Nitinol-Based Innovations in Endoscopic Surgery
AUG 6, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Nitinol in Endoscopy: Evolution and Objectives
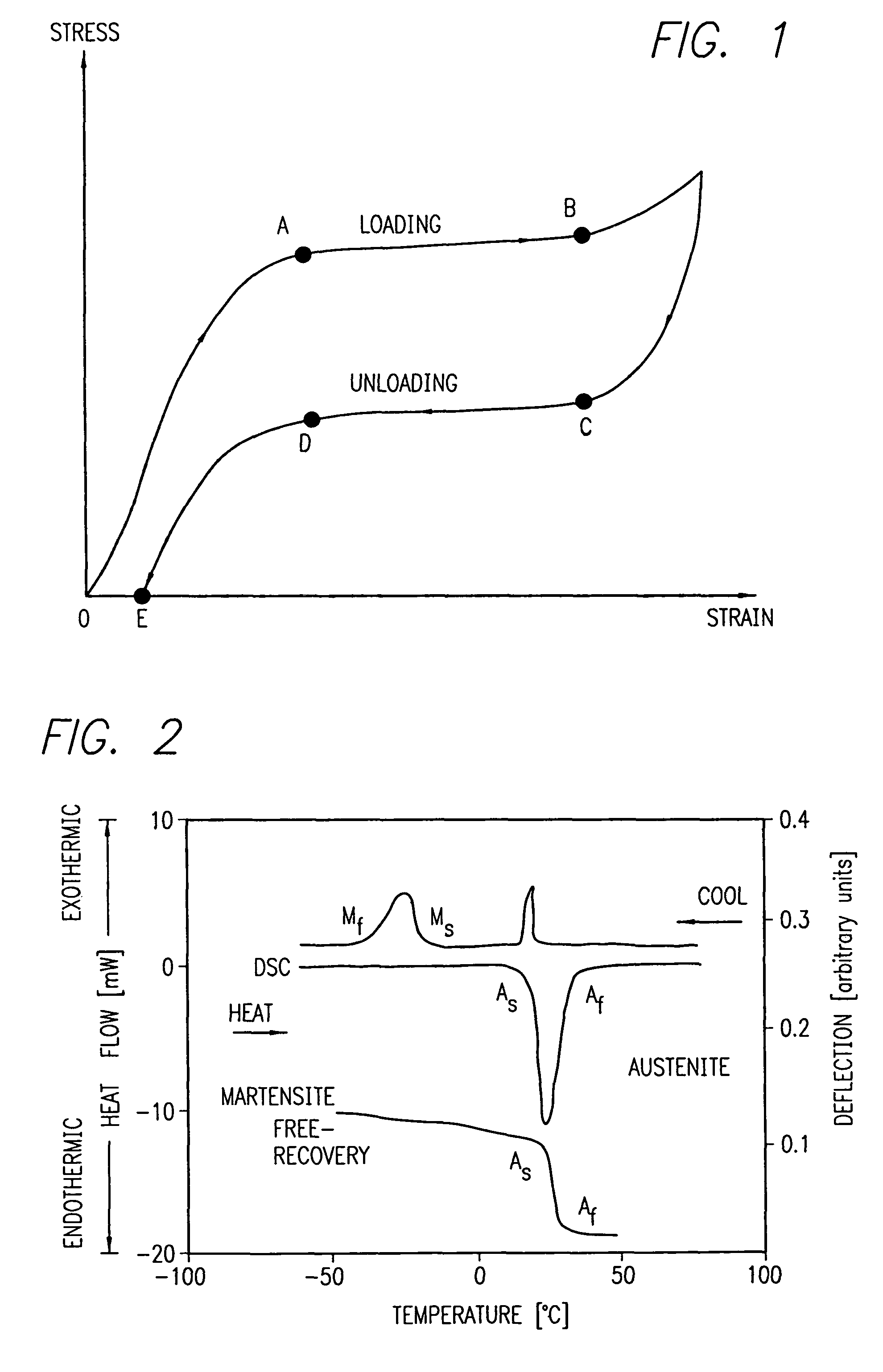
Nitinol, a remarkable shape memory alloy, has revolutionized the field of endoscopic surgery since its discovery in the 1960s. This unique material, composed of nickel and titanium, possesses the extraordinary ability to return to a predetermined shape when heated, making it an ideal candidate for minimally invasive surgical procedures.
The evolution of Nitinol in endoscopy can be traced back to the late 1980s when researchers began exploring its potential in medical applications. Initially, Nitinol was primarily used in orthodontics and orthopedics. However, its unique properties soon caught the attention of endoscopic device manufacturers, leading to a surge in research and development efforts focused on integrating Nitinol into endoscopic instruments.
Throughout the 1990s and early 2000s, significant advancements were made in Nitinol-based endoscopic devices. The introduction of Nitinol stents, guidewires, and retrieval baskets marked a turning point in endoscopic surgery, offering improved flexibility, durability, and precision compared to traditional materials. These innovations paved the way for more complex and less invasive procedures, reducing patient recovery times and improving overall outcomes.
The objectives of Nitinol-based innovations in endoscopic surgery are multifaceted and continue to evolve. Primarily, researchers and manufacturers aim to enhance the functionality and efficacy of endoscopic instruments. This includes developing devices with improved shape memory and superelasticity, allowing for better navigation through complex anatomical structures and more precise manipulation of tissues.
Another key objective is to expand the range of applications for Nitinol in endoscopic procedures. Current research focuses on creating novel devices for emerging minimally invasive techniques, such as natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery (NOTES) and single-incision laparoscopic surgery (SILS). These advanced procedures require instruments with exceptional flexibility and control, making Nitinol an ideal material for innovation.
Furthermore, there is a growing emphasis on improving the biocompatibility and long-term performance of Nitinol-based devices. Researchers are exploring surface modification techniques and novel alloy compositions to enhance the material's resistance to corrosion and reduce the risk of adverse reactions in patients. This ongoing work aims to ensure the safety and efficacy of Nitinol devices over extended periods of use.
