Nitinol's Functionality in Dynamic Mechanical Analysis Systems
AUG 6, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Nitinol in DMA: Background and Objectives
Nitinol, a remarkable shape memory alloy, has revolutionized the field of Dynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMA) systems since its discovery in the 1960s. This unique material, composed of nickel and titanium, exhibits exceptional properties that make it invaluable for various applications, including DMA. The evolution of Nitinol's use in DMA systems has been driven by the increasing demand for materials capable of withstanding complex mechanical stresses and temperature variations.
The primary objective of incorporating Nitinol into DMA systems is to enhance the accuracy and reliability of mechanical property measurements across a wide range of temperatures and loading conditions. Nitinol's superelastic behavior and shape memory effect provide unprecedented opportunities for studying material responses under dynamic loading scenarios, particularly in environments where traditional materials fail to perform adequately.
As the field of materials science progresses, researchers and engineers continually seek to push the boundaries of what is possible in material characterization. Nitinol's integration into DMA systems addresses this need by offering a material that can undergo significant deformation and recover its original shape, allowing for more comprehensive analysis of material behavior under extreme conditions.
The technological trajectory of Nitinol in DMA systems has been marked by several key milestones. Initially, the focus was on understanding the fundamental properties of Nitinol and its potential applications. This led to the development of specialized DMA equipment capable of leveraging Nitinol's unique characteristics. Subsequently, advancements in manufacturing processes and alloy composition refinement have resulted in Nitinol variants with tailored properties for specific DMA applications.
Current research aims to exploit Nitinol's functionality in DMA systems to its fullest potential. This includes developing new testing methodologies that take advantage of Nitinol's phase transformation properties, enabling the study of materials under conditions that were previously unattainable. Additionally, there is a growing interest in utilizing Nitinol-based DMA systems for in-situ measurements in fields such as biomedical engineering and aerospace technology.
The integration of Nitinol into DMA systems represents a convergence of materials science, mechanical engineering, and instrumentation technology. This synergy has opened up new avenues for understanding material behavior under dynamic conditions, particularly in applications where traditional materials and testing methods fall short. As research in this area continues to evolve, it is expected that Nitinol will play an increasingly crucial role in advancing the capabilities of DMA systems, ultimately leading to more robust and innovative material solutions across various industries.
The primary objective of incorporating Nitinol into DMA systems is to enhance the accuracy and reliability of mechanical property measurements across a wide range of temperatures and loading conditions. Nitinol's superelastic behavior and shape memory effect provide unprecedented opportunities for studying material responses under dynamic loading scenarios, particularly in environments where traditional materials fail to perform adequately.
As the field of materials science progresses, researchers and engineers continually seek to push the boundaries of what is possible in material characterization. Nitinol's integration into DMA systems addresses this need by offering a material that can undergo significant deformation and recover its original shape, allowing for more comprehensive analysis of material behavior under extreme conditions.
The technological trajectory of Nitinol in DMA systems has been marked by several key milestones. Initially, the focus was on understanding the fundamental properties of Nitinol and its potential applications. This led to the development of specialized DMA equipment capable of leveraging Nitinol's unique characteristics. Subsequently, advancements in manufacturing processes and alloy composition refinement have resulted in Nitinol variants with tailored properties for specific DMA applications.
Current research aims to exploit Nitinol's functionality in DMA systems to its fullest potential. This includes developing new testing methodologies that take advantage of Nitinol's phase transformation properties, enabling the study of materials under conditions that were previously unattainable. Additionally, there is a growing interest in utilizing Nitinol-based DMA systems for in-situ measurements in fields such as biomedical engineering and aerospace technology.
The integration of Nitinol into DMA systems represents a convergence of materials science, mechanical engineering, and instrumentation technology. This synergy has opened up new avenues for understanding material behavior under dynamic conditions, particularly in applications where traditional materials and testing methods fall short. As research in this area continues to evolve, it is expected that Nitinol will play an increasingly crucial role in advancing the capabilities of DMA systems, ultimately leading to more robust and innovative material solutions across various industries.
