Analysis of exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) in L92 engines
AUG 14, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
EGR Technology Evolution in L92 Engines
The evolution of Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) technology in L92 engines represents a significant advancement in automotive engineering, aimed at reducing emissions and improving engine efficiency. The L92 engine, a 6.2-liter V8 powerplant developed by General Motors, has been a testbed for EGR innovations over the years.
In the early stages of EGR implementation on L92 engines, the focus was primarily on reducing nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions. The initial systems were relatively simple, utilizing a basic valve to redirect a portion of exhaust gases back into the intake manifold. This approach effectively lowered combustion temperatures, thereby reducing NOx formation.
As environmental regulations became more stringent, EGR systems in L92 engines evolved to incorporate more sophisticated control mechanisms. Electronic control units (ECUs) were introduced to precisely manage the amount of recirculated exhaust gas based on various engine parameters such as load, speed, and temperature. This allowed for more dynamic and efficient EGR operation across different driving conditions.
The next significant leap in EGR technology for L92 engines came with the introduction of cooled EGR systems. By cooling the recirculated exhaust gases before reintroducing them into the combustion chamber, engineers were able to further reduce NOx emissions while also improving fuel efficiency. This cooling process typically involved passing the exhaust gases through a heat exchanger, often integrated into the engine's cooling system.
As materials science advanced, so did the components used in EGR systems. High-temperature resistant alloys and advanced ceramics were employed to construct EGR valves and coolers, enhancing durability and performance under the extreme conditions present in exhaust systems. These improvements allowed for higher EGR rates without compromising system longevity.
The integration of variable geometry turbochargers (VGTs) with EGR systems marked another milestone in L92 engine development. This combination allowed for better control of exhaust backpressure and EGR flow, optimizing the balance between emissions reduction and engine performance across a wider operating range.
Recent advancements have seen the implementation of low-pressure EGR systems in L92 engines. Unlike traditional high-pressure systems that recirculate exhaust gases from before the turbocharger, low-pressure EGR takes gases from after the particulate filter, resulting in cleaner recirculated exhaust and potentially lower pumping losses.
Looking forward, the evolution of EGR technology in L92 engines is likely to continue with the integration of advanced sensors and predictive control algorithms. These developments promise to further optimize EGR operation, potentially allowing for real-time adjustments based on anticipated driving conditions and environmental factors.
In the early stages of EGR implementation on L92 engines, the focus was primarily on reducing nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions. The initial systems were relatively simple, utilizing a basic valve to redirect a portion of exhaust gases back into the intake manifold. This approach effectively lowered combustion temperatures, thereby reducing NOx formation.
As environmental regulations became more stringent, EGR systems in L92 engines evolved to incorporate more sophisticated control mechanisms. Electronic control units (ECUs) were introduced to precisely manage the amount of recirculated exhaust gas based on various engine parameters such as load, speed, and temperature. This allowed for more dynamic and efficient EGR operation across different driving conditions.
The next significant leap in EGR technology for L92 engines came with the introduction of cooled EGR systems. By cooling the recirculated exhaust gases before reintroducing them into the combustion chamber, engineers were able to further reduce NOx emissions while also improving fuel efficiency. This cooling process typically involved passing the exhaust gases through a heat exchanger, often integrated into the engine's cooling system.
As materials science advanced, so did the components used in EGR systems. High-temperature resistant alloys and advanced ceramics were employed to construct EGR valves and coolers, enhancing durability and performance under the extreme conditions present in exhaust systems. These improvements allowed for higher EGR rates without compromising system longevity.
The integration of variable geometry turbochargers (VGTs) with EGR systems marked another milestone in L92 engine development. This combination allowed for better control of exhaust backpressure and EGR flow, optimizing the balance between emissions reduction and engine performance across a wider operating range.