As we look to the future, the objectives for Nitinol in endoscopy include the development of smart, responsive instruments capable of adapting to patient-specific anatomies and providing real-time feedback to surgeons. The integration of Nitinol with other advanced technologies, such as robotics and artificial intelligence, holds promise for creating next-generation endoscopic systems that can revolutionize minimally invasive surgery.
The evolution of Nitinol in endoscopy can be traced back to the late 1980s when researchers began exploring its potential in medical applications. Initially, Nitinol was primarily used in orthodontics and orthopedics. However, its unique properties soon caught the attention of endoscopic device manufacturers, leading to a surge in research and development efforts focused on integrating Nitinol into endoscopic instruments.
Throughout the 1990s and early 2000s, significant advancements were made in Nitinol-based endoscopic devices. The introduction of Nitinol stents, guidewires, and retrieval baskets marked a turning point in endoscopic surgery, offering improved flexibility, durability, and precision compared to traditional materials. These innovations paved the way for more complex and less invasive procedures, reducing patient recovery times and improving overall outcomes.
The objectives of Nitinol-based innovations in endoscopic surgery are multifaceted and continue to evolve. Primarily, researchers and manufacturers aim to enhance the functionality and efficacy of endoscopic instruments. This includes developing devices with improved shape memory and superelasticity, allowing for better navigation through complex anatomical structures and more precise manipulation of tissues.
Another key objective is to expand the range of applications for Nitinol in endoscopic procedures. Current research focuses on creating novel devices for emerging minimally invasive techniques, such as natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery (NOTES) and single-incision laparoscopic surgery (SILS). These advanced procedures require instruments with exceptional flexibility and control, making Nitinol an ideal material for innovation.
Furthermore, there is a growing emphasis on improving the biocompatibility and long-term performance of Nitinol-based devices. Researchers are exploring surface modification techniques and novel alloy compositions to enhance the material's resistance to corrosion and reduce the risk of adverse reactions in patients. This ongoing work aims to ensure the safety and efficacy of Nitinol devices over extended periods of use.
As we look to the future, the objectives for Nitinol in endoscopy include the development of smart, responsive instruments capable of adapting to patient-specific anatomies and providing real-time feedback to surgeons. The integration of Nitinol with other advanced technologies, such as robotics and artificial intelligence, holds promise for creating next-generation endoscopic systems that can revolutionize minimally invasive surgery.
Market Demand Analysis for Nitinol-Based Endoscopic Tools
The market demand for Nitinol-based endoscopic tools has been steadily increasing due to the unique properties of Nitinol and the growing prevalence of minimally invasive surgical procedures. Nitinol, a nickel-titanium alloy, offers exceptional shape memory and superelasticity, making it ideal for endoscopic applications.
The global endoscopy devices market, which includes Nitinol-based tools, is experiencing significant growth. This expansion is driven by factors such as the rising geriatric population, increasing incidence of gastrointestinal diseases, and technological advancements in endoscopic procedures. Nitinol-based instruments are particularly sought after for their ability to navigate complex anatomical structures with minimal trauma to surrounding tissues.
In the field of gastrointestinal endoscopy, there is a strong demand for Nitinol stents, guidewires, and biopsy forceps. These tools offer improved flexibility and durability compared to traditional materials, enabling more precise and less invasive procedures. The urology sector also shows a growing interest in Nitinol-based devices for procedures such as stone retrieval and ureteral stenting.
The cardiovascular market presents another significant opportunity for Nitinol-based endoscopic tools. With the increasing prevalence of cardiovascular diseases, there is a rising demand for minimally invasive cardiac procedures. Nitinol's properties make it an excellent choice for devices such as vena cava filters and cardiac occluders.
Emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to offer substantial growth opportunities for Nitinol-based endoscopic tools. These regions are witnessing rapid improvements in healthcare infrastructure and increasing adoption of advanced medical technologies. Additionally, the growing medical tourism industry in these areas is likely to further boost the demand for cutting-edge endoscopic devices.
However, the market faces challenges such as the high cost of Nitinol-based devices and stringent regulatory requirements. Despite these obstacles, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on expanding the applications of Nitinol in endoscopic surgery, which is expected to drive further market growth.
In conclusion, the market demand for Nitinol-based endoscopic tools is robust and expected to continue its upward trajectory. The unique properties of Nitinol, combined with the trend towards minimally invasive procedures, position these tools as key components in the future of endoscopic surgery. As technology advances and new applications are discovered, the market for Nitinol-based endoscopic tools is likely to expand further, offering significant opportunities for innovation and growth in the medical device industry.
The global endoscopy devices market, which includes Nitinol-based tools, is experiencing significant growth. This expansion is driven by factors such as the rising geriatric population, increasing incidence of gastrointestinal diseases, and technological advancements in endoscopic procedures. Nitinol-based instruments are particularly sought after for their ability to navigate complex anatomical structures with minimal trauma to surrounding tissues.
In the field of gastrointestinal endoscopy, there is a strong demand for Nitinol stents, guidewires, and biopsy forceps. These tools offer improved flexibility and durability compared to traditional materials, enabling more precise and less invasive procedures. The urology sector also shows a growing interest in Nitinol-based devices for procedures such as stone retrieval and ureteral stenting.
The cardiovascular market presents another significant opportunity for Nitinol-based endoscopic tools. With the increasing prevalence of cardiovascular diseases, there is a rising demand for minimally invasive cardiac procedures. Nitinol's properties make it an excellent choice for devices such as vena cava filters and cardiac occluders.
Emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and Latin America are expected to offer substantial growth opportunities for Nitinol-based endoscopic tools. These regions are witnessing rapid improvements in healthcare infrastructure and increasing adoption of advanced medical technologies. Additionally, the growing medical tourism industry in these areas is likely to further boost the demand for cutting-edge endoscopic devices.
