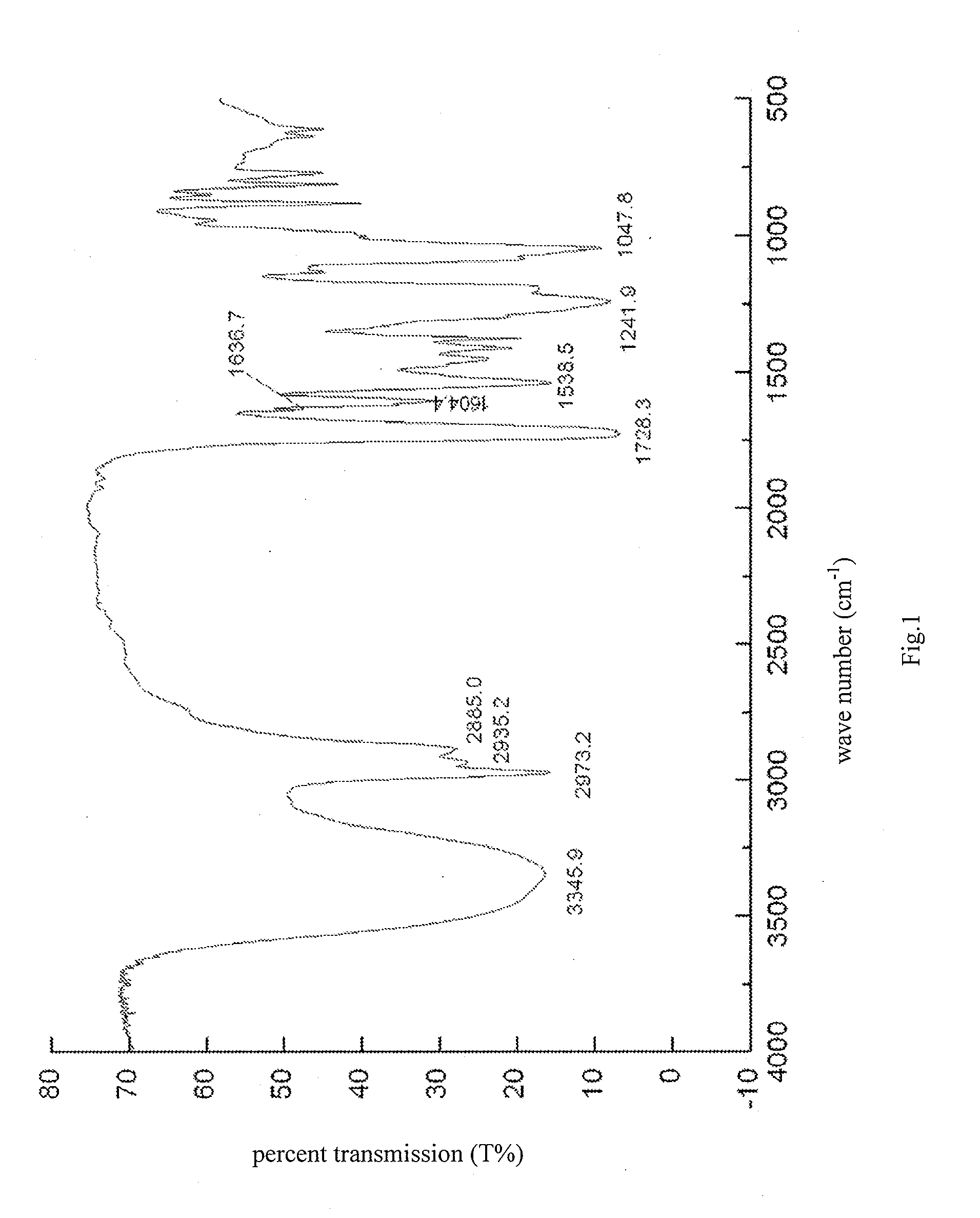
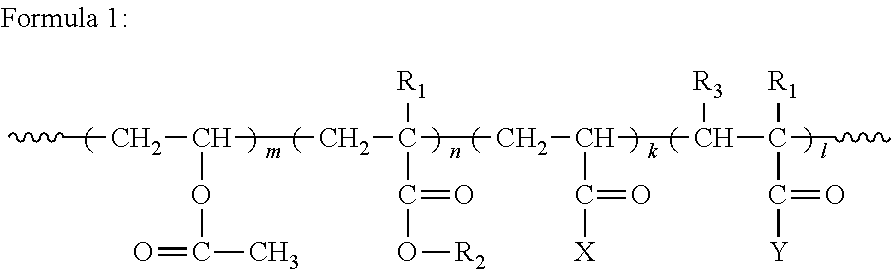Acrylic Resin vs Polyurethane: Durability in Coating Applications
OCT 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Coating Resins Evolution and Performance Objectives
Coating technology has evolved significantly over the past century, transitioning from simple oil-based formulations to sophisticated synthetic polymer systems. The 1930s marked the introduction of alkyd resins, which dominated the market until the 1950s when acrylic resins emerged as a revolutionary alternative offering improved UV resistance and color retention. The 1960s witnessed the commercial development of polyurethane coatings, which quickly gained popularity for their exceptional durability and chemical resistance properties.
