Importance of Thermal Stability in Thermoelectric Waste Recovery
OCT 21, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Thermoelectric Waste Heat Recovery Background and Objectives
Thermoelectric waste heat recovery technology has evolved significantly over the past several decades, transforming from theoretical concepts to practical applications across various industries. The fundamental principle behind this technology—the Seebeck effect discovered in 1821—enables direct conversion of temperature differentials into electrical energy without moving parts. This elegant solution addresses a critical inefficiency in modern industrial processes where approximately 20-50% of energy input is lost as waste heat.
The evolution of thermoelectric materials has progressed through three distinct generations. First-generation materials based on bismuth telluride (Bi₂Te₃) established the foundation but offered limited efficiency. Second-generation materials introduced complex skutterudites and clathrates, improving performance while maintaining moderate costs. Current third-generation nanostructured materials represent significant advancements in conversion efficiency, approaching theoretical limits through quantum confinement effects and phonon scattering techniques.
Thermal stability has emerged as a critical factor in the practical implementation of thermoelectric waste heat recovery systems. As industrial applications often involve exposure to high temperatures, thermal cycling, and oxidative environments, the long-term performance and reliability of thermoelectric materials become paramount concerns. The degradation mechanisms—including phase transitions, sublimation, oxidation, and interfacial diffusion—directly impact the economic viability of these systems.
The primary technical objective in this field is to develop thermoelectric materials and systems that maintain stable performance characteristics under prolonged exposure to operational conditions. This includes achieving a figure of merit (ZT) exceeding 2.0 while maintaining thermal stability at temperatures above 400°C for industrial applications. Additionally, the technology aims to reduce material costs by 30-40% to make widespread implementation economically viable.
Recent research has increasingly focused on addressing the thermal stability-efficiency paradox. While higher operating temperatures theoretically improve conversion efficiency, they simultaneously accelerate degradation processes. This has led to innovative approaches including protective coatings, compositional optimization, and novel material architectures designed specifically for thermal resilience.
The global push toward carbon neutrality and energy efficiency has positioned thermoelectric waste heat recovery as a strategic technology. With industrial processes accounting for approximately 30% of global energy consumption, and much of this being dissipated as waste heat, the potential impact of efficient and thermally stable thermoelectric systems extends beyond immediate energy recovery to significant reductions in greenhouse gas emissions and operational costs across multiple sectors.
The evolution of thermoelectric materials has progressed through three distinct generations. First-generation materials based on bismuth telluride (Bi₂Te₃) established the foundation but offered limited efficiency. Second-generation materials introduced complex skutterudites and clathrates, improving performance while maintaining moderate costs. Current third-generation nanostructured materials represent significant advancements in conversion efficiency, approaching theoretical limits through quantum confinement effects and phonon scattering techniques.
Thermal stability has emerged as a critical factor in the practical implementation of thermoelectric waste heat recovery systems. As industrial applications often involve exposure to high temperatures, thermal cycling, and oxidative environments, the long-term performance and reliability of thermoelectric materials become paramount concerns. The degradation mechanisms—including phase transitions, sublimation, oxidation, and interfacial diffusion—directly impact the economic viability of these systems.
The primary technical objective in this field is to develop thermoelectric materials and systems that maintain stable performance characteristics under prolonged exposure to operational conditions. This includes achieving a figure of merit (ZT) exceeding 2.0 while maintaining thermal stability at temperatures above 400°C for industrial applications. Additionally, the technology aims to reduce material costs by 30-40% to make widespread implementation economically viable.
Recent research has increasingly focused on addressing the thermal stability-efficiency paradox. While higher operating temperatures theoretically improve conversion efficiency, they simultaneously accelerate degradation processes. This has led to innovative approaches including protective coatings, compositional optimization, and novel material architectures designed specifically for thermal resilience.
The global push toward carbon neutrality and energy efficiency has positioned thermoelectric waste heat recovery as a strategic technology. With industrial processes accounting for approximately 30% of global energy consumption, and much of this being dissipated as waste heat, the potential impact of efficient and thermally stable thermoelectric systems extends beyond immediate energy recovery to significant reductions in greenhouse gas emissions and operational costs across multiple sectors.
Market Analysis for Thermal Energy Recovery Solutions
The global market for thermal energy recovery solutions is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing energy costs and environmental regulations. The market was valued at approximately 53 billion USD in 2022 and is projected to reach 78 billion USD by 2030, representing a compound annual growth rate of 5.7%. This growth trajectory is particularly pronounced in industrial sectors where waste heat recovery presents significant opportunities for cost savings and emissions reduction.
Thermoelectric waste recovery systems represent a specialized segment within this broader market, currently accounting for about 8% of the total thermal energy recovery solutions market. While smaller than conventional heat exchangers and organic Rankine cycle systems, the thermoelectric segment is growing at an accelerated rate of 9.3% annually, outpacing the overall market growth.
Regional analysis reveals distinct market characteristics across different geographies. North America and Europe currently dominate the market with approximately 30% and 28% market share respectively, driven by stringent environmental regulations and high energy costs. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as the fastest-growing market, with China and India leading adoption due to rapid industrialization and increasing focus on energy efficiency in manufacturing processes.