However, the market faces challenges such as the high cost of Nitinol-based devices and stringent regulatory requirements. Despite these obstacles, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on expanding the applications of Nitinol in endoscopic surgery, which is expected to drive further market growth.
In conclusion, the market demand for Nitinol-based endoscopic tools is robust and expected to continue its upward trajectory. The unique properties of Nitinol, combined with the trend towards minimally invasive procedures, position these tools as key components in the future of endoscopic surgery. As technology advances and new applications are discovered, the market for Nitinol-based endoscopic tools is likely to expand further, offering significant opportunities for innovation and growth in the medical device industry.
Current Challenges in Nitinol Endoscopic Applications
Despite the remarkable properties of Nitinol in endoscopic surgery, several challenges persist in its application. One of the primary issues is the complex manufacturing process of Nitinol devices. The material's unique shape memory and superelastic properties require precise control over heat treatment and shaping processes, which can lead to inconsistencies in product quality and performance.
Another significant challenge lies in the biocompatibility of Nitinol. While generally considered safe for medical use, concerns remain about the potential release of nickel ions in the body, which could trigger allergic reactions or other adverse effects in some patients. This necessitates ongoing research into surface treatments and coatings to enhance the material's long-term biocompatibility.
The durability of Nitinol devices in the harsh environment of the human body presents another hurdle. Repeated stress cycles and exposure to bodily fluids can lead to fatigue and corrosion, potentially compromising the device's integrity and functionality over time. Developing more robust Nitinol alloys and protective coatings remains an active area of research.
Furthermore, the high cost of Nitinol production and device manufacturing poses a significant barrier to widespread adoption in endoscopic applications. The specialized equipment and expertise required for working with this material contribute to elevated production costs, which can limit its use in certain medical settings or regions with budget constraints.
Control and precision in the deployment of Nitinol devices during endoscopic procedures also present challenges. The material's unique properties, while beneficial, can make it difficult to predict and control its behavior precisely in real-time surgical situations. This necessitates advanced training for surgeons and the development of more sophisticated deployment mechanisms.
Lastly, regulatory hurdles and the need for extensive clinical trials to validate new Nitinol-based devices can slow down innovation and market entry. The stringent requirements for medical device approval, particularly for implantable devices, create a lengthy and costly pathway from concept to clinical application.
Addressing these challenges requires a multidisciplinary approach, combining materials science, bioengineering, and clinical expertise to push the boundaries of Nitinol applications in endoscopic surgery.
Another significant challenge lies in the biocompatibility of Nitinol. While generally considered safe for medical use, concerns remain about the potential release of nickel ions in the body, which could trigger allergic reactions or other adverse effects in some patients. This necessitates ongoing research into surface treatments and coatings to enhance the material's long-term biocompatibility.
The durability of Nitinol devices in the harsh environment of the human body presents another hurdle. Repeated stress cycles and exposure to bodily fluids can lead to fatigue and corrosion, potentially compromising the device's integrity and functionality over time. Developing more robust Nitinol alloys and protective coatings remains an active area of research.
Furthermore, the high cost of Nitinol production and device manufacturing poses a significant barrier to widespread adoption in endoscopic applications. The specialized equipment and expertise required for working with this material contribute to elevated production costs, which can limit its use in certain medical settings or regions with budget constraints.
Control and precision in the deployment of Nitinol devices during endoscopic procedures also present challenges. The material's unique properties, while beneficial, can make it difficult to predict and control its behavior precisely in real-time surgical situations. This necessitates advanced training for surgeons and the development of more sophisticated deployment mechanisms.
Lastly, regulatory hurdles and the need for extensive clinical trials to validate new Nitinol-based devices can slow down innovation and market entry. The stringent requirements for medical device approval, particularly for implantable devices, create a lengthy and costly pathway from concept to clinical application.
Addressing these challenges requires a multidisciplinary approach, combining materials science, bioengineering, and clinical expertise to push the boundaries of Nitinol applications in endoscopic surgery.
Existing Nitinol Solutions for Endoscopic Procedures
01 Shape memory properties of Nitinol
Nitinol is a shape memory alloy that can return to its original shape when heated. This unique property makes it useful in various applications, including medical devices, aerospace, and automotive industries. The shape memory effect allows for the creation of compact, deployable structures and self-expanding devices.- Shape memory properties of Nitinol: Nitinol is a shape memory alloy that can return to its original shape when heated. This unique property makes it useful in various applications, including medical devices, aerospace, and automotive industries. The shape memory effect allows for the creation of compact, deployable structures and self-expanding devices.
- Superelasticity of Nitinol: Nitinol exhibits superelastic behavior, allowing it to undergo large deformations and return to its original shape without permanent damage. This property is particularly valuable in medical applications, such as stents and orthodontic wires, where flexibility and durability are crucial.
- Nitinol in medical devices: Nitinol is widely used in the medical field for various devices and implants. Its biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and unique mechanical properties make it suitable for applications such as cardiovascular stents, orthopedic implants, and surgical instruments. The material's ability to conform to body temperature and maintain its shape is particularly advantageous in these applications.
- Manufacturing and processing of Nitinol: The production and processing of Nitinol require specialized techniques due to its unique properties. This includes methods for shaping, heat treatment, and surface modification to optimize its performance for specific applications. Advanced manufacturing processes, such as laser cutting and additive manufacturing, are being explored to create complex Nitinol structures.
- Nitinol in actuators and sensors: Nitinol's shape memory and superelastic properties make it an excellent material for actuators and sensors. It can be used to create compact, efficient actuators that respond to temperature changes or electrical stimuli. In sensing applications, Nitinol can be used to detect and measure various physical parameters, such as strain, temperature, and pressure.