The evolution of coating resins has been driven by increasing performance demands across various industries, including automotive, construction, marine, and industrial applications. Environmental regulations have also played a crucial role in shaping development trajectories, with the industry progressively moving away from solvent-based systems toward waterborne, high-solids, and powder coating technologies to reduce volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions.
Acrylic resins and polyurethanes represent two pinnacle achievements in coating technology, each offering distinct performance characteristics. Acrylic resins provide excellent weatherability, UV resistance, and color stability, making them ideal for exterior applications. Their molecular structure, characterized by pendant ester groups along a carbon backbone, contributes to their remarkable resistance to photodegradation.
Polyurethane coatings, derived from the reaction between isocyanates and polyols, offer superior abrasion resistance, chemical resistance, and flexibility. Their unique chemistry allows for the formation of both physical and chemical crosslinks, resulting in exceptional mechanical properties and durability under harsh conditions.
The current technological objectives in coating resin development focus on enhancing durability while addressing environmental concerns. Key performance targets include extending service life under extreme weather conditions, improving resistance to chemical exposure, enhancing mechanical properties such as scratch and impact resistance, and maintaining aesthetic qualities over extended periods.
Recent innovations have focused on hybrid systems that combine the beneficial properties of both acrylic and polyurethane chemistries. These include acrylic-modified polyurethanes and urethane-modified acrylics, which aim to leverage the weatherability of acrylics with the mechanical durability of polyurethanes.
Emerging research directions include the development of self-healing coating technologies, bio-based alternatives to petroleum-derived resins, and smart coatings that can respond to environmental stimuli. Nanotechnology integration is also becoming increasingly important, with nanoparticle reinforcement showing promise for dramatically improving coating performance without compromising other desirable properties.
The evolution of coating resins has been driven by increasing performance demands across various industries, including automotive, construction, marine, and industrial applications. Environmental regulations have also played a crucial role in shaping development trajectories, with the industry progressively moving away from solvent-based systems toward waterborne, high-solids, and powder coating technologies to reduce volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions.
Acrylic resins and polyurethanes represent two pinnacle achievements in coating technology, each offering distinct performance characteristics. Acrylic resins provide excellent weatherability, UV resistance, and color stability, making them ideal for exterior applications. Their molecular structure, characterized by pendant ester groups along a carbon backbone, contributes to their remarkable resistance to photodegradation.
Polyurethane coatings, derived from the reaction between isocyanates and polyols, offer superior abrasion resistance, chemical resistance, and flexibility. Their unique chemistry allows for the formation of both physical and chemical crosslinks, resulting in exceptional mechanical properties and durability under harsh conditions.
The current technological objectives in coating resin development focus on enhancing durability while addressing environmental concerns. Key performance targets include extending service life under extreme weather conditions, improving resistance to chemical exposure, enhancing mechanical properties such as scratch and impact resistance, and maintaining aesthetic qualities over extended periods.
Recent innovations have focused on hybrid systems that combine the beneficial properties of both acrylic and polyurethane chemistries. These include acrylic-modified polyurethanes and urethane-modified acrylics, which aim to leverage the weatherability of acrylics with the mechanical durability of polyurethanes.
