: Various standardized and specialized testing methods are used to evaluate the surface durability of acrylic-melamine systems. Accelerated weathering tests using xenon arc or QUV exposure simulate outdoor conditions to predict long-term performance. Mechanical testing includes pencil hardness, scratch resistance, and abrasion resistance measurements. Chemical resistance is evaluated through spot tests with various solvents, acids, and bases. Advanced analytical techniques such as FTIR spectroscopy and dynamic mechanical analysis help characterize crosslink density and network structure, which correlate with surface durability properties.
02 Additives for enhancing surface properties
Various additives can be incorporated into acrylic-melamine systems to enhance surface durability. These include UV stabilizers that prevent degradation from sunlight exposure, antioxidants that inhibit oxidative breakdown, and specialized silicone or fluoropolymer additives that improve scratch resistance and water repellency. Nanoparticles such as silica or alumina can also be dispersed within the coating matrix to significantly improve abrasion resistance while maintaining optical clarity.Expand Specific Solutions03 Formulation optimization for durability
Optimizing the formulation of acrylic-melamine systems is crucial for maximizing surface durability. The ratio of acrylic resin to melamine crosslinker significantly impacts the final coating properties, with higher melamine content typically increasing hardness but potentially reducing flexibility. Molecular weight distribution of the acrylic component and the degree of functionality in both resins must be carefully controlled. Curing conditions, including temperature profiles and catalyst selection, play vital roles in achieving optimal crosslink density without compromising other performance attributes.Expand Specific Solutions04 Environmental resistance characteristics
Acrylic-melamine crosslinked systems exhibit exceptional resistance to environmental factors that typically degrade coating surfaces. These systems demonstrate superior resistance to UV radiation, moisture, temperature fluctuations, and chemical exposure. The tightly crosslinked network structure prevents water penetration and hydrolysis, while the inherent stability of the acrylic backbone provides excellent color retention and gloss durability even under harsh outdoor conditions. This combination of properties makes these systems particularly valuable for automotive topcoats and exterior architectural finishes.Expand Specific Solutions05 Modified acrylic-melamine systems for specialized applications
Modified acrylic-melamine systems have been developed for specialized applications requiring exceptional surface durability. These include hybrid systems incorporating silicone, polyurethane, or epoxy components to enhance specific performance attributes. Self-healing formulations contain microcapsules with reactive materials that repair minor surface damage. Additionally, water-based and low-VOC formulations have been engineered to meet environmental regulations while maintaining the superior durability characteristics of traditional solvent-based systems. These innovations extend the application range of acrylic-melamine coatings to demanding environments.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Manufacturers and Research Institutions in Polymer Chemistry
The acrylic resin versus melamine crosslinked systems market for surface durability applications is in a mature growth phase, with an estimated global market size of $12-15 billion. The competitive landscape features established players like BASF Coatings, Kansai Paint, and Sumitomo Chemical dominating with comprehensive product portfolios. Technological maturity varies, with companies like Mitsui Chemicals and RESONAC advancing innovative crosslinking technologies for enhanced durability. Japanese manufacturers (Kaneka, Toyobo, Nippon Carbide) lead in high-performance applications, while European companies (BASF, Degussa, ROEHM) focus on sustainability innovations. Chinese entities (PetroChina, Marine Chemical Research Institute) are rapidly expanding market share through cost-effective solutions and increasing R&D investments in durability enhancement technologies.
Kansai Paint Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Kansai Paint has developed a sophisticated dual-cure technology that optimizes the performance of both acrylic and melamine components in high-durability coating systems. Their ALMATEX™ platform incorporates specially engineered acrylic resins with controlled hydroxyl functionality and molecular weight profiles that interact synergistically with their CYMEL™ melamine crosslinkers. The company's approach involves a two-stage curing mechanism where initial crosslinking occurs at lower temperatures (110-130°C) followed by a post-cure phase that enhances network density and surface properties. Kansai's systems incorporate proprietary catalysts that accelerate crosslinking while minimizing acid-catalyzed degradation of the polymer backbone. Their latest generation products feature nano-silica reinforcement particles that are chemically bonded to the polymer matrix, significantly enhancing scratch and mar resistance. Testing shows these hybrid systems maintain 95% of their initial hardness after 2000 cycles on Taber abrasion tests, compared to 70-75% for conventional systems, while also demonstrating superior resistance to household chemicals and cleaning agents.
Strengths: Exceptional abrasion and scratch resistance; excellent chemical resistance; good balance of hardness and impact resistance; suitable for both industrial and architectural applications. Weaknesses: Requires precise temperature control during curing; higher cost than standard systems; more complex formulation requiring technical expertise; potential for acid catalyst residues affecting long-term durability.
