Analysis of Industry Regulations on Thermoelectric Waste Recovery
OCT 21, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Thermoelectric Waste Recovery Background and Objectives
Thermoelectric waste recovery technology has evolved significantly over the past several decades, transitioning from theoretical concepts to practical applications across various industries. Initially developed in the mid-20th century, thermoelectric generators (TEGs) were primarily used in specialized applications such as space exploration and remote power generation. The fundamental principle behind this technology—the Seebeck effect discovered in 1821—enables direct conversion of temperature differentials into electrical energy without moving parts, offering unique advantages in waste heat recovery scenarios.
The global focus on energy efficiency and carbon emission reduction has accelerated research and development in thermoelectric waste recovery systems since the early 2000s. Industrial sectors including automotive, manufacturing, power generation, and heavy industry have increasingly recognized the potential of harvesting waste heat that traditionally dissipates into the environment. This shift has been driven by stricter environmental regulations, rising energy costs, and corporate sustainability initiatives aimed at improving overall energy efficiency.
Current technological advancements are primarily focused on improving conversion efficiency, which has historically been a limiting factor for widespread adoption. Modern thermoelectric materials have achieved efficiency rates of 5-8%, with laboratory prototypes demonstrating potential for 10-15% efficiency. These improvements represent significant progress from earlier generations that operated at 2-3% efficiency, though they still lag behind some competing waste heat recovery technologies.
The regulatory landscape surrounding thermoelectric waste recovery has evolved considerably, with governments worldwide implementing policies to encourage adoption. These include tax incentives for energy-efficient technologies, carbon pricing mechanisms, and industry-specific emissions standards that indirectly promote waste heat recovery solutions. The European Union's Energy Efficiency Directive, the United States Department of Energy's Waste Heat Recovery initiatives, and similar programs in China and Japan have established frameworks that increasingly influence industrial practices.
The primary technical objectives in this field include developing higher-efficiency thermoelectric materials, reducing manufacturing costs, improving system integration capabilities, and extending operational lifespans under industrial conditions. Research is particularly focused on nanostructured materials, skutterudites, half-Heusler alloys, and other advanced compounds that promise significant improvements in the thermoelectric figure of merit (ZT).
Market projections indicate substantial growth potential, with the global thermoelectric generator market expected to reach $720 million by 2027, growing at a CAGR of approximately 8.3%. This growth trajectory reflects both technological maturation and increasing regulatory pressure to improve industrial energy efficiency across global markets.
The global focus on energy efficiency and carbon emission reduction has accelerated research and development in thermoelectric waste recovery systems since the early 2000s. Industrial sectors including automotive, manufacturing, power generation, and heavy industry have increasingly recognized the potential of harvesting waste heat that traditionally dissipates into the environment. This shift has been driven by stricter environmental regulations, rising energy costs, and corporate sustainability initiatives aimed at improving overall energy efficiency.
Current technological advancements are primarily focused on improving conversion efficiency, which has historically been a limiting factor for widespread adoption. Modern thermoelectric materials have achieved efficiency rates of 5-8%, with laboratory prototypes demonstrating potential for 10-15% efficiency. These improvements represent significant progress from earlier generations that operated at 2-3% efficiency, though they still lag behind some competing waste heat recovery technologies.
The regulatory landscape surrounding thermoelectric waste recovery has evolved considerably, with governments worldwide implementing policies to encourage adoption. These include tax incentives for energy-efficient technologies, carbon pricing mechanisms, and industry-specific emissions standards that indirectly promote waste heat recovery solutions. The European Union's Energy Efficiency Directive, the United States Department of Energy's Waste Heat Recovery initiatives, and similar programs in China and Japan have established frameworks that increasingly influence industrial practices.
The primary technical objectives in this field include developing higher-efficiency thermoelectric materials, reducing manufacturing costs, improving system integration capabilities, and extending operational lifespans under industrial conditions. Research is particularly focused on nanostructured materials, skutterudites, half-Heusler alloys, and other advanced compounds that promise significant improvements in the thermoelectric figure of merit (ZT).
Market projections indicate substantial growth potential, with the global thermoelectric generator market expected to reach $720 million by 2027, growing at a CAGR of approximately 8.3%. This growth trajectory reflects both technological maturation and increasing regulatory pressure to improve industrial energy efficiency across global markets.
Market Demand Analysis for Waste Heat Recovery Solutions
The global market for waste heat recovery solutions has been experiencing significant growth, driven primarily by increasing energy costs, environmental regulations, and corporate sustainability initiatives. Current market analysis indicates that the waste heat recovery market is valued at approximately 68 billion USD in 2023, with projections suggesting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.5% through 2030, potentially reaching 121 billion USD by the end of the decade.
Industrial sectors represent the largest demand segment, with manufacturing, power generation, and chemical processing industries collectively accounting for over 65% of the total market share. These industries generate substantial amounts of waste heat during their operations, creating significant opportunities for thermoelectric recovery technologies. The cement industry alone is estimated to waste nearly 40% of its input energy as heat, representing a substantial untapped resource.