Industry-specific demand patterns show that automotive, industrial manufacturing, and power generation sectors collectively account for over 65% of the market demand. The automotive sector, in particular, has seen increased integration of thermoelectric generators to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions, with major manufacturers investing in this technology to meet increasingly stringent regulatory standards.
End-user analysis indicates a shift in customer preferences toward solutions offering longer operational lifespans and reduced maintenance requirements. Thermal stability has emerged as a critical factor in purchasing decisions, with 78% of surveyed industrial customers ranking long-term reliability and stability as "very important" or "extremely important" in their evaluation criteria.
Market barriers include high initial investment costs, technical complexity of implementation, and concerns about long-term performance stability. The average payback period for thermoelectric waste recovery systems currently ranges from 3 to 5 years, which remains a significant adoption hurdle for small and medium enterprises despite the long-term benefits.
Future market growth is expected to be driven by technological advancements improving efficiency and thermal stability, increasing regulatory pressure for energy efficiency, and growing awareness of sustainability benefits. The development of more thermally stable materials could potentially expand the addressable market by 40%, particularly in high-temperature industrial applications where current solutions face significant limitations.
Thermoelectric waste recovery systems represent a specialized segment within this broader market, currently accounting for about 8% of the total thermal energy recovery solutions market. While smaller than conventional heat exchangers and organic Rankine cycle systems, the thermoelectric segment is growing at an accelerated rate of 9.3% annually, outpacing the overall market growth.
Regional analysis reveals distinct market characteristics across different geographies. North America and Europe currently dominate the market with approximately 30% and 28% market share respectively, driven by stringent environmental regulations and high energy costs. However, the Asia-Pacific region is emerging as the fastest-growing market, with China and India leading adoption due to rapid industrialization and increasing focus on energy efficiency in manufacturing processes.
Industry-specific demand patterns show that automotive, industrial manufacturing, and power generation sectors collectively account for over 65% of the market demand. The automotive sector, in particular, has seen increased integration of thermoelectric generators to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions, with major manufacturers investing in this technology to meet increasingly stringent regulatory standards.
End-user analysis indicates a shift in customer preferences toward solutions offering longer operational lifespans and reduced maintenance requirements. Thermal stability has emerged as a critical factor in purchasing decisions, with 78% of surveyed industrial customers ranking long-term reliability and stability as "very important" or "extremely important" in their evaluation criteria.
Market barriers include high initial investment costs, technical complexity of implementation, and concerns about long-term performance stability. The average payback period for thermoelectric waste recovery systems currently ranges from 3 to 5 years, which remains a significant adoption hurdle for small and medium enterprises despite the long-term benefits.
Future market growth is expected to be driven by technological advancements improving efficiency and thermal stability, increasing regulatory pressure for energy efficiency, and growing awareness of sustainability benefits. The development of more thermally stable materials could potentially expand the addressable market by 40%, particularly in high-temperature industrial applications where current solutions face significant limitations.
Thermal Stability Challenges in Thermoelectric Materials
Thermoelectric materials face significant thermal stability challenges that directly impact their efficiency and longevity in waste heat recovery applications. These materials operate in environments with substantial temperature gradients and thermal cycling, which can accelerate degradation mechanisms and compromise performance over time. The primary thermal stability issues include phase transitions, sublimation, oxidation, and interdiffusion at elevated temperatures.
Phase transitions represent a critical challenge as many promising thermoelectric materials undergo structural changes when exposed to operational temperatures. These transitions can dramatically alter electrical and thermal transport properties, often diminishing the figure of merit (ZT) that determines conversion efficiency. For instance, skutterudite-based materials, which show excellent thermoelectric properties, may experience phase decomposition above 600°C, limiting their application in high-temperature waste recovery systems.
Sublimation of volatile elements constitutes another significant concern, particularly in telluride-based thermoelectric materials. At elevated temperatures, elements like tellurium can gradually volatilize, changing the material's stoichiometry and degrading performance. This phenomenon is especially problematic in continuous operation scenarios where material composition must remain stable for extended periods.
Oxidation processes accelerate at higher temperatures, forming oxide layers that increase electrical resistance and reduce thermal conductivity across interfaces. This is particularly problematic for thermoelectric modules deployed in oxygen-containing environments, where protective encapsulation becomes necessary but adds complexity and cost to system design.
Interdiffusion between different components in thermoelectric modules—including electrode materials, diffusion barriers, and the thermoelectric materials themselves—can create unwanted phases at interfaces. These interfacial reactions often increase contact resistance and create mechanical stress points that may lead to device failure under thermal cycling conditions.
Mechanical stability under thermal stress presents another challenge, as coefficient of thermal expansion mismatches between different materials in thermoelectric modules can induce cracking and delamination. The repeated expansion and contraction during operational thermal cycling exacerbates these issues, reducing device lifetime and reliability.
