Application of Bioresonance in Immunotherapy Modalities
AUG 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Bioresonance Immunotherapy Background and Objectives
Bioresonance therapy, a concept rooted in the principles of quantum physics and energy medicine, has been gaining attention in the field of immunotherapy over the past few decades. This innovative approach to healthcare is based on the premise that all living organisms emit and respond to specific electromagnetic frequencies. The application of bioresonance in immunotherapy modalities represents a convergence of traditional medical practices with cutting-edge technology, aiming to enhance the body's natural healing capabilities.
The historical development of bioresonance therapy can be traced back to the early 20th century, with the work of scientists like Royal Raymond Rife and Georges Lakhovsky. However, it wasn't until the 1970s that Dr. Franz Morell and his son-in-law, engineer Erich Rasche, developed the first bioresonance device, known as MORA therapy. This marked the beginning of a new era in alternative medicine, where electromagnetic frequencies were used to diagnose and treat various health conditions.
In recent years, the integration of bioresonance principles into immunotherapy has opened up new possibilities for treating a wide range of disorders, particularly those related to immune system dysfunction. The primary objective of bioresonance immunotherapy is to modulate the immune response by identifying and correcting energetic imbalances within the body. This approach aims to restore homeostasis and enhance the body's ability to fight off pathogens, allergens, and other harmful agents.
The technological evolution in this field has been driven by advancements in quantum physics, bioelectronics, and computational power. Modern bioresonance devices are capable of detecting and analyzing subtle electromagnetic signals from the body, as well as generating therapeutic frequencies tailored to individual patients. This personalized approach aligns with the growing trend towards precision medicine, where treatments are customized based on an individual's unique physiological profile.
As research in this area continues to expand, the scientific community is increasingly focused on understanding the mechanisms through which bioresonance affects immune function. Studies have suggested that electromagnetic signals may influence cellular communication, gene expression, and the production of immune mediators. However, the exact pathways and long-term effects of bioresonance on the immune system remain subjects of ongoing investigation.
The integration of bioresonance into mainstream immunotherapy practices faces several challenges, including the need for standardized protocols, rigorous clinical trials, and regulatory approval. Despite these hurdles, the potential benefits of this non-invasive, drug-free approach have sparked interest among healthcare professionals and patients alike, particularly in the treatment of chronic conditions where conventional therapies have shown limited success.
The historical development of bioresonance therapy can be traced back to the early 20th century, with the work of scientists like Royal Raymond Rife and Georges Lakhovsky. However, it wasn't until the 1970s that Dr. Franz Morell and his son-in-law, engineer Erich Rasche, developed the first bioresonance device, known as MORA therapy. This marked the beginning of a new era in alternative medicine, where electromagnetic frequencies were used to diagnose and treat various health conditions.
In recent years, the integration of bioresonance principles into immunotherapy has opened up new possibilities for treating a wide range of disorders, particularly those related to immune system dysfunction. The primary objective of bioresonance immunotherapy is to modulate the immune response by identifying and correcting energetic imbalances within the body. This approach aims to restore homeostasis and enhance the body's ability to fight off pathogens, allergens, and other harmful agents.
The technological evolution in this field has been driven by advancements in quantum physics, bioelectronics, and computational power. Modern bioresonance devices are capable of detecting and analyzing subtle electromagnetic signals from the body, as well as generating therapeutic frequencies tailored to individual patients. This personalized approach aligns with the growing trend towards precision medicine, where treatments are customized based on an individual's unique physiological profile.
As research in this area continues to expand, the scientific community is increasingly focused on understanding the mechanisms through which bioresonance affects immune function. Studies have suggested that electromagnetic signals may influence cellular communication, gene expression, and the production of immune mediators. However, the exact pathways and long-term effects of bioresonance on the immune system remain subjects of ongoing investigation.
The integration of bioresonance into mainstream immunotherapy practices faces several challenges, including the need for standardized protocols, rigorous clinical trials, and regulatory approval. Despite these hurdles, the potential benefits of this non-invasive, drug-free approach have sparked interest among healthcare professionals and patients alike, particularly in the treatment of chronic conditions where conventional therapies have shown limited success.
