L92 engine contributions to lightweighting in vehicles
AUG 14, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
L92 Engine Background
The L92 engine, developed by General Motors, represents a significant milestone in automotive engineering, particularly in the context of vehicle lightweighting. Introduced in the mid-2000s, this engine was designed to address the growing demand for more fuel-efficient and environmentally friendly vehicles while maintaining high performance standards.
The L92 is a 6.2-liter V8 engine that belongs to the GM small-block engine family. It was primarily used in high-performance vehicles and luxury SUVs, including models from Chevrolet, GMC, and Cadillac. The engine's design incorporated several innovative features that contributed to weight reduction and improved efficiency.
One of the key aspects of the L92 engine's contribution to lightweighting is its aluminum construction. The engine block and cylinder heads are made from aluminum alloy, significantly reducing the overall weight compared to traditional iron-block engines. This weight reduction not only improves fuel efficiency but also enhances vehicle handling and performance.
The L92 engine also features variable valve timing (VVT) technology, which optimizes engine performance across different operating conditions. This technology allows for better fuel economy and reduced emissions without sacrificing power output. The VVT system itself is designed with lightweight components, further contributing to the engine's overall weight reduction.
Another notable feature of the L92 engine is its high-flow cylinder heads. These heads are designed to maximize airflow, which improves combustion efficiency and power output. The efficient design of these heads allows for better performance with less material, contributing to the engine's lightweight characteristics.
The engine's intake manifold is made from composite materials, further reducing weight compared to traditional metal manifolds. This not only contributes to the overall lightweighting of the vehicle but also improves heat management and engine efficiency.
The L92 engine's pistons are designed with a lightweight yet durable construction, featuring a flat-top design that enhances combustion efficiency. The connecting rods are also optimized for weight reduction while maintaining strength, contributing to the engine's overall lightweight design.
In the context of vehicle lightweighting, the L92 engine demonstrates how advanced engineering can achieve significant weight reductions in critical components without compromising performance. This approach aligns with the broader automotive industry trend towards creating more efficient and environmentally friendly vehicles.
The L92 is a 6.2-liter V8 engine that belongs to the GM small-block engine family. It was primarily used in high-performance vehicles and luxury SUVs, including models from Chevrolet, GMC, and Cadillac. The engine's design incorporated several innovative features that contributed to weight reduction and improved efficiency.
One of the key aspects of the L92 engine's contribution to lightweighting is its aluminum construction. The engine block and cylinder heads are made from aluminum alloy, significantly reducing the overall weight compared to traditional iron-block engines. This weight reduction not only improves fuel efficiency but also enhances vehicle handling and performance.
The L92 engine also features variable valve timing (VVT) technology, which optimizes engine performance across different operating conditions. This technology allows for better fuel economy and reduced emissions without sacrificing power output. The VVT system itself is designed with lightweight components, further contributing to the engine's overall weight reduction.
Another notable feature of the L92 engine is its high-flow cylinder heads. These heads are designed to maximize airflow, which improves combustion efficiency and power output. The efficient design of these heads allows for better performance with less material, contributing to the engine's lightweight characteristics.
The engine's intake manifold is made from composite materials, further reducing weight compared to traditional metal manifolds. This not only contributes to the overall lightweighting of the vehicle but also improves heat management and engine efficiency.
The L92 engine's pistons are designed with a lightweight yet durable construction, featuring a flat-top design that enhances combustion efficiency. The connecting rods are also optimized for weight reduction while maintaining strength, contributing to the engine's overall lightweight design.
In the context of vehicle lightweighting, the L92 engine demonstrates how advanced engineering can achieve significant weight reductions in critical components without compromising performance. This approach aligns with the broader automotive industry trend towards creating more efficient and environmentally friendly vehicles.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for lightweight vehicles has been steadily increasing in recent years, driven by stringent fuel efficiency regulations, environmental concerns, and consumer preferences for improved performance. The L92 engine, known for its lightweight design and high power output, has emerged as a significant contributor to vehicle lightweighting efforts.
In the automotive industry, there is a growing emphasis on reducing vehicle weight to improve fuel economy and reduce emissions. This trend has created a substantial market for lightweight components and materials, including advanced engine designs like the L92. The global automotive lightweight materials market is expected to grow significantly, reflecting the increasing demand for weight reduction solutions across various vehicle segments.