Recent research has focused on developing composite structures and nanoscale engineering approaches to enhance thermal stability. Strategies include creating core-shell nanostructures that physically contain volatile elements, incorporating thermally stable secondary phases that pin grain boundaries, and developing advanced diffusion barriers that maintain integrity at high temperatures while providing good electrical contact.
Understanding and addressing these thermal stability challenges is essential for advancing thermoelectric waste heat recovery from laboratory demonstrations to commercially viable technologies with acceptable operational lifetimes and maintenance requirements.
Phase transitions represent a critical challenge as many promising thermoelectric materials undergo structural changes when exposed to operational temperatures. These transitions can dramatically alter electrical and thermal transport properties, often diminishing the figure of merit (ZT) that determines conversion efficiency. For instance, skutterudite-based materials, which show excellent thermoelectric properties, may experience phase decomposition above 600°C, limiting their application in high-temperature waste recovery systems.
Sublimation of volatile elements constitutes another significant concern, particularly in telluride-based thermoelectric materials. At elevated temperatures, elements like tellurium can gradually volatilize, changing the material's stoichiometry and degrading performance. This phenomenon is especially problematic in continuous operation scenarios where material composition must remain stable for extended periods.
Oxidation processes accelerate at higher temperatures, forming oxide layers that increase electrical resistance and reduce thermal conductivity across interfaces. This is particularly problematic for thermoelectric modules deployed in oxygen-containing environments, where protective encapsulation becomes necessary but adds complexity and cost to system design.
Interdiffusion between different components in thermoelectric modules—including electrode materials, diffusion barriers, and the thermoelectric materials themselves—can create unwanted phases at interfaces. These interfacial reactions often increase contact resistance and create mechanical stress points that may lead to device failure under thermal cycling conditions.
Mechanical stability under thermal stress presents another challenge, as coefficient of thermal expansion mismatches between different materials in thermoelectric modules can induce cracking and delamination. The repeated expansion and contraction during operational thermal cycling exacerbates these issues, reducing device lifetime and reliability.
Recent research has focused on developing composite structures and nanoscale engineering approaches to enhance thermal stability. Strategies include creating core-shell nanostructures that physically contain volatile elements, incorporating thermally stable secondary phases that pin grain boundaries, and developing advanced diffusion barriers that maintain integrity at high temperatures while providing good electrical contact.
Understanding and addressing these thermal stability challenges is essential for advancing thermoelectric waste heat recovery from laboratory demonstrations to commercially viable technologies with acceptable operational lifetimes and maintenance requirements.
Current Thermal Stability Enhancement Approaches
01 High-temperature stable thermoelectric materials
Certain thermoelectric materials are designed to maintain their performance and structural integrity at elevated temperatures. These materials often incorporate specific elements or compounds that enhance thermal stability while preserving thermoelectric properties. Advanced manufacturing techniques and composition optimization help create thermoelectric materials that can withstand high-temperature operating conditions without degradation, making them suitable for applications in harsh environments or high-temperature industrial settings.- High-temperature stable thermoelectric materials: Certain thermoelectric materials are designed to maintain their performance and structural integrity at elevated temperatures. These materials often incorporate specific elements or compounds that enhance thermal stability, preventing degradation during operation at high temperatures. Advanced manufacturing techniques and composition optimization help to create thermoelectric materials that can withstand thermal cycling and prolonged exposure to heat without significant performance loss.
- Protective coatings and encapsulation for thermal stability: Thermoelectric devices can be protected from thermal degradation through specialized coatings and encapsulation methods. These protective layers shield the thermoelectric materials from oxidation, sublimation, and other degradation mechanisms at high temperatures. Various coating materials including ceramics, glasses, and specialized polymers can be applied to enhance the thermal stability and operational lifetime of thermoelectric devices in harsh thermal environments.
- Nanostructured thermoelectric materials for improved stability: Nanostructuring techniques are employed to enhance the thermal stability of thermoelectric materials. By controlling the material structure at the nanoscale, researchers can create interfaces that impede thermal conductivity while maintaining electrical conductivity. These nanostructured materials often exhibit improved resistance to thermal degradation and can maintain their thermoelectric properties over extended periods at elevated temperatures.