02 Superelasticity of Nitinol
Nitinol exhibits superelastic behavior, allowing it to undergo large deformations and return to its original shape upon unloading. This property is particularly valuable in applications requiring flexibility and durability, such as orthodontic wires, eyeglass frames, and medical stents.Expand Specific Solutions03 Nitinol in medical applications
Nitinol is widely used in medical devices due to its biocompatibility and unique properties. It is commonly used in stents, guidewires, orthodontic archwires, and surgical instruments. The material's ability to change shape at body temperature makes it ideal for minimally invasive procedures and implantable devices.Expand Specific Solutions04 Manufacturing and processing of Nitinol
The production and processing of Nitinol require specialized techniques due to its unique properties. This includes methods for melting, forming, heat treatment, and surface modification. Advanced manufacturing processes have been developed to create complex Nitinol structures and improve its performance in various applications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Nitinol in actuators and sensors
Nitinol's shape memory and superelastic properties make it suitable for use in actuators and sensors. These devices can respond to temperature changes or mechanical stress, enabling the development of smart systems in various fields, including robotics, automotive, and aerospace industries.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Nitinol-Enhanced Endoscopic Devices
The field of Nitinol-based innovations in endoscopic surgery is in a growth phase, with increasing market size and technological advancements. The global market for Nitinol medical devices is expected to expand significantly in the coming years, driven by the material's unique properties and its applications in minimally invasive procedures. Companies like Boston Scientific, Olympus Medical Systems, and Ethicon Endo-Surgery are at the forefront of developing Nitinol-based endoscopic devices, leveraging their expertise in medical technology. The technology's maturity is advancing rapidly, with ongoing research and development efforts by both established players and emerging companies like Neurvana Medical. Academic institutions such as Saint Louis University and the Institute of Metal Research Chinese Academy of Sciences are contributing to the field's progress through collaborative research, further accelerating innovation in Nitinol-based endoscopic surgery techniques and devices.
Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc.
Technical Solution: Ethicon Endo-Surgery has developed advanced Nitinol-based instruments for minimally invasive endoscopic procedures. Their innovative designs include shape memory Nitinol clips for tissue approximation and hemostasis[1]. These clips can be deployed through narrow endoscope channels and return to their pre-programmed shape upon release, providing secure closure of tissue defects or bleeding vessels. The company has also incorporated Nitinol into their endoscopic suturing devices, allowing for improved maneuverability and precision in confined spaces[3]. Additionally, Ethicon has pioneered the use of Nitinol-based stents for gastrointestinal applications, offering self-expanding properties that adapt to varying anatomical structures[5].
Strengths: Superior shape memory and superelasticity of Nitinol allows for complex instrument designs. Improved tissue manipulation and closure capabilities. Weaknesses: Higher cost compared to traditional materials. Potential for nickel sensitivity in some patients.
Covidien Pte Ltd.
Technical Solution: Covidien has leveraged Nitinol technology to create innovative endoscopic devices for various surgical applications. Their portfolio includes Nitinol-based stent systems for treating gastrointestinal strictures, featuring a unique braided design that provides flexibility and radial force for optimal lumen patency[2]. The company has also developed Nitinol-enhanced biopsy forceps with improved tissue acquisition capabilities due to the material's superelastic properties[4]. Covidien's endoscopic hemostasis devices incorporate Nitinol components, allowing for precise deployment and consistent performance in challenging anatomical locations[6]. Furthermore, they have introduced Nitinol-based retrieval devices that can navigate tortuous paths within the body while maintaining their shape and functionality.
