Nitinol's Role in Reshaping Electrofluidic Devices
AUG 6, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Nitinol in Electrofluidics: Background and Objectives
Nitinol, an alloy of nickel and titanium, has emerged as a revolutionary material in the field of electrofluidic devices. This shape memory alloy possesses unique properties that have captured the attention of researchers and engineers alike. The journey of Nitinol in electrofluidics began in the late 20th century when its potential for miniaturization and precise control in microfluidic systems was first recognized.
The evolution of Nitinol's application in electrofluidic devices has been driven by the increasing demand for more efficient, compact, and responsive systems in various industries. From medical devices to aerospace applications, the need for materials that can adapt to changing environments and provide controlled actuation has been paramount. Nitinol's ability to remember and return to a predetermined shape when subjected to temperature changes has opened up new possibilities in the design and functionality of electrofluidic devices.
As we delve into the technical background of Nitinol in electrofluidics, it's crucial to understand the fundamental principles that make this alloy so versatile. The shape memory effect and superelasticity of Nitinol are key to its performance in electrofluidic applications. These properties allow for the creation of devices that can change shape, apply force, or alter their physical characteristics in response to electrical or thermal stimuli.
The objectives of incorporating Nitinol into electrofluidic devices are multifaceted. Primarily, researchers aim to harness Nitinol's unique properties to enhance the control and manipulation of fluids at the micro and nano scales. This includes improving the precision of fluid dispensing, creating more responsive valves and pumps, and developing adaptive flow control mechanisms.
Another significant goal is to leverage Nitinol's biocompatibility and corrosion resistance for biomedical applications. The potential for creating implantable devices that can interact with bodily fluids in a controlled manner is particularly promising. This could lead to advancements in drug delivery systems, diagnostic tools, and therapeutic devices.
Furthermore, the integration of Nitinol in electrofluidic devices aims to address the limitations of traditional materials and actuators. By utilizing Nitinol's shape memory properties, engineers seek to create more energy-efficient systems that require less power for actuation. This aligns with the broader trend towards miniaturization and energy conservation in electronic and fluidic systems.
As we look towards the future, the objectives for Nitinol in electrofluidics extend to pushing the boundaries of what's possible in microfluidic technology. Researchers are exploring ways to combine Nitinol with other smart materials and advanced manufacturing techniques to create even more sophisticated and responsive electrofluidic devices. The ultimate goal is to develop systems that can autonomously adapt to their environment, self-heal, and perform complex fluidic operations with unprecedented precision and efficiency.
The evolution of Nitinol's application in electrofluidic devices has been driven by the increasing demand for more efficient, compact, and responsive systems in various industries. From medical devices to aerospace applications, the need for materials that can adapt to changing environments and provide controlled actuation has been paramount. Nitinol's ability to remember and return to a predetermined shape when subjected to temperature changes has opened up new possibilities in the design and functionality of electrofluidic devices.
As we delve into the technical background of Nitinol in electrofluidics, it's crucial to understand the fundamental principles that make this alloy so versatile. The shape memory effect and superelasticity of Nitinol are key to its performance in electrofluidic applications. These properties allow for the creation of devices that can change shape, apply force, or alter their physical characteristics in response to electrical or thermal stimuli.
The objectives of incorporating Nitinol into electrofluidic devices are multifaceted. Primarily, researchers aim to harness Nitinol's unique properties to enhance the control and manipulation of fluids at the micro and nano scales. This includes improving the precision of fluid dispensing, creating more responsive valves and pumps, and developing adaptive flow control mechanisms.
Another significant goal is to leverage Nitinol's biocompatibility and corrosion resistance for biomedical applications. The potential for creating implantable devices that can interact with bodily fluids in a controlled manner is particularly promising. This could lead to advancements in drug delivery systems, diagnostic tools, and therapeutic devices.
Furthermore, the integration of Nitinol in electrofluidic devices aims to address the limitations of traditional materials and actuators. By utilizing Nitinol's shape memory properties, engineers seek to create more energy-efficient systems that require less power for actuation. This aligns with the broader trend towards miniaturization and energy conservation in electronic and fluidic systems.
As we look towards the future, the objectives for Nitinol in electrofluidics extend to pushing the boundaries of what's possible in microfluidic technology. Researchers are exploring ways to combine Nitinol with other smart materials and advanced manufacturing techniques to create even more sophisticated and responsive electrofluidic devices. The ultimate goal is to develop systems that can autonomously adapt to their environment, self-heal, and perform complex fluidic operations with unprecedented precision and efficiency.