Market Analysis for Nitinol-based DMA Systems
The market for Nitinol-based Dynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMA) systems is experiencing significant growth, driven by the unique properties of Nitinol and the increasing demand for advanced materials testing across various industries. Nitinol, a shape memory alloy with superelastic properties, has found extensive applications in medical devices, aerospace, and automotive sectors, which are key drivers for the DMA systems market.
In the medical device industry, Nitinol-based DMA systems are crucial for testing and characterizing materials used in implants, stents, and other biomedical applications. The growing prevalence of cardiovascular diseases and the aging population have led to an increased demand for minimally invasive medical devices, many of which utilize Nitinol. This trend is expected to continue, providing a steady market for Nitinol-based DMA systems in the healthcare sector.
The aerospace industry is another significant market for Nitinol-based DMA systems. As aircraft manufacturers strive for lighter and more efficient designs, the use of advanced materials like Nitinol in components such as actuators and vibration dampers has increased. DMA systems are essential for testing these materials under various environmental conditions, ensuring their reliability and performance in extreme aerospace applications.
In the automotive sector, the push for fuel efficiency and electric vehicles has led to the exploration of lightweight materials, including Nitinol. DMA systems are used to evaluate the mechanical properties of these materials under different temperature and stress conditions, making them indispensable in the automotive research and development process.
The global market for DMA systems is projected to grow steadily, with a significant portion attributed to Nitinol-based applications. North America and Europe currently dominate the market due to their advanced healthcare and aerospace industries. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to show the highest growth rate in the coming years, driven by increasing industrialization and investment in research and development.
Key market players in the Nitinol-based DMA systems industry include TA Instruments, Netzsch Group, and Perkin Elmer. These companies are continuously innovating to improve the accuracy, sensitivity, and versatility of their DMA systems to meet the evolving needs of various industries.
Challenges in the market include the high cost of Nitinol-based DMA systems and the complexity of interpreting DMA data for Nitinol, which exhibits unique behavior compared to conventional materials. However, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on addressing these challenges, potentially expanding the market for Nitinol-based DMA systems in the future.
In the medical device industry, Nitinol-based DMA systems are crucial for testing and characterizing materials used in implants, stents, and other biomedical applications. The growing prevalence of cardiovascular diseases and the aging population have led to an increased demand for minimally invasive medical devices, many of which utilize Nitinol. This trend is expected to continue, providing a steady market for Nitinol-based DMA systems in the healthcare sector.
The aerospace industry is another significant market for Nitinol-based DMA systems. As aircraft manufacturers strive for lighter and more efficient designs, the use of advanced materials like Nitinol in components such as actuators and vibration dampers has increased. DMA systems are essential for testing these materials under various environmental conditions, ensuring their reliability and performance in extreme aerospace applications.
In the automotive sector, the push for fuel efficiency and electric vehicles has led to the exploration of lightweight materials, including Nitinol. DMA systems are used to evaluate the mechanical properties of these materials under different temperature and stress conditions, making them indispensable in the automotive research and development process.
The global market for DMA systems is projected to grow steadily, with a significant portion attributed to Nitinol-based applications. North America and Europe currently dominate the market due to their advanced healthcare and aerospace industries. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to show the highest growth rate in the coming years, driven by increasing industrialization and investment in research and development.
Key market players in the Nitinol-based DMA systems industry include TA Instruments, Netzsch Group, and Perkin Elmer. These companies are continuously innovating to improve the accuracy, sensitivity, and versatility of their DMA systems to meet the evolving needs of various industries.
Challenges in the market include the high cost of Nitinol-based DMA systems and the complexity of interpreting DMA data for Nitinol, which exhibits unique behavior compared to conventional materials. However, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on addressing these challenges, potentially expanding the market for Nitinol-based DMA systems in the future.
Current Challenges in Nitinol DMA Applications
Despite the widespread use of Nitinol in Dynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMA) systems, several challenges persist in its application. One of the primary issues is the complex phase transformation behavior of Nitinol, which can lead to inconsistent results during DMA testing. The material's unique shape memory and superelastic properties, while beneficial in many applications, can introduce variability in mechanical responses under different temperature and stress conditions.