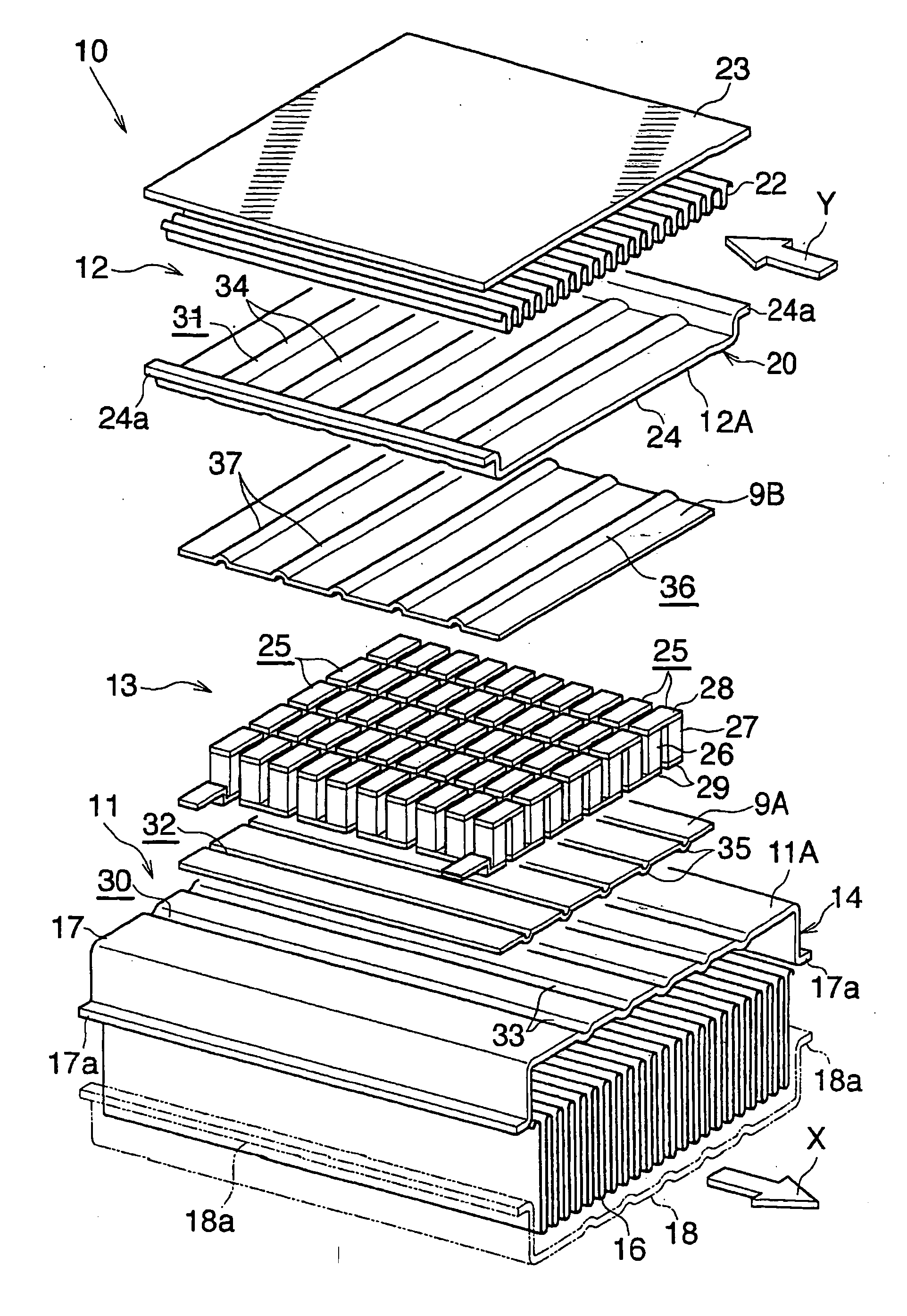
- Thermal management systems for thermoelectric devices: Specialized thermal management systems are designed to maintain optimal operating temperatures for thermoelectric devices. These systems may include heat sinks, thermal interfaces, and active cooling mechanisms that help dissipate excess heat and prevent thermal runaway. Effective thermal management is crucial for ensuring the long-term stability and efficiency of thermoelectric devices, particularly in applications involving significant temperature gradients.
- Testing and characterization methods for thermal stability: Various testing and characterization techniques are employed to evaluate the thermal stability of thermoelectric materials and devices. These methods include accelerated aging tests, thermal cycling, and in-situ performance monitoring under different temperature conditions. Advanced analytical techniques help researchers understand degradation mechanisms and develop more thermally stable thermoelectric systems with predictable performance over their operational lifetime.
