Adaptive Heat Control using Nitinol-Integrated Materials
AUG 6, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Nitinol-Based Adaptive Heat Control: Background and Objectives
Nitinol, an acronym for Nickel Titanium Naval Ordnance Laboratory, represents a groundbreaking class of shape memory alloys (SMAs) that have revolutionized various industries since their discovery in the 1960s. These unique materials possess the remarkable ability to "remember" and return to their original shape when subjected to specific temperature changes, a property known as the shape memory effect.
The development of adaptive heat control systems using Nitinol-integrated materials marks a significant advancement in thermal management technologies. This innovative approach leverages Nitinol's unique properties to create smart, responsive systems capable of autonomously regulating temperature in diverse applications, from aerospace to consumer electronics.
The evolution of Nitinol-based adaptive heat control systems can be traced through several key milestones. Initially, researchers focused on understanding and characterizing Nitinol's thermomechanical behavior. This foundational work paved the way for early applications in simple thermal actuators. As material science and manufacturing techniques progressed, more sophisticated Nitinol-based systems emerged, capable of precise and repeatable temperature-triggered responses.
Recent years have witnessed a surge in research aimed at integrating Nitinol into complex, multi-functional materials and structures. This has led to the development of advanced composite materials that combine Nitinol's adaptive properties with other desirable characteristics such as high strength, lightweight, or electrical conductivity.
The primary objective of Nitinol-based adaptive heat control research is to create intelligent thermal management solutions that can respond dynamically to changing environmental conditions or user requirements. This technology aims to enhance energy efficiency, improve thermal comfort, and enable new functionalities in various products and systems.
Key goals include developing Nitinol-integrated materials with faster response times, greater temperature control precision, and improved durability under repeated thermal cycling. Researchers are also exploring ways to optimize the integration of Nitinol elements into different host materials and structures, ensuring seamless operation and maximizing the overall system performance.
Another critical objective is to expand the temperature range over which Nitinol-based systems can effectively operate, broadening their potential applications. This involves not only material improvements but also innovative design strategies that leverage Nitinol's properties in novel ways.
As the field progresses, there is a growing focus on scalability and cost-effectiveness, aiming to transition Nitinol-based adaptive heat control from specialized, high-end applications to more mainstream use. This includes developing more efficient manufacturing processes and exploring new alloy compositions that could offer similar functionality at lower costs.
The development of adaptive heat control systems using Nitinol-integrated materials marks a significant advancement in thermal management technologies. This innovative approach leverages Nitinol's unique properties to create smart, responsive systems capable of autonomously regulating temperature in diverse applications, from aerospace to consumer electronics.
The evolution of Nitinol-based adaptive heat control systems can be traced through several key milestones. Initially, researchers focused on understanding and characterizing Nitinol's thermomechanical behavior. This foundational work paved the way for early applications in simple thermal actuators. As material science and manufacturing techniques progressed, more sophisticated Nitinol-based systems emerged, capable of precise and repeatable temperature-triggered responses.
Recent years have witnessed a surge in research aimed at integrating Nitinol into complex, multi-functional materials and structures. This has led to the development of advanced composite materials that combine Nitinol's adaptive properties with other desirable characteristics such as high strength, lightweight, or electrical conductivity.
The primary objective of Nitinol-based adaptive heat control research is to create intelligent thermal management solutions that can respond dynamically to changing environmental conditions or user requirements. This technology aims to enhance energy efficiency, improve thermal comfort, and enable new functionalities in various products and systems.
Key goals include developing Nitinol-integrated materials with faster response times, greater temperature control precision, and improved durability under repeated thermal cycling. Researchers are also exploring ways to optimize the integration of Nitinol elements into different host materials and structures, ensuring seamless operation and maximizing the overall system performance.
Another critical objective is to expand the temperature range over which Nitinol-based systems can effectively operate, broadening their potential applications. This involves not only material improvements but also innovative design strategies that leverage Nitinol's properties in novel ways.
As the field progresses, there is a growing focus on scalability and cost-effectiveness, aiming to transition Nitinol-based adaptive heat control from specialized, high-end applications to more mainstream use. This includes developing more efficient manufacturing processes and exploring new alloy compositions that could offer similar functionality at lower costs.