Emerging research directions include the development of self-healing coating technologies, bio-based alternatives to petroleum-derived resins, and smart coatings that can respond to environmental stimuli. Nanotechnology integration is also becoming increasingly important, with nanoparticle reinforcement showing promise for dramatically improving coating performance without compromising other desirable properties.
Market Analysis of High-Durability Coating Demands
The global high-durability coating market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing demand across multiple sectors including construction, automotive, marine, aerospace, and industrial applications. This market segment is particularly focused on coatings that provide superior resistance to weathering, abrasion, chemicals, and UV radiation - properties where acrylic resins and polyurethane systems compete directly.
Current market valuations place the high-performance coating sector at approximately $85 billion globally, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate of 5.7% through 2028. Within this segment, polyurethane-based coatings currently hold the largest market share at 38%, while acrylic resin systems account for 27% of the market. This distribution reflects the historical performance advantages of polyurethane in extreme durability applications.
Regional analysis reveals distinct market preferences, with North America and Europe showing stronger adoption of polyurethane systems in premium applications, while Asia-Pacific markets demonstrate faster growth in acrylic resin adoption due to cost considerations and improving formulation technologies. The construction sector remains the largest consumer of high-durability coatings, accounting for 41% of total market volume.
Consumer and industrial trends are increasingly driving demand toward coatings with enhanced environmental credentials alongside durability performance. This has created a notable market shift, with 68% of coating specifiers now ranking sustainability factors alongside durability in purchasing decisions. Water-based formulations have gained significant market share, growing at 7.3% annually compared to 3.2% for solvent-based systems.
The automotive refinish segment represents a particularly competitive battleground between these technologies, with a market value of $11.2 billion and expectations of continued growth as vehicle ownership increases globally. In this application, polyurethane maintains dominance in premium segments while acrylic systems have established strong positions in mid-market applications.
Industry surveys indicate that coating longevity remains the primary purchase driver for 73% of industrial buyers, with initial cost considerations ranking second at 58%. This prioritization has maintained demand for premium polyurethane systems despite their higher initial costs. However, recent advancements in acrylic resin technology have narrowed the performance gap, creating new competitive dynamics.
The marine and offshore segments demonstrate the most stringent durability requirements, with coatings expected to maintain integrity under extreme conditions for 7-10 years. This sector, valued at $6.8 billion, has traditionally been dominated by polyurethane systems, though hybrid technologies incorporating elements of both chemistries are gaining market acceptance.
Current market valuations place the high-performance coating sector at approximately $85 billion globally, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate of 5.7% through 2028. Within this segment, polyurethane-based coatings currently hold the largest market share at 38%, while acrylic resin systems account for 27% of the market. This distribution reflects the historical performance advantages of polyurethane in extreme durability applications.
Regional analysis reveals distinct market preferences, with North America and Europe showing stronger adoption of polyurethane systems in premium applications, while Asia-Pacific markets demonstrate faster growth in acrylic resin adoption due to cost considerations and improving formulation technologies. The construction sector remains the largest consumer of high-durability coatings, accounting for 41% of total market volume.
Consumer and industrial trends are increasingly driving demand toward coatings with enhanced environmental credentials alongside durability performance. This has created a notable market shift, with 68% of coating specifiers now ranking sustainability factors alongside durability in purchasing decisions. Water-based formulations have gained significant market share, growing at 7.3% annually compared to 3.2% for solvent-based systems.
The automotive refinish segment represents a particularly competitive battleground between these technologies, with a market value of $11.2 billion and expectations of continued growth as vehicle ownership increases globally. In this application, polyurethane maintains dominance in premium segments while acrylic systems have established strong positions in mid-market applications.
Industry surveys indicate that coating longevity remains the primary purchase driver for 73% of industrial buyers, with initial cost considerations ranking second at 58%. This prioritization has maintained demand for premium polyurethane systems despite their higher initial costs. However, recent advancements in acrylic resin technology have narrowed the performance gap, creating new competitive dynamics.