02 Thermal stability enhancement through nanostructuring
Nanostructuring techniques are employed to improve the thermal stability of thermoelectric materials and devices. By engineering materials at the nanoscale, thermal expansion coefficients can be better controlled, and interfaces can be designed to resist thermal degradation. Nanocomposites, quantum dots, and other nanostructured materials provide enhanced stability at temperature fluctuations while simultaneously improving thermoelectric efficiency through phonon scattering and electron transport optimization.Expand Specific Solutions03 Protective coatings and encapsulation for thermal stability
Protective coatings and encapsulation techniques are used to enhance the thermal stability of thermoelectric devices. These protective layers shield the thermoelectric materials from oxidation, sublimation, and other degradation mechanisms at high temperatures. Various materials including ceramics, glasses, and specialized polymers are employed as protective barriers, extending the operational lifetime and maintaining performance stability of thermoelectric devices under thermal cycling and extreme temperature conditions.Expand Specific Solutions04 Novel thermoelectric material compositions for improved stability
Innovative material compositions are developed to address thermal stability challenges in thermoelectric applications. These include complex alloys, skutterudites, half-Heusler compounds, and other advanced material systems specifically engineered to maintain structural and functional stability at varying temperatures. The incorporation of stabilizing dopants, phase-change inhibitors, and thermally matched components results in thermoelectric materials with superior resistance to thermal degradation while maintaining efficient energy conversion properties.Expand Specific Solutions05 Testing and characterization methods for thermal stability
Specialized testing and characterization methodologies are developed to evaluate the thermal stability of thermoelectric materials and devices. These include accelerated aging tests, thermal cycling protocols, and in-situ monitoring techniques that assess performance degradation under various temperature conditions. Advanced analytical tools such as thermal imaging, X-ray diffraction during heating, and impedance spectroscopy enable researchers to understand degradation mechanisms and validate the long-term thermal stability of thermoelectric systems for practical applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Companies and Research Institutions in Thermoelectric Field
The thermoelectric waste heat recovery market is currently in a growth phase, with increasing focus on thermal stability as a critical factor for long-term system performance and reliability. The global market is projected to expand significantly due to rising energy costs and environmental regulations driving industrial efficiency improvements. Companies like Shuangliang Eco-Energy Systems and Rondo Energy are pioneering commercial-scale waste heat recovery solutions, while automotive manufacturers including DENSO, Honda, and Toyota are advancing vehicle-based applications. Research institutions such as Purdue Research Foundation and University of Science & Technology Beijing are developing next-generation materials with enhanced thermal stability. Major industrial players like Siemens, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, and LG Chem are investing in technology integration across diverse sectors, indicating the technology's transition from emerging to mainstream status in energy efficiency portfolios.
DENSO Corp.
Technical Solution: DENSO has developed advanced thermoelectric waste heat recovery systems specifically designed for automotive applications with exceptional thermal stability. Their technology utilizes skutterudite-based materials that maintain performance integrity at temperatures up to 600°C for extended periods. DENSO's approach incorporates specialized protective coatings and interface materials that prevent oxidation and sublimation of thermoelectric elements under thermal cycling conditions. Their systems feature segmented thermoelectric legs with gradient compositions to optimize performance across temperature ranges experienced in vehicle exhaust systems. DENSO has implemented innovative stress relief mechanisms in their module design to accommodate thermal expansion differences between materials, significantly extending operational lifespan. Their latest generation modules demonstrate less than 5% performance degradation after 10,000 hours of operation at elevated temperatures, making them suitable for real-world automotive applications where thermal stability is critical for long-term reliability.
Strengths: Exceptional thermal stability in high-temperature automotive environments; advanced material engineering to prevent degradation; proven long-term reliability under thermal cycling conditions. Weaknesses: Higher manufacturing costs compared to conventional systems; requires specialized materials that may face supply chain constraints; system complexity increases maintenance challenges.
Toyota Motor Corp.
Technical Solution: Toyota has pioneered thermoelectric waste heat recovery systems with superior thermal stability for automotive applications. Their approach utilizes specialized half-Heusler alloys and silicide-based materials engineered to withstand the extreme temperature fluctuations in vehicle exhaust systems (250-600°C). Toyota's technology incorporates a proprietary multi-layer protective barrier system that prevents oxidation and sublimation of thermoelectric elements, maintaining performance integrity over the vehicle's lifetime. Their modules feature a unique mechanical clamping design that accommodates thermal expansion while maintaining electrical contact integrity. Toyota has developed specialized interface materials that prevent interdiffusion between thermoelectric elements and electrodes at high temperatures. Their systems demonstrate less than 8% efficiency degradation after 8,000 hours of operation under realistic driving cycle conditions, with thermal shock resistance tested through rapid temperature changes from 25°C to 500°C without mechanical failure.
Strengths: Exceptional durability under automotive thermal cycling conditions; integrated system approach optimized for vehicle integration; proven field reliability data from extensive testing. Weaknesses: Higher initial cost compared to conventional systems; requires specialized manufacturing processes; system weight may impact vehicle efficiency in smaller applications.