Recent advancements have seen the implementation of low-pressure EGR systems in L92 engines. Unlike traditional high-pressure systems that recirculate exhaust gases from before the turbocharger, low-pressure EGR takes gases from after the particulate filter, resulting in cleaner recirculated exhaust and potentially lower pumping losses.
Looking forward, the evolution of EGR technology in L92 engines is likely to continue with the integration of advanced sensors and predictive control algorithms. These developments promise to further optimize EGR operation, potentially allowing for real-time adjustments based on anticipated driving conditions and environmental factors.
Market Demand for EGR Systems
The market demand for Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) systems in L92 engines has been steadily growing due to increasingly stringent emissions regulations and the automotive industry's focus on improving fuel efficiency. As governments worldwide implement stricter emission standards, particularly for nitrogen oxides (NOx), the adoption of EGR technology has become crucial for engine manufacturers to meet these requirements.
In the passenger vehicle segment, where L92 engines are commonly used, there is a significant demand for EGR systems. This demand is driven by the need to reduce fuel consumption and emissions while maintaining or improving engine performance. The L92 engine, being a high-performance V8 engine, requires advanced EGR solutions to balance power output with environmental compliance.
The commercial vehicle sector also contributes to the growing market for EGR systems in L92 engines. As fleet operators seek to reduce operating costs and comply with emissions regulations, the demand for efficient EGR solutions has increased. This trend is particularly evident in markets where diesel engines are prevalent, as EGR technology is effective in reducing NOx emissions from diesel combustion.
The aftermarket segment presents another avenue for EGR system demand. As older vehicles equipped with L92 engines require upgrades to meet newer emissions standards, there is a market for retrofitting advanced EGR systems. This creates opportunities for aftermarket suppliers and service providers specializing in emissions control technologies.
Geographically, the demand for EGR systems in L92 engines varies across regions. North America and Europe, with their stringent emissions regulations, show strong market potential. Emerging markets in Asia and Latin America are also experiencing growth in demand as they adopt more rigorous environmental standards and seek to improve air quality in urban areas.
The market for EGR systems is influenced by technological advancements in engine design and materials. As manufacturers develop more efficient and durable EGR components, the overall system performance improves, driving further adoption. Additionally, the integration of EGR with other emissions control technologies, such as selective catalytic reduction (SCR), creates a more comprehensive solution for meeting emissions targets.
Looking ahead, the market demand for EGR systems in L92 engines is expected to continue its upward trajectory. This growth is supported by ongoing research and development efforts to enhance EGR efficiency, reduce system costs, and optimize integration with engine management systems. As the automotive industry transitions towards electrification, the demand for advanced EGR systems in hybrid powertrains incorporating L92 engines is likely to emerge as a new market segment.
In the passenger vehicle segment, where L92 engines are commonly used, there is a significant demand for EGR systems. This demand is driven by the need to reduce fuel consumption and emissions while maintaining or improving engine performance. The L92 engine, being a high-performance V8 engine, requires advanced EGR solutions to balance power output with environmental compliance.
The commercial vehicle sector also contributes to the growing market for EGR systems in L92 engines. As fleet operators seek to reduce operating costs and comply with emissions regulations, the demand for efficient EGR solutions has increased. This trend is particularly evident in markets where diesel engines are prevalent, as EGR technology is effective in reducing NOx emissions from diesel combustion.
The aftermarket segment presents another avenue for EGR system demand. As older vehicles equipped with L92 engines require upgrades to meet newer emissions standards, there is a market for retrofitting advanced EGR systems. This creates opportunities for aftermarket suppliers and service providers specializing in emissions control technologies.
Geographically, the demand for EGR systems in L92 engines varies across regions. North America and Europe, with their stringent emissions regulations, show strong market potential. Emerging markets in Asia and Latin America are also experiencing growth in demand as they adopt more rigorous environmental standards and seek to improve air quality in urban areas.