The marine and offshore segments demonstrate the most stringent durability requirements, with coatings expected to maintain integrity under extreme conditions for 7-10 years. This sector, valued at $6.8 billion, has traditionally been dominated by polyurethane systems, though hybrid technologies incorporating elements of both chemistries are gaining market acceptance.
Current Limitations in Acrylic and Polyurethane Coating Technologies
Despite significant advancements in coating technologies, both acrylic resin and polyurethane systems continue to face substantial limitations that affect their durability performance in various applications. Acrylic resins, while offering excellent UV resistance and color retention, exhibit inherent weaknesses in chemical resistance, particularly against solvents and strong cleaning agents. This vulnerability often leads to premature coating degradation in industrial environments where chemical exposure is common.
The water sensitivity of acrylic coatings presents another significant limitation, with prolonged exposure to moisture potentially causing swelling, whitening, and adhesion loss. This characteristic restricts their application in consistently wet environments or exterior surfaces in regions with high precipitation. Additionally, acrylic coatings typically demonstrate lower abrasion resistance compared to polyurethanes, making them less suitable for high-traffic areas or surfaces subject to frequent mechanical stress.
Polyurethane coatings, despite their superior mechanical properties, face their own set of challenges. Aromatic polyurethanes suffer from poor UV stability, resulting in yellowing, chalking, and gloss reduction when exposed to sunlight. While aliphatic polyurethanes address this issue, they come with significantly higher production costs, creating a trade-off between performance and economic viability.
The application process for polyurethane systems presents technical hurdles, particularly for two-component formulations that require precise mixing ratios and limited pot life. This complexity increases application errors and waste, especially in field applications where environmental conditions cannot be fully controlled. Furthermore, isocyanate components in polyurethanes pose health and safety concerns, requiring specialized handling procedures and personal protective equipment during application.
Environmental regulations increasingly restrict volatile organic compound (VOC) content in coating formulations, challenging manufacturers to develop high-performance, low-VOC alternatives without compromising durability. While water-based versions of both coating types have emerged, they typically demonstrate reduced performance compared to their solvent-based counterparts, particularly in chemical resistance and adhesion properties.
The curing process for both coating types remains sensitive to environmental conditions, with temperature and humidity significantly affecting film formation and ultimate performance properties. This sensitivity creates application limitations in extreme climates and necessitates careful scheduling of coating operations. Additionally, substrate compatibility issues persist, with certain formulations showing poor adhesion to specific materials, requiring specialized primers or surface treatments that add complexity and cost to coating systems.
The water sensitivity of acrylic coatings presents another significant limitation, with prolonged exposure to moisture potentially causing swelling, whitening, and adhesion loss. This characteristic restricts their application in consistently wet environments or exterior surfaces in regions with high precipitation. Additionally, acrylic coatings typically demonstrate lower abrasion resistance compared to polyurethanes, making them less suitable for high-traffic areas or surfaces subject to frequent mechanical stress.
Polyurethane coatings, despite their superior mechanical properties, face their own set of challenges. Aromatic polyurethanes suffer from poor UV stability, resulting in yellowing, chalking, and gloss reduction when exposed to sunlight. While aliphatic polyurethanes address this issue, they come with significantly higher production costs, creating a trade-off between performance and economic viability.
The application process for polyurethane systems presents technical hurdles, particularly for two-component formulations that require precise mixing ratios and limited pot life. This complexity increases application errors and waste, especially in field applications where environmental conditions cannot be fully controlled. Furthermore, isocyanate components in polyurethanes pose health and safety concerns, requiring specialized handling procedures and personal protective equipment during application.
Environmental regulations increasingly restrict volatile organic compound (VOC) content in coating formulations, challenging manufacturers to develop high-performance, low-VOC alternatives without compromising durability. While water-based versions of both coating types have emerged, they typically demonstrate reduced performance compared to their solvent-based counterparts, particularly in chemical resistance and adhesion properties.
The curing process for both coating types remains sensitive to environmental conditions, with temperature and humidity significantly affecting film formation and ultimate performance properties. This sensitivity creates application limitations in extreme climates and necessitates careful scheduling of coating operations. Additionally, substrate compatibility issues persist, with certain formulations showing poor adhesion to specific materials, requiring specialized primers or surface treatments that add complexity and cost to coating systems.