The L92 engine, with its aluminum construction and innovative design features, aligns well with this market demand. Its lightweight nature contributes to overall vehicle weight reduction, which is crucial for meeting fuel efficiency standards and reducing carbon emissions. This engine's ability to deliver high performance while maintaining a lower weight profile makes it particularly attractive to manufacturers seeking to balance power and efficiency.
Consumer preferences also play a significant role in driving the demand for lightweight vehicles. As fuel prices fluctuate and environmental awareness grows, consumers are increasingly seeking vehicles that offer better fuel economy without compromising on performance. The L92 engine's contribution to lightweighting helps address these consumer needs, potentially influencing purchasing decisions and market trends.
In the commercial vehicle sector, there is a strong demand for lightweight solutions to increase payload capacity and improve fuel efficiency. The L92 engine's lightweight design can contribute to these goals, making it relevant for a wide range of vehicle applications beyond passenger cars.
The market demand for lightweight technologies like the L92 engine is further amplified by government regulations aimed at reducing vehicle emissions and improving fuel economy. These regulations create a strong incentive for automakers to invest in and adopt lightweight technologies across their vehicle lineups.
As the automotive industry continues to evolve towards electrification, the demand for lightweight components remains critical. Even in hybrid and electric vehicles, weight reduction plays a crucial role in extending range and improving overall efficiency. The principles and technologies developed for engines like the L92 can potentially be applied to other vehicle systems, contributing to broader lightweighting efforts in the industry.
In the automotive industry, there is a growing emphasis on reducing vehicle weight to improve fuel economy and reduce emissions. This trend has created a substantial market for lightweight components and materials, including advanced engine designs like the L92. The global automotive lightweight materials market is expected to grow significantly, reflecting the increasing demand for weight reduction solutions across various vehicle segments.
The L92 engine, with its aluminum construction and innovative design features, aligns well with this market demand. Its lightweight nature contributes to overall vehicle weight reduction, which is crucial for meeting fuel efficiency standards and reducing carbon emissions. This engine's ability to deliver high performance while maintaining a lower weight profile makes it particularly attractive to manufacturers seeking to balance power and efficiency.
Consumer preferences also play a significant role in driving the demand for lightweight vehicles. As fuel prices fluctuate and environmental awareness grows, consumers are increasingly seeking vehicles that offer better fuel economy without compromising on performance. The L92 engine's contribution to lightweighting helps address these consumer needs, potentially influencing purchasing decisions and market trends.
In the commercial vehicle sector, there is a strong demand for lightweight solutions to increase payload capacity and improve fuel efficiency. The L92 engine's lightweight design can contribute to these goals, making it relevant for a wide range of vehicle applications beyond passenger cars.
The market demand for lightweight technologies like the L92 engine is further amplified by government regulations aimed at reducing vehicle emissions and improving fuel economy. These regulations create a strong incentive for automakers to invest in and adopt lightweight technologies across their vehicle lineups.
As the automotive industry continues to evolve towards electrification, the demand for lightweight components remains critical. Even in hybrid and electric vehicles, weight reduction plays a crucial role in extending range and improving overall efficiency. The principles and technologies developed for engines like the L92 can potentially be applied to other vehicle systems, contributing to broader lightweighting efforts in the industry.
Lightweighting Challenges
Lightweighting in vehicles remains a critical challenge for automotive manufacturers, driven by the need to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. The L92 engine, while contributing to lightweighting efforts, also presents its own set of challenges in this domain.
One of the primary challenges is balancing performance with weight reduction. The L92 engine, known for its high output, requires robust components to withstand the stresses of operation. This necessity often conflicts with lightweighting goals, as stronger materials typically come at the cost of increased weight.
Material selection poses another significant challenge. While lightweight materials such as aluminum and composites offer weight savings, they may not always meet the durability and heat resistance requirements of engine components. Engineers must carefully evaluate the trade-offs between weight reduction and material properties to ensure engine reliability and longevity.
Cost considerations also present a substantial hurdle in lightweighting efforts involving the L92 engine. Advanced lightweight materials and manufacturing processes often come with higher price tags, potentially impacting the overall vehicle cost. Striking a balance between weight reduction and economic viability is crucial for widespread adoption.
Thermal management is another critical challenge. Lightweight materials may have different thermal properties compared to traditional engine materials, potentially affecting heat dissipation and overall engine efficiency. Engineers must develop innovative cooling solutions to maintain optimal operating temperatures while adhering to lightweighting principles.
Manufacturing and assembly processes present additional challenges. Lightweight materials may require specialized tooling and techniques, necessitating changes in production lines and worker training. Ensuring consistent quality and reliability in manufacturing lightweight engine components is essential but can be complex.
