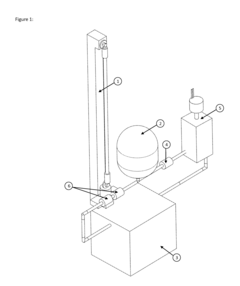
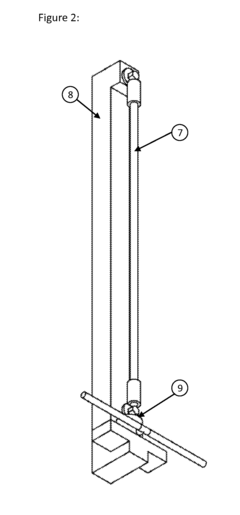
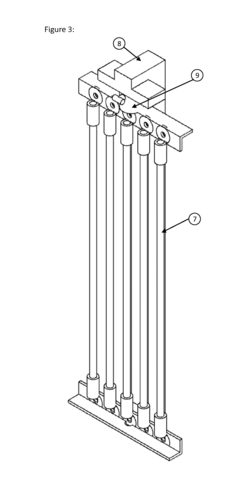
Applications of Nitinol in Spacecraft Thermal Management
AUG 6, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Nitinol in Spacecraft: Background and Objectives
Nitinol, an alloy of nickel and titanium, has emerged as a revolutionary material in spacecraft thermal management systems. This shape memory alloy (SMA) possesses unique properties that make it particularly suitable for space applications. The development of Nitinol can be traced back to the 1960s when it was discovered at the Naval Ordnance Laboratory. Since then, its potential in various industries, including aerospace, has been increasingly recognized.
The evolution of spacecraft thermal management systems has been driven by the need for more efficient, lightweight, and reliable solutions. Traditional thermal control methods often involve complex mechanical systems or fluid-based heat transfer mechanisms, which can be prone to failure in the harsh space environment. Nitinol's ability to change shape in response to temperature variations offers a promising alternative to these conventional approaches.
The primary objective of incorporating Nitinol in spacecraft thermal management is to leverage its shape memory and superelastic properties to create passive or semi-active thermal control systems. These systems aim to maintain optimal operating temperatures for spacecraft components without relying on power-intensive active cooling or heating mechanisms. By utilizing Nitinol's phase transformation characteristics, engineers seek to develop self-regulating thermal management solutions that can adapt to varying heat loads and environmental conditions.
Another key goal is to reduce the overall mass and complexity of thermal control systems in spacecraft. Nitinol-based solutions have the potential to replace multiple components with a single, multifunctional element, thereby streamlining the design and improving reliability. This aligns with the broader trend in spacecraft engineering towards miniaturization and increased efficiency.
The application of Nitinol in spacecraft thermal management also aims to address specific challenges posed by the space environment. These include rapid temperature fluctuations, vacuum conditions, and exposure to radiation. Researchers are exploring ways to enhance Nitinol's performance and durability under these extreme conditions, with the ultimate goal of developing long-lasting, maintenance-free thermal control systems.
As the space industry continues to evolve, with a growing emphasis on long-duration missions and small satellite constellations, the demand for advanced thermal management solutions is increasing. Nitinol's unique properties position it as a promising candidate to meet these emerging needs. The ongoing research and development in this field are focused on optimizing Nitinol's composition, manufacturing processes, and integration methods to fully exploit its potential in spacecraft thermal management applications.
The evolution of spacecraft thermal management systems has been driven by the need for more efficient, lightweight, and reliable solutions. Traditional thermal control methods often involve complex mechanical systems or fluid-based heat transfer mechanisms, which can be prone to failure in the harsh space environment. Nitinol's ability to change shape in response to temperature variations offers a promising alternative to these conventional approaches.
