Bioresonance Techniques in Managing Sleep Apnea Syndrome
AUG 11, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Bioresonance and Sleep Apnea: Background and Objectives
Bioresonance therapy, a form of alternative medicine, has gained attention in recent years for its potential application in managing various health conditions, including sleep apnea syndrome. This emerging field combines principles of quantum physics and traditional medicine, aiming to detect and correct energetic imbalances within the body.
The concept of bioresonance originated in the 1970s, developed by German physician Franz Morell. It is based on the theory that all cells emit electromagnetic waves, and that these waves can be measured and manipulated to improve health. Over the past few decades, the technology has evolved, incorporating more sophisticated electronic devices and software to analyze and modulate these frequencies.
Sleep apnea syndrome, a common sleep disorder characterized by repeated interruptions in breathing during sleep, affects millions of people worldwide. Traditional treatments include continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machines, oral appliances, and in some cases, surgery. However, these approaches often come with challenges such as discomfort, compliance issues, and potential side effects, leading researchers and clinicians to explore alternative or complementary therapies.
The application of bioresonance techniques to sleep apnea management represents a novel approach that aims to address the underlying physiological imbalances associated with the condition. Proponents of this method suggest that by identifying and correcting abnormal frequency patterns in the body, particularly those related to the respiratory system and sleep regulation, it may be possible to alleviate symptoms and improve overall sleep quality.
As research in this field progresses, several objectives have emerged for the exploration of bioresonance in sleep apnea treatment. These include:
1. Evaluating the efficacy of bioresonance therapy in reducing the frequency and severity of apnea episodes.
2. Investigating the potential of bioresonance to improve sleep quality and daytime functioning in patients with sleep apnea.
3. Comparing the outcomes of bioresonance therapy with conventional treatments for sleep apnea.
4. Assessing the long-term effects and safety profile of bioresonance techniques in managing sleep apnea syndrome.
5. Exploring the possibility of combining bioresonance with existing treatments to enhance overall therapeutic outcomes.
The integration of bioresonance techniques into sleep apnea management represents a convergence of alternative and conventional medicine. As the medical community continues to seek more effective and patient-friendly approaches to treating sleep disorders, bioresonance offers a promising avenue for investigation. However, rigorous scientific studies are necessary to establish its validity, efficacy, and safety in the context of sleep apnea syndrome.
The concept of bioresonance originated in the 1970s, developed by German physician Franz Morell. It is based on the theory that all cells emit electromagnetic waves, and that these waves can be measured and manipulated to improve health. Over the past few decades, the technology has evolved, incorporating more sophisticated electronic devices and software to analyze and modulate these frequencies.
Sleep apnea syndrome, a common sleep disorder characterized by repeated interruptions in breathing during sleep, affects millions of people worldwide. Traditional treatments include continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machines, oral appliances, and in some cases, surgery. However, these approaches often come with challenges such as discomfort, compliance issues, and potential side effects, leading researchers and clinicians to explore alternative or complementary therapies.
The application of bioresonance techniques to sleep apnea management represents a novel approach that aims to address the underlying physiological imbalances associated with the condition. Proponents of this method suggest that by identifying and correcting abnormal frequency patterns in the body, particularly those related to the respiratory system and sleep regulation, it may be possible to alleviate symptoms and improve overall sleep quality.
As research in this field progresses, several objectives have emerged for the exploration of bioresonance in sleep apnea treatment. These include:
1. Evaluating the efficacy of bioresonance therapy in reducing the frequency and severity of apnea episodes.
2. Investigating the potential of bioresonance to improve sleep quality and daytime functioning in patients with sleep apnea.
3. Comparing the outcomes of bioresonance therapy with conventional treatments for sleep apnea.
4. Assessing the long-term effects and safety profile of bioresonance techniques in managing sleep apnea syndrome.
5. Exploring the possibility of combining bioresonance with existing treatments to enhance overall therapeutic outcomes.
The integration of bioresonance techniques into sleep apnea management represents a convergence of alternative and conventional medicine. As the medical community continues to seek more effective and patient-friendly approaches to treating sleep disorders, bioresonance offers a promising avenue for investigation. However, rigorous scientific studies are necessary to establish its validity, efficacy, and safety in the context of sleep apnea syndrome.
Market Analysis for Sleep Apnea Management Solutions
The sleep apnea management solutions market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing awareness of sleep disorders and their impact on overall health. Sleep apnea, particularly obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), affects millions of people worldwide, with estimates suggesting that up to 1 billion individuals may be affected globally. This widespread prevalence has created a substantial market opportunity for innovative management solutions.
The market for sleep apnea management solutions encompasses a wide range of products and services, including diagnostic devices, therapeutic equipment, and emerging technologies such as bioresonance techniques. Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) devices currently dominate the market, accounting for a significant portion of sales. However, there is a growing demand for alternative treatments due to compliance issues associated with CPAP therapy.