The market for EGR systems is influenced by technological advancements in engine design and materials. As manufacturers develop more efficient and durable EGR components, the overall system performance improves, driving further adoption. Additionally, the integration of EGR with other emissions control technologies, such as selective catalytic reduction (SCR), creates a more comprehensive solution for meeting emissions targets.
Looking ahead, the market demand for EGR systems in L92 engines is expected to continue its upward trajectory. This growth is supported by ongoing research and development efforts to enhance EGR efficiency, reduce system costs, and optimize integration with engine management systems. As the automotive industry transitions towards electrification, the demand for advanced EGR systems in hybrid powertrains incorporating L92 engines is likely to emerge as a new market segment.
Current EGR Challenges in L92 Engines
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) systems in L92 engines face several significant challenges that impact their performance and efficiency. One of the primary issues is the precise control of EGR flow rates across varying engine operating conditions. The L92 engine, known for its high performance and power output, requires a delicate balance of EGR to maintain optimal combustion characteristics while reducing emissions.
The high exhaust gas temperatures in L92 engines pose a considerable challenge for EGR systems. These elevated temperatures can lead to thermal stress on EGR components, potentially causing premature wear or failure. Additionally, the high-temperature exhaust gases can contribute to increased formation of deposits in the EGR system, leading to reduced efficiency and potential blockages over time.
Another significant challenge is the integration of EGR systems with advanced engine management technologies. The L92 engine's sophisticated electronic control systems require seamless coordination with the EGR system to maintain optimal air-fuel ratios and combustion timing. This integration becomes increasingly complex as emissions standards become more stringent, necessitating more precise control over EGR rates.
The packaging constraints within the L92 engine compartment present another hurdle for EGR system design. The limited space available for EGR components, such as coolers and valves, can lead to compromises in system efficiency and cooling capacity. Engineers must balance the need for effective EGR with the spatial limitations imposed by the engine's compact design.
Durability and reliability of EGR components in the high-performance environment of L92 engines remain ongoing challenges. The frequent high-load operations and rapid temperature fluctuations can accelerate wear on EGR valves, coolers, and associated piping. Ensuring long-term reliability while maintaining system effectiveness is a critical concern for manufacturers and engine designers.
The impact of EGR on engine performance and fuel efficiency is another area of focus. While EGR is essential for emissions control, it can potentially reduce engine power output and fuel economy if not optimally implemented. Striking the right balance between emissions reduction and performance preservation is a delicate task that requires continuous refinement and innovation in EGR system design for L92 engines.
Lastly, the challenge of maintaining EGR system effectiveness across the engine's entire operating range persists. The L92 engine's wide power band and varied use cases, from idle to full throttle, demand an EGR system that can adapt quickly and efficiently to changing conditions. This requirement puts additional strain on the system's components and control algorithms, necessitating advanced engineering solutions to ensure consistent performance and emissions compliance.
The high exhaust gas temperatures in L92 engines pose a considerable challenge for EGR systems. These elevated temperatures can lead to thermal stress on EGR components, potentially causing premature wear or failure. Additionally, the high-temperature exhaust gases can contribute to increased formation of deposits in the EGR system, leading to reduced efficiency and potential blockages over time.
Another significant challenge is the integration of EGR systems with advanced engine management technologies. The L92 engine's sophisticated electronic control systems require seamless coordination with the EGR system to maintain optimal air-fuel ratios and combustion timing. This integration becomes increasingly complex as emissions standards become more stringent, necessitating more precise control over EGR rates.
The packaging constraints within the L92 engine compartment present another hurdle for EGR system design. The limited space available for EGR components, such as coolers and valves, can lead to compromises in system efficiency and cooling capacity. Engineers must balance the need for effective EGR with the spatial limitations imposed by the engine's compact design.
Durability and reliability of EGR components in the high-performance environment of L92 engines remain ongoing challenges. The frequent high-load operations and rapid temperature fluctuations can accelerate wear on EGR valves, coolers, and associated piping. Ensuring long-term reliability while maintaining system effectiveness is a critical concern for manufacturers and engine designers.