BASF Coatings GmbH
Technical Solution: BASF has developed advanced hybrid coating systems that combine acrylic and melamine chemistries for optimal surface durability. Their proprietary XSpark® technology incorporates modified acrylic resins with controlled molecular weight distribution and optimized functional groups that crosslink with specially formulated melamine resins. This creates a network structure with enhanced resistance to UV degradation, chemical attack, and mechanical abrasion. BASF's approach involves balancing the ratio of hydroxyl-functional acrylic components with methoxylated melamine crosslinkers to achieve optimal cure response at lower temperatures (130-150°C), reducing energy consumption while maintaining excellent hardness development. Their systems incorporate specialized UV stabilizers and hindered amine light stabilizers (HALS) that significantly extend coating lifetime in exterior applications, showing only 10-15% gloss reduction after 3000 hours of accelerated weathering tests.
Strengths: Superior weatherability and chemical resistance; optimized cure profiles for energy efficiency; excellent balance of hardness and flexibility. Weaknesses: Higher cost compared to standard systems; requires precise application parameters; more complex formulation requiring technical expertise for proper implementation.
Key Patents and Innovations in Crosslinking Chemistry
Coating Composition and Article Coated With Same
PatentInactiveUS20090018271A1
Innovation
- A coating composition comprising a (meth)acrylic resin with a hydroxyl group, obtained by copolymerizing polycaprolactone-modified hydroxyalkyl (meth)acrylate and a hydroxyl group-containing (meth)acrylate, combined with a polyisocyanate compound having multiple isocyanate groups, where the hydroxyl group is a primary hydroxyl group and the hydroxyl number is between 125 to 145, enhancing reactivity and improving scratch, chipping, and stain resistance.
Clear coat composition
PatentWO2022216029A1
Innovation
- A clear coat composition incorporating acrylic silane resin, acrylic resin, polyester resin, urethane oligomer, and melamine resin, which improves crosslinking density and provides flexibility and elasticity, enhancing scratch resistance and weather resistance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
The environmental impact of coating systems has become increasingly important in the selection of surface materials, with both acrylic resin and melamine crosslinked systems presenting distinct sustainability profiles. Acrylic resins generally offer advantages in terms of VOC (Volatile Organic Compound) emissions, with water-based acrylic formulations containing significantly lower levels of harmful compounds compared to traditional melamine systems. Recent industry data indicates that water-based acrylic coatings can reduce VOC emissions by up to 80% compared to conventional solvent-based melamine alternatives.
Manufacturing processes for acrylic resins typically require less energy input, with production temperatures averaging 20-30% lower than those needed for melamine crosslinked systems. This translates to a reduced carbon footprint across the production lifecycle. Additionally, acrylic systems often cure at lower temperatures, further decreasing energy consumption during application processes in industrial settings.
End-of-life considerations reveal that melamine crosslinked systems present greater challenges for recycling and disposal due to their highly crosslinked structure. These systems typically cannot be broken down and repurposed effectively, often resulting in landfill disposal. Acrylic resins, particularly thermoplastic varieties, offer better recyclability potential, though limitations still exist in current recycling infrastructure.
Raw material sourcing represents another critical environmental factor. Traditional melamine production relies heavily on urea and formaldehyde, with the latter raising significant health and environmental concerns. Modern bio-based acrylic alternatives are emerging, with several manufacturers developing resins containing 30-50% bio-sourced content derived from sustainable feedstocks.
Durability considerations create an interesting sustainability paradox. While melamine systems generally offer superior durability in harsh environments, potentially extending product lifecycles, this benefit must be weighed against their higher environmental impact during production and disposal. Acrylic systems, though potentially requiring more frequent replacement in demanding applications, may present a lower overall environmental burden when considering their full lifecycle impact.
Regulatory trends worldwide increasingly favor lower-impact coating systems, with stricter VOC limits and chemical restrictions being implemented across major markets. The EU's REACH regulations and similar frameworks in North America and Asia are progressively limiting the use of formaldehyde-containing systems, creating market pressure toward acrylic alternatives despite their potential durability limitations in certain applications.
Manufacturing processes for acrylic resins typically require less energy input, with production temperatures averaging 20-30% lower than those needed for melamine crosslinked systems. This translates to a reduced carbon footprint across the production lifecycle. Additionally, acrylic systems often cure at lower temperatures, further decreasing energy consumption during application processes in industrial settings.
End-of-life considerations reveal that melamine crosslinked systems present greater challenges for recycling and disposal due to their highly crosslinked structure. These systems typically cannot be broken down and repurposed effectively, often resulting in landfill disposal. Acrylic resins, particularly thermoplastic varieties, offer better recyclability potential, though limitations still exist in current recycling infrastructure.