The primary objective of incorporating Nitinol in spacecraft thermal management is to leverage its shape memory and superelastic properties to create passive or semi-active thermal control systems. These systems aim to maintain optimal operating temperatures for spacecraft components without relying on power-intensive active cooling or heating mechanisms. By utilizing Nitinol's phase transformation characteristics, engineers seek to develop self-regulating thermal management solutions that can adapt to varying heat loads and environmental conditions.
Another key goal is to reduce the overall mass and complexity of thermal control systems in spacecraft. Nitinol-based solutions have the potential to replace multiple components with a single, multifunctional element, thereby streamlining the design and improving reliability. This aligns with the broader trend in spacecraft engineering towards miniaturization and increased efficiency.
The application of Nitinol in spacecraft thermal management also aims to address specific challenges posed by the space environment. These include rapid temperature fluctuations, vacuum conditions, and exposure to radiation. Researchers are exploring ways to enhance Nitinol's performance and durability under these extreme conditions, with the ultimate goal of developing long-lasting, maintenance-free thermal control systems.
As the space industry continues to evolve, with a growing emphasis on long-duration missions and small satellite constellations, the demand for advanced thermal management solutions is increasing. Nitinol's unique properties position it as a promising candidate to meet these emerging needs. The ongoing research and development in this field are focused on optimizing Nitinol's composition, manufacturing processes, and integration methods to fully exploit its potential in spacecraft thermal management applications.
Space Thermal Management Market Analysis
The space thermal management market is experiencing significant growth driven by the increasing demand for advanced spacecraft and satellites. As space missions become more complex and long-duration, effective thermal control systems are crucial for ensuring the reliability and longevity of space assets. The market for thermal management solutions in spacecraft is expected to expand substantially over the next decade, with a compound annual growth rate projected to be in the double digits.
Key factors contributing to this market growth include the rising number of satellite launches, the development of reusable launch vehicles, and the expansion of space exploration programs. Commercial space activities, such as satellite-based communications and Earth observation, are also fueling the demand for innovative thermal management technologies. Additionally, the increasing miniaturization of satellites and the trend towards large constellations are creating new challenges and opportunities in thermal control systems.
The market for spacecraft thermal management solutions can be segmented into various categories, including active and passive thermal control systems, thermal protection materials, and heat transfer devices. Among these, the use of shape memory alloys like Nitinol is gaining traction due to their unique properties and potential applications in space thermal management.
Geographically, North America currently dominates the space thermal management market, primarily due to the presence of major aerospace companies and substantial government investments in space programs. However, emerging space powers such as China and India are rapidly expanding their capabilities, leading to increased market opportunities in the Asia-Pacific region.
The competitive landscape of the space thermal management market is characterized by a mix of established aerospace companies and innovative startups. Major players are investing heavily in research and development to create more efficient and lightweight thermal management solutions. Collaborations between industry and academic institutions are also driving technological advancements in this field.
Market trends indicate a growing interest in smart thermal management systems that can adapt to changing environmental conditions in space. There is also an increasing focus on developing sustainable and environmentally friendly thermal management solutions, aligning with the broader push for green technologies in the space industry.
As the space industry continues to evolve, the thermal management market is expected to see the introduction of novel materials and technologies. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in thermal control systems is anticipated to be a significant trend, enabling more precise and efficient temperature regulation in spacecraft.
Key factors contributing to this market growth include the rising number of satellite launches, the development of reusable launch vehicles, and the expansion of space exploration programs. Commercial space activities, such as satellite-based communications and Earth observation, are also fueling the demand for innovative thermal management technologies. Additionally, the increasing miniaturization of satellites and the trend towards large constellations are creating new challenges and opportunities in thermal control systems.
The market for spacecraft thermal management solutions can be segmented into various categories, including active and passive thermal control systems, thermal protection materials, and heat transfer devices. Among these, the use of shape memory alloys like Nitinol is gaining traction due to their unique properties and potential applications in space thermal management.