Market Analysis for Smart Thermal Management Systems
The smart thermal management systems market is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for energy-efficient solutions across various industries. This market segment encompasses a wide range of applications, including building automation, automotive climate control, industrial process optimization, and consumer electronics thermal regulation. The integration of adaptive heat control using Nitinol-integrated materials represents a cutting-edge development within this sector, offering unprecedented opportunities for precise and energy-efficient temperature management.
Market research indicates that the global smart thermal management systems market is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 8% from 2021 to 2026. This growth is primarily fueled by the rising adoption of Internet of Things (IoT) technologies, stringent energy efficiency regulations, and the increasing focus on sustainability across industries. The automotive sector, in particular, is expected to be a major contributor to this growth, as vehicle manufacturers seek innovative solutions to improve fuel efficiency and enhance passenger comfort.
The integration of Nitinol-based adaptive heat control systems presents a unique value proposition within this market. Nitinol, a shape memory alloy, offers exceptional thermal responsiveness and energy efficiency, making it an ideal material for smart thermal management applications. The ability of Nitinol-integrated materials to adapt to temperature changes without external power input addresses key market demands for passive, low-energy consumption solutions.
In the building automation segment, smart thermal management systems incorporating Nitinol technology are gaining traction due to their potential to significantly reduce energy consumption in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems. The market for these advanced systems in commercial and residential buildings is expected to grow substantially, driven by the increasing focus on green building initiatives and the need for cost-effective energy management solutions.
The industrial sector represents another significant market opportunity for Nitinol-based adaptive heat control systems. Process industries, such as chemical manufacturing and food processing, require precise temperature control to maintain product quality and operational efficiency. The self-regulating properties of Nitinol-integrated materials offer a compelling solution for these applications, potentially reducing energy costs and improving process stability.
Consumer electronics is emerging as a promising market segment for smart thermal management systems. As devices become more powerful and compact, effective heat dissipation becomes crucial for maintaining performance and longevity. Nitinol-based cooling solutions could provide an innovative approach to managing thermal issues in smartphones, laptops, and other portable devices, addressing a growing concern in the industry.
Despite the promising outlook, the market for smart thermal management systems faces challenges, including high initial implementation costs and the need for specialized expertise in system design and integration. However, as technology advances and economies of scale are achieved, these barriers are expected to diminish, further accelerating market growth.
Market research indicates that the global smart thermal management systems market is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 8% from 2021 to 2026. This growth is primarily fueled by the rising adoption of Internet of Things (IoT) technologies, stringent energy efficiency regulations, and the increasing focus on sustainability across industries. The automotive sector, in particular, is expected to be a major contributor to this growth, as vehicle manufacturers seek innovative solutions to improve fuel efficiency and enhance passenger comfort.
The integration of Nitinol-based adaptive heat control systems presents a unique value proposition within this market. Nitinol, a shape memory alloy, offers exceptional thermal responsiveness and energy efficiency, making it an ideal material for smart thermal management applications. The ability of Nitinol-integrated materials to adapt to temperature changes without external power input addresses key market demands for passive, low-energy consumption solutions.
In the building automation segment, smart thermal management systems incorporating Nitinol technology are gaining traction due to their potential to significantly reduce energy consumption in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems. The market for these advanced systems in commercial and residential buildings is expected to grow substantially, driven by the increasing focus on green building initiatives and the need for cost-effective energy management solutions.
The industrial sector represents another significant market opportunity for Nitinol-based adaptive heat control systems. Process industries, such as chemical manufacturing and food processing, require precise temperature control to maintain product quality and operational efficiency. The self-regulating properties of Nitinol-integrated materials offer a compelling solution for these applications, potentially reducing energy costs and improving process stability.
Consumer electronics is emerging as a promising market segment for smart thermal management systems. As devices become more powerful and compact, effective heat dissipation becomes crucial for maintaining performance and longevity. Nitinol-based cooling solutions could provide an innovative approach to managing thermal issues in smartphones, laptops, and other portable devices, addressing a growing concern in the industry.