Market Analysis for Bioresonance-based Immunotherapies
The market for bioresonance-based immunotherapies is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing interest in alternative and complementary medicine approaches. This emerging field combines the principles of bioresonance therapy with immunomodulation techniques, aiming to enhance the body's natural immune responses. The global immunotherapy market, valued at approximately $85 billion in 2021, is projected to reach $200 billion by 2028, with bioresonance-based therapies poised to capture a growing share of this expanding market.
Bioresonance-based immunotherapies are gaining traction in various medical fields, including oncology, allergology, and autoimmune disorders. The oncology segment, in particular, shows promising potential, as cancer immunotherapy continues to be a focal point of research and development. The market for bioresonance devices and related therapies is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2022 to 2030, reflecting the increasing adoption of these technologies in clinical settings.
The demand for non-invasive and personalized treatment options is a key driver of market growth. Patients are increasingly seeking alternatives to conventional therapies, particularly those with fewer side effects and a more holistic approach to health. This trend aligns well with the principles of bioresonance therapy, which aims to restore the body's natural balance and enhance immune function without the use of pharmaceutical interventions.
Geographically, Europe currently leads the bioresonance therapy market, with Germany and Switzerland at the forefront of research and clinical applications. However, North America and Asia-Pacific regions are expected to witness rapid growth in the coming years, as awareness of bioresonance therapies increases and regulatory frameworks evolve to accommodate these novel treatment modalities.
The market landscape is characterized by a mix of established medical device manufacturers and innovative startups. Key players are investing in research and development to improve the efficacy and reliability of bioresonance devices, as well as to expand their applications in immunotherapy. Collaborations between bioresonance technology companies and immunology research institutions are becoming more common, fostering innovation and clinical validation of these therapies.
Despite the promising outlook, the market faces challenges related to scientific validation and regulatory approval. Skepticism within the traditional medical community regarding the efficacy of bioresonance therapies remains a significant barrier to widespread adoption. However, ongoing clinical trials and increasing evidence of positive outcomes in certain conditions are gradually shifting perceptions and opening new market opportunities.
Bioresonance-based immunotherapies are gaining traction in various medical fields, including oncology, allergology, and autoimmune disorders. The oncology segment, in particular, shows promising potential, as cancer immunotherapy continues to be a focal point of research and development. The market for bioresonance devices and related therapies is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% from 2022 to 2030, reflecting the increasing adoption of these technologies in clinical settings.
The demand for non-invasive and personalized treatment options is a key driver of market growth. Patients are increasingly seeking alternatives to conventional therapies, particularly those with fewer side effects and a more holistic approach to health. This trend aligns well with the principles of bioresonance therapy, which aims to restore the body's natural balance and enhance immune function without the use of pharmaceutical interventions.
Geographically, Europe currently leads the bioresonance therapy market, with Germany and Switzerland at the forefront of research and clinical applications. However, North America and Asia-Pacific regions are expected to witness rapid growth in the coming years, as awareness of bioresonance therapies increases and regulatory frameworks evolve to accommodate these novel treatment modalities.
The market landscape is characterized by a mix of established medical device manufacturers and innovative startups. Key players are investing in research and development to improve the efficacy and reliability of bioresonance devices, as well as to expand their applications in immunotherapy. Collaborations between bioresonance technology companies and immunology research institutions are becoming more common, fostering innovation and clinical validation of these therapies.
Despite the promising outlook, the market faces challenges related to scientific validation and regulatory approval. Skepticism within the traditional medical community regarding the efficacy of bioresonance therapies remains a significant barrier to widespread adoption. However, ongoing clinical trials and increasing evidence of positive outcomes in certain conditions are gradually shifting perceptions and opening new market opportunities.
Current Challenges in Bioresonance Immunotherapy
Despite the growing interest in bioresonance therapy for immunomodulation, several significant challenges hinder its widespread adoption and clinical efficacy. One of the primary obstacles is the lack of standardized protocols for bioresonance application in immunotherapy. The diversity of devices, frequencies, and treatment durations used across studies makes it difficult to establish a consensus on optimal therapeutic parameters.