Durability and longevity concerns also arise when implementing lightweighting strategies in the L92 engine. Reduced material thickness or the use of alternative materials may impact the engine's ability to withstand wear and tear over time. Extensive testing and validation are required to ensure that lightweighting efforts do not compromise the engine's expected lifespan.
Regulatory compliance adds another layer of complexity to lightweighting challenges. While reducing weight contributes to meeting emissions standards, engineers must ensure that all lightweighting solutions adhere to safety regulations and performance requirements set by various governing bodies.
Addressing these challenges requires a multidisciplinary approach, combining expertise in materials science, mechanical engineering, thermal management, and manufacturing processes. Innovative solutions and continuous research and development efforts are essential to overcome these hurdles and advance lightweighting technologies in the L92 engine and vehicle design as a whole.
One of the primary challenges is balancing performance with weight reduction. The L92 engine, known for its high output, requires robust components to withstand the stresses of operation. This necessity often conflicts with lightweighting goals, as stronger materials typically come at the cost of increased weight.
Material selection poses another significant challenge. While lightweight materials such as aluminum and composites offer weight savings, they may not always meet the durability and heat resistance requirements of engine components. Engineers must carefully evaluate the trade-offs between weight reduction and material properties to ensure engine reliability and longevity.
Cost considerations also present a substantial hurdle in lightweighting efforts involving the L92 engine. Advanced lightweight materials and manufacturing processes often come with higher price tags, potentially impacting the overall vehicle cost. Striking a balance between weight reduction and economic viability is crucial for widespread adoption.
Thermal management is another critical challenge. Lightweight materials may have different thermal properties compared to traditional engine materials, potentially affecting heat dissipation and overall engine efficiency. Engineers must develop innovative cooling solutions to maintain optimal operating temperatures while adhering to lightweighting principles.
Manufacturing and assembly processes present additional challenges. Lightweight materials may require specialized tooling and techniques, necessitating changes in production lines and worker training. Ensuring consistent quality and reliability in manufacturing lightweight engine components is essential but can be complex.
Durability and longevity concerns also arise when implementing lightweighting strategies in the L92 engine. Reduced material thickness or the use of alternative materials may impact the engine's ability to withstand wear and tear over time. Extensive testing and validation are required to ensure that lightweighting efforts do not compromise the engine's expected lifespan.
Regulatory compliance adds another layer of complexity to lightweighting challenges. While reducing weight contributes to meeting emissions standards, engineers must ensure that all lightweighting solutions adhere to safety regulations and performance requirements set by various governing bodies.
Addressing these challenges requires a multidisciplinary approach, combining expertise in materials science, mechanical engineering, thermal management, and manufacturing processes. Innovative solutions and continuous research and development efforts are essential to overcome these hurdles and advance lightweighting technologies in the L92 engine and vehicle design as a whole.
L92 Lightweighting Tech
01 Engine weight reduction techniques
Various techniques are employed to reduce the weight of L92 engines, including the use of lightweight materials, optimized component designs, and advanced manufacturing processes. These weight reduction strategies aim to improve fuel efficiency and overall vehicle performance without compromising engine durability and power output.- Engine weight reduction techniques: Various methods are employed to reduce the weight of L92 engines, including the use of lightweight materials, optimized component design, and advanced manufacturing processes. These techniques aim to improve fuel efficiency and overall vehicle performance while maintaining engine durability and power output.
- Engine block design for L92: The L92 engine block is designed to balance strength and weight considerations. It may incorporate features such as thin-wall casting, strategic reinforcement, and integrated components to reduce overall engine weight while maintaining structural integrity and performance characteristics.
- Lightweight materials in L92 engine components: L92 engines may utilize lightweight materials such as aluminum alloys, magnesium alloys, or composite materials for various components, including the engine block, cylinder heads, and accessory brackets. These materials help reduce overall engine weight without compromising strength or durability.
- Weight distribution and balance in L92 engines: The design of L92 engines considers weight distribution and balance to optimize vehicle handling and performance. This may involve strategic placement of components, use of counterweights, and careful consideration of the engine's center of gravity within the vehicle.
- Weight measurement and analysis of L92 engines: Accurate measurement and analysis of L92 engine weight are crucial for design optimization and performance evaluation. This may involve specialized weighing equipment, computer-aided design tools, and simulation software to assess the weight impact of various design choices and materials.