Bioresonance techniques, as a potential management solution for sleep apnea syndrome, represent an emerging segment within this market. While still in the early stages of development and adoption, these techniques are attracting interest from both patients and healthcare providers seeking non-invasive, drug-free alternatives to traditional treatments. The potential of bioresonance to address the underlying causes of sleep apnea, rather than just managing symptoms, has sparked curiosity and research in the field.
Market trends indicate a shift towards more personalized and patient-friendly solutions. This trend aligns well with the principles of bioresonance, which aims to tailor treatment to individual patient needs. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on home-based diagnostic and treatment options, driven by the need for convenience and reduced healthcare costs. Bioresonance techniques, if proven effective, could potentially fit into this trend by offering a portable and user-friendly solution for managing sleep apnea.
The sleep apnea management solutions market is expected to continue its growth trajectory, with projections suggesting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 6% in the coming years. Factors contributing to this growth include the rising prevalence of sleep disorders, increasing awareness of the health risks associated with untreated sleep apnea, and technological advancements in diagnostic and treatment options.
As the market evolves, there is likely to be increased competition and innovation in alternative treatment methods, including bioresonance techniques. However, the adoption and market penetration of these novel approaches will depend heavily on clinical evidence demonstrating their efficacy and safety in managing sleep apnea syndrome. Regulatory approval and acceptance by healthcare professionals will be crucial factors in determining the commercial success of bioresonance techniques in this market.
The market for sleep apnea management solutions encompasses a wide range of products and services, including diagnostic devices, therapeutic equipment, and emerging technologies such as bioresonance techniques. Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) devices currently dominate the market, accounting for a significant portion of sales. However, there is a growing demand for alternative treatments due to compliance issues associated with CPAP therapy.
Bioresonance techniques, as a potential management solution for sleep apnea syndrome, represent an emerging segment within this market. While still in the early stages of development and adoption, these techniques are attracting interest from both patients and healthcare providers seeking non-invasive, drug-free alternatives to traditional treatments. The potential of bioresonance to address the underlying causes of sleep apnea, rather than just managing symptoms, has sparked curiosity and research in the field.
Market trends indicate a shift towards more personalized and patient-friendly solutions. This trend aligns well with the principles of bioresonance, which aims to tailor treatment to individual patient needs. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on home-based diagnostic and treatment options, driven by the need for convenience and reduced healthcare costs. Bioresonance techniques, if proven effective, could potentially fit into this trend by offering a portable and user-friendly solution for managing sleep apnea.
The sleep apnea management solutions market is expected to continue its growth trajectory, with projections suggesting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 6% in the coming years. Factors contributing to this growth include the rising prevalence of sleep disorders, increasing awareness of the health risks associated with untreated sleep apnea, and technological advancements in diagnostic and treatment options.
As the market evolves, there is likely to be increased competition and innovation in alternative treatment methods, including bioresonance techniques. However, the adoption and market penetration of these novel approaches will depend heavily on clinical evidence demonstrating their efficacy and safety in managing sleep apnea syndrome. Regulatory approval and acceptance by healthcare professionals will be crucial factors in determining the commercial success of bioresonance techniques in this market.
Current Challenges in Bioresonance for Sleep Apnea
Bioresonance techniques in managing Sleep Apnea Syndrome face several significant challenges that hinder their widespread adoption and efficacy. One of the primary obstacles is the lack of standardized protocols for bioresonance therapy in sleep apnea treatment. The absence of a unified approach makes it difficult to replicate results across different clinical settings and patient populations, limiting the technique's credibility within the medical community.
Another major challenge is the scarcity of large-scale, randomized controlled trials that demonstrate the long-term efficacy of bioresonance for sleep apnea. While some small studies have shown promising results, the lack of robust clinical evidence makes it challenging for healthcare providers to confidently recommend bioresonance as a primary or complementary treatment option.
The complexity of sleep apnea as a multifactorial disorder also poses a significant challenge for bioresonance techniques. Sleep apnea can be influenced by various factors, including obesity, anatomical abnormalities, and neuromuscular issues. Developing a bioresonance approach that effectively addresses all these aspects simultaneously remains a considerable technical hurdle.
Furthermore, the integration of bioresonance devices with existing sleep monitoring technologies presents both technical and practical challenges. Ensuring seamless data collection and interpretation between bioresonance equipment and polysomnography systems requires sophisticated software and hardware solutions that are not yet widely available or standardized.
The variability in patient response to bioresonance therapy is another significant challenge. Factors such as individual physiology, severity of sleep apnea, and comorbid conditions can greatly influence the effectiveness of the treatment. Developing personalized bioresonance protocols that can adapt to each patient's unique characteristics remains a complex task.