Strengths: Wide range of Nitinol-based endoscopic solutions. Enhanced device performance and durability. Weaknesses: Complexity in manufacturing processes. Potential for thermal sensitivity during sterilization procedures.
Core Innovations in Nitinol-Based Surgical Tools
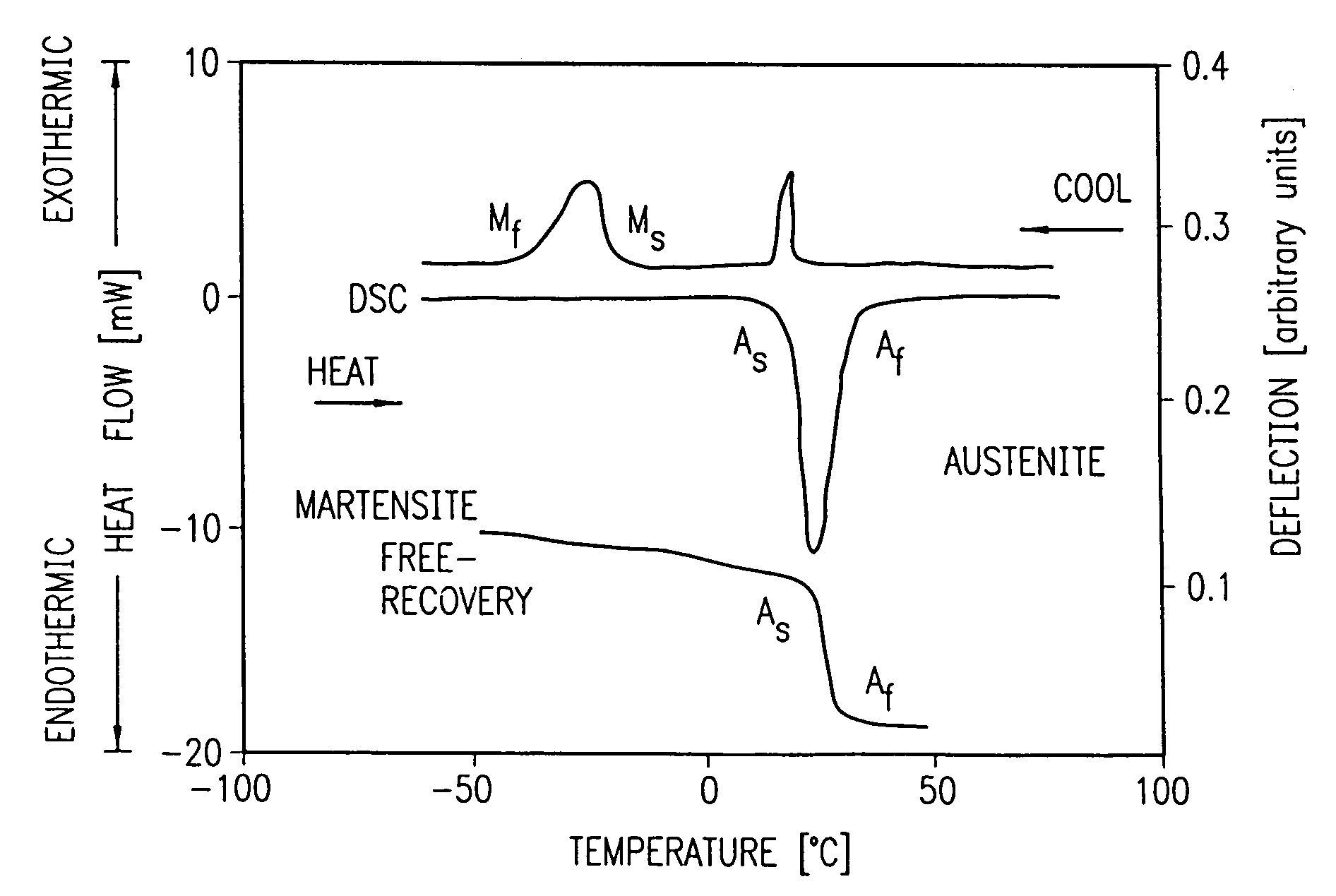
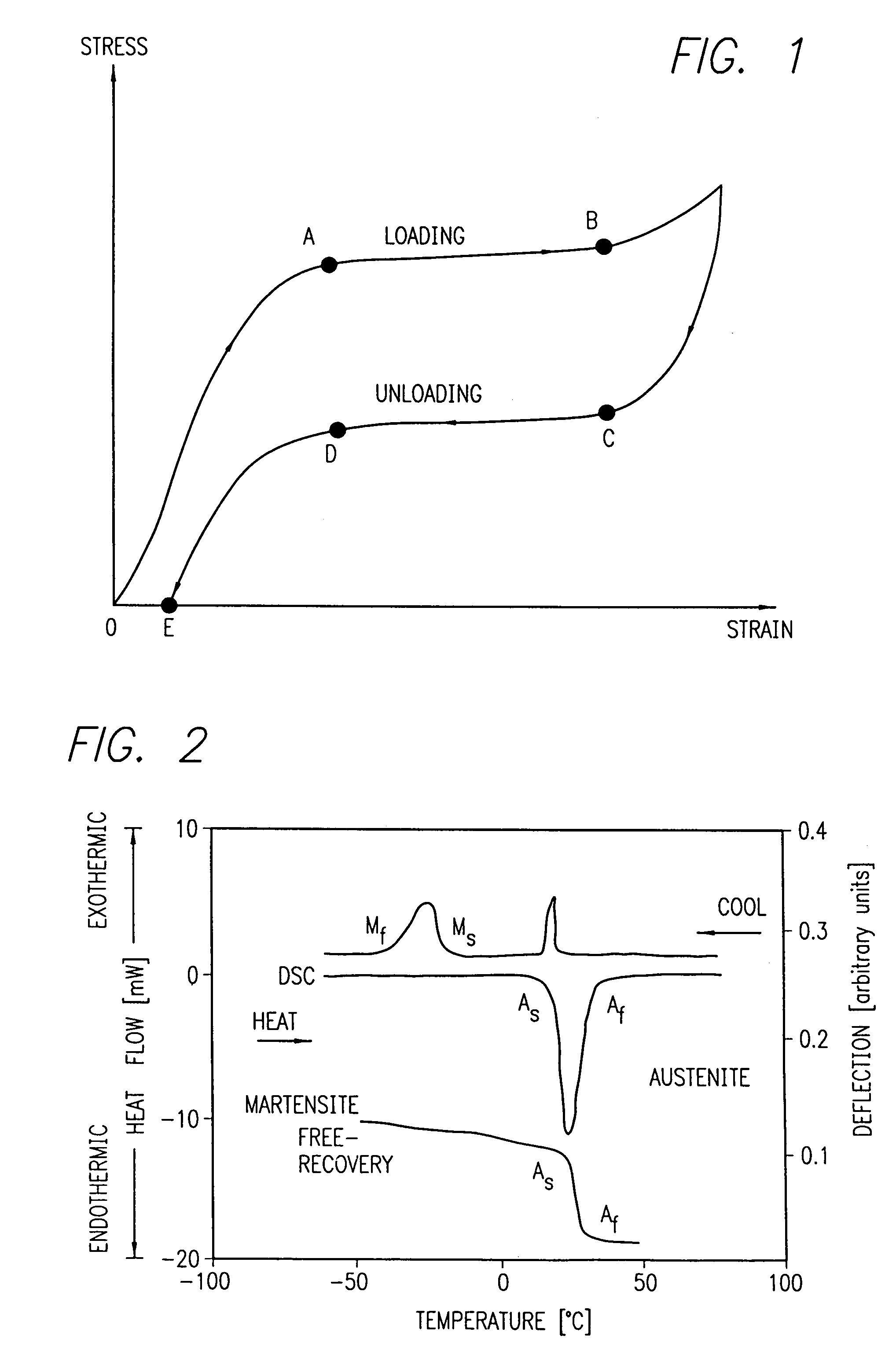
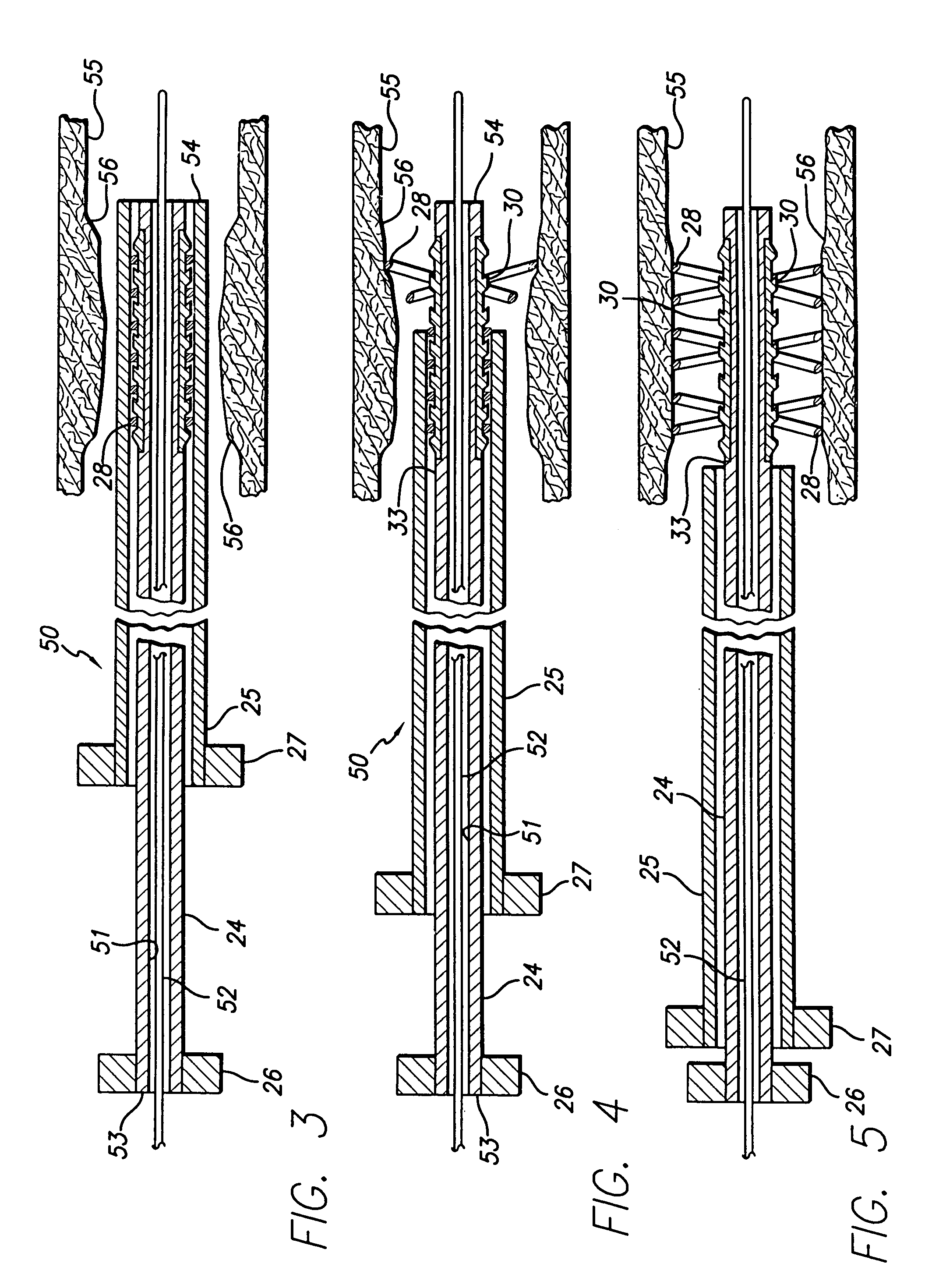
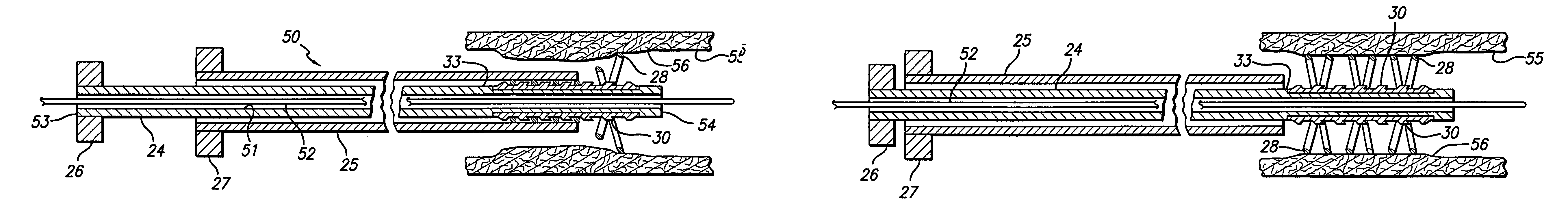
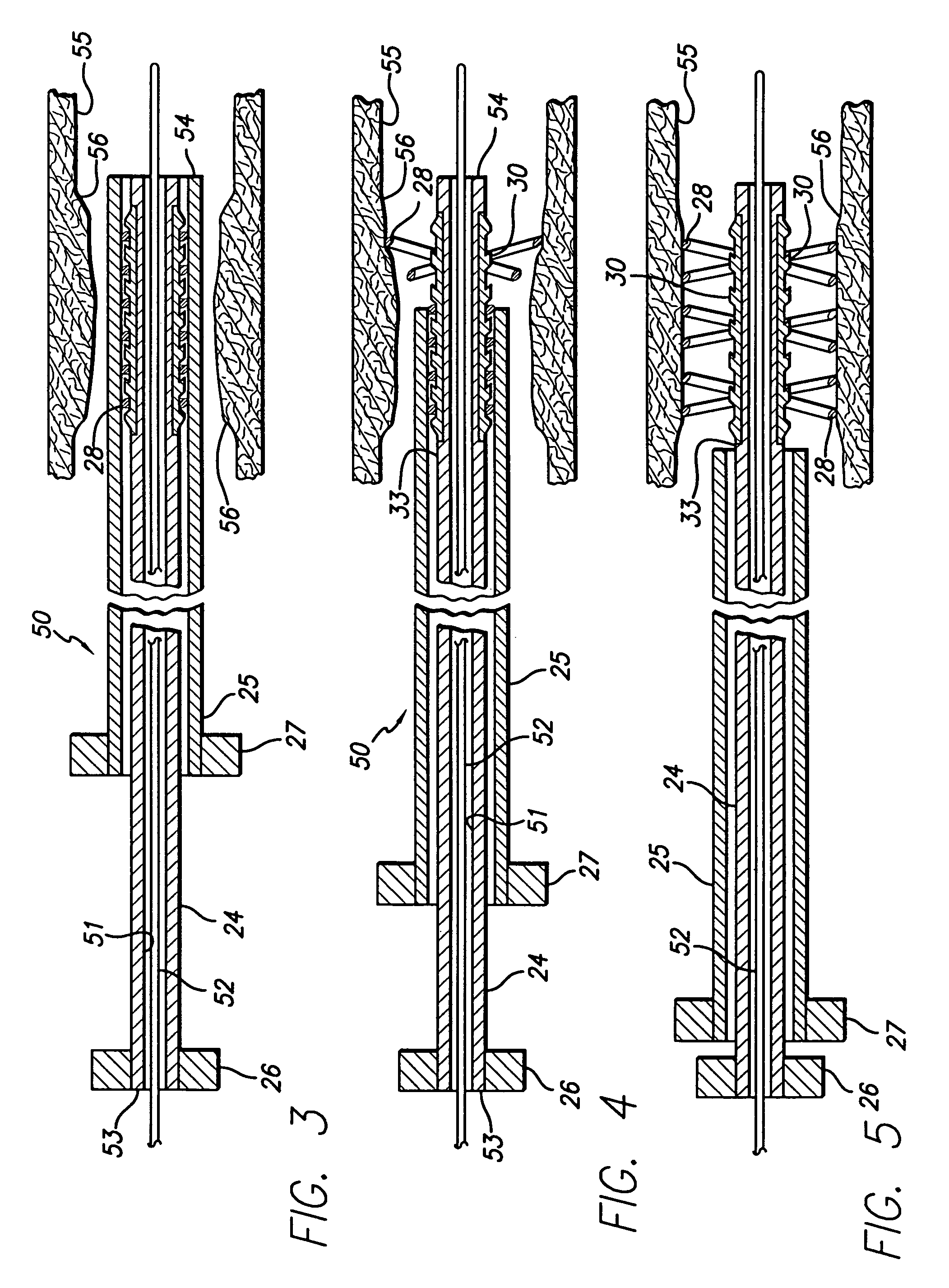
Avoiding stress-induced martensitic transformation in nickel titanium alloys used in medical devices
PatentInactiveUS7175655B1
Innovation
- A process involving heating a shape memory alloy to a temperature above its martensite deformation temperature (Md) to deform it into a restrained shape in an austenitic state, allowing it to be cooled and stored within a delivery system, such as a catheter, without inducing stress-induced martensite, ensuring the alloy remains in an austenitic state during deployment in the body.
Avoiding stress-induced martensitic transformation in nickel titanium alloys used in medical devices
PatentInactiveUS7875070B2
Innovation
- A method and apparatus for deforming nickel-titanium alloys in the austenitic state before deployment, avoiding stress-induced martensitic transformation by heating the alloy above its martensite deformation temperature and cooling it to room temperature within a delivery system, ensuring the alloy remains in an austenitic state during deployment.
Biocompatibility and Safety Considerations
Nitinol, a nickel-titanium alloy, has revolutionized endoscopic surgery due to its unique shape memory and superelastic properties. However, its widespread use in medical devices necessitates a thorough examination of its biocompatibility and safety profile. The biocompatibility of Nitinol is primarily influenced by its surface characteristics and the potential release of nickel ions.
Surface treatments play a crucial role in enhancing Nitinol's biocompatibility. Electropolishing and passivation techniques are commonly employed to create a stable titanium oxide layer, which acts as a barrier against nickel ion release. This protective layer significantly reduces the risk of adverse reactions and improves the overall safety of Nitinol-based devices.