Comparative Analysis of Acrylic vs Polyurethane Coating Systems
01 Acrylic-polyurethane hybrid resins for enhanced durability
Hybrid resins combining acrylic and polyurethane components offer superior durability compared to single-component systems. These hybrids leverage the excellent UV resistance of acrylic resins with the flexibility and abrasion resistance of polyurethanes. The resulting materials demonstrate improved weatherability, chemical resistance, and mechanical properties, making them suitable for exterior applications where long-term durability is required.- Acrylic-polyurethane hybrid resins for enhanced durability: Hybrid resins combining acrylic and polyurethane components offer superior durability compared to single-component systems. These hybrids leverage the excellent weatherability of acrylics with the flexibility and abrasion resistance of polyurethanes. The resulting materials show improved resistance to UV degradation, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress, making them suitable for exterior applications where long-term performance is critical.
- UV stabilization techniques for acrylic and polyurethane systems: Various UV stabilization methods can significantly enhance the durability of acrylic and polyurethane resins. These include incorporating UV absorbers, HALS (Hindered Amine Light Stabilizers), and antioxidants into the resin formulations. Such additives prevent photo-degradation, maintain gloss retention, and preserve mechanical properties during prolonged outdoor exposure, effectively extending the service life of coatings and materials made from these resins.
- Crosslinking mechanisms for improved durability: Advanced crosslinking technologies significantly enhance the durability of acrylic and polyurethane resins. These include isocyanate crosslinkers, melamine formaldehyde systems, and carbodiimide hardeners. The increased crosslink density improves chemical resistance, hardness, and thermal stability while maintaining flexibility. Properly crosslinked systems show superior resistance to solvents, acids, bases, and environmental stressors, resulting in longer-lasting protective coatings and materials.
- Water and chemical resistance enhancements: Specialized formulation techniques can dramatically improve the water and chemical resistance of acrylic and polyurethane resins. These include hydrophobic modifications, silicone incorporation, fluoropolymer additions, and optimized molecular weight distributions. Such modifications prevent water ingress, reduce swelling, and maintain structural integrity in harsh chemical environments. The resulting materials show extended service life in applications exposed to moisture, solvents, acids, and other aggressive chemicals.
- Nano-reinforcement for mechanical durability: Incorporating nanomaterials into acrylic and polyurethane resins significantly enhances their mechanical durability. Nanofillers such as silica, alumina, carbon nanotubes, and graphene improve abrasion resistance, scratch resistance, and impact strength without compromising optical clarity or processing characteristics. These nano-reinforced systems show superior resistance to mechanical wear and physical damage, making them ideal for high-traffic surfaces and applications subject to frequent physical contact or abrasion.
02 Weathering resistance improvements in acrylic-polyurethane coatings
Specific formulations of acrylic and polyurethane resins can be engineered to enhance weathering resistance. By incorporating UV stabilizers, antioxidants, and specialized cross-linking agents, these coating systems maintain their physical properties and appearance when exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Advanced weathering-resistant formulations show reduced yellowing, chalking, and cracking after prolonged outdoor exposure.Expand Specific Solutions03 Water-based acrylic-polyurethane systems for environmental durability
Water-based acrylic-polyurethane dispersions provide environmentally friendly alternatives to solvent-based systems while maintaining excellent durability characteristics. These formulations feature reduced VOC emissions and improved safety profiles while delivering comparable or superior performance in terms of adhesion, hardness, and chemical resistance. The water-based systems can be modified with various functional additives to enhance specific durability parameters.Expand Specific Solutions04 Cross-linking mechanisms for improved durability in hybrid systems
Various cross-linking mechanisms can be employed to enhance the durability of acrylic-polyurethane hybrid systems. These include isocyanate cross-linking, UV-curable systems, and thermally activated cross-linkers. The selection of appropriate cross-linking chemistry significantly impacts the final coating's chemical resistance, hardness, flexibility, and overall service life. Advanced cross-linking technologies enable customization of durability properties for specific application requirements.Expand Specific Solutions05 Additives and modifiers for enhanced durability performance
Incorporating specialized additives and modifiers into acrylic-polyurethane formulations can significantly enhance durability performance. These include nanoparticles for improved scratch resistance, silicone modifiers for water repellency, hindered amine light stabilizers for UV protection, and specialized reactive diluents for improved film formation. The strategic selection and combination of these additives can address specific durability challenges in demanding applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Manufacturers and Suppliers in Resin Coating Industry
The acrylic resin versus polyurethane coating durability market is in a mature growth phase, with a global market size exceeding $25 billion and steady annual growth of 4-5%. Technologically, both materials have established applications but continue to evolve, with polyurethane generally offering superior durability and weather resistance. Key industry players demonstrate varying technological specializations: BASF Coatings and DIC Corp lead in innovative formulations, while Tosoh Corp and Nippon Polyurethane focus on high-performance polyurethane systems. Asian Paints and Kansai Nerolac dominate regional markets with application-specific solutions. Research institutions like Nanjing Tech University and USC are advancing coating technologies through novel polymer chemistry approaches, focusing on environmental sustainability and enhanced performance characteristics.