Market Analysis for Nitinol-Enhanced Electrofluidic Devices
The market for Nitinol-enhanced electrofluidic devices is experiencing significant growth, driven by the unique properties of Nitinol and the increasing demand for advanced microfluidic technologies. Nitinol, a shape memory alloy, offers exceptional flexibility and responsiveness to temperature changes, making it ideal for creating dynamic and adaptive electrofluidic systems.
The global electrofluidic devices market is expanding rapidly, with applications spanning healthcare, environmental monitoring, and industrial processes. The integration of Nitinol into these devices is expected to accelerate market growth further. In the healthcare sector, Nitinol-enhanced electrofluidic devices show promise in drug delivery systems, diagnostic tools, and lab-on-a-chip applications.
Market research indicates that the adoption of Nitinol in electrofluidic devices is particularly strong in North America and Europe, where advanced healthcare infrastructure and research facilities drive innovation. Asia-Pacific is emerging as a key growth region, with increasing investments in biotechnology and medical research.
The market potential for Nitinol-enhanced electrofluidic devices is substantial, with projections suggesting steady growth over the next five years. Key factors contributing to this growth include the rising prevalence of chronic diseases, the need for point-of-care diagnostics, and the push for miniaturization in medical devices.
Competitive analysis reveals that several major players in the medical device and microfluidics industries are investing heavily in Nitinol-based technologies. Start-ups and research institutions are also contributing to market dynamism through innovative applications and collaborations with established companies.
Customer demand is primarily driven by the need for more efficient, reliable, and versatile electrofluidic devices. Nitinol's ability to enable precise control over fluid flow and its biocompatibility make it particularly attractive for medical applications. Industries such as aerospace and automotive are also showing interest in Nitinol-enhanced electrofluidic devices for various sensing and control applications.
Challenges in the market include the high cost of Nitinol and the complexity of integrating it into existing electrofluidic systems. However, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on addressing these issues, potentially leading to more cost-effective solutions in the future.
Overall, the market analysis suggests that Nitinol-enhanced electrofluidic devices represent a promising and rapidly evolving segment within the broader microfluidics industry. As technology advances and manufacturing processes improve, the market is expected to see continued expansion and diversification of applications.
The global electrofluidic devices market is expanding rapidly, with applications spanning healthcare, environmental monitoring, and industrial processes. The integration of Nitinol into these devices is expected to accelerate market growth further. In the healthcare sector, Nitinol-enhanced electrofluidic devices show promise in drug delivery systems, diagnostic tools, and lab-on-a-chip applications.
Market research indicates that the adoption of Nitinol in electrofluidic devices is particularly strong in North America and Europe, where advanced healthcare infrastructure and research facilities drive innovation. Asia-Pacific is emerging as a key growth region, with increasing investments in biotechnology and medical research.
The market potential for Nitinol-enhanced electrofluidic devices is substantial, with projections suggesting steady growth over the next five years. Key factors contributing to this growth include the rising prevalence of chronic diseases, the need for point-of-care diagnostics, and the push for miniaturization in medical devices.
Competitive analysis reveals that several major players in the medical device and microfluidics industries are investing heavily in Nitinol-based technologies. Start-ups and research institutions are also contributing to market dynamism through innovative applications and collaborations with established companies.
Customer demand is primarily driven by the need for more efficient, reliable, and versatile electrofluidic devices. Nitinol's ability to enable precise control over fluid flow and its biocompatibility make it particularly attractive for medical applications. Industries such as aerospace and automotive are also showing interest in Nitinol-enhanced electrofluidic devices for various sensing and control applications.
Challenges in the market include the high cost of Nitinol and the complexity of integrating it into existing electrofluidic systems. However, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on addressing these issues, potentially leading to more cost-effective solutions in the future.
Overall, the market analysis suggests that Nitinol-enhanced electrofluidic devices represent a promising and rapidly evolving segment within the broader microfluidics industry. As technology advances and manufacturing processes improve, the market is expected to see continued expansion and diversification of applications.
Current Challenges in Nitinol-Based Electrofluidic Systems
Despite the promising potential of Nitinol in electrofluidic devices, several challenges persist in the development and implementation of Nitinol-based electrofluidic systems. One of the primary obstacles is the complex phase transformation behavior of Nitinol, which can be sensitive to temperature variations and mechanical stress. This sensitivity can lead to inconsistent performance in electrofluidic applications, particularly in environments with fluctuating temperatures or under varying mechanical loads.
Another significant challenge lies in the integration of Nitinol components with other materials in electrofluidic devices. The unique properties of Nitinol, including its shape memory effect and superelasticity, can create compatibility issues with traditional manufacturing processes and materials used in microfluidic systems. This often necessitates the development of novel fabrication techniques and material combinations, which can be both time-consuming and costly.