Geographically, North America currently dominates the space thermal management market, primarily due to the presence of major aerospace companies and substantial government investments in space programs. However, emerging space powers such as China and India are rapidly expanding their capabilities, leading to increased market opportunities in the Asia-Pacific region.
The competitive landscape of the space thermal management market is characterized by a mix of established aerospace companies and innovative startups. Major players are investing heavily in research and development to create more efficient and lightweight thermal management solutions. Collaborations between industry and academic institutions are also driving technological advancements in this field.
Market trends indicate a growing interest in smart thermal management systems that can adapt to changing environmental conditions in space. There is also an increasing focus on developing sustainable and environmentally friendly thermal management solutions, aligning with the broader push for green technologies in the space industry.
As the space industry continues to evolve, the thermal management market is expected to see the introduction of novel materials and technologies. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in thermal control systems is anticipated to be a significant trend, enabling more precise and efficient temperature regulation in spacecraft.
Current Challenges in Spacecraft Thermal Control
Spacecraft thermal control systems face numerous challenges in maintaining optimal operating temperatures for onboard equipment and instruments. One of the primary issues is the extreme temperature fluctuations experienced in space, ranging from intense solar radiation to the frigid cold of deep space shadows. This dynamic thermal environment requires sophisticated and adaptive thermal management solutions.
The increasing complexity and miniaturization of spacecraft components have led to higher power densities and more concentrated heat generation. This trend poses significant challenges for traditional thermal control methods, necessitating innovative approaches to heat dissipation and distribution. Additionally, the limited power and mass budgets of spacecraft constrain the implementation of active thermal control systems, pushing engineers to develop more efficient passive solutions.
Reliability and longevity are critical concerns in spacecraft thermal control. The harsh space environment, including radiation exposure and micrometeoroid impacts, can degrade thermal control surfaces and materials over time. Ensuring the long-term performance of thermal management systems throughout extended missions is a persistent challenge.
The need for precise temperature control of sensitive instruments and payloads adds another layer of complexity. Many scientific instruments require stable thermal conditions to maintain calibration and accuracy, demanding highly responsive and accurate thermal control systems. This requirement often conflicts with the overall spacecraft thermal balance, necessitating careful thermal design and isolation strategies.
Launch and deployment phases present unique thermal challenges. Rapid temperature changes during ascent and initial orbit insertion can stress thermal control systems, requiring robust designs that can quickly adapt to changing conditions. Furthermore, deployable structures such as solar arrays and antennas introduce additional thermal management complexities, as their deployment alters the spacecraft's thermal profile.
Weight and volume constraints continue to be significant challenges in spacecraft thermal control. Every gram and cubic centimeter saved in thermal management systems can be allocated to payload or propulsion, driving the need for more compact and lightweight thermal solutions. This constraint often leads to trade-offs between thermal performance and system mass, requiring innovative material choices and design approaches.
The growing trend towards small satellites and CubeSats introduces new thermal control challenges. These compact platforms have limited surface area for radiators and minimal internal volume for thermal management hardware, necessitating novel approaches to maintain acceptable temperature ranges with minimal resources.
The increasing complexity and miniaturization of spacecraft components have led to higher power densities and more concentrated heat generation. This trend poses significant challenges for traditional thermal control methods, necessitating innovative approaches to heat dissipation and distribution. Additionally, the limited power and mass budgets of spacecraft constrain the implementation of active thermal control systems, pushing engineers to develop more efficient passive solutions.
Reliability and longevity are critical concerns in spacecraft thermal control. The harsh space environment, including radiation exposure and micrometeoroid impacts, can degrade thermal control surfaces and materials over time. Ensuring the long-term performance of thermal management systems throughout extended missions is a persistent challenge.
The need for precise temperature control of sensitive instruments and payloads adds another layer of complexity. Many scientific instruments require stable thermal conditions to maintain calibration and accuracy, demanding highly responsive and accurate thermal control systems. This requirement often conflicts with the overall spacecraft thermal balance, necessitating careful thermal design and isolation strategies.