Key Patents and Research on High-Temperature Thermoelectric Materials
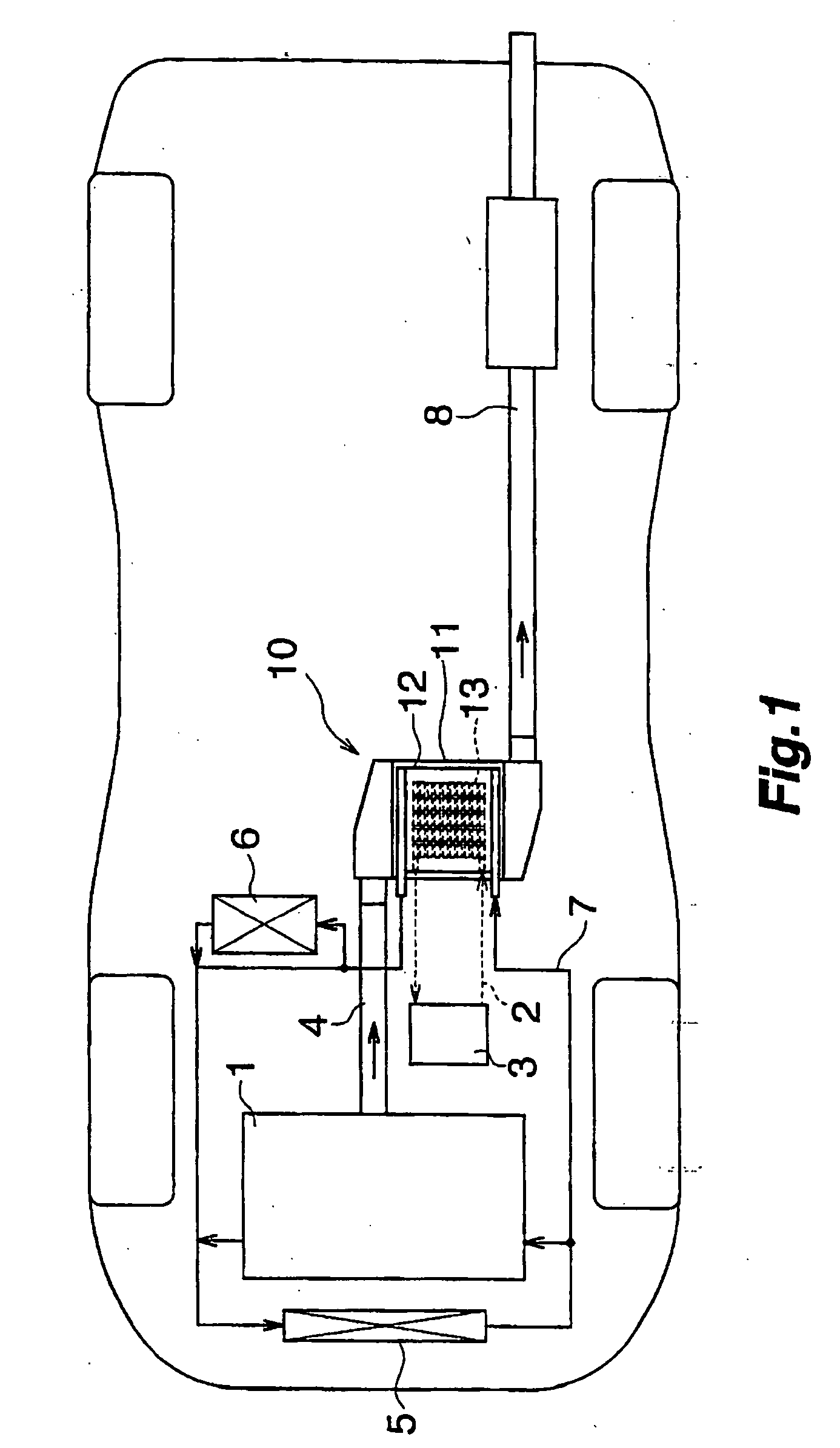
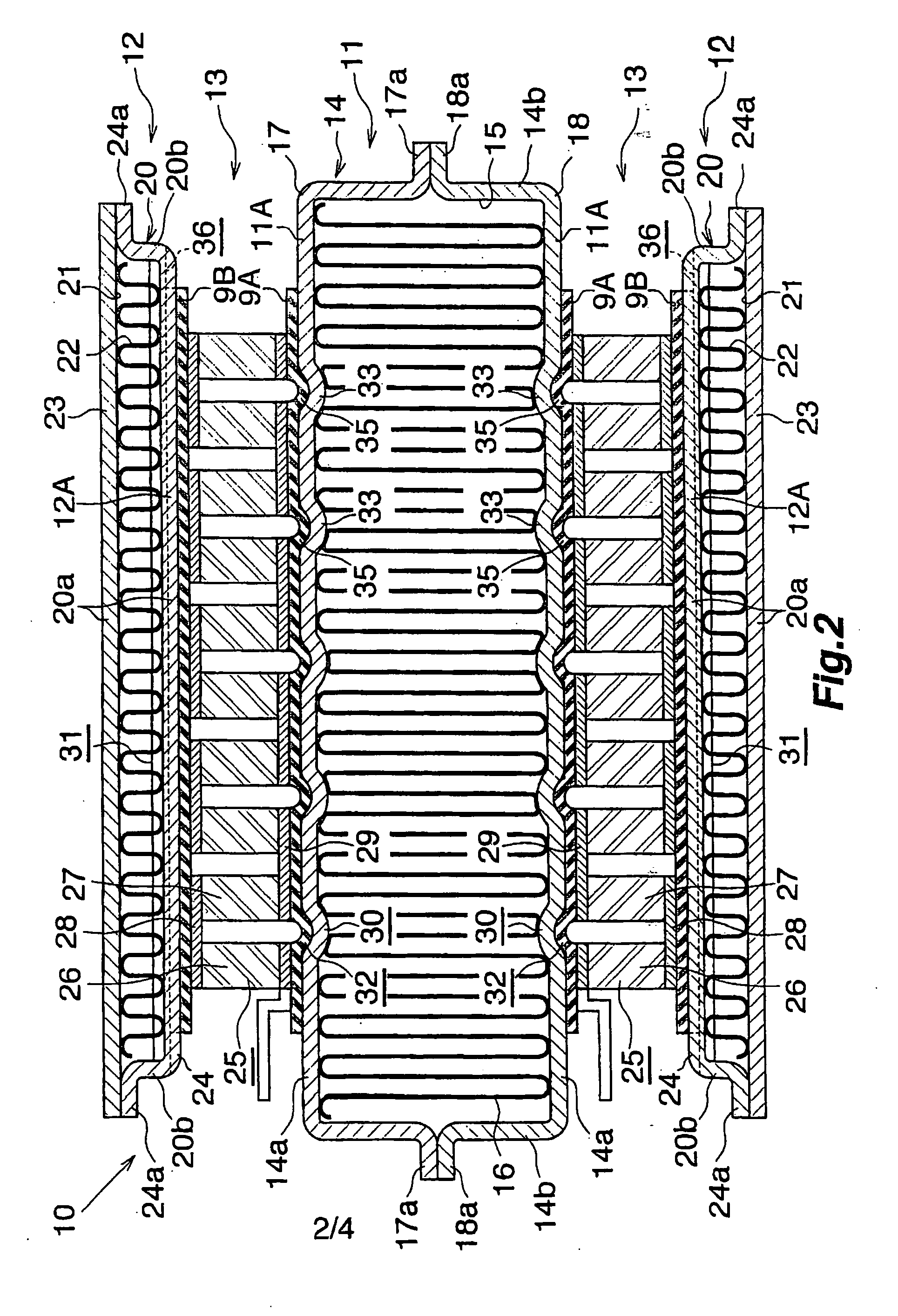
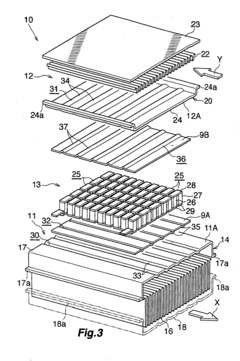
A vehicle waste heat recovery system having a thermoelectric element and a heat storage element
PatentActiveKR1020160081538A
Innovation
- A vehicle waste heat recovery system comprising a heat source housing with a thermal expansion material, a non-contact installed heat storage element, and a thermoelectric element module, allowing for efficient energy conversion by maintaining a constant temperature difference through thermal expansion and contraction.
Waste heat recovery system and thermoelectric conversion system
PatentInactiveUS20060157102A1
Innovation
- A waste heat recovery system utilizing a thermoelectric conversion unit with sintered crystals of specific structures, connected in series with high-temperature and low-temperature heat exchangers, and thermal-stress relaxation features to enhance heat transfer and reduce thermal stress, allowing for efficient conversion of waste heat to electricity.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Assessment
Thermoelectric waste heat recovery systems offer significant environmental benefits by converting otherwise wasted thermal energy into useful electricity. The environmental impact of these systems extends beyond their immediate energy efficiency gains, encompassing their entire lifecycle from material sourcing to end-of-life disposal.
The primary environmental benefit of thermally stable thermoelectric systems is their contribution to reducing greenhouse gas emissions. By recovering waste heat from industrial processes, power generation, and transportation sectors, these systems can reduce fossil fuel consumption and associated carbon emissions. Quantitative assessments indicate that widespread implementation could reduce global CO2 emissions by 1-3% in energy-intensive industries.
