Butyrate in Clinical Nutrition: Emerging Opportunities
Butyrate Research Background
Butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid (SCFA), has emerged as a significant focus in clinical nutrition research due to its potential health benefits. The exploration of butyrate's role in human health dates back to the early 20th century, with initial studies primarily focused on its presence in the gastrointestinal tract. However, it wasn't until the late 1970s and early 1980s that researchers began to uncover the broader implications of butyrate in human physiology.
The scientific interest in butyrate gained momentum in the 1990s when studies revealed its potential as a histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor, suggesting a role in epigenetic regulation. This discovery opened up new avenues for research, particularly in the fields of cancer biology and immunology. Concurrently, advancements in microbiome research techniques allowed for a more comprehensive understanding of the gut microbiota's role in butyrate production, further fueling interest in this compound.
In the early 2000s, the focus shifted towards understanding butyrate's effects on intestinal health and inflammation. Researchers discovered its ability to enhance the intestinal barrier function and modulate the immune response, leading to investigations into its potential therapeutic applications for inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) and other gastrointestinal disorders.
The past decade has witnessed an exponential growth in butyrate-related research, with studies expanding beyond gut health to explore its impact on metabolic disorders, neurological conditions, and even cardiovascular health. This broadening scope has been driven by the recognition of the gut-brain axis and the systemic effects of gut-derived metabolites.
Recent technological advancements, such as high-throughput sequencing and metabolomics, have enabled researchers to delve deeper into the mechanisms of butyrate production and its interactions with host cells. These tools have facilitated a more nuanced understanding of the complex relationship between diet, gut microbiota, butyrate production, and human health.
As we move forward, the research landscape for butyrate in clinical nutrition is evolving towards personalized approaches. Scientists are now exploring how individual variations in gut microbiota composition and genetic factors influence butyrate metabolism and its subsequent health effects. This personalized perspective is opening up new possibilities for targeted nutritional interventions and therapeutic strategies.
The current research goals in the field of butyrate and clinical nutrition are multifaceted. They include optimizing butyrate delivery methods for therapeutic use, understanding the long-term effects of butyrate supplementation, and exploring its potential in preventive medicine. Additionally, there is a growing interest in identifying novel sources of butyrate precursors in the diet and developing innovative strategies to enhance endogenous butyrate production through targeted modulation of the gut microbiome.
Clinical Nutrition Market Analysis
The clinical nutrition market has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by an aging population, increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, and growing awareness of the importance of nutrition in healthcare. The global clinical nutrition market was valued at approximately $51 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $75 billion by 2027, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 6.5% during this period.
Within this market, enteral nutrition holds the largest share, accounting for over 60% of the total market value. Parenteral nutrition follows, with oral nutrition supplements making up the remainder. The hospital segment dominates the end-user market, followed by long-term care facilities and home care settings.
Geographically, North America leads the clinical nutrition market, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific. The United States, in particular, holds the largest market share due to its advanced healthcare infrastructure and high healthcare expenditure. However, the Asia-Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth, driven by improving healthcare systems, rising disposable incomes, and increasing awareness of nutritional therapies.
The market is characterized by the presence of several key players, including Nestlé Health Science, Abbott Laboratories, Fresenius Kabi, and Danone Nutricia. These companies are continuously investing in research and development to introduce innovative products and expand their market presence.
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in specialized nutrition products tailored to specific patient needs, such as those with diabetes, cancer, or gastrointestinal disorders. This trend is expected to continue, driving further market growth and diversification.
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on the clinical nutrition market, highlighting the importance of nutrition in patient care and recovery. This has led to increased demand for immune-boosting nutritional products and has accelerated the adoption of home-based nutritional therapies.
Looking ahead, the clinical nutrition market is poised for continued growth, driven by factors such as the rising prevalence of malnutrition, increasing healthcare costs, and growing recognition of the role of nutrition in patient outcomes. Emerging opportunities in personalized nutrition, functional foods, and nutraceuticals are expected to shape the future of this market.
Butyrate Challenges in Nutrition
Butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid produced by gut microbiota, has gained significant attention in clinical nutrition due to its potential health benefits. However, several challenges hinder its widespread application in nutritional interventions. One of the primary obstacles is the limited bioavailability of oral butyrate supplements. The compound is rapidly absorbed in the upper gastrointestinal tract, making it difficult to deliver therapeutic concentrations to the colon where it exerts its beneficial effects.
Another challenge lies in the stability of butyrate formulations. The compound is highly volatile and has an unpleasant odor, which can affect patient compliance and product shelf-life. Developing stable, palatable formulations that can effectively deliver butyrate to the target sites in the gut remains a significant hurdle for researchers and manufacturers.
The dosage and timing of butyrate administration also present challenges. Optimal dosing regimens for different health conditions are not well-established, and the effects of butyrate may vary depending on the timing of intake relative to meals or other medications. This lack of standardization complicates the design of clinical trials and the development of evidence-based nutritional guidelines.