The control and actuation of Nitinol elements in electrofluidic systems present another set of challenges. While Nitinol's shape memory effect allows for precise actuation, achieving rapid and repeatable responses in microfluidic environments can be difficult. This is particularly true when dealing with small-scale devices where the heat transfer dynamics and mechanical forces at play are significantly different from macro-scale applications.
Durability and fatigue resistance of Nitinol components in electrofluidic systems also remain areas of concern. The repeated shape transformations and exposure to various fluids and electrical fields can potentially lead to material degradation over time. This necessitates extensive testing and optimization to ensure long-term reliability and performance stability of Nitinol-based electrofluidic devices.
Furthermore, the biocompatibility of Nitinol in certain electrofluidic applications, particularly those related to biomedical devices, requires careful consideration. While Nitinol is generally considered biocompatible, its interaction with specific fluids and tissues in electrofluidic environments may present unforeseen challenges that need to be addressed through rigorous testing and validation processes.
Lastly, the scalability of Nitinol-based electrofluidic systems poses a significant challenge. While Nitinol shows great promise in laboratory-scale devices, translating these successes to large-scale manufacturing and commercial applications remains a hurdle. This includes challenges in maintaining consistent material properties across larger production batches and ensuring cost-effectiveness in mass production scenarios.
Another significant challenge lies in the integration of Nitinol components with other materials in electrofluidic devices. The unique properties of Nitinol, including its shape memory effect and superelasticity, can create compatibility issues with traditional manufacturing processes and materials used in microfluidic systems. This often necessitates the development of novel fabrication techniques and material combinations, which can be both time-consuming and costly.