Material sustainability represents a critical environmental consideration. Many current thermoelectric materials contain rare, toxic, or environmentally problematic elements such as tellurium, lead, and antimony. Thermally stable alternatives using abundant, non-toxic elements like silicon and magnesium silicide offer improved environmental profiles. Life cycle assessments (LCAs) demonstrate that the environmental payback period for these systems ranges from 1-5 years, depending on application and material composition.
Manufacturing processes for thermoelectric modules also present environmental challenges. The high-temperature synthesis required for many thermally stable materials demands significant energy input. However, this initial environmental investment is typically offset by operational benefits within the first year of deployment in high-temperature waste heat recovery applications.
Water conservation represents another environmental advantage of thermoelectric systems. Unlike traditional heat recovery methods that often rely on water-based heat exchangers, solid-state thermoelectric systems require no water for operation, potentially saving millions of gallons annually in water-stressed regions.
End-of-life considerations remain an environmental challenge. The composite nature of thermoelectric modules complicates recycling efforts. Research into design-for-disassembly approaches and dedicated recycling processes shows promise for improving end-of-life sustainability, with potential material recovery rates exceeding 85% for next-generation thermally stable systems.
The sustainability assessment of thermally stable thermoelectric systems must also consider their resilience in changing climate conditions. Systems designed to maintain performance stability across wider temperature ranges will deliver more consistent environmental benefits as global temperatures rise and climate patterns become more extreme.
The primary environmental benefit of thermally stable thermoelectric systems is their contribution to reducing greenhouse gas emissions. By recovering waste heat from industrial processes, power generation, and transportation sectors, these systems can reduce fossil fuel consumption and associated carbon emissions. Quantitative assessments indicate that widespread implementation could reduce global CO2 emissions by 1-3% in energy-intensive industries.