Despite the promising outlook, the market for smart thermal management systems faces challenges, including high initial implementation costs and the need for specialized expertise in system design and integration. However, as technology advances and economies of scale are achieved, these barriers are expected to diminish, further accelerating market growth.
Current Challenges in Nitinol-Integrated Materials
Despite the promising potential of Nitinol-integrated materials for adaptive heat control, several significant challenges currently hinder their widespread adoption and optimal performance. These challenges span across material science, engineering, and practical implementation domains.
One of the primary obstacles is the complex manufacturing process of Nitinol-integrated materials. The precise control required during the production of Nitinol alloys, particularly in maintaining the correct ratio of nickel to titanium, poses significant difficulties. Any slight deviation in composition can dramatically alter the material's properties, affecting its shape memory and superelastic characteristics. Furthermore, integrating Nitinol into other materials while preserving its unique properties presents additional manufacturing hurdles.
The high cost associated with Nitinol production and integration is another major challenge. The raw materials, specialized equipment, and expertise required for manufacturing Nitinol-integrated materials contribute to their elevated price point. This cost factor often limits their application to high-value industries, hindering broader adoption in more cost-sensitive sectors.
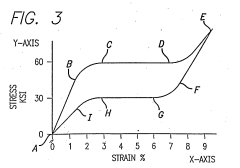
Durability and long-term reliability of Nitinol-integrated materials under repeated thermal cycling remain concerns. While Nitinol itself exhibits excellent fatigue resistance, the interface between Nitinol and the host material can be a weak point. Delamination, material degradation, and loss of shape memory properties over time are potential issues that need to be addressed to ensure the longevity of adaptive heat control systems.
Another significant challenge lies in the precise control of the shape memory effect in real-world applications. The transformation temperatures of Nitinol can be affected by factors such as stress, cycling frequency, and environmental conditions. Achieving consistent and predictable behavior across various operating conditions is crucial for reliable adaptive heat control but remains a complex task.
The limited range of transformation temperatures for commercially available Nitinol alloys also presents a challenge. While Nitinol can be engineered to have different transformation temperatures, the current range is not sufficient to cover all potential applications in adaptive heat control. Expanding this range without compromising other desirable properties of the material is an ongoing research challenge.
Lastly, the integration of Nitinol-based adaptive heat control systems with existing infrastructure and technologies poses significant engineering challenges. Developing seamless interfaces between Nitinol-integrated materials and conventional heating, cooling, and control systems requires innovative solutions in system design, sensor integration, and control algorithms.
One of the primary obstacles is the complex manufacturing process of Nitinol-integrated materials. The precise control required during the production of Nitinol alloys, particularly in maintaining the correct ratio of nickel to titanium, poses significant difficulties. Any slight deviation in composition can dramatically alter the material's properties, affecting its shape memory and superelastic characteristics. Furthermore, integrating Nitinol into other materials while preserving its unique properties presents additional manufacturing hurdles.
The high cost associated with Nitinol production and integration is another major challenge. The raw materials, specialized equipment, and expertise required for manufacturing Nitinol-integrated materials contribute to their elevated price point. This cost factor often limits their application to high-value industries, hindering broader adoption in more cost-sensitive sectors.
Durability and long-term reliability of Nitinol-integrated materials under repeated thermal cycling remain concerns. While Nitinol itself exhibits excellent fatigue resistance, the interface between Nitinol and the host material can be a weak point. Delamination, material degradation, and loss of shape memory properties over time are potential issues that need to be addressed to ensure the longevity of adaptive heat control systems.
Another significant challenge lies in the precise control of the shape memory effect in real-world applications. The transformation temperatures of Nitinol can be affected by factors such as stress, cycling frequency, and environmental conditions. Achieving consistent and predictable behavior across various operating conditions is crucial for reliable adaptive heat control but remains a complex task.
The limited range of transformation temperatures for commercially available Nitinol alloys also presents a challenge. While Nitinol can be engineered to have different transformation temperatures, the current range is not sufficient to cover all potential applications in adaptive heat control. Expanding this range without compromising other desirable properties of the material is an ongoing research challenge.