Launch and deployment phases present unique thermal challenges. Rapid temperature changes during ascent and initial orbit insertion can stress thermal control systems, requiring robust designs that can quickly adapt to changing conditions. Furthermore, deployable structures such as solar arrays and antennas introduce additional thermal management complexities, as their deployment alters the spacecraft's thermal profile.
Weight and volume constraints continue to be significant challenges in spacecraft thermal control. Every gram and cubic centimeter saved in thermal management systems can be allocated to payload or propulsion, driving the need for more compact and lightweight thermal solutions. This constraint often leads to trade-offs between thermal performance and system mass, requiring innovative material choices and design approaches.
The growing trend towards small satellites and CubeSats introduces new thermal control challenges. These compact platforms have limited surface area for radiators and minimal internal volume for thermal management hardware, necessitating novel approaches to maintain acceptable temperature ranges with minimal resources.
Existing Nitinol-based Thermal Management Solutions
01 Shape memory alloy thermal management systems
Nitinol, a shape memory alloy, is used in thermal management systems for various applications. These systems utilize the unique properties of Nitinol to control temperature and heat flow in devices and structures. The shape memory effect and superelasticity of Nitinol allow for efficient heat transfer and temperature regulation in compact designs.- Shape memory alloy thermal management systems: Nitinol, a shape memory alloy, is used in thermal management systems for various applications. These systems utilize the unique properties of Nitinol to control temperature and heat flow in devices and structures. The shape memory effect and superelasticity of Nitinol allow for efficient heat transfer and temperature regulation in compact designs.
- Nitinol-based actuators for thermal control: Nitinol is employed in actuators for thermal control applications. These actuators can respond to temperature changes, enabling automatic adjustment of thermal management systems. The temperature-dependent phase transformation of Nitinol allows for precise control of heat dissipation and thermal regulation in various devices and environments.
- Heat exchange systems incorporating Nitinol: Heat exchange systems utilize Nitinol components to enhance thermal management efficiency. The material's high thermal conductivity and unique phase transformation properties enable improved heat transfer and temperature control. These systems can be applied in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and electronics.
- Nitinol-based cooling devices: Cooling devices incorporating Nitinol elements are developed for efficient thermal management. These devices leverage the material's thermoelastic properties to achieve rapid and controlled cooling in various applications. The unique characteristics of Nitinol allow for compact and energy-efficient cooling solutions in electronic devices and industrial equipment.
- Thermal energy harvesting using Nitinol: Nitinol is utilized in thermal energy harvesting systems to convert temperature differentials into usable energy. These systems exploit the shape memory effect of Nitinol to generate mechanical work from thermal gradients, which can be used for power generation or to drive thermal management processes. This approach offers potential for energy-efficient thermal management solutions.
02 Nitinol-based actuators for thermal control
Nitinol actuators are employed in thermal management applications to provide precise control over temperature-sensitive components. These actuators can respond to temperature changes, enabling automatic adjustment of thermal systems. The use of Nitinol in actuators allows for compact, energy-efficient designs in various thermal control mechanisms.Expand Specific Solutions03 Heat exchange systems incorporating Nitinol
Heat exchangers utilizing Nitinol components offer enhanced thermal management capabilities. The unique properties of Nitinol allow for the design of compact and efficient heat exchange systems. These systems can adapt to changing thermal conditions, improving overall heat transfer performance in various applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Nitinol-based thermal switches and valves
Thermal switches and valves incorporating Nitinol elements provide responsive and reliable temperature control in various systems. These components can automatically adjust to temperature changes, enabling efficient thermal management in complex environments. The use of Nitinol in switches and valves allows for compact designs with minimal power requirements.Expand Specific Solutions05 Nitinol applications in aerospace thermal management
Nitinol is utilized in aerospace thermal management systems to address the unique challenges of space environments. These applications include thermal control systems for satellites, spacecraft, and other aerospace components. The shape memory and superelastic properties of Nitinol enable the development of lightweight, compact, and reliable thermal management solutions for aerospace applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Nitinol and Space Thermal Technologies
The applications of Nitinol in spacecraft thermal management represent an emerging field with significant potential. The market is in its early growth stage, characterized by ongoing research and development efforts. While the exact market size is not readily available, the increasing focus on advanced materials in aerospace suggests a growing demand. Technologically, Nitinol's unique shape memory and superelastic properties make it promising for thermal control systems, but its application in spacecraft is still evolving. Key players like NASA, Boeing, Lockheed Martin, and China Academy of Space Technology are likely at the forefront of developing and integrating Nitinol-based solutions for spacecraft thermal management, leveraging their extensive aerospace expertise and resources.