Regional analysis reveals that Europe currently leads the market demand for waste heat recovery solutions, largely due to stringent energy efficiency regulations and high energy costs. The European Union's Energy Efficiency Directive and carbon pricing mechanisms have created strong incentives for industrial facilities to invest in waste heat recovery technologies. Asia-Pacific follows closely, with China and India showing the fastest growth rates as their industrial sectors expand while simultaneously facing increasing pressure to reduce emissions.
Market research indicates shifting customer preferences toward integrated systems that offer both energy recovery and emissions reduction benefits. End-users increasingly demand solutions with shorter payback periods, typically seeking returns on investment within 2-5 years depending on the industry and application. This economic consideration remains a critical factor influencing market adoption rates.
The COVID-19 pandemic temporarily disrupted market growth in 2020-2021, but recovery has been robust, with many companies now accelerating their sustainability initiatives. This has created renewed interest in waste heat recovery technologies as organizations seek to simultaneously reduce operational costs and environmental impact.
Technological advancements are also reshaping market demand, with innovations in thermoelectric materials improving conversion efficiencies and expanding the temperature ranges at which these systems can operate effectively. This has opened new market segments previously considered economically unfeasible for waste heat recovery implementation.
Future market growth is expected to be particularly strong in developing economies where industrial expansion continues rapidly but must increasingly comply with international environmental standards. Additionally, the integration of waste heat recovery systems with smart factory concepts and Industry 4.0 technologies is creating new value propositions beyond simple energy recovery, including predictive maintenance capabilities and optimization of overall facility energy management.
Industrial sectors represent the largest demand segment, with manufacturing, power generation, and chemical processing industries collectively accounting for over 65% of the total market share. These industries generate substantial amounts of waste heat during their operations, creating significant opportunities for thermoelectric recovery technologies. The cement industry alone is estimated to waste nearly 40% of its input energy as heat, representing a substantial untapped resource.
Regional analysis reveals that Europe currently leads the market demand for waste heat recovery solutions, largely due to stringent energy efficiency regulations and high energy costs. The European Union's Energy Efficiency Directive and carbon pricing mechanisms have created strong incentives for industrial facilities to invest in waste heat recovery technologies. Asia-Pacific follows closely, with China and India showing the fastest growth rates as their industrial sectors expand while simultaneously facing increasing pressure to reduce emissions.
Market research indicates shifting customer preferences toward integrated systems that offer both energy recovery and emissions reduction benefits. End-users increasingly demand solutions with shorter payback periods, typically seeking returns on investment within 2-5 years depending on the industry and application. This economic consideration remains a critical factor influencing market adoption rates.
The COVID-19 pandemic temporarily disrupted market growth in 2020-2021, but recovery has been robust, with many companies now accelerating their sustainability initiatives. This has created renewed interest in waste heat recovery technologies as organizations seek to simultaneously reduce operational costs and environmental impact.
Technological advancements are also reshaping market demand, with innovations in thermoelectric materials improving conversion efficiencies and expanding the temperature ranges at which these systems can operate effectively. This has opened new market segments previously considered economically unfeasible for waste heat recovery implementation.
Future market growth is expected to be particularly strong in developing economies where industrial expansion continues rapidly but must increasingly comply with international environmental standards. Additionally, the integration of waste heat recovery systems with smart factory concepts and Industry 4.0 technologies is creating new value propositions beyond simple energy recovery, including predictive maintenance capabilities and optimization of overall facility energy management.
Current Regulatory Landscape and Technical Challenges
The global regulatory landscape for thermoelectric waste heat recovery (TEWHR) systems is characterized by a complex interplay of environmental policies, energy efficiency standards, and industrial emissions regulations. Currently, the European Union leads with its comprehensive regulatory framework under the Industrial Emissions Directive (IED) and the Energy Efficiency Directive (EED), which mandate large industrial facilities to implement best available techniques for energy recovery. These regulations have established benchmarks requiring industries to recover a minimum of 30-40% of waste heat where technically and economically feasible.
In the United States, regulations are more fragmented, with the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) providing guidelines through the Clean Air Act and various state-level incentive programs rather than imposing strict mandates. The Department of Energy's Better Plants Program offers voluntary frameworks for industrial energy efficiency, including waste heat recovery implementations, but lacks the enforcement mechanisms seen in European counterparts.
Asian markets present a diverse regulatory environment. China's 14th Five-Year Plan explicitly targets industrial waste heat recovery as part of its carbon neutrality goals, with specific efficiency targets for steel, cement, and chemical industries. Japan maintains stringent energy efficiency standards through its Energy Conservation Law, which indirectly promotes TEWHR technologies.
The primary technical challenges facing widespread TEWHR implementation stem from both regulatory inconsistencies and technological limitations. Regulatory barriers include the absence of standardized measurement protocols for quantifying recoverable waste heat, creating difficulties in establishing consistent compliance metrics across different jurisdictions and industries.
Material limitations represent a significant technical hurdle, as current thermoelectric materials struggle to maintain efficiency at the high temperatures common in industrial waste streams. Most commercially available thermoelectric generators operate optimally below 300°C, while many industrial processes generate waste heat at temperatures exceeding 500°C.
System integration challenges persist due to the lack of regulatory frameworks addressing the interconnection of TEWHR systems with existing industrial processes and power grids. This creates uncertainty regarding grid connection standards, safety protocols, and operational requirements for facilities implementing these technologies.