Another major challenge lies in the limited understanding of the precise mechanisms by which bioresonance influences immune function. While theories exist about electromagnetic field interactions with cellular processes, the specific pathways and molecular targets involved in immunomodulation remain largely unelucidated. This gap in knowledge impedes the development of targeted and personalized bioresonance therapies.
The scarcity of large-scale, randomized controlled trials (RCTs) presents a significant hurdle in validating the efficacy of bioresonance immunotherapy. Most existing studies are small-scale or observational, leading to skepticism within the mainstream medical community. The absence of robust clinical evidence makes it challenging to integrate bioresonance into conventional immunotherapy protocols.
Regulatory concerns pose another substantial challenge. Many countries lack clear guidelines for the approval and use of bioresonance devices in clinical settings. This regulatory ambiguity creates barriers to research funding, clinical trials, and widespread implementation of bioresonance therapies.
The complexity of the immune system itself adds another layer of difficulty. The intricate interplay between various immune components makes it challenging to predict and control the effects of bioresonance on overall immune function. Ensuring that bioresonance therapy enhances beneficial immune responses without triggering harmful autoimmune reactions remains a critical concern.
Additionally, the potential for placebo effects in bioresonance studies complicates the interpretation of results. Given the non-invasive nature of the therapy and the subjective nature of many immune-related symptoms, distinguishing genuine therapeutic effects from placebo responses requires carefully designed studies with appropriate controls.
Lastly, the integration of bioresonance with existing immunotherapy modalities presents both opportunities and challenges. While combining bioresonance with conventional treatments could potentially enhance outcomes, determining optimal combination strategies and avoiding potential interference effects requires extensive research and clinical validation.
Another major challenge lies in the limited understanding of the precise mechanisms by which bioresonance influences immune function. While theories exist about electromagnetic field interactions with cellular processes, the specific pathways and molecular targets involved in immunomodulation remain largely unelucidated. This gap in knowledge impedes the development of targeted and personalized bioresonance therapies.
The scarcity of large-scale, randomized controlled trials (RCTs) presents a significant hurdle in validating the efficacy of bioresonance immunotherapy. Most existing studies are small-scale or observational, leading to skepticism within the mainstream medical community. The absence of robust clinical evidence makes it challenging to integrate bioresonance into conventional immunotherapy protocols.
Regulatory concerns pose another substantial challenge. Many countries lack clear guidelines for the approval and use of bioresonance devices in clinical settings. This regulatory ambiguity creates barriers to research funding, clinical trials, and widespread implementation of bioresonance therapies.
The complexity of the immune system itself adds another layer of difficulty. The intricate interplay between various immune components makes it challenging to predict and control the effects of bioresonance on overall immune function. Ensuring that bioresonance therapy enhances beneficial immune responses without triggering harmful autoimmune reactions remains a critical concern.
Additionally, the potential for placebo effects in bioresonance studies complicates the interpretation of results. Given the non-invasive nature of the therapy and the subjective nature of many immune-related symptoms, distinguishing genuine therapeutic effects from placebo responses requires carefully designed studies with appropriate controls.
Lastly, the integration of bioresonance with existing immunotherapy modalities presents both opportunities and challenges. While combining bioresonance with conventional treatments could potentially enhance outcomes, determining optimal combination strategies and avoiding potential interference effects requires extensive research and clinical validation.
Existing Bioresonance Immunotherapy Modalities
01 Bioresonance diagnostic devices
Various devices have been developed for bioresonance diagnosis, which aim to detect and analyze electromagnetic frequencies emitted by the human body. These devices typically involve sensors or electrodes that are placed on specific points of the body to measure and interpret these frequencies, potentially providing insights into a person's health status or identifying imbalances.- Bioresonance diagnostic devices: These devices are designed to detect and analyze electromagnetic frequencies emitted by the human body. They are used for non-invasive diagnostic purposes, potentially identifying imbalances or health issues based on the body's energy patterns.
- Bioresonance therapy systems: These systems are used for therapeutic purposes, applying specific electromagnetic frequencies to the body. The goal is to restore balance and promote healing by interacting with the body's own electromagnetic fields.
- Portable bioresonance devices: Compact and portable devices that allow for bioresonance therapy or diagnosis outside of clinical settings. These may include wearable devices or handheld units for personal use or mobile healthcare applications.