Furthermore, individual variations in gut microbiota composition and metabolism can influence the production and utilization of butyrate. Some patients may have reduced capacity to produce or absorb butyrate due to dysbiosis or other gastrointestinal disorders. Tailoring butyrate supplementation to individual needs and gut microbiome profiles remains a complex challenge in personalized nutrition.
The regulatory landscape surrounding butyrate as a nutritional supplement or therapeutic agent is another area of concern. Classification of butyrate products as food supplements, medical foods, or drugs can vary between jurisdictions, affecting their development, marketing, and accessibility to patients.
Lastly, while butyrate has shown promise in preclinical studies, translating these findings into robust clinical evidence has been challenging. Many studies have been limited by small sample sizes, short durations, or inconsistent methodologies. Conducting large-scale, well-designed clinical trials to definitively establish the efficacy and safety of butyrate interventions across various health conditions is a significant undertaking that requires substantial resources and coordination among researchers, clinicians, and industry partners.
Current Butyrate Applications
01 Butyrate as a therapeutic agent
Butyrate is explored as a potential therapeutic agent for various health conditions. It has shown promise in treating inflammatory disorders, metabolic diseases, and gastrointestinal issues. Research indicates that butyrate may have beneficial effects on gut health, immune function, and cellular metabolism.- Butyrate as a therapeutic agent: Butyrate is used as a therapeutic agent in various medical applications. It has shown potential in treating inflammatory conditions, metabolic disorders, and certain types of cancer. The compound's ability to modulate gene expression and cellular processes makes it a promising candidate for pharmaceutical development.
- Butyrate in gut health and microbiome regulation: Butyrate plays a crucial role in maintaining gut health and regulating the microbiome. It serves as an energy source for colonic epithelial cells and has anti-inflammatory properties. Research focuses on developing butyrate-based formulations to improve digestive health and treat gastrointestinal disorders.
- Butyrate production by microorganisms: Various microorganisms, particularly certain bacterial strains, are capable of producing butyrate through fermentation processes. Research in this area aims to optimize butyrate production for industrial applications and to develop probiotic formulations that can enhance butyrate levels in the gut.
- Butyrate derivatives and their applications: Butyrate derivatives, such as esters and salts, are being developed for various applications. These modified forms of butyrate may offer improved stability, bioavailability, or targeted delivery compared to the parent compound. Research in this area explores the potential of butyrate derivatives in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and food industries.
- Butyrate in animal nutrition and agriculture: Butyrate and its derivatives are used in animal nutrition to improve growth performance, gut health, and overall well-being of livestock. Research in this field focuses on developing feed additives and supplements containing butyrate to enhance animal productivity and reduce the use of antibiotics in agriculture.
02 Butyrate production in the gut microbiome
Studies focus on enhancing butyrate production in the gut microbiome. This involves investigating the role of specific bacterial strains, dietary interventions, and prebiotic compounds that can stimulate butyrate-producing bacteria. Increasing butyrate levels in the gut is associated with improved intestinal health and overall well-being.Expand Specific Solutions03 Butyrate in animal nutrition
Butyrate is utilized in animal nutrition to improve growth performance, gut health, and overall animal welfare. Research explores the incorporation of butyrate or its precursors in animal feed formulations, particularly for livestock and poultry. The benefits include enhanced nutrient absorption and improved intestinal barrier function.Expand Specific Solutions04 Butyrate derivatives and delivery systems
Development of novel butyrate derivatives and delivery systems aims to enhance its bioavailability and targeted release. This includes the creation of butyrate prodrugs, encapsulation techniques, and controlled-release formulations. These innovations seek to overcome the limitations of butyrate's rapid metabolism and improve its therapeutic efficacy.Expand Specific Solutions05 Butyrate in cancer research
Butyrate is investigated for its potential anti-cancer properties. Studies explore its role in regulating gene expression, inducing apoptosis in cancer cells, and modulating the immune response against tumors. Research focuses on understanding the mechanisms of action and developing butyrate-based therapies for various types of cancer.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Butyrate Research
The butyrate market in clinical nutrition is in an emerging growth phase, driven by increasing recognition of its potential health benefits. The market size is expanding, with a growing number of companies investing in research and development. Technologically, the field is still evolving, with varying levels of maturity among key players. Companies like Nestlé, Baxter International, and Sanofi-Aventis Deutschland are at the forefront, leveraging their established presence in clinical nutrition. Emerging players such as PharmaBiome AG and Clasado Research Services are focusing on innovative approaches. Academic institutions like The University of Chicago and Louisiana State University are contributing significant research, potentially influencing future market directions. The competitive landscape is diverse, with both large pharmaceutical companies and specialized biotech firms vying for market share.
Société des Produits Nestlé SA
Baxter International, Inc.
Butyrate Mechanism Insights
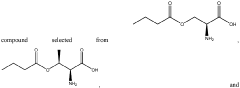
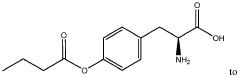
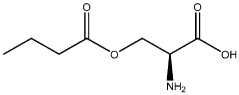
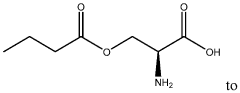
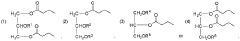
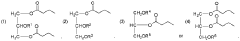
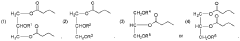
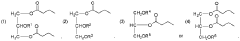
- Development of oral, systemically bioavailable butyrate conjugates with amino acids like serine, threonine, and tyrosine, which enhance bioavailability and allow butyrate to bypass initial metabolism, facilitating its transport into the bloodstream and across the blood-brain barrier.