The Boeing Co.
Technical Solution: Boeing has integrated Nitinol-based technologies into their spacecraft thermal management systems. They have developed Nitinol-actuated thermal switches that can rapidly change thermal conductivity paths within the spacecraft[5]. Boeing's approach also includes Nitinol-based variable emissivity coatings that can adjust the spacecraft's heat emission properties in response to temperature changes[6]. Furthermore, they have explored Nitinol-embedded multilayer insulation blankets that can dynamically alter their insulative properties to maintain optimal internal temperatures[7]. Boeing has also investigated Nitinol-based phase change material encapsulations for more efficient heat storage and release cycles in spacecraft thermal control systems[8].
Strengths: Highly responsive thermal control; integration with existing spacecraft systems; potential for significant mass savings. Weaknesses: Complexity in system integration; potential for increased initial costs.
Lockheed Martin Corp.
Technical Solution: Lockheed Martin has developed innovative applications of Nitinol in spacecraft thermal management. Their approach includes Nitinol-based thermal louvers with improved efficiency and reliability compared to traditional mechanical systems[9]. They have also created Nitinol-actuated radiator panels that can adjust their orientation to optimize heat rejection or retention based on the spacecraft's thermal needs[10]. Lockheed Martin has further explored Nitinol-based thermal switches for precise temperature control in sensitive instrument packages[11]. Additionally, they have investigated Nitinol-embedded structural components that can passively manage heat distribution throughout the spacecraft, reducing the need for active cooling systems[12].
Strengths: Reduced system complexity; improved reliability over mechanical systems; potential for significant weight reduction. Weaknesses: Higher upfront development costs; limited long-term performance data in space environments.
Innovative Nitinol Applications for Space Thermal Control
Tunable variable emissivity materials and methods for controlling the temperature of spacecraft using tunable variable emissivity materials
PatentActiveUS20080057204A1
Innovation
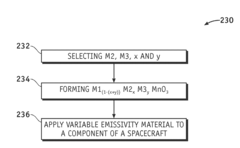
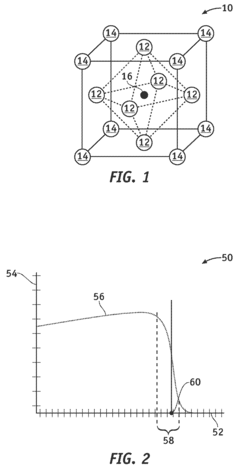
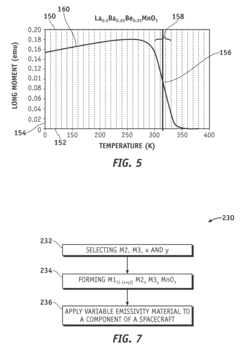
- A tunable variable emissivity material with a perovskite oxide structure, represented by M1(1−(x+y))M2xM3yMnO3, where M1 is lanthanum, scandium, yttrium, praseodymium, or samarium, and M2 and M3 are specific alkaline earth metals, which undergoes a phase change at a critical temperature (Tc) between 270 to 320 K, altering its emissivity and self-regulating temperature.