Additionally, the regulatory landscape for bioresonance devices in sleep apnea management is still evolving. Many countries have not yet established clear guidelines for the approval and use of these devices in clinical settings, creating uncertainty for manufacturers and healthcare providers alike.
Lastly, there is a notable gap in the understanding of the precise mechanisms by which bioresonance affects sleep apnea symptoms. While theories exist, the lack of a comprehensive scientific explanation for its efficacy hampers its acceptance in mainstream medicine and impedes the development of more targeted and effective bioresonance techniques for sleep apnea management.
Another major challenge is the scarcity of large-scale, randomized controlled trials that demonstrate the long-term efficacy of bioresonance for sleep apnea. While some small studies have shown promising results, the lack of robust clinical evidence makes it challenging for healthcare providers to confidently recommend bioresonance as a primary or complementary treatment option.
The complexity of sleep apnea as a multifactorial disorder also poses a significant challenge for bioresonance techniques. Sleep apnea can be influenced by various factors, including obesity, anatomical abnormalities, and neuromuscular issues. Developing a bioresonance approach that effectively addresses all these aspects simultaneously remains a considerable technical hurdle.
Furthermore, the integration of bioresonance devices with existing sleep monitoring technologies presents both technical and practical challenges. Ensuring seamless data collection and interpretation between bioresonance equipment and polysomnography systems requires sophisticated software and hardware solutions that are not yet widely available or standardized.
The variability in patient response to bioresonance therapy is another significant challenge. Factors such as individual physiology, severity of sleep apnea, and comorbid conditions can greatly influence the effectiveness of the treatment. Developing personalized bioresonance protocols that can adapt to each patient's unique characteristics remains a complex task.
Additionally, the regulatory landscape for bioresonance devices in sleep apnea management is still evolving. Many countries have not yet established clear guidelines for the approval and use of these devices in clinical settings, creating uncertainty for manufacturers and healthcare providers alike.
Lastly, there is a notable gap in the understanding of the precise mechanisms by which bioresonance affects sleep apnea symptoms. While theories exist, the lack of a comprehensive scientific explanation for its efficacy hampers its acceptance in mainstream medicine and impedes the development of more targeted and effective bioresonance techniques for sleep apnea management.
Existing Bioresonance Approaches for Sleep Apnea
01 Bioresonance diagnostic devices
Bioresonance techniques are used in diagnostic devices to measure and analyze electromagnetic frequencies emitted by the human body. These devices can detect imbalances or abnormalities in the body's energy field, potentially aiding in the early detection of health issues or guiding treatment plans.- Bioresonance diagnostic devices: These devices are designed to detect and analyze electromagnetic frequencies emitted by the human body. They are used for non-invasive diagnostic purposes, potentially identifying imbalances or health issues based on the body's energy patterns.
- Bioresonance therapy systems: These systems are used for therapeutic purposes, applying specific electromagnetic frequencies to the body. The aim is to restore balance and promote healing by interacting with the body's own electromagnetic fields.
- Portable bioresonance devices: Compact and portable devices that allow for bioresonance therapy or diagnosis outside of clinical settings. These may include wearable devices or handheld units for personal use or mobile healthcare applications.
- Bioresonance frequency generation and modulation: Techniques and systems for generating, modulating, and applying specific electromagnetic frequencies for bioresonance therapy. This includes methods for tailoring frequencies to individual patients or specific health conditions.
- Integration of bioresonance with other therapies: Approaches that combine bioresonance techniques with other therapeutic methods, such as traditional medicine, acupuncture, or other energy-based therapies. This integration aims to enhance overall treatment efficacy and provide comprehensive health solutions.
02 Therapeutic applications of bioresonance
Bioresonance therapy involves the use of electromagnetic frequencies to treat various health conditions. Devices are designed to emit specific frequencies that interact with the body's own electromagnetic field, potentially promoting healing and restoring balance in the body's systems.Expand Specific Solutions03 Bioresonance in stress reduction and relaxation
Bioresonance techniques are applied in devices aimed at reducing stress and promoting relaxation. These devices may use specific frequency patterns to influence the body's stress response and encourage a state of calmness and well-being.Expand Specific Solutions04 Integration of bioresonance with other therapies
Bioresonance techniques are often combined with other therapeutic approaches to enhance overall treatment efficacy. This may include integration with traditional medicine, acupuncture, or other alternative therapies to provide a more holistic approach to health and wellness.Expand Specific Solutions05 Bioresonance in performance enhancement
Bioresonance techniques are explored for their potential in enhancing physical and mental performance. Devices using these techniques may aim to optimize the body's energy flow, potentially improving athletic performance, cognitive function, or overall vitality.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Bioresonance and Sleep Medicine
The bioresonance techniques for managing Sleep Apnea Syndrome market is in an early growth stage, with increasing research and development efforts. The global sleep apnea devices market size is projected to reach $9.9 billion by 2026, driven by rising prevalence of sleep disorders. While traditional CPAP devices dominate, bioresonance approaches are emerging as potential alternatives. Companies like Inspire Medical Systems, ResMed, and Philips are leading in sleep apnea treatment technologies, with newer entrants like Elemind Technologies and WhisperSom exploring neurostimulation and personalized bioresonance solutions. However, the technology is still evolving, and further clinical validation is needed for widespread adoption.