- Development of butyrate-containing triglycerides with improved taste and odor profiles, specifically formulated to increase blood ketone levels and treat related conditions, using compounds like l,3-dibutyryl-2-palmitoylglycerol and other combinations of fatty acids, which are dairy-free and cholesterol-free, allowing for higher ketone production without additional mineral salts.
Regulatory Framework
The regulatory framework surrounding butyrate in clinical nutrition is complex and evolving, reflecting the growing interest in this short-chain fatty acid's potential therapeutic applications. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a crucial role in overseeing the use of butyrate in clinical settings. The regulatory status of butyrate largely depends on its intended use and formulation.
For dietary supplements, butyrate falls under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) of 1994. This allows for its sale as a dietary supplement without pre-market approval, provided manufacturers comply with good manufacturing practices and avoid making disease claims. However, the regulatory landscape becomes more intricate when considering butyrate for clinical nutrition applications.
In the context of medical foods, which are formulated to meet specific nutritional requirements for the management of diseases or conditions, butyrate-containing products may require more rigorous regulatory scrutiny. The FDA's guidance on medical foods stipulates that these products must be formulated for enteral administration under medical supervision and intended for the specific dietary management of a disease or condition.
For pharmaceutical applications, butyrate-based therapies would need to undergo the full FDA approval process, including extensive clinical trials to demonstrate safety and efficacy. This pathway is significantly more demanding and time-consuming but offers the potential for specific disease claims and medical indications.
Internationally, regulatory approaches to butyrate vary. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has assessed butyrate's safety and efficacy in various contexts, including as a feed additive for animals. For human use in clinical nutrition, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) would likely be involved in regulating pharmaceutical applications.
As research into butyrate's clinical potential expands, regulatory bodies are likely to refine their approaches. This may include developing specific guidelines for butyrate-based products in clinical nutrition, considering factors such as dosage, formulation, and intended use. Manufacturers and researchers must stay abreast of these evolving regulations to ensure compliance and maximize the potential of butyrate in clinical applications.
The regulatory framework also encompasses quality control and safety monitoring. Post-market surveillance and reporting of adverse events are critical components, especially as butyrate finds wider use in clinical settings. Regulatory bodies may require ongoing studies to assess long-term safety and efficacy, particularly for novel formulations or delivery methods.
Safety and Efficacy Studies
The safety and efficacy of butyrate in clinical nutrition have been extensively studied in recent years, with promising results emerging across various therapeutic applications. Safety studies have consistently demonstrated that butyrate supplementation is well-tolerated in most patient populations, with minimal adverse effects reported. Common side effects, when observed, are generally mild and transient, including gastrointestinal discomfort, nausea, and flatulence. These effects are typically dose-dependent and can be mitigated through gradual dose escalation or alternative delivery methods.
Long-term safety studies have shown no significant accumulation of butyrate in the body or adverse impacts on organ function, even with prolonged use. This favorable safety profile has been observed across diverse patient groups, including those with compromised gut health, metabolic disorders, and inflammatory conditions. However, it is important to note that safety data in certain vulnerable populations, such as pregnant women and young children, remain limited and warrant further investigation.
Efficacy studies have yielded encouraging results across a range of clinical applications. In gastrointestinal disorders, butyrate supplementation has shown significant benefits in managing inflammatory bowel diseases, such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. Clinical trials have reported improvements in disease activity scores, mucosal healing, and quality of life measures. Additionally, butyrate has demonstrated potential in alleviating symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome and functional gastrointestinal disorders.
Beyond gut health, emerging evidence suggests butyrate's efficacy in metabolic disorders. Studies have shown improvements in insulin sensitivity, lipid profiles, and body composition in patients with obesity and type 2 diabetes. These metabolic benefits are thought to be mediated through butyrate's effects on energy homeostasis, inflammation reduction, and gut microbiome modulation.
In the realm of immunology and inflammation, butyrate has shown promise in attenuating systemic inflammation markers and enhancing immune function. This has led to investigations into its potential applications in autoimmune disorders, allergies, and even certain cancers. While early results are encouraging, larger-scale clinical trials are needed to fully elucidate the extent of butyrate's immunomodulatory effects.
Neurological applications of butyrate are an exciting frontier in clinical research. Preliminary studies have suggested potential benefits in neurodegenerative disorders, such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease, as well as in mood disorders and cognitive function. These effects are hypothesized to be mediated through butyrate's neuroprotective and neuromodulatory properties, although more robust clinical evidence is required to confirm these findings.
As research continues to expand, novel delivery methods and formulations are being developed to enhance butyrate's bioavailability and targeted delivery. These advancements aim to optimize the therapeutic potential of butyrate while minimizing potential side effects, paving the way for more widespread clinical applications in the future.