Nitinol Heat Engine with Mechanical Storage Mechanism
PatentInactiveUS20160069331A1
Innovation
- A modularized nitinol heat engine system with reduced moving parts, hydraulic or mechanical energy transfer mechanisms, and a control system to decouple energy harvesting from power generation, utilizing hydraulic cylinders, ratchets, or rack and pinion gears to store energy efficiently and provide continuous power output.
Space Qualification and Testing of Nitinol Components
Space qualification and testing of Nitinol components for spacecraft thermal management applications is a critical process to ensure the reliability and performance of these shape memory alloys in the harsh space environment. The testing procedures are designed to simulate the extreme conditions encountered during space missions, including vacuum, thermal cycling, radiation exposure, and mechanical stress.
One of the primary focuses of space qualification is thermal cycling tests. Nitinol components are subjected to repeated temperature changes that mimic the extreme temperature fluctuations experienced in space. These tests evaluate the material's ability to maintain its shape memory properties and structural integrity over numerous cycles. Typically, the components are cycled between temperature extremes ranging from -150°C to +150°C, with the exact range depending on the specific mission requirements.
Vacuum testing is another crucial aspect of the qualification process. Nitinol components are placed in vacuum chambers that simulate the near-zero pressure environment of space. This testing helps identify any potential outgassing issues, which could lead to contamination of sensitive spacecraft systems or degradation of the material itself.
Radiation resistance testing is essential to ensure that Nitinol components can withstand the high levels of cosmic radiation encountered in space. Samples are exposed to various types of radiation, including gamma rays, protons, and heavy ions, to assess any changes in mechanical properties or shape memory behavior.
Mechanical stress testing is conducted to evaluate the fatigue resistance and long-term durability of Nitinol components. This includes tensile, compression, and torsion tests under various loading conditions that simulate the stresses experienced during launch and in-orbit operations.
Corrosion resistance testing is also performed, particularly for components that may come into contact with propellants or other reactive substances. This ensures that the Nitinol alloy maintains its integrity and does not degrade over the mission lifetime.
Additionally, electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) testing is carried out to verify that Nitinol components do not interfere with or are not affected by the spacecraft's electronic systems. This is particularly important for components used in proximity to sensitive instruments or communication equipment.
The qualification process also includes accelerated life testing, where components are subjected to conditions more severe than those expected during the mission to compress years of service into a shorter timeframe. This helps predict long-term performance and identify potential failure modes.
Finally, all test results are meticulously documented and analyzed to create a comprehensive qualification report. This report serves as a critical reference for spacecraft designers and mission planners, providing confidence in the suitability of Nitinol components for specific space applications.
One of the primary focuses of space qualification is thermal cycling tests. Nitinol components are subjected to repeated temperature changes that mimic the extreme temperature fluctuations experienced in space. These tests evaluate the material's ability to maintain its shape memory properties and structural integrity over numerous cycles. Typically, the components are cycled between temperature extremes ranging from -150°C to +150°C, with the exact range depending on the specific mission requirements.
Vacuum testing is another crucial aspect of the qualification process. Nitinol components are placed in vacuum chambers that simulate the near-zero pressure environment of space. This testing helps identify any potential outgassing issues, which could lead to contamination of sensitive spacecraft systems or degradation of the material itself.
Radiation resistance testing is essential to ensure that Nitinol components can withstand the high levels of cosmic radiation encountered in space. Samples are exposed to various types of radiation, including gamma rays, protons, and heavy ions, to assess any changes in mechanical properties or shape memory behavior.
Mechanical stress testing is conducted to evaluate the fatigue resistance and long-term durability of Nitinol components. This includes tensile, compression, and torsion tests under various loading conditions that simulate the stresses experienced during launch and in-orbit operations.
Corrosion resistance testing is also performed, particularly for components that may come into contact with propellants or other reactive substances. This ensures that the Nitinol alloy maintains its integrity and does not degrade over the mission lifetime.