Lastly, the integration of Nitinol-based adaptive heat control systems with existing infrastructure and technologies poses significant engineering challenges. Developing seamless interfaces between Nitinol-integrated materials and conventional heating, cooling, and control systems requires innovative solutions in system design, sensor integration, and control algorithms.
Existing Nitinol-Based Heat Control Solutions
01 Shape memory alloy-based heat control systems
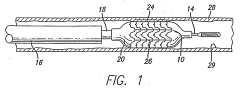
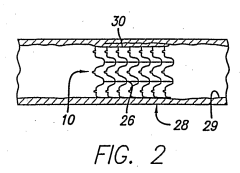
Nitinol, a shape memory alloy, is used in heat control systems due to its unique properties. These systems utilize Nitinol's ability to change shape at specific temperatures, allowing for efficient temperature regulation in various applications. The shape memory effect of Nitinol enables the creation of compact, responsive heat control mechanisms.- Shape memory alloy-based heat control systems: Nitinol, a shape memory alloy, is used in heat control systems due to its unique properties. These systems utilize Nitinol's ability to change shape in response to temperature variations, enabling efficient heat management and control in various applications. The shape memory effect allows for the design of compact and responsive thermal management solutions.
- Nitinol-integrated actuators for temperature regulation: Nitinol is incorporated into actuators for temperature regulation in different devices and systems. These actuators leverage Nitinol's shape memory properties to create motion or force in response to temperature changes, allowing for precise control of thermal conditions. Applications include HVAC systems, automotive components, and industrial equipment.
- Nitinol-based heat exchangers and thermal management: Heat exchangers and thermal management systems incorporating Nitinol take advantage of its high thermal conductivity and unique phase transformation properties. These systems offer improved efficiency in heat transfer and can be designed for specific temperature ranges, making them suitable for applications in electronics cooling, energy recovery, and industrial processes.
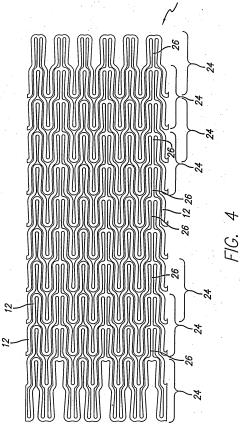
- Smart materials for adaptive thermal control: Nitinol is used in the development of smart materials that provide adaptive thermal control. These materials can respond to environmental changes autonomously, adjusting their properties to maintain desired thermal conditions. Applications include smart textiles, building materials, and aerospace components that can regulate temperature without external power sources.
- Nitinol-integrated microdevices for thermal management: Microdevices and MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems) incorporating Nitinol are developed for precise thermal management at small scales. These devices utilize the material's shape memory properties to create miniature heat switches, valves, and pumps that can control heat flow in microfluidic systems, electronic components, and medical devices.
02 Nitinol-integrated actuators for thermal management
Nitinol is incorporated into actuators for thermal management applications. These actuators can respond to temperature changes, providing controlled movement or force application. This technology is particularly useful in automotive, aerospace, and industrial settings where precise temperature-dependent actuation is required.Expand Specific Solutions03 Heat-activated Nitinol components in energy systems
Energy systems incorporate heat-activated Nitinol components to improve efficiency and control. These components can harvest thermal energy, convert it to mechanical work, or regulate energy flow based on temperature changes. This approach is applied in power generation, energy storage, and thermal management systems.Expand Specific Solutions04 Nitinol-based smart materials for thermal insulation
Smart materials incorporating Nitinol are developed for advanced thermal insulation applications. These materials can adapt their insulating properties based on temperature, providing dynamic thermal management. This technology is applicable in building materials, clothing, and protective equipment.Expand Specific Solutions05 Nitinol-integrated microfluidic devices for heat transfer
Microfluidic devices integrating Nitinol components are designed for enhanced heat transfer and control. These devices utilize Nitinol's shape-changing properties to manipulate fluid flow and heat distribution at the microscale. Applications include lab-on-a-chip systems, miniature heat exchangers, and thermal management in electronics.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Nitinol and Smart Materials Industry
The adaptive heat control using Nitinol-integrated materials market is in its early growth stage, characterized by ongoing research and development efforts. The market size is relatively small but expanding, driven by increasing applications in various industries. Technologically, it's still evolving, with companies like Smarter Alloys, Inc. and Abbott Laboratories leading innovation. Other players such as Canon, Inc. and TOTO Ltd. are exploring potential applications in their respective fields. The technology's maturity varies across sectors, with medical devices showing more advanced implementation compared to consumer products. As research progresses, particularly at institutions like Northwestern University and Huazhong University of Science & Technology, we can expect further advancements and broader market adoption in the coming years.