Cost-effectiveness remains problematic under current regulatory structures, as many jurisdictions fail to provide adequate financial incentives or carbon pricing mechanisms that would make TEWHR economically viable. The payback period for these systems typically ranges from 3-7 years, which exceeds the investment threshold for many industries without additional regulatory support.
Emerging regulatory trends suggest movement toward more harmonized international standards, with the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) developing specific guidelines for waste heat recovery assessment and implementation. These developments may address current technical challenges by establishing clear performance metrics and certification processes for TEWHR technologies.
In the United States, regulations are more fragmented, with the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) providing guidelines through the Clean Air Act and various state-level incentive programs rather than imposing strict mandates. The Department of Energy's Better Plants Program offers voluntary frameworks for industrial energy efficiency, including waste heat recovery implementations, but lacks the enforcement mechanisms seen in European counterparts.
Asian markets present a diverse regulatory environment. China's 14th Five-Year Plan explicitly targets industrial waste heat recovery as part of its carbon neutrality goals, with specific efficiency targets for steel, cement, and chemical industries. Japan maintains stringent energy efficiency standards through its Energy Conservation Law, which indirectly promotes TEWHR technologies.
The primary technical challenges facing widespread TEWHR implementation stem from both regulatory inconsistencies and technological limitations. Regulatory barriers include the absence of standardized measurement protocols for quantifying recoverable waste heat, creating difficulties in establishing consistent compliance metrics across different jurisdictions and industries.
Material limitations represent a significant technical hurdle, as current thermoelectric materials struggle to maintain efficiency at the high temperatures common in industrial waste streams. Most commercially available thermoelectric generators operate optimally below 300°C, while many industrial processes generate waste heat at temperatures exceeding 500°C.
System integration challenges persist due to the lack of regulatory frameworks addressing the interconnection of TEWHR systems with existing industrial processes and power grids. This creates uncertainty regarding grid connection standards, safety protocols, and operational requirements for facilities implementing these technologies.
Cost-effectiveness remains problematic under current regulatory structures, as many jurisdictions fail to provide adequate financial incentives or carbon pricing mechanisms that would make TEWHR economically viable. The payback period for these systems typically ranges from 3-7 years, which exceeds the investment threshold for many industries without additional regulatory support.