Additionally, electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) testing is carried out to verify that Nitinol components do not interfere with or are not affected by the spacecraft's electronic systems. This is particularly important for components used in proximity to sensitive instruments or communication equipment.
The qualification process also includes accelerated life testing, where components are subjected to conditions more severe than those expected during the mission to compress years of service into a shorter timeframe. This helps predict long-term performance and identify potential failure modes.
Finally, all test results are meticulously documented and analyzed to create a comprehensive qualification report. This report serves as a critical reference for spacecraft designers and mission planners, providing confidence in the suitability of Nitinol components for specific space applications.
Environmental Impact of Nitinol in Space Applications
The environmental impact of Nitinol in space applications is a crucial consideration as the use of this shape memory alloy becomes more prevalent in spacecraft thermal management systems. Nitinol's unique properties, such as its ability to change shape in response to temperature variations, make it an attractive material for space applications. However, its environmental implications must be carefully evaluated.
One of the primary environmental concerns related to Nitinol in space is the potential for space debris generation. As spacecraft components made from Nitinol age or become damaged, they may contribute to the growing problem of orbital debris. This issue is particularly significant given the increasing number of satellites and space missions utilizing Nitinol-based technologies.
The production of Nitinol also raises environmental considerations. The manufacturing process involves energy-intensive methods and the use of potentially hazardous materials. While these impacts are primarily terrestrial, they contribute to the overall environmental footprint of space missions utilizing Nitinol components.
In the space environment, Nitinol's interaction with cosmic radiation and extreme temperature fluctuations may lead to material degradation over time. This degradation could potentially release particles or alter the material's properties, although the extent of this impact in the vacuum of space requires further study.
On a positive note, Nitinol's efficiency in thermal management systems may contribute to reduced energy consumption in spacecraft operations. This increased efficiency could lead to smaller power systems and potentially reduce the overall mass of spacecraft, resulting in lower fuel requirements for launches and orbital maneuvers.
The recyclability and reusability of Nitinol components in space applications are areas of ongoing research. If effective recycling methods can be developed, it could significantly reduce the environmental impact associated with the production and disposal of these materials.
As space exploration and satellite deployment continue to expand, the cumulative environmental impact of Nitinol and other advanced materials in space applications will require ongoing assessment. Balancing the benefits of Nitinol's unique properties with its potential environmental consequences will be crucial for sustainable space exploration and utilization.
One of the primary environmental concerns related to Nitinol in space is the potential for space debris generation. As spacecraft components made from Nitinol age or become damaged, they may contribute to the growing problem of orbital debris. This issue is particularly significant given the increasing number of satellites and space missions utilizing Nitinol-based technologies.
The production of Nitinol also raises environmental considerations. The manufacturing process involves energy-intensive methods and the use of potentially hazardous materials. While these impacts are primarily terrestrial, they contribute to the overall environmental footprint of space missions utilizing Nitinol components.
In the space environment, Nitinol's interaction with cosmic radiation and extreme temperature fluctuations may lead to material degradation over time. This degradation could potentially release particles or alter the material's properties, although the extent of this impact in the vacuum of space requires further study.
On a positive note, Nitinol's efficiency in thermal management systems may contribute to reduced energy consumption in spacecraft operations. This increased efficiency could lead to smaller power systems and potentially reduce the overall mass of spacecraft, resulting in lower fuel requirements for launches and orbital maneuvers.
The recyclability and reusability of Nitinol components in space applications are areas of ongoing research. If effective recycling methods can be developed, it could significantly reduce the environmental impact associated with the production and disposal of these materials.
As space exploration and satellite deployment continue to expand, the cumulative environmental impact of Nitinol and other advanced materials in space applications will require ongoing assessment. Balancing the benefits of Nitinol's unique properties with its potential environmental consequences will be crucial for sustainable space exploration and utilization.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!