Koninklijke Philips NV
Technical Solution: Philips has developed a comprehensive approach to managing sleep apnea syndrome using bioresonance techniques. Their DreamStation 2 CPAP platform incorporates advanced pressure relief technology and machine learning algorithms to optimize therapy delivery[13]. The system uses a proprietary comfort feature called Flex, which analyzes breath-by-breath data to provide pressure relief at precise moments during the breathing cycle, enhancing patient comfort and adherence[14]. Philips' bioresonance approach extends to their DreamMapper mobile app, which utilizes behavioral change modules and personalized coaching to improve therapy engagement[15]. Additionally, the company has developed the NightBalance device, a positional therapy solution that uses gentle vibrations to encourage optimal sleeping positions, reducing apnea events without the need for positive airway pressure[16].
Strengths: Diverse range of sleep apnea management solutions, advanced data analytics for therapy optimization, and strong focus on patient engagement and comfort. Weaknesses: Potential for over-reliance on technology, higher costs associated with premium devices, and recent product recalls affecting consumer trust.
Medtronic, Inc.
Technical Solution: Medtronic has pioneered the use of neurostimulation in managing sleep apnea syndrome through bioresonance techniques. Their Inspire Upper Airway Stimulation therapy involves implanting a small device that delivers mild stimulation to key airway muscles during sleep[4]. This stimulation is synchronized with the patient's breathing cycle, using advanced sensing algorithms to detect respiratory effort and maintain airway patency[5]. The system incorporates a proprietary biofeedback mechanism that allows patients to adjust stimulation settings using a handheld remote, optimizing comfort and efficacy[6]. Medtronic's approach also includes a cloud-based platform for remote monitoring and therapy adjustment by healthcare providers.