Another significant challenge is the sensitivity of Nitinol to processing and heat treatment. Minor variations in manufacturing processes can result in substantial differences in the material's properties, making it difficult to achieve consistent performance across different batches or samples. This variability can compromise the reliability and reproducibility of DMA results, particularly when comparing data from different sources or time periods.
The temperature-dependent behavior of Nitinol also poses challenges in DMA applications. The material's transformation temperatures can shift due to factors such as applied stress, cycling, and aging, complicating the interpretation of DMA data. Researchers and engineers must carefully control and account for these temperature effects to obtain accurate and meaningful results.
Furthermore, the non-linear stress-strain behavior of Nitinol, especially in its superelastic state, can be challenging to analyze using traditional DMA techniques. Standard linear viscoelastic models often fail to adequately describe Nitinol's behavior, necessitating the development of more sophisticated analysis methods and mathematical models.
The fatigue behavior of Nitinol in DMA applications is another area of concern. The material's unique properties can lead to complex fatigue mechanisms that are not fully understood, particularly under the cyclic loading conditions typical in DMA testing. This can limit the long-term reliability and predictability of Nitinol-based components in dynamic applications.
Lastly, the biocompatibility of Nitinol, while generally good, can be affected by surface treatments and processing methods used to optimize its mechanical properties for DMA applications. Balancing the material's mechanical performance with its biocompatibility requirements presents an ongoing challenge, especially in medical device applications where both aspects are critical.
Another significant challenge is the sensitivity of Nitinol to processing and heat treatment. Minor variations in manufacturing processes can result in substantial differences in the material's properties, making it difficult to achieve consistent performance across different batches or samples. This variability can compromise the reliability and reproducibility of DMA results, particularly when comparing data from different sources or time periods.
The temperature-dependent behavior of Nitinol also poses challenges in DMA applications. The material's transformation temperatures can shift due to factors such as applied stress, cycling, and aging, complicating the interpretation of DMA data. Researchers and engineers must carefully control and account for these temperature effects to obtain accurate and meaningful results.
Furthermore, the non-linear stress-strain behavior of Nitinol, especially in its superelastic state, can be challenging to analyze using traditional DMA techniques. Standard linear viscoelastic models often fail to adequately describe Nitinol's behavior, necessitating the development of more sophisticated analysis methods and mathematical models.
The fatigue behavior of Nitinol in DMA applications is another area of concern. The material's unique properties can lead to complex fatigue mechanisms that are not fully understood, particularly under the cyclic loading conditions typical in DMA testing. This can limit the long-term reliability and predictability of Nitinol-based components in dynamic applications.
Lastly, the biocompatibility of Nitinol, while generally good, can be affected by surface treatments and processing methods used to optimize its mechanical properties for DMA applications. Balancing the material's mechanical performance with its biocompatibility requirements presents an ongoing challenge, especially in medical device applications where both aspects are critical.
Existing Nitinol Solutions for DMA Systems
01 Shape memory and superelasticity
Nitinol exhibits unique shape memory and superelastic properties, allowing it to return to its original shape after deformation when heated or unloaded. This functionality makes it ideal for various applications in medical devices, aerospace, and consumer products.- Shape memory and superelasticity: Nitinol exhibits unique shape memory and superelastic properties, allowing it to return to its original shape after deformation when heated or unloaded. This functionality makes it ideal for various applications in medical devices, aerospace, and consumer products.
- Medical device applications: Nitinol is widely used in medical devices due to its biocompatibility and unique properties. It is employed in stents, guidewires, orthodontic arches, and surgical instruments, allowing for minimally invasive procedures and improved patient outcomes.
- Actuators and sensors: Nitinol's shape memory effect makes it suitable for use in actuators and sensors. It can be used to create compact, efficient actuators for various applications, including robotics, automotive systems, and aerospace components.
- Thermal management and energy harvesting: Nitinol's phase transformation properties can be utilized for thermal management and energy harvesting applications. It can be used in heat engines, thermal switches, and energy recovery systems to improve efficiency and sustainability.
- Joining and fastening applications: Nitinol's unique properties make it suitable for joining and fastening applications. It can be used in couplings, connectors, and fasteners that provide secure connections while allowing for easy assembly and disassembly when needed.