Smarter Alloys, Inc.
Technical Solution: Smarter Alloys has developed a proprietary Multiple Memory Material (MMM) technology that allows for precise control of shape memory alloys like Nitinol. Their adaptive heat control system integrates Nitinol-based actuators into materials, enabling dynamic thermal management. The MMM technology allows for programming multiple shape memory effects into a single piece of material, creating complex and precise movements in response to temperature changes[1]. This enables the creation of self-regulating thermal management systems that can adapt to varying heat loads and environmental conditions without the need for external power or control systems[2].
Strengths: Precise control of shape memory effects, self-regulating capabilities, energy-efficient. Weaknesses: Potentially higher initial cost, limited to specific temperature ranges.
Northwestern University
Technical Solution: Northwestern University has developed an innovative approach to adaptive heat control using Nitinol-integrated materials. Their research focuses on creating smart thermal management systems by embedding Nitinol wires or thin films into polymer matrices. The resulting composite materials exhibit temperature-dependent shape changes, allowing for passive heat regulation. The team has demonstrated the ability to create self-ventilating structures that open and close in response to temperature fluctuations, effectively managing heat flow[3]. Additionally, they have explored the use of Nitinol-based actuators in microfluidic devices for thermal regulation in miniaturized systems[4].
Strengths: Advanced research in smart composites, potential for passive thermal management systems. Weaknesses: May be in early stages of development, potential scalability challenges.
Core Innovations in Nitinol-Integrated Materials
Nitinol alloy for with good mechanical stability and a good superelastic operating window
PatentWO2006081011A2
Innovation
- A nickel-titanium alloy with a ternary element such as platinum or palladium is used to enhance radiopacity while maintaining superelastic properties, allowing for a thinner strut design that maintains flexibility and mechanical stability.
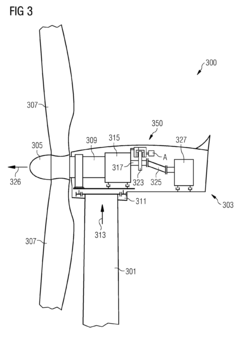
Braking system for a wind turbine
PatentInactiveEP2597329A1
Innovation
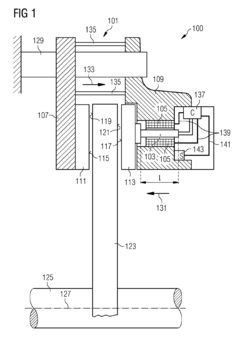
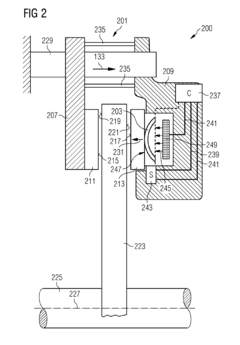
- A braking system utilizing shape memory material within a brake caliper, activated by heating, magnetic fields, or electromagnetic radiation, which changes shape to apply friction forces to a brake disk, eliminating the need for hydraulic or pneumatic fluids and associated components, thereby reducing weight, space, and energy consumption.
Energy Efficiency Impact of Nitinol-Based Systems
The integration of Nitinol-based systems in adaptive heat control mechanisms has the potential to significantly impact energy efficiency across various applications. These shape memory alloys, particularly Nitinol, exhibit unique properties that allow for precise temperature regulation and energy conservation.
In heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, Nitinol-integrated materials can lead to substantial energy savings. Traditional HVAC systems often operate on fixed schedules or rely on manual adjustments, resulting in energy waste during periods of low occupancy or changing environmental conditions. Nitinol-based systems, however, can automatically adjust to temperature fluctuations, optimizing energy consumption in real-time.
The adaptive nature of Nitinol allows for more efficient heat transfer in thermal management systems. By leveraging its shape memory properties, Nitinol-integrated materials can expand or contract in response to temperature changes, effectively regulating heat flow without the need for external power sources. This passive heat control mechanism reduces the overall energy demand of the system.
In industrial processes, Nitinol-based heat exchangers demonstrate improved efficiency compared to conventional designs. The material's ability to change shape with temperature variations enables more effective heat transfer between fluids, resulting in reduced energy requirements for heating or cooling operations. This enhanced performance can lead to significant energy savings in large-scale industrial applications.
Building envelopes incorporating Nitinol-integrated materials can dynamically respond to external temperature changes, reducing the load on heating and cooling systems. Smart windows utilizing Nitinol actuators can automatically adjust their opacity or position based on sunlight intensity, optimizing natural light and heat gain while minimizing energy consumption for artificial lighting and temperature control.
The energy efficiency impact of Nitinol-based systems extends to the transportation sector as well. In automotive applications, Nitinol-integrated components can improve engine thermal management, leading to better fuel efficiency and reduced emissions. Similarly, in aerospace, these materials can enhance the performance of thermal protection systems, potentially reducing the energy required for temperature regulation in aircraft and spacecraft.
While the initial implementation of Nitinol-based systems may require higher upfront costs, the long-term energy savings and reduced operational expenses often outweigh the initial investment. As the technology matures and production scales up, the cost-effectiveness of these systems is expected to improve further, making them increasingly attractive for widespread adoption across various industries.
In heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, Nitinol-integrated materials can lead to substantial energy savings. Traditional HVAC systems often operate on fixed schedules or rely on manual adjustments, resulting in energy waste during periods of low occupancy or changing environmental conditions. Nitinol-based systems, however, can automatically adjust to temperature fluctuations, optimizing energy consumption in real-time.
The adaptive nature of Nitinol allows for more efficient heat transfer in thermal management systems. By leveraging its shape memory properties, Nitinol-integrated materials can expand or contract in response to temperature changes, effectively regulating heat flow without the need for external power sources. This passive heat control mechanism reduces the overall energy demand of the system.
In industrial processes, Nitinol-based heat exchangers demonstrate improved efficiency compared to conventional designs. The material's ability to change shape with temperature variations enables more effective heat transfer between fluids, resulting in reduced energy requirements for heating or cooling operations. This enhanced performance can lead to significant energy savings in large-scale industrial applications.
Building envelopes incorporating Nitinol-integrated materials can dynamically respond to external temperature changes, reducing the load on heating and cooling systems. Smart windows utilizing Nitinol actuators can automatically adjust their opacity or position based on sunlight intensity, optimizing natural light and heat gain while minimizing energy consumption for artificial lighting and temperature control.
The energy efficiency impact of Nitinol-based systems extends to the transportation sector as well. In automotive applications, Nitinol-integrated components can improve engine thermal management, leading to better fuel efficiency and reduced emissions. Similarly, in aerospace, these materials can enhance the performance of thermal protection systems, potentially reducing the energy required for temperature regulation in aircraft and spacecraft.
While the initial implementation of Nitinol-based systems may require higher upfront costs, the long-term energy savings and reduced operational expenses often outweigh the initial investment. As the technology matures and production scales up, the cost-effectiveness of these systems is expected to improve further, making them increasingly attractive for widespread adoption across various industries.
Safety Considerations for Nitinol-Integrated Products
The integration of Nitinol into adaptive heat control materials presents unique safety considerations that must be thoroughly addressed to ensure product reliability and user safety. Nitinol's shape memory and superelastic properties, while advantageous for heat control applications, introduce potential risks that require careful management throughout the product lifecycle.