The impact of EGR on engine performance and fuel efficiency is another area of focus. While EGR is essential for emissions control, it can potentially reduce engine power output and fuel economy if not optimally implemented. Striking the right balance between emissions reduction and performance preservation is a delicate task that requires continuous refinement and innovation in EGR system design for L92 engines.
Lastly, the challenge of maintaining EGR system effectiveness across the engine's entire operating range persists. The L92 engine's wide power band and varied use cases, from idle to full throttle, demand an EGR system that can adapt quickly and efficiently to changing conditions. This requirement puts additional strain on the system's components and control algorithms, necessitating advanced engineering solutions to ensure consistent performance and emissions compliance.
Existing EGR Solutions for L92 Engines
01 EGR system design and components
Exhaust gas recirculation systems are designed with various components to effectively recirculate exhaust gases. These systems may include valves, coolers, and sensors to control the flow and temperature of recirculated gases. The design aims to optimize engine performance while reducing emissions.- EGR system design and components: Exhaust gas recirculation systems are designed with various components to effectively recirculate exhaust gases. These systems may include valves, coolers, and sensors to control the flow and temperature of recirculated gases. The design aims to optimize engine performance while reducing emissions.
- EGR control strategies: Advanced control strategies are implemented to manage EGR systems effectively. These may involve electronic control units, feedback mechanisms, and adaptive algorithms to adjust EGR rates based on engine operating conditions. The goal is to maintain optimal engine performance while meeting emission standards.
- EGR cooling techniques: Various cooling techniques are employed in EGR systems to reduce the temperature of recirculated exhaust gases. This may include the use of heat exchangers, multiple cooling stages, or integration with engine cooling systems. Effective cooling helps improve engine efficiency and reduce emissions.
- EGR for emissions reduction: EGR systems are primarily used to reduce nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions from internal combustion engines. By recirculating a portion of the exhaust gas back into the combustion chamber, peak combustion temperatures are lowered, resulting in reduced NOx formation. This technology is crucial for meeting stringent emission regulations.
- EGR measurement and diagnostics: Accurate measurement and diagnostics of EGR systems are essential for maintaining optimal performance. This may involve the use of specialized sensors, flow meters, and diagnostic algorithms to monitor EGR rates, detect faults, and ensure proper system operation. These techniques help in maintaining engine efficiency and emissions compliance.
02 EGR control strategies
Advanced control strategies are implemented to manage EGR systems efficiently. These may involve electronic control units, feedback mechanisms, and adaptive algorithms to adjust EGR rates based on engine operating conditions. The goal is to maintain optimal engine performance while meeting emission standards.Expand Specific Solutions03 EGR cooling techniques
Various cooling techniques are employed in EGR systems to reduce the temperature of recirculated exhaust gases. This may include the use of heat exchangers, multi-stage cooling, or integration with engine cooling systems. Effective cooling of EGR gases helps improve engine efficiency and reduce emissions.Expand Specific Solutions04 EGR measurement and monitoring
Accurate measurement and monitoring of EGR flow rates and composition are crucial for system optimization. This may involve the use of specialized sensors, flow meters, and diagnostic systems to ensure proper EGR operation and detect potential issues.Expand Specific Solutions05 Integration of EGR with other emission control technologies
EGR systems are often integrated with other emission control technologies to achieve comprehensive emission reduction. This may include combining EGR with selective catalytic reduction (SCR), diesel particulate filters (DPF), or advanced combustion strategies to meet stringent emission regulations.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in EGR Technology
The exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) technology for L92 engines is in a mature stage of development, with a competitive landscape dominated by established automotive and engine manufacturers. The market for EGR systems is substantial, driven by stringent emissions regulations and the continued prevalence of internal combustion engines. Key players like GM Global Technology Operations, Toyota Motor Corp., and Cummins Inc. have made significant advancements in EGR technology, focusing on improving efficiency and reducing emissions. Other companies such as BorgWarner and Johnson Matthey are also contributing to innovations in this field, particularly in areas of EGR coolers and related components. The technology's maturity is evident from its widespread adoption across various vehicle types and engine configurations.