The control and actuation of Nitinol elements in electrofluidic systems present another set of challenges. While Nitinol's shape memory effect allows for precise actuation, achieving rapid and repeatable responses in microfluidic environments can be difficult. This is particularly true when dealing with small-scale devices where the heat transfer dynamics and mechanical forces at play are significantly different from macro-scale applications.
Durability and fatigue resistance of Nitinol components in electrofluidic systems also remain areas of concern. The repeated shape transformations and exposure to various fluids and electrical fields can potentially lead to material degradation over time. This necessitates extensive testing and optimization to ensure long-term reliability and performance stability of Nitinol-based electrofluidic devices.
Furthermore, the biocompatibility of Nitinol in certain electrofluidic applications, particularly those related to biomedical devices, requires careful consideration. While Nitinol is generally considered biocompatible, its interaction with specific fluids and tissues in electrofluidic environments may present unforeseen challenges that need to be addressed through rigorous testing and validation processes.
Lastly, the scalability of Nitinol-based electrofluidic systems poses a significant challenge. While Nitinol shows great promise in laboratory-scale devices, translating these successes to large-scale manufacturing and commercial applications remains a hurdle. This includes challenges in maintaining consistent material properties across larger production batches and ensuring cost-effectiveness in mass production scenarios.
Existing Nitinol Applications in Electrofluidic Devices
01 Shape memory properties of Nitinol
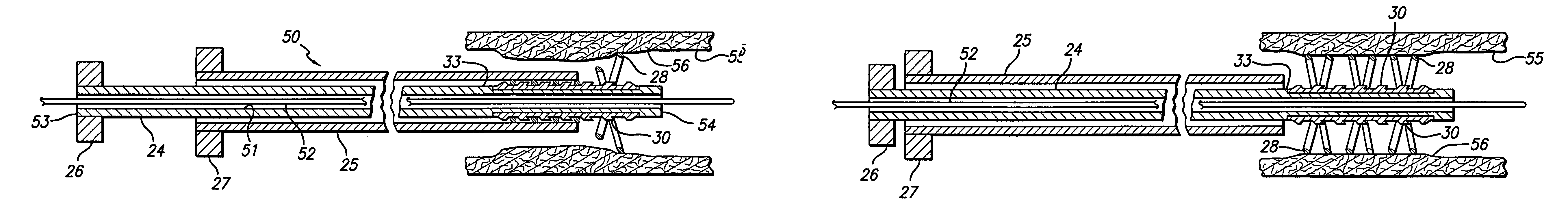
