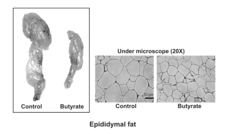
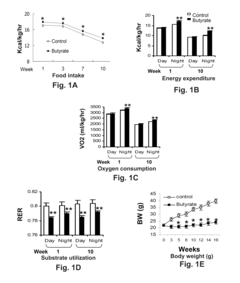
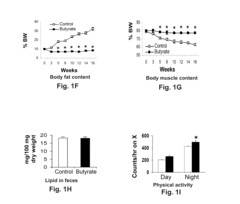
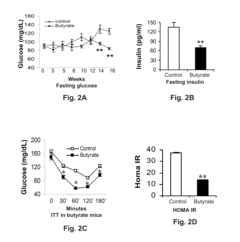
Butyrate as a Therapeutic Agent in Metabolic Syndrome
Butyrate in Metabolic Syndrome: Background and Objectives
Metabolic syndrome is a complex cluster of conditions that significantly increase the risk of cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and other serious health problems. As the prevalence of metabolic syndrome continues to rise globally, there is an urgent need for effective therapeutic interventions. In recent years, butyrate has emerged as a promising candidate for the treatment of metabolic syndrome, drawing attention from researchers and clinicians alike.
Butyrate is a short-chain fatty acid produced by the gut microbiota through the fermentation of dietary fibers. It plays a crucial role in maintaining intestinal health and has been shown to have numerous beneficial effects on metabolism. The growing interest in butyrate as a therapeutic agent for metabolic syndrome stems from its potential to address multiple aspects of the condition simultaneously.
The primary objective of this research is to comprehensively explore the therapeutic potential of butyrate in the context of metabolic syndrome. This involves investigating its mechanisms of action, evaluating its efficacy in various components of metabolic syndrome, and assessing its safety profile. By doing so, we aim to provide a solid foundation for the development of butyrate-based interventions that could potentially revolutionize the treatment of metabolic syndrome.
To fully understand the potential of butyrate, it is essential to examine its historical context and the evolution of research in this field. Early studies on butyrate focused primarily on its role in colonic health and cancer prevention. However, over the past decade, there has been a significant shift towards exploring its metabolic effects, particularly in relation to obesity, insulin resistance, and lipid metabolism.
The technological advancements in microbiome research and metabolomics have played a crucial role in advancing our understanding of butyrate's functions. These developments have enabled researchers to elucidate the complex interactions between butyrate, the gut microbiota, and host metabolism, providing new insights into its therapeutic potential.
As we delve deeper into the research on butyrate as a therapeutic agent for metabolic syndrome, it is important to consider the broader context of metabolic health interventions. This includes examining how butyrate compares to existing treatments, its potential synergies with other therapeutic approaches, and its place in the overall strategy for combating the global epidemic of metabolic disorders.
By thoroughly investigating the background and setting clear objectives for this research, we aim to lay the groundwork for innovative approaches to treating metabolic syndrome. This exploration of butyrate's therapeutic potential not only addresses a critical health need but also aligns with the growing trend towards microbiome-based therapies and personalized medicine in the management of complex metabolic disorders.
Market Analysis for Butyrate-Based Therapeutics
The market for butyrate-based therapeutics in metabolic syndrome is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing prevalence of metabolic disorders and the growing recognition of butyrate's potential therapeutic benefits. Metabolic syndrome, characterized by a cluster of conditions including obesity, high blood pressure, high blood sugar, and abnormal cholesterol levels, affects a substantial portion of the global population, creating a large potential market for effective treatments.
The demand for butyrate-based therapeutics is particularly strong in developed countries where lifestyle-related metabolic disorders are more prevalent. North America and Europe currently lead the market, with Asia-Pacific showing rapid growth potential due to changing dietary habits and increasing urbanization. The market is segmented based on formulation types, including oral supplements, topical applications, and injectable forms, each catering to different patient needs and preferences.