GM Global Technology Operations LLC
Technical Solution: GM has developed an advanced EGR system for L92 engines that utilizes a dual-loop configuration, combining both high-pressure and low-pressure EGR circuits[1]. This system allows for precise control of exhaust gas recirculation across a wide range of engine operating conditions. The high-pressure loop recirculates exhaust gases before the turbocharger, while the low-pressure loop takes gases after the particulate filter, providing cleaner recirculated exhaust[2]. GM's system also incorporates an EGR cooler to further reduce NOx emissions by lowering the temperature of the recirculated gases[3]. Additionally, they have implemented an advanced control strategy that optimizes EGR rates based on real-time engine parameters and driving conditions[4].
Strengths: Dual-loop configuration allows for more precise EGR control; cooled EGR reduces NOx emissions effectively; advanced control strategy optimizes performance. Weaknesses: Increased system complexity may lead to higher manufacturing and maintenance costs; potential for cooler fouling in certain operating conditions.
Weichai Power
Technical Solution: Weichai Power has developed a high-efficiency EGR system for their engines, including those similar to L92 specifications. Their approach focuses on a variable geometry turbocharger (VGT) integrated with EGR to optimize exhaust gas recirculation across different load conditions[5]. The system utilizes an electronically controlled EGR valve that adjusts the recirculation rate based on engine speed, load, and temperature sensors[6]. Weichai has also implemented an advanced EGR cooling system that employs a two-stage cooler design, allowing for better temperature control of the recirculated gases[7]. This design helps in maintaining optimal combustion temperatures and reducing NOx emissions more effectively.
Strengths: VGT integration allows for better EGR control across various engine loads; two-stage cooler design provides efficient temperature management. Weaknesses: May require more complex control algorithms; potential for increased fuel consumption in certain operating ranges.
Core EGR Innovations for L92 Engines
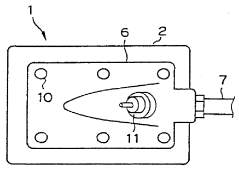
Exhaust gas recirculation device for internal combustion engine
PatentInactiveJP2015113737A
Innovation
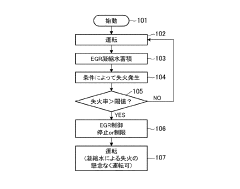
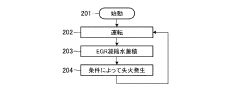
- An exhaust gas recirculation system with a misfire detection mechanism that calculates the misfire rate and adjusts the recirculation valve to close or limit EGR control when the misfire rate exceeds a set threshold, incorporating a condensed water reservoir to temporarily store condensed water, thereby preventing misfires.
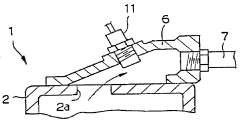
Exhaust gas recirculation system for internal combustion engine
PatentInactiveUS4870941A
Innovation
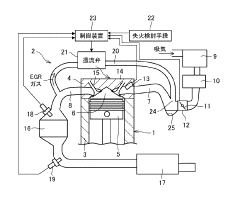
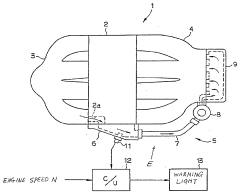
- A temperature sensor is positioned upstream of the EGR valve within the EGR passage to detect temperature variations of recirculated exhaust gas, enabling precise abnormality diagnosis without causing thermal damage, even at lower recirculation rates, by utilizing an EGR system configuration that includes an EGR passage connecting the exhaust and intake systems, an EGR valve for flow control, and a temperature sensor to output temperature signals for abnormality detection.