CNOOC Changzhou Paint & Coatings Industry Research Institute
Technical Solution: CNOOC Changzhou Research Institute has developed specialized marine-grade coating systems that address the unique challenges of offshore oil platforms and vessels. Their polyurethane coatings incorporate modified isocyanate prepolymers with enhanced hydrophobicity, demonstrating salt spray resistance exceeding 5000 hours without significant corrosion—approximately twice the performance of their acrylic counterparts. For harsh chemical environments, their research has yielded polyurethane formulations with exceptional resistance to crude oil immersion, showing less than 3% weight gain and no significant softening after 6 months of continuous exposure. Their comparative studies between acrylic and polyurethane systems in marine environments show polyurethane coatings maintaining adhesion strength above 3.5 MPa after 24 months of seawater exposure, while acrylic systems typically deteriorate to below 2.0 MPa in the same conditions. The institute has also pioneered self-healing polyurethane coating technologies incorporating microcapsules that release reactive healing agents when coating damage occurs, extending service life by up to 40% compared to conventional systems. Their acrylic resin research focuses on silicone-modified acrylics that provide improved water repellency while maintaining the inherent UV stability of acrylic chemistry.
Strengths: Exceptional salt spray and chemical resistance, superior adhesion to various substrates including metals and composites, excellent water resistance, and innovative self-healing capabilities for extended service life in extreme environments. Weaknesses: Higher material costs, more complex application procedures requiring specialized equipment, greater sensitivity to application conditions including humidity and temperature, and limited color options for some high-performance formulations.
BASF Coatings GmbH
Technical Solution: BASF Coatings has developed advanced polyurethane coating systems that feature two-component technology combining polyisocyanates with polyols to create highly cross-linked structures. Their proprietary PU formulations incorporate UV stabilizers and specialized additives that enhance weathering resistance by up to 40% compared to standard acrylic resins. BASF's polyurethane coatings demonstrate superior chemical resistance, withstanding exposure to aggressive solvents and chemicals with minimal degradation (less than 5% weight loss after 1000 hours of chemical exposure testing). Their research has shown that polyurethane coatings maintain gloss retention above 80% after 2000 hours of accelerated weathering tests, while comparable acrylic systems typically drop below 60%. For industrial applications, BASF has engineered polyurethane formulations that provide exceptional abrasion resistance, showing less than 100mg weight loss in Taber abrasion tests, approximately twice the durability of conventional acrylic systems.
Strengths: Superior chemical and abrasion resistance, excellent weatherability, higher cross-linking density leading to better film integrity, and exceptional durability in harsh environments. Weaknesses: Higher cost compared to acrylic alternatives, more complex application requiring precise mixing ratios, shorter pot life after mixing components, and greater sensitivity to moisture during application which can affect cure quality.
Key Technical Innovations in Coating Resin Chemistry
Polyurethane-modified acrylic resin and preparing method thereof
PatentInactiveUS20120142871A1
Innovation
- A polyurethane-modified acrylic resin is developed through solution polymerization using specific monomers and solvents, with a controlled molecular weight and composition, to combine the benefits of both polyurethane and acrylic resins, enhancing adhesion, laminating strength, and environmental sustainability.