02 Cylinder block and head design
The L92 engine's cylinder block and head design play a crucial role in determining its overall weight. Innovations in casting techniques, material selection, and structural optimization contribute to achieving a balance between strength and weight reduction in these critical components.Expand Specific Solutions03 Crankshaft and connecting rod materials
The choice of materials for the crankshaft and connecting rods significantly impacts the L92 engine's weight. High-strength, lightweight alloys and advanced manufacturing processes are utilized to reduce the weight of these rotating components while maintaining their structural integrity and performance characteristics.Expand Specific Solutions04 Intake and exhaust system optimization
Optimizing the intake and exhaust systems of the L92 engine contributes to weight reduction while enhancing performance. This includes the use of lightweight materials for manifolds, advanced air intake designs, and efficient exhaust routing to minimize overall engine weight without compromising airflow and power output.Expand Specific Solutions05 Accessory and peripheral component weight reduction
Efforts to reduce the weight of accessory and peripheral components, such as the alternator, starter motor, and cooling system, contribute to the overall weight reduction of the L92 engine. This involves redesigning components, using lightweight materials, and integrating functions to minimize the number of separate parts.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players
The L92 engine's contribution to vehicle lightweighting is part of a broader trend in the automotive industry, which is currently in a mature but evolving phase. The market for lightweight vehicle technologies is substantial, with major players like BMW, Toyota, Hyundai, and Kia investing heavily in this area. The technology's maturity varies across different applications, with companies like Aisin Technical Center of America and CIE Automotive leading in specific lightweight component developments. The competitive landscape is intense, with both traditional automakers and specialized suppliers like Delphi Technology and JFE Steel Corp. vying for market share in this critical sector that addresses fuel efficiency and environmental regulations.
Bayerische Motoren Werke AG
Technical Solution: BMW's approach to lightweighting in vehicles, including their engine technology, focuses on a holistic strategy called "Efficient Dynamics." For engine contributions, BMW has developed lightweight engine components using materials such as magnesium for engine blocks and carbon fiber reinforced plastic (CFRP) for engine covers[4]. Their TwinPower Turbo technology allows for smaller, lighter engines without compromising performance. BMW has also implemented a modular engine strategy, which enables the use of shared lightweight components across different engine variants, reducing overall vehicle weight and improving manufacturing efficiency[5].
Strengths: Comprehensive lightweighting strategy, innovative material use, and modular design for efficiency. Weaknesses: Higher material costs and potential challenges in recycling composite materials.
Hyundai Motor Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Hyundai's engine lightweighting strategy focuses on the development of their Smartstream engine series. These engines utilize aluminum for the block and head, reducing overall engine weight. Hyundai has implemented technologies such as Continuously Variable Valve Duration (CVVD), which allows for more efficient engine operation and contributes to weight reduction by optimizing engine size[8]. The company has also explored the use of integrated exhaust manifolds and plastic oil pans to further reduce engine weight. Hyundai's engine lightweighting efforts extend to their hybrid and electric powertrains, where they have developed compact, lightweight electric motors and power electronics[9].
Strengths: Innovative valve control technology, comprehensive approach to powertrain lightweighting. Weaknesses: Potential increased complexity in engine control systems and higher production costs.
L92 Core Innovations
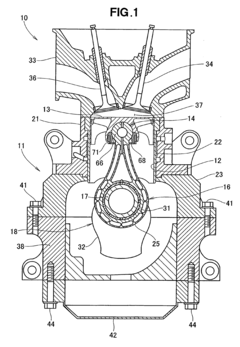
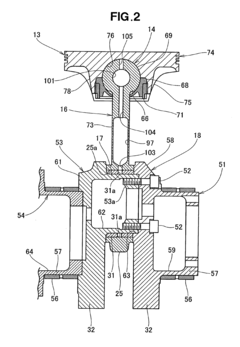
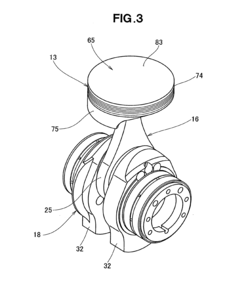
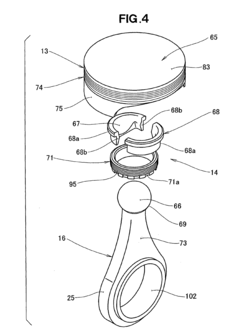
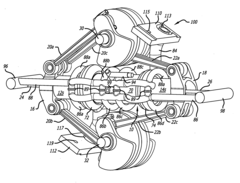
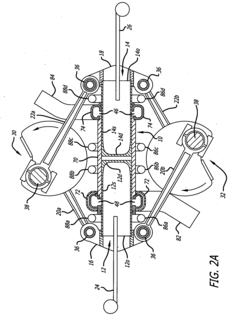
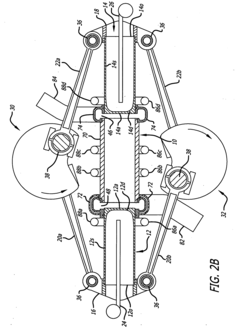
Internal combustion engine and connecting rod therefor
PatentInactiveEP1529992A2
Innovation
- The design incorporates a piston with a spherical joint and radial ribs, an integral connecting rod with an annular big end, and a hollow crank pin with a float bearing, eliminating the need for a piston pin and reducing the number of parts, allowing for a lighter, more rigid crankshaft and connecting rod with reduced frictional losses.