One primary safety concern is the potential for unexpected shape changes or mechanical failures. Nitinol's shape memory effect can lead to sudden deformations if the material is exposed to temperatures outside its designed operating range. This could result in product malfunction or, in extreme cases, injury to users. To mitigate this risk, manufacturers must implement robust temperature control mechanisms and clearly define operational limits for Nitinol-integrated products.
The biocompatibility of Nitinol is another critical safety aspect, particularly for applications involving direct contact with the human body. While Nitinol is generally considered biocompatible, the release of nickel ions from the alloy can cause allergic reactions in some individuals. Manufacturers must ensure proper surface treatments and coatings to minimize nickel leaching and conduct thorough biocompatibility testing in accordance with relevant standards such as ISO 10993.
Fatigue and wear resistance are essential considerations for long-term safety. Nitinol's unique properties can lead to complex fatigue behavior, potentially resulting in unexpected material failure over time. Comprehensive fatigue testing under various environmental conditions is necessary to establish reliable product lifespans and maintenance schedules.
Electrical safety is another crucial factor, especially in applications where Nitinol components may be in proximity to electrical systems. The alloy's electrical conductivity must be carefully managed to prevent short circuits or electrical hazards. Proper insulation and grounding techniques should be employed to ensure electrical safety compliance.
Thermal management is a key safety consideration, given Nitinol's heat-responsive nature. Designers must account for the material's thermal expansion and contraction, ensuring that surrounding components and structures can accommodate these changes without compromising overall product integrity. Additionally, fail-safe mechanisms should be incorporated to prevent overheating or uncontrolled thermal responses.
Quality control during manufacturing is paramount to safety. Consistency in Nitinol composition, heat treatment, and forming processes is critical to ensure uniform performance across all products. Stringent quality assurance protocols, including non-destructive testing methods, should be implemented to detect any defects or inconsistencies that could compromise safety.
Lastly, clear user guidelines and safety instructions are essential. End-users must be educated on the proper use, maintenance, and potential risks associated with Nitinol-integrated products. This includes information on temperature limitations, handling precautions, and signs of product wear or malfunction that require attention.
One primary safety concern is the potential for unexpected shape changes or mechanical failures. Nitinol's shape memory effect can lead to sudden deformations if the material is exposed to temperatures outside its designed operating range. This could result in product malfunction or, in extreme cases, injury to users. To mitigate this risk, manufacturers must implement robust temperature control mechanisms and clearly define operational limits for Nitinol-integrated products.
The biocompatibility of Nitinol is another critical safety aspect, particularly for applications involving direct contact with the human body. While Nitinol is generally considered biocompatible, the release of nickel ions from the alloy can cause allergic reactions in some individuals. Manufacturers must ensure proper surface treatments and coatings to minimize nickel leaching and conduct thorough biocompatibility testing in accordance with relevant standards such as ISO 10993.
Fatigue and wear resistance are essential considerations for long-term safety. Nitinol's unique properties can lead to complex fatigue behavior, potentially resulting in unexpected material failure over time. Comprehensive fatigue testing under various environmental conditions is necessary to establish reliable product lifespans and maintenance schedules.
Electrical safety is another crucial factor, especially in applications where Nitinol components may be in proximity to electrical systems. The alloy's electrical conductivity must be carefully managed to prevent short circuits or electrical hazards. Proper insulation and grounding techniques should be employed to ensure electrical safety compliance.
Thermal management is a key safety consideration, given Nitinol's heat-responsive nature. Designers must account for the material's thermal expansion and contraction, ensuring that surrounding components and structures can accommodate these changes without compromising overall product integrity. Additionally, fail-safe mechanisms should be incorporated to prevent overheating or uncontrolled thermal responses.
Quality control during manufacturing is paramount to safety. Consistency in Nitinol composition, heat treatment, and forming processes is critical to ensure uniform performance across all products. Stringent quality assurance protocols, including non-destructive testing methods, should be implemented to detect any defects or inconsistencies that could compromise safety.
Lastly, clear user guidelines and safety instructions are essential. End-users must be educated on the proper use, maintenance, and potential risks associated with Nitinol-integrated products. This includes information on temperature limitations, handling precautions, and signs of product wear or malfunction that require attention.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!