Emerging regulatory trends suggest movement toward more harmonized international standards, with the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) developing specific guidelines for waste heat recovery assessment and implementation. These developments may address current technical challenges by establishing clear performance metrics and certification processes for TEWHR technologies.
Current Compliance Solutions and Implementation Strategies
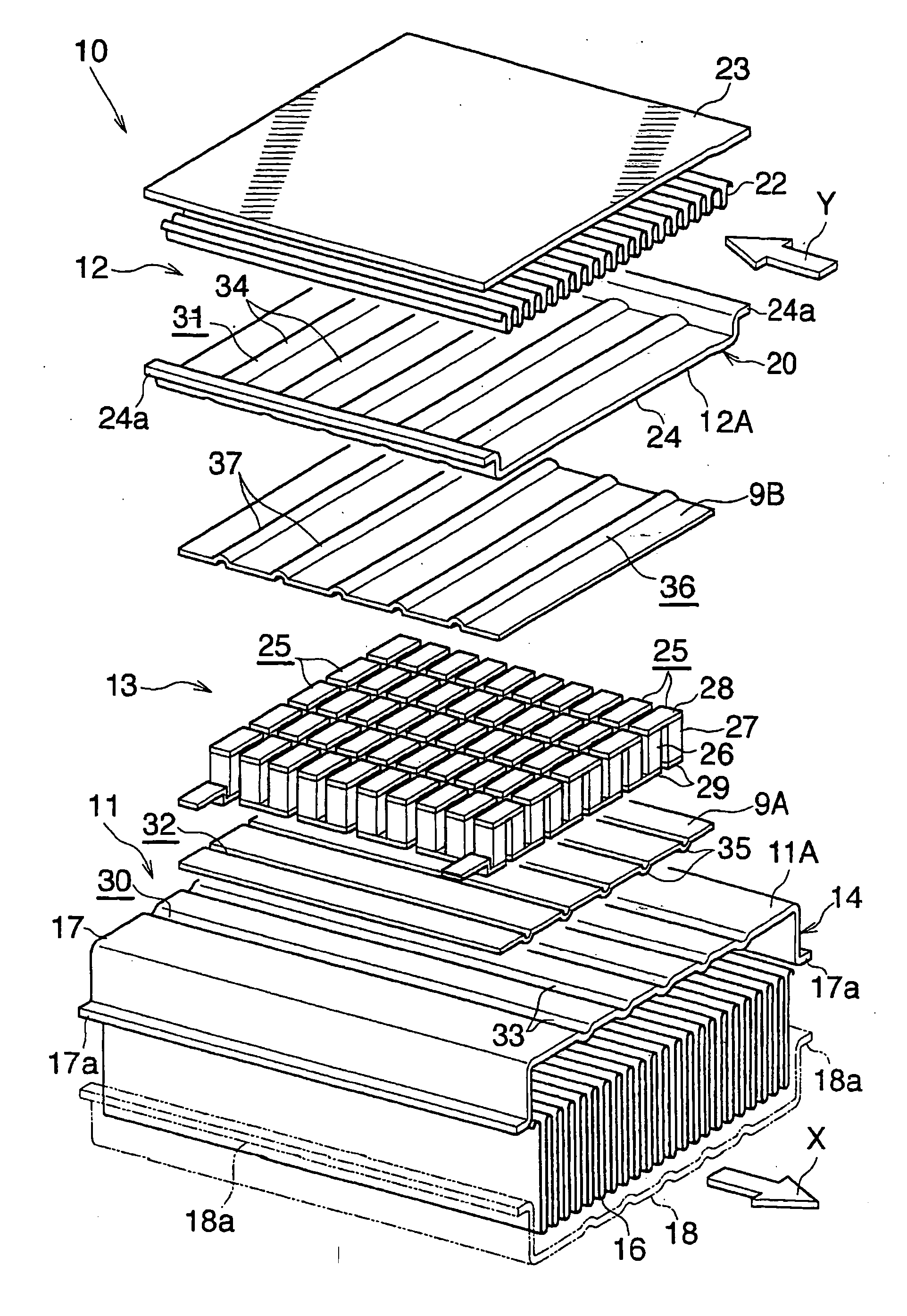
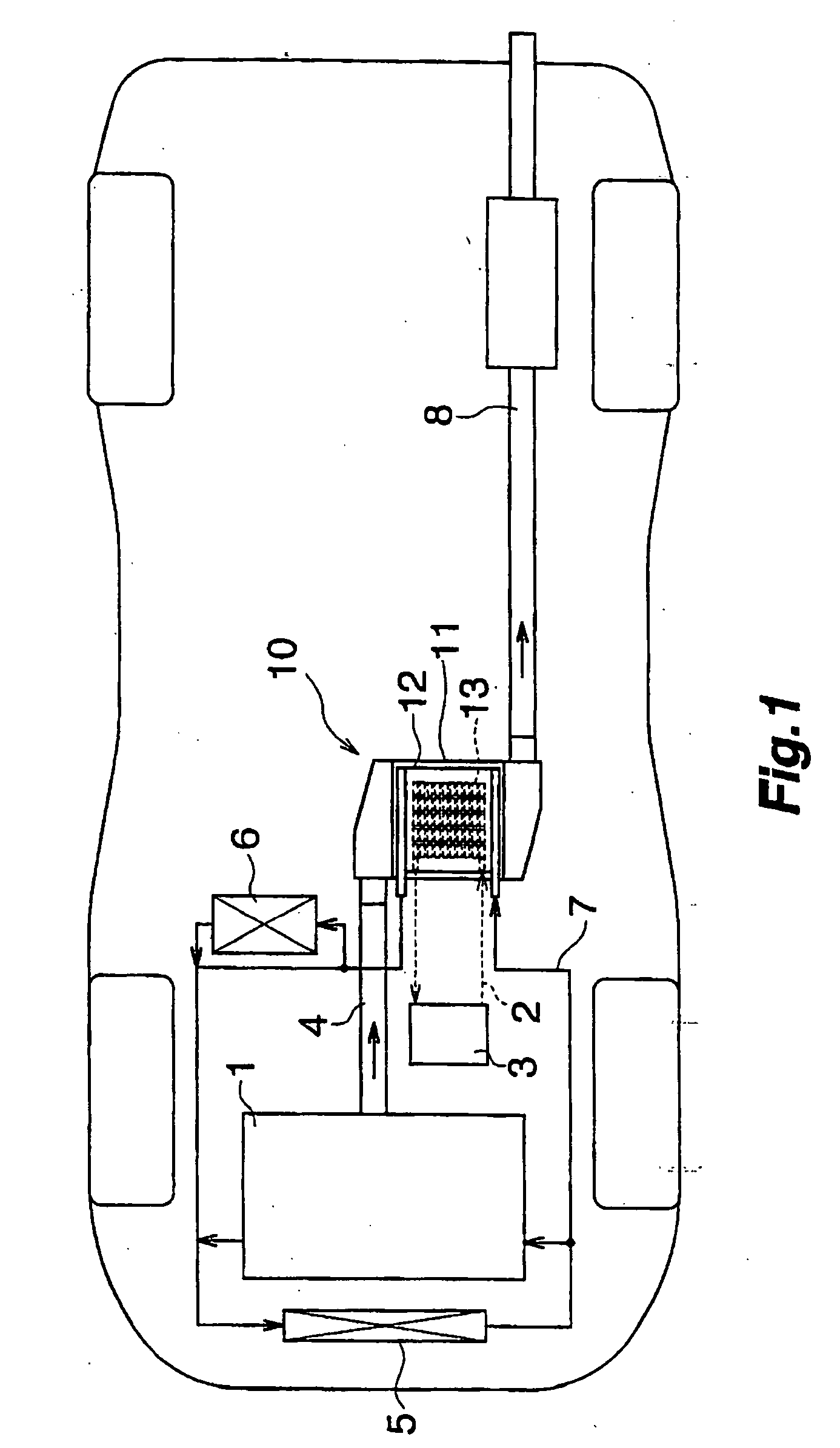
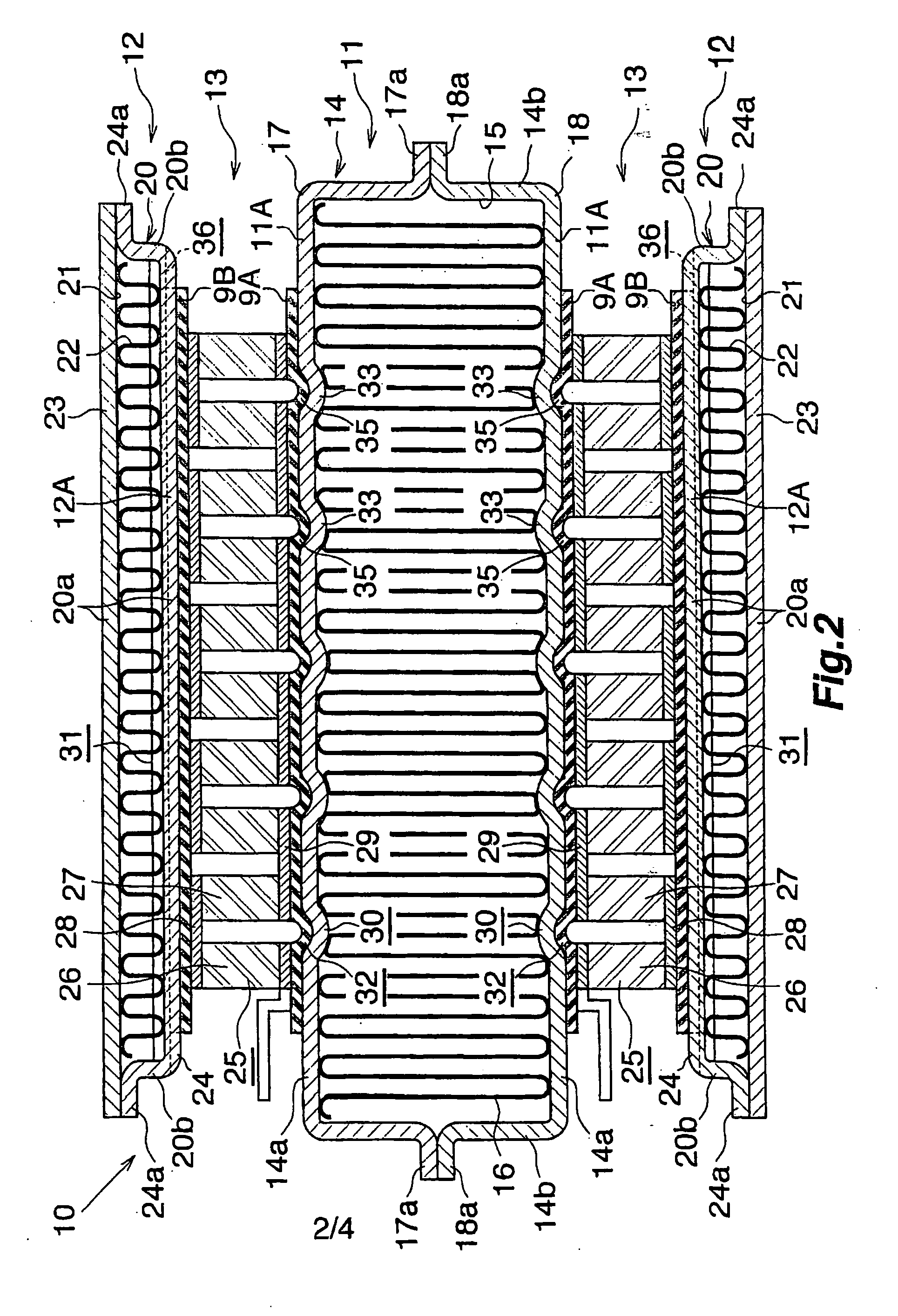
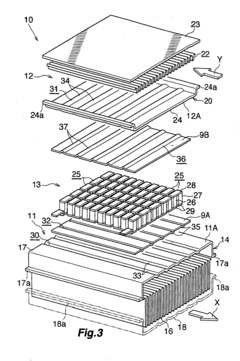
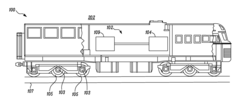
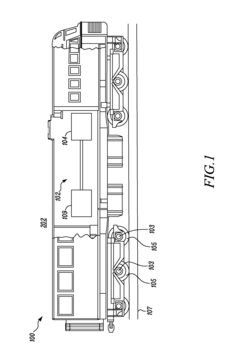
01 Thermoelectric waste heat recovery systems for vehicles
These systems are designed to capture and convert waste heat from vehicle engines and exhaust systems into usable electrical energy. By installing thermoelectric generators at strategic points in the vehicle's exhaust system, thermal energy that would otherwise be lost can be harvested. This recovered energy can be used to power vehicle electrical systems, reducing the load on the alternator and improving fuel efficiency. These systems typically include heat exchangers, thermoelectric modules, and power management electronics.- Thermoelectric waste heat recovery systems for vehicles: These systems are designed to capture and convert waste heat from vehicle engines and exhaust systems into usable electrical energy. The recovered energy can be used to power vehicle electrical systems, reducing the load on the alternator and improving fuel efficiency. These systems typically use thermoelectric generators positioned at strategic locations in the exhaust system or engine block to maximize heat capture and conversion efficiency.