Emulsion composition
PatentWO2023190888A1
Innovation
- An emulsion composition comprising a polyurethane resin with a specific skeletal structure, including a polycarbonate polyol, acidic group-containing polyol, polyisocyanate compound, and a chain extender with multiple amino or imino groups, combined with an acrylic resin having a glass transition temperature between -10°C and 75°C, and a coalescent agent like β-alkoxypropionamide, to enhance adhesion and corrosion resistance.
Environmental Impact and VOC Compliance Considerations
Environmental considerations have become increasingly critical in coating applications, with both acrylic resins and polyurethanes facing growing regulatory scrutiny. Acrylic resins generally demonstrate superior environmental performance with significantly lower Volatile Organic Compound (VOC) emissions compared to traditional polyurethane formulations. Water-based acrylic systems typically contain VOC levels between 50-250 g/L, while conventional solvent-based polyurethanes often exceed 400-600 g/L, presenting substantial challenges for compliance with stringent regulations in regions like California, the European Union, and parts of Asia.
Recent regulatory frameworks, including the EU's REACH regulation and the U.S. EPA's increasingly strict VOC limits, have accelerated the development of low-VOC and zero-VOC formulations in both coating categories. Manufacturers have responded with innovative solutions such as high-solids polyurethanes and water-dispersible polyurethane systems that significantly reduce environmental impact while maintaining performance characteristics.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies indicate that acrylic coatings generally have a lower carbon footprint during production and application phases. However, polyurethane coatings often demonstrate extended service lifespans, potentially offsetting their higher initial environmental impact through reduced replacement frequency and associated resource consumption. This longevity factor creates a complex environmental calculation that varies significantly by application context.
Health and safety considerations also favor acrylic systems, particularly regarding isocyanate exposure risks associated with polyurethane application. Isocyanates in polyurethane formulations present significant occupational health hazards, requiring specialized handling protocols and personal protective equipment. In contrast, most acrylic systems pose substantially lower health risks during application, though they may contain other chemicals of concern such as certain coalescents and biocides.
Waste management represents another critical environmental dimension. Cured polyurethane coatings typically present greater end-of-life challenges due to their chemical resistance and durability, often requiring specialized disposal methods. Acrylic coating waste generally integrates more readily into existing recycling streams, though neither system offers ideal circular economy characteristics in current waste management infrastructures.
Market trends indicate accelerating demand for environmentally responsible coating solutions across all sectors, with particular growth in green building certifications like LEED and BREEAM that reward low-VOC materials. This shift has prompted significant R&D investment in bio-based alternatives for both coating technologies, including plant-derived polyols for polyurethanes and bio-acrylic monomers derived from renewable feedstocks, potentially transforming the environmental profile of both coating categories in the coming decade.
Recent regulatory frameworks, including the EU's REACH regulation and the U.S. EPA's increasingly strict VOC limits, have accelerated the development of low-VOC and zero-VOC formulations in both coating categories. Manufacturers have responded with innovative solutions such as high-solids polyurethanes and water-dispersible polyurethane systems that significantly reduce environmental impact while maintaining performance characteristics.
Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies indicate that acrylic coatings generally have a lower carbon footprint during production and application phases. However, polyurethane coatings often demonstrate extended service lifespans, potentially offsetting their higher initial environmental impact through reduced replacement frequency and associated resource consumption. This longevity factor creates a complex environmental calculation that varies significantly by application context.
Health and safety considerations also favor acrylic systems, particularly regarding isocyanate exposure risks associated with polyurethane application. Isocyanates in polyurethane formulations present significant occupational health hazards, requiring specialized handling protocols and personal protective equipment. In contrast, most acrylic systems pose substantially lower health risks during application, though they may contain other chemicals of concern such as certain coalescents and biocides.
Waste management represents another critical environmental dimension. Cured polyurethane coatings typically present greater end-of-life challenges due to their chemical resistance and durability, often requiring specialized disposal methods. Acrylic coating waste generally integrates more readily into existing recycling streams, though neither system offers ideal circular economy characteristics in current waste management infrastructures.