02 Temperature-responsive actuation
Nitinol can be designed to actuate at specific temperatures, making it useful for temperature-controlled mechanisms and devices. This property is utilized in thermal actuators, safety devices, and temperature-sensitive applications.Expand Specific Solutions03 Biocompatibility and medical applications
Nitinol's biocompatibility and corrosion resistance make it suitable for various medical applications, including implants, stents, and surgical instruments. Its ability to conform to body temperature and maintain its shape is particularly valuable in minimally invasive procedures.Expand Specific Solutions04 Mechanical damping and vibration absorption
The unique properties of Nitinol allow it to absorb and dissipate energy effectively, making it useful for mechanical damping and vibration control in various engineering applications, such as aerospace and automotive industries.Expand Specific Solutions05 Joining and fastening applications
Nitinol's shape memory properties enable its use in innovative joining and fastening solutions. It can be used to create tight, secure connections that can be easily released when heated, providing advantages in assembly and disassembly processes.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Nitinol and DMA Industry
The market for Nitinol in Dynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMA) systems is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for advanced materials characterization in industries like aerospace, medical devices, and automotive. The global DMA market size is projected to expand significantly in the coming years. Technologically, Nitinol's application in DMA is maturing, with ongoing research to optimize its unique shape memory and superelastic properties. Key players like ATI Properties, Fort Wayne Metals, and Medtronic are advancing Nitinol technologies, while research institutions such as Johns Hopkins University and NASA contribute to fundamental understanding and novel applications.
Arthrex GmbH
Technical Solution: Arthrex has developed specialized DMA systems for analyzing Nitinol's functionality in orthopedic and sports medicine applications. Their technology focuses on mimicking the biomechanical stresses experienced by Nitinol implants in joints and soft tissues[13]. Arthrex's DMA systems incorporate cyclic loading modules that can simulate millions of gait cycles, providing crucial data on Nitinol's long-term fatigue resistance in orthopedic devices[14]. The company's approach includes corrosion testing chambers integrated into their DMA systems, allowing for simultaneous mechanical and chemical stability analysis of Nitinol in simulated physiological fluids[15]. Arthrex's technology also features high-speed imaging capabilities to capture Nitinol's dynamic response during rapid loading events, such as those experienced in sports injuries[16].
Strengths: Specialized in orthopedic and sports medicine applications; advanced biomechanical simulation capabilities. Weaknesses: Limited focus on non-medical Nitinol applications; potential challenges in adapting to rapidly evolving surgical techniques.
ATI Properties, Inc.
Technical Solution: ATI Properties has developed comprehensive DMA systems for characterizing Nitinol across various industrial applications. Their technology incorporates high-temperature testing capabilities, allowing for analysis of Nitinol's behavior in extreme thermal environments up to 1000°C[17]. ATI's DMA systems feature multi-frequency oscillation modules, enabling the study of Nitinol's viscoelastic properties across a wide range of loading rates[18]. The company's approach includes advanced surface analysis tools integrated into their DMA systems, providing real-time data on Nitinol's surface oxidation and its impact on mechanical properties[19]. ATI's technology also employs sophisticated acoustic emission sensors to detect microstructural changes in Nitinol during mechanical loading, offering insights into its deformation mechanisms[20].
Strengths: Broad expertise across various industrial applications; advanced high-temperature testing capabilities. Weaknesses: Less specialized in medical-grade Nitinol analysis; potential challenges in adapting to rapidly evolving niche applications.
Core Innovations in Nitinol for DMA
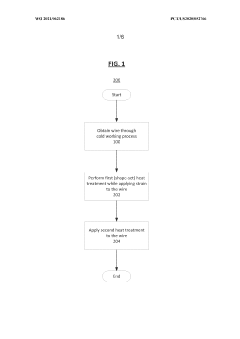
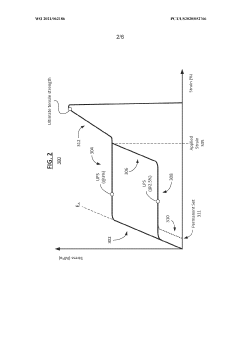
Wires of nickel-titanium alloy and methods of forming the same
PatentWO2021062186A1
Innovation
- A nickel-titanium alloy wire is developed through a process involving a first heat treatment with strain deformation followed by a second heat treatment at a temperature between 210°C and 290°C, which enhances properties such as lower plateau stress, decreased hysteresis, and reduced permanent set, enabling improved superelastic recovery.