- Industrial waste heat recovery applications: Thermoelectric generators are implemented in industrial settings to recover waste heat from manufacturing processes, power plants, and other industrial operations. These systems can capture heat from furnaces, boilers, and other high-temperature industrial equipment to generate electricity. The recovered energy can be fed back into the facility's power grid or used to power specific systems, improving overall energy efficiency and reducing operational costs.
- Novel thermoelectric materials and structures: Advanced materials and innovative structural designs are being developed to improve the efficiency of thermoelectric waste heat recovery. These include nanostructured materials, semiconductor alloys, and composite materials with enhanced thermoelectric properties. Novel module designs focus on improving thermal contact, reducing thermal resistance, and optimizing the temperature gradient across the thermoelectric elements to maximize power generation efficiency.
- Integrated cooling and power generation systems: These systems combine waste heat recovery with cooling functions, providing dual benefits. The thermoelectric modules simultaneously generate electricity from waste heat while creating a cooling effect that can be utilized for temperature regulation. Applications include combined cooling and power generation in electronics, refrigeration systems, and climate control systems where both functions are valuable.
- Portable and modular thermoelectric waste heat recovery: Compact, modular thermoelectric generator systems designed for flexibility and ease of installation in various applications. These systems can be deployed in remote locations, temporary installations, or retrofitted to existing equipment. The modular design allows for scalability, with multiple units combined to meet specific power requirements. These systems often include integrated power management electronics to optimize output for different load conditions.
02 Industrial waste heat recovery applications
Thermoelectric generators are implemented in industrial settings to recover waste heat from manufacturing processes, power plants, and other industrial operations. These systems can capture heat from furnaces, boilers, and other high-temperature industrial equipment. The recovered energy can be fed back into the facility's power grid or used to operate auxiliary systems. Industrial applications often require robust thermoelectric materials capable of withstanding harsh environments and high temperatures while maintaining efficient energy conversion.Expand Specific Solutions03 Novel thermoelectric materials and structures
Advanced materials and structural designs are being developed to improve the efficiency of thermoelectric waste heat recovery. These innovations include nanostructured materials, semiconductor alloys, and composite materials with enhanced Seebeck coefficients and reduced thermal conductivity. Some approaches focus on creating segmented or cascaded thermoelectric modules that can operate efficiently across wider temperature gradients. Other developments include flexible thermoelectric generators and thin-film technologies that can conform to irregular heat sources.Expand Specific Solutions04 Compact and modular thermoelectric generator designs
Compact and modular thermoelectric generator designs allow for easier integration into existing systems and scalability based on application requirements. These designs feature standardized components that can be assembled in various configurations to match specific waste heat sources. Modular approaches enable simplified maintenance, replacement of individual components, and system expansion. Some designs incorporate advanced heat exchanger geometries to maximize thermal transfer efficiency while minimizing size and weight constraints.Expand Specific Solutions05 Integrated energy management systems for thermoelectric recovery
These systems combine thermoelectric generators with sophisticated control electronics, energy storage solutions, and power conditioning circuits to optimize waste heat recovery. The integrated approach includes sensors and microcontrollers that continuously monitor temperature differentials and adjust operation for maximum efficiency. Some systems incorporate machine learning algorithms to predict heat flow patterns and optimize energy harvesting. These integrated solutions often include battery storage or supercapacitors to manage the intermittent nature of recovered energy and provide stable power output.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Industry Players and Regulatory Bodies
The thermoelectric waste recovery industry is currently in a growth phase, with increasing regulatory focus driving innovation and market expansion. The global market is projected to reach significant scale as industrial sectors seek energy efficiency solutions to meet emissions targets. Technologically, the field shows varying maturity levels, with established players like Toyota, DENSO, and Panasonic leading commercial applications, while companies such as Gentherm and Climeon are advancing specialized solutions. Academic-industrial partnerships involving Caltech, Oxford, and Tianjin University are accelerating technological breakthroughs. Shuangliang Eco-Energy and BASF are expanding industrial waste heat recovery applications, while automotive manufacturers are integrating thermoelectric systems into vehicle designs to meet stricter efficiency regulations.
Shuangliang Eco-Energy Systems Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Shuangliang has developed industrial-scale waste heat recovery systems that integrate thermoelectric generation with traditional heat exchangers for maximum efficiency. Their technology focuses on industrial applications, particularly in steel manufacturing, cement production, and chemical processing, where significant waste heat is generated. Shuangliang's systems comply with China's increasingly stringent industrial energy efficiency regulations, including the Energy Conservation Law and specific industry energy consumption standards. Their approach incorporates modular thermoelectric generation units that can be retrofitted to existing industrial facilities, helping these operations meet new emissions and efficiency requirements without major process redesigns. Shuangliang has also developed comprehensive monitoring and verification protocols that align with China's carbon trading schemes, allowing industrial customers to potentially monetize their emissions reductions. Their systems typically achieve payback periods of 3-5 years depending on energy prices and regulatory incentives.