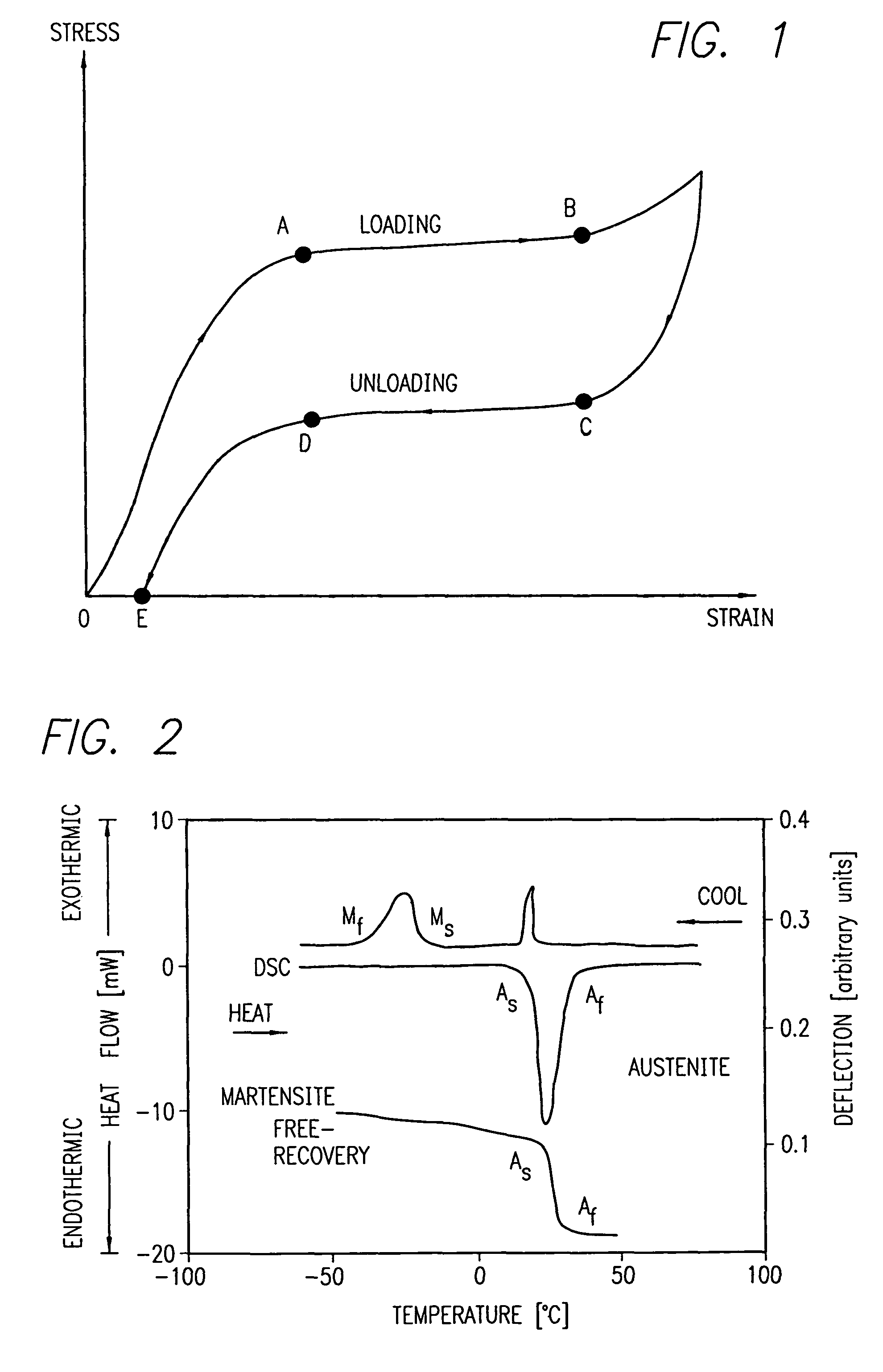
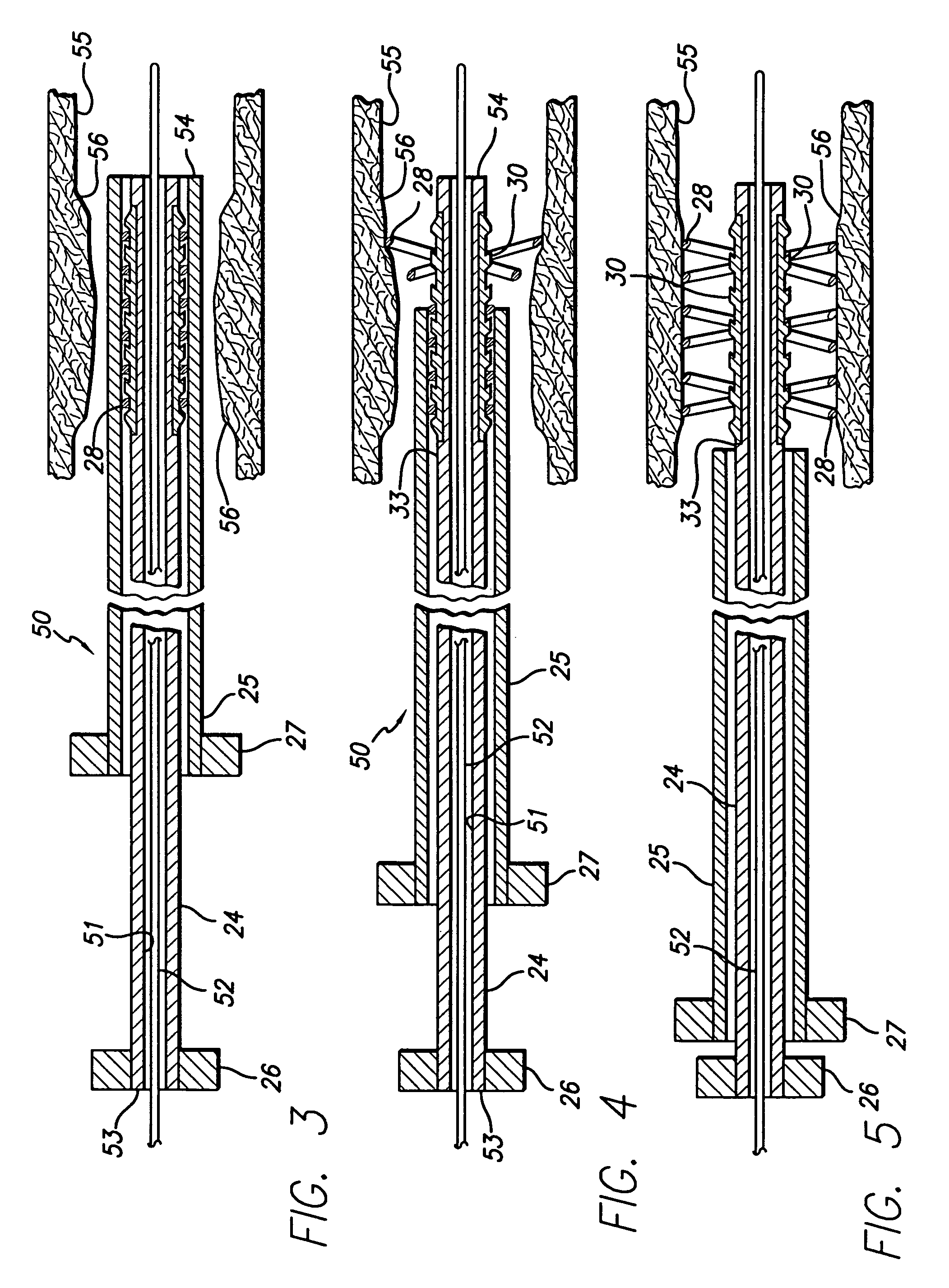
Nitinol, a nickel-titanium alloy, exhibits unique shape memory properties that allow it to be reshaped and return to its original form when heated. This characteristic makes it valuable in various applications, including medical devices, aerospace, and robotics. The reshaping process involves heating the material above its transformation temperature, deforming it to the desired shape, and then cooling it to set the new shape.- Shape memory properties of Nitinol: Nitinol, a nickel-titanium alloy, exhibits unique shape memory properties that allow it to be reshaped and return to its original form when heated. This characteristic makes it valuable in various applications, including medical devices, aerospace, and robotics. The reshaping process involves heating the material above its transformation temperature, deforming it to the desired shape, and then cooling it to set the new shape.
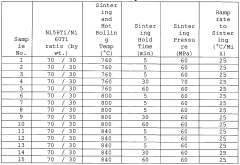
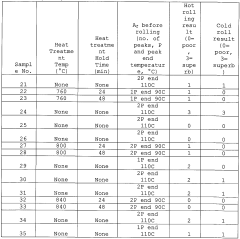
- Heat treatment methods for Nitinol reshaping: Various heat treatment methods are employed to reshape Nitinol, including laser heating, electrical resistance heating, and furnace heating. These techniques allow for precise control of temperature and duration, which are crucial factors in achieving the desired shape and properties. The specific heat treatment parameters depend on the composition of the Nitinol alloy and the intended application.
- Nitinol reshaping for medical applications: Nitinol reshaping is particularly important in the medical field, where it is used to create customized implants, stents, and surgical instruments. The ability to reshape Nitinol allows for the production of devices that can be compressed for minimally invasive procedures and then expand to their functional shape once inside the body. This property is especially useful in cardiovascular and orthopedic applications.