Key factors driving market growth include the rising awareness of gut health's impact on overall well-being, increasing research on microbiome-based therapies, and the shift towards preventive healthcare. The growing body of scientific evidence supporting butyrate's role in improving insulin sensitivity, reducing inflammation, and promoting weight loss has further fueled market interest.
The butyrate-based therapeutics market intersects with several other health sectors, including probiotics, prebiotics, and functional foods, creating opportunities for synergistic product development and market expansion. This convergence is attracting attention from both pharmaceutical companies and nutraceutical manufacturers, leading to increased investment in research and development.
Despite the promising outlook, the market faces challenges such as the need for more extensive clinical trials to establish efficacy and safety profiles, regulatory hurdles in different regions, and competition from established treatments for metabolic syndrome. Additionally, the complexity of butyrate's mechanisms of action and the variability in individual patient responses present obstacles to widespread adoption.
Looking ahead, the market for butyrate-based therapeutics in metabolic syndrome is expected to continue its growth trajectory. Factors such as the increasing focus on personalized medicine, advancements in drug delivery technologies, and the potential for combination therapies are likely to shape the market's future. As research progresses and more targeted applications are developed, butyrate-based therapeutics could play a significant role in addressing the global burden of metabolic syndrome.
Current Challenges in Butyrate Research and Application
Despite the promising potential of butyrate as a therapeutic agent for metabolic syndrome, several challenges hinder its widespread application and research progress. One of the primary obstacles is the limited bioavailability of oral butyrate supplements. The compound is rapidly absorbed in the upper gastrointestinal tract, leading to insufficient concentrations reaching the colon where it exerts its beneficial effects. This necessitates the development of novel delivery systems to ensure targeted release in the lower intestine.
Another significant challenge lies in the dosage optimization of butyrate for therapeutic use. The effective dose range for various metabolic conditions remains unclear, and there is a lack of standardized protocols for butyrate administration. This variability in dosing regimens across studies makes it difficult to draw conclusive evidence on its efficacy and safety profile.
The complex interplay between butyrate and the gut microbiome presents another hurdle. While butyrate is known to modulate the gut microbiota, the exact mechanisms and long-term effects of exogenous butyrate supplementation on microbial composition and function are not fully understood. This gap in knowledge complicates the development of personalized treatment strategies that account for individual variations in gut microbiota.
Furthermore, the potential side effects and long-term safety of butyrate supplementation require thorough investigation. Some studies have reported gastrointestinal discomfort and altered electrolyte balance with high doses of butyrate. Comprehensive long-term safety studies are needed to establish the risk-benefit profile of butyrate as a therapeutic agent.
The translation of preclinical findings to clinical applications poses another challenge. While animal studies have shown promising results, human clinical trials are limited in number and scale. The heterogeneity of metabolic syndrome and the multifactorial nature of its pathogenesis make it challenging to design and conduct large-scale, well-controlled clinical trials that can provide definitive evidence of butyrate's efficacy.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape for butyrate as a therapeutic agent remains complex. Its classification as a food supplement in some regions and a drug in others creates regulatory hurdles for its development and commercialization. Establishing a clear regulatory framework for butyrate-based therapies is crucial for advancing its clinical application in metabolic syndrome treatment.
Existing Butyrate Delivery Methods and Formulations
01 Butyrate as a therapeutic agent
Butyrate is explored as a potential therapeutic agent for various health conditions. It has shown promise in treating inflammatory disorders, metabolic diseases, and gastrointestinal issues. Research indicates that butyrate may have beneficial effects on gut health, immune function, and cellular processes.- Butyrate as a therapeutic agent: Butyrate is used as a therapeutic agent for various health conditions. It has shown potential in treating inflammatory diseases, metabolic disorders, and gastrointestinal issues. The compound is known for its anti-inflammatory properties and ability to modulate gut microbiota, making it a promising candidate for pharmaceutical applications.