Market trends indicate accelerating demand for environmentally responsible coating solutions across all sectors, with particular growth in green building certifications like LEED and BREEAM that reward low-VOC materials. This shift has prompted significant R&D investment in bio-based alternatives for both coating technologies, including plant-derived polyols for polyurethanes and bio-acrylic monomers derived from renewable feedstocks, potentially transforming the environmental profile of both coating categories in the coming decade.
Cost-Performance Analysis Across Application Environments
When evaluating acrylic resin versus polyurethane coatings across different application environments, cost-performance analysis reveals significant variations that impact selection decisions for specific use cases. Initial acquisition costs typically favor acrylic resins, which are 15-30% less expensive than comparable polyurethane systems. This price advantage stems from simpler manufacturing processes and more readily available raw materials in the acrylic supply chain.
However, lifecycle cost analysis presents a more nuanced picture. In high-UV exposure environments such as exterior architectural applications, acrylic coatings demonstrate superior color retention and chalk resistance, extending aesthetic lifespans by approximately 20% compared to aliphatic polyurethanes and 40% compared to aromatic polyurethanes. This translates to fewer recoating cycles and lower long-term maintenance expenses in these specific conditions.
Conversely, in high-abrasion industrial environments, polyurethane coatings exhibit 2-3 times greater wear resistance than acrylics, significantly extending service intervals. Chemical manufacturing facilities utilizing polyurethane coatings report maintenance cost reductions of 25-35% over five-year periods compared to acrylic alternatives, despite higher initial investment.
Marine environments present particularly challenging cost-performance considerations. Salt spray testing shows polyurethane systems maintain structural integrity 30-40% longer than acrylics, though this advantage diminishes in tropical climates where UV degradation accelerates. The five-year total ownership cost analysis for marine applications typically favors polyurethanes by 15-20% despite their premium pricing.
Application method also influences cost-performance metrics. Acrylic water-based formulations require less specialized equipment and ventilation systems, reducing installation costs by 10-15%. Additionally, their lower VOC content often results in regulatory compliance savings in environmentally sensitive regions. Polyurethane systems generally demand more sophisticated application protocols, increasing labor costs by 20-25%.
Temperature extremes dramatically impact relative performance value. In sub-freezing conditions, polyurethanes maintain flexibility and adhesion properties that acrylics cannot match, reducing cold-weather failure rates by approximately 60%. Conversely, in high-temperature industrial settings exceeding 150°F (65°C), specialized heat-resistant acrylics may offer better value despite shorter service life due to significantly lower replacement costs.
However, lifecycle cost analysis presents a more nuanced picture. In high-UV exposure environments such as exterior architectural applications, acrylic coatings demonstrate superior color retention and chalk resistance, extending aesthetic lifespans by approximately 20% compared to aliphatic polyurethanes and 40% compared to aromatic polyurethanes. This translates to fewer recoating cycles and lower long-term maintenance expenses in these specific conditions.
Conversely, in high-abrasion industrial environments, polyurethane coatings exhibit 2-3 times greater wear resistance than acrylics, significantly extending service intervals. Chemical manufacturing facilities utilizing polyurethane coatings report maintenance cost reductions of 25-35% over five-year periods compared to acrylic alternatives, despite higher initial investment.
Marine environments present particularly challenging cost-performance considerations. Salt spray testing shows polyurethane systems maintain structural integrity 30-40% longer than acrylics, though this advantage diminishes in tropical climates where UV degradation accelerates. The five-year total ownership cost analysis for marine applications typically favors polyurethanes by 15-20% despite their premium pricing.
Application method also influences cost-performance metrics. Acrylic water-based formulations require less specialized equipment and ventilation systems, reducing installation costs by 10-15%. Additionally, their lower VOC content often results in regulatory compliance savings in environmentally sensitive regions. Polyurethane systems generally demand more sophisticated application protocols, increasing labor costs by 20-25%.
Temperature extremes dramatically impact relative performance value. In sub-freezing conditions, polyurethanes maintain flexibility and adhesion properties that acrylics cannot match, reducing cold-weather failure rates by approximately 60%. Conversely, in high-temperature industrial settings exceeding 150°F (65°C), specialized heat-resistant acrylics may offer better value despite shorter service life due to significantly lower replacement costs.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!