The potential release of nickel ions from Nitinol implants has been a subject of extensive research. While nickel is an essential trace element in the human body, excessive exposure can lead to allergic reactions or toxicity. Studies have shown that properly treated Nitinol exhibits minimal nickel release, well below the levels that could cause adverse effects in most patients.
Long-term implantation studies have demonstrated the overall safety of Nitinol devices. In vivo experiments have shown good tissue compatibility and minimal inflammatory responses. However, it is essential to consider patient-specific factors, such as nickel sensitivity, when using Nitinol-based devices.
The manufacturing process of Nitinol devices also plays a critical role in ensuring safety. Strict quality control measures are implemented to maintain consistent alloy composition and minimize impurities. Advanced manufacturing techniques, such as laser cutting and shape setting, help create precise and reliable Nitinol components for endoscopic instruments.
Regulatory bodies, including the FDA and European Medicines Agency, have established guidelines for the evaluation of Nitinol-based medical devices. These guidelines encompass rigorous testing protocols for biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and mechanical properties. Manufacturers must adhere to these standards to ensure the safety and efficacy of their Nitinol products.
Despite the generally favorable safety profile of Nitinol, ongoing research continues to explore potential long-term effects and rare complications. This includes studies on the interaction between Nitinol and different biological environments, as well as the development of novel surface treatments to further enhance biocompatibility.
In conclusion, while Nitinol has demonstrated excellent biocompatibility and safety in endoscopic surgery applications, continuous vigilance and research are necessary to maintain and improve its safety profile. The balance between harnessing Nitinol's unique properties and ensuring patient safety remains a key focus in the development of innovative endoscopic surgical devices.