Strengths: Extensive experience with large-scale industrial applications; strong position in rapidly evolving Chinese regulatory environment; integrated approach combining multiple heat recovery technologies. Weaknesses: Less experience in international markets with different regulatory frameworks; technology primarily optimized for continuous industrial processes rather than intermittent operations.
Toyota Motor Corp.
Technical Solution: Toyota has developed an advanced exhaust heat recovery system (EHRS) that integrates thermoelectric generators into their hybrid vehicle platforms. Their approach focuses on capturing waste heat from the exhaust system to generate electricity, reducing the load on the alternator and improving overall fuel efficiency. Toyota's system complies with increasingly stringent CAFE (Corporate Average Fuel Economy) standards and global CO2 emission regulations. Their technology incorporates specialized heat exchangers that maintain optimal catalytic converter temperatures while extracting usable energy, ensuring compliance with emissions regulations. Toyota has also pioneered regulatory frameworks for thermoelectric materials in automotive applications, working with suppliers to ensure compliance with global material restrictions including EU End-of-Life Vehicle Directive and China's RoHS regulations. Their systems are designed to improve fuel economy by 2-5% depending on driving conditions.
Strengths: Extensive integration experience with hybrid powertrains; global regulatory expertise across multiple markets; established supply chain for thermoelectric materials. Weaknesses: System complexity adds cost and weight; performance benefits vary significantly with driving conditions; limited effectiveness in short-distance urban driving.
Critical Regulatory Standards and Technical Documentation
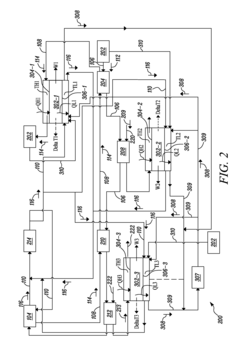
Waste heat recovery system and thermoelectric conversion system
PatentInactiveUS20060157102A1
Innovation
- A waste heat recovery system utilizing a thermoelectric conversion unit with sintered crystals of specific structures, connected in series with high-temperature and low-temperature heat exchangers, and thermal-stress relaxation features to enhance heat transfer and reduce thermal stress, allowing for efficient conversion of waste heat to electricity.
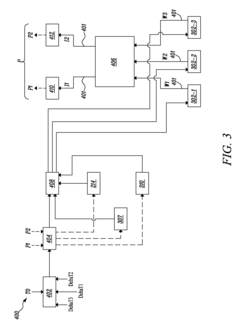
System and method for energy recovery
PatentInactiveUS20150101646A1
Innovation
- A thermoelectric module system is interfaced with various heat sources within a vehicle, including exhaust, intercooler, and aftercooler, to convert temperature differences into electrical power, with a controller optimizing low temperature heat sources based on temperature differences and vehicle operating parameters.
Economic Impact Assessment of Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance in thermoelectric waste heat recovery systems presents significant economic implications for industries across various sectors. The financial burden of adhering to environmental regulations often requires substantial capital investment, with initial compliance costs typically ranging between 2-5% of total operational expenditure for medium to large manufacturing facilities. These expenses encompass equipment upgrades, monitoring systems, certification processes, and specialized personnel training.
However, long-term economic analysis reveals that regulatory compliance frequently yields positive returns on investment. Companies implementing compliant thermoelectric waste recovery systems report average energy cost reductions of 15-22% within three years of implementation. This translates to approximately $150,000-$300,000 annual savings for a mid-sized industrial facility, depending on energy consumption patterns and local utility rates.
The market dynamics surrounding regulatory compliance create distinct competitive advantages for early adopters. Organizations proactively embracing stringent standards position themselves favorably as regulations inevitably tighten across global markets. This strategic positioning has demonstrated measurable impacts on market valuation, with compliant companies experiencing an average 7-12% premium in enterprise value compared to non-compliant competitors in the same sector.
Labor market effects must also be considered in economic impact assessments. Regulatory compliance in thermoelectric waste recovery typically generates specialized employment opportunities, with an estimated 5-8 new positions created per $1 million invested in compliance infrastructure. These positions generally command 15-20% higher compensation than traditional manufacturing roles, contributing to regional economic development.
Supply chain economics represent another critical dimension of compliance impact. Suppliers of regulatory-compliant components and systems experience enhanced market positioning, with the global market for compliant thermoelectric waste recovery solutions projected to grow at 18.7% CAGR through 2030. This creates cascading economic benefits throughout industrial ecosystems, particularly benefiting specialized engineering firms and component manufacturers.
Tax incentives and governmental support mechanisms significantly alter the economic calculus of compliance. Across major industrial economies, tax credits for waste heat recovery systems range from 10-30% of qualified expenditures, substantially reducing effective compliance costs. When combined with accelerated depreciation allowances, these incentives can improve project ROI by 25-40%, dramatically shortening payback periods.
However, long-term economic analysis reveals that regulatory compliance frequently yields positive returns on investment. Companies implementing compliant thermoelectric waste recovery systems report average energy cost reductions of 15-22% within three years of implementation. This translates to approximately $150,000-$300,000 annual savings for a mid-sized industrial facility, depending on energy consumption patterns and local utility rates.