- Butyrate in animal feed and nutrition: Butyrate is incorporated into animal feed formulations to improve gut health and overall performance in livestock. It has been shown to enhance nutrient absorption, promote growth, and strengthen the immune system in various animal species. The use of butyrate in animal nutrition has gained significant attention in the agricultural industry.
- Production methods for butyrate: Various methods have been developed for the production of butyrate, including fermentation processes and chemical synthesis. These methods aim to improve the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of butyrate production for industrial applications. Innovations in production techniques have focused on optimizing yield and purity of the final product.
- Butyrate derivatives and formulations: Research has been conducted on developing butyrate derivatives and novel formulations to enhance its stability, bioavailability, and targeted delivery. These modifications aim to improve the efficacy of butyrate in various applications, including pharmaceuticals and nutraceuticals. Encapsulation techniques and controlled-release formulations have been explored to optimize butyrate delivery.
- Butyrate in microbiome research: Butyrate plays a crucial role in microbiome research, particularly in studying the interactions between gut bacteria and host health. It is recognized as an important metabolite produced by certain gut bacteria, influencing various physiological processes. Research in this area focuses on understanding the mechanisms of butyrate production and its effects on the gut-brain axis.
02 Butyrate production in the gut microbiome
Studies focus on enhancing butyrate production in the gut microbiome. This involves investigating the role of specific bacteria in butyrate synthesis, developing prebiotic compounds to stimulate butyrate-producing bacteria, and exploring dietary interventions to increase butyrate levels in the intestine.Expand Specific Solutions03 Butyrate derivatives and formulations
Research is conducted on developing novel butyrate derivatives and formulations to improve its bioavailability and targeted delivery. This includes creating prodrugs, encapsulation techniques, and controlled-release systems to enhance the therapeutic potential of butyrate.Expand Specific Solutions04 Industrial applications of butyrate
Butyrate and its derivatives find applications in various industrial processes. These include their use as flavoring agents, preservatives, and intermediates in the production of plastics, perfumes, and other chemicals. Research focuses on improving production methods and exploring new industrial uses.Expand Specific Solutions05 Butyrate in animal nutrition and agriculture
Butyrate is investigated for its potential benefits in animal nutrition and agriculture. Studies explore its use as a feed additive to improve growth performance, gut health, and disease resistance in livestock. Additionally, research examines the role of butyrate in plant growth and soil health.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Butyrate and Metabolic Syndrome Research
The research on butyrate as a therapeutic agent for metabolic syndrome is in an early developmental stage, with growing interest from both academia and industry. The market size is expanding, driven by the increasing prevalence of metabolic disorders globally. While the technology is still maturing, several key players are actively involved in its development. Companies like Société des Produits Nestlé SA, Novartis AG, and Merck & Co., Inc. are leveraging their pharmaceutical expertise to explore butyrate's potential. Biotechnology firms such as Shenzhen Chipscreen Biosciences Co., Ltd. and BioKier, Inc. are focusing on innovative delivery methods. Academic institutions like The University of Chicago and Guangdong Pharmaceutical University are contributing to the fundamental research, enhancing the overall understanding of butyrate's therapeutic mechanisms in metabolic syndrome.
BioKier, Inc.
BioVie, Inc.
Breakthrough Studies on Butyrate in Metabolic Syndrome
- Novel butyrate delivery system for targeted release in the gut to enhance its therapeutic effects in metabolic syndrome.
- Identification of specific butyrate-responsive pathways involved in improving insulin sensitivity and reducing inflammation in metabolic syndrome.
- Development of a biomarker panel to predict and monitor individual patient response to butyrate therapy in metabolic syndrome.
- Chronic administration of dietary sodium butyrate, which inhibits histone deacetylases, enhances PGC-1α activity, leading to increased insulin sensitivity, reduced body weight, and improved metabolic parameters in non-ruminant mammals on a high-fat diet.