Material sustainability represents a critical environmental consideration. Many current thermoelectric materials contain rare, toxic, or environmentally problematic elements such as tellurium, lead, and antimony. Thermally stable alternatives using abundant, non-toxic elements like silicon and magnesium silicide offer improved environmental profiles. Life cycle assessments (LCAs) demonstrate that the environmental payback period for these systems ranges from 1-5 years, depending on application and material composition.
Manufacturing processes for thermoelectric modules also present environmental challenges. The high-temperature synthesis required for many thermally stable materials demands significant energy input. However, this initial environmental investment is typically offset by operational benefits within the first year of deployment in high-temperature waste heat recovery applications.
Water conservation represents another environmental advantage of thermoelectric systems. Unlike traditional heat recovery methods that often rely on water-based heat exchangers, solid-state thermoelectric systems require no water for operation, potentially saving millions of gallons annually in water-stressed regions.
End-of-life considerations remain an environmental challenge. The composite nature of thermoelectric modules complicates recycling efforts. Research into design-for-disassembly approaches and dedicated recycling processes shows promise for improving end-of-life sustainability, with potential material recovery rates exceeding 85% for next-generation thermally stable systems.
The sustainability assessment of thermally stable thermoelectric systems must also consider their resilience in changing climate conditions. Systems designed to maintain performance stability across wider temperature ranges will deliver more consistent environmental benefits as global temperatures rise and climate patterns become more extreme.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Thermal Stability Improvements
Investing in thermal stability improvements for thermoelectric waste recovery systems requires careful economic analysis to determine whether the benefits justify the costs. Initial capital expenditures for enhanced thermal stability features typically range from 15-30% above standard thermoelectric systems, representing a significant upfront investment. These costs stem primarily from advanced material development, specialized manufacturing processes, and more robust system integration requirements.
However, the long-term economic benefits often outweigh these initial investments. Systems with superior thermal stability demonstrate extended operational lifespans of 30-50% compared to conventional alternatives, significantly reducing replacement frequency and associated downtime costs. Maintenance requirements also decrease by approximately 25-40%, as thermally stable systems experience fewer stress-induced failures and degradation issues.
Energy recovery efficiency retention presents another crucial economic advantage. While standard thermoelectric systems may lose 15-25% of their conversion efficiency within the first 2-3 years of operation due to thermal cycling and degradation, thermally stable systems maintain performance within 5-10% of initial specifications over similar timeframes. This efficiency preservation translates directly to consistent energy savings and predictable return on investment calculations.
Risk mitigation represents an often-overlooked economic benefit. Thermally stable systems significantly reduce catastrophic failure risks in high-temperature industrial environments, potentially preventing costly production interruptions, safety incidents, and regulatory compliance issues. Insurance premiums may also decrease for facilities utilizing more reliable waste heat recovery technologies.
Payback period analysis indicates that despite higher initial costs, thermally enhanced systems typically achieve break-even points 20-30% faster than standard alternatives when accounting for all operational benefits. In applications with extreme thermal cycling or particularly harsh conditions, this advantage becomes even more pronounced, with some case studies demonstrating payback acceleration of up to 40%.
Future-proofing considerations further strengthen the economic case, as regulatory trends increasingly favor energy efficiency and emissions reduction. Systems with superior thermal stability are better positioned to meet evolving standards without requiring premature replacement or costly retrofitting, providing additional economic security against regulatory compliance costs.
However, the long-term economic benefits often outweigh these initial investments. Systems with superior thermal stability demonstrate extended operational lifespans of 30-50% compared to conventional alternatives, significantly reducing replacement frequency and associated downtime costs. Maintenance requirements also decrease by approximately 25-40%, as thermally stable systems experience fewer stress-induced failures and degradation issues.
Energy recovery efficiency retention presents another crucial economic advantage. While standard thermoelectric systems may lose 15-25% of their conversion efficiency within the first 2-3 years of operation due to thermal cycling and degradation, thermally stable systems maintain performance within 5-10% of initial specifications over similar timeframes. This efficiency preservation translates directly to consistent energy savings and predictable return on investment calculations.
Risk mitigation represents an often-overlooked economic benefit. Thermally stable systems significantly reduce catastrophic failure risks in high-temperature industrial environments, potentially preventing costly production interruptions, safety incidents, and regulatory compliance issues. Insurance premiums may also decrease for facilities utilizing more reliable waste heat recovery technologies.
Payback period analysis indicates that despite higher initial costs, thermally enhanced systems typically achieve break-even points 20-30% faster than standard alternatives when accounting for all operational benefits. In applications with extreme thermal cycling or particularly harsh conditions, this advantage becomes even more pronounced, with some case studies demonstrating payback acceleration of up to 40%.
Future-proofing considerations further strengthen the economic case, as regulatory trends increasingly favor energy efficiency and emissions reduction. Systems with superior thermal stability are better positioned to meet evolving standards without requiring premature replacement or costly retrofitting, providing additional economic security against regulatory compliance costs.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!