Strengths: Non-CPAP alternative for CPAP-intolerant patients, potential for long-term compliance improvement, and minimal lifestyle impact. Weaknesses: Invasive procedure required, limited to specific patient populations, and potential for device-related complications.
Core Innovations in Bioresonance for Sleep Disorders
Method and device for Anti-sleep apnea
PatentInactiveUS20080119896A1
Innovation
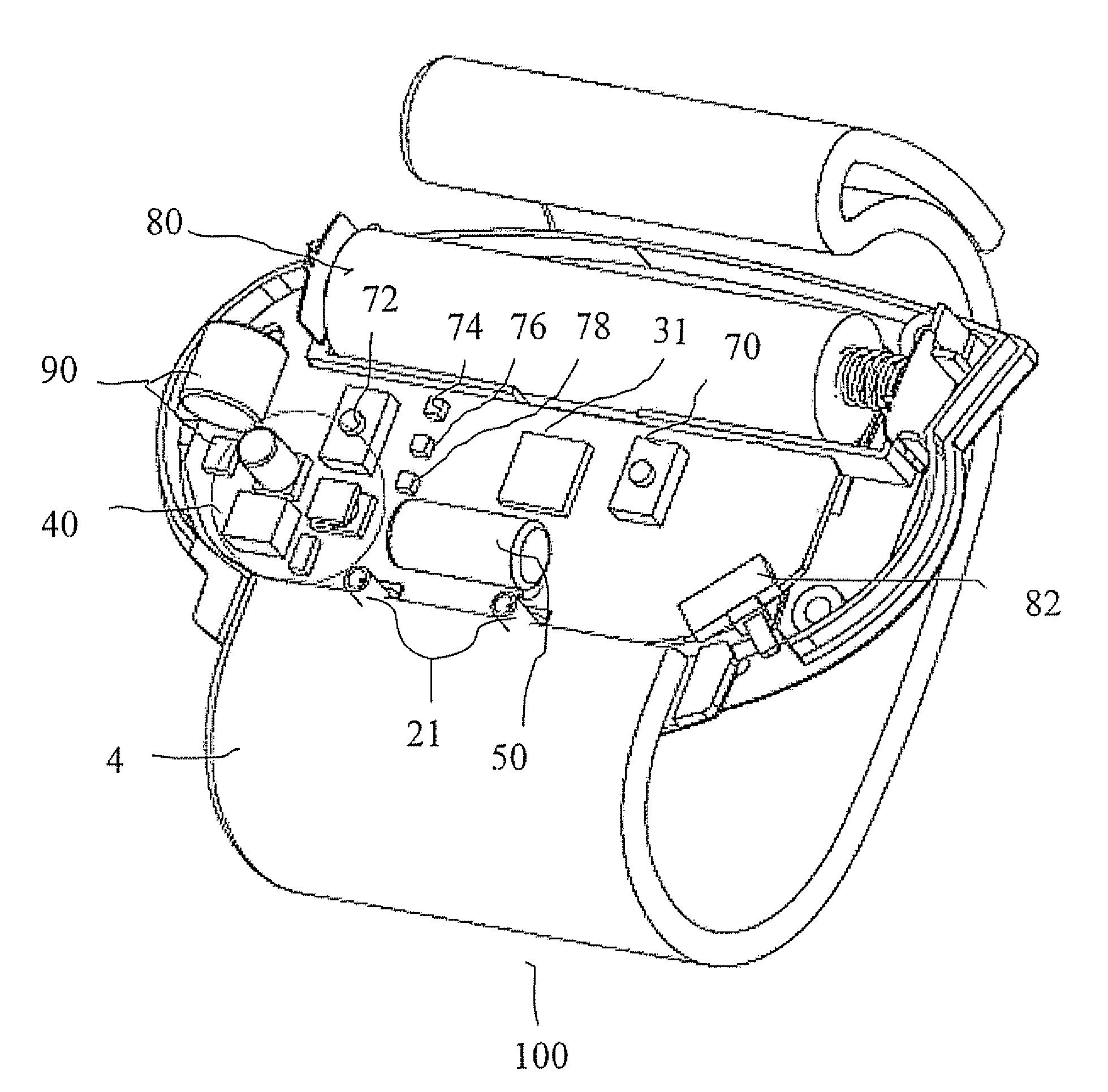
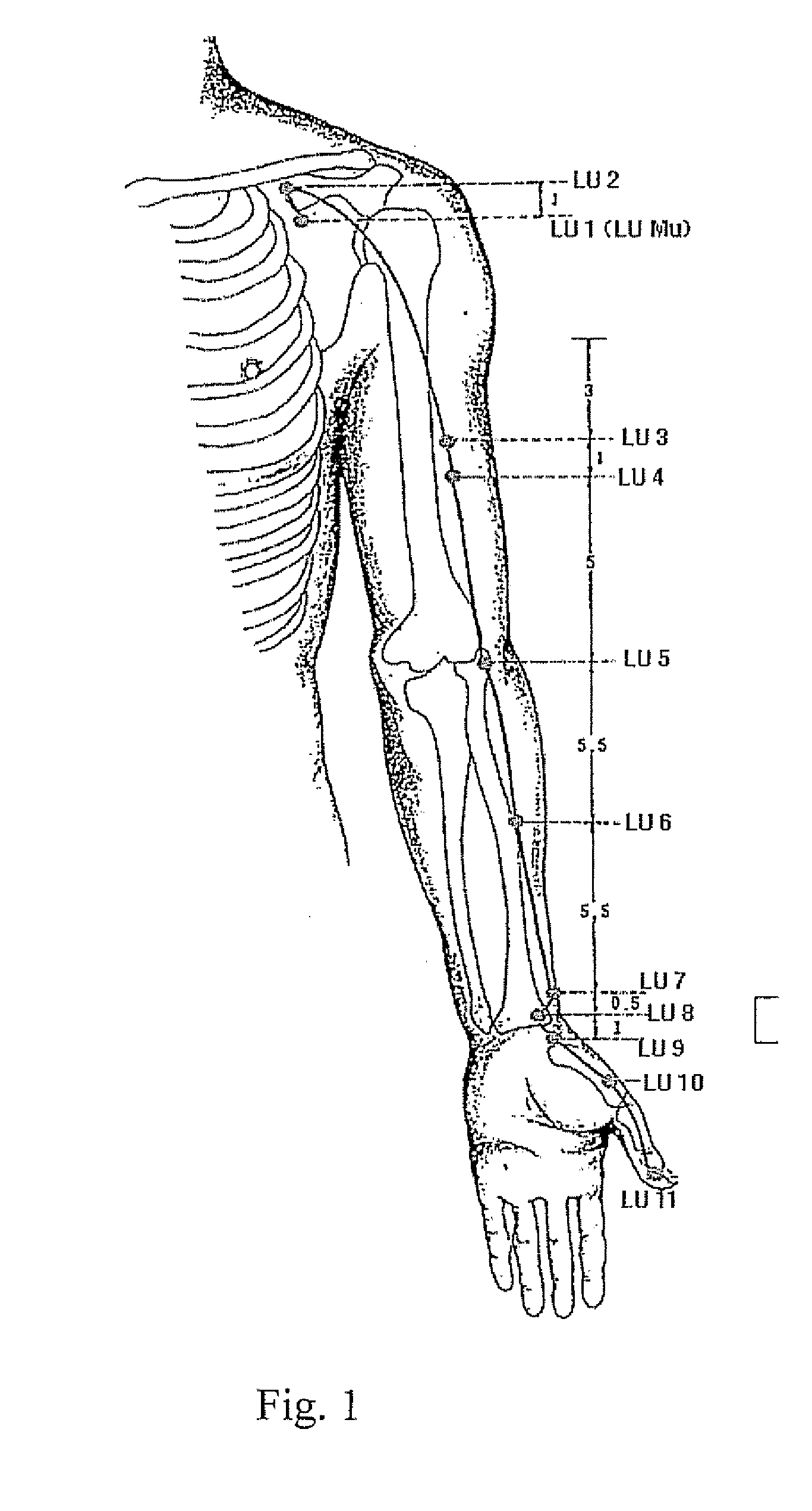
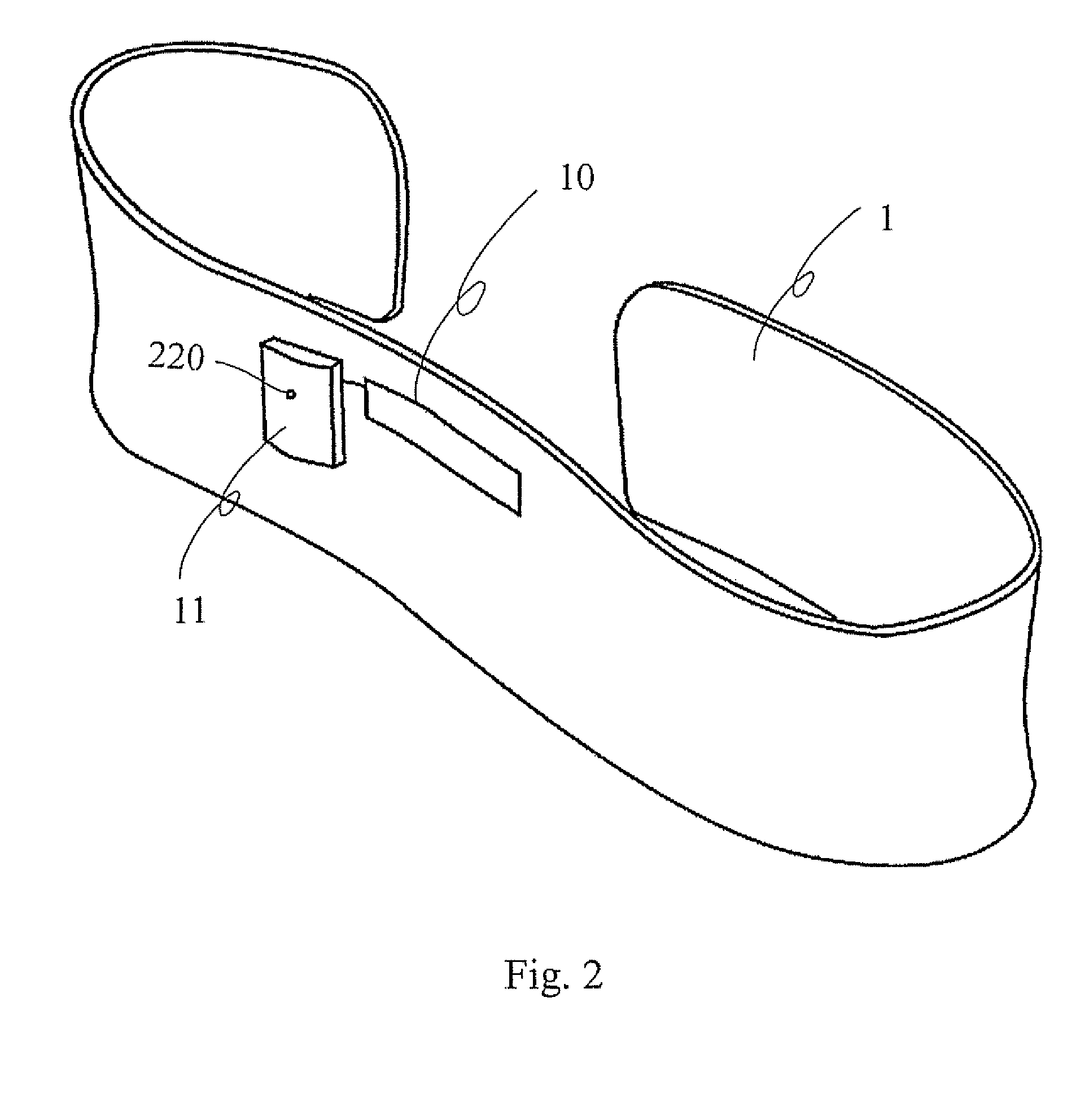
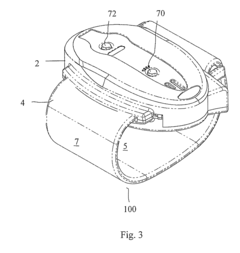
- An anti-sleep apnea device utilizing traditional Chinese medicine acupoint theory and smart textile technology, featuring a fabric strain sensor on an elastic belt to detect respiratory changes and transmit signals to a wristband that releases electrical pulses to the Lung Acupoint LU7, providing non-invasive and portable relief.