- Mechanical reshaping techniques for Nitinol: In addition to heat treatment, mechanical methods can be used to reshape Nitinol. These techniques include bending, twisting, and compressing the material at specific temperatures. The combination of mechanical force and temperature control allows for precise shaping of Nitinol components. This is particularly useful in applications requiring complex geometries or when localized reshaping is necessary.
- Nitinol reshaping for industrial and consumer applications: Beyond medical uses, Nitinol reshaping is employed in various industrial and consumer applications. These include actuators for robotics, temperature-sensitive switches, eyeglass frames, and automotive components. The ability to program Nitinol to change shape at specific temperatures makes it valuable in creating smart materials and adaptive structures that can respond to environmental changes.
02 Heat treatment methods for Nitinol reshaping
Various heat treatment methods are employed to reshape Nitinol, including laser heating, electrical resistance heating, and furnace heating. These techniques allow for precise control of temperature and duration, which are crucial factors in achieving the desired shape and properties. The specific heat treatment parameters depend on the composition of the Nitinol alloy and the intended application.Expand Specific Solutions03 Mechanical reshaping techniques for Nitinol
Mechanical methods can be used to reshape Nitinol, often in combination with heat treatment. These techniques include bending, twisting, and compression. The material's superelastic properties allow for significant deformation without permanent damage. Specialized tools and fixtures may be used to apply controlled force during the reshaping process.Expand Specific Solutions04 Applications of reshaped Nitinol in medical devices
Reshaped Nitinol finds extensive use in medical devices due to its biocompatibility and unique properties. Applications include stents, guidewires, orthodontic arches, and surgical instruments. The ability to reshape Nitinol allows for the creation of complex, patient-specific devices that can be deployed in minimally invasive procedures.Expand Specific Solutions05 Quality control and testing of reshaped Nitinol
Ensuring the quality and reliability of reshaped Nitinol components is crucial, especially for critical applications. Various testing methods are employed, including fatigue testing, thermal cycling, and shape recovery assessment. Advanced imaging techniques may be used to inspect the internal structure and detect any defects or inconsistencies in the reshaped material.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Nitinol and Electrofluidic Industries
The competitive landscape for Nitinol's role in reshaping electrofluidic devices is in an early growth stage, with a promising market potential driven by increasing demand for smart materials in medical and industrial applications. The market size is expanding, though still relatively niche, as companies explore Nitinol's unique shape memory and superelastic properties. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with key players like Abbott Laboratories, Boston Scientific, and Stryker Corporation leading in medical device applications. Research institutions such as Yale University and Naval Research Laboratory are contributing to fundamental advancements, while specialized firms like Fort Wayne Metals and Shape Change Technologies are developing novel Nitinol-based solutions for emerging electrofluidic applications.
W. L. Gore & Associates, Inc.
Technical Solution: W. L. Gore & Associates has developed innovative Nitinol-based electrofluidic technologies for both medical and industrial applications. Their approach combines Nitinol's unique properties with advanced polymer science to create smart composite materials. These materials integrate Nitinol wires or meshes within specialized polymer matrices, allowing for electrically controlled shape changes and fluid manipulation[7]. Gore's technology enables the creation of adaptive seals and valves that can dynamically respond to electrical stimuli, providing precise control over fluid flow in challenging environments[8]. The company has also developed Nitinol-enhanced membranes for selective filtration and separation processes, where electrical activation can modulate pore sizes and surface properties[9].
Strengths: Diverse application range beyond medical devices, strong materials science expertise, and established reputation for innovation. Weaknesses: Potential challenges in scaling up production for certain specialized applications.
Abbott Laboratories
Technical Solution: Abbott Laboratories has developed advanced Nitinol-based electrofluidic devices for medical applications. Their technology utilizes Nitinol's unique shape memory and superelastic properties to create responsive microfluidic systems. These systems incorporate Nitinol actuators that can be precisely controlled by electrical stimuli, allowing for dynamic manipulation of fluid flow and precise drug delivery[1]. Abbott's devices leverage Nitinol's biocompatibility and fatigue resistance to ensure long-term reliability in implantable medical devices[2]. The company has also developed novel surface treatments for Nitinol components to enhance their corrosion resistance and improve overall device performance in biological environments[3].
Strengths: Extensive experience in medical device development, strong R&D capabilities, and established market presence. Weaknesses: High development costs and regulatory hurdles in the medical device industry.
Innovative Nitinol-Electrofluidic Integration Techniques
Mixture of powders for preparing a sintered nickel-titanium-rare earth metal (ni-ti-re) alloy
PatentWO2013109846A1
Innovation
- A mixture of nickel-titanium-rare earth (Ni-Ti-RE) alloy powders with specific compositions and sintering conditions to produce a sintered alloy that maintains workability and superelasticity while enhancing radiopacity, using spark plasma sintering and thermomechanical processing.