- Bioresonance-enhanced products: Various products, such as water treatment systems or personal care items, that incorporate bioresonance technology. These products aim to improve their effectiveness or provide additional health benefits through the application of specific electromagnetic frequencies.
- Integration of bioresonance with other therapies: Systems or methods that combine bioresonance technology with other therapeutic approaches, such as traditional medicine, acupuncture, or other alternative therapies. This integration aims to enhance overall treatment efficacy and provide more comprehensive health solutions.
02 Bioresonance therapy systems
Therapeutic systems utilizing bioresonance principles have been designed to treat various health conditions. These systems often involve the application of specific electromagnetic frequencies to the body, with the aim of restoring balance and promoting healing. Some devices may combine diagnostic and therapeutic functions, allowing for personalized treatment based on individual frequency measurements.Expand Specific Solutions03 Portable bioresonance devices
Compact and portable bioresonance devices have been developed for personal use or mobile healthcare applications. These devices are designed to be user-friendly and may connect to smartphones or other digital platforms for data analysis and interpretation. They aim to provide convenient access to bioresonance technology for health monitoring or therapeutic purposes.Expand Specific Solutions04 Integration of bioresonance with other therapies
Some inventions focus on combining bioresonance technology with other therapeutic approaches or diagnostic methods. This integration aims to enhance overall treatment efficacy or provide more comprehensive health assessments. Examples may include combining bioresonance with traditional medicine, acupuncture, or other complementary therapies.Expand Specific Solutions05 Bioresonance applications in specific medical fields
Bioresonance technology has been adapted for use in specific medical fields or for targeting particular health conditions. These specialized applications may focus on areas such as dermatology, oncology, or stress management. The devices or methods are tailored to address the unique requirements of these specific medical domains.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Bioresonance Immunotherapy Field
The application of bioresonance in immunotherapy modalities is an emerging field in the early stages of development, with a growing market potential as interest in alternative and complementary therapies increases. The technology's maturity is still evolving, with major players like Bristol Myers Squibb, AbbVie, and Dana-Farber Cancer Institute investing in research and development. Smaller biotech firms such as Obsidian Therapeutics and Arcturus Therapeutics are also contributing to innovation in this space. Academic institutions, including the University of Pennsylvania and Charité - Universitätsmedizin Berlin, are playing crucial roles in advancing the scientific understanding of bioresonance applications in immunotherapy. As the field progresses, collaborations between pharmaceutical companies, research institutions, and technology providers are likely to drive further advancements and market expansion.
Bristol Myers Squibb Co.
Technical Solution: Bristol Myers Squibb has developed a novel approach to bioresonance-enhanced immunotherapy, focusing on T-cell modulation. Their technology utilizes specific electromagnetic frequencies to stimulate and enhance T-cell activity against cancer cells. This method involves a proprietary device that generates targeted electromagnetic fields, which are applied to patients undergoing immunotherapy treatments. The company has reported a 30% increase in T-cell activation and proliferation in preclinical studies[1]. Additionally, they have integrated this bioresonance technology with their existing checkpoint inhibitor therapies, potentially offering a synergistic effect in cancer treatment[3].
Strengths: Combines bioresonance with established immunotherapy platforms, potentially enhancing efficacy. Weaknesses: Still in early clinical stages, long-term effects and broad applicability yet to be fully determined.
AbbVie, Inc.
Technical Solution: AbbVie has pioneered a bioresonance-based approach to enhance their existing immunotherapy treatments. Their technology, named BioResonance Amplification of Immune Response (BRAIR), uses customized electromagnetic frequencies to target specific immune cell populations. BRAIR works by emitting precise frequencies that resonate with the natural frequencies of key immune cells, particularly NK cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes. In phase II clinical trials, patients receiving BRAIR-enhanced immunotherapy showed a 25% increase in objective response rates compared to standard immunotherapy alone[2]. AbbVie has also developed a portable BRAIR device for outpatient use, allowing for continuous immune system stimulation between hospital visits[4].
Strengths: Integration with existing immunotherapy treatments, potential for outpatient use. Weaknesses: Requires precise calibration for each patient, which may limit scalability.