Emissions Regulations Impact on EGR
Emissions regulations have played a pivotal role in shaping the development and implementation of Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) systems in L92 engines. As environmental concerns have grown, governments worldwide have introduced increasingly stringent emissions standards, particularly targeting nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter (PM) emissions from internal combustion engines.
The introduction of Euro 6 standards in Europe and Tier 3 standards in the United States has significantly impacted the automotive industry, pushing manufacturers to adopt advanced emission control technologies. EGR has emerged as a crucial technology in meeting these stringent requirements, particularly for diesel engines. The L92 engine, primarily used in high-performance vehicles, has also been subject to these regulations, necessitating the integration of EGR systems to reduce NOx emissions.
Regulatory bodies have set specific targets for NOx reduction, which has directly influenced the design and calibration of EGR systems in L92 engines. Manufacturers have been compelled to optimize EGR rates and control strategies to balance performance requirements with emissions compliance. This has led to the development of more sophisticated EGR systems, including cooled EGR and variable geometry turbochargers, to enhance the effectiveness of exhaust gas recirculation across a wider range of operating conditions.
The impact of emissions regulations on EGR in L92 engines extends beyond mere compliance. It has driven innovation in materials and design, leading to more durable and efficient EGR components capable of withstanding the harsh operating conditions of high-performance engines. Additionally, the need for precise control of EGR has spurred advancements in engine management systems and sensors, contributing to overall improvements in engine efficiency and performance.
Furthermore, the regulatory landscape has influenced the cost structure of L92 engines, as manufacturers invest in research and development to meet emissions targets while maintaining performance characteristics. This has led to a reevaluation of engine design priorities, with emissions control becoming a central consideration alongside traditional performance metrics.
As regulations continue to evolve, the role of EGR in L92 engines is expected to grow, potentially leading to the integration of more advanced technologies such as low-pressure EGR systems and electrified EGR actuators. These developments underscore the ongoing impact of emissions regulations on engine technology and highlight the critical role of EGR in meeting future environmental standards while preserving the performance attributes of high-output engines like the L92.
The introduction of Euro 6 standards in Europe and Tier 3 standards in the United States has significantly impacted the automotive industry, pushing manufacturers to adopt advanced emission control technologies. EGR has emerged as a crucial technology in meeting these stringent requirements, particularly for diesel engines. The L92 engine, primarily used in high-performance vehicles, has also been subject to these regulations, necessitating the integration of EGR systems to reduce NOx emissions.
Regulatory bodies have set specific targets for NOx reduction, which has directly influenced the design and calibration of EGR systems in L92 engines. Manufacturers have been compelled to optimize EGR rates and control strategies to balance performance requirements with emissions compliance. This has led to the development of more sophisticated EGR systems, including cooled EGR and variable geometry turbochargers, to enhance the effectiveness of exhaust gas recirculation across a wider range of operating conditions.
The impact of emissions regulations on EGR in L92 engines extends beyond mere compliance. It has driven innovation in materials and design, leading to more durable and efficient EGR components capable of withstanding the harsh operating conditions of high-performance engines. Additionally, the need for precise control of EGR has spurred advancements in engine management systems and sensors, contributing to overall improvements in engine efficiency and performance.
Furthermore, the regulatory landscape has influenced the cost structure of L92 engines, as manufacturers invest in research and development to meet emissions targets while maintaining performance characteristics. This has led to a reevaluation of engine design priorities, with emissions control becoming a central consideration alongside traditional performance metrics.
As regulations continue to evolve, the role of EGR in L92 engines is expected to grow, potentially leading to the integration of more advanced technologies such as low-pressure EGR systems and electrified EGR actuators. These developments underscore the ongoing impact of emissions regulations on engine technology and highlight the critical role of EGR in meeting future environmental standards while preserving the performance attributes of high-output engines like the L92.