Avoiding stress-induced martensitic transformation in nickel titanium alloys used in medical devices
PatentInactiveUS7875070B2
Innovation
- A method and apparatus for deforming nickel-titanium alloys in the austenitic state before deployment, avoiding stress-induced martensitic transformation by heating the alloy above its martensite deformation temperature and cooling it to room temperature within a delivery system, ensuring the alloy remains in an austenitic state during deployment.
Material Science Advancements for Nitinol in Electrofluidics
The field of material science has witnessed significant advancements in the application of Nitinol to electrofluidic devices, revolutionizing their design and functionality. Nitinol, a nickel-titanium alloy known for its shape memory and superelastic properties, has emerged as a game-changing material in this domain.
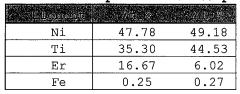
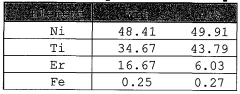
Recent research has focused on enhancing Nitinol's performance in electrofluidic applications through various material science techniques. One key area of improvement has been the optimization of Nitinol's composition and microstructure. By fine-tuning the nickel-titanium ratio and incorporating trace elements, researchers have successfully tailored Nitinol's transformation temperatures and mechanical properties to suit specific electrofluidic device requirements.
Surface modification techniques have also played a crucial role in advancing Nitinol's capabilities. Novel coating methods, such as plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition and atomic layer deposition, have been developed to improve Nitinol's biocompatibility and corrosion resistance. These coatings not only enhance the material's durability but also enable better integration with biological systems in biomedical electrofluidic devices.
Another significant advancement has been the development of Nitinol-based composite materials. By combining Nitinol with other materials like polymers or ceramics, researchers have created hybrid structures that exhibit enhanced electrical conductivity, improved thermal management, and superior mechanical properties. These composites have opened up new possibilities for designing more efficient and versatile electrofluidic devices.
Nanotechnology has also made substantial contributions to Nitinol's advancement in electrofluidics. The fabrication of Nitinol nanostructures, such as nanowires and nanoparticles, has enabled the creation of highly sensitive and responsive electrofluidic sensors. These nanostructures offer increased surface area and unique physical properties, leading to improved device performance and sensitivity.
Furthermore, advancements in manufacturing techniques have greatly expanded the potential applications of Nitinol in electrofluidic devices. Precision machining, additive manufacturing, and laser processing have enabled the production of complex Nitinol structures with intricate geometries and controlled porosity. These manufacturing capabilities have facilitated the development of novel electrofluidic device designs that were previously unattainable.
The integration of smart materials and adaptive systems has also been a key focus in recent Nitinol research. By combining Nitinol with other functional materials, such as piezoelectric or magnetostrictive elements, researchers have created multifunctional electrofluidic devices capable of responding to various external stimuli. This integration has led to the development of self-regulating and adaptive electrofluidic systems with enhanced performance and versatility.
Recent research has focused on enhancing Nitinol's performance in electrofluidic applications through various material science techniques. One key area of improvement has been the optimization of Nitinol's composition and microstructure. By fine-tuning the nickel-titanium ratio and incorporating trace elements, researchers have successfully tailored Nitinol's transformation temperatures and mechanical properties to suit specific electrofluidic device requirements.
Surface modification techniques have also played a crucial role in advancing Nitinol's capabilities. Novel coating methods, such as plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition and atomic layer deposition, have been developed to improve Nitinol's biocompatibility and corrosion resistance. These coatings not only enhance the material's durability but also enable better integration with biological systems in biomedical electrofluidic devices.
Another significant advancement has been the development of Nitinol-based composite materials. By combining Nitinol with other materials like polymers or ceramics, researchers have created hybrid structures that exhibit enhanced electrical conductivity, improved thermal management, and superior mechanical properties. These composites have opened up new possibilities for designing more efficient and versatile electrofluidic devices.
Nanotechnology has also made substantial contributions to Nitinol's advancement in electrofluidics. The fabrication of Nitinol nanostructures, such as nanowires and nanoparticles, has enabled the creation of highly sensitive and responsive electrofluidic sensors. These nanostructures offer increased surface area and unique physical properties, leading to improved device performance and sensitivity.
Furthermore, advancements in manufacturing techniques have greatly expanded the potential applications of Nitinol in electrofluidic devices. Precision machining, additive manufacturing, and laser processing have enabled the production of complex Nitinol structures with intricate geometries and controlled porosity. These manufacturing capabilities have facilitated the development of novel electrofluidic device designs that were previously unattainable.