Surface treatments play a crucial role in enhancing Nitinol's biocompatibility. Electropolishing and passivation techniques are commonly employed to create a stable titanium oxide layer, which acts as a barrier against nickel ion release. This protective layer significantly reduces the risk of adverse reactions and improves the overall safety of Nitinol-based devices.
The potential release of nickel ions from Nitinol implants has been a subject of extensive research. While nickel is an essential trace element in the human body, excessive exposure can lead to allergic reactions or toxicity. Studies have shown that properly treated Nitinol exhibits minimal nickel release, well below the levels that could cause adverse effects in most patients.
Long-term implantation studies have demonstrated the overall safety of Nitinol devices. In vivo experiments have shown good tissue compatibility and minimal inflammatory responses. However, it is essential to consider patient-specific factors, such as nickel sensitivity, when using Nitinol-based devices.
The manufacturing process of Nitinol devices also plays a critical role in ensuring safety. Strict quality control measures are implemented to maintain consistent alloy composition and minimize impurities. Advanced manufacturing techniques, such as laser cutting and shape setting, help create precise and reliable Nitinol components for endoscopic instruments.
Regulatory bodies, including the FDA and European Medicines Agency, have established guidelines for the evaluation of Nitinol-based medical devices. These guidelines encompass rigorous testing protocols for biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and mechanical properties. Manufacturers must adhere to these standards to ensure the safety and efficacy of their Nitinol products.
Despite the generally favorable safety profile of Nitinol, ongoing research continues to explore potential long-term effects and rare complications. This includes studies on the interaction between Nitinol and different biological environments, as well as the development of novel surface treatments to further enhance biocompatibility.
In conclusion, while Nitinol has demonstrated excellent biocompatibility and safety in endoscopic surgery applications, continuous vigilance and research are necessary to maintain and improve its safety profile. The balance between harnessing Nitinol's unique properties and ensuring patient safety remains a key focus in the development of innovative endoscopic surgical devices.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Nitinol in Endoscopic Surgery
The implementation of Nitinol in endoscopic surgery presents a complex cost-benefit scenario that requires careful analysis. On the cost side, Nitinol-based devices typically come with higher initial expenses compared to traditional materials. The specialized manufacturing processes, including precise heat treatments and shape-setting procedures, contribute to elevated production costs. Additionally, the unique properties of Nitinol often necessitate specialized handling and sterilization protocols, potentially increasing operational expenses for healthcare facilities.
However, these higher upfront costs must be weighed against the significant benefits that Nitinol brings to endoscopic procedures. The superelastic properties of Nitinol allow for the creation of instruments with enhanced flexibility and shape memory, enabling more precise and less invasive surgical techniques. This can lead to reduced procedure times, decreased risk of complications, and shorter patient recovery periods. Such improvements not only enhance patient outcomes but also contribute to overall cost savings in the healthcare system through reduced hospital stays and lower complication rates.
The durability of Nitinol instruments is another factor to consider in the cost-benefit analysis. While more expensive initially, Nitinol devices often demonstrate superior longevity compared to traditional alternatives, potentially reducing the frequency of replacements and associated costs over time. This extended lifespan can offset the higher acquisition costs, especially in high-volume surgical settings.
From a broader economic perspective, the adoption of Nitinol-based innovations in endoscopic surgery can drive technological advancements and stimulate competition in the medical device industry. This may lead to further innovations and eventual cost reductions as manufacturing processes become more efficient and widespread.
Patient satisfaction and quality of life improvements, although challenging to quantify financially, represent significant benefits of Nitinol-based endoscopic techniques. Reduced post-operative pain, faster recovery times, and improved surgical outcomes contribute to overall patient well-being and can have positive economic impacts through faster returns to work and reduced long-term healthcare needs.
In conclusion, while the initial costs of implementing Nitinol-based technologies in endoscopic surgery are higher, the long-term benefits in terms of improved surgical outcomes, reduced complications, and potential cost savings in overall patient care make a compelling case for their adoption. As with any medical technology, ongoing evaluation and real-world data collection will be crucial to fully understand and optimize the cost-benefit ratio of Nitinol in endoscopic applications.
However, these higher upfront costs must be weighed against the significant benefits that Nitinol brings to endoscopic procedures. The superelastic properties of Nitinol allow for the creation of instruments with enhanced flexibility and shape memory, enabling more precise and less invasive surgical techniques. This can lead to reduced procedure times, decreased risk of complications, and shorter patient recovery periods. Such improvements not only enhance patient outcomes but also contribute to overall cost savings in the healthcare system through reduced hospital stays and lower complication rates.
The durability of Nitinol instruments is another factor to consider in the cost-benefit analysis. While more expensive initially, Nitinol devices often demonstrate superior longevity compared to traditional alternatives, potentially reducing the frequency of replacements and associated costs over time. This extended lifespan can offset the higher acquisition costs, especially in high-volume surgical settings.
From a broader economic perspective, the adoption of Nitinol-based innovations in endoscopic surgery can drive technological advancements and stimulate competition in the medical device industry. This may lead to further innovations and eventual cost reductions as manufacturing processes become more efficient and widespread.
Patient satisfaction and quality of life improvements, although challenging to quantify financially, represent significant benefits of Nitinol-based endoscopic techniques. Reduced post-operative pain, faster recovery times, and improved surgical outcomes contribute to overall patient well-being and can have positive economic impacts through faster returns to work and reduced long-term healthcare needs.
In conclusion, while the initial costs of implementing Nitinol-based technologies in endoscopic surgery are higher, the long-term benefits in terms of improved surgical outcomes, reduced complications, and potential cost savings in overall patient care make a compelling case for their adoption. As with any medical technology, ongoing evaluation and real-world data collection will be crucial to fully understand and optimize the cost-benefit ratio of Nitinol in endoscopic applications.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!