The market dynamics surrounding regulatory compliance create distinct competitive advantages for early adopters. Organizations proactively embracing stringent standards position themselves favorably as regulations inevitably tighten across global markets. This strategic positioning has demonstrated measurable impacts on market valuation, with compliant companies experiencing an average 7-12% premium in enterprise value compared to non-compliant competitors in the same sector.
Labor market effects must also be considered in economic impact assessments. Regulatory compliance in thermoelectric waste recovery typically generates specialized employment opportunities, with an estimated 5-8 new positions created per $1 million invested in compliance infrastructure. These positions generally command 15-20% higher compensation than traditional manufacturing roles, contributing to regional economic development.
Supply chain economics represent another critical dimension of compliance impact. Suppliers of regulatory-compliant components and systems experience enhanced market positioning, with the global market for compliant thermoelectric waste recovery solutions projected to grow at 18.7% CAGR through 2030. This creates cascading economic benefits throughout industrial ecosystems, particularly benefiting specialized engineering firms and component manufacturers.
Tax incentives and governmental support mechanisms significantly alter the economic calculus of compliance. Across major industrial economies, tax credits for waste heat recovery systems range from 10-30% of qualified expenditures, substantially reducing effective compliance costs. When combined with accelerated depreciation allowances, these incentives can improve project ROI by 25-40%, dramatically shortening payback periods.
Cross-Border Regulatory Harmonization Prospects
The harmonization of cross-border regulations for thermoelectric waste recovery systems represents a critical frontier for global energy efficiency initiatives. Currently, significant regulatory disparities exist between major economic regions, creating barriers to technology transfer and implementation. The European Union's Ecodesign Directive and Energy Efficiency Directive provide comprehensive frameworks for waste heat recovery technologies, while the United States relies on a combination of federal tax incentives and state-level renewable portfolio standards that vary considerably in their treatment of thermoelectric recovery systems.
Emerging international standards such as ISO 50001 for energy management systems are beginning to create common reference points, though their specific application to thermoelectric waste recovery remains inconsistent. The International Energy Agency has identified regulatory harmonization as a priority area, estimating that aligned standards could accelerate global deployment of these technologies by 30-40% over the next decade.
Recent bilateral agreements between the EU and Japan have demonstrated the potential for regulatory convergence, with mutual recognition protocols for thermoelectric efficiency certification reducing compliance costs by approximately 22% for manufacturers operating across both markets. Similar discussions between the United States and Canada under the U.S.-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA) framework show promise for North American harmonization.
Industry stakeholders have formed the Global Thermoelectric Recovery Consortium (GTRC), which is actively developing technical standards proposals for consideration by international regulatory bodies. Their 2023 white paper outlines a three-phase approach to harmonization, beginning with standardized measurement protocols for waste heat recovery efficiency, followed by aligned incentive structures, and culminating in compatible certification processes.
The most promising pathway appears to be the "regulatory equivalence" model rather than complete standardization. This approach, successfully implemented in pharmaceutical regulations, acknowledges different regulatory traditions while ensuring comparable outcomes and safety standards. For thermoelectric waste recovery, this would mean establishing common performance metrics and safety standards while allowing flexibility in implementation mechanisms.
Challenges to harmonization include divergent national industrial policies, varying technical capabilities across regions, and competing economic interests. However, the growing recognition of climate change as a global challenge provides political momentum for overcoming these obstacles. The upcoming COP29 climate conference has specifically identified regulatory alignment for energy efficiency technologies as a key discussion area, potentially catalyzing formal international negotiations on this topic.
Emerging international standards such as ISO 50001 for energy management systems are beginning to create common reference points, though their specific application to thermoelectric waste recovery remains inconsistent. The International Energy Agency has identified regulatory harmonization as a priority area, estimating that aligned standards could accelerate global deployment of these technologies by 30-40% over the next decade.
Recent bilateral agreements between the EU and Japan have demonstrated the potential for regulatory convergence, with mutual recognition protocols for thermoelectric efficiency certification reducing compliance costs by approximately 22% for manufacturers operating across both markets. Similar discussions between the United States and Canada under the U.S.-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA) framework show promise for North American harmonization.
Industry stakeholders have formed the Global Thermoelectric Recovery Consortium (GTRC), which is actively developing technical standards proposals for consideration by international regulatory bodies. Their 2023 white paper outlines a three-phase approach to harmonization, beginning with standardized measurement protocols for waste heat recovery efficiency, followed by aligned incentive structures, and culminating in compatible certification processes.
The most promising pathway appears to be the "regulatory equivalence" model rather than complete standardization. This approach, successfully implemented in pharmaceutical regulations, acknowledges different regulatory traditions while ensuring comparable outcomes and safety standards. For thermoelectric waste recovery, this would mean establishing common performance metrics and safety standards while allowing flexibility in implementation mechanisms.
Challenges to harmonization include divergent national industrial policies, varying technical capabilities across regions, and competing economic interests. However, the growing recognition of climate change as a global challenge provides political momentum for overcoming these obstacles. The upcoming COP29 climate conference has specifically identified regulatory alignment for energy efficiency technologies as a key discussion area, potentially catalyzing formal international negotiations on this topic.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!