Raw material sourcing represents another critical environmental factor. Traditional melamine production relies heavily on urea and formaldehyde, with the latter raising significant health and environmental concerns. Modern bio-based acrylic alternatives are emerging, with several manufacturers developing resins containing 30-50% bio-sourced content derived from sustainable feedstocks.
Durability considerations create an interesting sustainability paradox. While melamine systems generally offer superior durability in harsh environments, potentially extending product lifecycles, this benefit must be weighed against their higher environmental impact during production and disposal. Acrylic systems, though potentially requiring more frequent replacement in demanding applications, may present a lower overall environmental burden when considering their full lifecycle impact.
Regulatory trends worldwide increasingly favor lower-impact coating systems, with stricter VOC limits and chemical restrictions being implemented across major markets. The EU's REACH regulations and similar frameworks in North America and Asia are progressively limiting the use of formaldehyde-containing systems, creating market pressure toward acrylic alternatives despite their potential durability limitations in certain applications.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Competing Resin Technologies
When evaluating acrylic resin versus melamine crosslinked systems for surface durability applications, cost-benefit analysis reveals significant economic considerations that influence industrial adoption decisions. Initial investment costs for acrylic resin systems typically range 15-20% higher than melamine alternatives, primarily due to raw material expenses and specialized manufacturing requirements. However, this cost differential must be examined within a comprehensive lifecycle framework.
Operational expenditure analysis demonstrates that acrylic systems often yield 25-30% longer service lifespans in high-wear environments, effectively amortizing the higher initial investment over extended periods. This translates to reduced replacement frequency and associated labor costs, particularly valuable in commercial and industrial applications where downtime carries substantial financial implications.
Maintenance economics further favor acrylic systems in specific applications, with field data indicating approximately 18% reduction in routine maintenance requirements compared to melamine alternatives. The superior UV resistance of acrylic formulations results in less frequent refinishing needs for exterior applications, generating cumulative savings that compound over the installation lifetime.
Energy consumption metrics during manufacturing present a more complex picture. Melamine crosslinked systems typically require 10-15% higher curing temperatures, increasing production energy costs. However, this disadvantage is partially offset by faster processing times, allowing higher production throughput that improves manufacturing economics for large-scale operations.
Environmental compliance costs increasingly favor acrylic technologies as regulatory frameworks evolve. Recent industry analyses indicate that VOC mitigation expenses for melamine systems exceed those for modern acrylic alternatives by approximately 22%, a gap projected to widen as environmental regulations become more stringent globally.
Market segmentation analysis reveals application-specific economic considerations. In high-end architectural applications, the premium aesthetics and durability of acrylic systems command 15-25% price premiums that offset higher production costs. Conversely, in mass-market applications where initial price sensitivity dominates purchasing decisions, melamine systems maintain significant market share despite higher lifetime costs.
Return-on-investment calculations demonstrate that the crossover point where acrylic systems become more economical typically occurs between 3-5 years after installation, depending on application conditions and usage intensity. This timeframe aligns with capital planning cycles for many commercial and institutional clients, supporting the business case for premium acrylic solutions in these sectors.
Operational expenditure analysis demonstrates that acrylic systems often yield 25-30% longer service lifespans in high-wear environments, effectively amortizing the higher initial investment over extended periods. This translates to reduced replacement frequency and associated labor costs, particularly valuable in commercial and industrial applications where downtime carries substantial financial implications.
Maintenance economics further favor acrylic systems in specific applications, with field data indicating approximately 18% reduction in routine maintenance requirements compared to melamine alternatives. The superior UV resistance of acrylic formulations results in less frequent refinishing needs for exterior applications, generating cumulative savings that compound over the installation lifetime.
Energy consumption metrics during manufacturing present a more complex picture. Melamine crosslinked systems typically require 10-15% higher curing temperatures, increasing production energy costs. However, this disadvantage is partially offset by faster processing times, allowing higher production throughput that improves manufacturing economics for large-scale operations.
Environmental compliance costs increasingly favor acrylic technologies as regulatory frameworks evolve. Recent industry analyses indicate that VOC mitigation expenses for melamine systems exceed those for modern acrylic alternatives by approximately 22%, a gap projected to widen as environmental regulations become more stringent globally.
Market segmentation analysis reveals application-specific economic considerations. In high-end architectural applications, the premium aesthetics and durability of acrylic systems command 15-25% price premiums that offset higher production costs. Conversely, in mass-market applications where initial price sensitivity dominates purchasing decisions, melamine systems maintain significant market share despite higher lifetime costs.
Return-on-investment calculations demonstrate that the crossover point where acrylic systems become more economical typically occurs between 3-5 years after installation, depending on application conditions and usage intensity. This timeframe aligns with capital planning cycles for many commercial and institutional clients, supporting the business case for premium acrylic solutions in these sectors.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!