System and method for low-power neuromodulation
PatentPendingUS20250128015A1
Innovation
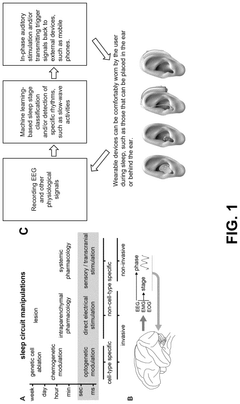
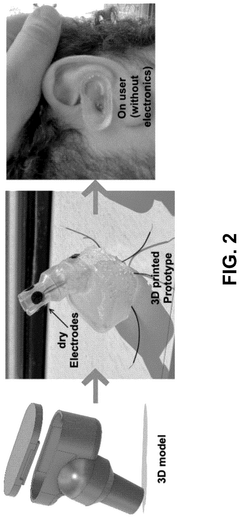
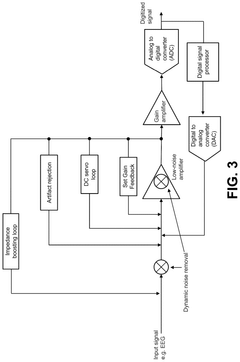
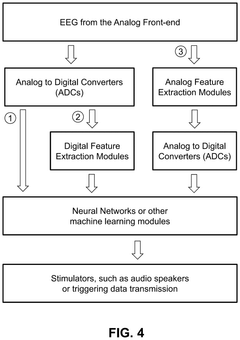
- A low-power neuromodulation system that uses in-ear electrodes to record EEG signals, integrated circuits for noise reduction, and a deep learning model for real-time sleep stage classification, enabling closed-loop on-device sleep modulation.
Clinical Efficacy and Safety Considerations
The clinical efficacy of bioresonance techniques in managing Sleep Apnea Syndrome (SAS) has been a subject of growing interest in recent years. Several studies have reported promising results, suggesting that bioresonance therapy may offer a non-invasive alternative or complementary approach to conventional treatments. Research indicates that bioresonance techniques can potentially help reduce the frequency and severity of apnea episodes, improve sleep quality, and alleviate associated symptoms such as daytime fatigue and cognitive impairment.
One notable study conducted over a 12-week period demonstrated a significant reduction in the Apnea-Hypopnea Index (AHI) among patients receiving bioresonance therapy compared to a control group. The treatment group also reported improved subjective sleep quality and reduced daytime sleepiness, as measured by standardized questionnaires. However, it is important to note that while these results are encouraging, larger-scale, randomized controlled trials are still needed to establish the long-term efficacy of bioresonance techniques for SAS management.
Safety considerations for bioresonance therapy in SAS patients are generally favorable. The non-invasive nature of the treatment minimizes the risk of adverse effects commonly associated with more invasive interventions. Most studies report no significant side effects or complications related to bioresonance therapy. However, some patients may experience mild and transient symptoms such as headaches or dizziness during the initial stages of treatment, which typically resolve as therapy progresses.
It is crucial to emphasize that bioresonance techniques should not be considered a standalone treatment for SAS, particularly in severe cases. Rather, they should be viewed as a potential adjunct to established therapies such as Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) or oral appliances. Patients considering bioresonance therapy should undergo a thorough medical evaluation and consult with sleep specialists to ensure appropriate management of their condition.
The mechanism of action by which bioresonance techniques may influence SAS is not yet fully understood. Proposed theories suggest that the therapy may help regulate autonomic nervous system function, improve upper airway muscle tone, or modulate central respiratory control mechanisms. Further research is needed to elucidate the precise physiological effects of bioresonance on sleep-disordered breathing.
While the current evidence base for bioresonance in SAS management is growing, it is important to approach these findings with cautious optimism. More robust, multi-center clinical trials are necessary to validate the efficacy and safety of this approach across diverse patient populations and to establish standardized treatment protocols. Additionally, long-term follow-up studies are required to assess the durability of treatment effects and identify any potential late-onset complications.
One notable study conducted over a 12-week period demonstrated a significant reduction in the Apnea-Hypopnea Index (AHI) among patients receiving bioresonance therapy compared to a control group. The treatment group also reported improved subjective sleep quality and reduced daytime sleepiness, as measured by standardized questionnaires. However, it is important to note that while these results are encouraging, larger-scale, randomized controlled trials are still needed to establish the long-term efficacy of bioresonance techniques for SAS management.