Two-cycle, opposed-piston internal combustion engine
PatentInactiveUS20090293820A1
Innovation
- The solution involves side-mounted crankshafts with tailored cooling systems, where liquid coolant is directed to the back surface of the piston crown and the outer surface of the cylinder to reduce thermal distortion and mechanical stresses, allowing for improved heat dissipation and maintaining a tight cylinder-piston seal without piston rings, and permitting some compliance between the cylinder and pistons for alignment.
Fuel Efficiency Impact
The L92 engine's contributions to lightweighting in vehicles have a significant impact on fuel efficiency. By reducing the overall weight of the vehicle, the L92 engine helps to decrease the energy required for acceleration and maintaining speed, thus improving fuel economy.
The lightweight design of the L92 engine, which utilizes aluminum alloy for its block and cylinder heads, contributes to a substantial reduction in engine mass compared to traditional cast-iron engines. This weight reduction directly translates to improved fuel efficiency, as the vehicle requires less energy to move its reduced mass.
Furthermore, the L92 engine's advanced design incorporates features that enhance combustion efficiency, such as variable valve timing and direct fuel injection. These technologies optimize fuel delivery and combustion processes, leading to more complete fuel burning and reduced waste. As a result, the engine extracts more energy from each unit of fuel, further improving overall fuel efficiency.
The engine's lightweight construction also allows for better weight distribution within the vehicle. This improved balance can lead to enhanced handling and reduced rolling resistance, both of which contribute to better fuel economy, especially during city driving with frequent stops and starts.
Additionally, the L92 engine's power-to-weight ratio is optimized due to its lightweight design. This means that the engine can provide sufficient power output while maintaining a lower overall weight, reducing the energy needed to propel the vehicle. The reduced inertia of lighter engine components also allows for more responsive acceleration, potentially reducing the time spent in lower-efficiency operating ranges.
The fuel efficiency improvements resulting from the L92 engine's lightweighting contributions extend beyond direct engine performance. The reduced vehicle weight allows for the use of smaller, more efficient auxiliary systems, such as power steering and air conditioning units. These downsized components further contribute to overall fuel savings.
Moreover, the lightweight nature of the L92 engine enables vehicle manufacturers to potentially reduce the size of other vehicle components, such as the suspension system or brakes, without compromising performance or safety. This cascading effect of weight reduction across multiple vehicle systems compounds the fuel efficiency benefits.
The lightweight design of the L92 engine, which utilizes aluminum alloy for its block and cylinder heads, contributes to a substantial reduction in engine mass compared to traditional cast-iron engines. This weight reduction directly translates to improved fuel efficiency, as the vehicle requires less energy to move its reduced mass.
Furthermore, the L92 engine's advanced design incorporates features that enhance combustion efficiency, such as variable valve timing and direct fuel injection. These technologies optimize fuel delivery and combustion processes, leading to more complete fuel burning and reduced waste. As a result, the engine extracts more energy from each unit of fuel, further improving overall fuel efficiency.
The engine's lightweight construction also allows for better weight distribution within the vehicle. This improved balance can lead to enhanced handling and reduced rolling resistance, both of which contribute to better fuel economy, especially during city driving with frequent stops and starts.
Additionally, the L92 engine's power-to-weight ratio is optimized due to its lightweight design. This means that the engine can provide sufficient power output while maintaining a lower overall weight, reducing the energy needed to propel the vehicle. The reduced inertia of lighter engine components also allows for more responsive acceleration, potentially reducing the time spent in lower-efficiency operating ranges.