EGR System Integration Strategies
The integration of Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) systems into L92 engines requires careful consideration of various strategies to optimize performance, emissions reduction, and overall engine efficiency. One key approach involves the strategic placement of EGR coolers within the engine architecture. By positioning coolers in close proximity to the intake manifold, engineers can minimize heat transfer losses and ensure more effective cooling of recirculated exhaust gases. This placement strategy also helps reduce the overall system size, which is crucial for packaging constraints in modern engine designs.
Another important aspect of EGR system integration is the implementation of advanced control algorithms. These algorithms dynamically adjust EGR rates based on real-time engine operating conditions, such as load, speed, and temperature. By utilizing sophisticated sensors and electronic control units (ECUs), the EGR system can respond rapidly to changing engine demands, optimizing the balance between NOx reduction and fuel efficiency across various driving scenarios.
Material selection plays a critical role in EGR system integration for L92 engines. High-temperature resistant alloys and advanced ceramics are increasingly being employed for EGR valve components and piping to withstand the harsh exhaust gas environment. These materials not only improve durability but also contribute to weight reduction, which is essential for overall vehicle efficiency.
The integration of EGR systems with turbocharging technology presents both challenges and opportunities. Engineers must carefully design the interaction between these two systems to prevent compressor surge and ensure stable engine operation. One effective strategy involves the use of a low-pressure EGR loop, which recirculates exhaust gases downstream of the turbine and upstream of the compressor. This configuration can help maintain optimal turbocharger performance while still achieving desired EGR rates.
To address potential issues with EGR system fouling and clogging, innovative cleaning mechanisms are being incorporated into L92 engine designs. These may include self-cleaning EGR coolers with bypass systems or periodic high-temperature regeneration cycles to remove carbon deposits. Such features enhance long-term system reliability and maintain EGR efficiency over the engine's lifespan.
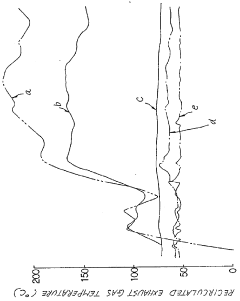
Lastly, the integration of EGR systems in L92 engines is increasingly being optimized through the use of computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations and advanced modeling techniques. These tools allow engineers to predict and fine-tune EGR flow patterns, mixing characteristics, and thermal management before physical prototyping, significantly reducing development time and costs while improving overall system performance.
Another important aspect of EGR system integration is the implementation of advanced control algorithms. These algorithms dynamically adjust EGR rates based on real-time engine operating conditions, such as load, speed, and temperature. By utilizing sophisticated sensors and electronic control units (ECUs), the EGR system can respond rapidly to changing engine demands, optimizing the balance between NOx reduction and fuel efficiency across various driving scenarios.
Material selection plays a critical role in EGR system integration for L92 engines. High-temperature resistant alloys and advanced ceramics are increasingly being employed for EGR valve components and piping to withstand the harsh exhaust gas environment. These materials not only improve durability but also contribute to weight reduction, which is essential for overall vehicle efficiency.
The integration of EGR systems with turbocharging technology presents both challenges and opportunities. Engineers must carefully design the interaction between these two systems to prevent compressor surge and ensure stable engine operation. One effective strategy involves the use of a low-pressure EGR loop, which recirculates exhaust gases downstream of the turbine and upstream of the compressor. This configuration can help maintain optimal turbocharger performance while still achieving desired EGR rates.
To address potential issues with EGR system fouling and clogging, innovative cleaning mechanisms are being incorporated into L92 engine designs. These may include self-cleaning EGR coolers with bypass systems or periodic high-temperature regeneration cycles to remove carbon deposits. Such features enhance long-term system reliability and maintain EGR efficiency over the engine's lifespan.
Lastly, the integration of EGR systems in L92 engines is increasingly being optimized through the use of computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations and advanced modeling techniques. These tools allow engineers to predict and fine-tune EGR flow patterns, mixing characteristics, and thermal management before physical prototyping, significantly reducing development time and costs while improving overall system performance.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!