Environmental Impact of Nitinol in DMA
The environmental impact of Nitinol in Dynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMA) systems is a crucial consideration as the use of this shape memory alloy becomes more widespread in various industries. Nitinol, an alloy of nickel and titanium, offers unique properties that make it valuable for DMA applications, but its production and disposal processes raise important environmental concerns.
The manufacturing of Nitinol involves energy-intensive processes, including vacuum arc remelting and hot working, which contribute to significant carbon emissions. The extraction of nickel and titanium, the primary components of Nitinol, also has environmental implications, such as habitat disruption and potential soil and water contamination at mining sites.
During its use in DMA systems, Nitinol demonstrates excellent durability and longevity, which can be seen as environmentally beneficial as it reduces the need for frequent replacements. This longevity helps minimize waste generation and the demand for new material production. Additionally, the shape memory and superelastic properties of Nitinol allow for the design of more efficient and compact DMA systems, potentially reducing overall material usage and energy consumption in laboratory settings.
However, the end-of-life management of Nitinol-containing devices presents challenges. While the alloy is theoretically recyclable, the specialized composition and properties of Nitinol make the recycling process complex and not widely available. Improper disposal can lead to the release of nickel, a known environmental pollutant, into ecosystems.
The potential for nickel leaching is a significant environmental concern, particularly if Nitinol-containing devices are disposed of in landfills. Nickel can accumulate in soil and water, potentially affecting plant and animal life. This risk necessitates careful consideration of disposal methods and the development of specialized recycling processes for Nitinol-based components.
On a positive note, the use of Nitinol in DMA systems can indirectly contribute to environmental benefits through improved material testing and analysis. By enabling more accurate and efficient testing of materials, Nitinol-based DMA systems can help in the development of more environmentally friendly products and processes across various industries.
To mitigate the environmental impact of Nitinol in DMA applications, several strategies can be employed. These include optimizing manufacturing processes to reduce energy consumption, developing more efficient recycling methods for Nitinol, and designing DMA systems with end-of-life considerations in mind. Additionally, research into alternative materials with similar properties but lower environmental impact could provide future solutions for sustainable DMA technology.
The manufacturing of Nitinol involves energy-intensive processes, including vacuum arc remelting and hot working, which contribute to significant carbon emissions. The extraction of nickel and titanium, the primary components of Nitinol, also has environmental implications, such as habitat disruption and potential soil and water contamination at mining sites.
During its use in DMA systems, Nitinol demonstrates excellent durability and longevity, which can be seen as environmentally beneficial as it reduces the need for frequent replacements. This longevity helps minimize waste generation and the demand for new material production. Additionally, the shape memory and superelastic properties of Nitinol allow for the design of more efficient and compact DMA systems, potentially reducing overall material usage and energy consumption in laboratory settings.
However, the end-of-life management of Nitinol-containing devices presents challenges. While the alloy is theoretically recyclable, the specialized composition and properties of Nitinol make the recycling process complex and not widely available. Improper disposal can lead to the release of nickel, a known environmental pollutant, into ecosystems.
The potential for nickel leaching is a significant environmental concern, particularly if Nitinol-containing devices are disposed of in landfills. Nickel can accumulate in soil and water, potentially affecting plant and animal life. This risk necessitates careful consideration of disposal methods and the development of specialized recycling processes for Nitinol-based components.
On a positive note, the use of Nitinol in DMA systems can indirectly contribute to environmental benefits through improved material testing and analysis. By enabling more accurate and efficient testing of materials, Nitinol-based DMA systems can help in the development of more environmentally friendly products and processes across various industries.