The fuel efficiency improvements resulting from the L92 engine's lightweighting contributions extend beyond direct engine performance. The reduced vehicle weight allows for the use of smaller, more efficient auxiliary systems, such as power steering and air conditioning units. These downsized components further contribute to overall fuel savings.
Moreover, the lightweight nature of the L92 engine enables vehicle manufacturers to potentially reduce the size of other vehicle components, such as the suspension system or brakes, without compromising performance or safety. This cascading effect of weight reduction across multiple vehicle systems compounds the fuel efficiency benefits.
Environmental Regulations
Environmental regulations play a crucial role in shaping the automotive industry's approach to vehicle design and engine development. The L92 engine's contributions to lightweighting in vehicles are significantly influenced by these regulations, which aim to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve fuel efficiency.
In recent years, governments worldwide have implemented increasingly stringent emissions standards and fuel economy requirements. The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) have set Corporate Average Fuel Economy (CAFE) standards, which mandate automakers to achieve specific fleet-wide fuel efficiency targets. Similarly, the European Union has established CO2 emissions limits for new passenger cars and light commercial vehicles.
These regulations have driven automotive manufacturers to prioritize lightweighting as a key strategy for meeting environmental goals. The L92 engine, with its aluminum construction and advanced design features, aligns well with these regulatory requirements. By reducing the overall weight of the vehicle, the L92 engine contributes to improved fuel efficiency and lower emissions, helping automakers comply with environmental regulations.
Furthermore, many countries have introduced incentives and penalties based on vehicle emissions. For instance, some European countries have implemented CO2-based taxation systems, where vehicles with lower emissions benefit from reduced taxes. This regulatory landscape creates a strong market demand for lightweight engines like the L92, as they contribute to overall vehicle weight reduction and improved environmental performance.
The L92 engine's lightweight design also supports compliance with regulations related to vehicle safety and crashworthiness. As safety standards become more stringent, automakers must balance the need for robust safety features with the imperative to reduce vehicle weight. The L92 engine's compact and lightweight nature allows for more flexibility in vehicle design, enabling manufacturers to incorporate advanced safety features without significantly increasing overall vehicle mass.
Looking ahead, upcoming environmental regulations are likely to further emphasize the importance of lightweighting in vehicles. For example, proposed regulations in various jurisdictions aim to accelerate the transition to electric and hybrid vehicles. While this shift may impact traditional internal combustion engines, the lightweight principles embodied in the L92 engine design will remain relevant for hybrid powertrains and range-extended electric vehicles, where weight reduction continues to be a critical factor in achieving efficiency targets.
In recent years, governments worldwide have implemented increasingly stringent emissions standards and fuel economy requirements. The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) have set Corporate Average Fuel Economy (CAFE) standards, which mandate automakers to achieve specific fleet-wide fuel efficiency targets. Similarly, the European Union has established CO2 emissions limits for new passenger cars and light commercial vehicles.
These regulations have driven automotive manufacturers to prioritize lightweighting as a key strategy for meeting environmental goals. The L92 engine, with its aluminum construction and advanced design features, aligns well with these regulatory requirements. By reducing the overall weight of the vehicle, the L92 engine contributes to improved fuel efficiency and lower emissions, helping automakers comply with environmental regulations.
Furthermore, many countries have introduced incentives and penalties based on vehicle emissions. For instance, some European countries have implemented CO2-based taxation systems, where vehicles with lower emissions benefit from reduced taxes. This regulatory landscape creates a strong market demand for lightweight engines like the L92, as they contribute to overall vehicle weight reduction and improved environmental performance.
The L92 engine's lightweight design also supports compliance with regulations related to vehicle safety and crashworthiness. As safety standards become more stringent, automakers must balance the need for robust safety features with the imperative to reduce vehicle weight. The L92 engine's compact and lightweight nature allows for more flexibility in vehicle design, enabling manufacturers to incorporate advanced safety features without significantly increasing overall vehicle mass.
Looking ahead, upcoming environmental regulations are likely to further emphasize the importance of lightweighting in vehicles. For example, proposed regulations in various jurisdictions aim to accelerate the transition to electric and hybrid vehicles. While this shift may impact traditional internal combustion engines, the lightweight principles embodied in the L92 engine design will remain relevant for hybrid powertrains and range-extended electric vehicles, where weight reduction continues to be a critical factor in achieving efficiency targets.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!