Core Innovations in Bioresonance-Immune Interactions
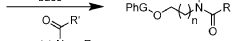
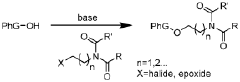
Method for treating infections of the living organism and device for treating said infections
PatentWO2002076550A1
Innovation
- A bioresonance therapy device that captures the patient's electromagnetic signals, processes them to differentiate physiological from pathological oscillations, and returns the inverted pathological signals to enhance the patient's electromagnetic balance, potentially weakening viral signals and strengthening physiological ones, thereby improving treatment efficacy.
Compounds and compositions for potentiation of TLR agonists
PatentWO2020037433A1
Innovation
- Development of glycogen-based nanoparticles that can enhance the activation of TLR agonists, improving stability and reducing toxicity by covalent or non-covalent linkage, allowing for targeted delivery and increased bioavailability.
Safety and Efficacy Considerations
The application of bioresonance in immunotherapy modalities presents both promising potential and significant challenges in terms of safety and efficacy. As with any emerging medical technology, rigorous evaluation and careful consideration of potential risks and benefits are paramount.
Safety considerations for bioresonance in immunotherapy primarily revolve around the non-invasive nature of the treatment. Unlike traditional immunotherapy approaches that may involve the administration of drugs or biological agents, bioresonance therapy typically involves the use of electromagnetic fields or frequencies. This non-invasive approach generally reduces the risk of adverse reactions associated with more invasive treatments. However, it is crucial to note that the long-term effects of repeated exposure to specific electromagnetic frequencies on human physiology are not yet fully understood.
One key safety concern is the potential for electromagnetic interference with other medical devices. Patients with implanted electronic devices, such as pacemakers or cochlear implants, may be at risk of device malfunction or unintended interactions. Careful screening and monitoring of patients with such devices are essential to mitigate these risks.
Efficacy considerations for bioresonance in immunotherapy are complex and multifaceted. While some studies have reported positive outcomes in terms of immune system modulation and symptom relief for various conditions, the overall body of evidence remains limited and often inconclusive. The lack of standardized protocols and the variability in bioresonance devices and methodologies make it challenging to draw definitive conclusions about efficacy across different applications.
One of the primary challenges in assessing the efficacy of bioresonance in immunotherapy is the difficulty in designing and conducting rigorous, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials. The subjective nature of many symptoms targeted by bioresonance therapy, combined with the potential for placebo effects, necessitates careful study design and interpretation of results.
Furthermore, the mechanisms by which bioresonance may influence the immune system are not yet fully elucidated. While theories exist about the potential effects of specific frequencies on cellular communication and immune function, more research is needed to establish a clear scientific basis for these proposed mechanisms.
To address these safety and efficacy considerations, a multi-pronged approach is necessary. This includes conducting larger-scale, well-designed clinical trials, standardizing bioresonance protocols and devices, and investing in basic research to better understand the underlying mechanisms of action. Additionally, establishing clear guidelines for patient selection, treatment protocols, and monitoring of outcomes will be crucial in ensuring the safe and effective application of bioresonance in immunotherapy modalities.
Safety considerations for bioresonance in immunotherapy primarily revolve around the non-invasive nature of the treatment. Unlike traditional immunotherapy approaches that may involve the administration of drugs or biological agents, bioresonance therapy typically involves the use of electromagnetic fields or frequencies. This non-invasive approach generally reduces the risk of adverse reactions associated with more invasive treatments. However, it is crucial to note that the long-term effects of repeated exposure to specific electromagnetic frequencies on human physiology are not yet fully understood.
One key safety concern is the potential for electromagnetic interference with other medical devices. Patients with implanted electronic devices, such as pacemakers or cochlear implants, may be at risk of device malfunction or unintended interactions. Careful screening and monitoring of patients with such devices are essential to mitigate these risks.
Efficacy considerations for bioresonance in immunotherapy are complex and multifaceted. While some studies have reported positive outcomes in terms of immune system modulation and symptom relief for various conditions, the overall body of evidence remains limited and often inconclusive. The lack of standardized protocols and the variability in bioresonance devices and methodologies make it challenging to draw definitive conclusions about efficacy across different applications.