To mitigate the environmental impact of Nitinol in DMA applications, several strategies can be employed. These include optimizing manufacturing processes to reduce energy consumption, developing more efficient recycling methods for Nitinol, and designing DMA systems with end-of-life considerations in mind. Additionally, research into alternative materials with similar properties but lower environmental impact could provide future solutions for sustainable DMA technology.
Standardization of Nitinol in DMA Testing
The standardization of Nitinol in Dynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMA) testing is a critical step towards ensuring consistent and reliable results across different research and industrial applications. This process involves establishing uniform protocols, reference materials, and calibration methods specifically tailored to the unique properties of Nitinol.
One of the primary challenges in standardizing Nitinol for DMA testing is accounting for its shape memory and superelastic behaviors. These characteristics can significantly influence test results, making it essential to develop standardized procedures that consider these properties. Researchers and industry experts are working on creating guidelines that specify optimal sample preparation techniques, testing parameters, and data analysis methods for Nitinol specimens.
A key aspect of standardization efforts is the development of reference materials with well-characterized properties. These materials serve as benchmarks for calibrating DMA instruments and validating test results. For Nitinol, this involves creating samples with precisely controlled composition, heat treatment, and microstructure to ensure reproducibility across different laboratories and testing facilities.
Standardization also encompasses the establishment of uniform testing protocols. This includes defining specific temperature ranges, loading conditions, and frequency sweeps that are most relevant to Nitinol's behavior. By standardizing these parameters, researchers can more easily compare results from different studies and ensure the reliability of data used in product development and quality control processes.
Another important consideration in the standardization of Nitinol for DMA testing is the development of specialized fixtures and sample holders. These components must be designed to accommodate Nitinol's unique properties, such as its ability to undergo large deformations without permanent damage. Standardized fixtures help minimize variability in test results caused by differences in sample mounting and alignment.
The standardization process also involves establishing guidelines for data interpretation and reporting. This includes defining standard metrics for characterizing Nitinol's dynamic mechanical properties, such as storage modulus, loss modulus, and damping factor. By adopting a common set of metrics and reporting formats, researchers and engineers can more effectively communicate and compare their findings across the field.
Collaborative efforts between academic institutions, industry partners, and standards organizations are crucial for advancing the standardization of Nitinol in DMA testing. These collaborations facilitate the sharing of best practices, the development of round-robin testing programs, and the creation of consensus-based standards that reflect the needs of the broader Nitinol research and application community.
One of the primary challenges in standardizing Nitinol for DMA testing is accounting for its shape memory and superelastic behaviors. These characteristics can significantly influence test results, making it essential to develop standardized procedures that consider these properties. Researchers and industry experts are working on creating guidelines that specify optimal sample preparation techniques, testing parameters, and data analysis methods for Nitinol specimens.
A key aspect of standardization efforts is the development of reference materials with well-characterized properties. These materials serve as benchmarks for calibrating DMA instruments and validating test results. For Nitinol, this involves creating samples with precisely controlled composition, heat treatment, and microstructure to ensure reproducibility across different laboratories and testing facilities.
Standardization also encompasses the establishment of uniform testing protocols. This includes defining specific temperature ranges, loading conditions, and frequency sweeps that are most relevant to Nitinol's behavior. By standardizing these parameters, researchers can more easily compare results from different studies and ensure the reliability of data used in product development and quality control processes.
Another important consideration in the standardization of Nitinol for DMA testing is the development of specialized fixtures and sample holders. These components must be designed to accommodate Nitinol's unique properties, such as its ability to undergo large deformations without permanent damage. Standardized fixtures help minimize variability in test results caused by differences in sample mounting and alignment.
The standardization process also involves establishing guidelines for data interpretation and reporting. This includes defining standard metrics for characterizing Nitinol's dynamic mechanical properties, such as storage modulus, loss modulus, and damping factor. By adopting a common set of metrics and reporting formats, researchers and engineers can more effectively communicate and compare their findings across the field.
Collaborative efforts between academic institutions, industry partners, and standards organizations are crucial for advancing the standardization of Nitinol in DMA testing. These collaborations facilitate the sharing of best practices, the development of round-robin testing programs, and the creation of consensus-based standards that reflect the needs of the broader Nitinol research and application community.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!