Safety considerations for bioresonance therapy in SAS patients are generally favorable. The non-invasive nature of the treatment minimizes the risk of adverse effects commonly associated with more invasive interventions. Most studies report no significant side effects or complications related to bioresonance therapy. However, some patients may experience mild and transient symptoms such as headaches or dizziness during the initial stages of treatment, which typically resolve as therapy progresses.
It is crucial to emphasize that bioresonance techniques should not be considered a standalone treatment for SAS, particularly in severe cases. Rather, they should be viewed as a potential adjunct to established therapies such as Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) or oral appliances. Patients considering bioresonance therapy should undergo a thorough medical evaluation and consult with sleep specialists to ensure appropriate management of their condition.
The mechanism of action by which bioresonance techniques may influence SAS is not yet fully understood. Proposed theories suggest that the therapy may help regulate autonomic nervous system function, improve upper airway muscle tone, or modulate central respiratory control mechanisms. Further research is needed to elucidate the precise physiological effects of bioresonance on sleep-disordered breathing.
While the current evidence base for bioresonance in SAS management is growing, it is important to approach these findings with cautious optimism. More robust, multi-center clinical trials are necessary to validate the efficacy and safety of this approach across diverse patient populations and to establish standardized treatment protocols. Additionally, long-term follow-up studies are required to assess the durability of treatment effects and identify any potential late-onset complications.
Regulatory Framework for Bioresonance Devices
The regulatory framework for bioresonance devices in the context of managing sleep apnea syndrome is a complex and evolving landscape. Currently, there is no unified global approach to regulating these devices, with different countries and regions implementing varying levels of oversight.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) classifies bioresonance devices as Class II medical devices. This classification requires manufacturers to submit a 510(k) premarket notification demonstrating that the device is substantially equivalent to a legally marketed predicate device. However, the FDA has not specifically approved any bioresonance devices for the treatment of sleep apnea syndrome, and their use for this purpose remains off-label.
The European Union, under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR), categorizes bioresonance devices as Class IIa medical devices. This classification necessitates a conformity assessment procedure involving a notified body. Manufacturers must demonstrate compliance with essential requirements, including clinical evaluation and risk management, to obtain CE marking for their devices.
In Australia, the Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) regulates bioresonance devices as therapeutic goods. Depending on their intended use and risk profile, they may be classified as Class IIa or higher. Manufacturers must include these devices in the Australian Register of Therapeutic Goods (ARTG) before they can be legally supplied in the country.
Many other countries, including Canada, Japan, and China, have their own regulatory frameworks for medical devices, which would apply to bioresonance devices used in sleep apnea management. These frameworks typically involve some form of premarket approval or registration process, as well as post-market surveillance requirements.
It is important to note that the regulatory status of bioresonance devices for sleep apnea management is often ambiguous due to the lack of robust clinical evidence supporting their efficacy. This has led to increased scrutiny from regulatory bodies and calls for more stringent oversight.
As research in this field progresses, it is likely that regulatory frameworks will evolve to address the specific challenges posed by bioresonance techniques in managing sleep apnea syndrome. This may include the development of specialized guidelines for clinical trials, standardized protocols for device performance evaluation, and more precise classification criteria based on the intended use and risk profile of these devices.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) classifies bioresonance devices as Class II medical devices. This classification requires manufacturers to submit a 510(k) premarket notification demonstrating that the device is substantially equivalent to a legally marketed predicate device. However, the FDA has not specifically approved any bioresonance devices for the treatment of sleep apnea syndrome, and their use for this purpose remains off-label.
The European Union, under the Medical Device Regulation (MDR), categorizes bioresonance devices as Class IIa medical devices. This classification necessitates a conformity assessment procedure involving a notified body. Manufacturers must demonstrate compliance with essential requirements, including clinical evaluation and risk management, to obtain CE marking for their devices.
In Australia, the Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) regulates bioresonance devices as therapeutic goods. Depending on their intended use and risk profile, they may be classified as Class IIa or higher. Manufacturers must include these devices in the Australian Register of Therapeutic Goods (ARTG) before they can be legally supplied in the country.
Many other countries, including Canada, Japan, and China, have their own regulatory frameworks for medical devices, which would apply to bioresonance devices used in sleep apnea management. These frameworks typically involve some form of premarket approval or registration process, as well as post-market surveillance requirements.
It is important to note that the regulatory status of bioresonance devices for sleep apnea management is often ambiguous due to the lack of robust clinical evidence supporting their efficacy. This has led to increased scrutiny from regulatory bodies and calls for more stringent oversight.
As research in this field progresses, it is likely that regulatory frameworks will evolve to address the specific challenges posed by bioresonance techniques in managing sleep apnea syndrome. This may include the development of specialized guidelines for clinical trials, standardized protocols for device performance evaluation, and more precise classification criteria based on the intended use and risk profile of these devices.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!