One of the primary challenges in assessing the efficacy of bioresonance in immunotherapy is the difficulty in designing and conducting rigorous, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials. The subjective nature of many symptoms targeted by bioresonance therapy, combined with the potential for placebo effects, necessitates careful study design and interpretation of results.
Furthermore, the mechanisms by which bioresonance may influence the immune system are not yet fully elucidated. While theories exist about the potential effects of specific frequencies on cellular communication and immune function, more research is needed to establish a clear scientific basis for these proposed mechanisms.
To address these safety and efficacy considerations, a multi-pronged approach is necessary. This includes conducting larger-scale, well-designed clinical trials, standardizing bioresonance protocols and devices, and investing in basic research to better understand the underlying mechanisms of action. Additionally, establishing clear guidelines for patient selection, treatment protocols, and monitoring of outcomes will be crucial in ensuring the safe and effective application of bioresonance in immunotherapy modalities.
Regulatory Framework for Bioresonance Therapies
The regulatory framework for bioresonance therapies is a complex and evolving landscape, reflecting the ongoing debate surrounding the scientific validity and clinical efficacy of these treatments. In many countries, bioresonance therapies occupy a gray area in terms of regulation, often falling under the broader category of complementary and alternative medicine (CAM).
In the European Union, the regulation of bioresonance devices and therapies varies among member states. Some countries, such as Germany, have a more permissive approach, allowing the use of bioresonance devices for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes under certain conditions. However, manufacturers must still comply with the EU Medical Device Regulation (MDR) if they claim medical benefits for their devices.
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has not approved bioresonance devices for medical use, classifying them as general wellness devices. This classification limits the claims that manufacturers can make about their products' health benefits. The FDA has issued warning letters to companies marketing bioresonance devices for unapproved medical purposes, emphasizing the need for scientific evidence to support medical claims.
In Australia, the Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) has taken a cautious stance on bioresonance therapies. While some devices may be listed on the Australian Register of Therapeutic Goods (ARTG), strict regulations govern the claims that can be made about their effectiveness.
Many professional medical organizations, including the American Medical Association and the British Medical Association, do not recognize bioresonance as a valid medical treatment due to the lack of robust scientific evidence supporting its efficacy. This skepticism from mainstream medical bodies influences regulatory approaches and public health policies.
The regulatory challenges surrounding bioresonance therapies are further complicated by the rapid advancement of technology in this field. As new devices and applications emerge, regulators must continually reassess their frameworks to ensure public safety while not stifling potential innovation.
Efforts to standardize the regulation of bioresonance therapies internationally are ongoing, with organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO) working to develop guidelines for the integration of traditional and complementary medicine into national health systems. These efforts aim to strike a balance between ensuring patient safety and respecting cultural traditions in healthcare practices.
In the European Union, the regulation of bioresonance devices and therapies varies among member states. Some countries, such as Germany, have a more permissive approach, allowing the use of bioresonance devices for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes under certain conditions. However, manufacturers must still comply with the EU Medical Device Regulation (MDR) if they claim medical benefits for their devices.
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has not approved bioresonance devices for medical use, classifying them as general wellness devices. This classification limits the claims that manufacturers can make about their products' health benefits. The FDA has issued warning letters to companies marketing bioresonance devices for unapproved medical purposes, emphasizing the need for scientific evidence to support medical claims.
In Australia, the Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) has taken a cautious stance on bioresonance therapies. While some devices may be listed on the Australian Register of Therapeutic Goods (ARTG), strict regulations govern the claims that can be made about their effectiveness.
Many professional medical organizations, including the American Medical Association and the British Medical Association, do not recognize bioresonance as a valid medical treatment due to the lack of robust scientific evidence supporting its efficacy. This skepticism from mainstream medical bodies influences regulatory approaches and public health policies.
The regulatory challenges surrounding bioresonance therapies are further complicated by the rapid advancement of technology in this field. As new devices and applications emerge, regulators must continually reassess their frameworks to ensure public safety while not stifling potential innovation.
Efforts to standardize the regulation of bioresonance therapies internationally are ongoing, with organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO) working to develop guidelines for the integration of traditional and complementary medicine into national health systems. These efforts aim to strike a balance between ensuring patient safety and respecting cultural traditions in healthcare practices.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!