The integration of smart materials and adaptive systems has also been a key focus in recent Nitinol research. By combining Nitinol with other functional materials, such as piezoelectric or magnetostrictive elements, researchers have created multifunctional electrofluidic devices capable of responding to various external stimuli. This integration has led to the development of self-regulating and adaptive electrofluidic systems with enhanced performance and versatility.
Environmental Impact of Nitinol-Based Electrofluidic Devices
The environmental impact of Nitinol-based electrofluidic devices is a crucial consideration in the development and deployment of these innovative technologies. As Nitinol continues to reshape the landscape of electrofluidic devices, it is essential to assess both the positive and negative environmental implications throughout their lifecycle.
One of the primary environmental benefits of Nitinol-based electrofluidic devices is their potential for increased energy efficiency. The unique shape memory and superelastic properties of Nitinol allow for the creation of more compact and responsive devices, potentially reducing overall energy consumption in various applications. This efficiency can lead to decreased power requirements and, consequently, lower greenhouse gas emissions associated with energy production.
However, the production of Nitinol itself raises environmental concerns. The alloy's primary components, nickel and titanium, are both energy-intensive to extract and process. The mining and refining of these metals can contribute to habitat destruction, water pollution, and increased carbon emissions. Additionally, the precise manufacturing processes required for Nitinol production often involve high temperatures and specialized equipment, further adding to the environmental footprint.
The durability and longevity of Nitinol-based devices present a double-edged sword from an environmental perspective. On one hand, the extended lifespan of these devices can reduce the frequency of replacement and disposal, potentially decreasing electronic waste. On the other hand, the complex composition of Nitinol alloys can make recycling and proper disposal challenging, potentially leading to accumulation in landfills or improper handling of hazardous materials.
In the context of electrofluidic devices, the use of Nitinol may also impact the types and quantities of fluids used in these systems. The material's unique properties could allow for more precise control and manipulation of fluids, potentially reducing waste and the need for harmful chemicals in certain applications. However, this benefit must be weighed against the potential for increased use of specialized fluids that may have their own environmental implications.
The miniaturization capabilities enabled by Nitinol in electrofluidic devices could lead to reduced material usage overall, contributing to resource conservation. This reduction in size and material requirements could also translate to more efficient transportation and distribution of these devices, further lowering their carbon footprint.
As research and development in this field progress, it is crucial to prioritize eco-friendly design principles and sustainable manufacturing processes for Nitinol-based electrofluidic devices. This includes exploring alternative production methods for Nitinol that minimize environmental impact, developing effective recycling techniques for end-of-life devices, and optimizing the overall lifecycle management of these technologies.
One of the primary environmental benefits of Nitinol-based electrofluidic devices is their potential for increased energy efficiency. The unique shape memory and superelastic properties of Nitinol allow for the creation of more compact and responsive devices, potentially reducing overall energy consumption in various applications. This efficiency can lead to decreased power requirements and, consequently, lower greenhouse gas emissions associated with energy production.
However, the production of Nitinol itself raises environmental concerns. The alloy's primary components, nickel and titanium, are both energy-intensive to extract and process. The mining and refining of these metals can contribute to habitat destruction, water pollution, and increased carbon emissions. Additionally, the precise manufacturing processes required for Nitinol production often involve high temperatures and specialized equipment, further adding to the environmental footprint.
The durability and longevity of Nitinol-based devices present a double-edged sword from an environmental perspective. On one hand, the extended lifespan of these devices can reduce the frequency of replacement and disposal, potentially decreasing electronic waste. On the other hand, the complex composition of Nitinol alloys can make recycling and proper disposal challenging, potentially leading to accumulation in landfills or improper handling of hazardous materials.
In the context of electrofluidic devices, the use of Nitinol may also impact the types and quantities of fluids used in these systems. The material's unique properties could allow for more precise control and manipulation of fluids, potentially reducing waste and the need for harmful chemicals in certain applications. However, this benefit must be weighed against the potential for increased use of specialized fluids that may have their own environmental implications.
The miniaturization capabilities enabled by Nitinol in electrofluidic devices could lead to reduced material usage overall, contributing to resource conservation. This reduction in size and material requirements could also translate to more efficient transportation and distribution of these devices, further lowering their carbon footprint.
As research and development in this field progress, it is crucial to prioritize eco-friendly design principles and sustainable manufacturing processes for Nitinol-based electrofluidic devices. This includes exploring alternative production methods for Nitinol that minimize environmental impact, developing effective recycling techniques for end-of-life devices, and optimizing the overall lifecycle management of these technologies.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!