Regulatory Pathway for Butyrate-Based Therapeutics
The regulatory pathway for butyrate-based therapeutics is a complex process that involves multiple stages of development and approval. Initially, preclinical studies must be conducted to establish the safety and efficacy of butyrate compounds in animal models. These studies typically include pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic analyses, as well as toxicology assessments to determine potential side effects and optimal dosing regimens.
Once preclinical data demonstrates promising results, the next step is to file an Investigational New Drug (IND) application with the relevant regulatory agency, such as the FDA in the United States or the EMA in Europe. This application includes comprehensive information on the drug's chemistry, manufacturing, and controls (CMC), as well as the proposed clinical trial protocols.
Upon IND approval, clinical trials can commence, starting with Phase I studies to evaluate safety and tolerability in healthy volunteers. Phase II trials then assess efficacy and further refine dosing in patients with metabolic syndrome. If successful, Phase III trials are conducted on a larger scale to confirm efficacy and monitor long-term safety.
Throughout the clinical development process, sponsors must adhere to Good Clinical Practice (GCP) guidelines and maintain open communication with regulatory agencies. Regular meetings and submissions, such as annual reports and safety updates, are required to keep authorities informed of the drug's progress.
Following the completion of clinical trials, a New Drug Application (NDA) or Marketing Authorization Application (MAA) is submitted to the regulatory agency for review. This comprehensive dossier includes all data from preclinical and clinical studies, along with detailed information on manufacturing processes and quality control measures.
The regulatory review process typically takes 6-12 months, during which time the agency may request additional information or clarifications. If approved, post-marketing surveillance is required to monitor the drug's safety and efficacy in real-world settings. This may include Phase IV studies and ongoing pharmacovigilance activities.
Given the unique properties of butyrate and its potential classification as a metabolite or dietary supplement, sponsors may need to navigate additional regulatory considerations. These may include discussions with agencies regarding the most appropriate regulatory pathway and potential opportunities for expedited review programs, such as Fast Track or Breakthrough Therapy designations, if applicable to the specific indications being pursued in metabolic syndrome.
Safety and Toxicity Considerations for Butyrate Therapy
While butyrate shows promise as a therapeutic agent for metabolic syndrome, it is crucial to consider the safety and toxicity aspects of its use. The primary route of administration for butyrate therapy is oral ingestion, which raises concerns about potential gastrointestinal side effects. Common adverse reactions reported in clinical trials include nausea, abdominal discomfort, and flatulence, particularly at higher doses.
Long-term safety data for butyrate supplementation is limited, necessitating further research to establish its chronic toxicity profile. Some studies have suggested that excessive butyrate intake may lead to electrolyte imbalances, particularly in patients with compromised renal function. Additionally, there are concerns about the potential for butyrate to alter the gut microbiome composition, which could have unintended consequences on overall health.
The pharmacokinetics of butyrate must be carefully considered when developing therapeutic regimens. Butyrate is rapidly metabolized in the liver and has a short half-life in circulation, which may necessitate frequent dosing or the development of sustained-release formulations. However, high systemic concentrations of butyrate could potentially lead to metabolic acidosis, highlighting the importance of dose optimization.
There is also a need to investigate potential drug interactions, as butyrate may affect the absorption and metabolism of other medications. Furthermore, the impact of butyrate therapy on vulnerable populations, such as pregnant women, children, and the elderly, requires thorough evaluation to ensure safety across diverse patient groups.
Regulatory considerations for butyrate as a therapeutic agent are complex, as it exists in a gray area between dietary supplement and pharmaceutical. Establishing clear guidelines for its use and manufacturing standards is essential to ensure consistent quality and safety. Additionally, long-term epidemiological studies are needed to assess any potential carcinogenic or mutagenic effects of chronic butyrate supplementation.
In conclusion, while butyrate shows promise in treating metabolic syndrome, a comprehensive safety and toxicity profile must be established before widespread clinical adoption. This includes conducting rigorous preclinical and clinical studies, monitoring for rare adverse events, and developing standardized protocols for its use in various patient populations.